Northeastern Iberian script on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
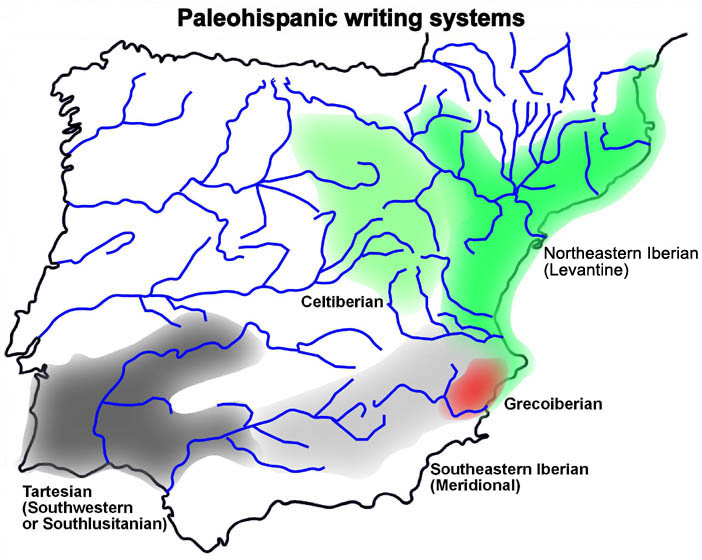




 The northeastern Iberian script, also known as Levantine Iberian or Iberian, was the main means of written expression of the
The northeastern Iberian script, also known as Levantine Iberian or Iberian, was the main means of written expression of the
''Novetats sobre el sistema dual de diferenciació gràfica de les oclusives sordes i sonores''
''Palaeohispanica'' 5, pp. 957–982. * Ferrer i Jane Joan (2013)
«Els sistemes duals de les escriptures ibèriques»
''Palaeohispanica'' 13, pp. 451-479. * Gómez-Moreno, Manuel (1922): «De Epigrafia ibérica: el plomo de Alcoy», ''Revista de filología española'' 9, pp. 34–66. * Hoz, Javier de (1985): «El nuevo plomo inscrito de Castell y el problema de las oposiciones de sonoridad en ibérico», ''Symbolae Ludouico Mitxelena septuagenario oblatae'', pp. 443–453. * Maluquer de Motes, Joan (1968): ''Epigrafía prelatina de la península ibérica'', Barcelona. * Quintanilla, Alberto (1993): «Sobre la notación en la escritura ibérica del modo de articulación de las consonantes oclusivas», ''Studia Palaeohispanica et Indogermánica J. Untermann ab Amicis Hispanicis Oblata'', pp. 239–250. * Rodríguez Ramos, Jesús (2004): ''Análisis de epigrafía íbera'', Vitoria-Gasteiz. * Untermann, Jürgen (1990): ''Monumenta Linguarum Hispanicarum. III Die iberischen Inschriften aus Spanien'', Wiesbaden. * Velaza, Javier (1996): ''Epigrafía y lengua ibéricas'', Barcelona.
The levantine Iberian writing- Jesús Rodríguez Ramos
{{DEFAULTSORT:Northeastern Iberian Script Northeastern Iberian script Palaeohispanic writing





 The northeastern Iberian script, also known as Levantine Iberian or Iberian, was the main means of written expression of the
The northeastern Iberian script, also known as Levantine Iberian or Iberian, was the main means of written expression of the Iberian language
The Iberian language was the language of an indigenous western European people identified by Greek and Roman sources who lived in the eastern and southeastern regions of the Iberian Peninsula in the pre- Migration Era (before about 375 AD). The ...
. The language is also expressed by the southeastern Iberian script
The southeastern Iberian script, also known as Meridional Iberian, was one of the means of written expression of the Iberian language, which was written mainly in the northeastern Iberian script and residually by the Greco-Iberian alphabet. Abo ...
and the Greco-Iberian alphabet
The Greco-Iberian alphabet is a direct adaptation of an Ionic variant of a Greek alphabet to the specifics of the Iberian language, thus this script is an alphabet and lacks the distinctive characteristic of the paleohispanic scripts that present ...
