Nizhegorodskaya Oblast on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Nizhny Novgorod Oblast (russian: link=no, Нижегородская область, ''Nizhegorodskaya oblast''), is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the
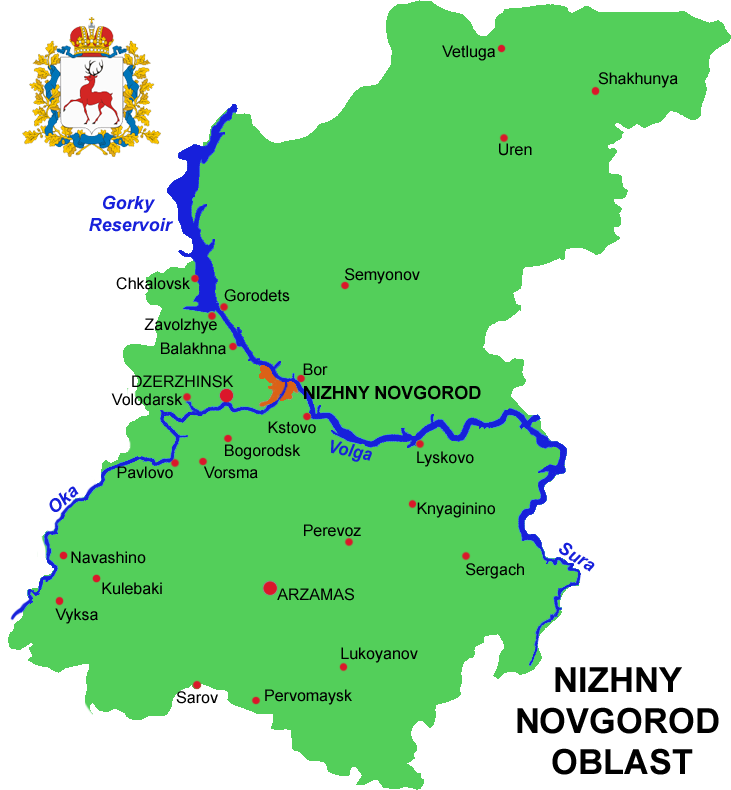 The oblast covers an area of , which is approximately equal to the entire area of the Benelux countries or Czech Republic. Agricultural land occupies 41% of this area; forests, 48%, lakes and rivers, 2%; and other lands, 9%. Nizhny Novgorod Oblast borders Kostroma Oblast (N),
The oblast covers an area of , which is approximately equal to the entire area of the Benelux countries or Czech Republic. Agricultural land occupies 41% of this area; forests, 48%, lakes and rivers, 2%; and other lands, 9%. Nizhny Novgorod Oblast borders Kostroma Oblast (N),
 The unique architectural construction—the
The unique architectural construction—the
 Population:
According to the 2010 Census, ethnic Russians at 3,109,661 made up 95.1% of the oblast's population. Other ethnic groups included Tatars (44,103, or 1.4%), Mordva (19,138, or 0.6%), Ukrainians (17,657, or 0.5%), and various smaller groups, each accounting for less than 0.5% of the total. Additionally, 42,349 people were registered from administrative databases, and could not declare an ethnicity. It is estimated that the proportion of ethnicities in this group is the same as that of the declared group.
*Births (2011): 36,315 (11.0 per 1000)
*Deaths (2011): 54,184 (16.4 per 1000)
Deaths decreased by 8.5% in 2011 compared to 2010.
;Vital statistics for 2012
*Births: 38,881 (11.8 per 1000)
*Deaths: 52,771 (16.0 per 1000)
*Total fertility rate:
2009 – 1.43 , 2010 – 1.42 , 2011 – 1.44 , 2012 – 1.55 , 2013 – 1.56 , 2014 – 1.59 , 2015 – 1.67 , 2016 – 1.65(e)
According to the Federal Migration Service, 20,450 foreign citizens were registered in the oblast in 2006. The actual number of foreigners residing in the oblast as of June 1, 2006 was estimated to be over 22,000.
;Religion
According to a 2012 surveyArena – Atlas of Religions and Nationalities in Russia
Population:
According to the 2010 Census, ethnic Russians at 3,109,661 made up 95.1% of the oblast's population. Other ethnic groups included Tatars (44,103, or 1.4%), Mordva (19,138, or 0.6%), Ukrainians (17,657, or 0.5%), and various smaller groups, each accounting for less than 0.5% of the total. Additionally, 42,349 people were registered from administrative databases, and could not declare an ethnicity. It is estimated that the proportion of ethnicities in this group is the same as that of the declared group.
