Nisbis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Nusaybin (; '; ar, نُصَيْبِيْن, translit=Nuṣaybīn; syr, ܢܨܝܒܝܢ, translit=Nṣībīn), historically known as Nisibis () or Nesbin, is a city in
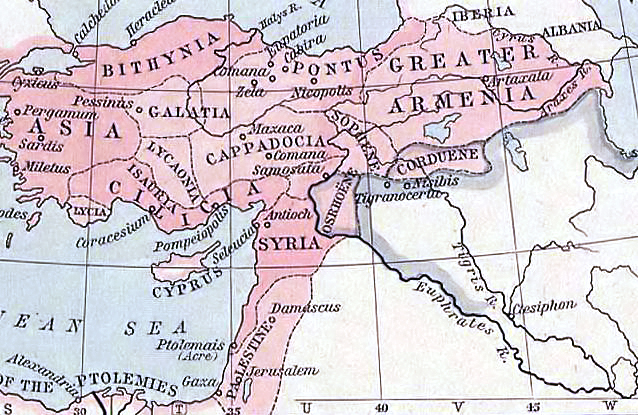 In 67 BCE, during Rome's first war with
In 67 BCE, during Rome's first war with 
 With the fresh energy of the new
With the fresh energy of the new
 On the eve of World War I, Nusaybin had a Christian community of 2000, along with a Jewish population of 600. A massacre of Christians took place in August 1915, after which the Christian community of Nusaybin diminished to 1200. Syrian Jacobites, Chaldean Catholics, Protestants, and Armenians were targeted.
As agreed upon by the governments of France and the new Republic of
On the eve of World War I, Nusaybin had a Christian community of 2000, along with a Jewish population of 600. A massacre of Christians took place in August 1915, after which the Christian community of Nusaybin diminished to 1200. Syrian Jacobites, Chaldean Catholics, Protestants, and Armenians were targeted.
As agreed upon by the governments of France and the new Republic of

 Nisibis ( syr, ܢܨܝܒܝܢ, ''Nṣibin'', later Syriac , ''Ṣōbā'') had an Assyrian people, Assyrian Christianity, Christian
Nisibis ( syr, ܢܨܝܒܝܢ, ''Nṣibin'', later Syriac , ''Ṣōbā'') had an Assyrian people, Assyrian Christianity, Christian
Nisibis
''Catholic Encyclopedia''
GCatholic, Armenian Catholic titular see
Turkish News - Latest News from Turkey
Hürriyet Daily News and Economic Review
The Battle of Nisibis, AD 217
{{Authority control Nusaybin, Archaeological sites in Southeastern Anatolia Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Turkey Seleucid colonies in Anatolia Roman legionary fortresses in Turkey Sasanian cities Catholic titular sees in Asia, Nisibis Towns in Turkey Assyrian communities in Turkey Populated places in Mardin Province Divided cities on the Turkish-Syrian border Syria–Turkey border crossings Districts of Mardin Province Mesopotamia (Roman province) Roman towns and cities in Turkey Kurdish settlements in Turkey
Mardin Province
Mardin Province ( tr, Mardin ili; ku, Parêzgeha Mêrdînê; ar, محافظة ماردين) is a province of Turkey with a population of 809,719 in 2017, slightly down from the population of 835,173 in 2000. Kurds form the majority of the popu ...
, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
. The population of the city is 83,832 as of 2009 and is predominantly Kurdish
Kurdish may refer to:
*Kurds or Kurdish people
*Kurdish languages
*Kurdish alphabets
*Kurdistan, the land of the Kurdish people which includes:
**Southern Kurdistan
**Eastern Kurdistan
**Northern Kurdistan
**Western Kurdistan
See also
* Kurd (dis ...
. Nusaybin is separated from the larger Kurdish-majority city of Qamishli
Qamishli ( ar, ٱلْقَامِشْلِي, Al-Qāmišlī, ku, قامشلۆ, Qamişlo, syc, ܒܝܬ ܙܠܝ̈ܢ, Bēṯ Zālīn, lit=House of Reeds or syr, ܩܡܫܠܐ, translit=Qamishlo)
by the Syria–Turkey border
The border between the Syrian Arab Republic and the Republic of Turkey ( ar, الحدود السورية التركية, translit=alhudud alsuwriat alturkia; tr, Suriye–Türkiye sınırı) is about long, and runs from the Mediterranean Sea ...
.
The city is at the foot of the Mount Izla
Mount Izla ( syr, ܛܘܪ ܐܝܙܠܐ ''Ṭūr Īzlā' ''),Thomas A. Carlson et al., “Izla — ܛܘܪܐ ܕܐܝܙܠܐ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modified January 14, 2014, http://syriaca.org/place/100. also Mountain of Nisibis or briefly ...
escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''escar ...
at the southern edge of the Tur Abdin
Tur Abdin ( syr, ܛܽܘܪ ܥܰܒ݂ܕܺܝܢ or ܛܘܼܪ ܥܲܒ݂ܕܝܼܢ, Ṭūr ʿAḇdīn) is a hilly region situated in southeast Turkey, including the eastern half of the Mardin Province, and Şırnak Province west of the Tigris, on the borde ...
hills, standing on the banks of the Jaghjagh River
The Jaghjagh River ( ar, نهر جقجق ''Nahr Jaqjaq'', ''Nahr al-Jaghjagh'', or ''Nahr al-Hirmas'', tr, Çağ-çağ Deresi, syr, ܢܗܕܐ ܕܔܩܔܩ ''Nahro dJaqjaq'', ku, Çemê Nisêbînê or Cexcex) is a tributary of the Khabur River in ...
(), the ancient Mygdonius ( grc, Μυγδόνιος). The city existed in the Assyrian Empire
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyr ...
and is recorded in Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo- syllabi ...
inscriptions as ''Naṣibīna''. Having been part of the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
, in the Hellenistic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 3 ...
the settlement was re-founded as a ''polis
''Polis'' (, ; grc-gre, πόλις, ), plural ''poleis'' (, , ), literally means "city" in Greek. In Ancient Greece, it originally referred to an administrative and religious city center, as distinct from the rest of the city. Later, it also ...
'' named "Antioch on the Mygdonius" by the Seleucid dynasty
The Seleucid dynasty or the Seleucidae (from el, Σελευκίδαι, ') was a Macedonian Greeks (ancient), Macedonian Greek royal family, founded by Seleucus I Nicator, which ruled the Seleucid Empire centered in the Near East and regions o ...
after the conquests of Alexander the Great
The wars of Alexander the Great were a series of conquests that were carried out by Alexander III of Macedon from 336 BC to 323 BC. They began with battles against the Achaemenid Persian Empire, then under the rule of Darius III of Persia. ...
. A part of first the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kin ...
and then the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
, the city (; ) was mainly Syriac Syriac may refer to:
*Syriac language, an ancient dialect of Middle Aramaic
*Sureth, one of the modern dialects of Syriac spoken in the Nineveh Plains region
* Syriac alphabet
** Syriac (Unicode block)
** Syriac Supplement
* Neo-Aramaic languages a ...
