Norman Ramsey on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Norman Foster Ramsey Jr. (August 27, 1915 – November 4, 2011) was an American
 In 1940, he married Elinor Jameson of
In 1940, he married Elinor Jameson of
 The first thing he had to do was determine the characteristics of the aircraft that would be used. There were only two
The first thing he had to do was determine the characteristics of the aircraft that would be used. There were only two
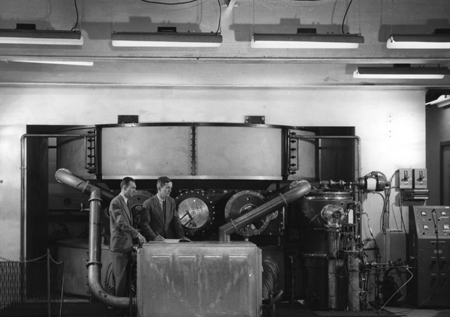 Ramsey's research in the immediate post-war years looked at measuring fundamental properties of atoms and molecules by use of molecular beams. On moving to Harvard, his objective was to carry out accurate molecular beam magnetic resonance experiments, based on the techniques developed by Rabi. However, the accuracy of the measurements depended on the uniformity of the magnetic field, and Ramsey found that it was difficult to create sufficiently uniform magnetic fields. He developed the separated oscillatory field method in 1949 as a means of achieving the accuracy he wanted.
Ramsey and his PhD student
Ramsey's research in the immediate post-war years looked at measuring fundamental properties of atoms and molecules by use of molecular beams. On moving to Harvard, his objective was to carry out accurate molecular beam magnetic resonance experiments, based on the techniques developed by Rabi. However, the accuracy of the measurements depended on the uniformity of the magnetic field, and Ramsey found that it was difficult to create sufficiently uniform magnetic fields. He developed the separated oscillatory field method in 1949 as a means of achieving the accuracy he wanted.
Ramsey and his PhD student
"Proton–Proton Scattering at 105 MeV and 75 MeV"
"Inelastic Scattering Of Electrons By Protons"
Department of Physics at
"Determination of the Neutron Magnetic Moment"
Oak Ridge National Laboratory,
Group photograph
taken at The International Conference on Lasers and Applications, Lasers 'XX, ''Lasers'' '93 including (right to left) Norman F. Ramsey, Marlan Scully, and F. J. Duarte.
Norman Ramsey, an oral history conducted in 1995 by Andrew Goldstein, IEEE History Center, New Brunswick, NJ, USA.
Papers relating to the Manhattan Project, 1945–1946, collected by Norman Ramsey
Dibner Library of the History of Science and Technology, Smithsonian Libraries, from SIRIS * including the Nobel Lecture, December 8, 1989 ''Experiments with Separated Oscillatory Fields and Hydrogen Masers'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Ramsey, Norman Foster 1915 births 2011 deaths Columbia College (New York) alumni Columbia Graduate School of Arts and Sciences alumni Columbia University faculty Harvard University faculty Nobel laureates in Physics National Medal of Science laureates American Nobel laureates IEEE Medal of Honor recipients Vannevar Bush Award recipients Manhattan Project people Members of the French Academy of Sciences Members of the United States National Academy of Sciences American physicists People associated with the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki University of Michigan staff Fellows of the American Physical Society Presidents of the American Physical Society Members of the American Philosophical Society
physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe.
Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate caus ...
who was awarded the 1989 Nobel Prize in Physics
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then " ...
, for the invention of the separated oscillatory field method, which had important applications in the construction of atomic clock
An atomic clock is a clock that measures time by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms. It is based on atoms having different energy levels. Electron states in an atom are associated with different energy levels, and in transitions betwee ...
s. A physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which r ...
professor at Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
for most of his career, Ramsey also held several posts with such government and international agencies as NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
and the United States Atomic Energy Commission
The United States Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) was an agency of the United States government established after World War II by U.S. Congress to foster and control the peacetime development of atomic science and technology. President H ...
. Among his other accomplishments are helping to found the United States Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and manages the research and development of nuclear power and nuclear weapons in the United Stat ...
's Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL) is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory located in Upton, Long Island, and was formally established in 1947 at the site of Camp Upton, a former U.S. Army base and Japanese internment c ...
and Fermilab
Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab), located just outside Batavia, Illinois, near Chicago, is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory specializing in high-energy particle physics. Since 2007, Fermilab has been operat ...
