Noida Metro on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Noida Metro is a
The Noida Metro is a
Noida Aqua-Line Extension Project
was conducted thrice between June 2020 and February 2021 but all three times they were cancelled due to relatively low response from the construction companies. *June 2021: Tender for the Noida Metro Aqua Line Extension has been floated for the fourth time *July 2021: This time NMRC has received 3 bids from Sam India Builtwell, GR Infra Projects, and Ashoka Buildcon. After the technical evaluation of bids NMRC has final candidates.
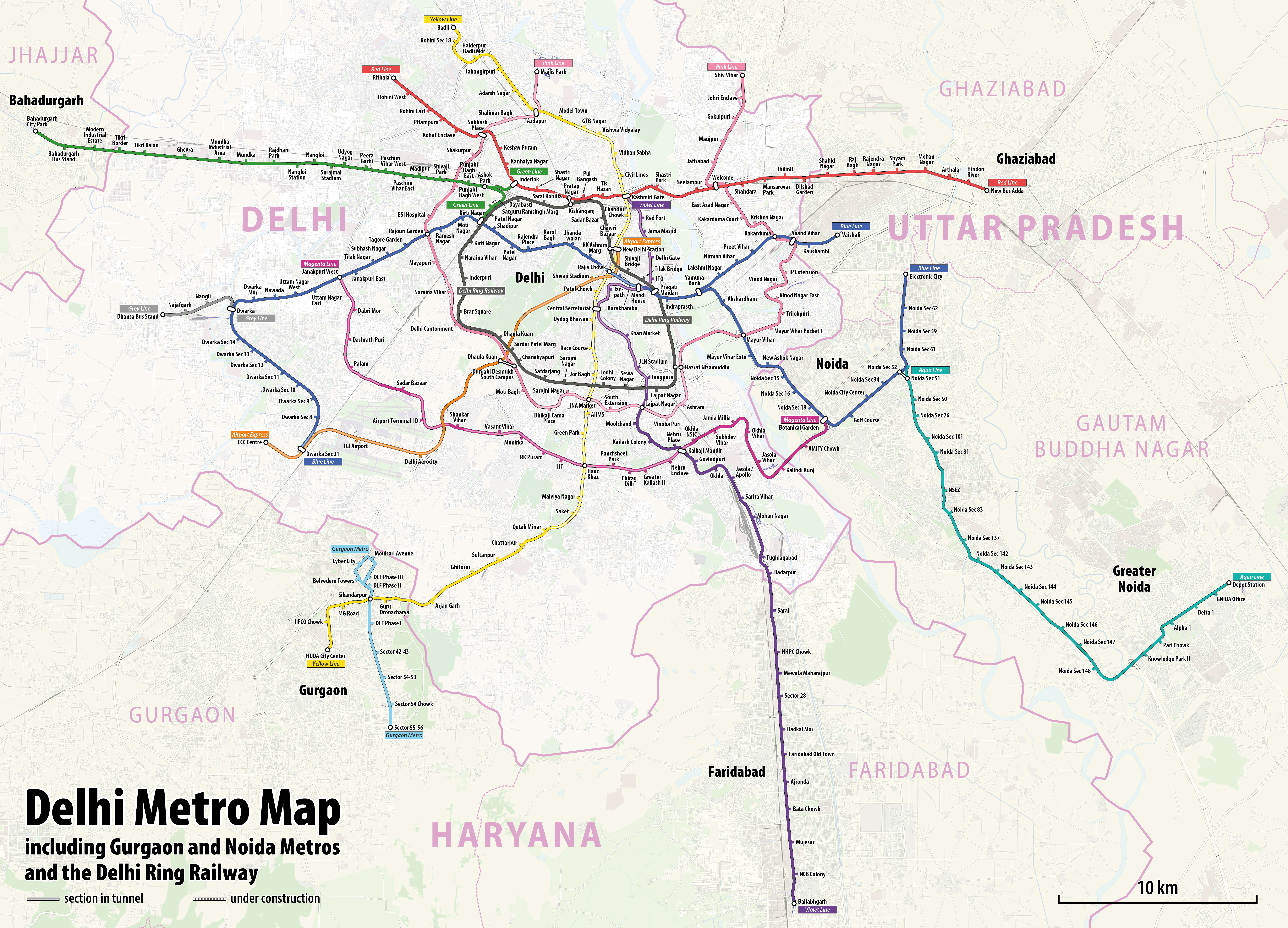
Noida – Greater Noida Metro Rail
{{DEFAULTSORT:Noida Metro Transport in Noida Metropolitan transport agencies of India Standard gauge railways in India 2019 establishments in Uttar Pradesh
rapid transit
Rapid transit or mass rapid transit (MRT), also known as heavy rail or metro, is a type of high-capacity public transport generally found in urban areas. A rapid transit system that primarily or traditionally runs below the surface may be c ...
