nontropical sprue on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Coeliac disease (
 The vast majority of people with coeliac have one of two types (out of seven) of the
The vast majority of people with coeliac have one of two types (out of seven) of the  Most people with coeliac bear a two-gene HLA-DQ2
Most people with coeliac bear a two-gene HLA-DQ2
 Membrane leaking permits peptides of gliadin that stimulate two levels of the immune response: the innate response, and the adaptive (T-helper cell-mediated) response. One protease-resistant peptide from α-gliadin contains a region that stimulates lymphocytes and results in the release of
Membrane leaking permits peptides of gliadin that stimulate two levels of the immune response: the innate response, and the adaptive (T-helper cell-mediated) response. One protease-resistant peptide from α-gliadin contains a region that stimulates lymphocytes and results in the release of


 An
An
British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in ...
) or celiac disease (American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the Languages of the United States, most widely spoken lan ...
) is a long-term autoimmune disorder
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly a ...
, primarily affecting the small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the p ...
, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten
Gluten is a structural protein naturally found in certain cereal grains. Although "gluten" often only refers to wheat proteins, in medical literature it refers to the combination of prolamin and glutelin proteins naturally occurring in all grain ...
, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barley. Classic symptoms include gastrointestinal problems such as chronic diarrhoea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin wi ...
, abdominal distention
Abdominal distension occurs when substances, such as air (gas) or fluid, accumulate in the abdomen causing its expansion. It is typically a symptom of an underlying disease or dysfunction in the body, rather than an illness in its own right. Pe ...
, malabsorption
Malabsorption is a state arising from abnormality in absorption of food nutrients across the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Impairment can be of single or multiple nutrients depending on the abnormality. This may lead to malnutrition and a variety ...
, loss of appetite
Anorexia is a medical term for a loss of appetite. While the term in non-scientific publications is often used interchangeably with anorexia nervosa, many possible causes exist for a loss of appetite, some of which may be harmless, while others i ...
, and among children failure to grow normally. This often begins between six months and two years of age. Non-classic symptoms are more common, especially in people older than two years. There may be mild or absent gastrointestinal symptoms, a wide number of symptoms involving any part of the body, or no obvious symptoms. Coeliac disease was first described in childhood; however, it may develop at any age. It is associated with other autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly a ...
s, such as Type 1 diabetes mellitus
Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that originates when cells that make insulin (beta cells) are destroyed by the immune system. Insulin is a hormone required for the cells to use blood sugar for ...
and Hashimoto's thyroiditis
Hashimoto's thyroiditis, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis and Hashimoto's disease, is an autoimmune disease in which the thyroid gland is gradually destroyed. Early on, symptoms may not be noticed. Over time, the thyroid may enlarg ...
, among others.
Coeliac disease is caused by a reaction to gluten, a group of various proteins found in wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
and in other grains such as barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley pr ...
and rye
Rye (''Secale cereale'') is a grass grown extensively as a grain, a cover crop and a forage crop. It is a member of the wheat tribe (Triticeae) and is closely related to both wheat (''Triticum'') and barley (genus ''Hordeum''). Rye grain is u ...
. Moderate quantities of oats
The oat (''Avena sativa''), sometimes called the common oat, is a species of cereal grain grown for its seed, which is known by the same name (usually in the plural, unlike other cereals and pseudocereals). While oats are suitable for human con ...
, free of contamination with other gluten-containing grains, are usually tolerated. The occurrence of problems may depend on the variety
Variety may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Entertainment formats
* Variety (radio)
* Variety show, in theater and television
Films
* ''Variety'' (1925 film), a German silent film directed by Ewald Andre Dupont
* ''Variety'' (1935 film), ...
of oat. It occurs more often in people who are genetically predisposed. Upon exposure to gluten, an abnormal immune
In biology, immunity is the capability of multicellular organisms to resist harmful microorganisms. Immunity involves both specific and nonspecific components. The nonspecific components act as barriers or eliminators of a wide range of pathogens ...
response may lead to the production of several different autoantibodies
An autoantibody is an antibody (a type of protein) produced by the immune system that is directed against one or more of the individual's own proteins. Many autoimmune diseases (notably lupus erythematosus) are associated with such antibodies.
Pr ...
that can affect a number of different organs
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a fu ...
. In the small bowel, this causes an inflammatory reaction and may produce shortening of the villi lining the small intestine (villous atrophy
Intestinal villi (singular: villus) are small, finger-like projections that extend into the lumen of the small intestine. Each villus is approximately 0.5–1.6 mm in length (in humans), and has many microvilli projecting from the enterocyte ...
). This affects the absorption of nutrients, frequently leading to anaemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, th ...
.
Diagnosis is typically made by a combination of blood antibody tests and intestinal biopsies
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a diseas ...
, helped by specific genetic testing
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or ...
. Making the diagnosis is not always straightforward. About 10% of the time, the autoantibodies in the blood are negative, and many people have only minor intestinal changes with normal villi. People may have severe symptoms and they may be investigated for years before a diagnosis is achieved. Increasingly, the diagnosis is being made in people without symptoms, as a result of screening
Screening may refer to:
* Screening cultures, a type a medical test that is done to find an infection
* Screening (economics), a strategy of combating adverse selection (includes sorting resumes to select employees)
* Screening (environmental), a ...
. Evidence regarding the effects of screening, however, is not sufficient to determine its usefulness. While the disease is caused by a permanent intolerance to gluten proteins, it is distinct from wheat allergy
Wheat allergy is an allergy to wheat which typically presents itself as a food allergy, but can also be a contact allergy resulting from occupational exposure. Like all allergies, wheat allergy involves immunoglobulin E and mast cell response. T ...
, which is much more rare.
The only known effective treatment is a strict lifelong gluten-free diet
A gluten-free diet (GFD) is a nutritional plan that strictly excludes gluten, which is a mixture of proteins found in wheat (and all of its species and hybrids, such as spelt, kamut, and triticale), as well as barley, rye, and oats. The inclus ...
, which leads to recovery of the intestinal lining (mucous membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is ...
), improves symptoms, and reduces the risk of developing complications in most people. If untreated, it may result in cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
s such as intestinal lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlar ...
, and a slightly increased risk of early death. Rates vary between different regions of the world, from as few as 1 in 300 to as many as 1 in 40, with an average of between 1 in 100 and 1 in 170 people. It is estimated that 80% of cases remain undiagnosed, usually because of minimal or absent gastrointestinal complaints and lack of knowledge of symptoms and diagnostic criteria. Coeliac disease is slightly more common in women than in men.
Signs and symptoms
The classic symptoms of untreated coeliac disease include pale, loose, or greasy stools (steatorrhoea
Steatorrhea (or steatorrhoea) is the presence of excess fat in feces. Stools may be bulky and difficult to flush, have a pale and oily appearance, and can be especially foul-smelling. An oily anal leakage or some level of fecal incontinence may o ...
), and weight loss or failure to gain weight. Other common symptoms may be subtle or primarily occur in organs other than the bowel itself. It is also possible to have coeliac disease without any of the classic symptoms at all. This has been shown to comprise at least 43% of presentations in children. Further, many adults with subtle disease may only present with fatigue, anaemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, th ...
or low bone mass. Many undiagnosed individuals who consider themselves asymptomatic are in fact not, but rather have become accustomed to living in a state of chronically compromised health. Indeed, after starting a gluten-free diet and subsequent improvement becomes evident, such individuals are often able to retrospectively recall and recognise prior symptoms of their untreated disease that they had mistakenly ignored.
Gastrointestinal
Diarrhoea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin wi ...
that is characteristic of coeliac disease is chronic, sometimes pale, of large volume, and abnormally foul in odor. Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than ...
, cramping, bloating with abdominal distension
Abdominal distension occurs when substances, such as air (gas) or fluid, accumulate in the abdomen causing its expansion. It is typically a symptom of an underlying disease or dysfunction in the body, rather than an illness in its own right. Pe ...
(thought to be the result of fermentative production of bowel gas), and mouth ulcer
A mouth ulcer (aphtha) is an ulcer that occurs on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. Mouth ulcers are very common, occurring in association with many diseases and by many different mechanisms, but usually there is no serious underlying cause ...
s may be present. As the bowel becomes more damaged, a degree of lactose intolerance
Lactose intolerance is a common condition caused by a decreased ability to digest lactose, a sugar found in dairy products. Those affected vary in the amount of lactose they can tolerate before symptoms develop. Symptoms may include abdominal pa ...
may develop. Frequently, the symptoms are ascribed to irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a "disorder of gut-brain interaction" characterized by a group of symptoms that commonly include abdominal pain and or abdominal bloating and changes in the consistency of bowel movements. These symptoms may ...
(IBS), only later to be recognised as coeliac disease. In populations of people with symptoms of IBS, a diagnosis of coeliac disease can be made in about 3.3% of cases, or four times more likely than in general. Screening them for coeliac disease is recommended by the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care in England that publishes guidelines in four areas:
* the use of health technologies withi ...
(NICE), the British Society of Gastroenterology The British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) is a British professional organisation of gastroenterologists, surgeons, pathologists, radiologists, scientists, nurses, dietitians and others amongst its members, which number over 3,000. It was founde ...
and the American College of Gastroenterology
The American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) is a Bethesda, Maryland–based medical association of gastroenterologists.
The association was founded in 1932 and holds annual meetings and regional postgraduate continuing education courses, est ...
, but is of unclear benefit in North America.
Coeliac disease leads to an increased risk of both adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma (; plural adenocarcinomas or adenocarcinomata ) (AC) is a type of cancerous tumor that can occur in several parts of the body. It is defined as neoplasia of epithelial tissue that has glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or ...
and lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlar ...
of the small bowel (enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma
Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma (EATL), previously termed enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma, type I and at one time termed enteropathy-type T-cell lymphoma (ETTL), is a complication of coeliac disease in which a malignant T-cell lympho ...
(EATL) or other non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), also known as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a group of blood cancers that includes all types of lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphomas. Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and tiredness. ...
s). This risk is also higher in first-degree relatives such as siblings, parents and children. Whether a gluten-free diet brings this risk back to baseline is not clear. Long-standing and untreated disease may lead to other complications, such as ulcerative jejunitis (ulcer formation of the small bowel) and stricturing (narrowing as a result of scarring with obstruction of the bowel).
Malabsorption-related
The changes in the bowel reduce its ability to absorb nutrients, minerals, and thefat-soluble vitamins
A vitamin is an organic molecule (or a set of molecules closely related chemically, i.e. vitamers) that is an essential micronutrient that an organism needs in small quantities for the proper functioning of its metabolism. Essential nutrien ...