-speaking, and control of it was contested between the Kingdom of Armenia, the Romans, and the Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conque ...
. After a peace treaty contracted between the Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
and the Romans in 298 and enduring until 337, Nisibis was capital of Roman Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia was the name of a Roman province, initially a short-lived creation of the Roman emperor Trajan in 116–117 and then re-established by Emperor Septimius Severus in c. 198. Control of the province was subsequently fought over betwe ...
and the seat of its governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
(). Jacob of Nisibis
Saint Jacob of Nisibis ( syr, ܝܥܩܘܒ ܢܨܝܒܢܝܐ, '; Greek: Ἅγιος Ἰάκωβος Ἐπίσκοπος Μυγδονίας; Armenian: Յակոբ Մծբնայ, '), also known as Saint Jacob of Mygdonia, Saint Jacob the Great, and Saint J ...
, the city's first known bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ca ...
, constructed its first cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the '' cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denomination ...
between 313 and 320. Nisibis was a focus of international trade, and according to the Greek history of Peter the Patrician, the primary point of contact between Roman and Persian empires.
Nisibis was besieged three times by the Sasanian army
The Sasanian army was the primary military body of the Sasanian armed forces, serving alongside the Sasanian navy. The birth of the army dates back to the rise of Ardashir I (r. 224–241), the founder of the Sasanian Empire, to the throne. A ...
under Shapur II
Shapur II ( pal, 𐭱𐭧𐭯𐭥𐭧𐭥𐭩 ; New Persian: , ''Šāpur'', 309 – 379), also known as Shapur the Great, was the tenth Sasanian King of Kings (Shahanshah) of Iran. The longest-reigning monarch in Iranian history, he reigned fo ...
() in the first half of the 4th century; each time, the city's fortifications held. The Syriac poet Ephrem the Syrian
Ephrem the Syrian ( syc, ܡܪܝ ܐܦܪܝܡ ܣܘܪܝܝܐ, Mār ʾAp̄rêm Sūryāyā, ; grc-koi, Ἐφραὶμ ὁ Σῦρος, Efrém o Sýros; la, Ephraem Syrus; am, ቅዱስ ኤፍሬም ሶርያዊ; ), also known as Saint Ephrem, Saint ...
witnessed all three sieges, and praised Nisibis's successive bishops for their contributions to the defences in his , while the Roman ''caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman people, Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caes ...
'' Julian () described the third siege in his panegyric to his senior co-emperor, the ''augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
'' Constantius II
Constantius II (Latin: ''Flavius Julius Constantius''; grc-gre, Κωνστάντιος; 7 August 317 – 3 November 361) was Roman emperor from 337 to 361. His reign saw constant warfare on the borders against the Sasanian Empire and Germani ...
(). The Roman soldier and Latin historian Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus (occasionally Anglicisation, anglicised as Ammian) (born , died 400) was a Roman soldier and historian who wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from Ancient history, antiquity (preceding Procopius). His w ...
described Nisibis, fortified with walls, towers, and a citadel, as "the strongest bulwark of the Orient".
After the defeat of the Romans in Julian's Persian War
Julian's Persian expedition was the last military undertaking of the Roman emperor Julian which began in March 363. It was a war against the Sasanian Empire which was ruled by Shapur II.
Aiming for the Sasanian winter capital Ctesiphon, Julia ...
, Julian's successor Jovian
Jovian is the adjectival form of Jupiter and may refer to:
* Jovian (emperor) (Flavius Iovianus Augustus), Roman emperor (363–364 AD)
* Jovians and Herculians, Roman imperial guard corps
* Jovian (lemur), a Coquerel's sifaka known for ''Zoboomafo ...
() was forced to cede the five Transtigritine provinces to the Persians, including Nisibis. The city was evacuated and its citizens forced to migrate to Amida (Diyarbakır
Diyarbakır (; ; ; ) is the largest Kurdish-majority city in Turkey. It is the administrative center of Diyarbakır Province.
Situated around a high plateau by the banks of the Tigris river on which stands the historic Diyarbakır Fortress, ...
) – which was expanded to accommodate them – and to Edessa
Edessa (; grc, Ἔδεσσα, Édessa) was an ancient city (''polis'') in Upper Mesopotamia, founded during the Hellenistic period by King Seleucus I Nicator (), founder of the Seleucid Empire. It later became capital of the Kingdom of Osroene ...
(Urfa
Urfa, officially known as Şanlıurfa () and in ancient times as Edessa, is a city in southeastern Turkey and the capital of Şanlıurfa Province. Urfa is situated on a plain about 80 km east of the Euphrates River. Its climate features e ...
). According to the Latin historian Eutropius, the cession of Nisibis was supposed to last 120 years. Nisibis remained a major entrepôt
An ''entrepôt'' (; ) or transshipment port is a port, city, or trading post where merchandise may be imported, stored, or traded, usually to be exported again. Such cities often sprang up and such ports and trading posts often developed into c ...
; one of only three such cities of commercial exchange allowed by Roman law
Roman law is the law, legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables (c. 449 BC), to the ''Corpus Juris Civilis'' (AD 529) ordered by Eastern Roman emperor J ...
promulgated in 408/9. However, despite several Roman attempts to recapture Nisibis through the remainder of the Roman–Persian Wars
The Roman–Persian Wars, also known as the Roman–Iranian Wars, were a series of conflicts between states of the Greco-Roman world and two successive Iranian empires: the Parthian and the Sasanian. Battles between the Parthian Empire and the ...
and the construction of nearby Dara
Dara is a given name used for both males and females, with more than one origin. Dara is found in the Bible's Old Testament Books of Chronicles. Dara �רעwas a descendant of Judah (son of Jacob). (The Bible. 1 Chronicles 2:6). Dara (also known ...
to defend against Persian attack, Nisibis was not returned to Roman control before it was conquered in 639 by the Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate ( ar, اَلْخِلَافَةُ ٱلرَّاشِدَةُ, al-Khilāfah ar-Rāšidah) was the first caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was ruled by the first four successive caliphs of Muhammad after his ...
during the Muslim conquest of the Levant
The Muslim conquest of the Levant ( ar, فَتْحُ الشَّام, translit=Feth eş-Şâm), also known as the Rashidun conquest of Syria, occurred in the first half of the 7th century, shortly after the rise of Islam."Syria." Encyclopædia Br ...
.
Under Sasanian rule and after, Nisibis was a major centre of the Christian Church
In ecclesiology, the Christian Church is what different Christian denominations conceive of as being the true body of Christians or the original institution established by Jesus. "Christian Church" has also been used in academia as a synonym fo ...
