Etymology
 Norway has two official names: ''Norge'' in
Norway has two official names: ''Norge'' in Noregr tyder nok vegen mot nord, likevel
".''Namn og nemne'', 2016. Vol 33, 13–37. In a Latin manuscript of 840, the name ''Northuagia'' is mentioned. King Alfred's edition of the Orosius World History (dated 880), uses the term ''Norðweg''. A French chronicle of c. 900 uses the names ''Northwegia'' and ''Norwegia''.Sigurðsson and Riisøy: ''Norsk historie 800–1536'', p. 24. When
History
Prehistory
 The first inhabitants were the
The first inhabitants were the Bronze Age
 Between 3000 and 2500 BC, new settlers (Corded Ware culture) arrived in eastern Norway. They were Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European farmers who grew grain and kept cows and sheep. The hunting-fishing population of the west coast was also gradually replaced by farmers, though hunting and fishing remained useful secondary means of livelihood.
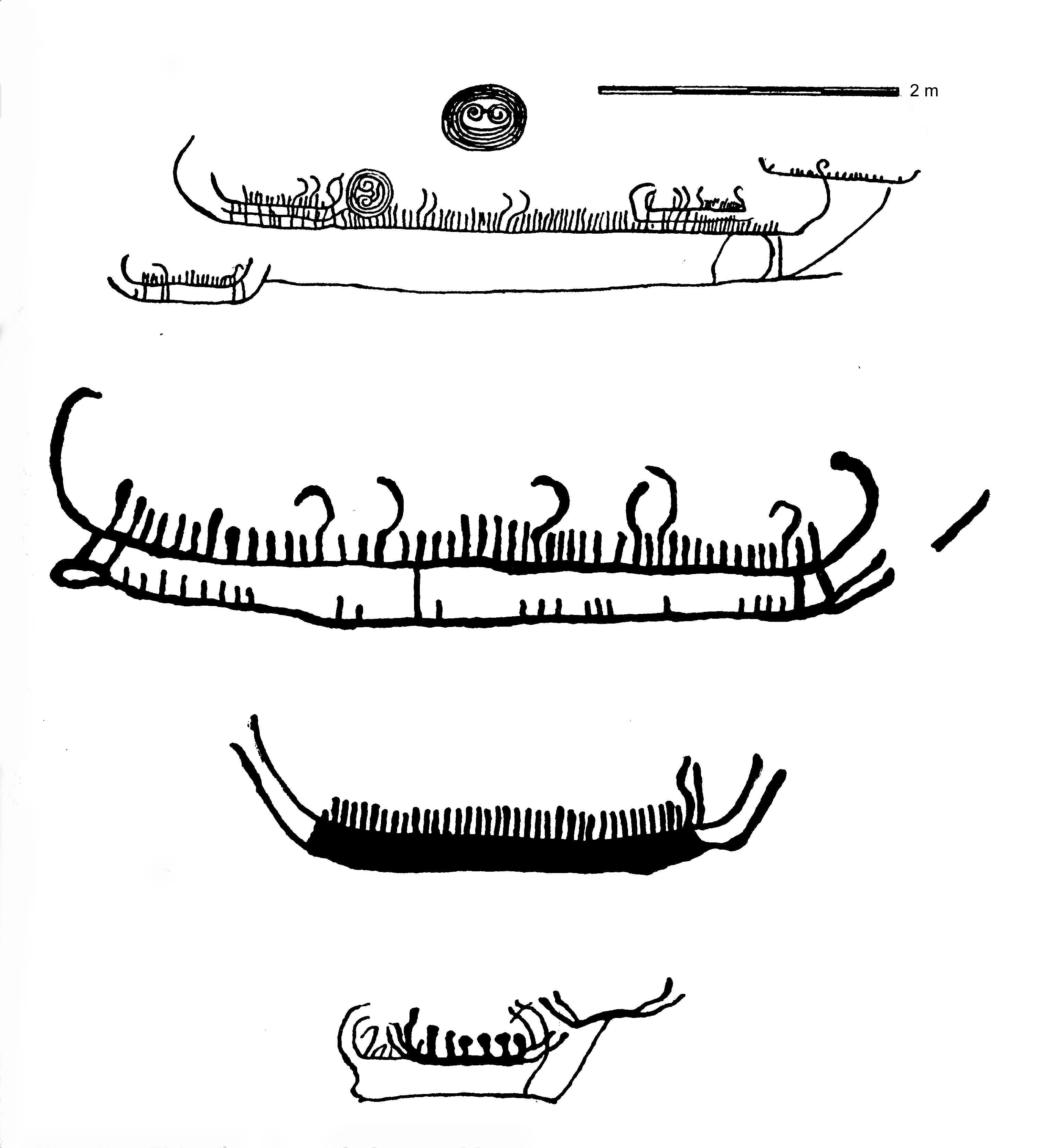
From about 1500 BC, bronze was gradually introduced, but the use of stone implements continued; Norway had few riches to barter for bronze goods, and the few finds consist mostly of elaborate weapons and brooches that only chieftains could afford. Huge burial cairns built close to the sea as far north as Harstad and also inland in the south are characteristic of this period. The motifs of the rock carvings differ slightly from those typical of the Stone Age. Representations of the Sun, animals, trees, weapons, ships, and people are all strongly stylised.
Thousands of rock carvings from this period depict ships, and the large stone burial monuments known as stone ships, suggest that ships and seafaring played an important role in the culture at large. The depicted ships most likely represent sewn plank built canoes used for warfare, fishing and trade. These ship types may have their origin as far back as the neolithic period and they continue into the Pre-Roman Iron Age, as exemplified by the Hjortspring boat.
Between 3000 and 2500 BC, new settlers (Corded Ware culture) arrived in eastern Norway. They were Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European farmers who grew grain and kept cows and sheep. The hunting-fishing population of the west coast was also gradually replaced by farmers, though hunting and fishing remained useful secondary means of livelihood.
From about 1500 BC, bronze was gradually introduced, but the use of stone implements continued; Norway had few riches to barter for bronze goods, and the few finds consist mostly of elaborate weapons and brooches that only chieftains could afford. Huge burial cairns built close to the sea as far north as Harstad and also inland in the south are characteristic of this period. The motifs of the rock carvings differ slightly from those typical of the Stone Age. Representations of the Sun, animals, trees, weapons, ships, and people are all strongly stylised.
Thousands of rock carvings from this period depict ships, and the large stone burial monuments known as stone ships, suggest that ships and seafaring played an important role in the culture at large. The depicted ships most likely represent sewn plank built canoes used for warfare, fishing and trade. These ship types may have their origin as far back as the neolithic period and they continue into the Pre-Roman Iron Age, as exemplified by the Hjortspring boat.
Iron Age
 Little has been found dating from the early Iron Age (the last 500 years BC). The dead were cremated, and their graves contain few burial goods. During the first four centuries AD, the people of Norway were in contact with Roman-occupied Gaul. About 70 Roman bronze cauldrons, often used as burial urns, have been found. Contact with the civilised countries farther south brought a knowledge of runes; the oldest known Norwegian runic inscription dates from the third century. At this time, the amount of settled area in the country increased, a development that can be traced by coordinated studies of topography, archaeology, and place-names. The oldest root names, such as nes, vik, and bø ("cape," "bay," and "farm"), are of great antiquity, dating perhaps from the Bronze Age, whereas the earliest of the groups of compound names with the suffixes vin ("meadow") or heim ("settlement"), as in Bjǫrgvin (Bergen) or Sǿheim (Seim), usually date from the first century AD.
Archaeologists first made the decision to divide the Iron Age of Northern Europe into distinct pre-Roman and Roman Iron Ages after Emil Vedel unearthed a number of Iron Age artefacts in 1866 on the island of Bornholm. They did not exhibit the same permeating Roman influence seen in most other artefacts from the early centuries AD, indicating that parts of northern Europe had not yet come into contact with the Romans at the beginning of the Iron Age.
Little has been found dating from the early Iron Age (the last 500 years BC). The dead were cremated, and their graves contain few burial goods. During the first four centuries AD, the people of Norway were in contact with Roman-occupied Gaul. About 70 Roman bronze cauldrons, often used as burial urns, have been found. Contact with the civilised countries farther south brought a knowledge of runes; the oldest known Norwegian runic inscription dates from the third century. At this time, the amount of settled area in the country increased, a development that can be traced by coordinated studies of topography, archaeology, and place-names. The oldest root names, such as nes, vik, and bø ("cape," "bay," and "farm"), are of great antiquity, dating perhaps from the Bronze Age, whereas the earliest of the groups of compound names with the suffixes vin ("meadow") or heim ("settlement"), as in Bjǫrgvin (Bergen) or Sǿheim (Seim), usually date from the first century AD.
Archaeologists first made the decision to divide the Iron Age of Northern Europe into distinct pre-Roman and Roman Iron Ages after Emil Vedel unearthed a number of Iron Age artefacts in 1866 on the island of Bornholm. They did not exhibit the same permeating Roman influence seen in most other artefacts from the early centuries AD, indicating that parts of northern Europe had not yet come into contact with the Romans at the beginning of the Iron Age.
Migration period
The destruction of the Western Roman Empire by the Germanic peoples in the fifth century is characterised by rich finds, including tribal chiefs' graves containing magnificent weapons and gold objects. Hill forts were built on precipitous rocks for defence. Excavation has revealed stone foundations of farmhouses long—one even long—the roofs of which were supported on wooden posts. These houses were family homesteads where several generations lived together, with people and cattle under one roof. These states were based on either clans or tribes (e.g., the Horder of Hordaland in western Norway). By the ninth century, each of these small states had Thing (assembly), ''things'' (local or regional assemblies) for negotiating and settling disputes. The ''thing'' meeting places, each eventually with a hörgr (open-air sanctuary) or a heathen hof (temple; literally "hill"), were usually situated on the oldest and best farms, which belonged to the chieftains and wealthiest farmers. The regional ''things'' united to form even larger units: assemblies of deputy yeomen from several regions. In this way, the ''lagting'' (assemblies for negotiations and lawmaking) developed. The Gulating had its meeting place by Sognefjord and may have been the centre of an aristocratic confederation along the western fjords and islands called the Gulatingslag. The Frostating was the assembly for the leaders in the Trondheimsfjord area; the Earls of Lade, near Trondheim, seem to have enlarged the Frostatingslag by adding the coastland from Romsdalsfjord to Lofoten.Viking Age
From the eighth to the tenth century, the wider Scandinavian region was the source of Vikings. The looting of the monastery at Lindisfarne in Northeast England in 793 by North Germanic peoples, Norse people has long been regarded as the event which marked the beginning of the Viking Age. This age was characterised by expansion and emigration by Viking seafarers. They colonised, raided, and traded in all parts of Europe. Norwegian Viking explorers discovered Iceland by accident in the ninth century when heading for the Faroe Islands, and eventually came across Vinland, known today as Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland, in Canada. The Vikings from Norway were most active in the northern and western British Isles and eastern Norse colonization of North America, North America isles.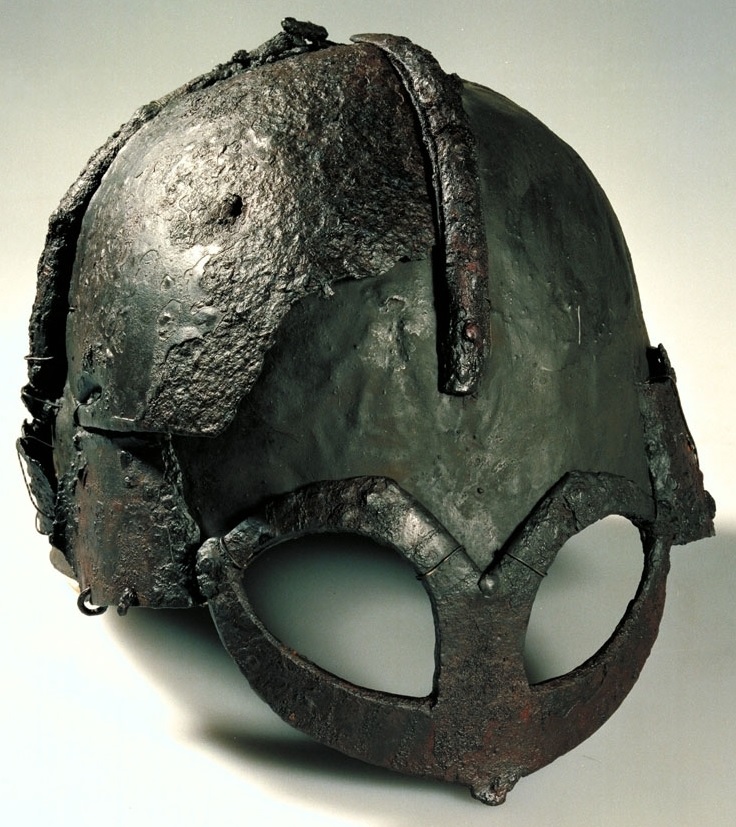 According to tradition, Harald Fairhair unified them into one in 872 after the Battle of Hafrsfjord in Stavanger, thus becoming the first king of a united Norway. Harald's realm was mainly a South Norwegian coastal state. Fairhair ruled with a strong hand and according to the sagas, many Norwegians left the country to live in Iceland, the Faroe Islands, Greenland, and parts of Great Britain, Britain and Ireland. The modern-day Irish cities of Dublin, Limerick and Waterford were founded by Norwegian settlers.
Norse mythology, Norse traditions were replaced slowly by Christian mythology, Christian ones in the late 10th and early 11th centuries. One of the most important sources for the history of the 11th century Vikings is the treaty between the Icelanders and Olaf Haraldsson, king of Norway circa 1015 to 1028. This is largely attributed to the missionary kings Olaf I of Norway, Olav Tryggvasson and Olaf II of Norway, St. Olav. Haakon I of Norway, Haakon the Good was Norway's first Christian king, in the mid-10th century, though his attempt to introduce the religion was rejected. Born sometime in between 963 and 969, Olav Tryggvasson set off raiding in England with 390 ships. He attacked London during this raiding. Arriving back in Norway in 995, Olav landed in Moster (island), Moster. There he built a church which became the first Old Moster Church, Christian church ever built in Norway. From Moster, Olav sailed north to Trondheim where he was proclaimed King of Norway by the Eyrathing in 995.
Feudalism never really developed in Norway or Sweden, as it did in the rest of Europe. However, the administration of government took on a very conservative feudal character. The Hanseatic League forced the royalty to cede to them greater and greater concessions over foreign trade and the economy. The League had this hold over the royalty because of the loans the Hansa had made to the royalty and the large debt the kings were carrying. The League's monopolistic control over the economy of Norway put pressure on all classes, especially the peasantry, to the degree that no real burgher (title), burgher class existed in Norway.
According to tradition, Harald Fairhair unified them into one in 872 after the Battle of Hafrsfjord in Stavanger, thus becoming the first king of a united Norway. Harald's realm was mainly a South Norwegian coastal state. Fairhair ruled with a strong hand and according to the sagas, many Norwegians left the country to live in Iceland, the Faroe Islands, Greenland, and parts of Great Britain, Britain and Ireland. The modern-day Irish cities of Dublin, Limerick and Waterford were founded by Norwegian settlers.
Norse mythology, Norse traditions were replaced slowly by Christian mythology, Christian ones in the late 10th and early 11th centuries. One of the most important sources for the history of the 11th century Vikings is the treaty between the Icelanders and Olaf Haraldsson, king of Norway circa 1015 to 1028. This is largely attributed to the missionary kings Olaf I of Norway, Olav Tryggvasson and Olaf II of Norway, St. Olav. Haakon I of Norway, Haakon the Good was Norway's first Christian king, in the mid-10th century, though his attempt to introduce the religion was rejected. Born sometime in between 963 and 969, Olav Tryggvasson set off raiding in England with 390 ships. He attacked London during this raiding. Arriving back in Norway in 995, Olav landed in Moster (island), Moster. There he built a church which became the first Old Moster Church, Christian church ever built in Norway. From Moster, Olav sailed north to Trondheim where he was proclaimed King of Norway by the Eyrathing in 995.