A, D, E, and K.
*Malabsorption
Malabsorption is a state arising from abnormality in absorption of food nutrients across the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Impairment can be of single or multiple nutrients depending on the abnormality. This may lead to malnutrition and a variety ...
of carbohydrates and fats may cause weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat (adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other conn ...
(or failure to thrive
Failure to thrive (FTT), also known as weight faltering or faltering growth, indicates insufficient weight gain or absence of appropriate physical growth in children. FTT is usually defined in terms of weight, and can be evaluated either by a low ...
or stunted growth
Stunted growth is a reduced growth rate in human development. It is a primary manifestation of malnutrition (or more precisely undernutrition) and recurrent infections, such as diarrhea and helminthiasis, in early childhood and even before birth, ...
in children) and fatigue
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve ...
or lack of energy.
*Anaemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, th ...
may develop in several ways: iron malabsorption may cause iron deficiency anaemia
Iron-deficiency anemia is anemia caused by a lack of iron. Anemia is defined as a decrease in the number of red blood cells or the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. When onset is slow, symptoms are often vague such as feeling tired, weak, shor ...
, and folic acid
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing and ...
and vitamin B12 malabsorption may give rise to megaloblastic anaemia
Megaloblastic anemia is a type of macrocytic anemia. An anemia is a red blood cell defect that can lead to an undersupply of oxygen. Megaloblastic anemia results from inhibition of DNA synthesis during red blood cell production. When DNA synthes ...
.
*Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to ...
and vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (c ...
malabsorption (and compensatory secondary hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is an increase in parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels in the blood. This occurs from a disorder either within the parathyroid glands (primary hyperparathyroidism) or as response to external stimuli (secondary hyperparathyroidism). ...
) may cause osteopenia
Osteopenia, known as "low bone mass" or "low bone density", is a condition in which bone mineral density is low. Because their bones are weaker, people with osteopenia may have a higher risk of fractures, and some people may go on to develop osteop ...
(decreased mineral content of the bone) or osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to bone fragility, and consequent increase in fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone ...
(bone weakening and risk of fragility fractures).
*Selenium
Selenium is a chemical element with the symbol Se and atomic number 34. It is a nonmetal (more rarely considered a metalloid) with properties that are intermediate between the elements above and below in the periodic table, sulfur and tellurium, ...
malabsorption in coeliac disease, combined with low selenium content in many gluten-free foods, confers a risk of selenium deficiency
Selenium deficiency occurs when an organism lacks the required levels of selenium, a critical nutrient in many species. Deficiency, although relatively rare in healthy well-nourished individuals, can have significant negative results, affecting the ...
.
*Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
and zinc deficiencies have also been associated with coeliac disease.
*A small proportion have abnormal coagulation
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanism o ...
because of vitamin K deficiency
Vitamin K deficiency results from insufficient dietary vitamin K1 or vitamin K2 or both.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms include bruising, petechiae,
hematomas, oozing of blood at surgical or puncture sites, stomach pains; risk of massive uncontr ...
and are at a slight risk of abnormal bleeding.
Miscellaneous
Coeliac disease has been linked with many conditions. In many cases, it is unclear whether the gluten-induced bowel disease is a causative factor or whether these conditions share a common predisposition. *IgA deficiency
Selective immunoglobulin A (IgA) deficiency (SIgAD) is a genetic immunodeficiency, a type of hypogammaglobulinemia. People with this deficiency lack immunoglobulin A (IgA), a type of antibody that protects against infections of the mucous membrane ...
is present in 2.3% of people with coeliac disease, and is itself associated with a tenfold increased risk of coeliac disease. Other features of this condition are an increased risk of infections and autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly a ...
.
*Dermatitis herpetiformis
Dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) is a chronic autoimmune blistering skin condition, characterised by intensely itchy blisters filled with a watery fluid. DH is a cutaneous manifestation of coeliac disease, although the exact causal mechanism is not k ...
, an itchy cutaneous condition that has been linked to a transglutaminase enzyme in the skin, features small-bowel changes identical to those in coeliac disease and may respond to gluten withdrawal even if no gastrointestinal symptoms are present.
*Growth failure
Failure to thrive (FTT), also known as weight faltering or faltering growth, indicates insufficient weight gain or absence of appropriate physical growth in children. FTT is usually defined in terms of weight, and can be evaluated either by a low ...
and/or pubertal delay in later childhood can occur even without obvious bowel symptoms or severe malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
. Evaluation of growth failure often includes coeliac screening.
*Pregnancy complication
Complications of pregnancy are health problems that are related to pregnancy. Complications that occur primarily during childbirth are termed obstetric labor complications, and problems that occur primarily after childbirth are termed puerperal di ...
s can occur if coeliac disease is pre-existing or later acquired, with significant outcomes including miscarriage
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion and pregnancy loss, is the death of an embryo or fetus before it is able to survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks of gestation is defined by ESHRE as biochemical lo ...
, intrauterine growth restriction
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), or fetal growth restriction, refers to poor growth of a fetus while in the womb during pregnancy. IUGR is defined by clinical features of malnutrition and evidence of reduced growth regardless of an infant's ...
, low birthweight
Birth weight is the body weight of a baby at its birth. The average birth weight in babies of European descent is , with the normative range between . On average, babies of South Asian and Chinese descent weigh about . As far as low birth weight ...
and preterm birth
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the Childbirth, birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks Gestational age (obstetrics), gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 we ...
.
*Hyposplenism
Asplenia refers to the absence of normal spleen function and is associated with some serious infection risks. Hyposplenism is used to describe reduced ('hypo-') splenic functioning, but not as severely affected as with asplenism.
''Functional'' a ...
(a small and underactive spleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .
) occurs in about a third of cases and may predispose to infection given the role of the spleen in protecting against harmful bacteria.
*Abnormal liver function test
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial thromboplastin ti ...
s (randomly detected on blood tests) may be seen.
Coeliac disease is associated with several other medical conditions, many of which are autoimmune disorders: diabetes mellitus type 1
Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that originates when cells that make insulin (beta cells) are destroyed by the immune system. Insulin is a hormone required for the cells to use blood sugar f ...
, hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as po ...
, primary biliary cholangitis
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), previously known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is an autoimmune disease of the liver. It results from a slow, progressive destruction of the small bile ducts of the liver, causing bile and other toxins to build ...
, microscopic colitis
Microscopic colitis refers to two related medical conditions which cause diarrhea: collagenous colitis and lymphocytic colitis. Both conditions are characterized by the presence of chronic non-bloody watery diarrhea, normal appearances on colonosco ...
, gluten ataxia
Ataxia is a neurological sign consisting of lack of voluntary Motor coordination, coordination of muscle movements that can include gait abnormality, speech changes, and abnormalities in eye movements. Ataxia is a clinical manifestation indicati ...
, psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to complete ...
, vitiligo
Vitiligo is a disorder that causes the skin to lose its color. Specific causes are unknown but studies suggest a link to immune system changes.
Signs and symptoms
The only sign of vitiligo is the presence of pale patchy areas of depigmen ...
, autoimmune hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis, formerly known as lupoid hepatitis, plasma cell hepatitis, or autoimmune chronic active hepatitis, is a chronic, autoimmune disease of the liver that occurs when the body's immune system attacks liver cells, causing the liv ...
, primary sclerosing cholangitis
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a long-term progressive disease of the liver and gallbladder characterized by inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts, which normally allow bile to drain from the gallbladder. Affected individuals may ha ...
, and more.
Cause
Coeliac disease is caused by an inflammatory reaction togliadin
Gliadin (a type of prolamin) is a class of proteins present in wheat and several other cereals within the grass genus ''Triticum''. Gliadins, which are a component of gluten, are essential for giving bread the ability to rise properly during baki ...
s and glutenin
Glutenin (a type of glutelin) is a major protein within wheat flour, making up 47% of the total protein content. The glutenins are protein aggregates of high-molecular-mass (HMW) and low-molecular-mass (LMW) subunits with molar masses from about ...
s (gluten
Gluten is a structural protein naturally found in certain cereal grains. Although "gluten" often only refers to wheat proteins, in medical literature it refers to the combination of prolamin and glutelin proteins naturally occurring in all grain ...
proteins) found in wheat and to similar proteins found in the crops of the tribe
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English language, English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in p ...
Triticeae
Triticeae is a botanical tribe within the subfamily Pooideae of grasses that includes genera with many domesticated species. Major crop genera found in this tribe include wheat (see wheat taxonomy), barley, and rye; crops in other genera include ...
(which includes other common grains such as barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley pr ...
and rye
Rye (''Secale cereale'') is a grass grown extensively as a grain, a cover crop and a forage crop. It is a member of the wheat tribe (Triticeae) and is closely related to both wheat (''Triticum'') and barley (genus ''Hordeum''). Rye grain is u ...
) and to the tribe Aveneae
The Poeae are the largest tribe of the grasses, with around 2,500 species in 121 genera. The tribe includes many lawn and pasture grasses.
Taxonomy
Two separate tribes, Poeae and Aveneae, used to be distinguished based on morphology, but phylog ...
(oat
The oat (''Avena sativa''), sometimes called the common oat, is a species of cereal grain grown for its seed, which is known by the same name (usually in the plural, unlike other cereals and pseudocereals). While oats are suitable for human con ...
s). Wheat subspecies (such as spelt
Spelt (''Triticum spelta''), also known as dinkel wheat or hulled wheat, is a species of wheat that has been cultivated since approximately 5000 BC.
Spelt was an important staple food in parts of Europe from the Bronze Age to medieval times. No ...
, durum
Durum wheat (), also called pasta wheat or macaroni wheat (''Triticum durum'' or ''Triticum turgidum'' subsp. ''durum''), is a tetraploid species of wheat. It is the second most cultivated species of wheat after common wheat, although it represen ...
, and Kamut
Khorasan wheat or Oriental wheat (''Triticum turgidum'' ssp. ''turanicum'' also called ''Triticum turanicum''), commercially known as Kamut, is a tetraploid wheat species. The grain is twice the size of modern-day wheat, and has a rich, nutty ...
) and wheat hybrids (such as triticale
Triticale (; × ''Triticosecale'') is a hybrid of wheat (''Triticum'') and rye (''Secale'') first bred in laboratories during the late 19th century in Scotland and Germany. Commercially available triticale is almost always a second-generation h ...
) also cause symptoms of coeliac disease.