system connecting the twin cities of Noida
Noida, short for New Okhla Industrial Development Authority, is a planned city located in Gautam Buddha Nagar district of the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. Noida is a satellite city of Delhi and is a part of the National Capital Region (NCR) o ...
and Greater Noida
Greater Noida is a planned city located in Gautam Buddha Nagar district of the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The city was created as an extension to Noida area under the ''UP Industrial Area Development Act, 1976''. Situated south-east of t ...
in Gautam Buddh Nagar
Gautam Buddha Nagar district is a district of Uttar Pradesh, named after Gautama Buddha. It is a part of Delhi NCR and is divided into 4 sub-divisions i.e. Noida, Greater Noida, Dadri and Jewar. Greater Noida is the administrative headquarters ...
, Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 1950 ...
, India. The metro network consists of one line (called Aqua Line), with a total length of serving 21 stations. A second line is planned. The system has all elevated stations using standard-gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), International gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge and European gauge in Europe, and SGR in Ea ...
tracks.
The services are available from 6:00am to 10:00pm from Monday to Saturday. On Sundays, trains are available between 8:00am and 10:00pm. The trains make 163 trips a day from Monday to Friday using a fleet of 10 trains and the frequency is 10 minutes during peak hours (8:00am–11:00am and 5:00pm–8:00pm) and 15 minutes during off-peak hours. On Saturday and Sunday the frequency is 10 minutes. Initially, the trains are composed of four cars to be extended up to six in the future.
Noida Metro is the 11th Metro system to be built in India and 2nd in Uttar Pradesh after Lucknow Metro
Lucknow Metro is a rapid transit system serving the largest city and the capital of Uttar Pradesh, Lucknow. Construction of the line begun on 27 September 2014 with the stretch from to Charbagh Railway Station which began its commercial op ...
. It is the sixth longest operational metro network in India after the Delhi Metro
The Delhi Metro is a mass rapid transit (MRT) system serving Delhi and its satellite cities of Ghaziabad, Faridabad, Gurgaon, Noida, Bahadurgarh and Ballabhgarh, in the National Capital Region of India. The network consists of 10 colour-cod ...
, Hyderabad Metro
The Hyderabad Metro is a rapid transit system, serving the city of Hyderabad, Telangana, India. It is the second longest operational metro network in India after the Delhi Metro (285 stations) with 57 stations and the lines are arranged in a ...
, Chennai Metro
The Chennai Metro is a rapid transit system serving the city of Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. It is the 4th longest metro system In india. The system commenced service in 2015 after partially opening the first phase of the project. The network c ...
, Namma Metro
Namma Metro ("Our Metro" in Kannada), also known as Bengaluru Metro, is a rapid transit system serving the city of Bengaluru, India. Upon its inauguration, it became the first underground metro system in South India. Namma Metro has a mix of u ...
and Kolkata Metro
The Kolkata Metro is a rapid transit system serving the city of Kolkata in West Bengal, India. , it has two operational lines, a line from Dakshineswar to Kavi Subhash and a line from Salt Lake Sector V to Sealdah, for a total of . Four ...
.
Noida Metro Rail Corporation (NMRC), a state-owned corporation
A state-owned enterprise (SOE) is a government entity which is established or nationalised by the ''national government'' or ''provincial government'' by an executive order or an act of legislation in order to earn profit for the government ...
, is building and owns the system. However, the operations and maintenance of Noida Metro lies with Delhi Metro Rail Corporation
Delhi Metro Rail Corporation Limited (DMRC) is a centre-state joint venture that operates the Delhi Metro. The DMRC is also involved in the planning and implementation of metro rail, monorail, and high-speed rail projects in India and abroad. T ...
. The line is connected to Delhi Metro
The Delhi Metro is a mass rapid transit (MRT) system serving Delhi and its satellite cities of Ghaziabad, Faridabad, Gurgaon, Noida, Bahadurgarh and Ballabhgarh, in the National Capital Region of India. The network consists of 10 colour-cod ...
at Noida Sector 51 station by a footbridge. Foundation for the NMRC project was laid down in October 2014, with the construction being commenced by the end of December 2014 by then Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh Akhilesh Yadav Akhilesh is a given name. Notable people with the name include:
* Akhilesh Das (1961–2017), educationist, professor, Indian politician and philanthropist
* Akhilesh K. Gaharwar (born 1982), Indian academic and Professor at Texas A&M University
* ...
