Northwest Center on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four
 * The four
* The four
 * The sixteen ''quarter-winds'' are the direction points obtained by bisecting the angles between the points on the 16-wind compass rose (above). The quarter-winds are: (in first quadrant) north by east (NbE), northeast by north (NEbN), northeast by east (NEbE), and east by north (EbN); (in second quadrant) east by south (EbS), southeast by east (SEbE), southeast by south (SEbS), and south by east (SbE); (in third quadrant) south by west (SbW), southwest by south (SWbS), southwest by west (SWbW), and west by south (WbS); (in fourth quadrant) west by north (WbN), northwest by west (NWbW), northwest by north (NWbN), and north by west (NbW).
* All of the points in the 16-wind compass rose plus the sixteen quarter-winds together form the ''32-wind compass rose''.
* If breaking down for study/signalling the subcomponents are called the "principal" followed by the "cardinal" wind/direction. As a mnemonic (memory device), minds familiar encode the meaning of "X by Y" as "one small measure" ''from'' X ''towards'' Y". It can be noted such measure is °. So, for example, "northeast by east" means "one quarter of the gap from NE towards E".
In summary, the 32-wind compass rose comes from the eight principal winds, eight half-winds and sixteen quarter-winds combined, with each compass point at an ° angle from the next.
In the mariner's exercise of ''boxing the compass'', all thirty-two points of the compass are named in clockwise order.
* The sixteen ''quarter-winds'' are the direction points obtained by bisecting the angles between the points on the 16-wind compass rose (above). The quarter-winds are: (in first quadrant) north by east (NbE), northeast by north (NEbN), northeast by east (NEbE), and east by north (EbN); (in second quadrant) east by south (EbS), southeast by east (SEbE), southeast by south (SEbS), and south by east (SbE); (in third quadrant) south by west (SbW), southwest by south (SWbS), southwest by west (SWbW), and west by south (WbS); (in fourth quadrant) west by north (WbN), northwest by west (NWbW), northwest by north (NWbN), and north by west (NbW).
* All of the points in the 16-wind compass rose plus the sixteen quarter-winds together form the ''32-wind compass rose''.
* If breaking down for study/signalling the subcomponents are called the "principal" followed by the "cardinal" wind/direction. As a mnemonic (memory device), minds familiar encode the meaning of "X by Y" as "one small measure" ''from'' X ''towards'' Y". It can be noted such measure is °. So, for example, "northeast by east" means "one quarter of the gap from NE towards E".
In summary, the 32-wind compass rose comes from the eight principal winds, eight half-winds and sixteen quarter-winds combined, with each compass point at an ° angle from the next.
In the mariner's exercise of ''boxing the compass'', all thirty-two points of the compass are named in clockwise order.