, and the bishop of Nisibis attended the Council of Seleucia-Ctesiphon
The Council of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, also called the Council of Mar Isaac, met in AD 410 in Seleucia-Ctesiphon, the capital of the Persian Sassanid Empire. Convoked by King Yazdegerd I (399–421), it organized the Christians of his empire into a ...
convened in 410 by the emperor Yazdegerd I
Yazdegerd I (also spelled Yazdgerd and Yazdgird; pal, 𐭩𐭦𐭣𐭪𐭥𐭲𐭩) was the Sasanian King of Kings () of Iran from 399 to 420. A son of Shapur III (), he succeeded his brother Bahram IV () after the latter's assassination.
Yazde ...
(). As a result of this council, the Church of the East
The Church of the East ( syc, ܥܕܬܐ ܕܡܕܢܚܐ, ''ʿĒḏtā d-Maḏenḥā'') or the East Syriac Church, also called the Church of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, the Persian Church, the Assyrian Church, the Babylonian Church or the Nestorian C ...
was set up, and the bishop of Nisibis became the metropolitan bishop
In Christian churches with episcopal polity, the rank of metropolitan bishop, or simply metropolitan (alternative obsolete form: metropolite), pertains to the diocesan bishop or archbishop of a metropolis.
Originally, the term referred to the b ...
of the five erstwhile Transtigritine provinces. Narsai
Narsai (sometimes spelt ''Narsay'', ''Narseh'' or ''Narses''; syc, ܢܪܣܝ, ''Narsai'', name derived from Pahlavi ''Narsēh'' from Avestan ''Nairyō.saȵhō'', meaning 'potent utterance', the name of a yazata; ) was one of the foremost of Assy ...
, formerly a theologian at the School of Edessa
The School of Edessa ( syr, ܐܣܟܘܠܐ ܕܐܘܪܗܝ) was a Christian theological school of great importance to the Syriac-speaking world. It had been founded as long ago as the 2nd century by the kings of the Abgar dynasty. In 363, Nisibis fell t ...
, founded the famous School of Nisibis
The School of Nisibis ( syr, ܐܣܟܘܠܐ ܕܢܨܝܒܝܢ, for a time absorbed into the School of Edessa) was an educational establishment in Nisibis (now Nusaybin, Turkey). It was an important spiritual centre of the early Church of the East, and ...
with the bishop, Barsauma
Barsauma ( syr, ܒܪܨܘܡܐ, ''Barṣaumâ''), nicknamed ''Bar Sawma'', "son of the Lent" in Syriac, was Metropolitan of Nisibis in the 5th century, and a major figure in the history of the Church of the East. Under his leadership the church mo ...
, in the 470s. When the Roman emperor Zeno
Zeno ( grc, Ζήνων) may refer to:
People
* Zeno (name), including a list of people and characters with the name
Philosophers
* Zeno of Elea (), philosopher, follower of Parmenides, known for his paradoxes
* Zeno of Citium (333 – 264 BC), ...
() closed the School of Edessa in 489, the scholars migrated to Nisibis's school and established the city as the foremost centre of Christian thought in the Church of the East. According to the Damascene Damascene may refer to:
* Topics directly associated with the city of Damascus in Syria:
** A native or inhabitant of Damascus
** Damascus Arabic, the local dialect of Damascus
** Damascus steel, developed for swordmaking
** "Damascene moment", the ...
monk John Moschus
John Moschus ( el, Ἰωάννης Μόσχος, c. 550 – 619; name from the grc, ὁ τοῦ Μόσχου, o tou Moschou, (son) of Moschos, was a Byzantine monk and ascetical writer.
Biography
He was born about 550 probably at Damascus. He ...
, the city's cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the '' cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denomination ...
had five doors in the 7th century, and the monastic and later bishop of Harran
Harran (), historically known as Carrhae ( el, Kάρραι, Kárrhai), is a rural town and district of the Şanlıurfa Province in southeastern Turkey, approximately 40 kilometres (25 miles) southeast of Urfa and 20 kilometers from the border cr ...
, Symeon of the Olives, was recorded as having renewed several ecclesiastical buildings in the early period of Arab rule. The monasteries
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which ...
of the nearby Tur Abdin, led by the reforms of Abraham the Great of Kashkar
Abraham the Great of Kashkar was the father of the Assyrian monastic revival in the 6th century. He is a doctor and saint of the Assyrian Church of the East.
He was born in Kashkar in Persia around 492. He left there to preach the Gospel at Al ...
, founder of the "Great Monastery" of Mount Izla, underwent substantial revival in the years after the Muslim conquest. However, besides the baptistery
In Christian architecture the baptistery or baptistry (Old French ''baptisterie''; Latin ''baptisterium''; Greek , 'bathing-place, baptistery', from , baptízein, 'to baptize') is the separate centrally planned structure surrounding the baptismal ...
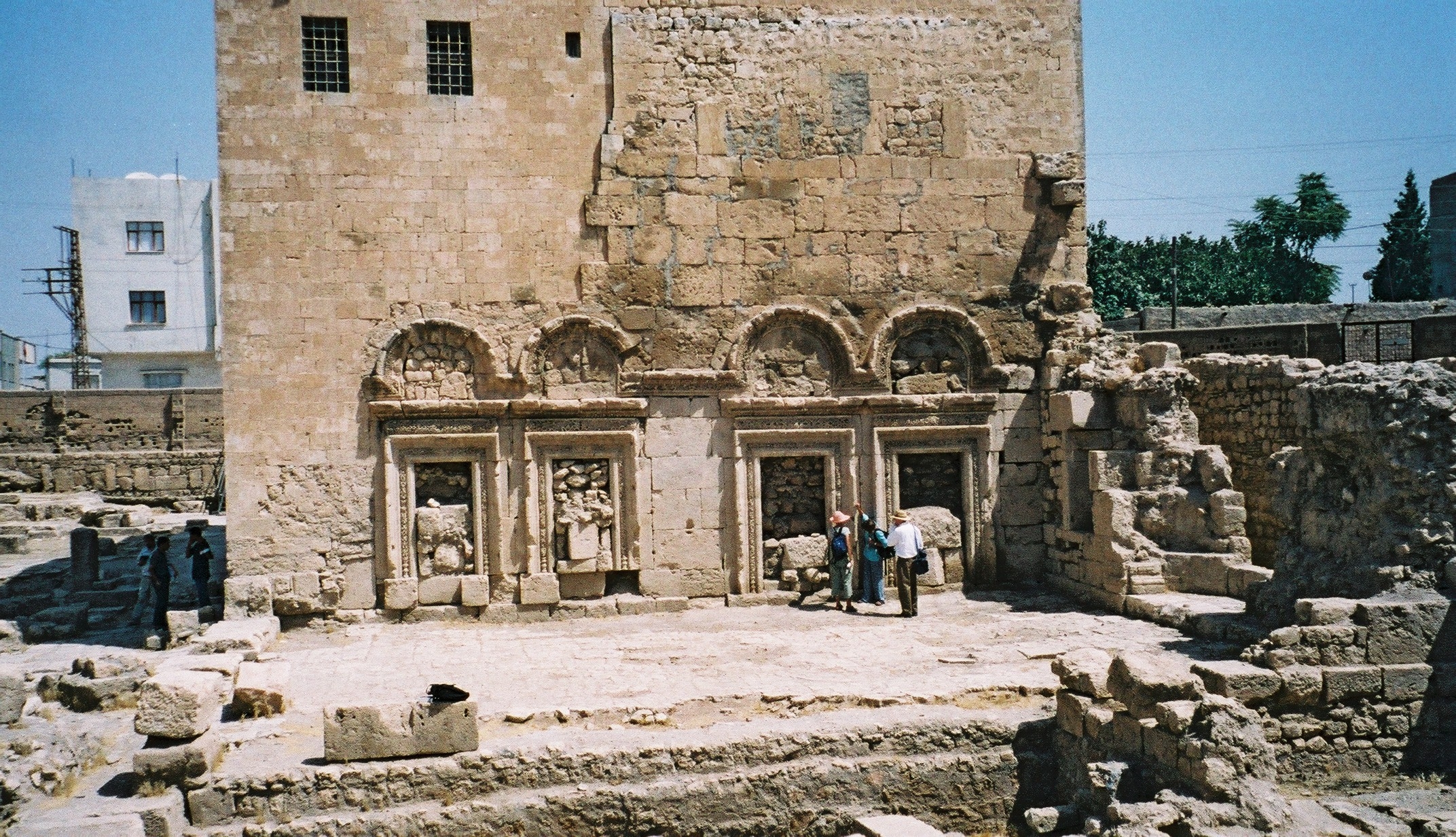
known as the Church of Saint Jacob (''Mar Ya‘qub'') and built in 359 by bishop Vologeses, little remains of ancient Nisibis, probably because of ruinous earthquake in 717. Archaeological excavations
In archaeology, excavation is the exposure, processing and recording of archaeological remains. An excavation site or "dig" is the area being studied. These locations range from one to several areas at a time during a project and can be condu ...