. Trial runs started in August 2018, and the metro was inaugurated on 25 January 2019 by Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 1950 ...
, Yogi Adityanath
Yogi Adityanath (born on 5 June 1972 as Ajay Singh Bisht),
. Noida metro is planned to be connected with blue line of DMRC and proposed Jewar Airport
Noida International Airport is an international airport being constructed near Jewar in Gautam Buddha Nagar District, Uttar Pradesh in India. Once completed, it is planned to be India's largest airport. The Noida International Airport Limit ...
through Aqua line of NMRC.
History
The Uttar Pradesh government approved the construction of a metro line linking Noida with Greater Noida in October 2014. The government also appointed theDelhi Metro Rail Corporation
Delhi Metro Rail Corporation Limited (DMRC) is a centre-state joint venture that operates the Delhi Metro. The DMRC is also involved in the planning and implementation of metro rail, monorail, and high-speed rail projects in India and abroad. T ...
(DMRC) as the turnkey consultant for the project.
The detailed project report (DPR) was prepared by the DMRC. A Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) called the Noida Metro Rail Corporation (NMRC) was formed to implement the project. The Uttar Pradesh Cabinet approved the project and forwarded the DPR to Government of India in October 2013. The Government of India and UP will each bear 20% of the costs and loans from external agencies would be taken to fund the rest 60% of the project. Twenty percent funding from UP will be shared by Noida and Greater Noida Authorities, based on the length of track that passes through the two areas.
The NMRC announced on 30 November 2016 that the first line of the metro would be called the Aqua Line. Explaining the choice, NMRC managing director Santosh Yadav stated, "Aqua signifies an eco-friendly colour, which is what we want to portray." The project received safety clearance from the commissioner of metro rail safety on 21 December 2018.
The Greater Noida Industrial Development Authority (GNIDA) approved an extension of the Aqua Line as part of Phase 2 of the metro project on 4 December 2018. The 15 km extension will link Noida Sector 71 to Knowledge Park 5 in Greater Noida. The extension will consist of nine stations and is expected to cost . The new stations are Sector 122 and Sector 123 in Noida and Sector 4, Ecotech 12, Sectors 2, Sector 3, Sector 10, Sector 12 and Knowledge Park V in Greater Noida.
Timeline
Phase 1
Noida Sector 51 to Depot *Oct 2014: UP Government approves the metro project. * Sep 2015: Work progress in around Sec-71, Noida. * Nov 2015: 700 piles (pillar foundation) out of total 5000 have been made. * Feb 2016: NMRC completes first phase of construction in eight months. At this rate, the corridor is expected to be operational publicly by May 2017. * Feb 2017: 70% work completed. * Mar 2017: Train trials to start by December 2017 and commercial operations by April 2018. * June 2017: Commercial operations to start by April 2018. * July 2017: 95% civil work of track and metro station completed, trial to start by year end. * Aug 2017: Metro train trial to start by year end on 6-km track from Depot station to Knowledge Park station. * Sep 2017: Commercial operations to start by April 2018. * Oct 2017: 97% civil work done. All stations to be ready by October end. * Nov 2017: The last girder was placed thus completing viaduct work for whole metro line. * Dec 2017: Four Aqua Line coaches arrive from China, each costing INR 11 crores. Trial run to begin soon. * Jan 2018: Limited trial run started on stretch. * Mar 2018: Full-fledged trial run to start in April. * Jun 2018: Trial runs going on from Gr Noida Depot to Noida Sector-148 slowly it will be extended to terminating station in Noida Sector-71. The line will become fully operational by Dec 2018. * Sep 2018: Trials continued for extended month till November 2018. * Nov 2018: Currently, the corridor is undergoing extensive trials prior to final inspection by the commissioner of metro rail safety. *Dec 2018: Safety trial successfully conducted and fares decided. *Jan 2019: On 25 January, Aqua line was inaugurated by Uttar Pradesh Chief MinisterYogi Adityanath
Yogi Adityanath (born on 5 June 1972 as Ajay Singh Bisht),
& cabinet minister for Housing and Urban Affairs Hardeep Singh Puri
Hardeep Singh Puri (born 15 February 1952) is an Indian politician and former Indian diplomat who is currently serving as the Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas and Minister of Housing and Urban Affairs in the Government of India. He present ...