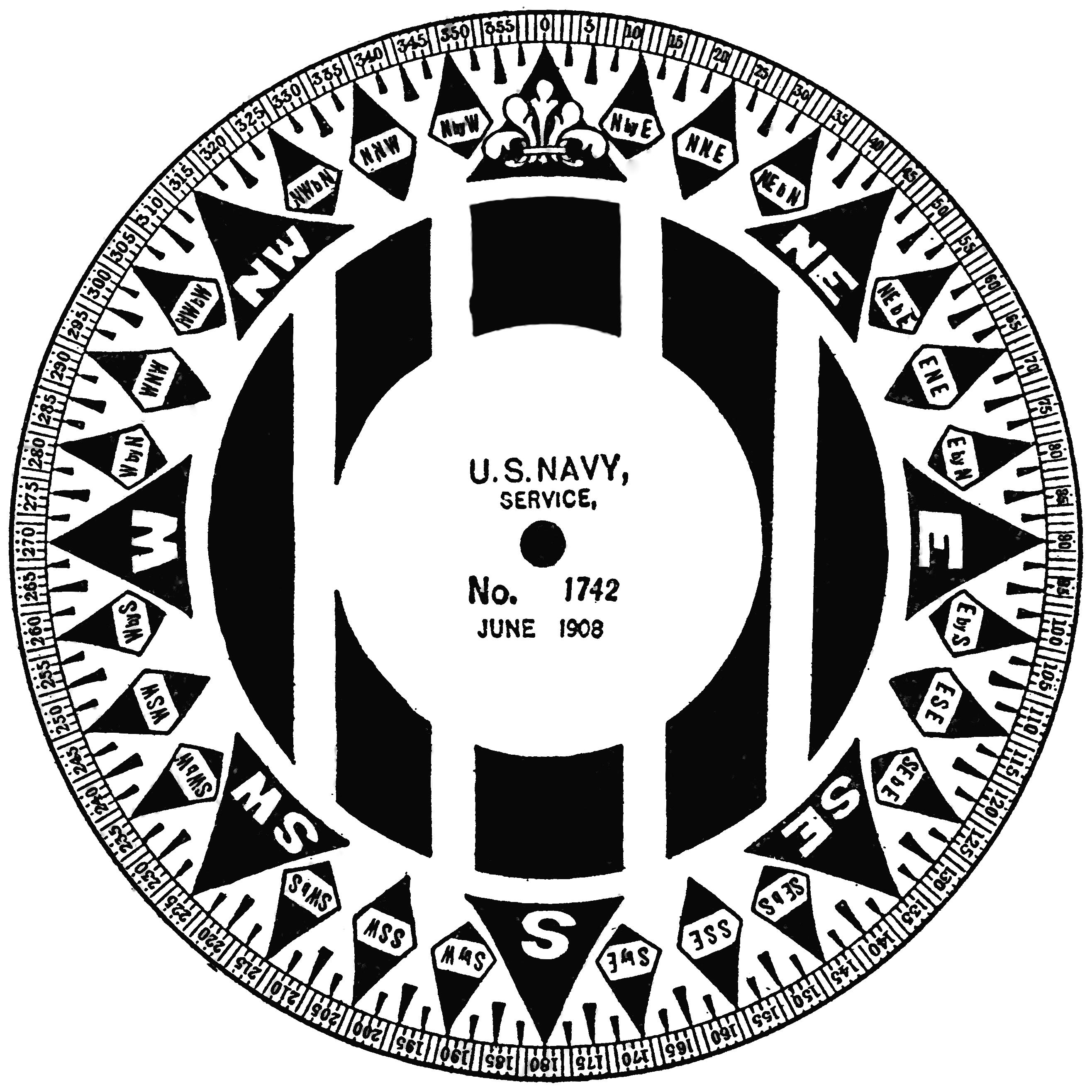 By the middle of the 18th century, the 32-point system had been further extended by using half- and quarter-points to give a total of 128 directions.E. Chambers ''Cyclopaedia: or, an Universal Dictionary of Arts and Science'', 5th Ed, 1743, pp. 206–7, "Points ''of the Compass'', or ''Horizon'', &c., in Geography and Navigation, are the points of division when the whole circle, quite around, is divided into 32 equal parts. These points are therefore at the distance of the 32d part of the circuit, or 11° 15′, from each other; hence 5° ′ is the distance of the half points and 2° ′ is the distance of the quarter points.
These fractional points are named by appending, for example east, east, or east to the name of one of the 32 points. Each of the 96 fractional points can be named in two ways, depending on which of the two adjoining whole points is used, for example, NE is equivalent to NbEN. Either form is easily understood, but alternative conventions as to correct usage developed in different countries and organisations. "It is the custom in the United States Navy to box ''from'' north and south ''toward'' east and west, with the exception that divisions adjacent to a cardinal or inter-cardinal point are always referred to that point." The Royal Navy used the additional "rule that quarter points were never read from a point beginning and ending with the same letter."
Compass roses very rarely named the fractional points and only showed small, unlabelled markers as a guide for helmsmen.
By the middle of the 18th century, the 32-point system had been further extended by using half- and quarter-points to give a total of 128 directions.E. Chambers ''Cyclopaedia: or, an Universal Dictionary of Arts and Science'', 5th Ed, 1743, pp. 206–7, "Points ''of the Compass'', or ''Horizon'', &c., in Geography and Navigation, are the points of division when the whole circle, quite around, is divided into 32 equal parts. These points are therefore at the distance of the 32d part of the circuit, or 11° 15′, from each other; hence 5° ′ is the distance of the half points and 2° ′ is the distance of the quarter points.
These fractional points are named by appending, for example east, east, or east to the name of one of the 32 points. Each of the 96 fractional points can be named in two ways, depending on which of the two adjoining whole points is used, for example, NE is equivalent to NbEN. Either form is easily understood, but alternative conventions as to correct usage developed in different countries and organisations. "It is the custom in the United States Navy to box ''from'' north and south ''toward'' east and west, with the exception that divisions adjacent to a cardinal or inter-cardinal point are always referred to that point." The Royal Navy used the additional "rule that quarter points were never read from a point beginning and ending with the same letter."