Feudalism never really developed in Norway or Sweden, as it did in the rest of Europe. However, the administration of government took on a very conservative feudal character. The Hanseatic League forced the royalty to cede to them greater and greater concessions over foreign trade and the economy. The League had this hold over the royalty because of the loans the Hansa had made to the royalty and the large debt the kings were carrying. The League's monopolistic control over the economy of Norway put pressure on all classes, especially the peasantry, to the degree that no real burgher (title), burgher class existed in Norway.
Civil war and peak of power
 From the 1040s to 1130, the country was at peace. In 1130, the civil war era in Norway, civil war era broke out on the basis of line of succession to the Norwegian throne, unclear succession laws, which allowed all the king's sons to rule jointly. For periods there could be peace, before a lesser son allied himself with a chieftain and started a new conflict. The Archdiocese of Nidaros was created in 1152 and attempted to control the appointment of kings. The church inevitably had to take sides in the conflicts, with the civil wars also becoming an issue regarding the church's influence of the king. The wars ended in 1217 with the appointment of Håkon Håkonsson, who introduced clear law of succession.
From 1000 to 1300, the population increased from 150,000 to 400,000, resulting both in more land being cleared and the subdivision of farms. While in the Viking Age all farmers owned their own land, by 1300, seventy percent of the land was owned by the king, the church, or the aristocracy. This was a gradual process which took place because of farmers borrowing money in poor times and not being able to repay. However, tenants always remained free men and the large distances and often scattered ownership meant that they enjoyed much more freedom than continental serfs. In the 13th century, about twenty percent of a farmer's yield went to the king, church and landowners.
The 14th century is described as Norway's Golden Age, with peace and increase in trade, especially with the British Islands, although Germany became increasingly important towards the end of the century. Throughout the High Middle Ages, the king established Norway as a sovereign state with a central administration and local representatives.
In 1349, the Black Death spread to Norway and had within a year killed a third of the population. Later plagues reduced the population to half the starting point by 1400. Many communities were entirely wiped out, resulting in an abundance of land, allowing farmers to switch to more animal husbandry. The reduction in taxes weakened the king's position, and many aristocrats lost the basis for their surplus, reducing some to mere farmers. High tithes to church made it increasingly powerful and the archbishop became a member of the Norwegian Council of State, Council of State.Stenersen: 45
From the 1040s to 1130, the country was at peace. In 1130, the civil war era in Norway, civil war era broke out on the basis of line of succession to the Norwegian throne, unclear succession laws, which allowed all the king's sons to rule jointly. For periods there could be peace, before a lesser son allied himself with a chieftain and started a new conflict. The Archdiocese of Nidaros was created in 1152 and attempted to control the appointment of kings. The church inevitably had to take sides in the conflicts, with the civil wars also becoming an issue regarding the church's influence of the king. The wars ended in 1217 with the appointment of Håkon Håkonsson, who introduced clear law of succession.
From 1000 to 1300, the population increased from 150,000 to 400,000, resulting both in more land being cleared and the subdivision of farms. While in the Viking Age all farmers owned their own land, by 1300, seventy percent of the land was owned by the king, the church, or the aristocracy. This was a gradual process which took place because of farmers borrowing money in poor times and not being able to repay. However, tenants always remained free men and the large distances and often scattered ownership meant that they enjoyed much more freedom than continental serfs. In the 13th century, about twenty percent of a farmer's yield went to the king, church and landowners.
The 14th century is described as Norway's Golden Age, with peace and increase in trade, especially with the British Islands, although Germany became increasingly important towards the end of the century. Throughout the High Middle Ages, the king established Norway as a sovereign state with a central administration and local representatives.
In 1349, the Black Death spread to Norway and had within a year killed a third of the population. Later plagues reduced the population to half the starting point by 1400. Many communities were entirely wiped out, resulting in an abundance of land, allowing farmers to switch to more animal husbandry. The reduction in taxes weakened the king's position, and many aristocrats lost the basis for their surplus, reducing some to mere farmers. High tithes to church made it increasingly powerful and the archbishop became a member of the Norwegian Council of State, Council of State.Stenersen: 45
Kalmar Union
Upon the death of Haakon V of Norway, Haakon V (King of Norway) in 1319, Magnus IV of Sweden, Magnus Erikson, at just three years old, inherited the throne as King Magnus VII of Norway. At the same time, a movement to make Magnus King of Sweden proved successful, and both the kings of Sweden and of Denmark were elected to the throne by their respective nobles, Thus, with his election to the throne of Sweden, both Sweden and Norway were united under King Magnus VII.#Larsen, Larsen, p. 192. In 1349, the Black Death radically altered Norway, killing between 50% and 60% of its population and leaving it in a period of social and economic decline. The plague left Norway very poor. Although the death rate was comparable with the rest of Europe, economic recovery took much longer because of the small, scattered population. Even before the plague, the population was only about 500,000.#Larsen, Larsen, pp. 202–03. After the plague, many farms lay idle while the population slowly increased. However, the few surviving farms' tenants found their bargaining positions with their landlords greatly strengthened.Union with Denmark
After Sweden broke out of the Kalmar Union in 1521, Norway tried to follow suit, but the subsequent rebellion was defeated, and Norway remained in a union with Denmark until 1814, a total of 434 years. During the Romantic nationalism, national romanticism of the 19th century, this period was Nicolai Wergeland, by some referred to as the "400-Year Night", since all of the kingdom's royal, intellectual, and administrative power was centred in Copenhagen in Denmark. In fact, it was a period of great prosperity and progress for Norway, especially in terms of shipping and foreign trade, and it also secured the country's revival from the demographic catastrophe it suffered in the Black Death. Based on the respective natural resources, Denmark–Norway was in fact a very good match since Denmark supported Norway's needs for grain and food supplies, and Norway supplied Denmark with timber, metal, and fish. With the Reformation in Denmark–Norway and Holstein, introduction of Protestantism in 1536, the archbishopric in Trondheim was dissolved, and Norway lost its independence, and effectually became a colony of Denmark. The Church's incomes and possessions were instead redirected to the court in Copenhagen. Norway lost the steady stream of pilgrims to the relics of Olaf II of Norway, St. Olav at the Nidaros shrine, and with them, much of the contact with cultural and economic life in the rest of Europe.
Eventually restored as a kingdom (albeit in legislative union with Denmark) in 1661, Norway saw its land area decrease in the 17th century with the loss of the provinces Bohuslän, Båhuslen, Jämtland, Jemtland, and Härjedalen, Herjedalen to Sweden, as the result of a number of disastrous wars with Sweden. In the north, however, its territory was increased by the acquisition of the northern provinces of Troms and Finnmark, at the expense of Sweden and Russia.
The Great Famine of 1695–1697, famine of 1695–1696 killed roughly 10% of Norway's population. The harvest failed in Scandinavia at least nine times between 1740 and 1800, with great loss of life.
With the Reformation in Denmark–Norway and Holstein, introduction of Protestantism in 1536, the archbishopric in Trondheim was dissolved, and Norway lost its independence, and effectually became a colony of Denmark. The Church's incomes and possessions were instead redirected to the court in Copenhagen. Norway lost the steady stream of pilgrims to the relics of Olaf II of Norway, St. Olav at the Nidaros shrine, and with them, much of the contact with cultural and economic life in the rest of Europe.
Eventually restored as a kingdom (albeit in legislative union with Denmark) in 1661, Norway saw its land area decrease in the 17th century with the loss of the provinces Bohuslän, Båhuslen, Jämtland, Jemtland, and Härjedalen, Herjedalen to Sweden, as the result of a number of disastrous wars with Sweden. In the north, however, its territory was increased by the acquisition of the northern provinces of Troms and Finnmark, at the expense of Sweden and Russia.
The Great Famine of 1695–1697, famine of 1695–1696 killed roughly 10% of Norway's population. The harvest failed in Scandinavia at least nine times between 1740 and 1800, with great loss of life.
Union with Sweden
 After Denmark–Norway was attacked by the United Kingdom at the 1807 Battle of Copenhagen (1807), Battle of Copenhagen, it entered into an alliance with Napoleon, with the war leading to dire conditions and mass starvation in 1812. As the Danish kingdom found itself on the losing side in 1814, it was forced, under terms of the Treaty of Kiel, to cede Norway to the king of Sweden, while the old Norwegian provinces of Iceland, Greenland, and the Faroe Islands remained with the Danish crown. Norway took this opportunity to declare independence, adopted a constitution based on United States Constitution, American and Constitution of France, French models, and elected the Crown Prince of Denmark and Norway, Christian VIII of Denmark, Christian Frederick, as king on 17 May 1814. This is the famous Norwegian Constitution Day, Syttende mai (Seventeenth of May) holiday celebrated by Norwegians and Norwegian-Americans alike. ''Syttende mai'' is also called ''Norwegian Constitution Day''.
Norwegian opposition to the great powers' decision to link Norway with Sweden caused the Swedish–Norwegian War (1814), Norwegian–Swedish War to break out as Sweden tried to subdue Norway by military means. As Sweden's military was not strong enough to defeat the Norwegian forces outright, and Norway's treasury was not large enough to support a protracted war, and as British and Russian navies blockaded the Norwegian coast, the belligerents were forced to negotiate the Convention of Moss. According to the terms of the convention, Christian Frederik abdicated the Norwegian throne and authorised the Parliament of Norway to make the necessary constitutional amendments to allow for the personal union that Norway was forced to accept. On 4 November 1814, the Parliament (Storting) elected Charles XIII of Sweden as king of Norway, thereby establishing the Union between Sweden and Norway, union with Sweden. Under this arrangement, Norway kept its liberal constitution and its own independent institutions, though it shared a common monarch and common foreign policy with Sweden. Following the recession caused by the Napoleonic Wars, economic development of Norway remained slow until economic growth began around 1830.
After Denmark–Norway was attacked by the United Kingdom at the 1807 Battle of Copenhagen (1807), Battle of Copenhagen, it entered into an alliance with Napoleon, with the war leading to dire conditions and mass starvation in 1812. As the Danish kingdom found itself on the losing side in 1814, it was forced, under terms of the Treaty of Kiel, to cede Norway to the king of Sweden, while the old Norwegian provinces of Iceland, Greenland, and the Faroe Islands remained with the Danish crown. Norway took this opportunity to declare independence, adopted a constitution based on United States Constitution, American and Constitution of France, French models, and elected the Crown Prince of Denmark and Norway, Christian VIII of Denmark, Christian Frederick, as king on 17 May 1814. This is the famous Norwegian Constitution Day, Syttende mai (Seventeenth of May) holiday celebrated by Norwegians and Norwegian-Americans alike. ''Syttende mai'' is also called ''Norwegian Constitution Day''.
Norwegian opposition to the great powers' decision to link Norway with Sweden caused the Swedish–Norwegian War (1814), Norwegian–Swedish War to break out as Sweden tried to subdue Norway by military means. As Sweden's military was not strong enough to defeat the Norwegian forces outright, and Norway's treasury was not large enough to support a protracted war, and as British and Russian navies blockaded the Norwegian coast, the belligerents were forced to negotiate the Convention of Moss. According to the terms of the convention, Christian Frederik abdicated the Norwegian throne and authorised the Parliament of Norway to make the necessary constitutional amendments to allow for the personal union that Norway was forced to accept. On 4 November 1814, the Parliament (Storting) elected Charles XIII of Sweden as king of Norway, thereby establishing the Union between Sweden and Norway, union with Sweden. Under this arrangement, Norway kept its liberal constitution and its own independent institutions, though it shared a common monarch and common foreign policy with Sweden. Following the recession caused by the Napoleonic Wars, economic development of Norway remained slow until economic growth began around 1830.
 This period also saw the rise of the Norwegian romantic nationalism, as Norwegians sought to define and express a distinct national character. The movement covered all branches of culture, including literature (Henrik Wergeland [1808–1845], Bjørnstjerne Bjørnson [1832–1910], Peter Christen Asbjørnsen [1812–1845], Jørgen Moe [1813–1882]), painting (Hans Gude [1825–1903], Adolph Tidemand [1814–1876]), music (Edvard Grieg [1843–1907]), and even language policy, where attempts to define a native written language for Norway led to today's two official written forms for Norwegian:
This period also saw the rise of the Norwegian romantic nationalism, as Norwegians sought to define and express a distinct national character. The movement covered all branches of culture, including literature (Henrik Wergeland [1808–1845], Bjørnstjerne Bjørnson [1832–1910], Peter Christen Asbjørnsen [1812–1845], Jørgen Moe [1813–1882]), painting (Hans Gude [1825–1903], Adolph Tidemand [1814–1876]), music (Edvard Grieg [1843–1907]), and even language policy, where attempts to define a native written language for Norway led to today's two official written forms for Norwegian:  Still, Norway remained a conservative society. Life in Norway (especially economic life) was "dominated by the aristocracy of professional men who filled most of the important posts in the central government". There was no strong bourgeosie class in Norway to demand a breakdown of this aristocratic control of the economy.See "The Civil War in Switzerland" by Frederick Engels contained in Marx & Engels, ''Collected Works: Volume 6'' (International Publishers, New York, 1976) p. 368. Thus, even while revolution swept over most of the countries of Europe in 1848, Norway was largely unaffected by revolts that year.
Still, Norway remained a conservative society. Life in Norway (especially economic life) was "dominated by the aristocracy of professional men who filled most of the important posts in the central government". There was no strong bourgeosie class in Norway to demand a breakdown of this aristocratic control of the economy.See "The Civil War in Switzerland" by Frederick Engels contained in Marx & Engels, ''Collected Works: Volume 6'' (International Publishers, New York, 1976) p. 368. Thus, even while revolution swept over most of the countries of Europe in 1848, Norway was largely unaffected by revolts that year.
 Marcus Thrane was a Utopian socialism, Utopian socialist. He made his appeal to the labouring classes urging a change of social structure "from below upwards." In 1848, he organised a labour society in Drammen. In just a few months, this society had a membership of 500 and was publishing its own newspaper. Within two years, 300 societies had been organised all over Norway, with a total membership of 20,000 persons. The membership was drawn from the lower classes of both urban and rural areas; for the first time these two groups felt they had a common cause. In the end, the revolt was easily crushed; Thrane was captured and in 1855, after four years in jail, was sentenced to three additional years for crimes against the safety of the state. Upon his release, Marcus Thrane attempted unsuccessfully to revitalise his movement, but after the death of his wife, he migrated to the United States.
In 1898, all men were granted universal suffrage, followed by all Women's suffrage, women in 1913.
Marcus Thrane was a Utopian socialism, Utopian socialist. He made his appeal to the labouring classes urging a change of social structure "from below upwards." In 1848, he organised a labour society in Drammen. In just a few months, this society had a membership of 500 and was publishing its own newspaper. Within two years, 300 societies had been organised all over Norway, with a total membership of 20,000 persons. The membership was drawn from the lower classes of both urban and rural areas; for the first time these two groups felt they had a common cause. In the end, the revolt was easily crushed; Thrane was captured and in 1855, after four years in jail, was sentenced to three additional years for crimes against the safety of the state. Upon his release, Marcus Thrane attempted unsuccessfully to revitalise his movement, but after the death of his wife, he migrated to the United States.
In 1898, all men were granted universal suffrage, followed by all Women's suffrage, women in 1913.