*Births (2011): 36,315 (11.0 per 1000)
*Deaths (2011): 54,184 (16.4 per 1000)
Deaths decreased by 8.5% in 2011 compared to 2010.
;Vital statistics for 2012
*Births: 38,881 (11.8 per 1000)
*Deaths: 52,771 (16.0 per 1000)
*Total fertility rate:
2009 – 1.43 , 2010 – 1.42 , 2011 – 1.44 , 2012 – 1.55 , 2013 – 1.56 , 2014 – 1.59 , 2015 – 1.67 , 2016 – 1.65(e)
According to the Federal Migration Service, 20,450 foreign citizens were registered in the oblast in 2006. The actual number of foreigners residing in the oblast as of June 1, 2006 was estimated to be over 22,000.
;Religion
According to a 2012 surveyArena – Atlas of Religions and Nationalities in Russia
Sreda.org 69.2% of the population of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast adheres to the Russian Orthodox Church, 2% are unaffiliated generic Christians, 2% are Orthodox Christian believers without belonging to any church or members of other Orthodox churches, and 1% are adherents of the Slavic native faith (Rodnovery). In addition, 15% of the population declares to be "spiritual but not religious", 10% is

 The oblast ranks seventh in Russia in industrial output. Processing industries predominate in the local economy. More than 650 industrial companies employ nearly 700,000 people, or 62% of the workforce involved in material production. Industry generates 83% of the regional GDP and accounts for 89% of all material expenditures. The leading sectors are engineering and metalworking, followed by chemical and petrochemical industries and forestry, woodworking, and paper industries. The first three sectors account for about 75% of all industrial production.
The oblast has traditionally been attractive to investors. In 2002, Moody's rating agency confirmed a Caa1rating based on the region's long-term foreign currency liabilities.
The oblast ranks seventh in Russia in industrial output. Processing industries predominate in the local economy. More than 650 industrial companies employ nearly 700,000 people, or 62% of the workforce involved in material production. Industry generates 83% of the regional GDP and accounts for 89% of all material expenditures. The leading sectors are engineering and metalworking, followed by chemical and petrochemical industries and forestry, woodworking, and paper industries. The first three sectors account for about 75% of all industrial production.
The oblast has traditionally been attractive to investors. In 2002, Moody's rating agency confirmed a Caa1rating based on the region's long-term foreign currency liabilities.
 The region maintains trade relations with many countries and has an export surplus. The largest volume of exports goes to Ukraine, Belarus,
The region maintains trade relations with many countries and has an export surplus. The largest volume of exports goes to Ukraine, Belarus,
File:Narrow gauge railway of Alcevskoye peat enterprise 2013.jpg,
File:Narrow gauge railway of Caprolactam factory.png,
File:Narrow gauge railway of Peshelan Gupsym mine.png,
File:Narrow gauge railway of Kerzenetsc peat enterprise.png,
Official website of the Government of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast
Official website of the Legislative Assembly of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast
Nizhny Novgorod City Guide
Travel and business guide to Nizhny Novgorod
Central Eurasian Information Resource; Images of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast
– University of Washington Digital Collections {{Use mdy dates, date=February 2014 States and territories established in 1929 1936 establishments in the Soviet Union
city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
of Nizhny Novgorod. It has a population of 3,310,597 as of the 2010 Census. From 1932 to 1990 it was known as Gorky Oblast.
The oblast is crossed by the Volga River. Apart from Nizhny Novgorod's metropolitan area (including Dzerzhinsk, Bor and Kstovo
Kstovo (russian: Ксто́во) is a town and the administrative center of Kstovsky District in Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Russia, located on the right bank of the Volga River, southeast of Nizhny Novgorod, the administrative center of the oblas ...
) the biggest city is Arzamas. Near the town of Sarov there is the Serafimo-Diveyevsky Monastery
Serafimo-Diveevsky Monastery, or Saint Seraphim-Diveyevo Monastery, or Holy Trinity-Saint Seraphim-Diveyevo Monastery (russian: Свято-Троицкий Серафимо-Дивеевский Монастырь) is a monastery of nuns ( conven ...
