Nile Hippo on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large
 Until 1909, naturalists classified hippos together with pigs based on molar patterns. Several lines of evidence, first from blood proteins, then from
Until 1909, naturalists classified hippos together with pigs based on molar patterns. Several lines of evidence, first from blood proteins, then from  The most recent theory of the origins of Hippopotamidae suggests hippos and whales shared a common semiaquatic ancestor that branched off from other artiodactyls around . This hypothesised ancestral group likely split into two branches again around .
One branch would evolve into cetaceans, possibly beginning about , with the protowhale ''
The most recent theory of the origins of Hippopotamidae suggests hippos and whales shared a common semiaquatic ancestor that branched off from other artiodactyls around . This hypothesised ancestral group likely split into two branches again around .
One branch would evolve into cetaceans, possibly beginning about , with the protowhale ''
semiaquatic
In biology, semiaquatic can refer to various types of animals that spend part of their time in water, or plants that naturally grow partially submerged in water. Examples are given below.
Semiaquatic animals
Semi aquatic animals include:
* Ve ...
mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two extant species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
in the family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
Hippopotamidae
Hippopotamidae is a family of stout, naked-skinned, and semiaquatic artiodactyl mammals, possessing three-chambered stomachs and walking on four toes on each foot. While they resemble pigs physiologically, their closest living relatives are t ...
, the other being the pygmy hippopotamus
The pygmy hippopotamus or pygmy hippo (''Choeropsis liberiensis'') is a small hippopotamid which is native to the forests and swamps of West Africa, primarily in Liberia, with small populations in Sierra Leone, Guinea, and Ivory Coast. It has ...
(''Choeropsis liberiensis'' or ''Hexaprotodon liberiensis''). Its name comes from the ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
for "river horse" ().
Aside from elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae ...
s and rhino
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct species o ...
s, the hippopotamus is the largest land mammal
The following is a list of largest mammals by family.
Tenrecs and allies (Afrosoricida)
*The largest of these insectivorous mammals is the giant otter shrew (''Potamogale velox''), native to Central Africa. This species can weigh up to and mea ...
. It is also the largest extant land artiodactyl
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing poster ...
. Despite their physical resemblance to pig
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), often called swine, hog, or domestic pig when distinguishing from other members of the genus '' Sus'', is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is variously considered a subspecies of ''Sus ...
s and other terrestrial even-toed ungulates
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing poster ...
, the closest living relatives of the hippopotamids are cetaceans (whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and ...
s, dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (the ...
s, porpoises, etc.), from which they diverged about 55 million years ago. Hippos are recognisable for their barrel-shaped torsos, wide-opening mouths with large canine tusks, nearly hairless bodies, pillar-like legs, and large size: adults average for bulls (males) and for cows (females). Despite its stocky shape and short legs, it is capable of running over short distances.
Hippos inhabit rivers, lakes, and mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evolution in severa ...
swamps. Territorial bulls each preside over a stretch of water and a group of five to thirty cows and calves. Mating and birth both occur in the water. During the day, hippos remain cool by staying in water or mud, emerging at dusk to graze on grasses. While hippos rest near each other in the water, grazing is a solitary activity and hippos typically do not display territorial
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or a ...
behaviour on land. Hippos are among the most dangerous animals in the world due to their aggressive and unpredictable nature. They are threatened by habitat loss
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby ...
and poaching
Poaching has been defined as the illegal hunting or capturing of wild animals, usually associated with land use rights.
Poaching was once performed by impoverished peasants for subsistence purposes and to supplement meager diets. It was set a ...
for their meat and ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals i ...
(canine teeth).
Etymology
TheLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
word is derived from the ancient Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
(), from () and () , together meaning . In English, the plural
The plural (sometimes abbreviated pl., pl, or ), in many languages, is one of the values of the grammatical category of number. The plural of a noun typically denotes a quantity greater than the default quantity represented by that noun. This de ...
is "hippopotamuses", but "hippopotami" is also used.
Taxonomy and origins
Classification
The modern hippopotamus and thepygmy hippopotamus
The pygmy hippopotamus or pygmy hippo (''Choeropsis liberiensis'') is a small hippopotamid which is native to the forests and swamps of West Africa, primarily in Liberia, with small populations in Sierra Leone, Guinea, and Ivory Coast. It has ...
are the only living members of the family Hippopotamidae. Some taxonomists place hippos and anthracotheres in the superfamily Anthracotheroidea. Hippopotamidae are classified along with other even-toed ungulates
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing poster ...
in the order Artiodactyla
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing poster ...
.