A small number of people with coeliac disease react to oats. Oat toxicity in coeliac people depends on the oat cultivar
A cultivar is a type of cultivated plant that people have selected for desired traits and when propagated retain those traits. Methods used to propagate cultivars include: division, root and stem cuttings, offsets, grafting, tissue culture, ...
consumed because the prolamin genes, protein amino acid sequences, and the immunoreactivities of toxic prolamins are different in different oat varieties. Also, oats are frequently cross-contaminated with other grains containing gluten. The term "pure oats" refers to oats uncontaminated with other gluten-containing cereals. The long-term effects of pure oat consumption are still unclear, and further studies identifying the cultivars used are needed before making final recommendations on their inclusion in a gluten-free diet
A gluten-free diet (GFD) is a nutritional plan that strictly excludes gluten, which is a mixture of proteins found in wheat (and all of its species and hybrids, such as spelt, kamut, and triticale), as well as barley, rye, and oats. The inclus ...
. Coeliac people who choose to consume oats need a more rigorous lifelong follow-up, possibly including periodic intestinal biopsies.
Other grains
Other cereals such ascorn
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th ...
, millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most species generally referred to as millets belong to the tribe Paniceae, but some millets al ...
, sorghum
''Sorghum'' () is a genus of about 25 species of flowering plants in the grass family (Poaceae). Some of these species are grown as cereals for human consumption and some in pastures for animals. One species is grown for grain, while many othe ...
, teff
''Eragrostis tef'', also known as teff, Williams lovegrass or annual bunch grass, is an annual grass, a species of lovegrass native to the Horn of Africa, notably to both Eritrea and Ethiopia. It is cultivated for its edible seeds, also known as ...
, rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown i ...
, and wild rice
Wild rice, also called manoomin, Canada rice, Indian rice, or water oats, is any of four species of grasses that form the genus ''Zizania'', and the grain that can be harvested from them. The grain was historically gathered and eaten in both ...
are safe for people with coeliac disease to consume, as well as noncereals such as amaranth
''Amaranthus'' is a cosmopolitan genus of annual or short-lived perennial plants collectively known as amaranths. Some amaranth species are cultivated as leaf vegetables, pseudocereals, and ornamental plants. Catkin-like cymes of densely pack ...
, quinoa
Quinoa (''Chenopodium quinoa''; , from Quechua ' or ') is a flowering plant in the amaranth family. It is a herbaceous annual plant grown as a crop primarily for its edible seeds; the seeds are rich in protein, dietary fiber, B vitamins, and ...
, and buckwheat
Buckwheat (''Fagopyrum esculentum''), or common buckwheat, is a flowering plant in the knotweed family Polygonaceae cultivated for its grain-like seeds and as a cover crop. The name "buckwheat" is used for several other species, such as '' Fago ...
. Noncereal carbohydrate-rich foods such as potatoes and bananas do not contain gluten and do not trigger symptoms.
Risk modifiers
There are various theories as to what determines whether a genetically susceptible individual will go on to develop coeliac disease. Major theories include surgery, pregnancy, infection and emotional stress. The eating of gluten early in a baby's life does not appear to increase the risk of coeliac disease but later introduction after 6 months may increase it. There is uncertainty whether being breastfed reduces risk. Prolongingbreastfeeding
Breastfeeding, or nursing, is the process by which human breast milk is fed to a child. Breast milk may be from the breast, or may be expressed by hand or pumped and fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that br ...
until the introduction of gluten-containing grains into the diet appears to be associated with a 50% reduced risk of developing coeliac disease in infancy; whether this persists into adulthood is not clear. These factors may just influence the timing of onset.
Pathophysiology
Almost all people (95%) with coeliac disease have either the variantHLA-DQ2
HLA-DQ3 (DQ3) is a serotype group within HLA-DQ (DQ) serotyping system. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of β2 subset of DQ β-chains. The β-chain of DQ is encoded by HLA-DQB1 locus and DQ2 are encoded by the HLA-DQB1 a ...
allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
or (less commonly) the HLA-DQ8
HLA-DQ8 (DQ8) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within the HLA-DQ (DQ) serotype group. DQ8 is a split antigen of the DQ3 broad antigen. DQ8 is determined by the antibody recognition of β8 and this generally detects the gene product of DQ ...
allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
. However, about 20–30% of people without coeliac disease have also inherited either of these alleles. This suggests that additional factors are needed for coeliac disease to develop; that is, the predisposing HLA risk allele is necessary but not sufficient to develop coeliac disease. Furthermore, around 5% of those people who do develop coeliac disease do not have typical HLA-DQ2 or HLA-DQ8 alleles (see below).
Genetics
HLA-DQ
HLA-DQ (DQ) is a cell surface receptor protein found on antigen-presenting cells. It is an αβ heterodimer of type MHC class II. The α and β chains are encoded by two loci, HLA-DQA1 and HLA-DQB1, that are adjacent to each other on chromos ...
protein.
There are seven HLA-DQ
HLA-DQ (DQ) is a cell surface receptor protein found on antigen-presenting cells. It is an αβ heterodimer of type MHC class II. The α and β chains are encoded by two loci, HLA-DQA1 and HLA-DQB1, that are adjacent to each other on chromos ...
variants (DQ2 and DQ4–DQ9). Over 95% of people with coeliac have the isoform of DQ2 or DQ8, which is inherited in families. The reason these genes produce an increase in the risk of coeliac disease is that the receptors formed by these genes bind to gliadin peptides more tightly than other forms of the antigen-presenting receptor. Therefore, these forms of the receptor are more likely to activate T lymphocytes
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell rec ...
and initiate the autoimmune process.
haplotype
A haplotype ( haploid genotype) is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent.
Many organisms contain genetic material ( DNA) which is inherited from two parents. Normally these organisms have their DNA or ...
referred to as DQ2.5 haplotype. This haplotype is composed of two adjacent gene allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
s, DQA1*0501 and DQB1*0201, which encode the two subunits, DQ α5 and DQ β2. In most individuals, this DQ2.5 isoform is encoded by one of two chromosomes 6 inherited from parents (DQ2.5cis). Most coeliacs inherit only one copy of this DQ2.5 haplotype, while some inherit it from ''both'' parents; the latter are especially at risk for coeliac disease as well as being more susceptible to severe complications.
Some individuals inherit DQ2.5 from one parent and an additional portion of the haplotype (either DQB1*02 or DQA1*05) from the other parent, increasing risk. Less commonly, some individuals inherit the DQA1*05 allele from one parent and the DQB1*02 from the other parent (DQ2.5trans) (called a trans-haplotype association), and these individuals are at similar risk for coeliac disease as those with a single DQ2.5-bearing chromosome 6, but in this instance, the disease tends not to be familial. Among the 6% of European coeliacs that do not have DQ2.5 (cis or trans) or DQ8 (encoded by the haplotype DQA1*03:DQB1*0302), 4% have the DQ2.2 isoform, and the remaining 2% lack DQ2 or DQ8.
The frequency of these genes varies geographically. DQ2.5 has high frequency in peoples of North and Western Europe ( Basque Country and Ireland with highest frequencies) and portions of Africa and is associated with disease in India, but it is not found along portions of the West Pacific rim. DQ8 has a wider global distribution than DQ2.5 and is particularly common in South and Central America; up to 90% of individuals in certain Amerindian populations carry DQ8 and thus may display the coeliac phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological proper ...
.
Other genetic factors have been repeatedly reported in coeliac disease; however, involvement in disease has variable geographic recognition. Only the HLA-DQ loci show a consistent involvement over the global population. Many of the loci detected have been found in association with other autoimmune diseases. One locus, the LPP or lipoma-preferred partner gene, is involved in the adhesion of extracellular matrix to the cell surface, and a minor variant ( SNP=rs1464510) increases the risk of disease by approximately 30%. This gene strongly associates with coeliac disease ( p < 10−39) in samples taken from a broad area of Europe and the US.
The prevalence of coeliac disease genotypes in the modern population is not completely understood. Given the characteristics of the disease and its apparent strong heritability, it would normally be expected that the genotypes would undergo negative selection and to be absent in societies where agriculture has been practised the longest (compare with a similar condition, lactose intolerance
Lactose intolerance is a common condition caused by a decreased ability to digest lactose, a sugar found in dairy products. Those affected vary in the amount of lactose they can tolerate before symptoms develop. Symptoms may include abdominal pa ...
, which has been negatively selected so strongly that its prevalence went from ~100% in ancestral populations to less than 5% in some European countries). This expectation was first proposed by Simoons (1981). By now, however, it is apparent that this is not the case; on the contrary, there is evidence of ''positive'' selection in coeliac disease genotypes. It is suspected that some of them may have been beneficial by providing protection against bacterial infections.
Prolamins
The majority of the proteins in food responsible for the immune reaction in coeliac disease are theprolamin
Prolamins are a group of plant storage proteins having a high proline amino acid content. They are found in plants, mainly in the seeds of cereal grains such as wheat (gliadin), barley (hordein), rye (secalin), corn (zein), sorghum (kafirin), and ...
s. These are storage proteins rich in proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the prot ...
(''prol-'') and glutamine
Glutamine (symbol Gln or Q) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral, ...
(''-amin'') that dissolve in alcohols and are resistant to protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the ...
s and peptidase
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the fo ...
s of the gut. Prolamins are found in cereal grains with different grains having different but related prolamins: wheat (gliadin), barley (hordein
Hordein is a prolamin glycoprotein, present in barley and some other cereals, together with gliadin and other glycoproteins (such as glutelins) coming under the general name of gluten. Horedeins are found in the endosperm where one of their functi ...
), rye (secalin
Secalin is a prolamin glycoprotein found in the grain rye, ''Secale cereale''.
Secalin is one of the forms of gluten proteins that people with coeliac disease cannot tolerate, and thus rye should be avoided by people with this disease. It is gene ...
) and oat
The oat (''Avena sativa''), sometimes called the common oat, is a species of cereal grain grown for its seed, which is known by the same name (usually in the plural, unlike other cereals and pseudocereals). While oats are suitable for human con ...
s (avenin
The oat (''Avena sativa''), sometimes called the common oat, is a species of cereal grain grown for its seed, which is known by the same name (usually in the plural, unlike other cereals and pseudocereals). While oats are suitable for human con ...
). One region of α-gliadin stimulates membrane cells, enterocyte
Enterocytes, or intestinal absorptive cells, are simple columnar epithelial cells which line the inner surface of the small and large intestines. A glycocalyx surface coat contains digestive enzymes. Microvilli on the apical surface increase its ...
s, of the intestine to allow larger molecules around the sealant between cells. Disruption of tight junctions
Tight junctions, also known as occluding junctions or ''zonulae occludentes'' (singular, ''zonula occludens''), are multiprotein junctional complexes whose canonical function is to prevent leakage of solutes and water and seals between the epith ...
allow peptides larger than three amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
s to enter the intestinal lining.