, one of the largest convents in Russia, established by Saint Seraphim of Sarov. The Makaryev Monastery opposite of the town of Lyskovo used to be the location of the largest fair in Eastern Europe. Other historic towns include Gorodets and Balakhna
Balakhna (russian: Балахна́) is a town and the administrative center of Balakhninsky District in Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Russia, located on the right bank of the Volga River, north of Nizhny Novgorod, the administrative center of ...
, located on the Volga to the north from Nizhny Novgorod.
Geography
 The oblast covers an area of , which is approximately equal to the entire area of the Benelux countries or Czech Republic. Agricultural land occupies 41% of this area; forests, 48%, lakes and rivers, 2%; and other lands, 9%. Nizhny Novgorod Oblast borders Kostroma Oblast (N),
The oblast covers an area of , which is approximately equal to the entire area of the Benelux countries or Czech Republic. Agricultural land occupies 41% of this area; forests, 48%, lakes and rivers, 2%; and other lands, 9%. Nizhny Novgorod Oblast borders Kostroma Oblast (N), Kirov Oblast
Kirov Oblast (russian: Ки́ровская о́бласть, ''Kirovskaya oblast'') is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast) in Eastern Europe. Its administrative center is the city of Kirov. Population: 1,341,312 ( 2010 Census).
Geography
Na ...
(NE), the Mari El Republic
The Mari El Republic (russian: Респу́блика Мари́й Эл, ''Respublika Mariy El''; Meadow Mari: ; Hill Mari: ) is a republic of Russia. It is in the European Russia region of the country, along the northern bank of the Volga Rive ...
(E), the Chuvash Republic
Chuvashia (russian: Чувашия; cv, Чӑваш Ен), officially the Chuvash Republic — Chuvasia,; cv, Чӑваш Республики — Чӑваш Ен is a republic of Russia located in Eastern Europe. It is the homeland of the Chuv ...
(E), the Republic of Mordovia
The Republic of Mordovia (russian: Респу́блика Мордо́вия, r=Respublika Mordoviya, p=rʲɪsˈpublʲɪkə mɐrˈdovʲɪjə; mdf, Мордовия Республиксь, ''Mordovija Respublikś''; myv, Мордовия Рес ...
(S), Ryazan Oblast (SW), Vladimir Oblast (W), and Ivanovo Oblast
Ivanovo Oblast (russian: Ива́новская о́бласть, ''Ivanovskaya oblast'') is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). It had a population of 927,828 as of the 2021 Russian Census.
Its three largest cities are Ivanovo (the ...
(NW).
Natural resources
Nizhny Novgorod Oblast is not rich in natural resources, which are limited to commercial deposits of sand (including titanium-zirconium sands), clay, gypsum, peat, mineral salt, and timber.History
The sites of Pustyn I and the settlement of Naumovka I, Krasny Bor 5 and others belong to the Mesolithic era in the Nizhny Novgorod region. Burial grounds of the Fatyanovo culture of the Bronze Age were found in the Chkalovsky, Vetluzhsky and Krasnobakovsky districts. In the course of the regional reform of Peter I in 1708, Nizhny Novgorod with the surrounding lands was added to theKazan province The Kazan Province (russian: Каза́нская прови́нция) - province of Kazan Governorate of the Russian Empire, which existed 1719–1775. Its center was the city of Kazan.
Kazan province was formed as part of the Kazan gubernya b ...
. In 1714, the Nizhny Novgorod province
Nizhny (russian: Ни́жний; masculine), Nizhnyaya (; feminine), or Nizhneye (russian: Ни́жнее; neuter), literally meaning "lower", is the name of several Russian localities. It may refer to:
* Nizhny Novgorod, a Russian city colloquial ...
was created.
On January 14, 1929, the Nizhny Novgorod Oblast was formed. On July 15 of the same year, it was transformed into the Nizhny Novgorod Territory.
On October 7, 1932, the Nizhny Novgorod Territory was renamed the Gorky Territory (in honor of the writer Maxim Gorky). On December 5, 1936, the Gorky Territory was transformed into the Gorky Oblast (the Mari and Chuvash Republics were taken from the former territory).
On January 7, 1954, the Arzamas Oblast was separated from the Gorky Oblast. On April 23, 1957, the Arzamas Oblast was abolished, and its territory was returned to the Gorky Oblast.