. To understand the relationship between northeastern Iberian and southeastern Iberian scripts, one should point out that they are two different scripts with different values for the same signs. However, it is clear they have a common origin and the most accepted hypothesis is that northeastern Iberian script was derived from the southeastern Iberian script
The southeastern Iberian script, also known as Meridional Iberian, was one of the means of written expression of the Iberian language, which was written mainly in the northeastern Iberian script and residually by the Greco-Iberian alphabet. Abo ...
. Some researchers have concluded that it is linked to the Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet is an alphabet (more specifically, an abjad) known in modern times from the Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions found across the Mediterranean region. The name comes from the Phoenician civilization.
The Phoenician a ...
alone, but others believe the Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BCE. It is derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and was the earliest known alphabetic script to have distinct letters for vowels as ...
also had a role.
Typology and variants
All thepaleohispanic scripts
The Paleohispanic scripts are the writing systems created in the Iberian peninsula before the Latin alphabet became the main script. Most of them are unusual in that they are semi-syllabic rather than purely alphabetic, despite having su ...
, with the exception of the Greco-Iberian alphabet
The Greco-Iberian alphabet is a direct adaptation of an Ionic variant of a Greek alphabet to the specifics of the Iberian language, thus this script is an alphabet and lacks the distinctive characteristic of the paleohispanic scripts that present ...
, share a common distinctive typological characteristic: they represent syllabic value for the occlusives
In phonetics, an occlusive, sometimes known as a stop, is a consonant sound produced by occluding (i.e. blocking) airflow in the vocal tract, but not necessarily in the nasal tract. The duration of the block is the ''occlusion'' of the conson ...
, and monophonemic value for the rest of the consonants
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are and pronounced with the lips; and pronounced with the front of the tongue; and pronounced w ...
and vowels
A vowel is a syllabic speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness and also in quantity (l ...
. In a writing system
A writing system is a method of visually representing verbal communication, based on a script and a set of rules regulating its use. While both writing and speech are useful in conveying messages, writing differs in also being a reliable for ...
they are neither alphabets
An alphabet is a standardized set of basic written graphemes (called letters) that represent the phonemes of certain spoken languages. Not all writing systems represent language in this way; in a syllabary, each character represents a syl ...
nor syllabaries
In the linguistic study of written languages, a syllabary is a set of written symbols that represent the syllables or (more frequently) moras which make up words.
A symbol in a syllabary, called a syllabogram, typically represents an (option ...
, but are rather mixed scripts that are normally identified as semi-syllabaries
A semi-syllabary is a writing system that behaves partly as an alphabet and partly as a syllabary. The main group of semi-syllabic writing are the Paleohispanic scripts of ancient Spain, a group of semi-syllabaries that transform redundant plos ...
. The basic signary contains 28 sign
A sign is an Physical object, object, quality (philosophy), quality, event, or Non-physical entity, entity whose presence or occurrence indicates the probable presence or occurrence of something else. A natural sign bears a causal relation to ...
s: 5 vowels
A vowel is a syllabic speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness and also in quantity (l ...
, 15 syllabic and 8 consonantic (one lateral
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Healthcare
*Lateral (anatomy), an anatomical direction
* Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
* Lateral release (surgery), a surgical procedure on the side of a kneecap
Phonetics
*Lateral co ...
, two sibilants
Sibilants are fricative consonants of higher amplitude and pitch, made by directing a stream of air with the tongue towards the teeth. Examples of sibilants are the consonants at the beginning of the English words ''sip'', ''zip'', ''ship'', and ...
, two rhotic and three nasals). The northeastern script was very nearly deciphered in 1922 by Manuel Gómez-Moreno Martínez
Manuel Gómez-Moreno Martínez (21 February 1870 in Granada, Spain – 7 June 1970 in Madrid, Spain), was a Spanish archaeologist and historian.