 Membrane leaking permits peptides of gliadin that stimulate two levels of the immune response: the innate response, and the adaptive (T-helper cell-mediated) response. One protease-resistant peptide from α-gliadin contains a region that stimulates lymphocytes and results in the release of
Membrane leaking permits peptides of gliadin that stimulate two levels of the immune response: the innate response, and the adaptive (T-helper cell-mediated) response. One protease-resistant peptide from α-gliadin contains a region that stimulates lymphocytes and results in the release of interleukin-15
Interleukin-15 (IL-15) is a cytokine with structural similarity to Interleukin-2 (IL-2). Like IL-2, IL-15 binds to and signals through a complex composed of IL-2/IL-15 receptor beta chain (CD122) and the common gamma chain (gamma-C, CD132). IL- ...
. This innate response to gliadin results in immune-system signalling that attracts inflammatory cells and increases the release of inflammatory chemicals. The strongest and most common adaptive response to gliadin is directed toward an α2-gliadin fragment of 33 amino acids in length.
The response to the 33mer occurs in most coeliacs who have a DQ2 isoform
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isof ...
. This peptide, when altered by intestinal transglutaminase, has a high density of overlapping T-cell epitopes. This increases the likelihood that the DQ2 isoform will bind, and stay bound to, peptide when recognised by T-cells. Gliadin in wheat is the best-understood member of this family, but other prolamins exist, and hordein (from barley), secalin (from rye), and avenin (from oats) may contribute to coeliac disease. Avenin's toxicity in people with coeliac disease depends on the oat cultivar
A cultivar is a type of cultivated plant that people have selected for desired traits and when propagated retain those traits. Methods used to propagate cultivars include: division, root and stem cuttings, offsets, grafting, tissue culture, ...
consumed, as prolamin genes, protein amino acid sequences, and the immunoreactivities of toxic prolamins vary among oat varieties.
Tissue transglutaminase

Anti-transglutaminase antibodies
Anti-transglutaminase antibodies (ATA) are autoantibodies against the transglutaminase protein. Antibodies serve an important role in the immune system by detecting cells and substances that the rest of the immune system then eliminates. These cel ...
to the enzyme tissue transglutaminase
Tissue transglutaminase (abbreviated as tTG or TG2) is a 78-kDa, calcium-dependent enzyme () of the protein-glutamine γ-glutamyltransferases family (or simply transglutaminase family). Like other transglutaminases, it crosslinks proteins between ...
(tTG) are found in the blood of the majority of people with classic symptoms and complete villous atrophy, but only in 70% of the cases with partial villous atrophy and 30% of the cases with minor mucosal lesions. Tissue transglutaminase modifies gluten peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
A ...
s into a form that may stimulate the immune system more effectively. These peptides are modified by tTG in two ways, deamidation
Deamidation is a chemical reaction in which an amide functional group in the side chain of the amino acids asparagine or glutamine is removed or converted to another functional group. Typically, asparagine is converted to aspartic acid or isoaspa ...
or transamidation Transamidation is a chemical reaction in which an amide reacts with an amine to generate a new amide:
:RC(O)NR'2 + HNR"2 → RC(O)NR"2 + HNR'2
The reaction is typically very slow, but it can be accelerated with Lewis acid and organometallic ...
.
Deamidation is the reaction by which a glutamate residue is formed by cleavage of the epsilon-amino group of a glutamine side chain. Transamidation, which occurs three times more often than deamidation, is the cross-linking of a glutamine residue from the gliadin peptide to a lysine residue of tTg in a reaction that is catalysed by the transglutaminase. Crosslinking may occur either within or outside the active site of the enzyme. The latter case yields a permanently covalently linked complex between the gliadin and the tTg. This results in the formation of new epitopes believed to trigger the primary immune response by which the autoantibodies against tTg develop.
Stored biopsies from people with suspected coeliac disease have revealed that autoantibody
An autoantibody is an antibody (a type of protein) produced by the immune system that is directed against one or more of the individual's own proteins. Many autoimmune diseases (notably lupus erythematosus) are associated with such antibodies.
Pr ...
deposits in the subclinical
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered asym ...
coeliacs are detected prior to clinical disease. These deposits are also found in people who present with other autoimmune diseases, anaemia, or malabsorption phenomena at a much increased rate over the normal population. Endomysial components of antibodies (EMA) to tTG are believed to be directed toward cell-surface transglutaminase, and these antibodies are still used in confirming a coeliac disease diagnosis. However, a 2006 study showed that EMA-negative people with coeliac tend to be older males with more severe abdominal symptoms and a lower frequency of "atypical" symptoms, including autoimmune disease. In this study, the anti-tTG antibody deposits did not correlate with the severity of villous destruction. These findings, coupled with recent work showing that gliadin has an innate response component, suggest that gliadin may be more responsible for the primary manifestations of coeliac disease, whereas tTG is a bigger factor in secondary effects such as allergic responses and secondary autoimmune diseases. In a large percentage of people with coeliac, the anti-tTG antibodies also recognise a rotavirus
''Rotavirus'' is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses in the family ''Reoviridae''. Rotaviruses are the most common cause of diarrhoeal disease among infants and young children. Nearly every child in the world is infected with a rotavirus a ...
protein called VP7. These antibodies stimulate monocyte
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and conventional dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also inf ...
proliferation, and rotavirus infection might explain some early steps in the cascade of immune cell
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mult ...
proliferation.
Indeed, earlier studies of rotavirus damage in the gut showed this causes villous atrophy.
Other intestinal disorders may have biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a diseas ...
that look like coeliac disease including lesions caused by Candida.
Villous atrophy and malabsorption
Alternative causes of this tissue damage have been proposed and involve the release ofinterleukin 15
Interleukin-15 (IL-15) is a cytokine with structural similarity to Interleukin-2 (IL-2). Like IL-2, IL-15 binds to and signals through a complex composed of IL-2/IL-15 receptor beta chain (CD122) and the common gamma chain (gamma-C, CD132). IL- ...
and activation of the innate immune system by a shorter gluten peptide (p31–43/49). This would trigger killing of enterocyte
Enterocytes, or intestinal absorptive cells, are simple columnar epithelial cells which line the inner surface of the small and large intestines. A glycocalyx surface coat contains digestive enzymes. Microvilli on the apical surface increase its ...
s by lymphocytes in the epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellul ...
. The villous atrophy seen on biopsy may also be due to unrelated causes, such as tropical sprue
Tropical sprue is a malabsorption disease commonly found in tropical regions, marked with abnormal flattening of the villi and inflammation of the lining of the small intestine. It differs significantly from coeliac sprue. It appears to be a mor ...
, giardiasis
Giardiasis is a parasitic disease caused by ''Giardia duodenalis'' (also known as ''G. lamblia'' and ''G. intestinalis''). Infected individuals who experience symptoms (about 10% have no symptoms) may have diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight los ...
and radiation enteritis
Radiation enteropathy is a syndrome that may develop following abdominal or pelvic radiation therapy for cancer. Many affected people are cancer survivors who had treatment for cervical cancer or prostate cancer; it has also been termed pelvic ra ...
. While positive serology and typical biopsy are highly suggestive of coeliac disease, lack of response to the diet may require these alternative diagnoses to be considered.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " cause and effect". In systems engin ...
is often difficult and as of 2019, there continues to be a lack of awareness among physicians about the variability of presentations of coeliac disease and the diagnostic criteria, such that most cases are diagnosed with great delay. It can take up to 12 years to receive a diagnosis from the onset of symptoms and the majority of those affected in most countries never receive it.
Several tests can be used. The level of symptom
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showin ...
s may determine the order of the tests, but ''all'' tests lose their usefulness if the person is already eating a gluten-free diet
A gluten-free diet (GFD) is a nutritional plan that strictly excludes gluten, which is a mixture of proteins found in wheat (and all of its species and hybrids, such as spelt, kamut, and triticale), as well as barley, rye, and oats. The inclus ...
. Intestinal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans ...
damage begins to heal within weeks of gluten being removed from the diet, and antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
levels decline over months. For those who have already started on a gluten-free diet, it may be necessary to perform a rechallenge with some gluten-containing food in one meal a day over 6 weeks before repeating the investigations.
Blood tests

Serological
Serology is the scientific study of serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the diagnostic identification of antibodies in the serum. Such antibodies are typically formed in response to an infection (against a given mi ...
blood tests are the first-line investigation required to make a diagnosis of coeliac disease. Its sensitivity correlates with the degree of histological lesions. People who present with minor damage to the small intestine may have seronegative findings so many patients with coeliac disease often are missed. In patients with villous atrophy, anti- endomysial (EMA) antibodies of the immunoglobulin A
Immunoglobulin A (Ig A, also referred to as sIgA in its secretory form) is an antibody that plays a role in the immune function of mucous membranes. The amount of IgA produced in association with mucosal membranes is greater than all other ty ...
(IgA) type can detect coeliac disease with a sensitivity and specificity
''Sensitivity'' and ''specificity'' mathematically describe the accuracy of a test which reports the presence or absence of a condition. Individuals for which the condition is satisfied are considered "positive" and those for which it is not are ...
of 90% and 99%, respectively. Serology
Serology is the scientific study of Serum (blood), serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the medical diagnosis, diagnostic identification of Antibody, antibodies in the serum. Such antibodies are typically formed in r ...
for anti-transglutaminase antibodies
Anti-transglutaminase antibodies (ATA) are autoantibodies against the transglutaminase protein. Antibodies serve an important role in the immune system by detecting cells and substances that the rest of the immune system then eliminates. These cel ...
(anti-tTG) was initially reported to have a higher sensitivity (99%) and specificity (>90%). However, it is now thought to have similar characteristics to anti-endomysial antibodies. Both anti-transglutaminase and anti-endomysial antibodies have high sensitivity to diagnose people with classic symptoms and complete villous atrophy, but they are only found in 30–89% of the cases with partial villous atrophy and in less than 50% of the people who have minor mucosal lesions (duodenal lymphocytosis
Duodenal lymphocytosis, sometimes called lymphocytic duodenitis, lymphocytic duodenosis, or duodenal intraepithelial lymphocytosis, is a condition where an increased number of intra-epithelial lymphocytes is seen in biopsies of the duodenal mucosa ...
) with normal villi.