On October 22, 1990, by the Decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the RSFSR, the Gorky Oblast was renamed the Nizhny Novgorod Oblast. On April 21, 1992, the Congress of People's Deputies of Russia approved the decision of the presidium of the parliament to rename the region, amending Art. 71 of the Constitution of the RSFSR of 1978, which entered into force on May 16, 1992.
Politics
During the Soviet period, the high authority in the oblast was shared between three persons: the first secretary of the Nizhny Novgorod (then Gorki) CPSU Committee (who in reality had the greatest authority); the chairman of the oblast Soviet (legislative power); and the chairman of the oblast Executive Committee (executive power). After the abolition of Article 6 of the Constitution of the USSR in March 1990, the CPSU lost its monopoly on power. The head of the Oblast administration, and eventually the governor, was appointed/elected alongside the elected regional parliament. The Charter of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast is the fundamental law of the region. The Legislative Assembly of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast is the province's standing legislative (representative) body. The Legislative Assembly exercises its authority by passing laws, resolutions, and other legal acts and by supervising the implementation and observance of the laws and other legal acts passed by it. The highest executive body is the Oblast Government, which includes territorial executive bodies such as district administrations, committees, and commissions that facilitate development and run the day to day matters of the province. The Oblast administration supports the activities of the Governor who is the highest official and acts as guarantor of the observance of the oblast Charter in accordance with the Constitution of Russia.Sights
 The unique architectural construction—the
The unique architectural construction—the steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
lattice hyperboloid tower built by the Russian engineer and scientist Vladimir Grigorievich Shukhov in 1929—is located near the town of Dzerzhinsk on the left bank of the Oka River
The Oka (russian: Ока́, ) is a river in central Russia, the largest right tributary of the Volga. It flows through the regions of Oryol, Tula, Kaluga, Moscow, Ryazan, Vladimir and Nizhny Novgorod and is navigable over a large part of its ...
.
Administrative divisions
Demographics
 Population:
According to the 2010 Census, ethnic Russians at 3,109,661 made up 95.1% of the oblast's population. Other ethnic groups included Tatars (44,103, or 1.4%), Mordva (19,138, or 0.6%), Ukrainians (17,657, or 0.5%), and various smaller groups, each accounting for less than 0.5% of the total. Additionally, 42,349 people were registered from administrative databases, and could not declare an ethnicity. It is estimated that the proportion of ethnicities in this group is the same as that of the declared group.
*Births (2011): 36,315 (11.0 per 1000)
*Deaths (2011): 54,184 (16.4 per 1000)
Deaths decreased by 8.5% in 2011 compared to 2010.
;Vital statistics for 2012
*Births: 38,881 (11.8 per 1000)
*Deaths: 52,771 (16.0 per 1000)
*Total fertility rate:
2009 – 1.43 , 2010 – 1.42 , 2011 – 1.44 , 2012 – 1.55 , 2013 – 1.56 , 2014 – 1.59 , 2015 – 1.67 , 2016 – 1.65(e)
According to the Federal Migration Service, 20,450 foreign citizens were registered in the oblast in 2006. The actual number of foreigners residing in the oblast as of June 1, 2006 was estimated to be over 22,000.
;Religion
According to a 2012 surveyArena – Atlas of Religions and Nationalities in Russia
Population:
According to the 2010 Census, ethnic Russians at 3,109,661 made up 95.1% of the oblast's population. Other ethnic groups included Tatars (44,103, or 1.4%), Mordva (19,138, or 0.6%), Ukrainians (17,657, or 0.5%), and various smaller groups, each accounting for less than 0.5% of the total. Additionally, 42,349 people were registered from administrative databases, and could not declare an ethnicity. It is estimated that the proportion of ethnicities in this group is the same as that of the declared group.
*Births (2011): 36,315 (11.0 per 1000)
*Deaths (2011): 54,184 (16.4 per 1000)
Deaths decreased by 8.5% in 2011 compared to 2010.
;Vital statistics for 2012
*Births: 38,881 (11.8 per 1000)
*Deaths: 52,771 (16.0 per 1000)
*Total fertility rate:
2009 – 1.43 , 2010 – 1.42 , 2011 – 1.44 , 2012 – 1.55 , 2013 – 1.56 , 2014 – 1.59 , 2015 – 1.67 , 2016 – 1.65(e)
According to the Federal Migration Service, 20,450 foreign citizens were registered in the oblast in 2006. The actual number of foreigners residing in the oblast as of June 1, 2006 was estimated to be over 22,000.