were conducted in the vicinity of the 4th-century baptistery in the early 21st century, revealing various buildings including the 4th-century cathedral.
History
Antiquity
First mentioned in 901 BCE, Naṣibīna was anAramean
The Arameans ( oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; syc, ܐܪ̈ܡܝܐ, Ārāmāyē) were an ancient Semitic-speaking people in the Near East, first recorded in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. The Aramean ...
kingdom captured by the Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
n king Adad-Nirari II
Adad-nirari II (reigned from 911 to 891 BC) was the first King of Assyria in the Neo-Assyrian period.
Biography
Adad-nirari II's father was Ashur-dan II, whom he succeeded after a minor dynastic struggle. It is probable that the accession encour ...
in 896. By 852 BCE, Naṣibīna had been fully annexed to the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
and appeared in the Assyrian Eponym List as the seat of an Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
n provincial governor named Shamash-Abua.
It was under Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
n control until 536 BCE, when it fell to the Achaemenid Persians, and remained so until taken by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
in 332 BCE.
Hellenistic period
The Seleucids re-founded the city as Antiochia Mygdonia ( el, Ἀντιόχεια τῆς Μυγδονίας), mentioned for the first time inPolybius
Polybius (; grc-gre, Πολύβιος, ; ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , which covered the period of 264–146 BC and the Punic Wars in detail.
Polybius is important for his analysis of the mixed ...
' description of the march of Antiochus III the Great
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the re ...
against Molon
Molon ( or ) or Molo (; grc, Mόλων; died 220 BC) was a general and satrap of the Seleucid king Antiochus the Great (223–187 BC). He held the satrapy of Media at the accession of that monarch (223 BC); in addition to which, Antiochus c ...
(Polybius
Polybius (; grc-gre, Πολύβιος, ; ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , which covered the period of 264–146 BC and the Punic Wars in detail.
Polybius is important for his analysis of the mixed ...
, V, 51). The Greek historian Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''P ...
suggested that the city was populated by descendants of Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
ns. Around the 1st century CE, Nisibis ( he, נציבין, translit=Netzivin) was the home of Judah ben Bethera, who founded a famous yeshiva
A yeshiva (; he, ישיבה, , sitting; pl. , or ) is a traditional Jewish educational institution focused on the study of Rabbinic literature, primarily the Talmud and halacha (Jewish law), while Torah and Jewish philosophy are s ...
there.
 In 67 BCE, during Rome's first war with
In 67 BCE, during Rome's first war with Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''Ox ...
, the Roman general Lucullus
Lucius Licinius Lucullus (; 118–57/56 BC) was a Roman general and statesman, closely connected with Lucius Cornelius Sulla. In culmination of over 20 years of almost continuous military and government service, he conquered the eastern kingd ...
took Nisibis () from the brother of Tigranes
Tigranes (, grc, Τιγράνης) is the Greek transliteration of the Old Iranian name ''*Tigrāna''. This was the name of a number of historical figures, primarily kings of Armenia.
The name of Tigranes, which was theophoric in nature, was u ...
.
Like many other cities in the marches
In medieval Europe, a march or mark was, in broad terms, any kind of borderland, as opposed to a national "heartland". More specifically, a march was a border between realms or a neutral buffer zone under joint control of two states in which diff ...
where Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
and Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
n powers confronted one another, Nisibis was often taken and retaken. In 115 CE, it was captured by the Roman Emperor Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
, for which he gained the name of ''Parthicus'', then lost to and regained from the Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
during the Kitos War
The Kitos War (115–117; he, מרד הגלויות, mered ha-galuyot, or ''mered ha-tfutzot''; "rebellion of the diaspora" la, Tumultus Iudaicus) was one of the major Jewish–Roman wars (66–136). The rebellions erupted in 115, when most ...
. After the Romans again lost the city in 194, it was once more conquered by Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa (Roman province), Africa. As a young man he advanced thro ...
, who made it his headquarters and re-established a colony there. The last battle between Rome and Parthia was fought in the vicinity of the city in 217.

Late Antiquity
 With the fresh energy of the new
With the fresh energy of the new Sassanid dynasty
The Sasanian dynasty was the house that founded the Sasanian Empire, ruling this empire from 224 to 651 AD in Persia (modern-day Iran). It began with Ardashir I, who named the dynasty as ''Sasanian'' in honour of his grandfather (or father), Sasa ...
, Shapur I
Shapur I (also spelled Shabuhr I; pal, 𐭱𐭧𐭯𐭥𐭧𐭥𐭩, Šābuhr ) was the second Sasanian King of Kings of Iran. The dating of his reign is disputed, but it is generally agreed that he ruled from 240 to 270, with his father Ardas ...
conquered Nisibis, was driven out, and returned in the 260s. In 298, by a treaty
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations
An international organization or international o ...
with Narseh
Narseh (also spelled Narses or Narseus; pal, 𐭭𐭥𐭮𐭧𐭩, New Persian: , ''Narsē'') was the seventh Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 293 to 303.
The youngest son of Shapur I (), Narseh served as the governor of Sakastan, Hind and ...