Tissue transglutaminase modifies gluten peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
A ...
s into a form that may stimulate the immune system more effectively. These peptides are modified by tTG in two ways, deamidation or transamidation. Modern anti-tTG assays rely on a human recombinant protein
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be fou ...
as an antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. ...
. tTG testing should be done first as it is an easier test to perform. An equivocal result on tTG testing should be followed by anti-endomysial antibodies.
Guidelines recommend that a total serum IgA level is checked in parallel, as people with coeliac with IgA deficiency may be unable to produce the antibodies on which these tests depend ("false negative"). In those people, IgG antibodies against transglutaminase (IgG-tTG) may be diagnostic.
If all these antibodies are negative, then anti-DGP antibodies (antibodies against deamidated gliadin peptides) should be determined. IgG class anti-DGP antibodies may be useful in people with IgA deficiency. In children younger than two years, anti-DGP antibodies perform better than anti-endomysial and anti-transglutaminase antibodies tests.
Because of the major implications of a diagnosis of coeliac disease, professional guidelines recommend that a positive blood test
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a cholester ...
is still followed by an endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are insert ...
/gastroscopy
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) or oesophagogastroduodenoscopy (OGD), also called by various other names, is a diagnostic endoscopic procedure that visualizes the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract down to the duodenum. It is considered ...
and biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a diseas ...
. A negative serology test may still be followed by a recommendation for endoscopy and duodenal
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine m ...
biopsy if clinical suspicion remains high.
Historically three other antibodies were measured: anti-reticulin
Reticular fibers, reticular fibres or reticulin is a type of fiber in connective tissue composed of type III collagen secreted by reticular cells. Reticular fibers crosslink to form a fine meshwork (reticulin). This network acts as a supportin ...
(ARA), anti-gliadin
Gliadin (a type of prolamin) is a class of proteins present in wheat and several other cereals within the grass genus ''Triticum''. Gliadins, which are a component of gluten, are essential for giving bread the ability to rise properly during baki ...
(AGA
Aga or AGA may refer to:
Business
* Architectural Glass and Aluminum (AGA), a glazing contractor, established in 1970
* AGA (automobile), ''Autogen Gasaccumulator AG'', 1920s German car company
*AGA AB, ''Aktiebolaget Svenska Gasaccumulator'', a ...
) and anti-endomysial (EMA) antibodies. ARA testing, however, is not accurate enough for routine diagnostic use. Serology may be unreliable in young children, with anti-gliadin
Gliadin (a type of prolamin) is a class of proteins present in wheat and several other cereals within the grass genus ''Triticum''. Gliadins, which are a component of gluten, are essential for giving bread the ability to rise properly during baki ...
performing somewhat better than other tests in children under five. Serology tests are based on indirect immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence is a technique used for light microscopy with a fluorescence microscope and is used primarily on microbiological samples. This technique uses the specificity of antibodies to their antigen to target fluorescent dyes to spec ...
(reticulin, gliadin and endomysium) or ELISA
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay uses a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence ...
(gliadin or tissue transglutaminase
Transglutaminases are enzymes that in nature primarily catalyze the formation of an isopeptide bond between γ-carboxamide groups ( -(C=O)NH2 ) of glutamine residue side chains and the ε-amino groups ( -NH2 ) of lysine residue side cha ...
, tTG).
Other antibodies such as anti–Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies occur in some people with coeliac disease but also occur in other autoimmune disorders and about 5% of those who donate blood.
Antibody testing may be combined with HLA testing if the diagnosis is unclear. TGA and EMA testing are the most sensitive serum antibody tests, but as a negative HLA-DQ type excludes the diagnosis of coeliac disease, testing also for HLA-DQ2 or DQ8 maximises sensitivity and negative predictive values. In the United Kingdom, the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care in England that publishes guidelines in four areas:
* the use of health technologies withi ...
(NICE) does not (as of 2015) recommend the use of HLA typing to rule out coeliac disease outside of a specialist setting, for example, in children who are not having a biopsy, or in patients who already have limited gluten ingestion and opt not to have a gluten challenge.
Endoscopy
 An
An upper endoscopy
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) or oesophagogastroduodenoscopy (OGD), also called by various other names, is a diagnostic endoscopic procedure that visualizes the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract down to the duodenum. It is considered ...
with biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a diseas ...
of the duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine m ...
(beyond the duodenal bulb
The duodenal bulb is the portion of the duodenum closest to the stomach. It normally has a length of about 5 centimeters. The duodenal bulb begins at the pylorus and ends at the neck of the gallbladder. It is located posterior to the liver and the ...
) or jejunum
The jejunum is the second part of the small intestine in humans and most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. Its lining is specialised for the absorption by enterocytes of small nutrient molecules which have been previous ...
is performed to obtain multiple samples (four to eight) from the duodenum. Not all areas may be equally affected; if biopsies are taken from healthy bowel tissue, the result would be a false negative. Even in the same bioptic fragment, different degrees of
damage may be present.
Most people with coeliac disease have a small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the p ...
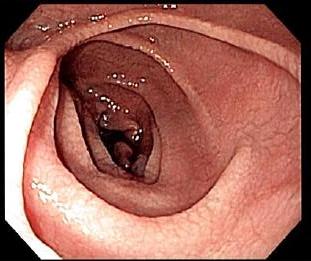
that appears to be normal on endoscopy before the biopsies are examined. However, five findings have been associated with high specificity for coeliac disease: scalloping of the small bowel folds (''pictured''), paucity in the folds, a mosaic
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly pop ...
pattern to the mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is ...
(described as a "cracked-mud" appearance), prominence of the submucosa
The submucosa (or tela submucosa) is a thin layer of tissue (biology), tissue in various organ (anatomy), organs of the gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal, respiratory tract, respiratory, and genitourinary system, genitourinary tracts. It i ...
blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away ...
s, and a nodular pattern to the mucosa.
European guidelines suggest that in children and adolescents with symptoms compatible with coeliac disease, the diagnosis can be made without the need for intestinal biopsy if anti-tTG antibodies titres are very high (10 times the upper limit of normal).
Until the 1970s, biopsies were obtained using metal capsules attached to a suction device. The capsule was swallowed and allowed to pass into the small intestine. After x-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
verification of its position, suction was applied to collect part of the intestinal wall inside the capsule. Often-utilised capsule systems were the Watson capsule and the Crosby–Kugler capsule. This method has now been largely replaced by fibre-optic
An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means to ...
endoscopy, which carries a higher sensitivity and a lower frequency of errors.
Capsule endoscopy
Capsule endoscopy is a medical procedure used to record internal images of the gastrointestinal tract for use in disease diagnosis. Newer developments are also able to take biopsies and release medication at specific locations of the entire ...
(CE) allows identification of typical mucosal changes observed in coeliac disease but has a lower sensitivity compared to regular endoscopy and histology. CE is therefore not the primary diagnostic tool for coeliac disease. However, CE can be used for diagnosing T-cell lymphoma, ulcerative jejunoileitis, and adenocarcinoma in refractory or complicated coeliac disease.
Pathology
The classic pathology changes of coeliac disease in the small bowel are categorised by the "Marsh classification": *Marsh stage 0: normal mucosa *Marsh stage 1: increased number of intra-epitheliallymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic ad ...
s (IELs), usually exceeding 20 per 100 enterocyte
Enterocytes, or intestinal absorptive cells, are simple columnar epithelial cells which line the inner surface of the small and large intestines. A glycocalyx surface coat contains digestive enzymes. Microvilli on the apical surface increase its ...
s
*Marsh stage 2: a proliferation of the crypts of Lieberkühn
In histology, an intestinal gland (also crypt of Lieberkühn and intestinal crypt) is a gland found in between villi in the intestinal epithelium lining of the small intestine and large intestine (or colon). The glands and intestinal villi are co ...
*Marsh stage 3: partial or complete villous
Villus ( la, "shaggy hair", plural villi) may refer to:
* Intestinal villus, refers to any one of the small, finger-shaped outgrowths of the epithelial lining of the wall of the intestine. Clusters of projections are referred as intestinal villi.
...
atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), poor nourishment, poor circulation, loss of hormonal support, loss of nerve supply t ...
and crypt hypertrophy
*Marsh stage 4: hypoplasia
Hypoplasia (from Ancient Greek ὑπo- ''hypo-'' 'under' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'; adjective form ''hypoplastic'') is underdevelopment or incomplete development of a tissue or organ.small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the p ...
architecture
Marsh's classification, introduced in 1992, was subsequently modified in 1999 to six stages, where the previous stage 3 was split in three substages. Further studies demonstrated that this system was not always reliable and that the changes observed in coeliac disease could be described in one of three stages:
*A representing lymphocytic infiltration with normal villous appearance;
*B1 describing partial villous atrophy; and
*B2 describing complete villous atrophy.
The changes classically improve or reverse after gluten
Gluten is a structural protein naturally found in certain cereal grains. Although "gluten" often only refers to wheat proteins, in medical literature it refers to the combination of prolamin and glutelin proteins naturally occurring in all grain ...
is removed from the diet. However, most guidelines do not recommend a repeat biopsy unless there is no improvement in the symptoms on diet. In some cases, a deliberate gluten challenge, followed by a biopsy, may be conducted to confirm or refute the diagnosis. A normal biopsy and normal serology after challenge indicates the diagnosis may have been incorrect.
In untreated coeliac disease, villous atrophy is more common in children younger than three years, but in older children and adults, it is common to find minor intestinal lesions (duodenal lymphocytosis
Duodenal lymphocytosis, sometimes called lymphocytic duodenitis, lymphocytic duodenosis, or duodenal intraepithelial lymphocytosis, is a condition where an increased number of intra-epithelial lymphocytes is seen in biopsies of the duodenal mucosa ...
) with normal intestinal villi
Intestinal villi (singular: villus) are small, finger-like projections that extend into the lumen of the small intestine. Each villus is approximately 0.5–1.6 mm in length (in humans), and has many microvilli projecting from the enterocy ...
.
Other diagnostic tests
At the time of diagnosis, further investigations may be performed to identify complications, such asiron deficiency
Iron deficiency, or sideropenia, is the state in which a body lacks enough iron to supply its needs. Iron is present in all cells in the human body and has several vital functions, such as carrying oxygen to the tissues from the lungs as a key ...
(by full blood count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cells and plat ...
and iron studies), folic acid
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing and ...
and vitamin B12 deficiency and hypocalcaemia
Hypocalcemia is a medical condition characterized by low calcium levels in the blood serum. The normal range of blood calcium is typically between 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.8–10.7 mg/dL, 4.3–5.2 mEq/L) while levels less than 2.1 mmol ...