Compass roses very rarely named the fractional points and only showed small, unlabelled markers as a guide for helmsmen.
 This Italianate patois was used to designate the names of the principal winds on the compass rose found in mariners' compasses and portolan charts of the 14th and 15th centuries. The "traditional" names of the eight principal winds are:
* (N) – ''Tramontana''
* (NE) – ''Greco'' (or '' Bora'' in some Venetian sources)
* (E) – ''Levante'' (sometimes ''Oriente'')
* (SE) – ''Scirocco'' (or ''Exaloc'' in Catalan)
* (S) – ''Ostro'' (or ''Mezzogiorno'' in Venetian)
* (SW) – ''Libeccio'' (or ''Garbino'', ''Eissalot'' in Provençal)
* (W) – ''Ponente'' (or ''Zephyrus'' in Greek)
* (NW) – ''Maestro'' (or ''Mistral'' in Provençal)
Local spelling variations are far more numerous than listed, e.g. Tramutana, Gregale, Grecho, Sirocco, Xaloc, Lebeg, Libezo, Leveche, Mezzodi, Migjorn, Magistro, Mestre, etc. Traditional compass roses will typically have the initials T, G, L, S, O, L, P, and M on the main points. Portolan charts also colour-coded the compass winds: black for the eight principal winds, green for the eight half-winds, and red for the sixteen quarter-winds.
Each half-wind name is simply a combination of the two principal winds that it bisects, with the shortest name usually placed first, for example: NNE is "Greco-Tramontana"; ENE is "Greco-Levante"; SSE is "Ostro-Scirocco", etc. The quarter winds are expressed with an Italian phrase, "''Quarto di ''X'' verso ''Y" ( one quarter from X towards Y), or "X ''al'' Y" (X to Y) or "X ''per'' Y" (X by Y). There are no irregularities to trip over; the closest principal wind always comes first, the more distant one second, for example: north-by-east is "''Quarto di Tramontana verso Greco''"; and northeast-by-north is "''Quarto di Greco verso Tramontana''".
The table below shows how the 32 compass points are named. Each point has an angular range of degrees where the azimuth ''midpoint'' is the horizontal angular direction (clockwise from north) of the given compass bearing; ''minimum'' is the lower (counterclockwise) angular limit of the compass point; and ''maximum'' is the upper (clockwise) angular limit of the compass point.
::
This Italianate patois was used to designate the names of the principal winds on the compass rose found in mariners' compasses and portolan charts of the 14th and 15th centuries. The "traditional" names of the eight principal winds are:
* (N) – ''Tramontana''
* (NE) – ''Greco'' (or '' Bora'' in some Venetian sources)
* (E) – ''Levante'' (sometimes ''Oriente'')
* (SE) – ''Scirocco'' (or ''Exaloc'' in Catalan)
* (S) – ''Ostro'' (or ''Mezzogiorno'' in Venetian)
* (SW) – ''Libeccio'' (or ''Garbino'', ''Eissalot'' in Provençal)
* (W) – ''Ponente'' (or ''Zephyrus'' in Greek)
* (NW) – ''Maestro'' (or ''Mistral'' in Provençal)
Local spelling variations are far more numerous than listed, e.g. Tramutana, Gregale, Grecho, Sirocco, Xaloc, Lebeg, Libezo, Leveche, Mezzodi, Migjorn, Magistro, Mestre, etc. Traditional compass roses will typically have the initials T, G, L, S, O, L, P, and M on the main points. Portolan charts also colour-coded the compass winds: black for the eight principal winds, green for the eight half-winds, and red for the sixteen quarter-winds.
Each half-wind name is simply a combination of the two principal winds that it bisects, with the shortest name usually placed first, for example: NNE is "Greco-Tramontana"; ENE is "Greco-Levante"; SSE is "Ostro-Scirocco", etc. The quarter winds are expressed with an Italian phrase, "''Quarto di ''X'' verso ''Y" ( one quarter from X towards Y), or "X ''al'' Y" (X to Y) or "X ''per'' Y" (X by Y). There are no irregularities to trip over; the closest principal wind always comes first, the more distant one second, for example: north-by-east is "''Quarto di Tramontana verso Greco''"; and northeast-by-north is "''Quarto di Greco verso Tramontana''".
The table below shows how the 32 compass points are named. Each point has an angular range of degrees where the azimuth ''midpoint'' is the horizontal angular direction (clockwise from north) of the given compass bearing; ''minimum'' is the lower (counterclockwise) angular limit of the compass point; and ''maximum'' is the upper (clockwise) angular limit of the compass point.