, the province of Nisibis was acquired by the Roman Empire.
During the Roman–Persian Wars (337–363 CE) Nisibis was unsuccessfully besieged by the Sassanid Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
thrice, in 337, 346 and 350. According to the ''Expositio totius mundi et gentium Expositio totius mundi et gentium ("A description of the world and its people") refers to a brief "commercial-geographical" survey written by an anonymous citizen of the Roman Empire living during the reign of Constantius II. The Greek original, co ...
'' bronze and iron were forbidden to be exported to the Persians, but for other goods, Nisibis was the site of substantial trade across the Roman–Persian frontier.
Upon the death of Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christiani ...
in 337 CE, the Sassanid Shah
Shah (; fa, شاه, , ) is a royal title that was historically used by the leading figures of Iranian monarchies.Yarshater, EhsaPersia or Iran, Persian or Farsi, ''Iranian Studies'', vol. XXII no. 1 (1989) It was also used by a variety of ...
Shapur II
Shapur II ( pal, 𐭱𐭧𐭯𐭥𐭧𐭥𐭩 ; New Persian: , ''Šāpur'', 309 – 379), also known as Shapur the Great, was the tenth Sasanian King of Kings (Shahanshah) of Iran. The longest-reigning monarch in Iranian history, he reigned fo ...
marched against Roman held Nisibis with a vast army composed of cavalry, infantry and elephants. His combat engineers raised siege works, including towers, so his archers could rain down arrows at the defenders. They also undermined the walls, dammed the Mygdonius River and constructed dikes to direct the river against the walls. On the seventieth day of the siege, the water was released and the torrent struck the walls; entire sections of the city walls collapsed. The water passed through the city and knocked down a section of the opposite wall as well. The Persians were unable to assault the city because the approaches to the breaches were impassable due to floodwater, mud and debris. The soldiers and citizens inside the city worked all night and by dawn the breaches were closed with makeshift barriers. Shapur's assault troops attacked the breaches, but their assault was repulsed. A few days later the Persian lifted the siege.
Nisibis was besieged a second time in 346 CE. The details of the second siege have not survived. Shapur besieged the city for seventy-eight days and then lifted the siege.
In 350 CE, while the Roman Emperor Constantius II
Constantius II (Latin: ''Flavius Julius Constantius''; grc-gre, Κωνστάντιος; 7 August 317 – 3 November 361) was Roman emperor from 337 to 361. His reign saw constant warfare on the borders against the Sasanian Empire and Germani ...
was engaged in a civil war against the usurper Magnentius
Magnus Magnentius ( 303 – 11 August 353) was a Roman general and usurper against Constantius II from 350 to 353. Of Germanic descent, Magnentius served with distinction in Gaul under the Western emperor Constans. On 18 January 350 Magnentius ...
in the West, the Persians invaded and laid siege to Nisibis for the third time. The siege lasted between 100 and 160 days. The Persian engineers tried several innovative siege technics; using the River Mygdonius to bring down a section of the walls, and creating a lake around the city and using boats with siege engines to bring down another section. Unlike the first siege, as the walls fell, Persian assault troops immediately entered the breaches supported by war elephants. Despite all this they failed to break through the breaches and the attack stalled. The Romans, experts at close-quarter combat, and supported by arrows and bolts from the walls and towers checked the assault and a sortie from one of the gates forced the Persians to withdraw. Shortly after the Persian Army, suffering heavy casualties from combat and disease, lifted the siege and withdrew.
The Roman historian of the 4th century, Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus (occasionally Anglicisation, anglicised as Ammian) (born , died 400) was a Roman soldier and historian who wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from Ancient history, antiquity (preceding Procopius). His w ...
, gained his first practical experience of warfare as a young man at Nisibis under the ''magister equitum
The , in English Master of the Horse or Master of the Cavalry, was a Roman magistrate appointed as lieutenant to a dictator. His nominal function was to serve as commander of the Roman cavalry in time of war, but just as a dictator could be nomi ...
'', Ursicinus. From 360 to 363, Nisibis was the camp of Legio I Parthica
Legio I ''Parthica'' (Latin language, Latin for "1st Parthian Legion") was a Roman legion, legion of the Imperial Roman army founded in AD 197 by the emperor Septimius Severus (r. 193–211) for his forthcoming war against Parthia. The legion's ...
. Because of its strategic importance on the Persian border, Nisibis was heavily fortified. Ammianus lovingly calls Nisibis the "impregnable city" (''urbs inexpugnabilis'') and "bulwark of the provinces" (''murus provinciarum'').
Sozomen
Salamanes Hermias Sozomenos ( grc-gre, Σαλαμάνης Ἑρμείας Σωζομενός; la, Sozomenus; c. 400 – c. 450 AD), also known as Sozomen, was a Roman lawyer and historian of the Christian Church.
Family and home
He was born arou ...
writes that when the inhabitants of Nisibis asked for help because the Persians were about to invade the Roman territories and attack them, Emperor Julian refused to assist them because they were Christianized
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
, and he told them that he would not help them if they did not return to paganism.
In 363 Nisibis was ceded to the Sassanian Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
after the defeat of Julian. Before that time the population of the town was forced by the Roman authorities to leave Nisibis and move to Amida. Emperor Jovian
Jovian is the adjectival form of Jupiter and may refer to:
* Jovian (emperor) (Flavius Iovianus Augustus), Roman emperor (363–364 AD)
* Jovians and Herculians, Roman imperial guard corps
* Jovian (lemur), a Coquerel's sifaka known for ''Zoboomafo ...
allowed them only three days for the evacuation. Historian Ammianus Marcellinus was again an eyewitness and condemns Emperor Jovian for giving up the fortified town without a fight. Marcellinus' point-of-view is certainly in line with contemporary Roman public opinion.
According to Al-Tabari
( ar, أبو جعفر محمد بن جرير بن يزيد الطبري), more commonly known as al-Ṭabarī (), was a Muslim historian and scholar from Amol, Tabaristan. Among the most prominent figures of the Islamic Golden Age, al-Tabari ...
, some 12,000 Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
of good lineage from Istakhr
Istakhr (Middle Persian romanized: ''Stakhr'', fa, اصطخر, translit=Istakhr also spelt استخر in modern literature) was an ancient city in Fars province, north of Persepolis in southwestern Iran. It flourished as the capital of the Persi ...
, Isfahan
Isfahan ( fa, اصفهان, Esfahân ), from its Achaemenid empire, ancient designation ''Aspadana'' and, later, ''Spahan'' in Sassanian Empire, middle Persian, rendered in English as ''Ispahan'', is a major city in the Greater Isfahan Regio ...
, and other regions settled at Nisibis in the fourth century, and their descendants were still there at the beginning of the seventh century.
The School of Nisibis
The School of Nisibis ( syr, ܐܣܟܘܠܐ ܕܢܨܝܒܝܢ, for a time absorbed into the School of Edessa) was an educational establishment in Nisibis (now Nusaybin, Turkey). It was an important spiritual centre of the early Church of the East, and ...