(low calcium levels, often due to decreased vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (c ...
levels). Thyroid function tests
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thy ...
may be requested during blood tests to identify hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as po ...
, which is more common in people with coeliac disease.
Osteopenia
Osteopenia, known as "low bone mass" or "low bone density", is a condition in which bone mineral density is low. Because their bones are weaker, people with osteopenia may have a higher risk of fractures, and some people may go on to develop osteop ...
and osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to bone fragility, and consequent increase in fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone ...
, mildly and severely reduced bone mineral density, are often present in people with coeliac disease, and investigations to measure bone density may be performed at diagnosis, such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA, or DEXA) is a means of measuring bone mineral density (BMD) using spectral imaging. Two X-ray beams, with different energy levels, are aimed at the patient's bones. When soft tissue absorption is subtracted ...
(DXA) scanning, to identify the risk of fracture and need for bone protection medication.
Gluten withdrawal
Although blood antibody tests, biopsies, and genetic tests usually provide a clear diagnosis, occasionally the response to gluten withdrawal on agluten-free diet
A gluten-free diet (GFD) is a nutritional plan that strictly excludes gluten, which is a mixture of proteins found in wheat (and all of its species and hybrids, such as spelt, kamut, and triticale), as well as barley, rye, and oats. The inclus ...
is needed to support the diagnosis. Currently, gluten challenge is no longer required to confirm the diagnosis in patients with intestinal lesions compatible with coeliac disease and a positive response to a gluten-free diet. Nevertheless, in some cases, a gluten challenge with a subsequent biopsy may be useful to support the diagnosis, for example in people with a high suspicion for coeliac disease, without a biopsy confirmation, who have negative blood antibodies and are already on a gluten-free diet. Gluten challenge is discouraged before the age of 5 years and during pubertal
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a boy. ...
growth. The alternative diagnosis of non-coeliac gluten sensitivity may be made where there is only symptomatic evidence of gluten sensitivity. Gastrointestinal and extraintestinal symptoms of people with non-coeliac gluten sensitivity can be similar to those of coeliac disease, and improve when gluten is removed from the diet, after coeliac disease and wheat allergy
Wheat allergy is an allergy to wheat which typically presents itself as a food allergy, but can also be a contact allergy resulting from occupational exposure. Like all allergies, wheat allergy involves immunoglobulin E and mast cell response. T ...
are reasonably excluded.
Up to 30% of people often continue having or redeveloping symptoms after starting a gluten-free diet. A careful interpretation of the symptomatic response is needed, as a lack of response in a person with coeliac disease may be due to continued ingestion of small amounts of gluten, either voluntary or inadvertent, or be due to other commonly associated conditions such as small intestinal bacterial overgrowth
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), also termed bacterial overgrowth, or small bowel bacterial overgrowth syndrome (SBBOS), is a disorder of excessive bacterial growth in the small intestine. Unlike the colon (or large bowel), which is r ...
(SIBO), lactose intolerance
Lactose intolerance is a common condition caused by a decreased ability to digest lactose, a sugar found in dairy products. Those affected vary in the amount of lactose they can tolerate before symptoms develop. Symptoms may include abdominal pa ...
, fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galacto ...
, sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
, and sorbitol
Sorbitol (), less commonly known as glucitol (), is a sugar alcohol with a sweet taste which the human body metabolizes slowly. It can be obtained by reduction of glucose, which changes the converted aldehyde group (−CHO) to a primary alcohol g ...
malabsorption, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) is the inability to properly digest food due to a lack of digestive enzymes made by the pancreas. EPI is found in humans afflicted with cystic fibrosis and Shwachman–Diamond syndrome, and is common in ...
, and microscopic colitis
Microscopic colitis refers to two related medical conditions which cause diarrhea: collagenous colitis and lymphocytic colitis. Both conditions are characterized by the presence of chronic non-bloody watery diarrhea, normal appearances on colonosco ...
, among others. In untreated coeliac disease, these are often transient conditions derived from the intestinal damage. They normally revert or improve several months after starting a gluten-free diet, but may need temporary interventions such as supplementation with pancreatic enzymes
Digestive enzymes are a group of enzymes that break down polymeric macromolecules into their smaller building blocks, in order to facilitate their absorption into the cells of the body. Digestive enzymes are found in the digestive tracts of anima ...
, dietary restrictions of lactose, fructose, sucrose or sorbitol containing foods, or treatment with oral antibiotics in the case of associated bacterial overgrowth. In addition to gluten withdrawal, some people need to follow a low-FODMAP
FODMAPs or fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols are short chain carbohydrates that are poorly absorbed in the small intestine and are prone to absorb water and ferment in the colon. They include short chain o ...
s diet or avoid consumption of commercial gluten-free products, which are usually rich in preservative
A preservative is a substance or a chemical that is added to products such as food products, beverages, pharmaceutical drugs, paints, biological samples, cosmetics, wood, and many other products to prevent decomposition by microbial growth or by ...
s and additives
Additive may refer to:
Mathematics
* Additive function, a function in number theory
* Additive map, a function that preserves the addition operation
* Additive set-functionn see Sigma additivity
* Additive category, a preadditive category with fi ...
(such as sulfite
Sulfites or sulphites are compounds that contain the sulfite ion (or the sulfate(IV) ion, from its correct systematic name), . The sulfite ion is the conjugate base of bisulfite. Although its acid ( sulfurous acid) is elusive, its salts are wide ...
s, glutamates
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synt ...
, nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion
A polyatomic ion, also known as a molecular ion, is a covalent bonded set of two or more atoms, or of a metal complex, that can be considered to behave as a single unit and that has a net charge that is not zer ...
s and benzoates Benzoates (salts of benzoic acid) can refer to:
*Ammonium benzoate
*Calcium benzoate
*Magnesium benzoate
*Potassium benzoate
* Sodium benzoate
Sodium benzoate is the sodium salt of benzoic acid, widely used as a food preservative (with an E num ...
) and might have a role in triggering functional gastrointestinal symptoms.
Screening
There is debate as to the benefits of screening. As of 2017, theUnited States Preventive Services Task Force
The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) is "an independent panel of experts in primary care and prevention that systematically reviews the evidence of effectiveness and develops recommendations for clinical preventive services". ...
found insufficient evidence to make a recommendation among those without symptoms. In the United Kingdom, the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care in England that publishes guidelines in four areas:
* the use of health technologies withi ...
(NICE) recommend testing for coeliac disease in first-degree relatives of those with the disease already confirmed, in people with persistent fatigue, abdominal or gastrointestinal symptoms, faltering growth, unexplained weight loss or iron, vitamin B12 or folate deficiency, severe mouth ulcers, and with diagnoses of type 1 diabetes, autoimmune thyroid disease, and with newly diagnosed chronic fatigue syndrome
Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), also called myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME) or ME/CFS, is a complex, debilitating, long-term medical condition. The causes and mechanisms of the disease are not fully understood. Distinguishing core symptoms are ...
and irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a "disorder of gut-brain interaction" characterized by a group of symptoms that commonly include abdominal pain and or abdominal bloating and changes in the consistency of bowel movements. These symptoms may ...
. Dermatitis herpetiformis
Dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) is a chronic autoimmune blistering skin condition, characterised by intensely itchy blisters filled with a watery fluid. DH is a cutaneous manifestation of coeliac disease, although the exact causal mechanism is not k ...
is included in other recommendations. The NICE also recommend offering serological testing for coeliac disease in people with metabolic bone disease
Metabolic bone disease is an abnormality of bones caused by a broad spectrum of disorders. Most commonly these disorders are caused by deficiencies of minerals such as calcium, phosphorus, magnesium or vitamin D leading to dramatic clinical disord ...
(reduced bone mineral density or osteomalacia
Osteomalacia is a disease characterized by the softening of the bones caused by impaired bone metabolism primarily due to inadequate levels of available phosphate, calcium, and vitamin D, or because of resorption of calcium. The impairment of bone ...
), unexplained neurological disorders (such as peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, is a general term describing disease affecting the peripheral nerves, meaning nerves beyond the brain and spinal cord. Damage to peripheral nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland, or or ...
and ataxia
Ataxia is a neurological sign consisting of lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements that can include gait abnormality, speech changes, and abnormalities in eye movements. Ataxia is a clinical manifestation indicating dysfunction of ...
), fertility problems or recurrent miscarriage
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion and pregnancy loss, is the death of an embryo or fetus before it is able to survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks of gestation is defined by ESHRE as biochemical lo ...
, persistently raised liver enzymes with unknown cause, dental enamel defects and with diagnose of Down syndrome
Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. It is usually associated with physical growth delays, mild to moderate intellectual dis ...
or Turner syndrome
Turner syndrome (TS), also known as 45,X, or 45,X0, is a genetic condition in which a female is partially or completely missing an X chromosome. Signs and symptoms vary among those affected. Often, a short and webbed neck, low-set ears, low hair ...
.
Some evidence has found that early detection may decrease the risk of developing health complications, such as osteoporosis, anaemia, and certain types of cancer, neurological disorders, cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, h ...
s, and reproductive problems. They thus recommend screening in people with certain health problems.
Serology
Serology is the scientific study of Serum (blood), serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the medical diagnosis, diagnostic identification of Antibody, antibodies in the serum. Such antibodies are typically formed in r ...
has been proposed as a screening
Screening may refer to:
* Screening cultures, a type a medical test that is done to find an infection
* Screening (economics), a strategy of combating adverse selection (includes sorting resumes to select employees)
* Screening (environmental), a ...
measure, because the presence of antibodies would detect some previously undiagnosed cases of coeliac disease and prevent its complications in those people. However, serologic tests have high sensitivity only in people with total villous atrophy and have a very low ability to detect cases with partial villous atrophy or minor intestinal lesions. Testing for coeliac disease may be offered to those with commonly associated conditions.
Treatment
Diet
At present, the only effective treatment is a lifelonggluten-free diet
A gluten-free diet (GFD) is a nutritional plan that strictly excludes gluten, which is a mixture of proteins found in wheat (and all of its species and hybrids, such as spelt, kamut, and triticale), as well as barley, rye, and oats. The inclus ...
. No medication exists that prevents damage or prevents the body from attacking the gut when gluten is present. Strict adherence to the diet helps the intestines heal, leading to resolution of all symptoms in most cases and, depending on how soon the diet is begun, can also eliminate the heightened risk of osteoporosis and intestinal cancer and in some cases sterility.