.
Early life
Norman Foster Ramsey Jr. was born inWashington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, on August 27, 1915, to Minna Bauer Ramsey, an instructor at the University of Kansas
The University of Kansas (KU) is a public research university with its main campus in Lawrence, Kansas, United States, and several satellite campuses, research and educational centers, medical centers, and classes across the state of Kansas. Tw ...
, and Norman Foster Ramsey, a 1905 graduate of the United States Military Academy
The United States Military Academy (USMA), also known metonymically as West Point or simply as Army, is a United States service academy in West Point, New York. It was originally established as a fort, since it sits on strategic high groun ...
at West Point
The United States Military Academy (USMA), also known Metonymy, metonymically as West Point or simply as Army, is a United States service academies, United States service academy in West Point, New York. It was originally established as a f ...
and an officer in the Ordnance Department
The United States Army Ordnance Corps, formerly the United States Army Ordnance Department, is a sustainment branch of the United States Army, headquartered at Fort Lee, Virginia. The broad mission of the Ordnance Corps is to supply Army comb ...
who rose to the rank of brigadier general
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointed ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, commanding the Rock Island Arsenal
The Rock Island Arsenal comprises , located on Arsenal Island, originally known as Rock Island, on the Mississippi River between the cities of Davenport, Iowa, and Rock Island, Illinois. It lies within the state of Illinois. Rock Island ...
. He was raised as an Army brat
A military brat (colloquial or military slang) is a child of serving or retired military personnel. Military brats are associated with a unique subcultureDavid C. Pollock, Ruth E. van Reken. ''Third Culture Kids: Growing Up Among Worlds'', Revis ...
, frequently moving from post to post, and lived in France for a time when his father was Liaison Officer with the ''Direction d'Artillerie'' and Assistant Military Attaché
A military attaché is a military expert who is attached to a diplomatic mission, often an embassy. This type of attaché post is normally filled by a high-ranking military officer, who retains a commission while serving with an embassy. Opport ...
. This allowed him to skip a couple of grades along the way, so that he graduated from Leavenworth High School
Leavenworth High School is a public high school located in Leavenworth, Kansas, operated by Leavenworth USD 453 school district. The school was established in 1865, making it one of the first high schools in Kansas. The school colors are blue and ...
in Leavenworth, Kansas
Leavenworth () is the county seat and largest city of Leavenworth County, Kansas, United States and is part of the Kansas City metropolitan area. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 37,351. It is located on the west bank of t ...
, at the age of 15.
Ramsey's parents hoped that he would go to West Point, but at 15, he was too young to be admitted. He was awarded a scholarship to the University of Kansas
The University of Kansas (KU) is a public research university with its main campus in Lawrence, Kansas, United States, and several satellite campuses, research and educational centers, medical centers, and classes across the state of Kansas. Tw ...
, but in 1930 his father was posted to Governors Island
Governors Island is a island in New York Harbor, within the New York City borough of Manhattan. It is located approximately south of Manhattan Island, and is separated from Brooklyn to the east by the Buttermilk Channel. The National Park ...
, New York. Ramsey therefore entered Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
in 1931, and began studying engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific method, scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad rang ...
. He became interested in mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
, and switched to this as his academic major
An academic major is the academic discipline to which an undergraduate student formally commits. A student who successfully completes all courses required for the major qualifies for an undergraduate degree. The word ''major'' (also called ''conce ...
. By the time he received his BA from Columbia in 1935, he had become interested in physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which r ...
. Columbia awarded him a Kellett Fellowship to Cambridge University
, mottoeng = Literal: From here, light and sacred draughts.
Non literal: From this place, we gain enlightenment and precious knowledge.
, established =
, other_name = The Chancellor, Masters and Schola ...
where he studied physics at Cavendish Laboratory
The Cavendish Laboratory is the Department of Physics at the University of Cambridge, and is part of the School of Physical Sciences. The laboratory was opened in 1874 on the New Museums Site as a laboratory for experimental physics and is named ...
under Lord Rutherford
Ernest Rutherford, 1st Baron Rutherford of Nelson, (30 August 1871 – 19 October 1937) was a New Zealand physicist who came to be known as the father of nuclear physics.