Five subspecies of hippos have been described based on morphological differences in their skulls as well as differences in geographical range:
*''H. a. amphibius'' – (the nominate subspecies) ranges from Gambia east to Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
and then south to Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
and historically ranged as far north as Egypt; its skull is distinguished by a moderately reduced preorbital region, a bulging dorsal surface, elongated mandibular symphysis and larger chewing teeth.
*''H. a. kiboko'' – found in Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
...
and Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constituti ...
; was noted to be smaller and more lightly coloured than other hippos with wider nostrils, somewhat longer snout and more rounded and relatively raised orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as ...
s with the space between them being incurved.
*''H. a. capensis'' – found in Zambia
Zambia (), officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central, Southern and East Africa, although it is typically referred to as being in Southern Africa at its most central point. Its neighbours are t ...
and South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
; distinguished by wider orbits.
*''H. a. tschadensis'' – ranges between Chad and Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languagesDemocratic Republic of Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
to Angola
, national_anthem = " Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordina ...
and Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and ea ...
; skull characterised by a thicker preorbital region, shorter snout, flatter dorsal surface, reduced mandibular symphysis and smaller chewing teeth.
The suggested subspecies above were never widely used or validated by field biologists; the described morphological differences were small enough that they could have resulted from simple variation in nonrepresentative samples. A study examining mitochondrial DNA from skin biopsies taken from 13 sampling locations found "low, but significant, genetic differentiation" among ''H. a. amphibius'', ''H. a. capensis'', and ''H. a. kiboko''. Neither ''H. a. tschadensis'' nor ''H. a. constrictus'' have been tested.
Evolution
 Until 1909, naturalists classified hippos together with pigs based on molar patterns. Several lines of evidence, first from blood proteins, then from
Until 1909, naturalists classified hippos together with pigs based on molar patterns. Several lines of evidence, first from blood proteins, then from molecular systematics
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to ...
and DNA and the fossil record
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
, show their closest living relatives are cetaceans (whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and ...
s, dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (the ...
s, and porpoises). The common ancestor of hippos and whales branched off from Ruminantia
Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. The ...
and the rest of the even-toed ungulates; the cetacean and hippo lineages split soon afterwards.
 The most recent theory of the origins of Hippopotamidae suggests hippos and whales shared a common semiaquatic ancestor that branched off from other artiodactyls around . This hypothesised ancestral group likely split into two branches again around .
One branch would evolve into cetaceans, possibly beginning about , with the protowhale ''
The most recent theory of the origins of Hippopotamidae suggests hippos and whales shared a common semiaquatic ancestor that branched off from other artiodactyls around . This hypothesised ancestral group likely split into two branches again around .
One branch would evolve into cetaceans, possibly beginning about , with the protowhale ''Pakicetus
''Pakicetus'' is an extinct genus of amphibious cetacean of the family Pakicetidae, which was endemic to Pakistan during the Eocene, about 50 million years ago. It was a wolf-like animal, about to long, and lived in and around water where it a ...
'' and other early whale ancestors collectively known as Archaeoceti
Archaeoceti ("ancient whales"), or Zeuglodontes in older literature, is a paraphyletic group of primitive cetaceans that lived from the Early Eocene to the late Oligocene (). Representing the earliest cetacean radiation, they include the initial ...
. This group eventually underwent aquatic adaptation
Several groups of tetrapods have undergone secondary aquatic adaptation, an evolutionary transition from being purely terrestrial to living at least part of the time in water. These animals are called "secondarily aquatic" because although their a ...
into the completely aquatic cetaceans. The other branch became the anthracotheres, a large family of four-legged beasts, the earliest of which in the late Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " ...
would have resembled skinny hippos with comparatively smaller, narrower heads. All branches of the anthracotheres, except that which evolved into Hippopotamidae
Hippopotamidae is a family of stout, naked-skinned, and semiaquatic artiodactyl mammals, possessing three-chambered stomachs and walking on four toes on each foot. While they resemble pigs physiologically, their closest living relatives are t ...
, became extinct during the Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58
A rough evolutionary lineage of the hippo can thus be traced from Eocene and Oligocene species: from ''
Anthracotherium
''Anthracotherium'' (from el, ἄνθραξ , 'coal' and el, θηρίον 'beast') was a genus of extinct artiodactyl ungulate mammals, characterized by having 44 teeth, with five semi-crescentic cusps on the crowns of the upper molars. The ...
'' and ''Elomeryx
''Elomeryx'' is an extinct genus of artiodactyl ungulate, and is among the earliest known anthracotheres. The genus was extremely widespread, first being found in Asia in the middle Eocene, in Europe during the latest Eocene, and having spread t ...