Dietitian
A dietitian, medical dietitian, or dietician is an expert in identifying and treating disease-related malnutrition and in conducting medical nutrition therapy, for example designing an enteral tube feeding regimen or mitigating the effects of ca ...
input is generally requested to ensure the person is aware which foods contain gluten, which foods are safe, and how to have a balanced diet despite the limitations. In many countries, gluten-free products are available on prescription and may be reimbursed by health insurance
Health insurance or medical insurance (also known as medical aid in South Africa) is a type of insurance that covers the whole or a part of the risk of a person incurring medical expenses. As with other types of insurance, risk is shared among ma ...
plans. Gluten-free products are usually more expensive and harder to find than common gluten-containing foods. Since ready-made products often contain traces of gluten, some coeliacs may find it necessary to cook from scratch.
The term "gluten-free" is generally used to indicate a supposed harmless level of gluten rather than a complete absence. The exact level at which gluten is harmless is uncertain and controversial. A recent systematic review
A systematic review is a Literature review, scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from publ ...
tentatively concluded that consumption of less than 10 mg of gluten per day is unlikely to cause histological abnormalities, although it noted that few reliable studies had been done. Regulation of the label "gluten-free" varies. In the European Union, the European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body o ...
issued regulations in 2009 limiting the use of "gluten-free" labels for food products to those with less than 20 mg/kg of gluten, and "very low gluten" labels for those with less than 100 mg/kg. In the United States, the FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food s ...
issued regulations in 2013 limiting the use of "gluten-free" labels for food products to those with less than 20 ppm of gluten. The current international Codex Alimentarius
The Codex Alimentarius () is a collection of internationally recognized standards, codes of practice, guidelines, and other recommendations published by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations relating to food, food production ...
standard allows for 20 ppm of gluten in so-called "gluten-free" foods.
Gluten-free diet improves healthcare-related quality of life, and strict adherence to the diet gives more benefit than incomplete adherence. Nevertheless, gluten-free diet doesn't completely normalise the quality of life.
Vaccination
Even though it is unclear if coeliac patients have a generally increased risk of infectious diseases, they should generally be encouraged to receive all common vaccines against vaccine preventable diseases (VPDs) as the general population. Moreover, some pathogens could be harmful to coeliac patients. According to the European Society for the Study of Celiac Disease (ESsCD), coeliac disease can be associated with hyposplenism or functional asplenia, which could result in impaired immunity to encapsulated bacteria, with an increased risk of such infections. For this reason, patients who are known to be hyposplenic should be administered at least the pneumococcal vaccine. However, the ESsCD states that it is not clear whether vaccination with the conjugated vaccine is preferable in this setting and whether additional vaccination againstHaemophilus
''Haemophilus'' is a genus of Gram-negative, pleomorphic, coccobacilli bacteria belonging to the family Pasteurellaceae. While ''Haemophilus'' bacteria are typically small coccobacilli, they are categorized as pleomorphic bacteria because of ...
, meningococcus
''Neisseria meningitidis'', often referred to as meningococcus, is a Gram-negative bacterium that can cause meningitis and other forms of meningococcal disease such as meningococcemia, a life-threatening sepsis. The bacterium is referred to as a ...
, and influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms ...
should be considered if not previously given. However, Mårild et al. suggested considering additional vaccination against influenza because of an observed increased risk of hospital admission for this infection in celiac patients.
Refractory disease
Between 0.3% and 10% of affected people have refractory disease, which means that they have persistent villous atrophy on a gluten-free diet despite the lack of gluten exposure for more than 12 months. Nevertheless, inadvertent exposure to gluten is the main cause of persistent villous atrophy, and must be ruled out before a diagnosis of refractory disease is made. People with poor basic education and understanding of gluten-free diet often believe that they are strictly following the diet, but are making regular errors. Also, a lack of symptoms is not a reliable indicator of intestinal recuperation. If alternative causes of villous atrophy have been eliminated,steroids
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and a ...
or immunosuppressants
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified into ...
(such as azathioprine
Azathioprine (AZA), sold under the brand name Imuran, among others, is an immunosuppressive medication. It is used in rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and systemic lupus erythematosus, ...
) may be considered in this scenario.
Refractory coeliac disease should not be confused with the persistence of symptoms despite gluten withdrawal caused by transient conditions derived from the intestinal damage, which generally revert or improve several months after starting a gluten-free diet, such as small intestinal bacterial overgrowth
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), also termed bacterial overgrowth, or small bowel bacterial overgrowth syndrome (SBBOS), is a disorder of excessive bacterial growth in the small intestine. Unlike the colon (or large bowel), which is r ...
, lactose intolerance
Lactose intolerance is a common condition caused by a decreased ability to digest lactose, a sugar found in dairy products. Those affected vary in the amount of lactose they can tolerate before symptoms develop. Symptoms may include abdominal pa ...
, fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galacto ...
, sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
, and sorbitol
Sorbitol (), less commonly known as glucitol (), is a sugar alcohol with a sweet taste which the human body metabolizes slowly. It can be obtained by reduction of glucose, which changes the converted aldehyde group (−CHO) to a primary alcohol g ...
malabsorption, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) is the inability to properly digest food due to a lack of digestive enzymes made by the pancreas. EPI is found in humans afflicted with cystic fibrosis and Shwachman–Diamond syndrome, and is common in ...
, and microscopic colitis among others.
Epidemiology
Globally coeliac disease affects between 1 in 100 and 1 in 170 people. Rates, however, vary between different regions of the world from as few as 1 in 300 to as many as 1 in 40. In the United States it is thought to affect between 1 in 1750 (defined as clinical disease including dermatitis herpetiformis with limited digestive tract symptoms) to 1 in 105 (defined by presence of IgA TG in blood donors). Due to variable signs and symptoms it is believed that about 85% of people affected are undiagnosed. The percentage of people with clinically diagnosed disease (symptoms prompting diagnostic testing) is 0.05–0.27% in various studies. However, population studies from parts of Europe, India, South America, Australasia and the USA (using serology and biopsy) indicate that the percentage of people with the disease may be between 0.33 and 1.06% in children (but 5.66% in one study of children of the predisposedSahrawi people
The Sahrawi, or Saharawi people ( ar, صحراويون '; es, Saharaui), are an ethnic group and nation native to the western part of the Sahara desert, which includes the Western Sahara, southern Morocco, much of Mauritania, and along the s ...
) and 0.18–1.2% in adults. Among those in primary care populations who report gastrointestinal symptoms, the rate of coeliac disease is about 3%. In Australia, approximately 1 in 70 people have the disease. The rate amongst adult blood donors in Iran, Israel, Syria and Turkey is 0.60%, 0.64%, 1.61% and 1.15%, respectively.
People of African, Japanese and Chinese descent are rarely diagnosed; this reflects a much lower prevalence of the genetic risk factors
In epidemiology, a risk factor or determinant is a variable associated with an increased risk of disease or infection.
Due to a lack of harmonization across disciplines, determinant, in its more widely accepted scientific meaning, is often use ...
, such as HLA-B8
HLA-B8 (B8) is an HLA- B serotype. The serotype identifies the HLA-B*08 gene products. (For terminology help see: HLA-serotype tutorial) HLA-B8, previously known as HL-A8 was one of the first identified of the HLA antigens. It coined the "Supe ...
. People of Indian ancestry seem to have a similar risk to those of Western Caucasian ancestry. Population studies also indicate that a large proportion of coeliacs remain undiagnosed; this is due, in part, to many clinicians being unfamiliar with the condition and also due to the fact it can be asymptomatic. Coeliac disease is slightly more common in women than in men. A large multicentre study in the U.S. found a prevalence of 0.75% in not-at-risk groups, rising to 1.8% in symptomatic people, 2.6% in second-degree relatives (like grandparents, aunt or uncle, grandchildren, etc.) of a person with coeliac disease and 4.5% in first-degree relatives (siblings, parents or children). This profile is similar to the prevalence in Europe. Other populations at increased risk for coeliac disease, with prevalence rates ranging from 5% to 10%, include individuals with Down and Turner syndrome
Turner syndrome (TS), also known as 45,X, or 45,X0, is a genetic condition in which a female is partially or completely missing an X chromosome. Signs and symptoms vary among those affected. Often, a short and webbed neck, low-set ears, low hair ...
s, type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that originates when cells that make insulin (beta cells) are destroyed by the immune system. Insulin is a hormone required for the cells to use blood sugar for ...
, and autoimmune thyroid disease, including both hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism ...
(overactive thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thy ...
) and hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as po ...
(underactive thyroid).
Historically, coeliac disease was thought to be rare, with a prevalence of about 0.02%. The reason for the recent increases in the number of reported cases is unclear. It may be at least in part due to changes in diagnostic practice. There also appears to be an approximately 4.5 fold true increase that may be due to less exposure to bacteria and other pathogens in Western environments. In the United States, the median age at diagnosis is 38 years. Roughly 20 percent of individuals with coeliac disease are diagnosed after 60 years of age.
History
The term "coeliac" is from the Greek κοιλιακός (''koiliakós'', "abdominal") and was introduced in the 19th century in a translation of what is generally regarded as anAncient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
description of the disease by Aretaeus of Cappadocia
Aretaeus ( grc-gre, Ἀρεταῖος) is one of the most celebrated of the ancient Greek physicians. Little is known of his life. He presumably was a native or at least a citizen of Cappadocia (Roman province), Cappadocia, a Roman province in ...
.
Humans first started to cultivate grains in the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
period (beginning about 9500 BCE) in the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent ( ar, الهلال الخصيب) is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine and Jordan, together with the northern region of Kuwait, southeastern region of ...
in Western Asia, and, likely, coeliac disease did not occur before this time. Aretaeus of Cappadocia
Aretaeus ( grc-gre, Ἀρεταῖος) is one of the most celebrated of the ancient Greek physicians. Little is known of his life. He presumably was a native or at least a citizen of Cappadocia (Roman province), Cappadocia, a Roman province in ...
, living in the second century in the same area, recorded a malabsorptive syndrome with chronic diarrhoea, causing a debilitation of the whole body. His "Cœliac Affection" (''coeliac'' from Greek κοιλιακός ''koiliakos'', "abdominal") gained the attention of Western medicine when Francis Adams presented a translation of Aretaeus's work at the Sydenham Society in 1856. The patient described in Aretaeus' work had stomach pain and was atrophied, pale, feeble, and incapable of work. The diarrhoea manifested as loose stools that were white, malodorous, and flatulent, and the disease was intractable and liable to periodic return. The problem, Aretaeus believed, was a lack of heat in the stomach necessary to digest the food and a reduced ability to distribute the digestive products throughout the body, this incomplete digestion resulting in diarrhoea. He regarded this as an affliction of the old and more commonly affecting women, explicitly excluding children. The cause, according to Aretaeus, was sometimes either another chronic disease or even consuming "a copious draught of cold water."