, founded at the introduction of Christianity into the city by ethnic Assyrians of the Assyrian Church of the East
The Assyrian Church of the East,, ar, كنيسة المشرق الآشورية sometimes called Church of the East, officially the Holy Apostolic Catholic Assyrian Church of the East,; ar, كنيسة المشرق الآشورية الرسول� ...
, was closed when the province was ceded to the Persians. Ephrem the Syrian
Ephrem the Syrian ( syc, ܡܪܝ ܐܦܪܝܡ ܣܘܪܝܝܐ, Mār ʾAp̄rêm Sūryāyā, ; grc-koi, Ἐφραὶμ ὁ Σῦρος, Efrém o Sýros; la, Ephraem Syrus; am, ቅዱስ ኤፍሬም ሶርያዊ; ), also known as Saint Ephrem, Saint ...
, an Assyrian poet, commentator, preacher and defender of orthodoxy, joined the general exodus of Christians and re-established the school on more securely Roman soil at Edessa
Edessa (; grc, Ἔδεσσα, Édessa) was an ancient city (''polis'') in Upper Mesopotamia, founded during the Hellenistic period by King Seleucus I Nicator (), founder of the Seleucid Empire. It later became capital of the Kingdom of Osroene ...
. In the fifth century, the school became a center of Nestorian Christianity
The Church of the East ( syc, ܥܕܬܐ ܕܡܕܢܚܐ, ''ʿĒḏtā d-Maḏenḥā'') or the East Syriac Church, also called the Church of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, the Persian Church, the Assyrian Church, the Babylonian Church or the Nestorian C ...
, and was closed down by Archbishop Cyrus in 489. The expelled masters and pupils withdrew once more, back to Nisibis, under the care of Barsauma
Barsauma ( syr, ܒܪܨܘܡܐ, ''Barṣaumâ''), nicknamed ''Bar Sawma'', "son of the Lent" in Syriac, was Metropolitan of Nisibis in the 5th century, and a major figure in the history of the Church of the East. Under his leadership the church mo ...
, who had been trained at Edessa, under the patronage of Narses, who established the statutes of the new school. Those that have been discovered and published belong to Osee, the successor of Barsauma in the See of Nisibis, and bear the date 496; they must be substantially the same as those of 489. In 590, they were again modified. The monastery school was under a superior called ''Rabban'' ("master"), a title also given to the instructors. The administration was confided to a major-domo, who was steward, prefect of discipline and librarian, but under the supervision of a council. Unlike the Jacobite schools, devoted chiefly to profane studies, the School of Nisibis was above all a school of theology. The two chief masters were the instructors in reading and in the interpretation of Holy Scripture, explained chiefly with the aid of Theodore of Mopsuestia. The free course of studies lasted three years, the students providing for their own support. During their sojourn at the university, masters and students led a monastic life under somewhat special conditions. The school had a tribunal and enjoyed the right of acquiring all sorts of property. Its rich library possessed a most beautiful collection of Nestorian works; from its remains Ebed-Jesus, Bishop of Nisibis in the 14th century, composed his celebrated catalogue of ecclesiastical writers. The disorders and dissensions, which arose in the sixth century in the school of Nisibis, favoured the development of its rivals, especially that of Seleucia; however, it did not really begin to decline until after the foundation of the School of Baghdad (832). Notable people associated with the school include its founder Narses; Abraham, his nephew and successor; Abraham the Great of Kaskhar, Abraham of Kashgar, the restorer of monastic life; and ArchbishopElijah of Nisibis.
As a fortified frontier city, Nisibis played a major role in the Roman-Persian Wars. It became the capital of the newly created province of Mesopotamia after Diocletian's organization of the eastern Roman frontier. It became known as the "Shield of the Empire" after a successful resistance in 337–350. The city changed hands several times, and once in Sasanian hands, Nisibis was the base of operations against the Romans. The city was also one of the main crossing points for merchants, although elaborate counter-espionage safeguards were also in place.
Islamic period
The city was taken without resistance by the forces of theRashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate ( ar, اَلْخِلَافَةُ ٱلرَّاشِدَةُ, al-Khilāfah ar-Rāšidah) was the first caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was ruled by the first four successive caliphs of Muhammad after his ...
under Umar in 639 or 640. Under early Islamic rule, the city served as a local administrative centre. In 717, it was struck by an earthquake and in 927 it was Qarmatian invasion of Iraq, raided by the Qarmatians. Nisibis was captured in 942 by the Byzantine Empire but was subsequently recaptured by the Hamdanid dynasty. It was attacked by the Byzantines once again in 972. Following the Hamdanids, the city was administered by the Marwanids (Diyar Bakr), Marwanids and the Uqaylid dynasty, Uqaylids. From the middle of the 11th century onwards, it was subjected to Turkish raids and being threatened by the County of Edessa, being attacked and damaged by Seljuq Empire, Seljuq forces under Tughril in 1043. The city nevertheless remained an important centre of commerce and transport.
In 1120, it was captured by the Artuqids under Ilghazi, Necmeddin Ilgazi, followed by the Zengid dynasty, Zengids and Ayyubid dynasty, Ayyubids. The city is described as a very prosperous one by the period's Arab geographers and historians, with imposing baths, walls, lavish houses, a bridge and a hospital. In 1230, the city was invaded by the Mongol Empire. Mongol sovereignty was followed by that of the Ag Qoyunlu, Kara Koyunlu and Safavids. In 1515, it was taken by the Ottoman Empire under Selim I thanks to the efforts of Idris Bitlisi.
Modern history
 On the eve of World War I, Nusaybin had a Christian community of 2000, along with a Jewish population of 600. A massacre of Christians took place in August 1915, after which the Christian community of Nusaybin diminished to 1200. Syrian Jacobites, Chaldean Catholics, Protestants, and Armenians were targeted.
As agreed upon by the governments of France and the new Republic of
On the eve of World War I, Nusaybin had a Christian community of 2000, along with a Jewish population of 600. A massacre of Christians took place in August 1915, after which the Christian community of Nusaybin diminished to 1200. Syrian Jacobites, Chaldean Catholics, Protestants, and Armenians were targeted.
As agreed upon by the governments of France and the new Republic of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
in the 1923 Treaty of Lausanne, the Turkey-Syria border would follow the line of the Baghdad Railway until Nusaybin, after which it would follow the path of a Roman road leading to Cizre. After the establishment of the French Mandate for Syria and Lebanon, Nusaybin lost over 60% of its population to the settlements there, most prominently Qamishli
Qamishli ( ar, ٱلْقَامِشْلِي, Al-Qāmišlī, ku, قامشلۆ, Qamişlo, syc, ܒܝܬ ܙܠܝ̈ܢ, Bēṯ Zālīn, lit=House of Reeds or syr, ܩܡܫܠܐ, translit=Qamishlo)
.