''Encyclopædia Britannica'' considers him to be the greatest ...
and Maurice Goldhaber
Maurice Goldhaber (April 18, 1911 – May 11, 2011) was an American physicist, who in 1957 (with Lee Grodzins and Andrew Sunyar) established that neutrinos have negative helicity.
Early life and childhood
He was born on April 18, 1911, in L ...
, and encountered notable physicists including Edward Appleton, Max Born
Max Born (; 11 December 1882 – 5 January 1970) was a German physicist and mathematician who was instrumental in the development of quantum mechanics. He also made contributions to solid-state physics and optics and supervised the work of a n ...
, Edward Bullard
Sir Edward Crisp Bullard FRS (21 September 1907 – 3 April 1980) was a British geophysicist who is considered, along with Maurice Ewing, to have founded the discipline of marine geophysics. He developed the theory of the geodynamo, pioneered ...
, James Chadwick
Sir James Chadwick, (20 October 1891 – 24 July 1974) was an English physicist who was awarded the 1935 Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery of the neutron in 1932. In 1941, he wrote the final draft of the MAUD Report, which inspi ...
, John Cockcroft
Sir John Douglas Cockcroft, (27 May 1897 – 18 September 1967) was a British physicist who shared with Ernest Walton the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1951 for splitting the atomic nucleus, and was instrumental in the development of nuclea ...
, Paul Dirac
Paul Adrien Maurice Dirac (; 8 August 1902 – 20 October 1984) was an English theoretical physicist who is regarded as one of the most significant physicists of the 20th century. He was the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at the Univer ...
, Arthur Eddington
Sir Arthur Stanley Eddington (28 December 1882 – 22 November 1944) was an English astronomer, physicist, and mathematician. He was also a philosopher of science and a populariser of science. The Eddington limit, the natural limit to the lumin ...
, Ralph Fowler, Mark Oliphant
Sir Marcus Laurence Elwin Oliphant, (8 October 1901 – 14 July 2000) was an Australian physicist and humanitarian who played an important role in the first experimental demonstration of nuclear fusion and in the development of nuclear weapon ...
and J.J. Thomson
Sir Joseph John Thomson (18 December 1856 – 30 August 1940) was a British physicist and Nobel Laureate in Physics, credited with the discovery of the electron, the first subatomic particle to be discovered.
In 1897, Thomson showed that ...
. At Cambridge, he took the tripos
At the University of Cambridge, a Tripos (, plural 'Triposes') is any of the examinations that qualify an undergraduate for a bachelor's degree or the courses taken by a student to prepare for these. For example, an undergraduate studying mathe ...
in order to study quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, ...
, which had not been covered at Columbia, resulting in being awarded a second BA degree by Cambridge.
A term paper Ramsey wrote for Goldhaber on magnetic moment
In electromagnetism, the magnetic moment is the magnetic strength and orientation of a magnet or other object that produces a magnetic field. Examples of objects that have magnetic moments include loops of electric current (such as electromagnets ...
s caused him to read recent papers on the subject by Isidor Isaac Rabi
Isidor Isaac Rabi (; born Israel Isaac Rabi, July 29, 1898 – January 11, 1988) was an American physicist who won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1944 for his discovery of nuclear magnetic resonance, which is used in magnetic resonance ima ...
, and this stimulated an interest in molecular beam A molecular beam is produced by allowing a gas at higher pressure to expand through a small orifice into a chamber at lower pressure to form a beam of particles (atoms, free radicals, molecules or ions) moving at approximately equal velocities, with ...
s, and in doing research for a PhD under Rabi at Columbia. Soon after Ramsey arrived at Columbia, Rabi invented molecular beam resonance spectroscopy, for which he was awarded the Nobel prize in physics
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then " ...
in 1944. Ramsey was part of Rabi's team that also included Jerome Kellogg
Jerome (; la, Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος Σωφρόνιος Ἱερώνυμος; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was a Christian presbyter, priest, Confessor of the Faith, confessor, th ...
, Polykarp Kusch
Polykarp Kusch (January 26, 1911 – March 20, 1993) was a German-born American physicist. In 1955, the Nobel Committee gave a divided Nobel Prize for Physics, with one half going to Kusch for his accurate determination that the magnetic momen ...