The paediatrician
Pediatrics (American and British English differences, also spelled ''paediatrics'' or ''pædiatrics'') is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, Adolescence, adolescents, and young adults. In the United King ...
Samuel Gee
Samuel Jones Gee (13 September 1839 – 3 August 1911) was an English physician and paediatrician. In 1888, Gee published the first complete modern description of the clinical picture of coeliac disease, and theorised on the importance of diet i ...
gave the first modern-day description of the condition in children in a lecture at Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London, in 1887. Gee acknowledged earlier descriptions and terms for the disease and adopted the same term as Aretaeus (coeliac disease). He perceptively stated: "If the patient can be cured at all, it must be by means of diet." Gee recognised that milk intolerance is a problem with coeliac children and that highly starched foods should be avoided. However, he forbade rice, sago, fruit, and vegetables, which all would have been safe to eat, and he recommended raw meat as well as thin slices of toasted bread. Gee highlighted particular success with a child "who was fed upon a quart of the best Dutch mussel
Mussel () is the common name used for members of several families of bivalve molluscs, from saltwater and Freshwater bivalve, freshwater habitats. These groups have in common a shell whose outline is elongated and asymmetrical compared with other ...
s daily." However, the child could not bear this diet for more than one season.
Christian Archibald Herter, an American physician, wrote a book in 1908 on children with coeliac disease, which he called "intestinal infantilism". He noted their growth was retarded and that fat was better tolerated than carbohydrate. The eponym
An eponym is a person, a place, or a thing after whom or which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. The adjectives which are derived from the word eponym include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''.
Usage of the word
The term ''epon ...
''Gee-Herter disease'' was sometimes used to acknowledge both contributions. as cited by WhoNamedIt Sidney V. Haas
Sidney Valentine Haas, M.D. (1870–1964) was a U.S. pediatrician whose research determined a dietary means of combating celiac disease.
Haas was born in Chicago and moved to New York City when he was six years old. He attended New York University ...
, an American paediatrician, reported positive effects of a diet of bananas in 1924. This diet remained in vogue until the actual cause of coeliac disease was determined.
While a role for carbohydrates had been suspected, the link with wheat was not made until the 1940s by the Dutch paediatrician Dr Willem Karel Dicke Willem Karel Dicke (15 February 1905, Dordrecht – 27 April 1962, De Bilt) was a Dutch paediatrician who was the first to develop the gluten-free diet and to show that in coeliac disease some types of flour cause relapse.
Life
From 1922 until 1929 ...
. It is likely that clinical improvement of his patients during the Dutch famine of 1944
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
(during which flour was scarce) may have contributed to his discovery. Dicke noticed that the shortage of bread led to a significant drop in the death rate among children affected by coeliac disease from greater than 35% to essentially zero. He also reported that once wheat was again available after the conflict, the mortality rate soared to previous levels. The link with the gluten component of wheat was made in 1952 by a team from Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the West ...
, England. Villous atrophy was described by British physician John W. Paulley in 1954 on samples taken at surgery. This paved the way for biopsy samples taken by endoscopy.
Throughout the 1960s, other features of coeliac disease were elucidated. Its hereditary character was recognised in 1965. In 1966, dermatitis herpetiformis was linked to gluten sensitivity
Non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS) or gluten sensitivity is "a clinical entity induced by the ingestion of gluten leading to intestinal and/or extraintestinal symptoms that improve once the gluten-containing foodstuff is removed from the diet, a ...
.
Social and culture
May has been designated as "Coeliac Awareness Month" by several coeliac organisations.Christian churches and the Eucharist
Speaking generally, the various denominations of Christians celebrate aEucharist
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instit ...
in which a wafer or small piece of sacramental bread
Sacramental bread, also called Communion bread, Eucharistic bread, the Lamb or simply the host ( la, hostia, lit=sacrificial victim), is the bread used in the Christian ritual of the Eucharist. Along with sacramental wine, it is one of two elemen ...
from wheat bread is blessed and then eaten. A typical wafer weighs about half a gram.
Many Christian churches offer their communicants gluten-free alternatives, usually in the form of a rice-based cracker or gluten-free bread. These include the United Methodist
The United Methodist Church (UMC) is a worldwide mainline Protestant denomination based in the United States, and a major part of Methodism. In the 19th century, its main predecessor, the Methodist Episcopal Church, was a leader in evangelic ...
, Christian Reformed
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρισ ...
, Episcopal
Episcopal may refer to:
*Of or relating to a bishop, an overseer in the Christian church
*Episcopate, the see of a bishop – a diocese
*Episcopal Church (disambiguation), any church with "Episcopal" in its name
** Episcopal Church (United State ...
, the Anglican Church (Church of England, UK) and Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
. Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
may receive from the Chalice alone, or ask for gluten-reduced hosts; gluten-free ones however are not considered to still be wheat bread and hence invalid matter.
Roman Catholic position
Roman Catholicdoctrine
Doctrine (from la, doctrina, meaning "teaching, instruction") is a codification of beliefs or a body of teachings or instructions, taught principles or positions, as the essence of teachings in a given branch of knowledge or in a belief system ...
states that for a valid Eucharist
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instit ...
, the bread to be used at Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementar ...
must be made from wheat. Low-gluten hosts
A host is a person responsible for guests at an event or for providing hospitality during it.
Host may also refer to:
Places
*Host, Pennsylvania, a village in Berks County
People
*Jim Host (born 1937), American businessman
*Michel Host ( ...
meet all of the Catholic Church's requirements, but they are not entirely gluten free. Requests to use rice wafers have been denied.
The issue is more complex for priests. As a celebrant, a priest is, for the fullness of the sacrifice of the Mass, absolutely required to receive under both species. On 24 July 2003, the Congregation for the Doctrine of the Faith stated, "Given the centrality of the celebration of the Eucharist in the life of a priest, one must proceed with great caution before admitting to Holy Orders those candidates unable to ingest gluten or alcohol without serious harm."
By January 2004, extremely low-gluten Church-approved hosts had become available in the United States, Italy and Australia. As of July 2017, the Vatican still outlawed the use of gluten-free bread for Holy Communion.
Passover
Spelling
Coeliac disease is the preferred spelling inBritish English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in ...
, while celiac disease is typically used in North American English
North American English (NAmE, NAE) is the most generalized variety of the English language as spoken in the United States and Canada. Because of their related histories and cultures, plus the similarities between the pronunciations (accents), v ...
.
Research directions
The search for environmental factors that could be responsible for genetically susceptible people becoming intolerant to gluten has resulted in increasing research activity looking at gastrointestinal infections. Research published in April 2017 suggests that an often-symptomless infection by a common strain ofreovirus
''Reoviridae'' is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses. Member viruses have a wide host range, including vertebrates, invertebrates, plants, protists and fungi. They lack lipid envelopes and package their segmented genome within multi-layered ...
can increase sensitivity to foods such as gluten.
Various treatment approaches are being studied, including some that would reduce the need for dieting. All are still under development, and are not expected to be available to the general public for a while.
Three main approaches have been proposed as new therapeutic modalities for coeliac disease: gluten detoxification, modulation of the intestinal permeability
Intestinal permeability is a term describing the control of material passing from inside the gastrointestinal tract through the cells lining the gut wall, into the rest of the body. The intestine normally exhibits some permeability, which allows ...
, and modulation of the immune response.
Using genetically engineered
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including t ...
wheat species, or wheat species that have been selectively bred
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant mal ...
to be minimally immunogenic, may allow the consumption of wheat. This, however, could interfere with the effects that gliadin has on the quality of dough. Alternatively, gluten exposure can be minimised by the ingestion of a combination of enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
s (prolyl endopeptidase
Prolyl endopeptidase (PE) also known as prolyl oligopeptidase or post-proline cleaving enzyme is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PREP'' gene.
Function
Prolyl endopeptidase is a large cytosolic enzyme that belongs to a distinct cla ...
and a barley glutamine-specific cysteine endopeptidase
Cysteine proteases, also known as thiol proteases, are hydrolase enzymes that degrade proteins. These proteases share a common catalysis, catalytic mechanism that involves a nucleophile, nucleophilic cysteine thiol in a catalytic triad or dyad.
D ...
(EP-B2
Endoprotease B, isoform 2 (EP-B2) is a cysteine protease found in barley. In studies, it has shown promise as a possible therapeutic for coeliac disease. Aspergillopepsin from ''Aspergillus niger
''Aspergillus niger'' is a mold classified withi ...
)) that degrade the putative 33-mer peptide in the duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine m ...
.
Alternative treatments under investigation include the inhibition of zonulin
Zonulin (haptoglobin 2 precursor) is a protein that increases the permeability of tight junctions between cells of the wall of the digestive tract. It was discovered in 2000 by Alessio Fasano and his team at the University of Maryland School of ...
, an endogenous signalling protein linked to increased permeability of the bowel wall and hence increased presentation of gliadin to the immune system. One inhibitor of this pathway is larazotide acetate
Larazotide (INN; also known as AT-1001; formulated as the salt with acetic acid, larazotide acetate) is a synthetic eight amino acid peptide that functions as a tight junction regulator and reverses leaky junctions to their normally closed state ...
, which is currently scheduled for phase 3 clinical trials. Other modifiers of other well-understood steps in the pathogenesis of coeliac disease, such as the action of HLA-DQ2 or tissue transglutaminase and the MICA/NKG2D interaction that may be involved in the killing of enterocytes.
Attempts to modulate the immune response concerning coeliac disease are mostly still in phase I of clinical testing; one agent (CCX282-B) has been evaluated in a phase II clinical trial based on small-intestinal biopsies taken from people with coeliac disease before and after gluten exposure.
Although popularly used as an alternative treatment for people with autism, there is no good evidence that a gluten-free diet
A gluten-free diet (GFD) is a nutritional plan that strictly excludes gluten, which is a mixture of proteins found in wheat (and all of its species and hybrids, such as spelt, kamut, and triticale), as well as barley, rye, and oats. The inclus ...
is of benefit in the treatment of autism. In the subset of people who have gluten sensitivity
Non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS) or gluten sensitivity is "a clinical entity induced by the ingestion of gluten leading to intestinal and/or extraintestinal symptoms that improve once the gluten-containing foodstuff is removed from the diet, a ...
there is limited evidence that suggests that a gluten free diet may improve some autistic behaviors.
References
External links
* {{Authority control Autoimmune diseases Gastrointestinal tract disorders Genetic diseases and disorders Gluten sensitivity Malnutrition Pediatrics Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate