Northern Region, Nigeria on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Northern Nigeria (or Arewancin Nijeriya) was an autonomous division within
 The
The
Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
, distinctly different from the southern part of the country, with independent customs, foreign relations and security structures. In 1962, it acquired the territory of the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
Northern Cameroons, which voted to become a province within Northern Nigeria.
In 1967, Northern Nigeria was divided into the North-Eastern State, North-Western State North-Western State is a former administrative division of Nigeria. It was created on 27 May 1967 from parts of the Northern Region and existed until 3 February 1976, when it was divided into two states – Niger and Sokoto. The city of Sokoto
...
, Kano State
Kano (Hausa language, Hausa: ) is one of the 36 States of Nigeria, states of Nigeria, located in the Northern Region, Nigeria, northern region of the country. According to the national census done in 2006, Kano State is the List of Nigerian st ...
, Kaduna State
Kaduna (, جىِهَر كَدُنا; مدينة كدونا; , ; ) is a States of Nigeria, state in the northwest geopolitical zone of Nigeria. The state capital is its namesake, the city of Kaduna (city), Kaduna, which was the List of Nigerian ...
, Kwara State
Kwara () is a state in Western Nigeria, bordered to the east by Kogi State, to the north by Niger State, and to the south by Ekiti, Osun, and Oyo states, while its western border makes up part of the international border with Benin. Its ca ...
, and the Benue-Plateau State, each with its own Governor.
History
Prehistory
 The
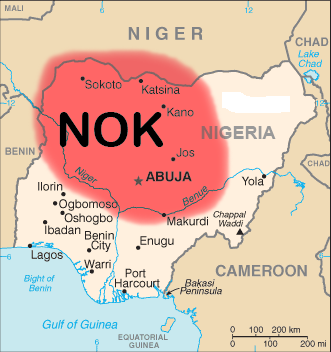
The Nok culture
The Nok culture is a population whose material remains are named after the Ham people, Ham village of Nok in Southern Kaduna, southern Kaduna State of Nigeria, where their terracotta sculptures were first discovered in 1928. The Nok people and ...
, an ancient culture dominated most of what is now Northern Nigeria
Northern Nigeria (or Arewa, Arewancin Nijeriya) was an autonomous division within Nigeria, distinctly different from the southern part of the country, with independent customs, foreign relations and security structures. In 1962, it acquired t ...
in prehistoric times, its legacy in the form of terracotta statues and megaliths have been discovered in Sokoto
Sokoto (Hausa language, Hausa: ; Fulfulde, Fula: , ''Leydi Sokoto'') is one of the 36 states of Nigeria, located in the extreme northwest of the country. It is bounded by Niger, Republic of the Niger to the north and west for 363 km (226 m ...
, Kano, Birinin Kudu, Nok and Zaria
Zaria is a List of Nigerian cities by population, metropolitan city in Nigeria, located at present time within four local government areas in Kaduna State. It serves as the capital of the Zazzau Emirate Council and is one of the original sev ...
. The Kwatarkwashi culture, a variant of the Nok culture
The Nok culture is a population whose material remains are named after the Ham people, Ham village of Nok in Southern Kaduna, southern Kaduna State of Nigeria, where their terracotta sculptures were first discovered in 1928. The Nok people and ...
centred mostly around Zamfara in Sokoto Province is thought by some to be the same or an offshoot of the Nok.
The Fourteen Kingdoms
The Fourteen Kingdoms unified the diverse lore and heritage of Northern Nigeria into a cohesive ethno-historical system. Seven of these kingdoms developed from the Kabara legacy of theHausa people
The Hausa (Endonym, autonyms for singular: Bahaushe (male, m), Bahaushiya (female, f); plural: Hausawa and general: Hausa; exonyms: Ausa; Ajami script, Ajami: ) are a native ethnic group in West Africa. They speak the Hausa language, which is the ...
. In the 9th century as vibrant trading centers competing with Kanem-Bornu and Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
slowly developed in the Central Sudan, a collection of kingdoms merged – the Hausa Kingdoms
Hausa Kingdoms, also known as Hausa Kingdom or Hausaland, was a collection of states ruled by the Hausa people, before the Fulani jihads. It was situated between the Niger River and Lake Chad (modern day northern Nigeria). Hausaland lay betwe ...
or Hausa Bakwai – dominating the great savannah
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) biome and ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach th ...
plains of Hausaland. Their primary exports were leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning (leather), tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffal ...
, gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
, cloth
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, and different types of fabric. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is n ...
, salt
In common usage, salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). When used in food, especially in granulated form, it is more formally called table salt. In the form of a natural crystalline mineral, salt is also known as r ...
, kola nuts, animal hides, and henna.
The seven Hausa states included:
* Daura, ? - 1806
* Kano, 998 - 1807
* Katsina, c. 1400 - 1805
* Zazzau (Zaria), c. 1200 - 1808
* Gobir, ? - 1808
* Rano
* Biram, c. 1100 - 1805
The growth and conquest of the Hausa Bakwai resulted in the founding of additional states with rulers tracing their lineage to a concubine of the Hausa founding father, Bayajidda
Bayajidda ( Hausa with tone markings: Bàyā̀jiddà) (real name: Abu Yazid) was, according to the legends surrounding most West African states before the 19th century, the founder of the Hausa states.
Most accounts say that Bayajidda came from B ...