, Sidney Millman
Sidney may refer to:
People
* Sidney (surname), English surname
* Sidney (given name), including a list of people with the given name
* Sidney (footballer, born 1972), full name Sidney da Silva Souza, Brazilian football defensive midfielder
* ...
and Jerrold Zacharias
Jerrold Reinach Zacharias (January 23, 1905 – July 16, 1986) was an American physicist and Institute Professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, as well as an education reformer. His scientific work was in the area of nuclear physics ...
. Ramsey worked with them on the first experiments making use of the new technique, and shared with Rabi and Zacharias in the discovery that the deuteron
Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol or deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being protium, or hydrogen-1). The nucleus of a deuterium atom, called a deuteron, contains one proton and one n ...
was a magnetic quadrupole
A quadrupole or quadrapole is one of a sequence of configurations of things like electric charge or current, or gravitational mass that can exist in ideal form, but it is usually just part of a multipole expansion of a more complex structure refl ...
. This meant that the atomic nucleus
The atomic nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom, discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron i ...
was not spherical, as had been thought. He received his PhD in physics from Columbia in 1940, and became a fellow at the Carnegie Institution
The Carnegie Institution of Washington (the organization's legal name), known also for public purposes as the Carnegie Institution for Science (CIS), is an organization in the United States established to fund and perform scientific research. Th ...
in Washington, D.C., where he studied neutron
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol or , which has a neutral (not positive or negative) charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the nuclei of atoms. Since protons and neutrons beh ...
-proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ...
and proton-helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
scattering
Scattering is a term used in physics to describe a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities (including ...
.
World War II
Radiation laboratory
 In 1940, he married Elinor Jameson of
In 1940, he married Elinor Jameson of Brooklyn, New York
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
, and accepted a teaching position at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (U of I, Illinois, University of Illinois, or UIUC) is a public land-grant research university in Illinois in the twin cities of Champaign and Urbana. It is the flagship institution of the Universit ...
. The two expected to spend the rest of their lives there, but World War II intervened. In September 1940 the British Tizard Mission
The Tizard Mission, officially the British Technical and Scientific Mission, was a British delegation that visited the United States during WWII to obtain the industrial resources to exploit the military potential of the research and development ( ...
brought a number of new technologies to the United States, including a cavity magnetron
The cavity magnetron is a high-power vacuum tube used in early radar systems and currently in microwave ovens and linear particle accelerators. It generates microwaves using the interaction of a stream of electrons with a magnetic field while ...
, a high-powered device that generates microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency ran ...
s using the interaction of a stream of electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no kn ...
s with a magnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ...
, which promised to revolutionize radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, w ...
. Alfred Lee Loomis
Alfred Lee Loomis (November 4, 1887 – August 11, 1975) was an American attorney, investment banker, philanthropist, scientist, physicist, inventor of the LORAN Long Range Navigation System and a lifelong patron of scientific research. He estab ...
of the National Defense Research Committee
The National Defense Research Committee (NDRC) was an organization created "to coordinate, supervise, and conduct scientific research on the problems underlying the development, production, and use of mechanisms and devices of warfare" in the Un ...
established the Radiation Laboratory
The Radiation Laboratory, commonly called the Rad Lab, was a microwave and radar research laboratory located at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It was first created in October 1940 and operated until 31 ...
at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the ...
to develop this technology. Ramsey was one of the scientists recruited by Rabi for this work.
Initially, Ramsey was in Rabi's magnetron group. When Rabi became a division head, Ramsey became the group leader. The role of the group was to develop the magnetron to permit a reduction in wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tro ...
from to , and then to or X-Band. Microwave radar promised to be small, lighter and more efficient than older types. Ramsey's group started with the design produced by Oliphant's team in Britain, and attempted to improve it. The Radiation Laboratory produced the designs, which were prototyped by Raytheon
Raytheon Technologies Corporation is an American multinational aerospace and defense conglomerate headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. It is one of the largest aerospace and defense manufacturers in the world by revenue and market capitaliza ...
, and then tested by the laboratory. In June 1941, Ramsey travelled to Britain, where he met with Oliphant, and the two exchanged ideas. He brought back some British components which were incorporated into the final design. A night fighter
A night fighter (also known as all-weather fighter or all-weather interceptor for a period of time after the Second World War) is a fighter aircraft adapted for use at night or in other times of bad visibility. Night fighters began to be used i ...
aircraft, the Northrop P-61 Black Widow
The Northrop P-61 Black Widow is a twin-engine United States Army Air Forces fighter aircraft of World War II. It was the first operational U.S. warplane designed as a night fighter, and the first aircraft designed specifically as a night fight ...