::
 Headings mid-way in-between are compounds as in English. For instance, refers to the direction halfway between point and point , or °. This technique is referred to as a double-needle () compass.
Headings mid-way in-between are compounds as in English. For instance, refers to the direction halfway between point and point , or °. This technique is referred to as a double-needle () compass.
Wind Rose (archived)
– discusses the origins of the names for compass directions. {{Compass direction Navigational equipment Orientation (geometry) Units of angle
cardinal direction
The four cardinal directions, or cardinal points, are the four main compass directions: north, east, south, and west, commonly denoted by their initials N, E, S, and W respectively. Relative to north, the directions east, south, and west are at ...
s— north, east, south
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
, and west—each separated by 90 degrees, and secondarily divided by four ordinal (intercardinal) directions—northeast, southeast, southwest, and northwest—each located halfway between two cardinal directions. Some disciplines such as meteorology and navigation further divide the compass with additional azimuths. Within European tradition, a fully defined compass has 32 'points' (and any finer subdivisions are described in fractions of points).
Compass points are valuable in that they allow a user to refer to a specific azimuth in a colloquial fashion, without having to compute or remember degrees.
Designations
The names of the compass point directions follow these rules:8-wind compass rose
cardinal direction
The four cardinal directions, or cardinal points, are the four main compass directions: north, east, south, and west, commonly denoted by their initials N, E, S, and W respectively. Relative to north, the directions east, south, and west are at ...
s are north (N), east (E), south (S), west (W), at 90° angles on the compass rose.
* The four intercardinal (or ordinal) directions are formed by bisecting the above, giving: northeast (NE), southeast (SE), southwest (SW) and northwest (NW). In English and many other tongues, these are compound words. Different style guide
A style guide or manual of style is a set of standards for the writing, formatting, and design of documents. It is often called a style sheet, although that term also has multiple other meanings. The standards can be applied either for gene ...
s for the four mandate spaces, dashes, or none.
** In Bulgarian, Catalan, Czech, Danish, Dutch, English, Esperanto, French, Galician, German, Greek, Hungarian, Ido, Italian, Japanese (usually), Macedonian, Norwegian (both Bokmal and Nynorsk), Polish, Portuguese, Romansch, Russian, Serbian, Croatian, Spanish, Swedish, Ukrainian and Welsh the part meaning north or south precedes the part meaning east or west.See Wiktionary definitions: north; northeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
; east; southeast; south
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
; southwest; west; northwest
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sep ...
** In Chinese, Vietnamese, Gaelic and less commonly in Japanese, the part meaning east or west precedes the other.
** In Estonian, Finnish, the "Italianate system", and Telugu, the intercardinals have distinct words.
* The eight ''principal winds'' (or ''main winds'') are the set union
In set theory, the union (denoted by ∪) of a collection of sets is the set of all elements in the collection. It is one of the fundamental operations through which sets can be combined and related to each other.
A refers to a union of ze ...
of the cardinals and intercardinals. Taken in turn, each is 45° from the next. These form the ''8-wind compass rose'', the rose at its usual basic level today.
16-wind compass rose
* The eight ''half-winds'' are the direction points obtained by bisecting the angles between the principal winds. The half-winds are north-northeast (NNE), east-northeast (ENE), east-southeast (ESE), south-southeast (SSE), south-southwest (SSW), west-southwest (WSW), west-northwest (WNW) and north-northwest (NNW). The name of each half-wind is constructed by combining the names of the principal winds to either side, with the cardinal wind coming first and the intercardinal wind second. * The eight principal winds and the eight half-winds together form the ''16-wind compass rose'', with each compass point at a ° angle from its two neighbours.32-wind compass rose
Half- and quarter-points
 By the middle of the 18th century, the 32-point system had been further extended by using half- and quarter-points to give a total of 128 directions.E. Chambers ''Cyclopaedia: or, an Universal Dictionary of Arts and Science'', 5th Ed, 1743, pp. 206–7, "Points ''of the Compass'', or ''Horizon'', &c., in Geography and Navigation, are the points of division when the whole circle, quite around, is divided into 32 equal parts. These points are therefore at the distance of the 32d part of the circuit, or 11° 15′, from each other; hence 5° ′ is the distance of the half points and 2° ′ is the distance of the quarter points.