. Thus, they are called the Banza Bakwai, meaning Bastard Seven. The Banza Bakwai adopted many of the customs and institutions of the Hausa Bakwai but were considered unsanctioned or copy-cat kingdoms by non-Hausa people. These states include:
* Zamfara
* Kebbi
* Yauri (also called Yawuri)
* Gwari (also called Gwariland)
* Kwararafa (a Jukun state)
* Nupe mainly where is presently called Niger State
Niger State is a state in the North Central (Nigeria), North Central region of Nigeria, bordered to the east by Kaduna State and the Federal Capital Territory (Nigeria), Federal Capital Territory, to the north by Kebbi State and Zamfara State, ...
(of the Nupe people)
Hausa States
Between 500 and 700,Hausa people
The Hausa (Endonym, autonyms for singular: Bahaushe (male, m), Bahaushiya (female, f); plural: Hausawa and general: Hausa; exonyms: Ausa; Ajami script, Ajami: ) are a native ethnic group in West Africa. They speak the Hausa language, which is the ...
, who are thought to have slowly moved from Nubia
Nubia (, Nobiin language, Nobiin: , ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the confluence of the Blue Nile, Blue and White Nile, White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), and the Cataracts of the Nile, first cataract ...
and mixing in with the local Northern population, established a number of strong states in what is now Northern Nigeria and Eastern Niger. With the decline of the Nok and Sokoto, who had previously controlled Central and Northern Nigeria between 800 BCE and 200, the Hausa were able to emerge as the new power in the region. They are closely linked with the Kanuri people
The Kanuri people (Kanouri, Kanowri, also Yerwa, Barebari and several subgroup names) are an African ethnic group living largely in the lands of the former Kanem and Bornu Empires in Niger, Nigeria, Chad, and Cameroon, as well as a diaspora c ...
of Kanem-Bornu (Lake Chad
Lake Chad (, Kanuri language, Kanuri: ''Sádǝ'', ) is an endorheic freshwater lake located at the junction of four countries: Nigeria, Niger, Chad, and Cameroon, in western and central Africa respectively, with a catchment area in excess of . ...
), the Birom, Gwari, Nupe and Jukun.
The Hausa aristocracy
Aristocracy (; ) is a form of government that places power in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocracy (class), aristocrats.
Across Europe, the aristocracy exercised immense Economy, economic, Politics, political, and soc ...
, under influence from the Mali Empire
The Mali Empire (Manding languages, Manding: ''Mandé''Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: ''UNESCO General History of Africa, Vol. IV, Abridged Edition: Africa from the Twelfth to the Sixteenth Century'', p. 57. University of California Press, 1997. or ''Manden ...
adopted Islam in the 11th century. By the 12th century, the Hausa were becoming one of Africa's major powers. The architecture of the Hausa is perhaps one of the least known but most beautiful of the medieval age. Many of their early mosques and palaces are bright and colourful and often include intricate engraving or elaborate symbols designed into the facade. By 1500, the Hausa utilized a modified Arabic script known as Ajami to record their own language; the Hausa compiled several written histories, the most popular being the Kano Chronicle
The ''Kano Chronicle'' (Arabic: تاريخ أرباب هذا البلاد المصممة كان; ''The history of the masters of this country it was designed'') is an Arabic-language manuscript that lists the rulers of Kano.
Summary
The ''Kano ...
."Kano Chronicle," ed. Palmer, pp. 70-72.
Fulani Empire and Bornu Empire
Usman Dan Fodio
Shehu Usman dan Fodio (; full name; 15 December 1754 – 20 April 1817). (Uthman ibn Muhammad ibn Uthman ibn Saalih ibn Haarun ibn Muhammad Ghurdu ibn Muhammad Jubba ibn Muhammad Sambo ibn Maysiran ibn Ayyub ibn Buba Baba ibn Musa Jokolli ibn ...
, the 18th century revolutionary and a social, religious and political reformer finally united the seven Hausa States with newly created provinces into the Sokoto Caliphate
The Sokoto Caliphate (, literally: Caliphate in the Lands of Sudan), also known as the Sultanate of Sokoto, was a Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim caliphate in West Africa. It was founded by Usman dan Fodio in 1804 during the Fula jihads, Fulani jihads ...
. The Sokoto Caliphate
The Sokoto Caliphate (, literally: Caliphate in the Lands of Sudan), also known as the Sultanate of Sokoto, was a Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim caliphate in West Africa. It was founded by Usman dan Fodio in 1804 during the Fula jihads, Fulani jihads ...
was under the overall authority of the Commander of the Faithful. Under Dan Fodio, the Empire was bicephalous and divided into two territories each controlled by an appointed vizier
A vizier (; ; ) is a high-ranking political advisor or Minister (government), minister in the Near East. The Abbasids, Abbasid caliphs gave the title ''wazir'' to a minister formerly called ''katib'' (secretary), who was at first merely a help ...
. Each of the territories was further divided into autonomous Emirate
An emirate is a territory ruled by an emir, a title used by monarchs or high officeholders in the Muslim world. From a historical point of view, an emirate is a political-religious unit smaller than a caliphate. It can be considered equivalent ...
s under mainly hereditary local Emir
Emir (; ' (), also Romanization of Arabic, transliterated as amir, is a word of Arabic language, Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocratic, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person po ...
s. The Bornu Empire Bornu may refer to:
* Bornu Empire, a historical state of West Africa
* Borno State, Nigeria
{{disambig