, was designed around the new radar. Ramsey returned to Washington in late 1942 as an adviser on the use of the new 3 cm microwave radar sets that were now coming into service, working for Edward L. Bowles
Edward is an English language, English given name. It is derived from the Old English, Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements ''wikt:ead#Old English, ēad'' "wealth, fortune; prosperous" and ''wikt:weard#Old English, weard'' "gua ...
in the office of the Secretary of War
The secretary of war was a member of the U.S. president's Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's administration. A similar position, called either "Secretary at War" or "Secretary of War", had been appointed to serve the Congress of the ...
, Henry L. Stimson
Henry Lewis Stimson (September 21, 1867 – October 20, 1950) was an American statesman, lawyer, and Republican Party politician. Over his long career, he emerged as a leading figure in U.S. foreign policy by serving in both Republican and D ...
.
Manhattan Project
In 1943, Ramsey was approached byRobert Oppenheimer
J. Robert Oppenheimer (; April 22, 1904 – February 18, 1967) was an American theoretical physicist. A professor of physics at the University of California, Berkeley, Oppenheimer was the wartime head of the Los Alamos Laboratory and is often ...
and Robert Bacher, who asked him to join the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
. Ramsey agreed to do so, but the intervention of the Project director, Brigadier General Leslie R. Groves Jr.
Lieutenant general (United States), Lieutenant General Leslie Richard Groves Jr. (17 August 1896 – 13 July 1970) was a United States Army Corps of Engineers Officer (armed forces), officer who oversaw the construction of the Pentagon and di ...
, was necessary in order to prise him away from the Secretary of War's office. A compromise was agreed to, whereby Ramsey remained on the payroll of the Secretary of War, and was merely seconded to the Manhattan Project. In October 1943, Group E-7 of the Ordnance Division was created at the Los Alamos Laboratory
The Los Alamos Laboratory, also known as Project Y, was a secret laboratory established by the Manhattan Project and operated by the University of California during World War II. Its mission was to design and build the first atomic bombs. Ro ...
with Ramsey as group leader, with the task of integrating the design and delivery of the nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bom ...
s being built by the laboratory.
 The first thing he had to do was determine the characteristics of the aircraft that would be used. There were only two
The first thing he had to do was determine the characteristics of the aircraft that would be used. There were only two Allied
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
aircraft large enough: the British Avro Lancaster
The Avro Lancaster is a British Second World War heavy bomber. It was designed and manufactured by Avro as a contemporary of the Handley Page Halifax, both bombers having been developed to the same specification, as well as the Short Stirlin ...
and the US Boeing B-29 Superfortress
The Boeing B-29 Superfortress is an American four-engined propeller-driven heavy bomber, designed by Boeing and flown primarily by the United States during World War II and the Korean War. Named in allusion to its predecessor, the B-17 Fl ...
. The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) wanted to use the B-29 if at all possible, even though it required substantial modification. Ramsey supervised the test drop program, which began at Dahlgren, Virginia
Dahlgren is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in King George County, Virginia, United States. The population was 2,946 at the time of the 2020 census, up from 2,653 at the 2010 census, and up from 997 in 2000.
History ...
, in August 1943, before moving to Muroc Dry Lake, California, in March 1944. Mock ups of Thin Man and Fat Man
"Fat Man" (also known as Mark III) is the codename for the type of nuclear bomb the United States detonated over the Japanese city of Nagasaki on 9 August 1945. It was the second of the only two nuclear weapons ever used in warfare, the fir ...
bombs were dropped and tracked by an SCR-584
The SCR-584 (short for '' Set, Complete, Radio # 584'') was an automatic-tracking microwave radar developed by the MIT Radiation Laboratory during World War II. It was one of the most advanced ground-based radars of its era, and became one of the ...
ground-based radar set of the kind that Ramsey had helped develop at the Radiation laboratory. Numerous problems were discovered with the bombs and the aircraft modifications, and corrected.
Plans for the delivery of the weapons in combat were assigned to the Weapons Committee, which was chaired by Ramsey, and answerable to Captain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, e ...
