Normal Cylindrical Equal-area Projection on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
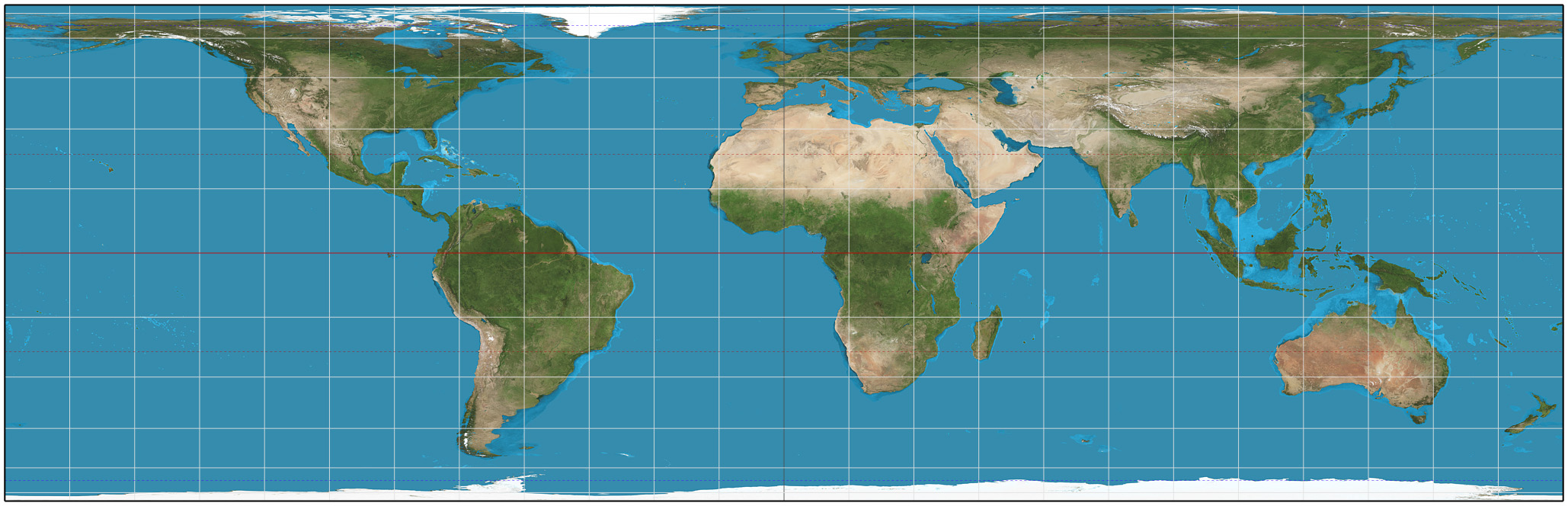
 In
In
 The projection:
* is
The projection:
* is
Table of examples and properties of all common projections
from radicalcartography.net {{Map projections Map projections Equal-area projections Cylindrical projections

cartography
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an im ...
, the normal cylindrical equal-area projection is a family of normal cylindrical, equal-area map projection
In cartography, map projection is the term used to describe a broad set of transformations employed to represent the two-dimensional curved surface of a globe on a plane. In a map projection, coordinates, often expressed as latitude and longitud ...
s.
History
The invention of the Lambert cylindrical equal-area projection is attributed to theSwiss
Swiss may refer to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
* Swiss people
Places
* Swiss, Missouri
* Swiss, North Carolina
*Swiss, West Virginia
* Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
*Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports
*Swiss Internation ...
mathematician Johann Heinrich Lambert in 1772. Variations of it appeared over the years by inventors who stretched the height of the Lambert and compressed the width commensurately in various ratios.
Description
 The projection:
* is
The projection:
* is cylindrical
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infini ...
, that means it has a cylindrical projection surface
* is normal, that means has a normal aspect
Aspect or Aspects may refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Aspect magazine'', a biannual DVD magazine showcasing new media art
* Aspect Co., a Japanese video game company
* Aspects (band), a hip hop group from Bristol, England
* ''Aspects'' (Benny Carter ...