Nusaybin was a place on the transit routes of Syrian Jews leaving the country after the 1948 formation of Israel and the subsequent Jewish exodus from Arab and Muslim countries. Upon reaching Turkey, after a route that took them through Aleppo and the Jazira Canton, Jazira sometimes with the help of Bedouin smugglers, most headed for Israel. There had been a large Jewish community in Nisbis since antiquity, many of whom moved to Qamishli in the early 20th century for economic reasons. A synagogue in Jerusalem practises the Nisibis and Qamishli rites today.
21st century
Nusaybin made headlines in 2006 when villagers near Kuru uncovered a mass grave, suspected of belonging to Ottoman Armenians and Assyrian people, Assyrians killed during the Armenian genocide, Armenian and Assyrian genocides. Swedish historian David Gaunt visited the site to investigate its origins, but left after finding evidence of tampering. Gaunt, who has studied 150 massacres carried out in the summer of 1915 in Mardin, said that the Committee of Union and Progress's governor for Mardin, Halil Edip, had likely ordered the massacre on 14 June 1915, leaving 150 Armenians and 120 Assyrians dead. The settlement was then known asDara
Dara is a given name used for both males and females, with more than one origin. Dara is found in the Bible's Old Testament Books of Chronicles. Dara �רעwas a descendant of Judah (son of Jacob). (The Bible. 1 Chronicles 2:6). Dara (also known ...
(now Oğuz). Gaunt added that the death squad, named ''El-Hamşin'' (meaning "fifty men"), was headed by officer Refik Nizamettin Kaddur. The president of the Turkish Historical Society, Yusuf Halaçoğlu, following the Turkish government's policy of Armenian genocide denial, said that the remains dated back to Roman times. ''Özgür Gündem'' reported that the Turkish military and police pressed the Turkish media not to report the discovery.
The Turkish Interior Ministry looked into dissolving Nusaybin city council in 2012 after it decided to use Arabic, Armenian language, Armenian, Aramaic, and Kurmanji on signposts in the town, in addition to the Turkish language.
= Tensions and violence
= In November 2013, Nusaybin's mayor, Ayşe Gökkan, commenced a hunger strike to protest against the construction of a wall between Nusaybin and the neighboring Kurdish-majority city ofQamishli
Qamishli ( ar, ٱلْقَامِشْلِي, Al-Qāmišlī, ku, قامشلۆ, Qamişlo, syc, ܒܝܬ ܙܠܝ̈ܢ, Bēṯ Zālīn, lit=House of Reeds or syr, ܩܡܫܠܐ, translit=Qamishlo)
in Syria. Construction of the wall stopped as a result of this and other protests.
On 13 November 2015, the town was placed under a curfew by the Turkish government, and Ali Atalan and Gülser Yıldırım, two elected members of the Grand National Assembly of Turkey, Grand National Assembly from the pro-Kurdish Peoples' Democratic Party (Turkey), Peoples' Democratic Party (HDP), began a hunger strike in protest. Two civilians and ten Kurdistan Workers' Party, PKK Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present), fighters were killed by security forces in the ensuing unrest. By March 2016, PKK forces controlled about half of Nusaybin according to ''Al-Masdar News'' and the Civil Protection Units, YPS controlled "much" of it, according to ''The Independent''. The Turkish state imposed eight successive curfews over several months and employed the use of heavy weapons in defeating the Kurdish militants, resulting in large swathes of Nusaybin being destroyed. 61 members of the security forces had been killed by May 2016. By 9 April, 60,000 residents of the city had been displaced, yet 30,000 civilians remained in the city, including in the six neighborhoods where fighting continued. YPS reportedly had 700–800 militants in the city, of which the Turkish army claimed that 325 were "neutralised" by 4 May. A curfew was in place between 14 March and 25 July in the majority of the town. After the fighting ended in a Turkish Army victory, in late September 2016 the Turkish government began demolishing a quarter of the city's residential buildings. This rendered 30,000 citizens homeless and caused a mass evacuation of tens of thousands of residents to neighboring towns and villages. Over 6,000 houses were bulldozed. After demolition was completed in March 2017, over one hundred apartment towers were built. The Turkish government offered to compensate homeowners at 12% of the value of their destroyed houses if they agreed to certain relocation conditions.
Economy
As a result of Turkish government policy to close all border crossings with the Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria, the city's border with Syria (i.e. the large Syrian city of Qamishli) has been closed, with claims that the cessation in smuggling has led to a 90% rise in unemployment in the city.Transportation
Nusaybin is served by the European route E90, E90 roadway and other roads to surrounding towns. The Nusaybin Railway Station is served by two daily trains. The closest airport is Qamishli Airport five kilometers to the south, in Qamishli in Syria. The closest Turkish airport is Mardin Airport, 55 kilometers northwest of Nusaybin.Geography
Nusaybin is on the north side of the Syria-Turkey border, which divides it from the city of Qamishli. TheJaghjagh River
The Jaghjagh River ( ar, نهر جقجق ''Nahr Jaqjaq'', ''Nahr al-Jaghjagh'', or ''Nahr al-Hirmas'', tr, Çağ-çağ Deresi, syr, ܢܗܕܐ ܕܔܩܔܩ ''Nahro dJaqjaq'', ku, Çemê Nisêbînê or Cexcex) is a tributary of the Khabur River in ...
flows through both cities. The Nusaybin side of the border has a minefield, with a total of some 600,000 landmines having been set by the Turkish Armed Forces since the 1950s. Located to the east is Mount Judi, which people (including Muslims) consider to be the place where the Noah's Ark, ark of Noah in Islam, Nuh or Noah (who is regarded as a ''Prophets and messengers in Islam, Nabi'' or Prophet in Abrahamic religions) came to rest. In fact, some people from Nusaybin are reported to have gone to the mountain, in search of the ark.

Climate
Nusaybin has a semi-arid climate with extremely hot summers and cool winters. Rainfall is generally sparse.Demographics
Nusaybin is predominantly ethnically Kurdish. The city's people have historically close ties with those of neighboring Qamishli, and cross-border marriages are a common practice. The city also contains a minority Arab population. A very small Assyrian population remains in the city; what remained of the Assyrian population emigrated during the height of the Kurdish-Turkish conflict in the 1990s and as a result of the Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present), resumption of the conflict in 2016, only one Assyrian family reportedly remained in the city.Villages
Christianity
 Nisibis ( syr, ܢܨܝܒܝܢ, ''Nṣibin'', later Syriac , ''Ṣōbā'') had an Assyrian people, Assyrian Christianity, Christian
Nisibis ( syr, ܢܨܝܒܝܢ, ''Nṣibin'', later Syriac , ''Ṣōbā'') had an Assyrian people, Assyrian Christianity, Christian bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ca ...
from 300, founded by Babu (bishop), Babu (died 309). Shapur II
Shapur II ( pal, 𐭱𐭧𐭯𐭥𐭧𐭥𐭩 ; New Persian: , ''Šāpur'', 309 – 379), also known as Shapur the Great, was the tenth Sasanian King of Kings (Shahanshah) of Iran. The longest-reigning monarch in Iranian history, he reigned fo ...
besieged the city in 338, 346, and 350, when Jacob of Nisibis, St Jacob or James of Nisibis, Babu's successor, was its bishop. Nisibis was the home of Ephrem the Syrian
Ephrem the Syrian ( syc, ܡܪܝ ܐܦܪܝܡ ܣܘܪܝܝܐ, Mār ʾAp̄rêm Sūryāyā, ; grc-koi, Ἐφραὶμ ὁ Σῦρος, Efrém o Sýros; la, Ephraem Syrus; am, ቅዱስ ኤፍሬም ሶርያዊ; ), also known as Saint Ephrem, Saint ...