William S. Parsons. Ramsey drew up tables of organization and equipment for the Project Alberta
Project Alberta, also known as Project A, was a section of the Manhattan Project which assisted in delivering the first nuclear weapons in the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki during World War II.
Project Alberta was formed in March 19 ...
detachment that would accompany the USAAF's 509th Composite Group
The 509th Composite Group (509 CG) was a unit of the United States Army Air Forces created during World War II and tasked with the operational deployment of nuclear weapons. It conducted the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Japan, in ...
to Tinian
Tinian ( or ; old Japanese name: 天仁安島, ''Tenian-shima'') is one of the three principal islands of the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands. Together with uninhabited neighboring Aguiguan, it forms Tinian Municipality, one of th ...
. Ramsey briefed the 509th's commander, Lieutenant Colonel Paul W. Tibbets
Paul Warfield Tibbets Jr. (23 February 1915 – 1 November 2007) was a brigadier general in the United States Air Force. He is best known as the aircraft captain who flew the B-29 Superfortress known as the '' Enola Gay'' (named after his mot ...
, on the nature of the mission when the latter assumed command of the 509th. Ramsey went to Tinian with the Project Alberta detachment as Parsons's scientific and technical deputy. He was involved in the assembly of the Fat Man bomb, and relayed Parsons's message indicating the success of the bombing of Hiroshima
The United States detonated two atomic bombs over the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki on 6 and 9 August 1945, respectively. The two bombings killed between 129,000 and 226,000 people, most of whom were civilians, and remain the on ...
to Groves in Washington, D.C.
Research
At the end of the war, Ramsey returned to Columbia as a professor and research scientist. Rabi and Ramsey picked up where they had left off before the war with their molecular beam experiments. Ramsey and his first graduate student, William Nierenberg, measured various nuclearmagnetic dipole
In electromagnetism, a magnetic dipole is the limit of either a closed loop of electric current or a pair of poles as the size of the source is reduced to zero while keeping the magnetic moment constant. It is a magnetic analogue of the electric ...
and electric quadrupole
A quadrupole or quadrapole is one of a sequence of configurations of things like electric charge or current, or gravitational mass that can exist in ideal form, but it is usually just part of a multipole expansion of a more complex structure ref ...
moments. With Rabi, he helped establish the Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL) is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory located in Upton, Long Island, and was formally established in 1947 at the site of Camp Upton, a former U.S. Army base and Japanese internment c ...
on Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York, part of the New York metropolitan area. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United Sta ...
. In 1946, he became the first head of the Physics Department there. His time there was brief, for in 1947, he joined the physics faculty at Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
, where he would remain for the next 40 years, except for brief visiting professorships at Middlebury College
Middlebury College is a private liberal arts college in Middlebury, Vermont. Founded in 1800 by Congregationalists, Middlebury was the first operating college or university in Vermont. The college currently enrolls 2,858 undergraduates from all ...
, Oxford University
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
, Mt. Holyoke College
Mount Holyoke College is a Private college, private liberal arts college, liberal arts Women's colleges in the United States, women's college in South Hadley, Massachusetts. It is the oldest member of the historic Seven Sisters (colleges), Seve ...
and the University of Virginia
The University of Virginia (UVA) is a Public university#United States, public research university in Charlottesville, Virginia. Founded in 1819 by Thomas Jefferson, the university is ranked among the top academic institutions in the United S ...
. During the 1950s, he was the first science adviser to NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
, and initiated a series of fellowships, grants and summer school programs to train European scientists.
 Ramsey's research in the immediate post-war years looked at measuring fundamental properties of atoms and molecules by use of molecular beams. On moving to Harvard, his objective was to carry out accurate molecular beam magnetic resonance experiments, based on the techniques developed by Rabi. However, the accuracy of the measurements depended on the uniformity of the magnetic field, and Ramsey found that it was difficult to create sufficiently uniform magnetic fields. He developed the separated oscillatory field method in 1949 as a means of achieving the accuracy he wanted.