.
Phase 2
* Dec 2018: Uttar Pradesh government approved the project on 04-Dec-2018. * Aug 2019: Project to get delayed due to financial viability. PPP mode to be explored. * Dec 2019: Project approved in Uttar Pradesh cabinet meeting, project deadline set to 2022 * Jun 2020: Tenders invited and to be submitted by end of June-2020. * July 2020: Tender for construction to be awarded by September. *Feb 2021: The tender and bidding process foNoida Aqua-Line Extension Project
was conducted thrice between June 2020 and February 2021 but all three times they were cancelled due to relatively low response from the construction companies. *June 2021: Tender for the Noida Metro Aqua Line Extension has been floated for the fourth time *July 2021: This time NMRC has received 3 bids from Sam India Builtwell, GR Infra Projects, and Ashoka Buildcon. After the technical evaluation of bids NMRC has final candidates.
Network

Phase 1
The operated Aqua Line has 21 stations. The line starts from Noida Sector 51 metro station and will run through sectors 50, 76, 101, 81, NSEZ, 83, 137, 142, 143, 144, 145, 146, 147 and 148; after this it will enter Greater Noida and will go through Knowledge Park-II, Pari Chowk, Alpha-1, Delta-1 and GNIDA Office before terminating in Depot Station. The entire route is on elevated track. All stations are equipped with platform screen doors. The corridor was completed at a cost of ₹5,503 crore, according to the NMRC. This line has an interchange station with theDelhi Metro
The Delhi Metro is a mass rapid transit (MRT) system serving Delhi and its satellite cities of Ghaziabad, Faridabad, Gurgaon, Noida, Bahadurgarh and Ballabhgarh, in the National Capital Region of India. The network consists of 10 colour-cod ...
at Noida Sector 52 metro station
The Noida Sector 52 is a metro station on the Blue Line extension of the Delhi Metro railway, in the city of Noida in India.
The station is connected to the Noida Sector 51 metro station on the Noida Metro's Aqua Line by a 300-metre-long pe ...
.
Phase 2
Noida Sector 51 to Knowledge Park V
The Greater Noida Industrial Development Authority (GNIDA) on 4 December 2018, approved the Noida Metro Phase 2 from Noida Sector 51 to Knowledge Park V in Greater Noida. The extension will cover up to 15 km and comprise 9 stations and cost Rs 2602 crore. According to the detailed project report (DPR), the new track would be completed in two phases and the entire project would connect Sector 51 in Noida and Knowledge Park V in Greater Noida. The first phase would be between Sector 51 and Greater Noida Sector 2, while the second phase would be between Greater Noida Sector 2 and Knowledge Park V stations, the DPR stated. There will be five stations in the first phase—Noida Sector 122, Sector 123, Greater Noida Sector 4, Eco Tech, and Greater Noida 2, while four stations in second phase—Greater Noida Sector 3, Sector 10, Sector 12 and Knowledge Park V. The construction cost of the first phase of the Noida Aqua Line Extension Project will be Rs 536.04 crore and the completion period of the project is 2 years. If all goes well, construction work is expected to start in 2023.Knowledge Park II to Noida International Airport
DPR prepared for extension from Greater Noida to upcomingNoida International Airport
Noida International Airport is an international airport being constructed near Jewar in Gautam Buddha Nagar District, Uttar Pradesh in India. Once completed, it is planned to be India's largest airport. The Noida International Airport Limit ...
at Jewar that will cover around 35.64 km and comprises 25 stations. The project cost is estimated to be Rs 5708 crore as per YEIDA officials.
Noida Sector 142 to Botanical Garden
DPR prepared for extension from Noida Sec 142 to Botanical Garden metro station that will cover around 11.5 km and comprises 11 stations. The project is expected to finish by 2023 and provide direct connectivity between expressway sectors and greater Noida to Delhi metro without having to leave the metro system. The DPR is being vetted by the board of the NMRC before being sent across for approvals.Infrastructure
Rolling stock
The metro uses lightweight rakes made of stainless steel and aluminum, manufactured by China'sCRRC Corporation
CRRC Corporation Limited (known as CRRC) is a Chinese state-owned and publicly traded rolling stock manufacturer. It is the world's largest rolling stock manufacturer in terms of revenue, eclipsing its major competitors of Alstom and Siemens.
It ...
. Each train has a seating capacity of 186 and a standing capacity of 848, with total capacity of 1,034 passengers. Nineteen rakes with four coaches each, a total of 76 coaches, will operate of the Aqua Line. The cost of each coach is . Trains are equipped with a passenger information system, a public address system and an emergency announcement system from the operation control centre.