Dissolution of the union and the first World War
Christian Michelsen, a shipping magnate and statesman, and Prime Minister of Norway from 1905 to 1907, played a central role in the peaceful separation of Norway from Sweden on 7 June 1905. A national referendum confirmed the people's preference for a monarchy over a republic. However, no Norwegian could legitimately claim the throne, since none of Norway's noble families could claim descent from medieval royalty. In European tradition, Royal descent, royal or "blue" blood is a precondition for laying claim to the throne. The government then offered the throne of Norway to Prince Carl of Denmark, a prince of the Dano-German royal house of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg and a distant relative of several of Norway's medieval kings. After centuries of close ties between Norway and Denmark, a prince from the latter was the obvious choice for a European prince who could best relate to the Norwegian people. Following the plebiscite, he was unanimously elected king by the Norwegian Parliament of Norway, Parliament, the first king of a fully independent Norway in 508 years (1397: Kalmar Union); he took the name Haakon VII of Norway, Haakon VII. In 1905, the country welcomed the prince from neighbouring Denmark, his wife Maud of Wales and their young son to re-establish Norway's royal house. Throughout theSecond World War
 Norway once more proclaimed its neutrality during the World War II, Second World War, but this time, it was Operation Weserübung, invaded by German forces on 9 April 1940. Although Norway was unprepared for the German surprise attack (see: Battle of Drøbak Sound, Norwegian Campaign, and Invasion of Norway), military and naval resistance lasted for two months. Norwegian armed forces in the north launched an offensive against the German forces in the Battles of Narvik, until they were forced to surrender on 10 June after losing British support which had been diverted to France during the Battle of France, German invasion of France.
Haakon VII of Norway, King Haakon and the Norwegian government escaped to Rotherhithe in London. Throughout the war they sent inspirational radio speeches and supported clandestine military actions in Norway against the Germans. On the day of the invasion, the leader of the small National-Socialist party Nasjonal Samling, Vidkun Quisling, tried to seize power, but was forced by the German occupiers to step aside. Real power was wielded by the leader of the German occupation authority, Reichskommissar Josef Terboven. Quisling, as ''minister president'', later formed a Quisling regime, collaborationist government under German control. Up to 15,000 Norwegians volunteered to fight in German units, including the Waffen-SS.
The fraction of the Norwegian population that supported Germany was traditionally smaller than in Sweden, but greater than is generally appreciated today. It included a number of prominent personalities such as the Nobel-prize winning novelist Knut Hamsun. The concept of a "Germanic Union" of member states fit well into their thoroughly nationalist-patriotic ideology.
Norway once more proclaimed its neutrality during the World War II, Second World War, but this time, it was Operation Weserübung, invaded by German forces on 9 April 1940. Although Norway was unprepared for the German surprise attack (see: Battle of Drøbak Sound, Norwegian Campaign, and Invasion of Norway), military and naval resistance lasted for two months. Norwegian armed forces in the north launched an offensive against the German forces in the Battles of Narvik, until they were forced to surrender on 10 June after losing British support which had been diverted to France during the Battle of France, German invasion of France.
Haakon VII of Norway, King Haakon and the Norwegian government escaped to Rotherhithe in London. Throughout the war they sent inspirational radio speeches and supported clandestine military actions in Norway against the Germans. On the day of the invasion, the leader of the small National-Socialist party Nasjonal Samling, Vidkun Quisling, tried to seize power, but was forced by the German occupiers to step aside. Real power was wielded by the leader of the German occupation authority, Reichskommissar Josef Terboven. Quisling, as ''minister president'', later formed a Quisling regime, collaborationist government under German control. Up to 15,000 Norwegians volunteered to fight in German units, including the Waffen-SS.
The fraction of the Norwegian population that supported Germany was traditionally smaller than in Sweden, but greater than is generally appreciated today. It included a number of prominent personalities such as the Nobel-prize winning novelist Knut Hamsun. The concept of a "Germanic Union" of member states fit well into their thoroughly nationalist-patriotic ideology.
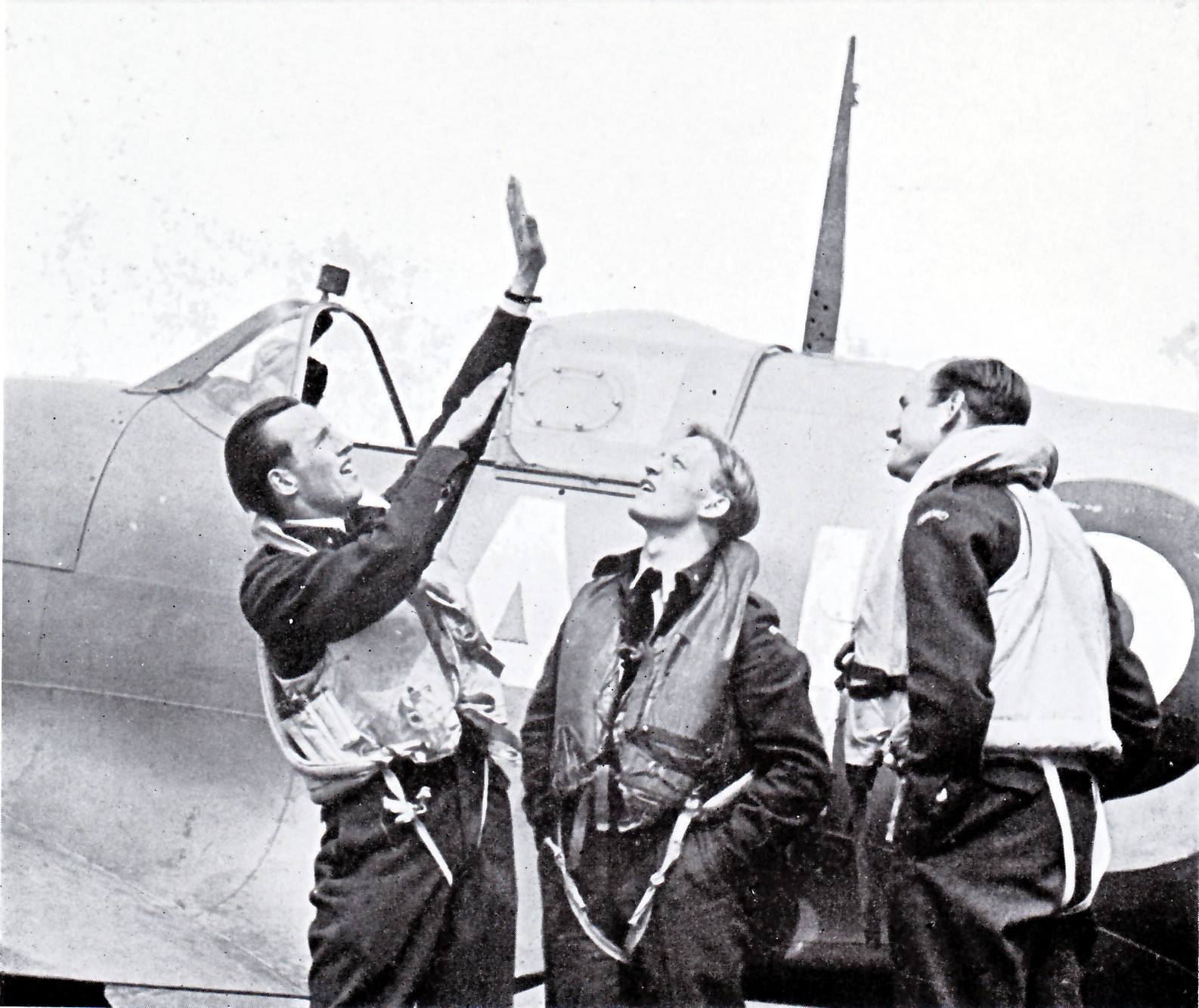 Many Norwegians and persons of Norwegian descent joined the Allied forces as well as the Free Norwegian Forces. In June 1940, a small group had left Norway following their king to Britain. This group included 13 ships, five aircraft, and 500 men from the Royal Norwegian Navy. By the end of the war, the force had grown to 58 ships and 7,500 men in service in the Royal Norwegian Navy, 5 squadrons of aircraft (including Spitfires, Sunderland flying boats and Mosquitos) in the newly formed Norwegian Air Force, and land forces including the Norwegian Independent Company 1 and 5 Troop as well as No. 10 British Commandos, Commandos.
During the five years of German occupation of Norway, German occupation, Norwegians built a Norwegian resistance movement, resistance movement which fought the German occupation forces with both civil disobedience and armed resistance including the destruction of Norsk Hydro's heavy water plant and stockpile of heavy water at Vemork, which crippled the German nuclear programme (see: ''Norwegian heavy water sabotage''). More important to the Allies of World War II, Allied war effort, however, was the role of the Norwegian Merchant Navy, Merchant Marine. At the time of the invasion, Norway had the fourth-largest merchant marine fleet in the world. It was led by the Norwegian shipping company Nortraship under the Allies throughout the war and took part in every war operation from the Dunkirk evacuation, evacuation of Dunkirk to the Normandy landings. Every December Norway gives a Christmas tree to the United Kingdom as thanks for the British assistance during the Second World War. A ceremony takes place to erect the tree in London's Trafalgar Square.
Many Norwegians and persons of Norwegian descent joined the Allied forces as well as the Free Norwegian Forces. In June 1940, a small group had left Norway following their king to Britain. This group included 13 ships, five aircraft, and 500 men from the Royal Norwegian Navy. By the end of the war, the force had grown to 58 ships and 7,500 men in service in the Royal Norwegian Navy, 5 squadrons of aircraft (including Spitfires, Sunderland flying boats and Mosquitos) in the newly formed Norwegian Air Force, and land forces including the Norwegian Independent Company 1 and 5 Troop as well as No. 10 British Commandos, Commandos.
During the five years of German occupation of Norway, German occupation, Norwegians built a Norwegian resistance movement, resistance movement which fought the German occupation forces with both civil disobedience and armed resistance including the destruction of Norsk Hydro's heavy water plant and stockpile of heavy water at Vemork, which crippled the German nuclear programme (see: ''Norwegian heavy water sabotage''). More important to the Allies of World War II, Allied war effort, however, was the role of the Norwegian Merchant Navy, Merchant Marine. At the time of the invasion, Norway had the fourth-largest merchant marine fleet in the world. It was led by the Norwegian shipping company Nortraship under the Allies throughout the war and took part in every war operation from the Dunkirk evacuation, evacuation of Dunkirk to the Normandy landings. Every December Norway gives a Christmas tree to the United Kingdom as thanks for the British assistance during the Second World War. A ceremony takes place to erect the tree in London's Trafalgar Square.
Post-World War II history
From 1945 to 1962, the Labour Party (Norway), Labour Party held an absolute majority in the parliament. The government, led by prime minister Einar Gerhardsen, embarked on a programme inspired by Keynesian economics, emphasising state financed industrialisation and co-operation between trade unions and employers' organisations. Many measures of state control of the economy imposed during the war were continued, although the rationing of dairy products was lifted in 1949, while price controls and rationing of housing and cars continued until 1960. The wartime alliance with the United Kingdom and the United States was continued in the post-war years. Although pursuing the goal of a socialist economy, the Labour Party distanced itself from the Communists, especially after the Communists' seizure of power in Czechoslovakia in 1948, and strengthened its foreign policy and defence policy ties with the US. Norway received Marshall Plan aid from the United States starting in 1947, joined the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) one year later, and became a founding member of the NATO, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) in 1949.
The first oil was discovered at the small Balder field in 1967, but production only began in 1999. In 1969, the Phillips Petroleum Company discovered petroleum resources at the Ekofisk oil field, Ekofisk field west of Norway. In 1973, the Norwegian government founded the State oil company, Statoil. Oil production did not provide net income until the early 1980s because of the large capital investment that was required to establish the country's petroleum industry. Around 1975, both the proportion and absolute number of workers in industry peaked. Since then labour-intensive industries and services like factory mass production and shipping have largely been outsourced.
Norway was a founding member of the
The wartime alliance with the United Kingdom and the United States was continued in the post-war years. Although pursuing the goal of a socialist economy, the Labour Party distanced itself from the Communists, especially after the Communists' seizure of power in Czechoslovakia in 1948, and strengthened its foreign policy and defence policy ties with the US. Norway received Marshall Plan aid from the United States starting in 1947, joined the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) one year later, and became a founding member of the NATO, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) in 1949.
The first oil was discovered at the small Balder field in 1967, but production only began in 1999. In 1969, the Phillips Petroleum Company discovered petroleum resources at the Ekofisk oil field, Ekofisk field west of Norway. In 1973, the Norwegian government founded the State oil company, Statoil. Oil production did not provide net income until the early 1980s because of the large capital investment that was required to establish the country's petroleum industry. Around 1975, both the proportion and absolute number of workers in industry peaked. Since then labour-intensive industries and services like factory mass production and shipping have largely been outsourced.
Norway was a founding member of the  In 1981, a Conservative Party (Norway), Conservative Party government led by Kåre Willoch replaced the Labour Party with a policy of stimulating the stagflation, stagflated economy with tax cuts, economic liberalisation, deregulation of markets, and measures to curb record-high inflation (13.6% in 1981).
Norway's first female prime minister Gro Harlem Brundtland of the Labour Party continued many of the reforms of her Conservative predecessor, while backing traditional Labour concerns such as social security, high taxes, the industrialisation of nature, and feminism. By the late 1990s, Norway had paid off its foreign debt and had started accumulating a
In 1981, a Conservative Party (Norway), Conservative Party government led by Kåre Willoch replaced the Labour Party with a policy of stimulating the stagflation, stagflated economy with tax cuts, economic liberalisation, deregulation of markets, and measures to curb record-high inflation (13.6% in 1981).
Norway's first female prime minister Gro Harlem Brundtland of the Labour Party continued many of the reforms of her Conservative predecessor, while backing traditional Labour concerns such as social security, high taxes, the industrialisation of nature, and feminism. By the late 1990s, Norway had paid off its foreign debt and had started accumulating a Geography
 Norway's core territory comprises the western and northernmost portion of the
Norway's core territory comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Climate
 The southern and western parts of Norway, fully exposed to Atlantic storm fronts, experience more precipitation and have milder winters than the eastern and far northern parts. Areas to the east of the coastal mountains are in a rain shadow, and have lower rain and snow totals than the west. The lowlands around Oslo have the warmest summers, but also cold weather and snow in wintertime. The sunniest weather is along the south coast, but sometimes even the coast far north can be very sunny – the sunniest month with 430 sun hours was recorded in Tromsø.
Because of Norway's high latitude, there are large seasonal variations in daylight. From late May to late July, the sun never completely descends beneath the horizon in areas north of the Arctic Circle (hence Norway's description as the "Land of the Midnight sun"), and the rest of the country experiences up to 20 hours of daylight per day. Conversely, from late November to late January, the sun never rises above the horizon in the north, and daylight hours are very short in the rest of the country.
The coastal climate of Norway is exceptionally mild compared with areas on similar latitudes elsewhere in the world, with the Gulf Stream passing directly offshore the northern areas of the Atlantic coast, continuously warming the region in the winter. Temperature anomalies found in coastal locations are exceptional, with southern Lofoten and Bø, Nordland, Bø having all monthly means above freezing (lacking a meteorological winter) in spite of being north of the Arctic Circle. The very northernmost coast of Norway would thus be ice-covered in winter if not for the Gulf Stream. The east of the country has a more continental climate, and the mountain ranges have subarctic and tundra climates. There is also higher rainfall in areas exposed to the Atlantic, especially the western slopes of the mountain ranges and areas close, such as Bergen. The valleys east of the mountain ranges are the driest; some of the valleys are sheltered by mountains in most directions. Saltdal (81 m) in Nordland is the driest place with precipitation annually (1991–2020). In southern Norway, Skjåk in Innlandet get precipitation. Finnmarksvidda and some interior valleys of Troms receive around annually, and the high Arctic Longyearbyen .
Parts of southeastern Norway including parts of Mjøsa have a humid continental climates (Köppen climate classification, Köppen Dfb), while the southern and western coasts and also the coast north to Bodø have a oceanic climate (Cfb), while the outer coast further north almost to North Cape have a subpolar oceanic climate (Cfc). Further inland in the south and at higher altitudes, and also in much of Northern Norway, the subarctic climate (Dfc) dominates. A small strip of land along the coast east of North Cape (including Vardø) earlier had Polar climate, tundra/alpine/polar climate (ET), but this is mostly gone with the updated 1991–2020 climate normals, making this also subarctic. Large parts of Norway are covered by mountains and high altitude plateaus, and about one third of the land is above the treeline and thus exhibit Tundra climate, tundra/alpine/polar climate (ET).
The southern and western parts of Norway, fully exposed to Atlantic storm fronts, experience more precipitation and have milder winters than the eastern and far northern parts. Areas to the east of the coastal mountains are in a rain shadow, and have lower rain and snow totals than the west. The lowlands around Oslo have the warmest summers, but also cold weather and snow in wintertime. The sunniest weather is along the south coast, but sometimes even the coast far north can be very sunny – the sunniest month with 430 sun hours was recorded in Tromsø.
Because of Norway's high latitude, there are large seasonal variations in daylight. From late May to late July, the sun never completely descends beneath the horizon in areas north of the Arctic Circle (hence Norway's description as the "Land of the Midnight sun"), and the rest of the country experiences up to 20 hours of daylight per day. Conversely, from late November to late January, the sun never rises above the horizon in the north, and daylight hours are very short in the rest of the country.
The coastal climate of Norway is exceptionally mild compared with areas on similar latitudes elsewhere in the world, with the Gulf Stream passing directly offshore the northern areas of the Atlantic coast, continuously warming the region in the winter. Temperature anomalies found in coastal locations are exceptional, with southern Lofoten and Bø, Nordland, Bø having all monthly means above freezing (lacking a meteorological winter) in spite of being north of the Arctic Circle. The very northernmost coast of Norway would thus be ice-covered in winter if not for the Gulf Stream. The east of the country has a more continental climate, and the mountain ranges have subarctic and tundra climates. There is also higher rainfall in areas exposed to the Atlantic, especially the western slopes of the mountain ranges and areas close, such as Bergen. The valleys east of the mountain ranges are the driest; some of the valleys are sheltered by mountains in most directions. Saltdal (81 m) in Nordland is the driest place with precipitation annually (1991–2020). In southern Norway, Skjåk in Innlandet get precipitation. Finnmarksvidda and some interior valleys of Troms receive around annually, and the high Arctic Longyearbyen .
Parts of southeastern Norway including parts of Mjøsa have a humid continental climates (Köppen climate classification, Köppen Dfb), while the southern and western coasts and also the coast north to Bodø have a oceanic climate (Cfb), while the outer coast further north almost to North Cape have a subpolar oceanic climate (Cfc). Further inland in the south and at higher altitudes, and also in much of Northern Norway, the subarctic climate (Dfc) dominates. A small strip of land along the coast east of North Cape (including Vardø) earlier had Polar climate, tundra/alpine/polar climate (ET), but this is mostly gone with the updated 1991–2020 climate normals, making this also subarctic. Large parts of Norway are covered by mountains and high altitude plateaus, and about one third of the land is above the treeline and thus exhibit Tundra climate, tundra/alpine/polar climate (ET).
Biodiversity
 The total number of species include 16,000 species of insects (probably 4,000 more species yet to be described), 20,000 species of algae, 1,800 species of lichen, 1,050 species of mosses, 2,800 species of vascular plants, up to 7,000 species of fungus, fungi, 450 species of birds (250 species nesting in Norway), 90 species of mammals, 45 fresh-water species of fish, 150 salt-water species of fish, 1,000 species of fresh-water invertebrates, and 3,500 species of salt-water invertebrates. About 40,000 of these species have been described by science. The IUCN Red List, red list of 2010 encompasses 4,599 species.Norwegian Red List 2010
The total number of species include 16,000 species of insects (probably 4,000 more species yet to be described), 20,000 species of algae, 1,800 species of lichen, 1,050 species of mosses, 2,800 species of vascular plants, up to 7,000 species of fungus, fungi, 450 species of birds (250 species nesting in Norway), 90 species of mammals, 45 fresh-water species of fish, 150 salt-water species of fish, 1,000 species of fresh-water invertebrates, and 3,500 species of salt-water invertebrates. About 40,000 of these species have been described by science. The IUCN Red List, red list of 2010 encompasses 4,599 species.Norwegian Red List 2010Artsdatabanken.no Norway contains five terrestrial ecoregions: Sarmatic mixed forests, Scandinavian coastal conifer forests, Scandinavian and Russian taiga, Kola Peninsula tundra, and Scandinavian montane birch forest and grasslands. Seventeen species are listed mainly because they are endangered on a global scale, such as the Eurasian beaver, European beaver, even if the population in Norway is not seen as endangered. The number of threatened and near-threatened species equals to 3,682; it includes 418 fungi species, many of which are closely associated with the small remaining areas of old-growth forests, 36 bird species, and 16 species of mammals. In 2010, 2,398 species were listed as endangered or vulnerable; of these were 1250 listed as vulnerable (VU), 871 as endangered (EN), and 276 species as critically endangered (CR), among which were the grey wolf, the Arctic fox (healthy population on Svalbard) and the pool frog. The largest predator in Norwegian waters is the sperm whale, and the largest fish is the basking shark. The largest predator on land is the polar bear, while the brown bear is the largest predator on the Norwegian mainland. The largest land animal on the mainland is the elk (American English: moose). The elk in Norway is known for its size and strength and is often called ''skogens konge'', "king of the forest".
Environment
Attractive and dramatic scenery and landscape are found throughout Norway. The west coast of southern Norway and the coast of northern Norway present some of the most visually impressive coastal sceneries in the world. National Geographic Society, National Geographic has listed the Norwegian fjords as the world's top tourist attraction. The country is also home to the natural phenomena of the Midnight sun (during summer), as well as the Aurora, Aurora borealis known also as the Northern lights. The 2016 Environmental Performance Index from Yale University, Columbia University and the World Economic Forum put Norway in seventeenth place, immediately below Croatia and Switzerland. The index is based on environmental risks to human health, habitat loss, and changes in emissions. The index notes over-exploitation of fisheries, but not Whaling in Norway, Norway's whaling or Energy in Norway, oil exports. Norway had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 6.98/10, ranking it 60th globally out of 172 countries.Politics and government

Administrative divisions
Dependencies of Norway
There are three Antarctica, Antarctic andLargest populated areas
Judicial system and law enforcement
Norway uses a civil law (legal system), civil law system where laws are created and amended in Parliament and the system regulated through the Courts of justice of Norway. It consists of the Supreme Court of Norway, Supreme Court of 20 permanent judges and a Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of Norway, Chief Justice, appellate courts, city and Courts of justice of Norway#District courts, district courts, and conciliation councils. The judiciary is independent of executive and legislative branches. While the Prime Minister nominates Supreme Court Justices for office, their nomination must be approved by Parliament and formally confirmed by the Monarch in the Council of State. Usually, judges attached to regular courts are formally appointed by the Monarch on the advice of the Prime Minister. The Courts' strict and formal mission is to regulate the Norwegian judicial system, interpret the Constitution, and as such implement the legislation adopted by Parliament. In its judicial reviews, it monitors the legislative and executive branches to ensure that they comply with provisions of enacted legislation. The Law enforcement in Norway, law is enforced in Norway by the Norwegian Police Service. It is a Unified National Police Service made up of 27 Police Districts and several specialist agencies, such as Norwegian National Authority for the Investigation and Prosecution of Economic and Environmental Crime, known as ''Økokrim''; and the National Criminal Investigation Service (Norway), National Criminal Investigation Service, known as ''Kripos'', each headed by a chief of police. The Police Service is headed by the National Police Directorate, which reports to the Ministry of Justice and the Police. The Police Directorate is headed by a National Police Commissioner. The only exception is the Norwegian Police Security Service, Norwegian Police Security Agency, whose head answers directly to the Ministry of Justice and the Police. Norway abolished the death penalty for regular criminal acts in 1902. The legislature abolished the death penalty for high treason in war and war-crimes in 1979. Reporters Without Borders, in its 2007 Worldwide Press Freedom Index, ranked Norway at a shared first place (along with Iceland) out of 169 countries. In general, the legal and institutional framework in Norway is characterised by a high degree of transparency, accountability and integrity, and the perception and the occurrence of corruption are very low. Norway has ratified all relevant international anti-corruption conventions, and its standards of implementation and enforcement of anti-corruption legislation are considered very high by many international anti-corruption working groups such as the OECD Anti-Bribery Working Group. However, there are some isolated cases showing that some municipalities have abused their position in public procurement processes. Norwegian prisons are humane, rather than tough, with emphasis on rehabilitation. At 20%, Norway's re-conviction rate is among the lowest in the world.Human rights
Norway has been considered a progressive country, which has adopted legislation and policies to support women's rights, minority rights, and LGBT rights in Norway, LGBT rights. As early as 1884, 171 of the leading figures, among them five Prime Ministers for the Liberal Party and the Conservative Party, co-founded the Norwegian Association for Women's Rights. They successfully campaigned for women's right to education, women's suffrage, the right to work, and other gender equality policies. From the 1970s, gender equality also came high on the state agenda, with the establishment of a public body to promote gender equality, which evolved into the Gender Equality and Anti-Discrimination Ombud. Civil society organisations also continue to play an important role, and the women's rights organisations are today organised in the Norwegian Women's Lobby umbrella organisation. In 1990, the Norwegian constitution was amended to grant absolute primogeniture to the Norwegian throne, meaning that the eldest child, regardless of gender, takes precedence in the line of succession. As it was not retroactive, the current successor to the throne is the eldest son of the King, rather than his eldest child. The Norwegian constitution Article 6 states that "For those born before the year 1990 it shall...be the case that a male shall take precedence over a female." The Sámi people have for centuries been the subject of discrimination and abuse by the dominant cultures in Scandinavia and Russia, those countries claiming possession of Sámi lands. The Sámi people have never been a single community in a single region of Sápmi. Norway has been greatly criticised by the international community for the politics of Norwegianization of and discrimination against the indigenous population of the country. Nevertheless, Norway was, in 1990, the first country to recognise Indigenous and Tribal Peoples Convention, 1989, ILO-convention 169 on indigenous people recommended by the UN.
In regard to LGBT rights, Norway was the first country in the world to enact an anti-discrimination law protecting the rights of gays and lesbians. In 1993, Norway became the second country to legalise civil union partnerships for same-sex couples, and on 1 January 2009 Same-sex marriage in Norway, Norway became the sixth country to legalise same-sex marriage. As a promoter of human rights, Norway has held the annual Oslo Freedom Forum conference, a gathering described by ''The Economist'' as "on its way to becoming a human-rights equivalent of the Davos economic forum."
The Sámi people have for centuries been the subject of discrimination and abuse by the dominant cultures in Scandinavia and Russia, those countries claiming possession of Sámi lands. The Sámi people have never been a single community in a single region of Sápmi. Norway has been greatly criticised by the international community for the politics of Norwegianization of and discrimination against the indigenous population of the country. Nevertheless, Norway was, in 1990, the first country to recognise Indigenous and Tribal Peoples Convention, 1989, ILO-convention 169 on indigenous people recommended by the UN.
In regard to LGBT rights, Norway was the first country in the world to enact an anti-discrimination law protecting the rights of gays and lesbians. In 1993, Norway became the second country to legalise civil union partnerships for same-sex couples, and on 1 January 2009 Same-sex marriage in Norway, Norway became the sixth country to legalise same-sex marriage. As a promoter of human rights, Norway has held the annual Oslo Freedom Forum conference, a gathering described by ''The Economist'' as "on its way to becoming a human-rights equivalent of the Davos economic forum."
Foreign relations
 Norway maintains embassies in 82 countries. 60 countries maintain an embassy in Norway, all of them in the capital, Oslo.
Norway is a founding member of the United Nations (UN), the NATO, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), the
Norway maintains embassies in 82 countries. 60 countries maintain an embassy in Norway, all of them in the capital, Oslo.
Norway is a founding member of the United Nations (UN), the NATO, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), the Military
 The Norwegian Armed Forces numbers about 25,000 personnel, including civilian employees. According to 2009 mobilisation plans, full mobilisation produces approximately 83,000 combatant personnel. Norway has conscription (including 6–12 months of training); in 2013, the country became the first in Europe and NATO to draft women as well as men. However, due to less need for conscripts after the Cold War ended with the break-up of the Soviet Union, few people have to serve if they are not motivated. The Armed Forces are subordinate to the Norwegian Ministry of Defence. The Commander-in-Chief is Harald V of Norway, King Harald V. The military of Norway is divided into the following branches: the Norwegian Army, the Royal Norwegian Navy, the Royal Norwegian Air Force, the Norwegian Cyber Defence Force and the Home Guard (Norway), Home Guard.
In response to its being overrun by Germany in 1940, the country was one of the founding nations of the NATO, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) on 4 April 1949. Norway contributed in the International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) in War in Afghanistan (2001–present), Afghanistan. Additionally, Norway has contributed in several missions in contexts of the United Nations, NATO, and the Common Security and Defence Policy of the European Union.
The Norwegian Armed Forces numbers about 25,000 personnel, including civilian employees. According to 2009 mobilisation plans, full mobilisation produces approximately 83,000 combatant personnel. Norway has conscription (including 6–12 months of training); in 2013, the country became the first in Europe and NATO to draft women as well as men. However, due to less need for conscripts after the Cold War ended with the break-up of the Soviet Union, few people have to serve if they are not motivated. The Armed Forces are subordinate to the Norwegian Ministry of Defence. The Commander-in-Chief is Harald V of Norway, King Harald V. The military of Norway is divided into the following branches: the Norwegian Army, the Royal Norwegian Navy, the Royal Norwegian Air Force, the Norwegian Cyber Defence Force and the Home Guard (Norway), Home Guard.
In response to its being overrun by Germany in 1940, the country was one of the founding nations of the NATO, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) on 4 April 1949. Norway contributed in the International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) in War in Afghanistan (2001–present), Afghanistan. Additionally, Norway has contributed in several missions in contexts of the United Nations, NATO, and the Common Security and Defence Policy of the European Union.
Economy
Resources

 ;Oil industry
;Oil industry
 Export revenues from oil and gas have risen to over 40% of total exports and constitute almost 20% of the GDP. Norway is the fifth-largest oil exporter and third-largest gas exporter in the world, but it is not a member of OPEC. In 1995, the Norwegian government established the sovereign wealth fund (The Government Pension Fund of Norway, "Government Pension Fund – Global"), which would be funded with oil revenues, including taxes, dividends, sales revenues and licensing fees. This was intended to reduce overheating in the economy from oil revenues, minimise uncertainty from volatility in oil price, and provide a cushion to compensate for expenses associated with the ageing of the population.
The government controls its petroleum resources through a combination of state ownership in major operators in the oil fields (with approximately 62% ownership in Statoil in 2007) and the fully state-owned Petoro, which has a market value of about twice Statoil, and State's Direct Financial Interest, SDFI. Finally, the government controls licensing of exploration and production of fields. The fund invests in developed financial markets outside Norway. Spending from the fund is constrained by the budgetary rule (''Handlingsregelen''), which limits spending over time to no more than the real value yield of the fund, originally assumed to be 4% a year, but lowered in 2017 to 3% of the fund's total value.
Between 1966 and 2013, Norwegian companies drilled 5,085 oil wells, mostly in the North Sea.Ole Mathismoen (5 August 2013) ''Aftenposten'' p. 5 Of these, 3,672 are ''utviklingsbrønner'' (regular production); 1,413 are ''letebrønner'' (exploration); and 1,405 have been terminated (''avsluttet'').
Oil fields not yet in the production phase include: Wisting Central—calculated size in 2013 at 65–156 million barrels of oil and , (''utvinnbar'') of gas. and the Castberg Oil Field (''Castberg-feltet'')—calculated size at 540 million barrels of oil, and (''utvinnbar'') of gas. Both oil fields are located in the
Export revenues from oil and gas have risen to over 40% of total exports and constitute almost 20% of the GDP. Norway is the fifth-largest oil exporter and third-largest gas exporter in the world, but it is not a member of OPEC. In 1995, the Norwegian government established the sovereign wealth fund (The Government Pension Fund of Norway, "Government Pension Fund – Global"), which would be funded with oil revenues, including taxes, dividends, sales revenues and licensing fees. This was intended to reduce overheating in the economy from oil revenues, minimise uncertainty from volatility in oil price, and provide a cushion to compensate for expenses associated with the ageing of the population.