Ramsey and his PhD student
Ramsey's research in the immediate post-war years looked at measuring fundamental properties of atoms and molecules by use of molecular beams. On moving to Harvard, his objective was to carry out accurate molecular beam magnetic resonance experiments, based on the techniques developed by Rabi. However, the accuracy of the measurements depended on the uniformity of the magnetic field, and Ramsey found that it was difficult to create sufficiently uniform magnetic fields. He developed the separated oscillatory field method in 1949 as a means of achieving the accuracy he wanted.
Ramsey and his PhD student Daniel Kleppner
Daniel Kleppner, born 1932, is the Lester Wolfe Professor Emeritus of Physics at MIT and co-director of the MIT-Harvard Center for Ultracold Atoms. His areas of science include Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics, and his research interest ...
developed the atomic hydrogen maser
A maser (, an acronym for microwave amplification by stimulated emission of radiation) is a device that produces coherent electromagnetic waves through amplification by stimulated emission. The first maser was built by Charles H. Townes, Ja ...
, looking to increase the accuracy with which the hyperfine
In atomic physics, hyperfine structure is defined by small shifts in otherwise degenerate energy levels and the resulting splittings in those energy levels of atoms, molecules, and ions, due to electromagnetic multipole interaction between the nuc ...
separations of atomic hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
, deuterium
Deuterium (or hydrogen-2, symbol or deuterium, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two Stable isotope ratio, stable isotopes of hydrogen (the other being Hydrogen atom, protium, or hydrogen-1). The atomic nucleus, nucleus of a deuterium ato ...
and tritium
Tritium ( or , ) or hydrogen-3 (symbol T or H) is a rare and radioactive isotope of hydrogen with half-life about 12 years. The nucleus of tritium (t, sometimes called a ''triton'') contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus o ...
could be measured, as well as to investigate how much the hyperfine structure was affected by external magnetic and electric fields. He also participated in developing an extremely stable clock based on a hydrogen maser. From 1967 until 2019, the second has been defined based on 9,192,631,770 hyperfine transition of a cesium-133
Caesium (55Cs) has 40 known isotopes, making it, along with barium and mercury (element), mercury, one of the elements with the most isotopes. The atomic masses of these isotopes range from 112 to 151. Only one isotope, 133Cs, is stable. The longe ...
atom; the atomic clock
An atomic clock is a clock that measures time by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms. It is based on atoms having different energy levels. Electron states in an atom are associated with different energy levels, and in transitions betwee ...
which is used to set this standard is an application of Ramsey's work. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then " ...
in 1989 "for the invention of the separated oscillatory fields method and its use in the hydrogen maser and other atomic clocks". The Prize was shared with Hans G. Dehmelt
Hans Georg Dehmelt (; 9 September 1922 – 7 March 2017) was a German and American physicist, who was awarded a Nobel Prize in Physics in 1989, for co-developing the ion trap technique (Penning trap) with Wolfgang Paul, for which they shared one- ...
and Wolfgang Paul
Wolfgang Paul (; 10 August 1913 – 7 December 1993) was a German physicist, who co-developed the non-magnetic quadrupole mass filter which laid the foundation for what is now called an ion trap. He shared one-half of the Nobel Prize in Ph ...
.
In collaboration with the Institut Laue–Langevin
The Institut Laue–Langevin (ILL) is an internationally financed scientific facility, situated on the Polygone Scientifique in Grenoble, France. It is one of the world centres for research using neutrons. Founded in 1967 and honouring the phy ...
, Ramsey also worked on applying similar methods to beams of neutrons, measuring the neutron magnetic moment
The nucleon magnetic moments are the intrinsic magnetic dipole moments of the proton and neutron, symbols ''μ''p and ''μ''n. Protons and neutrons, both nucleons, comprise the atomic nucleus, nucleus of atoms, and both nucleons behave as small ...
and finding a limit to its neutron electric dipole moment, electric dipole moment. As President of the Universities Research Association during the 1960s he was involved in the design and construction of the Fermilab
Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab), located just outside Batavia, Illinois, near Chicago, is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory specializing in high-energy particle physics. Since 2007, Fermilab has been operat ...
in Batavia, Illinois. He also headed a 1982 United States National Research Council, National Research Council committee that concluded that, contrary to the findings of the House of Representatives Select Committee on Assassinations, John F. Kennedy assassination Dictabelt recording, acoustic evidence did not indicate the presence of a second gunman's involvement in the assassination of President John F. Kennedy.