Biography
Martinez was born 21 February 1870 in Granada, Spain. He is the son of noted painte ...
, who systematically linked the syllabic signs with the occlusive
In phonetics, an occlusive, sometimes known as a stop, is a consonant sound produced by occluding (i.e. blocking) airflow in the vocal tract, but not necessarily in the nasal tract. The duration of the block is the ''occlusion'' of the consonan ...
values. The decipherment was based on the existence of a large number of coin
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in orde ...
legends (some of them bearing Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
inscriptions) that could easily be linked to ancient place names known from Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
and Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
sources. There are two variants of the northeastern Iberian script: the dual variant is almost exclusive to the ancient inscriptions from the 4th and 3rd centuries BCE and its distinctive characteristic is the use of the dual system. This system was discovered by Joan Maluquer de Motes in 1968 and allows differentiation of the occlusive
In phonetics, an occlusive, sometimes known as a stop, is a consonant sound produced by occluding (i.e. blocking) airflow in the vocal tract, but not necessarily in the nasal tract. The duration of the block is the ''occlusion'' of the consonan ...
signs ( dentals and velars
Velars are consonants articulated with the back part of the tongue (the dorsum) against the soft palate, the back part of the roof of the mouth (known also as the velum).
Since the velar region of the roof of the mouth is relatively extensive a ...
) between voiced
Voice or voicing is a term used in phonetics and phonology to characterize speech sounds (usually consonants). Speech sounds can be described as either voiceless (otherwise known as ''unvoiced'') or voiced.
The term, however, is used to refe ...
and unvoiced
In linguistics, voicelessness is the property of sounds being pronounced without the larynx vibrating. Phonologically, it is a type of phonation, which contrasts with other states of the larynx, but some object that the word phonation implies vo ...
by the use of an additional stroke. The simple sign represents the voiced value whilst the complex sign represents the unvoiced
In linguistics, voicelessness is the property of sounds being pronounced without the larynx vibrating. Phonologically, it is a type of phonation, which contrasts with other states of the larynx, but some object that the word phonation implies vo ...
value. The non-dual variant is almost exclusive of the modern inscriptions from the 2nd and 1st centuries BCE.
Location of findings
The inscriptions that use the northeastern Iberian script have been found mainly in the northeastern quadrant of theIberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
: largely along the coast from Roussillon
Roussillon ( , , ; ca, Rosselló ; oc, Rosselhon ) is a historical province of France that largely corresponded to the County of Roussillon and part of the County of Cerdagne of the former Principality of Catalonia. It is part of th ...
to Alicante
Alicante ( ca-valencia, Alacant) is a city and municipality in the Valencian Community, Spain. It is the capital of the province of Alicante and a historic Mediterranean port. The population of the city was 337,482 , the second-largest in th ...
, but also with a deep penetration in the Ebro
, name_etymology =
, image = Zaragoza shel.JPG
, image_size =
, image_caption = The Ebro River in Zaragoza
, map = SpainEbroBasin.png
, map_size =
, map_caption = The Ebro ...
Valley. The northeastern Iberian inscriptions have been found on different object types (silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, whi ...
and bronze coins
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to ...
, silver and ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelai ...
recipients, lead
Lead is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metals, heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale of mineral hardness#Intermediate ...
plaques, mosaics
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly pop ...
, amphores, stones ( steles), spindle
Spindle may refer to:
Textiles and manufacturing
* Spindle (textiles), a straight spike to spin fibers into yarn
* Spindle (tool), a rotating axis of a machine tool
Biology
* Common spindle and other species of shrubs and trees in genus '' Euony ...
-whorls etc.), representing 95% of the total finds (over 2000 items), and nearly all the scripts were written from left to right. The oldest northeastern Iberian script date to the 4th or maybe the 5th century BCE. The modern ones date from the end of the 1st century BCE or maybe the beginning of the 1st century CE.