, who remained until its surrender to the Sassanian Empire, Sassanid Persians by Roman Emperor Jovian
Jovian is the adjectival form of Jupiter and may refer to:
* Jovian (emperor) (Flavius Iovianus Augustus), Roman emperor (363–364 AD)
* Jovians and Herculians, Roman imperial guard corps
* Jovian (lemur), a Coquerel's sifaka known for ''Zoboomafo ...
in 363. The bishop of Nisibis was the Metropolitan Archbishop of the Ecclesiastical province of Bit-Arbaye. By 410, it had six suffragan sees and as early as the middle of the 5th century was the most important episcopal see of the Church of the East
The Church of the East ( syc, ܥܕܬܐ ܕܡܕܢܚܐ, ''ʿĒḏtā d-Maḏenḥā'') or the East Syriac Church, also called the Church of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, the Persian Church, the Assyrian Church, the Babylonian Church or the Nestorian C ...
after Seleucia on the Tigris, Seleucia-Ctesiphon. Many of its Nestorian Church, Nestorian or Assyrian Church of the East
The Assyrian Church of the East,, ar, كنيسة المشرق الآشورية sometimes called Church of the East, officially the Holy Apostolic Catholic Assyrian Church of the East,; ar, كنيسة المشرق الآشورية الرسول� ...
and Syriac Orthodox Church, Jacobite bishops were renowned for their writings, including Barsumas, Osee, Narses, Jesusyab and Ebed-Jesus. The Roman Catholic Church has defined titular archbishoprics of Nisibis, for various rites – one Latin and four Eastern Catholic for particular churches ''sui iuris'', notably the Chaldean Catholic Church and the Maronite Catholic Church.''Annuario Pontificio 2013'' (Libreria Editrice Vaticana, 2013, ), p. 941]
When the Syriac Catholic Eparchy of Hassaké was promoted to archiepiscopal rank, it added Nisibi to its name, becoming the Syriac Catholic Archeparchy of Hassaké-Nisibi (not Metropolitan, directly dependent on the Syriac Catholic Patriarch of Antioch).
= Latin titular see
= Established in the 18th century as Titular Archiepiscopal see of Nisibis (informally Nisibis of the Romans). It has been vacant for several decades, having previously had the following incumbents, all of the (intermediary) archiepiscopal rank: * Giambattista Braschi (1724.12.20 – 1736.11.24) * José Calzado López (Bolaños de Calatrava, 17/04/1680 – Madrid, 7/04/1761) Discalced Franciscans (O.F.M. Disc.) (1738.11.24 – 1761.04.07) * Cesare Brancadoro (1789.10.20 – 1800.08.11) (later Cardinal)* * Lorenzo Caleppi (1801.02.23 – 1816.03.08) (later Cardinal)* * Vincenzo Macchi (1818.10.02 – 1826.10.02)(later Cardinal)* * Carlo Luigi Morichini (1845.04.21 – 1852.03.15) (later Cardinal)* * Vincenzo Tizzani, C.R.L. (1855.03.26 – 1886.01.15) (later Patriarch)* * Johann Gabriel Léon Louis Meurin, Jesuits (S.J.) (1887.09.15 – 1887.09.27) * Giuseppe Giusti (1891.12.14 – 1897.03.31) * Federico Pizza (1897.04.19 – 1909.03.28) * Francis McCormack (1909.06.21 – 1909.11.14) * Joseph Petrelli (1915.03.30 – 1962.04.29) * José de la Cruz Turcios y Barahona, Salesians (S.D.B.) (1962.05.18 – 1968.07.18)= Armenian Catholic titular see
= Established as Titular Archiepiscopal see of Nisibis (informally Nisibis of the Armenians) in ''circa'' 1910. It was suppressed in 1933, having had a single incumbent, of the (intermediary) archiepiscopal rank : * Gregorio Govrik, Mechitarists (C.A.M.) (1910.05.07 – 1931.01.26) Chaldean Catholic titular see: Established as Titular Archiepiscopal see of Nisibis (informally Nisibis of the Chaldeans) in the late 19th century, suppressed in 1927, restored in 1970. It has had the following incumbents, all of the (intermediary) archiepiscopal rank : * Giuseppe Elis Khayatt (1895.04.22 – 1900.07.13) * Hormisdas Etienne Djibri (1902.11.30 – 1917.08.31) * Thomas Michel Bidawid (1970.08.24 – 1971.03.29) * Gabriel Koda (1977.12.14 – 1992.03) * Jacques Ishaq (2005.12.21 – ...), Bishop of Curia emeritus of the Chaldean Catholic Patriarchate of Babylon= Maronite titular see
= Established as Titular Archiepiscopal see of Nisibis (informally Nisibis of the Maronites) in 1960. It is vacant, having had a single incumbent of the (intermediary) archiepiscopal rank: * Pietro Sfair (1960.03.11 – 1974.05.18)Notable people
* Ephraim the Syrian (4th century), Christian Saint was native of Nisibis (modern Nusaybin) * Musa Anter (1920-1992), Kurdish people, Kurdish writer, journalist and intellectual * Gülser Yıldırım (1963*), Politician * Mithat Sancar (1963*), professor of Public law, public and constitutional law, columnist and translator * Sara Kaya (1970*), Politician * Ferhad Ayaz (1994*), FootballerSee also
* Febronia of Nisibis * Mor Yakup Church * Nisibis (East Syrian Ecclesiastical Province) * Thamanin * Zeynel Abidin Mosque ComplexReferences
Sources and external links
*Nisibis
''Catholic Encyclopedia''
GCatholic, Armenian Catholic titular see
Turkish News - Latest News from Turkey
Hürriyet Daily News and Economic Review
The Battle of Nisibis, AD 217
{{Authority control Nusaybin, Archaeological sites in Southeastern Anatolia Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Turkey Seleucid colonies in Anatolia Roman legionary fortresses in Turkey Sasanian cities Catholic titular sees in Asia, Nisibis Towns in Turkey Assyrian communities in Turkey Populated places in Mardin Province Divided cities on the Turkish-Syrian border Syria–Turkey border crossings Districts of Mardin Province Mesopotamia (Roman province) Roman towns and cities in Turkey Kurdish settlements in Turkey