Later life
Ramsey eventually became the Eugene Higgins professor of physics at Harvard and retired in 1986. However, he remained active in physics, spending a year as a research fellow at the Joint Institute for Laboratory Astrophysics (JILA) at the University of Colorado. He also continued visiting professorships at the University of Chicago, Williams College and the University of Michigan. In addition to the Nobel Prize in Physics, Ramsey received a number of awards, including the Ernest Orlando Lawrence Award in 1960, Davisson-Germer Prize in 1974, the IEEE Medal of Honor in 1984, the I. I. Rabi Award, Rabi Prize in 1985, the Rumford Prize, Rumford Premium Prize in 1985, the Compton Medal in 1986, and the Oersted Medal and the National Medal of Science in 1988. In 1990, Ramsey received the Golden Plate Award of the Academy of Achievement, American Academy of Achievement. He was an elected member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, the United States National Academy of Sciences, and the American Philosophical Society. In 2004, he signed a letter along with 47 other Nobel laureates endorsing John Kerry for President of the United States as someone who would "restore science to its appropriate place in government". His first wife, Elinor, died in 1983, after which he married Ellie Welch of Brookline, Massachusetts. Ramsey died on November 4, 2011. He was survived by his wife Ellie, his four daughters from his first marriage, and his stepdaughter and stepson from his second marriage.Bibliography
*Ramsey, N. F.; Birge, R. W. & U. E. Kruse"Proton–Proton Scattering at 105 MeV and 75 MeV"
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
, United States Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and manages the research and development of nuclear power and nuclear weapons in the United Stat ...
(through predecessor agency the United States Atomic Energy Commission
The United States Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) was an agency of the United States government established after World War II by U.S. Congress to foster and control the peacetime development of atomic science and technology. President H ...
), (January 31, 1951).
*Ramsey, N. F.; Cone, A. A.; Chen, K. W.; Dunning, J. R. Jr.; Hartwig, G.; Walker, J. K. & R. Wilson"Inelastic Scattering Of Electrons By Protons"
Department of Physics at
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
, United States Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and manages the research and development of nuclear power and nuclear weapons in the United Stat ...
(through predecessor agency the United States Atomic Energy Commission
The United States Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) was an agency of the United States government established after World War II by U.S. Congress to foster and control the peacetime development of atomic science and technology. President H ...
), (December 1966).
*Greene, G. L.; Ramsey, N. F.; Mampe, W.; Pendlebury, J. M.; Smith, K. ; Dress, W. B.; Miller, P. D. & P. Perrin"Determination of the Neutron Magnetic Moment"
Oak Ridge National Laboratory,
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
, Institut Laue–Langevin
The Institut Laue–Langevin (ILL) is an internationally financed scientific facility, situated on the Polygone Scientifique in Grenoble, France. It is one of the world centres for research using neutrons. Founded in 1967 and honouring the phy ...
, Astronomy Centre of Sussex University, United States Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and manages the research and development of nuclear power and nuclear weapons in the United Stat ...
, (June 1981).
*Ramsey, N. F. Molecular beam, ''Molecular Beams'', Oxford University Press (First edition 1956, Reprinted 1986).
Notes
References
* * * * * * *External links
Group photograph
taken at The International Conference on Lasers and Applications, Lasers 'XX, ''Lasers'' '93 including (right to left) Norman F. Ramsey, Marlan Scully, and F. J. Duarte.
Norman Ramsey, an oral history conducted in 1995 by Andrew Goldstein, IEEE History Center, New Brunswick, NJ, USA.
Papers relating to the Manhattan Project, 1945–1946, collected by Norman Ramsey
Dibner Library of the History of Science and Technology, Smithsonian Libraries, from SIRIS * including the Nobel Lecture, December 8, 1989 ''Experiments with Separated Oscillatory Fields and Hydrogen Masers'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Ramsey, Norman Foster 1915 births 2011 deaths Columbia College (New York) alumni Columbia Graduate School of Arts and Sciences alumni Columbia University faculty Harvard University faculty Nobel laureates in Physics National Medal of Science laureates American Nobel laureates IEEE Medal of Honor recipients Vannevar Bush Award recipients Manhattan Project people Members of the French Academy of Sciences Members of the United States National Academy of Sciences American physicists People associated with the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki University of Michigan staff Fellows of the American Physical Society Presidents of the American Physical Society Members of the American Philosophical Society