In recent years four northeastern Iberian abecedaries or signaries have been published: the Castellet de Bernabé signary
Castellet-en-Luberon (before 2018: ''Castellet'')Décret n° 2018-956
5 November 20 ...
, the Tos Pelat signary, the Ger signary and the Bolvir signary, all of them belonging to the dual variant of the script.
5 November 20 ...
See also
*Greco-Iberian alphabet
The Greco-Iberian alphabet is a direct adaptation of an Ionic variant of a Greek alphabet to the specifics of the Iberian language, thus this script is an alphabet and lacks the distinctive characteristic of the paleohispanic scripts that present ...
*Iberian scripts
The Iberian scripts are the Paleohispanic scripts that were used to represent the extinct Iberian language. Most of them are typologically unusual in that they are semi-syllabic rather than purely alphabetic.Ferrer, J., Moncunill, N., Ve ...
*Paleohispanic scripts
The Paleohispanic scripts are the writing systems created in the Iberian peninsula before the Latin alphabet became the main script. Most of them are unusual in that they are semi-syllabic rather than purely alphabetic, despite having su ...
**Celtiberian script
The Celtiberian script is a Paleohispanic script that was the main writing system of the Celtiberian language, an extinct Continental Celtic language, which was also occasionally written using the Latin alphabet. This script is a direct adap ...
**Southeastern Iberian script
The southeastern Iberian script, also known as Meridional Iberian, was one of the means of written expression of the Iberian language, which was written mainly in the northeastern Iberian script and residually by the Greco-Iberian alphabet. Abo ...
**Tartessian script
The Southwest Script or Southwestern Script, also known as Tartessian or South Lusitanian, is a Paleohispanic script used to write an unknown language usually identified as Tartessian. Southwest inscriptions have been found mainly in the sout ...
*Paleohispanic languages
The paleo-Hispanic languages were the languages of the Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula, excluding languages of foreign colonies, such as Greek in Emporion and Phoenician in Qart Hadast. After the Roman conquest of Hispania the Paleo ...
*Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula
This is a list of the pre- Roman people of the Iberian Peninsula (the Roman Hispania, i. e., modern Portugal, Spain and Andorra). Some closely fit the concept of a people, ethnic group or tribe. Others are confederations or even unions of t ...
Notes
Bibliography
* Correa, José Antonio (1992): «Representación gráfica de la oposición de sonoridad en las oclusivas ibéricas (semisilabario levantino)», ''AION'' 14, pp. 253–292. * Ferrer i Jané, Joan (2005)''Novetats sobre el sistema dual de diferenciació gràfica de les oclusives sordes i sonores''
''Palaeohispanica'' 5, pp. 957–982. * Ferrer i Jane Joan (2013)
«Els sistemes duals de les escriptures ibèriques»
''Palaeohispanica'' 13, pp. 451-479. * Gómez-Moreno, Manuel (1922): «De Epigrafia ibérica: el plomo de Alcoy», ''Revista de filología española'' 9, pp. 34–66. * Hoz, Javier de (1985): «El nuevo plomo inscrito de Castell y el problema de las oposiciones de sonoridad en ibérico», ''Symbolae Ludouico Mitxelena septuagenario oblatae'', pp. 443–453. * Maluquer de Motes, Joan (1968): ''Epigrafía prelatina de la península ibérica'', Barcelona. * Quintanilla, Alberto (1993): «Sobre la notación en la escritura ibérica del modo de articulación de las consonantes oclusivas», ''Studia Palaeohispanica et Indogermánica J. Untermann ab Amicis Hispanicis Oblata'', pp. 239–250. * Rodríguez Ramos, Jesús (2004): ''Análisis de epigrafía íbera'', Vitoria-Gasteiz. * Untermann, Jürgen (1990): ''Monumenta Linguarum Hispanicarum. III Die iberischen Inschriften aus Spanien'', Wiesbaden. * Velaza, Javier (1996): ''Epigrafía y lengua ibéricas'', Barcelona.
External links
The levantine Iberian writing- Jesús Rodríguez Ramos
{{DEFAULTSORT:Northeastern Iberian Script Northeastern Iberian script Palaeohispanic writing