The government controls its petroleum resources through a combination of state ownership in major operators in the oil fields (with approximately 62% ownership in Statoil in 2007) and the fully state-owned Petoro, which has a market value of about twice Statoil, and State's Direct Financial Interest, SDFI. Finally, the government controls licensing of exploration and production of fields. The fund invests in developed financial markets outside Norway. Spending from the fund is constrained by the budgetary rule (''Handlingsregelen''), which limits spending over time to no more than the real value yield of the fund, originally assumed to be 4% a year, but lowered in 2017 to 3% of the fund's total value.
Between 1966 and 2013, Norwegian companies drilled 5,085 oil wells, mostly in the North Sea.Ole Mathismoen (5 August 2013) ''Aftenposten'' p. 5 Of these, 3,672 are ''utviklingsbrønner'' (regular production); 1,413 are ''letebrønner'' (exploration); and 1,405 have been terminated (''avsluttet'').
Oil fields not yet in the production phase include: Wisting Central—calculated size in 2013 at 65–156 million barrels of oil and , (''utvinnbar'') of gas. and the Castberg Oil Field (''Castberg-feltet'')—calculated size at 540 million barrels of oil, and (''utvinnbar'') of gas. Both oil fields are located in the Transport
 Due to the low population density, narrow shape and long coastlines of Norway, its public transport is less developed than in many European countries, especially outside the major cities. The country has long-standing water transport traditions, but the Norwegian Ministry of Transport and Communications has in recent years implemented rail, road, and air transport through numerous subsidiaries to develop the country's infrastructure. Under discussion is development of a new high-speed rail system between the nation's largest cities.
Norway's main railway network consists of of standard gauge lines, of which is double track and high-speed rail (210 km/h) while 62% is electrified at . The railways transported 56,827,000 passengers 2,956 million Units of transportation measurement, passenger-kilometres and 24,783,000 tonnes of cargo 3,414 million Units of transportation measurement, tonne-kilometres.Norwegian National Rail Administration, 2008: 4 The entire network is owned by the Norwegian National Rail Administration. All domestic passenger trains except the Flytoget, Airport Express Train are operated by Norwegian State Railways, Norges Statsbaner (NSB).Norwegian National Rail Administration, 2008: 13 Several companies operate freight trains.Norwegian National Rail Administration, 2008: 16
Investment in new infrastructure and maintenance is financed through the state budget, and subsidies are provided for passenger train operations. NSB operates long-haul trains, including NSB Night Train, night trains, regional services and four commuter rail, commuter train systems, around Oslo Commuter Rail, Oslo, Trøndelag Commuter Rail, Trondheim, Bergen Commuter Rail, Bergen and Jæren Line, Stavanger.
Due to the low population density, narrow shape and long coastlines of Norway, its public transport is less developed than in many European countries, especially outside the major cities. The country has long-standing water transport traditions, but the Norwegian Ministry of Transport and Communications has in recent years implemented rail, road, and air transport through numerous subsidiaries to develop the country's infrastructure. Under discussion is development of a new high-speed rail system between the nation's largest cities.
Norway's main railway network consists of of standard gauge lines, of which is double track and high-speed rail (210 km/h) while 62% is electrified at . The railways transported 56,827,000 passengers 2,956 million Units of transportation measurement, passenger-kilometres and 24,783,000 tonnes of cargo 3,414 million Units of transportation measurement, tonne-kilometres.Norwegian National Rail Administration, 2008: 4 The entire network is owned by the Norwegian National Rail Administration. All domestic passenger trains except the Flytoget, Airport Express Train are operated by Norwegian State Railways, Norges Statsbaner (NSB).Norwegian National Rail Administration, 2008: 13 Several companies operate freight trains.Norwegian National Rail Administration, 2008: 16
Investment in new infrastructure and maintenance is financed through the state budget, and subsidies are provided for passenger train operations. NSB operates long-haul trains, including NSB Night Train, night trains, regional services and four commuter rail, commuter train systems, around Oslo Commuter Rail, Oslo, Trøndelag Commuter Rail, Trondheim, Bergen Commuter Rail, Bergen and Jæren Line, Stavanger.
 Norway has approximately of road network, of which are paved and are motorway. The four tiers of road routes are national, county, municipal and private, with national and primary county roads numbered en route. The most important national routes are part of the International E-road network, European route scheme. The two most prominent are the European route E6 going north–south through the entire country, and the European route E39, E39, which follows the West Coast. National and county roads are managed by the Norwegian Public Roads Administration.
Norway has the world's largest registered stock of plug-in electric vehicles in Norway, plug-in electric vehicles per capita. ''See table "Elbilsalg i 2011 fordelt på måned og merke" (Electric vehicle sales in 2011, by month and brand) to see monthly sales for 2011.'' In March 2014, Norway became the first country where over 1 in every 100 passenger cars on the roads is a plug-in electric. The plug-in electric segment market share of new car sales is also the highest in the world. According to a report by ''Dagens Næringsliv'' in June 2016, the country would like to ban sales of gasoline and diesel powered vehicles as early as 2025. In June 2017, 42% of new cars registered were electric.
Of the 98 airports in Norway, 52 are public, and 46 are operated by the state-owned Avinor. List of the largest airports in the Nordic countries, Seven airports have more than one million passengers annually. A total of 41,089,675 passengers passed through Norwegian airports in 2007, of whom 13,397,458 were international.
The central gateway to Norway by air is Oslo Airport, Gardermoen. Located about northeast of Oslo, it is airline hub, hub for the two major Norwegian airlines: Scandinavian Airlines and Norwegian Air Shuttle, and for regional aircraft from Western Norway. There are departures to most European countries and some intercontinental destinations. A direct high-speed train connects to Oslo Central Station every 10 minutes for a 20 min ride.
Norway has approximately of road network, of which are paved and are motorway. The four tiers of road routes are national, county, municipal and private, with national and primary county roads numbered en route. The most important national routes are part of the International E-road network, European route scheme. The two most prominent are the European route E6 going north–south through the entire country, and the European route E39, E39, which follows the West Coast. National and county roads are managed by the Norwegian Public Roads Administration.
Norway has the world's largest registered stock of plug-in electric vehicles in Norway, plug-in electric vehicles per capita. ''See table "Elbilsalg i 2011 fordelt på måned og merke" (Electric vehicle sales in 2011, by month and brand) to see monthly sales for 2011.'' In March 2014, Norway became the first country where over 1 in every 100 passenger cars on the roads is a plug-in electric. The plug-in electric segment market share of new car sales is also the highest in the world. According to a report by ''Dagens Næringsliv'' in June 2016, the country would like to ban sales of gasoline and diesel powered vehicles as early as 2025. In June 2017, 42% of new cars registered were electric.
Of the 98 airports in Norway, 52 are public, and 46 are operated by the state-owned Avinor. List of the largest airports in the Nordic countries, Seven airports have more than one million passengers annually. A total of 41,089,675 passengers passed through Norwegian airports in 2007, of whom 13,397,458 were international.
The central gateway to Norway by air is Oslo Airport, Gardermoen. Located about northeast of Oslo, it is airline hub, hub for the two major Norwegian airlines: Scandinavian Airlines and Norwegian Air Shuttle, and for regional aircraft from Western Norway. There are departures to most European countries and some intercontinental destinations. A direct high-speed train connects to Oslo Central Station every 10 minutes for a 20 min ride.
Research
 Internationally recognised Norwegian scientists include the mathematicians Niels Henrik Abel and Sophus Lie, who are recognized as some of the most influential mathematicians of all time. Caspar Wessel was the first to describe Vector (mathematics and physics), vectors and complex numbers in the complex plane. Ernst Sejersted Selmer, Ernst S. Selmer's advanced research lead to the modernisation of Cryptography, crypto-algorithms. Thoralf Skolem made revolutionary contributions to mathematical logic. Øystein Ore and Peter Ludwig Mejdell Sylow, Ludwig Sylow made important contributions in group theory. Atle Selberg was one of the most significant mathematicians of the 20th century, for which he was awarded a Fields Medal, Wolf Prize in Mathematics, Wolf Prize and Abel Prize.
Other scientists include the physicists Ægidius Elling, Ivar Giaever, Carl Anton Bjerknes, Christopher Hansteen, William Houlder Zachariasen, William Zachariasen and Kristian Birkeland, the neuroscientists May-Britt Moser and Edvard Moser, and the chemists Lars Onsager, Odd Hassel, Peter Waage, Erik Rotheim, and Cato Maximilian Guldberg. Mineralogist Victor Goldschmidt is considered to be one of two founders of modern geochemistry. The meteorologists Vilhelm Bjerknes and Ragnar Fjørtoft played a central role in the history of numerical weather prediction. Web pioneer Håkon Wium Lie developed CSS, Cascading Style Sheets, one of the three main pillars of the World Wide Web. Pål Spilling participated in the development of the Internet Protocol and brought the Internet to Europe, establishing the first network outside United States to be connected to the American Internet. Computer scientists Ole-Johan Dahl and Kristen Nygaard are considered to be the fathers of the tremendously influential Simula and object-oriented programming, for which they were awarded a Turing Award.
In the 20th century, Norwegian academics have been pioneering in many social sciences, including criminology, sociology and peace and conflict studies. Prominent academics include Arne Næss, a philosopher and founder of deep ecology; Johan Galtung, the founder of peace studies; Nils Christie and Thomas Mathiesen, criminologists; Fredrik Barth, a social anthropologist; Vilhelm Aubert, Harriet Holter and Erik Grønseth, sociologists; Tove Stang Dahl, a pioneer of women's law; Stein Rokkan, a political scientist; and Ragnar Frisch, Trygve Haavelmo, and Finn E. Kydland, economists.
The Kingdom of Norway has produced thirteen List of Nobel laureates by country, Nobel laureates. Norway was ranked 20th in the Global Innovation Index in 2020 and 2021, down from 19th in 2019.
Internationally recognised Norwegian scientists include the mathematicians Niels Henrik Abel and Sophus Lie, who are recognized as some of the most influential mathematicians of all time. Caspar Wessel was the first to describe Vector (mathematics and physics), vectors and complex numbers in the complex plane. Ernst Sejersted Selmer, Ernst S. Selmer's advanced research lead to the modernisation of Cryptography, crypto-algorithms. Thoralf Skolem made revolutionary contributions to mathematical logic. Øystein Ore and Peter Ludwig Mejdell Sylow, Ludwig Sylow made important contributions in group theory. Atle Selberg was one of the most significant mathematicians of the 20th century, for which he was awarded a Fields Medal, Wolf Prize in Mathematics, Wolf Prize and Abel Prize.
Other scientists include the physicists Ægidius Elling, Ivar Giaever, Carl Anton Bjerknes, Christopher Hansteen, William Houlder Zachariasen, William Zachariasen and Kristian Birkeland, the neuroscientists May-Britt Moser and Edvard Moser, and the chemists Lars Onsager, Odd Hassel, Peter Waage, Erik Rotheim, and Cato Maximilian Guldberg. Mineralogist Victor Goldschmidt is considered to be one of two founders of modern geochemistry. The meteorologists Vilhelm Bjerknes and Ragnar Fjørtoft played a central role in the history of numerical weather prediction. Web pioneer Håkon Wium Lie developed CSS, Cascading Style Sheets, one of the three main pillars of the World Wide Web. Pål Spilling participated in the development of the Internet Protocol and brought the Internet to Europe, establishing the first network outside United States to be connected to the American Internet. Computer scientists Ole-Johan Dahl and Kristen Nygaard are considered to be the fathers of the tremendously influential Simula and object-oriented programming, for which they were awarded a Turing Award.
In the 20th century, Norwegian academics have been pioneering in many social sciences, including criminology, sociology and peace and conflict studies. Prominent academics include Arne Næss, a philosopher and founder of deep ecology; Johan Galtung, the founder of peace studies; Nils Christie and Thomas Mathiesen, criminologists; Fredrik Barth, a social anthropologist; Vilhelm Aubert, Harriet Holter and Erik Grønseth, sociologists; Tove Stang Dahl, a pioneer of women's law; Stein Rokkan, a political scientist; and Ragnar Frisch, Trygve Haavelmo, and Finn E. Kydland, economists.
The Kingdom of Norway has produced thirteen List of Nobel laureates by country, Nobel laureates. Norway was ranked 20th in the Global Innovation Index in 2020 and 2021, down from 19th in 2019.
Tourism
In 2008, Norway ranked 17th in the World Economic Forum's Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Report. Tourism in Norway contributed to 4.2% of the gross domestic product as reported in 2016. Every one in fifteen people throughout the country work in the tourism industry. Tourism is seasonal in Norway, with more than half of total tourists visiting between the months of May and August. The main attractions of Norway are the varied landscapes that extend across the Arctic Circle. It is famous for its fjord-indented coastline and its mountains, ski resorts, lakes and woods. Popular tourist destinations in Norway includeDemographics
Population
ssb.no of the total population have at least one parent who was born in Norway. In 2020 approximately 980,000 individuals (18.2%) were immigrants and their descendants. Among these approximately 189,000 are children of immigrants, born in Norway.
 Of these 980,000 immigrants and their descendants:
* 485,500 (49.5%) have a Western culture, Western background (Europe, USA, Canada and Oceania).
* 493,700 (50.5%) have a non-Western background (Asia, Africa, South and Central America).
In 2013, the Norwegian government said that 14% of the Norwegian population were immigrants or children of two immigrant parents. About 6% of the population are immigrants from EU, North America and Australia, and about 8.1% come from Asia, Africa and Latin America.12 prosent av befolkningen er innvandrere
Of these 980,000 immigrants and their descendants:
* 485,500 (49.5%) have a Western culture, Western background (Europe, USA, Canada and Oceania).
* 493,700 (50.5%) have a non-Western background (Asia, Africa, South and Central America).
In 2013, the Norwegian government said that 14% of the Norwegian population were immigrants or children of two immigrant parents. About 6% of the population are immigrants from EU, North America and Australia, and about 8.1% come from Asia, Africa and Latin America.12 prosent av befolkningen er innvandrereStatistics Norway retrieved 26 April 2013 In 2012, of the total 660,000 with immigrant background, 407,262 had Norwegian citizenship (62.2%).
Statistics Norway. 26 April 2012. Retrieved 27 April 2012. [https://www.webcitation.org/60kwqnxn8?url=http://www.ssb.no/innvbef_en/tab-2011-04-28-02-en.html Archived] 7 August 2011. Immigrants have settled in all Norwegian municipalities. The cities or municipalities with the highest share of immigrants in 2012 were
Statistics Norway. Retrieved 30 December 2013 The share in Stavanger was 16%. According to Reuters, Oslo is the "fastest growing city in Europe because of increased immigration". In recent years, immigration has accounted for most of Norway's population growth. In 2011, 16% of newborn children were of immigrant background. The
Migration
 Particularly in the 19th century, when economic conditions were difficult in Norway, tens of thousands of people migrated to the United States and Canada, where they could work and buy land in frontier areas. Many went to the Midwest and Pacific Northwest. In 2006, according to the US Census Bureau, almost 4.7 million persons identified as Norwegian Americans, which was larger than the population of ethnic Norwegians in Norway itself. In the 2011 Canadian census, 452,705 Canadian citizens identified as having Norwegian Canadians, Norwegian ancestry.
, the number of immigrants or children of two immigrants residing in Norway was 710,465, or 14.1% of the total population, up from 183,000 in 1992. Yearly immigration has increased since 2005. While yearly net immigration in 2001–2005 was on average 13,613, it increased to 37,541 between 2006 and 2010, and in 2011 net immigration reached 47,032. This is mostly because of increased immigration by residents of the EU, in particular from Poland.
In 2012, the immigrant community (which includes immigrants and children born in Norway of immigrant parents) grew by 55,300, a record high. Net immigration from abroad reached 47,300 (300 higher than in 2011), while immigration accounted for 72% of Norway's population growth. 17% of newborn children were born to immigrant parents. Children of Pakistani, Somali and Norwegian Vietnamese, Vietnamese parents made up the largest groups of all Norwegians born to immigrant parents.
