NorthGRIP on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The drilling site of the North Greenland Ice Core Project (NGRIP or NorthGRIP) is near the center of
The drilling site of the North Greenland Ice Core Project (NGRIP or NorthGRIP) is near the center of


 The drilling site of the North Greenland Ice Core Project (NGRIP or NorthGRIP) is near the center of
The drilling site of the North Greenland Ice Core Project (NGRIP or NorthGRIP) is near the center of Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is t ...
(75.1 N, 42.32 W, 2917 m, ice thickness 3085). Drilling began in 1999 and was completed at bedrock
In geology, bedrock is solid Rock (geology), rock that lies under loose material (regolith) within the crust (geology), crust of Earth or another terrestrial planet.
Definition
Bedrock is the solid rock that underlies looser surface mater ...
in 2003. The cores are cylinders of ice 11 centimeters in diameter that were brought to the surface in 3.5-meter lengths. The NGRIP site was chosen to extract a long and undisturbed record stretching into the last glacial
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betw ...
, and it succeeded. The site was chosen for a flat basal topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sci ...
to avoid the flow distortions that render the bottom of the GRIP and GISP cores unreliable. Unusually, there is melting at the bottom of the NGRIP core - believed to be due to a high geothermal heat flux locally. This has the advantage that the bottom layers are less compressed by thinning than they would otherwise be: NGRIP annual layers at 10.5 kyr age are 1.1 cm thick, twice the GRIP thicknesses at equal age.
The NGRIP record helps to resolve a problem with the GRIP and GISP2 records - the unreliability of the Eemian Stage
The Eemian (also called the last interglacial, Sangamonian Stage, Ipswichian, Mikulin, Kaydaky, penultimate,NOAA - Penultimate Interglacial Period http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/global-warming/penultimate-interglacial-period Valdivia or Riss-Würm) wa ...
portion of the record. NGRIP covers 5 kyr of the Eemian, and shows that temperatures then were roughly as stable as the pre-industrial Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togethe ...
temperatures were. This is confirmed by sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand an ...
cores, in particular MD95-2042.
In 2003, NGRIP recovered what seem to be plant remnants nearly two miles below the surface, and they may be several million years old.
"Several of the pieces look very much like blades of grass or pine needles," said University of Colorado at Boulder geological sciences Professor James White, an NGRIP principal investigator. "If confirmed, this will be the first organic material ever recovered from a deep ice-core drilling project," he said.
See also
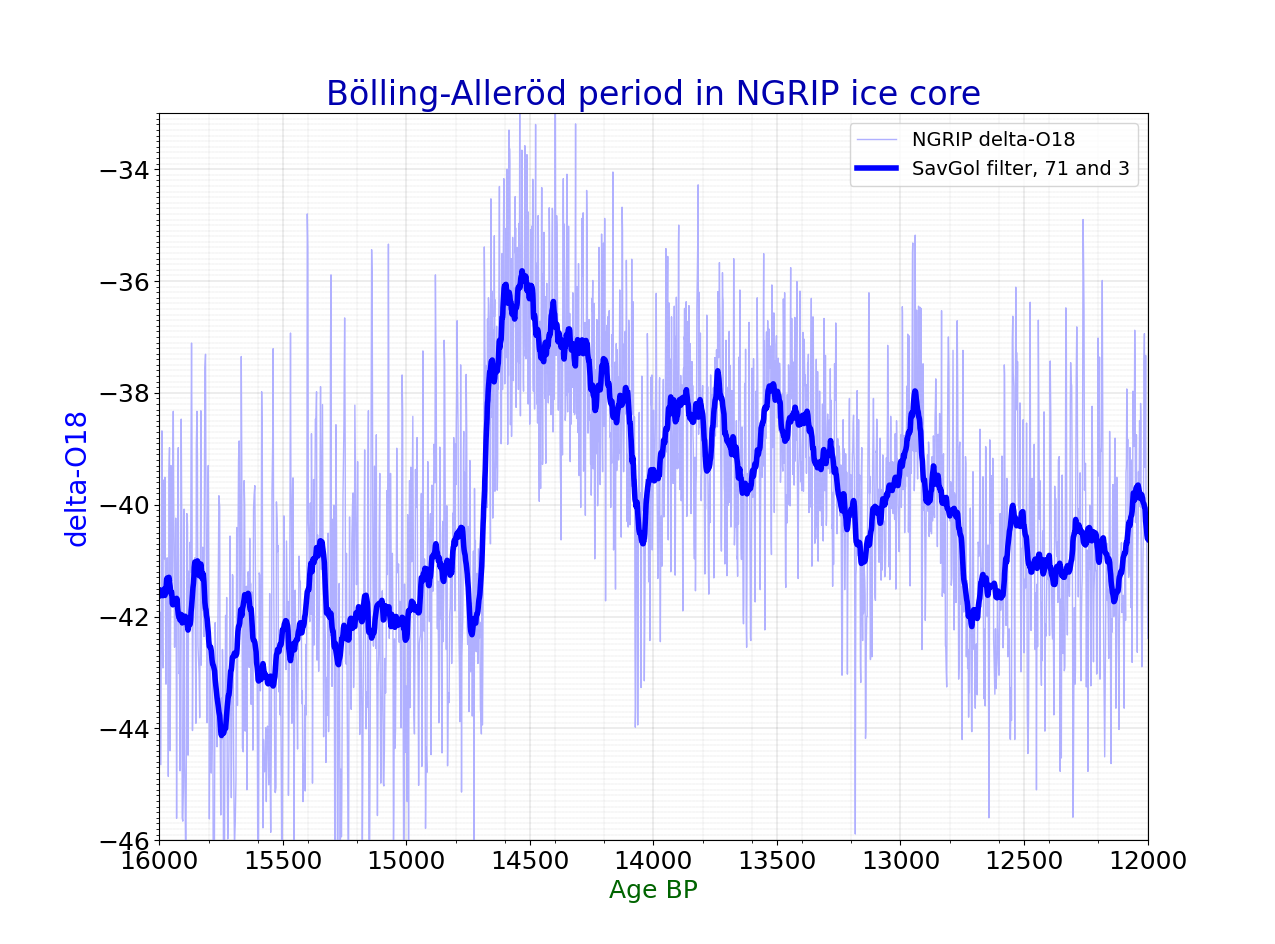
* Bølling-Allerød warming *Northgrippian
In the geologic time scale, the Northgrippian is the middle one of three ages or stages of the Holocene Epoch or Series. It was officially ratified by the International Commission on Stratigraphy in June 2018 along with the earlier Greenlandia ...
*Greenlandian
In the geologic time scale, the Greenlandian is the earliest age or lowest stage of the Holocene Epoch or Series, part of the Quaternary. Beginning in 11,650 BP (9701 BCE or 300 HE) and ending 8,276 BP (6237 BCE or 3764 HE), it is the earlies ...
References
External links
The original web page of the NGRIP project with field diaries and pictures. * https://web.archive.org/web/20120101002118/http://www.gfy.ku.dk/~www-glac/ngrip/index_eng.htm The NGRIP project was run by an international consortium of scientists, and drilling and logistics were managed by what is now called Centre for Ice and Climate at the Niels Bohr Institute, University of Copenhagen, Denmark. This research centre maintains a web page about ice core research: * http://www.iceandclimate.nbi.ku.dk/research/drill_analysing/history_drilling/search_eemian/ {{coord, 75, 01, N, 42, 32, W, source:kolossus-eswiki, display=title Geochronological institutions and organizations Natural history of Greenland Arctic research 20th century in the Arctic 21st century in the Arctic