;Religion
According to a 2012 surveyArena – Atlas of Religions and Nationalities in RussiaSreda.org 69.2% of the population of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast adheres to the Russian Orthodox Church, 2% are unaffiliated generic Christians, 2% are Orthodox Christian believers without belonging to any church or members of other Orthodox churches, and 1% are adherents of the Slavic native faith (Rodnovery). In addition, 15% of the population declares to be "spiritual but not religious", 10% is
atheist
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no ...
, and 0.8% follows other religions or did not give an answer to the question.
Economy

 The oblast ranks seventh in Russia in industrial output. Processing industries predominate in the local economy. More than 650 industrial companies employ nearly 700,000 people, or 62% of the workforce involved in material production. Industry generates 83% of the regional GDP and accounts for 89% of all material expenditures. The leading sectors are engineering and metalworking, followed by chemical and petrochemical industries and forestry, woodworking, and paper industries. The first three sectors account for about 75% of all industrial production.
The oblast has traditionally been attractive to investors. In 2002, Moody's rating agency confirmed a Caa1rating based on the region's long-term foreign currency liabilities.
The oblast ranks seventh in Russia in industrial output. Processing industries predominate in the local economy. More than 650 industrial companies employ nearly 700,000 people, or 62% of the workforce involved in material production. Industry generates 83% of the regional GDP and accounts for 89% of all material expenditures. The leading sectors are engineering and metalworking, followed by chemical and petrochemical industries and forestry, woodworking, and paper industries. The first three sectors account for about 75% of all industrial production.
The oblast has traditionally been attractive to investors. In 2002, Moody's rating agency confirmed a Caa1rating based on the region's long-term foreign currency liabilities.
 The region maintains trade relations with many countries and has an export surplus. The largest volume of exports goes to Ukraine, Belarus,
The region maintains trade relations with many countries and has an export surplus. The largest volume of exports goes to Ukraine, Belarus, Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
, Kazakhstan, Belgium, and France. Imports come mainly from Ukraine, Germany, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Austria, Netherlands, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, and the United States.
The stock market infrastructure is quite well developed in Nizhny Novgorod, and the exchange business is expanding. Companies and organizations registered in the region include 1153 joint-stock companies, 63 investment institutions, 34 commercial banks, 35 insurance companies, 1 voucher investment fund, 1 investment fund, 17 nongovernmental pension funds, 2 associations of professional stock market dealers, and 3 exchanges (stock, currency, and agricultural). The oblast is noted for having relatively highly developed market relations.
Today, the region needs serious partners interested in equitable, long-term, mutually beneficial partnerships.
There are 650+ industrial companies in the region, most of them engaged in the following sectors:
*Machine-building and engineering
*Chemical & petrochemical
*Fuel & energy
*Ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy
*Construction materials
*Glass
*Wood and paper
*Cloth-making
*Food & food processing
*Medical & pharmaceuticals
*Printing & publishing.
*Peat extraction.
These key industries are supplemented by other sectors of the economy such as agriculture, trade, services, communications and transport.
Transportation
*The Altsevo peat narrow gauge railway is located in the work settlement of Pizhma *The Pizhemskaya narrow gauge railway is located in the work settlement of Pizhma *The narrow gauge railway of Caprolactam factory is located in Dzerzhinsk *The Kerzhenets peat narrow gauge railway is located in the Borsky District *Thenarrow gauge railway of Decor-1 factory
The Decor-1 factory railway is in the Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Russia. The railway was opened in 1946, and has a total length of its track gauge is . The railway is used for the transportation of gypsum from the mine to the «Dekor-1» factory.
...
is located in the Arzamassky District
Narrow gauge railways in the region:
References
Notes
Sources
*External links
*Official website of the Government of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast
Official website of the Legislative Assembly of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast
Nizhny Novgorod City Guide
Travel and business guide to Nizhny Novgorod
Central Eurasian Information Resource; Images of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast
– University of Washington Digital Collections {{Use mdy dates, date=February 2014 States and territories established in 1929 1936 establishments in the Soviet Union