Pakistani Norwegians are the largest non-European minority group in Norway. Most of their 32,700 members live in and around Oslo. The Iraqis in Norway, Iraqi and Somali immigrant populations have increased significantly in recent years. After the enlargement of the EU in 2004, a wave of immigrants arrived from Central and Northern Europe, particularly Poland, Sweden and Lithuania. The fastest growing immigrant groups in 2011 in absolute numbers were from Poland, Lithuania and Sweden. The policies of immigration and integration have been the subject of much debate in Norway.
Particularly in the 19th century, when economic conditions were difficult in Norway, tens of thousands of people migrated to the United States and Canada, where they could work and buy land in frontier areas. Many went to the Midwest and Pacific Northwest. In 2006, according to the US Census Bureau, almost 4.7 million persons identified as Norwegian Americans, which was larger than the population of ethnic Norwegians in Norway itself. In the 2011 Canadian census, 452,705 Canadian citizens identified as having Norwegian Canadians, Norwegian ancestry.
, the number of immigrants or children of two immigrants residing in Norway was 710,465, or 14.1% of the total population, up from 183,000 in 1992. Yearly immigration has increased since 2005. While yearly net immigration in 2001–2005 was on average 13,613, it increased to 37,541 between 2006 and 2010, and in 2011 net immigration reached 47,032. This is mostly because of increased immigration by residents of the EU, in particular from Poland.
In 2012, the immigrant community (which includes immigrants and children born in Norway of immigrant parents) grew by 55,300, a record high. Net immigration from abroad reached 47,300 (300 higher than in 2011), while immigration accounted for 72% of Norway's population growth. 17% of newborn children were born to immigrant parents. Children of Pakistani, Somali and Norwegian Vietnamese, Vietnamese parents made up the largest groups of all Norwegians born to immigrant parents.
Pakistani Norwegians are the largest non-European minority group in Norway. Most of their 32,700 members live in and around Oslo. The Iraqis in Norway, Iraqi and Somali immigrant populations have increased significantly in recent years. After the enlargement of the EU in 2004, a wave of immigrants arrived from Central and Northern Europe, particularly Poland, Sweden and Lithuania. The fastest growing immigrant groups in 2011 in absolute numbers were from Poland, Lithuania and Sweden. The policies of immigration and integration have been the subject of much debate in Norway.
Religion
Church of Norway
 Separation of church and state#Norway, Separation of church and state happened significantly later in Norway than in most of Europe, and remains incomplete. In 2012, the Norwegian parliament voted to grant the Church of Norway greater autonomy, a decision which was confirmed in a constitutional amendment on 21 May 2012.
Until 2012 parliamentary officials were required to be members of the Evangelical-Lutheran Church of Norway, and at least half of all government ministers had to be a member of the state church. As state church, the Church of Norway's clergy were viewed as state employees, and the central and regional church administrations were part of the state administration. Members of the Royal family are required to be members of the Lutheran church. On 1 January 2017, Norway made the church independent of the state, but retained the Church's status as the "people's church".
Most Norwegians are registered at baptism as members of the Church of Norway, which has been Norway's state church since its establishment. In recent years the church has been granted increasing internal autonomy, but it retains its special constitutional status and other special ties to the state, and the constitution requires that the reigning monarch must be a member and states that the country's values are based on its Christian and humanist heritage. Many remain in the church to participate in the community and practices such as baptism, confirmation, marriage and burial rites. About 70.6% of Norwegians were members of the Church of Norway in 2017. In 2017, about 53.6% of all newborns were baptised and about 57.9% of all 15-year-old persons were Confirmation (Lutheran Church), confirmed in the church.
Separation of church and state#Norway, Separation of church and state happened significantly later in Norway than in most of Europe, and remains incomplete. In 2012, the Norwegian parliament voted to grant the Church of Norway greater autonomy, a decision which was confirmed in a constitutional amendment on 21 May 2012.
Until 2012 parliamentary officials were required to be members of the Evangelical-Lutheran Church of Norway, and at least half of all government ministers had to be a member of the state church. As state church, the Church of Norway's clergy were viewed as state employees, and the central and regional church administrations were part of the state administration. Members of the Royal family are required to be members of the Lutheran church. On 1 January 2017, Norway made the church independent of the state, but retained the Church's status as the "people's church".
Most Norwegians are registered at baptism as members of the Church of Norway, which has been Norway's state church since its establishment. In recent years the church has been granted increasing internal autonomy, but it retains its special constitutional status and other special ties to the state, and the constitution requires that the reigning monarch must be a member and states that the country's values are based on its Christian and humanist heritage. Many remain in the church to participate in the community and practices such as baptism, confirmation, marriage and burial rites. About 70.6% of Norwegians were members of the Church of Norway in 2017. In 2017, about 53.6% of all newborns were baptised and about 57.9% of all 15-year-old persons were Confirmation (Lutheran Church), confirmed in the church.
Religious affiliation
According to the 2010 Eurobarometer Poll, 22% of Norwegian citizens responded that "they believe there is a God", 44% responded that "they believe there is some sort of spirit or life force" and 29% responded that "they don't believe there is any sort of spirit, God or life force". Five percent gave no response. In the early 1990s, studies estimated that between 4.7% and 5.3% of Norwegians attended church on a weekly basis. This figure has dropped to about 2%. In 2010, 10% of the population was Irreligion, religiously unaffiliated, while another 9% were members of religious communities outside the Church of Norway. Other Christian denominations total about 4.9% of the population, the largest of which is the Roman Catholic Church, with 83,000 members, according to 2009 government statistics. The ''Aftenposten'' (Norwegian, The Evening Post) in October 2012 reported there were about 115,234 registered Roman Catholics in Norway; the reporter estimated that the total number of people with a Roman Catholic background may be 170,000–200,000 or higher. Others include Pentecostalism, Pentecostals (39,600), the Evangelical Lutheran Free Church of Norway (19,600), Methodists (11,000), Baptists (9,900), Eastern Orthodox (9,900), Brunstad Christian Church (6,800), Seventh-day Adventists (5,100), Religion in Iraq#Christianity, Assyrians and Chaldeans, and others. The Swedish, Finnish and Icelandic Lutheran congregations in Norway have about 27,500 members in total. Other Christian denominations comprise less than 1% each, including 4,000 members in the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints and 12,000 Jehovah's Witnesses. Among non-Christian religions, Islam in Norway, Islam is the largest, with 166,861 registered members (2018), and probably fewer than 200,000 in total. It is practised mainly by Somali, Arab diaspora, Arab, Bosniaks, Bosniak, Kurds, Kurdish and Turkish people, Turkish immigrants, as well as Norwegians of Pakistani descent. Other religions comprise less than 1% each, including 819 adherents of History of the Jews in Norway, Judaism. Indian immigrants introduced Hinduism to Norway, which in 2011 has slightly more than 5,900 adherents, or 1% of non-Lutheran Norwegians. Sikhism has approximately 3,000 adherents, with most living in Oslo, which has two gurdwaras. Sikhs first came to Norway in the early 1970s. The troubles in Punjab after Operation Blue Star and riots committed against Sikhs in India after the assassination of Indira Gandhi led to an increase in Sikh refugees moving to Norway. Drammen also has a sizeable population of Sikhs; the largest gurdwara in north Europe was built in Lier, Norway, Lier. There are eleven Buddhist organisations, grouped under the Buddhist Federation of Norway, Buddhistforbundet organisation, with slightly over 14,000 members, which make up 0.2% of the population. The Baháʼí Faith religion has slightly more than 1,000 adherents. Around 1.7% (84,500) of Norwegians belong to the secular Norwegian Humanist Association. From 2006 to 2011, the fastest-growing religious communities in Norway were Eastern Orthodoxy in Norway, Eastern Orthodox Christianity and Oriental Orthodoxy in Norway, Oriental Orthodox Christianity, which grew in membership by 80%; however, their share of the total population remains small, at 0.2%. It is associated with the immigration from Eritrea and Ethiopia, and to a lesser extent from Central Europe, Central and Eastern European and Middle Eastern countries. Other fast-growing religions were Roman Catholicism in Norway, Roman Catholicism (78.7%), Hinduism in Norway, Hinduism (59.6%), Islam in Norway, Islam (48.1%), and Buddhism in Norway, Buddhism (46.7%).Indigenous religions
As in other Scandinavian countries, the ancient Norse followed a form of native Germanic paganism known as Norse paganism. By the end of the 11th century, when Norway had been Christianization of Scandinavia, Christianised, the indigenous Norse religion and practices were prohibited. Remnants of the native religion and beliefs of Norway survive today in the form of names, referential names of cities and locations, the days of the week, and other parts of everyday language. Modern interest in the old ways has led to a revival of pagan religious practices in the form of ''Germanic Neopaganism, Åsatru.'' The Norwegian ''Åsatrufellesskapet Bifrost'' formed in 1996; in 2011, the fellowship had about 300 members. ''Foreningen Forn Sed'' was formed in 1999 and has been recognised by the Norwegian government. The Sámi minority retained their Sámi shamanism, shamanistic religion well into the 18th century, when most converted to Christianity under the influence of Dano-Norwegian Lutheran missionaries. Although some insist that "indigenous Sámi religion had effectively been eradicated,' anthropologist Gutorm Gjessing's ''Changing Lapps'' (1954) argues that the Sámi's "were outwardly and to all practical purposes converted to Christianity, but at the subconscious and unconscious level, the shamistic frenzy survived, more or less latent, only awaiting the necessary stimulus to break out into the open." Today there is a renewed appreciation for the Sámi traditional way of life, which has led to a revival of ''Noaidevuohta''. Some Norwegian and Sámi celebrities are reported to visit shamans for guidance.Health
Education
 Higher education in Norway is offered by a range of seven List of universities in Norway, universities, five specialised colleges, 25 university colleges as well as a range of private colleges. Education follows the Bologna Process involving Bachelor's degree, Bachelor (3 years), Master's degree, Master (2 years) and PhD (3 years) degrees. Acceptance is offered after finishing Education in Norway, upper secondary school with general study competence.
Public education is virtually free, regardless of nationality. The academic year has two Academic term, semesters, from August to December and from January to June. The ultimate responsibility for the education lies with the Norwegian Ministry of Education and Research.
Higher education in Norway is offered by a range of seven List of universities in Norway, universities, five specialised colleges, 25 university colleges as well as a range of private colleges. Education follows the Bologna Process involving Bachelor's degree, Bachelor (3 years), Master's degree, Master (2 years) and PhD (3 years) degrees. Acceptance is offered after finishing Education in Norway, upper secondary school with general study competence.
Public education is virtually free, regardless of nationality. The academic year has two Academic term, semesters, from August to December and from January to June. The ultimate responsibility for the education lies with the Norwegian Ministry of Education and Research.
Languages
 Norwegian in its two forms,
Norwegian in its two forms, Norwegian
Norwegian is a North Germanic languages, North Germanic language descended fromSámi and Kven
Several Uralic languages, Uralic Sámi languages, which are related but not generally mutually intelligible, are traditionally spoken by the Sámi people primarily in Northern Norway and to much lesser extent in some parts of Central Norway. Around 15,000 people have officially registered as Sámi in the Sámi census (''Samemanntallet''), but the number of people of recent Sámi heritage is often estimated at 50,000 people. The number of people who have some knowledge of Northern Sámi, including as a second language, is estimated at 25,000 people, but only a minority are native speakers. The other Sámi languages are heavily endangered and spoken by at most a few hundred people. Most people of Sámi heritage are today native speakers of Norwegian as a result of past assimilation policies. Speakers have a right to be educated and to receive communication from the government in their own language in a special ''forvaltningsområde'' (administrative area) for Sámi languages. The Kven people, Kven minority historically spoke the Uralic Kven language (considered a separate language in Norway, but generally perceived as a Finnish dialect in Finland). Today the majority of ethnic Kven have little or no knowledge of the language. According to the Kainun institutti, "The typical modern Kven is a Norwegian-speaking Norwegian who knows his genealogy." As Norway has ratified the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages (ECRML) the Kven language together with Romani language, Romani and Scandoromani language has become officially recognised minority languages.Other languages
Some supporters have also advocated making Norwegian Sign Language an official language of the country. Students who are children of immigrant parents are encouraged to learn the Norwegian language. The Norwegian government offers language instructional courses for immigrants wishing to obtain Norwegian citizenship. With increasing concern about assimilating immigrants, since 1 September 2008, the government has required that an applicant for Norwegian citizenship give evidence of proficiency in either Norwegian or in one of the Sámi languages, or give proof of having attended classes in Norwegian for 300 hours, or meet the language requirements for university studies in Norway (that is, by being proficient in one of the Scandinavian languages). The primary foreign language taught in Norwegian schools is English, considered an international language since the post-WWII era. The majority of the population is fairly fluent in English, especially those born after World War II. German, French and Spanish are also commonly taught as second or, more often, third languages. Russian, Japanese, Italian, Latin, and rarely Standard Mandarin, Chinese (Mandarin) are offered in some schools, mostly in the cities. Traditionally, English, German and French were considered the main foreign languages in Norway. These languages, for instance, were used on Norwegian passports until the 1990s, and university students have a general right to use these languages when submitting their theses.Culture
 The Norwegian farm culture continues to play a role in contemporary Norwegian culture. In the 19th century, it inspired a strong Norwegian romantic nationalism, romantic nationalistic movement, which is still visible in the Norwegian language and :Mass media in Norway, media. Norwegian culture blossomed with nationalist efforts to achieve an independent identity in the areas of literature, art and music. This continues today in the performing arts and as a result of government support for exhibitions, cultural projects and artwork.
The Norwegian farm culture continues to play a role in contemporary Norwegian culture. In the 19th century, it inspired a strong Norwegian romantic nationalism, romantic nationalistic movement, which is still visible in the Norwegian language and :Mass media in Norway, media. Norwegian culture blossomed with nationalist efforts to achieve an independent identity in the areas of literature, art and music. This continues today in the performing arts and as a result of government support for exhibitions, cultural projects and artwork.
Cinema
The Norwegian cinema has received international recognition. The documentary film ''Kon-Tiki (1950 film), Kon-Tiki'' (1950) won an Academy Awards, Academy Award. In 1957, Arne Skouen's ''Nine Lives (1957 film), Nine Lives'' was nominated, but failed to win. Another notable film is ''The Pinchcliffe Grand Prix'', an animated feature film directed by Ivo Caprino. The film was released in 1975 and is based on characters from Norwegian cartoonist Kjell Aukrust. It is the most widely seen Norwegian film of all time. Nils Gaup's ''Pathfinder (1987 film), Pathfinder'' (1987), the story of the Sámi people, Sámi, was nominated for an Oscar. Berit Nesheim's ''The Other Side of Sunday'' was nominated for an Oscar in 1997. Since the 1990s, the film industry has thrived, producing up to 20 feature films each year. Particular successes were ''Kristin Lavransdatter'', based on a novel by a Nobel Prize winner; ''The Telegraphist'' and ''Gurin with the Foxtail''. Knut Erik Jensen was among the more successful new directors, together with Erik Skjoldbjærg, who is remembered for ''Insomnia (1997 film), Insomnia''. ''Elling'' and the 2012 adaption of Kon-Tiki (2012 film), ''Kon-Tiki'' was nominated for an Oscar for the best foreign language film. The TV-series Skam (TV series), ''Skam'' created by Julie Andem received a cult following and international recognition, with many countries making their own adaptations of the series.