These fractional points are named by appending, for example east, east, or east to the name of one of the 32 points. Each of the 96 fractional points can be named in two ways, depending on which of the two adjoining whole points is used, for example, NE is equivalent to NbEN. Either form is easily understood, but alternative conventions as to correct usage developed in different countries and organisations. "It is the custom in the United States Navy to box ''from'' north and south ''toward'' east and west, with the exception that divisions adjacent to a cardinal or inter-cardinal point are always referred to that point." The Royal Navy used the additional "rule that quarter points were never read from a point beginning and ending with the same letter."
Compass roses very rarely named the fractional points and only showed small, unlabelled markers as a guide for helmsmen.
By the middle of the 18th century, the 32-point system had been further extended by using half- and quarter-points to give a total of 128 directions.E. Chambers ''Cyclopaedia: or, an Universal Dictionary of Arts and Science'', 5th Ed, 1743, pp. 206–7, "Points ''of the Compass'', or ''Horizon'', &c., in Geography and Navigation, are the points of division when the whole circle, quite around, is divided into 32 equal parts. These points are therefore at the distance of the 32d part of the circuit, or 11° 15′, from each other; hence 5° ′ is the distance of the half points and 2° ′ is the distance of the quarter points.
These fractional points are named by appending, for example east, east, or east to the name of one of the 32 points. Each of the 96 fractional points can be named in two ways, depending on which of the two adjoining whole points is used, for example, NE is equivalent to NbEN. Either form is easily understood, but alternative conventions as to correct usage developed in different countries and organisations. "It is the custom in the United States Navy to box ''from'' north and south ''toward'' east and west, with the exception that divisions adjacent to a cardinal or inter-cardinal point are always referred to that point." The Royal Navy used the additional "rule that quarter points were never read from a point beginning and ending with the same letter."
Compass roses very rarely named the fractional points and only showed small, unlabelled markers as a guide for helmsmen.
128 compass directions
The table below shows how each of the 128 directions are named. The first two columns give the number of points and degrees clockwise from north. The third gives the equivalent bearing to the nearest degree from north or south towards east or west. The "CW" column gives the fractional-point bearings increasing in the clockwise direction and "CCW" counterclockwise. The final three columns show three common naming conventions: No "by" avoids the use of "by" with fractional points. Colour coding shows whether each of the three naming systems matches the "CW" or "CCW" column. :::Traditional Mediterranean compass points
The traditional compass rose of eight winds (and its 16-wind and 32-wind derivatives) was invented by seafarers in the Mediterranean Sea during the Middle Ages (with no obvious connection to the twelve classical compass winds of the ancient Greeks and Romans). The traditional mariner's wind names were expressed in Italian, or more precisely, the Italianate Mediterranean lingua franca common among sailors in the 13th and 14th centuries, which was principally composed of Genoese ( Ligurian), mixed withVenetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
, Sicilian, Provençal
Provençal may refer to:
*Of Provence, a region of France
* Provençal dialect, a dialect of the Occitan language, spoken in the southeast of France
*''Provençal'', meaning the whole Occitan language
*Franco-Provençal language, a distinct Roman ...
, Catalan, Greek and Arabic terms from around the Mediterranean basin.
Chinese compass points
Navigation texts dating from the Yuan, Ming, andQing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaki ...
dynasties in China use a 24-pointed compass with named directions. These are based on the twelve Earthly Branches
The twelve Earthly Branches or Terrestrial Branches are a Chinese ordering system used throughout East Asia in various contexts, including its ancient dating system, astrological traditions, zodiac and ordinals.
Origin
This system was built ...
, which also form the basis of the Chinese zodiac. When a single direction is specified, it may be prefaced by the character (meaning single) or .
 Headings mid-way in-between are compounds as in English. For instance, refers to the direction halfway between point and point , or °. This technique is referred to as a double-needle () compass.
Headings mid-way in-between are compounds as in English. For instance, refers to the direction halfway between point and point , or °. This technique is referred to as a double-needle () compass.
See also
*Bearing (navigation)
In navigation, bearing or azimuth is the horizontal angle between the direction of an object and north or another object. The angle value can be specified in various angular units, such as degrees, mils, or grad. More specifically:
* Absolu ...
* Course (navigation)
* Heading (navigation)
In navigation, the heading of a vessel or aircraft is the compass direction in which the craft's bow or nose is pointed. Note that the heading may not necessarily be the direction that the vehicle actually travels, which is known as its ''cours ...
* TVMDC
* Wind rose
References
External links
Wind Rose (archived)
– discusses the origins of the names for compass directions. {{Compass direction Navigational equipment Orientation (geometry) Units of angle