* is an equal-area projection, that means any two areas in the map have the same relative size compared to their size on the sphere.
The term "normal cylindrical projection" is used to refer to any projection in which meridians are mapped to equally spaced vertical lines and circles of latitude
A circle of latitude or line of latitude on Earth is an abstract east–west small circle connecting all locations around Earth (ignoring elevation) at a given latitude coordinate line.
Circles of latitude are often called parallels because ...
are mapped to horizontal lines (or, '' mutatis mutandis'', more generally, radial lines from a fixed point are mapped to equally spaced parallel lines and concentric circles around it are mapped to perpendicular lines).
The mapping of meridians to vertical lines can be visualized by imagining a cylinder of which the axis coincides with the Earth's axis of rotation, and then projecting onto the cylinder, and subsequently unfolding the cylinder.
By the geometry of their construction, cylindrical projections stretch distances east-west. The amount of stretch is the same at any chosen latitude on all cylindrical projections, and is given by the secant of the latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
as a multiple of the equator's scale. The various cylindrical projections are distinguished from each other solely by their north-south stretching (where latitude is given by ''φ''):
The only normal cylindrical projections that preserve area have a north-south compression precisely the reciprocal of east-west stretching ( cos ''φ''). This divides north-south distances by a factor equal to the secant of the latitude, preserving area but distorting shapes.
East–west scale matching the north–south scale
Depending on the stretch factor S, any particular cylindrical equal-area projection either has zero, one or two latitudes for which the east–west scale matches the north–south scale. * S>1 : zero * S=1 : one, that latitude is the equator * S<1 : a pair of identical latitudes of opposite signFormulae
The formulae presume a spherical model and use these definitions: * ''λ'' is the longitude * ''λ'' is the central meridian * ''φ'' is the latitude * ''φ'' is the standard latitude * ''S'' is the stretch factor * ''x'' is the horizontal coordinate of the projected location on the map * ''y'' is the vertical coordinate of the projected location on the map Except for the Lambrecht case one of ''φ'' and S has to be provided. Relationship between ''S'' and ''φ'': * ''S'' = (cos ''φ''0)2 * ''φ'' = arccos(''S''0.5)Specializations
The specializations differ only in the ratio of the vertical to horizontal axis. Some specializations have been described, promoted, or otherwise named.Snyder, John P. (1989). ''An Album of Map Projections'' p. 19. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1453. (Mathematical properties of the Gall–Peters and related projections.)Monmonier, Mark (2004). ''Rhumb Lines and Map Wars: A Social History of the Mercator Projection'' p. 152. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press. (Thorough treatment of the social history of the Mercator projection and Gall–Peters projections.)Smyth, C. Piazzi. (1870). ''On an Equal-Surface Projection and its Anthropological Applications''. Edinburgh: Edmonton & Douglas. (Monograph describing an equal-area cylindric projection and its virtues, specifically disparaging Mercator's projection.) Weisstein, Eric W. "Cylindrical Equal-Area Projection." From MathWorld—A Wolfram Web Resource. https://mathworld.wolfram.com/CylindricalEqual-AreaProjection.html Tobler, Waldo and Chen, Zi-tan(1986). ''A Quadtree for Global Information Storage''. http://www.geog.ucsb.edu/~kclarke/Geography232/Tobler1986.pdfDerivatives
The Tobler hyperelliptical projection, first described by Tobler in 1973, is a further generalization of the cylindrical equal-area family. TheHEALPix
HEALPix (sometimes written as Healpix), an acronym for Hierarchical Equal Area isoLatitude Pixelisation of a 2-sphere, is an algorithm for pixelisation of the 2-sphere and the associated class of map projections. The pixelisation algorithm was de ...
projection is an equal-area hybrid combination of: the Lambert cylindrical equal-area projection, for the equatorial regions of the sphere; and an interrupted Collignon projection, for the polar regions.
References
External links
Table of examples and properties of all common projections
from radicalcartography.net {{Map projections Map projections Equal-area projections Cylindrical projections