Norwegian directors such as Joachim Rønning, Anja Breien, Espen Sandberg, Liv Ullmann and Morten Tyldum has made international success with their films and TV series. Which includes movies such as ''The Imitation Game'', Passengers (2016 film), ''Passengers'', Pirates of the Caribbean: Dead Men Tell No Tales, ''Pirates of the Caribbean: Salazar's Revenge'' and ''Maleficent: Mistress of Evil'', as well as the TV-series Jack Ryan (TV series), ''Jack Ryan'' and Marco Polo (TV series), ''Marco Polo''. Composers include Thomas Bergersen, who has composed for many picture campaigns, including Avatar (2009 film), ''Avatar'', The Dark Knight (film), ''The Dark Knight'', Harry Potter (film series), ''Harry Potter'' and The Chronicles of Narnia (film series), ''Narnia''. Egil Monn-Iversen has been one of the most influential modern composers in Norway, having composed scores to over 100 Norwegian movies and TV series.
The country has also been used as filming location for several Hollywood and other international productions, including Star Wars ''The Empire Strikes Back'' (1980), for which the producers used Hardangerjøkulen glacier as a filming location for scenes of the ice planet Hoth. It included a memorable battle in the snow. Among the thousands of films that have been filmed in Norway include ''Die Another Day'', ''No Time to Die'', ''The Golden Compass (film), The Golden Compass'', ''Spies Like Us'', ''Mission: Impossible – Fallout'' and ''Mission: Impossible – Dead Reckoning Part One'', Black Widow (2021 film), ''Black Widow'', Tenet (film), ''Tenet'', Harry Potter and the Half-Blood Prince (film), Harry Potter and the Half-Blood prince and ''The Heroes of Telemark, Heroes of Telemark,'' as well as the TV series ''Lilyhammer'' and ''Vikings (2013 TV series), Vikings'' also had scenes set in Norway. A short film, ''The Spirit of Norway'', was featured at Maelstrom (ride), Maelstrom at Norway (Epcot), Norway Pavilion at Epcot located within Walt Disney World Resort in Florida in the United States. The attraction and the film ceased their operations on 5 October 2014.
Since the 1990s, the film industry has thrived, producing up to 20 feature films each year. Particular successes were ''Kristin Lavransdatter'', based on a novel by a Nobel Prize winner; ''The Telegraphist'' and ''Gurin with the Foxtail''. Knut Erik Jensen was among the more successful new directors, together with Erik Skjoldbjærg, who is remembered for ''Insomnia (1997 film), Insomnia''. ''Elling'' and the 2012 adaption of Kon-Tiki (2012 film), ''Kon-Tiki'' was nominated for an Oscar for the best foreign language film. The TV-series Skam (TV series), ''Skam'' created by Julie Andem received a cult following and international recognition, with many countries making their own adaptations of the series.
Norwegian directors such as Joachim Rønning, Anja Breien, Espen Sandberg, Liv Ullmann and Morten Tyldum has made international success with their films and TV series. Which includes movies such as ''The Imitation Game'', Passengers (2016 film), ''Passengers'', Pirates of the Caribbean: Dead Men Tell No Tales, ''Pirates of the Caribbean: Salazar's Revenge'' and ''Maleficent: Mistress of Evil'', as well as the TV-series Jack Ryan (TV series), ''Jack Ryan'' and Marco Polo (TV series), ''Marco Polo''. Composers include Thomas Bergersen, who has composed for many picture campaigns, including Avatar (2009 film), ''Avatar'', The Dark Knight (film), ''The Dark Knight'', Harry Potter (film series), ''Harry Potter'' and The Chronicles of Narnia (film series), ''Narnia''. Egil Monn-Iversen has been one of the most influential modern composers in Norway, having composed scores to over 100 Norwegian movies and TV series.
The country has also been used as filming location for several Hollywood and other international productions, including Star Wars ''The Empire Strikes Back'' (1980), for which the producers used Hardangerjøkulen glacier as a filming location for scenes of the ice planet Hoth. It included a memorable battle in the snow. Among the thousands of films that have been filmed in Norway include ''Die Another Day'', ''No Time to Die'', ''The Golden Compass (film), The Golden Compass'', ''Spies Like Us'', ''Mission: Impossible – Fallout'' and ''Mission: Impossible – Dead Reckoning Part One'', Black Widow (2021 film), ''Black Widow'', Tenet (film), ''Tenet'', Harry Potter and the Half-Blood Prince (film), Harry Potter and the Half-Blood prince and ''The Heroes of Telemark, Heroes of Telemark,'' as well as the TV series ''Lilyhammer'' and ''Vikings (2013 TV series), Vikings'' also had scenes set in Norway. A short film, ''The Spirit of Norway'', was featured at Maelstrom (ride), Maelstrom at Norway (Epcot), Norway Pavilion at Epcot located within Walt Disney World Resort in Florida in the United States. The attraction and the film ceased their operations on 5 October 2014.
Music
 The classical music of Norway, music of the romanticism, romantic composers Edvard Grieg, Rikard Nordraak and Johan Svendsen is internationally known, as is the modern music of Arne Nordheim. Norway's classical performers include Leif Ove Andsnes, one of the world's more famous pianists; Truls Mørk, an outstanding cellist; and the great Wagnerian soprano Kirsten Flagstad.
The jazz scene in Norway is thriving. Jan Garbarek, Terje Rypdal, Mari Boine, Arild Andersen and Bugge Wesseltoft are internationally recognised while Paal Nilssen-Love, Supersilent, Jaga Jazzist and Wibutee are becoming world-class artists of the younger generation.
Norway has a strong folk music tradition which remains popular to this day. Among the most prominent folk musicians are Hardanger fiddlers Andrea Een, Olav Jørgen Hegge and Annbjørg Lien, and the vocalists Agnes Buen Garnås, Kirsten Bråten Berg and Odd Nordstoga.
The classical music of Norway, music of the romanticism, romantic composers Edvard Grieg, Rikard Nordraak and Johan Svendsen is internationally known, as is the modern music of Arne Nordheim. Norway's classical performers include Leif Ove Andsnes, one of the world's more famous pianists; Truls Mørk, an outstanding cellist; and the great Wagnerian soprano Kirsten Flagstad.
The jazz scene in Norway is thriving. Jan Garbarek, Terje Rypdal, Mari Boine, Arild Andersen and Bugge Wesseltoft are internationally recognised while Paal Nilssen-Love, Supersilent, Jaga Jazzist and Wibutee are becoming world-class artists of the younger generation.
Norway has a strong folk music tradition which remains popular to this day. Among the most prominent folk musicians are Hardanger fiddlers Andrea Een, Olav Jørgen Hegge and Annbjørg Lien, and the vocalists Agnes Buen Garnås, Kirsten Bråten Berg and Odd Nordstoga.
 Early Norwegian black metal scene, Norwegian black metal, a form of rock music in Norway, has been an influence in world music since the late 20th century. Since the 1990s, Norway's export of black metal, a lo-fi, dark and raw form of heavy metal music, heavy metal, has been developed by such bands as Emperor (band), Emperor, Darkthrone, Gorgoroth, Mayhem (band), Mayhem, Burzum and Immortal (band), Immortal. More recently, bands such as Enslaved (band), Enslaved, Kvelertak, Dimmu Borgir and Satyricon (band), Satyricon have evolved the genre into the present day while still garnering worldwide fans. Controversial events associated with the black metal movement in the early 1990s included several Church arson, church burnings and two prominent Black metal#Aarseth's murder, murder cases.
Ylvis rose to international stardom with the song The Fox (What Does the Fox Say?), What Does the Fox Say?, which received over 1 billion views on YouTube. A-ha initially rose to global fame during the mid-1980s. In the 1990s and 2000s, the group maintained its popularity domestically, and has remained successful outside Norway, especially in Germany, Switzerland, France, and Brazil. A-ha's most memorable song and music video Take On Me has currently over 1.3 billion views
Some of the most memorable female solo artists from Norway are Susanne Sundfør, Sigrid (singer), Sigrid, Astrid S, Adelén, Julie Bergan, Maria Mena, Tone Damli, Margaret Berger, Lene Marlin, Christel Alsos, Maria Arredondo, Marion Raven and Marit Larsen (both former members of the defunct pop-rock group M2M (band), M2M), Lene Nystrøm (vocalist of the Danish eurodance group Aqua (band), Aqua) and Anni-Frid Lyngstad (vocalist of the Swedish pop group ABBA). Norwegian songwriters and producers for international artists include Stargate (production team), Stargate, Espen Lind, Lene Marlin and Ina Wroldsen.
Norway enjoys many music festivals throughout the year, all over the country. Norway is the host of one of the world's biggest extreme sport festivals with music, Ekstremsportveko—a festival held annually in Voss. Oslo is the host of many festivals, such as Øyafestivalen and by:Larm. Oslo used to have a summer parade similar to the German Love Parade. In 1992, the city of Oslo wanted to adopt the French music festival ''Fête de la Musique''. Fredrik Carl Størmer established the festival. Even in its first year, "Musikkens Dag" gathered thousands of people and artists in the streets of Oslo. "Musikkens Dag" is now renamed ''Musikkfest Oslo''.
Early Norwegian black metal scene, Norwegian black metal, a form of rock music in Norway, has been an influence in world music since the late 20th century. Since the 1990s, Norway's export of black metal, a lo-fi, dark and raw form of heavy metal music, heavy metal, has been developed by such bands as Emperor (band), Emperor, Darkthrone, Gorgoroth, Mayhem (band), Mayhem, Burzum and Immortal (band), Immortal. More recently, bands such as Enslaved (band), Enslaved, Kvelertak, Dimmu Borgir and Satyricon (band), Satyricon have evolved the genre into the present day while still garnering worldwide fans. Controversial events associated with the black metal movement in the early 1990s included several Church arson, church burnings and two prominent Black metal#Aarseth's murder, murder cases.
Ylvis rose to international stardom with the song The Fox (What Does the Fox Say?), What Does the Fox Say?, which received over 1 billion views on YouTube. A-ha initially rose to global fame during the mid-1980s. In the 1990s and 2000s, the group maintained its popularity domestically, and has remained successful outside Norway, especially in Germany, Switzerland, France, and Brazil. A-ha's most memorable song and music video Take On Me has currently over 1.3 billion views
Some of the most memorable female solo artists from Norway are Susanne Sundfør, Sigrid (singer), Sigrid, Astrid S, Adelén, Julie Bergan, Maria Mena, Tone Damli, Margaret Berger, Lene Marlin, Christel Alsos, Maria Arredondo, Marion Raven and Marit Larsen (both former members of the defunct pop-rock group M2M (band), M2M), Lene Nystrøm (vocalist of the Danish eurodance group Aqua (band), Aqua) and Anni-Frid Lyngstad (vocalist of the Swedish pop group ABBA). Norwegian songwriters and producers for international artists include Stargate (production team), Stargate, Espen Lind, Lene Marlin and Ina Wroldsen.
Norway enjoys many music festivals throughout the year, all over the country. Norway is the host of one of the world's biggest extreme sport festivals with music, Ekstremsportveko—a festival held annually in Voss. Oslo is the host of many festivals, such as Øyafestivalen and by:Larm. Oslo used to have a summer parade similar to the German Love Parade. In 1992, the city of Oslo wanted to adopt the French music festival ''Fête de la Musique''. Fredrik Carl Størmer established the festival. Even in its first year, "Musikkens Dag" gathered thousands of people and artists in the streets of Oslo. "Musikkens Dag" is now renamed ''Musikkfest Oslo''.
Literature
 The history of Norwegian literature starts with the Norse paganism, pagan Poetic Edda, Eddaic poems and skaldic verse of the ninth and tenth centuries, with poets such as Bragi Boddason and Eyvindr skáldaspillir. The arrival of Christianity around the year 1000 brought Norway into contact with European medieval learning, hagiography and history writing. Merged with native oral tradition and Icelandic influence, this influenced the literature written in the late 12th and early 13th centuries. Major works of that period include ''Historia Norwegiæ'', ''Þiðrekssaga'' and ''Konungs skuggsjá''.
Little Norwegian literature came out of the period of the Scandinavian Union and the subsequent Dano-Norwegian union (1387–1814), with some notable exceptions such as Petter Dass and Ludvig Holberg. In his play ''Peer Gynt'', Ibsen characterised this period as "Twice two hundred years of darkness/brooded o'er the race of monkeys." The first line of this couplet is frequently quoted. During the union with Denmark, the government imposed using only written Danish, which decreased the writing of Norwegian literature.
Two major events precipitated a major resurgence in Norwegian literature: in 1811 a Norwegian university was established in Oslo, Christiania. Secondly, seized by the spirit of revolution following the American Revolution, American and French Revolution, French revolutions, the Norwegians created their first Constitution of Norway, Constitution in 1814. Strong authors were inspired who became recognised first in Scandinavia, and then worldwide; among them were Henrik Wergeland, Peter Christen Asbjørnsen, Jørgen Moe and Camilla Collett.
By the late 19th century, in the Golden Age of Norwegian literature, the so-called "Great Four" emerged: Henrik Ibsen, Bjørnstjerne Bjørnson, Alexander Kielland, and Jonas Lie (writer), Jonas Lie. Bjørnson's "peasant novels", such as ''Ein glad gut'' (A Happy Boy) and ''Synnøve Solbakken'', are typical of the Norwegian romantic nationalism of their day. Kielland's novels and short stories are mostly naturalistic. Although an important contributor to early romantic nationalism, (especially ''Peer Gynt''), Henrik Ibsen is better known for his pioneering realistic dramas such as ''The Wild Duck'' and ''A Doll's House.'' They caused an uproar because of his candid portrayals of the middle classes, complete with infidelity, unhappy marriages, and corrupt businessmen.
In the 20th century, three Norwegian novelists were awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature: Bjørnstjerne Bjørnson in 1903, Knut Hamsun for the book ''Growth of the Soil, Markens grøde'' ("Growth of the Soil") in 1920, and Sigrid Undset (known for ''Kristin Lavransdatter, Kristinlavransdatter'') in 1928. Writers such as the following also made important contributions: Dag Solstad, Jon Fosse, Cora Sandel, Olav Duun, Olav H. Hauge, Gunvor Hofmo, Stein Mehren, Kjell Askildsen, Hans Herbjørnsrud, Aksel Sandemose, Bergljot Hobæk Haff, Jostein Gaarder, Erik Fosnes Hansen, Jens Bjørneboe, Kjartan Fløgstad, Lars Saabye Christensen, Johan Borgen, Herbjørg Wassmo, Jan Erik Vold, Rolf Jacobsen (poet), Rolf Jacobsen, Olaf Bull, Jan Kjærstad, Georg Johannesen, Tarjei Vesaas, Sigurd Hoel, Arnulf Øverland, Karl Ove Knausgård and Johan Falkberget.
The history of Norwegian literature starts with the Norse paganism, pagan Poetic Edda, Eddaic poems and skaldic verse of the ninth and tenth centuries, with poets such as Bragi Boddason and Eyvindr skáldaspillir. The arrival of Christianity around the year 1000 brought Norway into contact with European medieval learning, hagiography and history writing. Merged with native oral tradition and Icelandic influence, this influenced the literature written in the late 12th and early 13th centuries. Major works of that period include ''Historia Norwegiæ'', ''Þiðrekssaga'' and ''Konungs skuggsjá''.
Little Norwegian literature came out of the period of the Scandinavian Union and the subsequent Dano-Norwegian union (1387–1814), with some notable exceptions such as Petter Dass and Ludvig Holberg. In his play ''Peer Gynt'', Ibsen characterised this period as "Twice two hundred years of darkness/brooded o'er the race of monkeys." The first line of this couplet is frequently quoted. During the union with Denmark, the government imposed using only written Danish, which decreased the writing of Norwegian literature.
Two major events precipitated a major resurgence in Norwegian literature: in 1811 a Norwegian university was established in Oslo, Christiania. Secondly, seized by the spirit of revolution following the American Revolution, American and French Revolution, French revolutions, the Norwegians created their first Constitution of Norway, Constitution in 1814. Strong authors were inspired who became recognised first in Scandinavia, and then worldwide; among them were Henrik Wergeland, Peter Christen Asbjørnsen, Jørgen Moe and Camilla Collett.