Power
All 21 stations, the train depot, and the NMRC offices will be powered by solar energy. The NMRC will install solar panels on the rooftops of all stations, footbridges, its main office building, the depot and parking lot boundary walls to generate an estimated 12 MW of solar power daily. The metro system will also be supplemented with conventional electricity, which will also be used as a backup. Trains will not be powered by solar power, and will instead use conventional power supply.Signaling
The metro is operated underCBTC
Communications-based train control (CBTC) is a railway signaling system that uses telecommunications between the train and track equipment for traffic management and infrastructure control. CBTC allows a train's position to be known more accurat ...
control, supplied by Ansaldo STS
Hitachi Rail STS SpA (from ''Hitachi Rail Signalling and Transportation Systems'') or Hitachi Rail STS (previously Ansaldo STS) is a transportation company owned by Hitachi with a global presence in the field of railway signalling and integrated t ...
.
City bus & Feeder bus
In the first phase, 50 AC CNG buses low floor buses are being operated on 6 routes. Noida and Greater Noida authorities were given the responsibility of running the City Bus Service in the ratio of 70:30 to the Noida Metro Rail Corporation. Urban Mass Transit Company (UMTC) presented the assessment of requirement of buses on 27 routes by conducting a survey for the city bus service and monitoring will be done byUttar Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation
The Uttar Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation (UPSRTC) is a public sector passenger road transport corporation which services Uttar Pradesh, India, and adjoining states of North India. It operates as a state and interstate bus service and ...
. While one route will provide service as Metro feeder buses, two routes will cover intra city service, while one route will be for intra connectivity in Greater Noida city. Two routes have also been dedicated for connectivity between the cities of Noida and Greater Noida.
The salient features of buses operated are:
1. All buses are air conditioned buses propelled with BS-IV CNG fuel
2. Technical specification of buses compatible with Urban Bus Specification –II as published by MOUD Govt. of India
3. The entry floor height of the bus is 340 mm, the first of its kind in India
4. The bus has provision of a kneeling mechanism with manual ramp for disabled persons
5. The bus is completely ITS equipped with PIS Boards and LED boards
6. CCTV have been fitted inside the bus for safety of passengers
Operations
Trains operate at an average speed of with a headway of ten minutes during non-peak hours and 7.30 minutes during peak hours from Monday to Friday, 15 minutes headway for Saturday and Sunday.Network Map
See also
*Urban rail transit in India
Urban rail transit in India plays an important role in intracity transportation in the major cities which are highly populated. It consists of rapid transit, suburban rail, monorail and tram systems. According to a report published in 2021, a ...
** List of Noida Metro stations
** Delhi Metro
The Delhi Metro is a mass rapid transit (MRT) system serving Delhi and its satellite cities of Ghaziabad, Faridabad, Gurgaon, Noida, Bahadurgarh and Ballabhgarh, in the National Capital Region of India. The network consists of 10 colour-cod ...
*** Blue Line (Delhi Metro)
The Blue Line (Line 3 & Line 4) is a metro rail line of the Delhi Metro, a rapid transit system in Delhi, India. It is the longest line (by total length) of the network and consists of a Main Line (Line 3) with 50 stations from Noida Electron ...
** Rapid Metro Gurgaon
Rapid Metro Gurgaon is a light metro system serving the city of Gurgaon, Haryana, India. Rapid Metro connects the commercial areas of Gurgaon, and acts as a feeder link to the Delhi Metro with an interchange with its Yellow Line at Sikander ...
* National Capital Region (India)
The National Capital Region (NCR) is a planning region centred upon the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi in India. It encompasses Delhi and several districts surrounding it from the states of Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and Rajasthan. The N ...
** Yamuna Expressway
Yamuna Expressway is a 6- lane wide (expandable to 8) and 165.5 km long access-controlled expressway in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is presently India's 3rd longest expressway since February 2017. It was built to de-congest the old ...
** Noida–Greater Noida Expressway
The Noida–Greater Noida Expressway is a six-lane highway connecting Noida, Uttar Pradesh, an industrial suburb of Delhi to Greater Noida, a new suburb. This expressway is under expansion to Taj Economic Zone, International Airport and Aviatio ...
References
External links
Noida – Greater Noida Metro Rail
{{DEFAULTSORT:Noida Metro Transport in Noida Metropolitan transport agencies of India Standard gauge railways in India 2019 establishments in Uttar Pradesh