By the late 19th century, in the Golden Age of Norwegian literature, the so-called "Great Four" emerged: Henrik Ibsen, Bjørnstjerne Bjørnson, Alexander Kielland, and Jonas Lie (writer), Jonas Lie. Bjørnson's "peasant novels", such as ''Ein glad gut'' (A Happy Boy) and ''Synnøve Solbakken'', are typical of the Norwegian romantic nationalism of their day. Kielland's novels and short stories are mostly naturalistic. Although an important contributor to early romantic nationalism, (especially ''Peer Gynt''), Henrik Ibsen is better known for his pioneering realistic dramas such as ''The Wild Duck'' and ''A Doll's House.'' They caused an uproar because of his candid portrayals of the middle classes, complete with infidelity, unhappy marriages, and corrupt businessmen.
In the 20th century, three Norwegian novelists were awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature: Bjørnstjerne Bjørnson in 1903, Knut Hamsun for the book ''Growth of the Soil, Markens grøde'' ("Growth of the Soil") in 1920, and Sigrid Undset (known for ''Kristin Lavransdatter, Kristinlavransdatter'') in 1928. Writers such as the following also made important contributions: Dag Solstad, Jon Fosse, Cora Sandel, Olav Duun, Olav H. Hauge, Gunvor Hofmo, Stein Mehren, Kjell Askildsen, Hans Herbjørnsrud, Aksel Sandemose, Bergljot Hobæk Haff, Jostein Gaarder, Erik Fosnes Hansen, Jens Bjørneboe, Kjartan Fløgstad, Lars Saabye Christensen, Johan Borgen, Herbjørg Wassmo, Jan Erik Vold, Rolf Jacobsen (poet), Rolf Jacobsen, Olaf Bull, Jan Kjærstad, Georg Johannesen, Tarjei Vesaas, Sigurd Hoel, Arnulf Øverland, Karl Ove Knausgård and Johan Falkberget.
Architecture
 With expansive forests, Norway has long had a tradition of building in wood. Many of today's most interesting new buildings are made of wood, reflecting the strong appeal that this material continues to hold for Norwegian designers and builders.
With Norway's conversion to Christianity some 1,000 years ago, churches were built. Stonework architecture was introduced from Europe for the most important structures, beginning with the construction of Nidaros Cathedral in Trondheim. In the early Middle Ages, wooden stave churches were constructed throughout Norway. Some of them have survived; they represent Norway's most unusual contribution to architectural history. A fine example, Urnes Stave Church in inner Sognefjord, is on UNESCO's World Heritage List. Another notable example of wooden architecture is the buildings at Bryggen Wharf in Bergen, also on the list for World Cultural Heritage sites, consisting of a row of tall, narrow wooden structures along the quayside.
In the 17th century, under the Danish monarchy, cities and villages such as Kongsberg and Røros were established. The city Kongsberg had a church built in the Baroque style. Traditional wooden buildings that were constructed in Røros have survived.
With expansive forests, Norway has long had a tradition of building in wood. Many of today's most interesting new buildings are made of wood, reflecting the strong appeal that this material continues to hold for Norwegian designers and builders.
With Norway's conversion to Christianity some 1,000 years ago, churches were built. Stonework architecture was introduced from Europe for the most important structures, beginning with the construction of Nidaros Cathedral in Trondheim. In the early Middle Ages, wooden stave churches were constructed throughout Norway. Some of them have survived; they represent Norway's most unusual contribution to architectural history. A fine example, Urnes Stave Church in inner Sognefjord, is on UNESCO's World Heritage List. Another notable example of wooden architecture is the buildings at Bryggen Wharf in Bergen, also on the list for World Cultural Heritage sites, consisting of a row of tall, narrow wooden structures along the quayside.
In the 17th century, under the Danish monarchy, cities and villages such as Kongsberg and Røros were established. The city Kongsberg had a church built in the Baroque style. Traditional wooden buildings that were constructed in Røros have survived.
 After Norway's union with Denmark was dissolved in 1814, Oslo became the capital. The architect Christian Heinrich Grosch, Christian H. Grosch designed the earliest parts of the University of Oslo, the Oslo Stock Exchange, and many other buildings and churches constructed in that early national period.
At the beginning of the 20th century, the city of Ålesund was rebuilt in the Art Nouveau style, influenced by styles of France. The 1930s, when functionalism dominated, became a strong period for Norwegian architecture. It is only since the late 20th century that Norwegian architects have achieved international renown. One of the most striking modern buildings in Norway is the Sámi Parliament in Karasjok, Kárášjohka, designed by Stein Halvorson and Christian Sundby. Its debating chamber, in timber, is an abstract version of a ''Lavvu, lavvo,'' the traditional tent used by the nomadic
After Norway's union with Denmark was dissolved in 1814, Oslo became the capital. The architect Christian Heinrich Grosch, Christian H. Grosch designed the earliest parts of the University of Oslo, the Oslo Stock Exchange, and many other buildings and churches constructed in that early national period.
At the beginning of the 20th century, the city of Ålesund was rebuilt in the Art Nouveau style, influenced by styles of France. The 1930s, when functionalism dominated, became a strong period for Norwegian architecture. It is only since the late 20th century that Norwegian architects have achieved international renown. One of the most striking modern buildings in Norway is the Sámi Parliament in Karasjok, Kárášjohka, designed by Stein Halvorson and Christian Sundby. Its debating chamber, in timber, is an abstract version of a ''Lavvu, lavvo,'' the traditional tent used by the nomadic Art
 For an extended period, the Norwegian art scene was dominated by artwork from Germany and Holland as well as by the influence of Copenhagen. It was in the 19th century that a truly Norwegian era began, first with portraits, later with impressive landscapes. Johan Christian Dahl (1788–1857), originally from the Dresden school, eventually returned to paint the landscapes of western Norway, defining Norwegian painting for the first time."
Norway's newly found independence from Denmark encouraged painters to develop their Norwegian identity, especially with landscape painting by artists such as Kitty Lange Kielland, Kitty Kielland, a female painter who studied under Hans Gude, and Harriet Backer, another pioneer among female artists, influenced by impressionism. Frits Thaulow, an impressionist, was influenced by the art scene in Paris as was Christian Krohg, a realist painter, famous for his paintings of prostitutes.
Of particular note is Edvard Munch, a symbolist/expressionist painter who became world-famous for ''The Scream'' which is said to represent the anxiety of modern man. Other notable works from Munch includes The Sick Child (Munch), The Sick Child, Madonna (Munch), Madonna and Puberty (Munch), Puberty.
Other artists of note include Harald Sohlberg, a neo-romantic painter remembered for his paintings of Røros, and Odd Nerdrum, a figurative painter who maintains that his work is not art, but kitsch.
For an extended period, the Norwegian art scene was dominated by artwork from Germany and Holland as well as by the influence of Copenhagen. It was in the 19th century that a truly Norwegian era began, first with portraits, later with impressive landscapes. Johan Christian Dahl (1788–1857), originally from the Dresden school, eventually returned to paint the landscapes of western Norway, defining Norwegian painting for the first time."
Norway's newly found independence from Denmark encouraged painters to develop their Norwegian identity, especially with landscape painting by artists such as Kitty Lange Kielland, Kitty Kielland, a female painter who studied under Hans Gude, and Harriet Backer, another pioneer among female artists, influenced by impressionism. Frits Thaulow, an impressionist, was influenced by the art scene in Paris as was Christian Krohg, a realist painter, famous for his paintings of prostitutes.
Of particular note is Edvard Munch, a symbolist/expressionist painter who became world-famous for ''The Scream'' which is said to represent the anxiety of modern man. Other notable works from Munch includes The Sick Child (Munch), The Sick Child, Madonna (Munch), Madonna and Puberty (Munch), Puberty.
Other artists of note include Harald Sohlberg, a neo-romantic painter remembered for his paintings of Røros, and Odd Nerdrum, a figurative painter who maintains that his work is not art, but kitsch.
Cuisine
:Norwegian cuisine, Norway's culinary traditions show the influence of long seafaring and farming traditions, with salmon (fresh and cured), herring (pickled or marinated), trout, codfish, and other seafood, balanced by cheeses (such as brunost, Jarlsberg cheese, and gamalost), dairy products, and breads (predominantly dark/darker). Lefse is a Norwegian potato flatbread, usually topped with large amounts of butter and sugar, most commonly eaten around Christmas. Traditional Norwegian dishes include lutefisk, smalahove, pinnekjøtt, raspeball, and fårikål. A Norwegian speciality is rakefisk, which is fermented trout, consumed with thin flatbread (flatbrød, not lefse) and sour cream. The most popular pastry is vaffel; it is different from the Belgian vaffel in taste and consistency and is served with sour cream, brown cheese, butter and sugar, or strawberry or raspberry jam, which can all be mixed or eaten separately.Sports
 Sports are a central part of Norwegian culture, and popular sports include association football, handball, biathlon, cross-country skiing (sport), cross-country skiing, ski jumping, Long track speed skating, speed skating, and, to a lesser degree, ice hockey.
Association football is the most popular sport in Norway in terms of active membership. In 2014–2015 polling, football ranked far behind biathlon and cross-country skiing (sport), cross-country skiing in terms of popularity as spectator sports. Ice hockey is the biggest indoor sport. The Norway women's national handball team, women's handball national team has won several titles, including two Summer Olympics championships (Handball at the 2008 Summer Olympics, 2008, Handball at the 2012 Summer Olympics, 2012), three World Women's Handball Championship, World Championships (1999 World Women's Handball Championship, 1999, 2011 World Women's Handball Championship, 2011, 2015 World Women's Handball Championship, 2015), and six European Women's Handball Championship, European Championship (1998 European Women's Handball Championship, 1998, 2004 European Women's Handball Championship, 2004, 2006 European Women's Handball Championship, 2006, 2008 European Women's Handball Championship, 2008, 2010 European Women's Handball Championship, 2010, 2014 European Women's Handball Championship, 2014).
In association football, the Norway women's national football team, women's national team has won the FIFA Women's World Cup in 1995 FIFA Women's World Cup, 1995 and the Football at the Olympics, Olympic Football Tournament in Football at the 2000 Summer Olympics – Women's tournament, 2000. The women's team also has two UEFA European Women's Championship titles (1987 European Competition for Women's Football, 1987, UEFA Women's Euro 1993, 1993). The Norway national football team, men's national football team has participated three times in the FIFA World Cup (1938 FIFA World Cup, 1938, 1994 FIFA World Cup, 1994, and 1998 FIFA World Cup, 1998), and once in the UEFA European Football Championship, European Championship (UEFA Euro 2000, 2000). The highest FIFA ranking Norway has achieved is second, a position it has held twice, in 1993 and in 1995.
Norwegian players in the National Football League include Halvor Hagen, Bill Irgens, Leif Olve Dolonen Larsen, Mike Mock, and Jan Stenerud.
Bandy is a traditional sport in Norway and the country is one of the four founders of Federation of International Bandy. In terms of licensed athletes, it is the second biggest winter sport in the world. As of January 2018, Norway national bandy team, the men's national team has captured one silver and one bronze, while Norway women's national bandy team, the women's national team has managed five bronzes at Bandy#International competition, the World Championships.
Norway first participated at the Olympic Games in 1900, and has sent athletes to compete in every Games since then, except for the sparsely attended 1904 Summer Olympics, 1904 Games and the 1980 Summer Olympics in Moscow when they participated in the 1980 Summer Olympics boycott, American-led boycott. Norway leads All-time Olympic Games medal table, the overall medal tables at the Winter Olympic Games by a considerable margin.
Norway has hosted the Games on two occasions:
* 1952 Winter Olympics in Oslo
* 1994 Winter Olympics in Lillehammer
It also hosted the 2016 Winter Youth Olympics in Lillehammer, making Norway the first country to host both Winter regular and Youth Olympics.
Norway featured a women's national team in beach volleyball that competed at the 2018–2020 CEV Beach Volleyball Continental Cup.
Chess has gained huge popularity in Norway. Magnus Carlsen, a Norwegian is the current five-time world champion.
Sports are a central part of Norwegian culture, and popular sports include association football, handball, biathlon, cross-country skiing (sport), cross-country skiing, ski jumping, Long track speed skating, speed skating, and, to a lesser degree, ice hockey.
Association football is the most popular sport in Norway in terms of active membership. In 2014–2015 polling, football ranked far behind biathlon and cross-country skiing (sport), cross-country skiing in terms of popularity as spectator sports. Ice hockey is the biggest indoor sport. The Norway women's national handball team, women's handball national team has won several titles, including two Summer Olympics championships (Handball at the 2008 Summer Olympics, 2008, Handball at the 2012 Summer Olympics, 2012), three World Women's Handball Championship, World Championships (1999 World Women's Handball Championship, 1999, 2011 World Women's Handball Championship, 2011, 2015 World Women's Handball Championship, 2015), and six European Women's Handball Championship, European Championship (1998 European Women's Handball Championship, 1998, 2004 European Women's Handball Championship, 2004, 2006 European Women's Handball Championship, 2006, 2008 European Women's Handball Championship, 2008, 2010 European Women's Handball Championship, 2010, 2014 European Women's Handball Championship, 2014).
In association football, the Norway women's national football team, women's national team has won the FIFA Women's World Cup in 1995 FIFA Women's World Cup, 1995 and the Football at the Olympics, Olympic Football Tournament in Football at the 2000 Summer Olympics – Women's tournament, 2000. The women's team also has two UEFA European Women's Championship titles (1987 European Competition for Women's Football, 1987, UEFA Women's Euro 1993, 1993). The Norway national football team, men's national football team has participated three times in the FIFA World Cup (1938 FIFA World Cup, 1938, 1994 FIFA World Cup, 1994, and 1998 FIFA World Cup, 1998), and once in the UEFA European Football Championship, European Championship (UEFA Euro 2000, 2000). The highest FIFA ranking Norway has achieved is second, a position it has held twice, in 1993 and in 1995.
Norwegian players in the National Football League include Halvor Hagen, Bill Irgens, Leif Olve Dolonen Larsen, Mike Mock, and Jan Stenerud.
Bandy is a traditional sport in Norway and the country is one of the four founders of Federation of International Bandy. In terms of licensed athletes, it is the second biggest winter sport in the world. As of January 2018, Norway national bandy team, the men's national team has captured one silver and one bronze, while Norway women's national bandy team, the women's national team has managed five bronzes at Bandy#International competition, the World Championships.
Norway first participated at the Olympic Games in 1900, and has sent athletes to compete in every Games since then, except for the sparsely attended 1904 Summer Olympics, 1904 Games and the 1980 Summer Olympics in Moscow when they participated in the 1980 Summer Olympics boycott, American-led boycott. Norway leads All-time Olympic Games medal table, the overall medal tables at the Winter Olympic Games by a considerable margin.
Norway has hosted the Games on two occasions:
* 1952 Winter Olympics in Oslo
* 1994 Winter Olympics in Lillehammer
It also hosted the 2016 Winter Youth Olympics in Lillehammer, making Norway the first country to host both Winter regular and Youth Olympics.
Norway featured a women's national team in beach volleyball that competed at the 2018–2020 CEV Beach Volleyball Continental Cup.
Chess has gained huge popularity in Norway. Magnus Carlsen, a Norwegian is the current five-time world champion.
See also
* Outline of NorwayNotes
References
Citations
Sources
*External links
regjeringen.no
official Norwegian government website
Norway.no
Norway's official portal *
Statistics Norway
State of the Environment Norway
Norway
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Norway
entry at ''Britannica.com'' * * *
Norway
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs''
Norway profile
from the BBC News
Norway.info
official foreign portal of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Norway), Norwegian Ministry of Foreign Affairs * *
Official facts about Norway
VisitNorway.com
official travel guide to Norway. *
Key Development Forecasts for Norway
from International Futures
World Bank Summary Trade Statistics Norway
{{Authority control Northwestern European countries Member states of the United Nations Member states of the Council of Europe Member states of NATO Members of the Nordic Council Member states of the European Free Trade Association Scandinavian countries States and territories established in the 870s 872 establishments States and territories established in 1814 States and territories established in 1905 Countries in Europe Christian states Norway, Countries of Europe with multiple official languages OECD members