'' to the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
species ''Merycopotamus
''Merycopotamus'' is an extinct genus of Asian anthracothere that appeared during the Middle Miocene, and died out in the Late Pliocene. At the height of the genus' influence, species ranged throughout southern Asia. With the extinction of th ...
'' and ''Libycosaurus
''Libycosaurus'' (" Lizard of Libya") was one of the last anthracothere genera. It lived from the Middle to the Late Miocene, and ranged throughout Central and Northern Africa, and in Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Afri ...
'' and finally the very latest anthracotheres in the Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58 These groups lived across Eurasia and Africa. The discovery of ''Epirigenys'' in East Africa, which was likely a descent of Asian anthracotheres and a 
 The hippopotamus is a
The hippopotamus is a  Hippo skin is thick across much of its body with little hair. The animal is mostly purplish-grey or blue-black, but brownish-pink on the underside and around the eyes and ears. Their skin secretes a natural, red-coloured sunscreen substance that is sometimes referred to as "blood sweat" but is neither blood nor sweat. This secretion is initially colourless and turns red-orange within minutes, eventually becoming brown. Two highly acidic pigments have been identified in the secretions; one red ( hipposudoric acid) and one orange (norhipposudoric acid), which inhibit the growth of disease-causing bacteria and their light-absorption profile peaks in the
Hippo skin is thick across much of its body with little hair. The animal is mostly purplish-grey or blue-black, but brownish-pink on the underside and around the eyes and ears. Their skin secretes a natural, red-coloured sunscreen substance that is sometimes referred to as "blood sweat" but is neither blood nor sweat. This secretion is initially colourless and turns red-orange within minutes, eventually becoming brown. Two highly acidic pigments have been identified in the secretions; one red ( hipposudoric acid) and one orange (norhipposudoric acid), which inhibit the growth of disease-causing bacteria and their light-absorption profile peaks in the
 ''Hippopotamus amphibius'' was widespread in
''Hippopotamus amphibius'' was widespread in
English translation
 It is challenging to study the interaction of bulls and cows because hippos are not
It is challenging to study the interaction of bulls and cows because hippos are not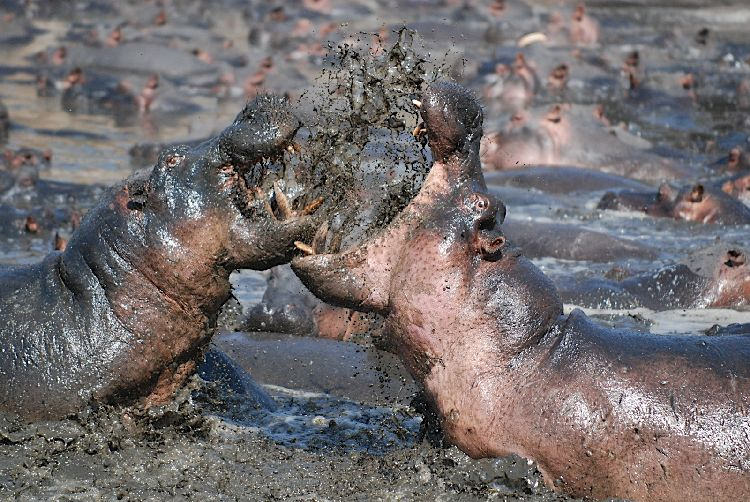  Hippos engage in "muck-spreading" which involves defecating while spinning their tails to distribute the faeces over a greater area. Muck-spreading occurs both on land and in water and its function is not well understood. It is unlikely to server to territorial, as the animals only establish territories in the water. They may be used as trails between the water and grazing areas. "Yawning" serves as a threat display. When fighting, bulls use their incisors to block each other's attacks and their large canines as offensive weapons. When hippos become over-populated or a habitat shrinks, bulls sometimes attempt infanticide, but this behaviour is not common under normal conditions.
The most common hippo vocalisation is the "wheeze honk", which can travel over long distances in air. This call starts as a high-pitched squeal followed by a deeper, resonant call. The animals can recognise the calls of other individuals. Hippos are more likely to react to the wheeze honks of strangers than those they are more familiar with. When threatened or alarmed, they produce exhalations, and fighting bulls will bellow loudly. Hippos are recorded to produce clicks underwater which may have echolocative properties. They have the unique ability to hold their heads partially above the water and send out a cry that travels through both water and air; individuals respond both above and below water.
Hippos engage in "muck-spreading" which involves defecating while spinning their tails to distribute the faeces over a greater area. Muck-spreading occurs both on land and in water and its function is not well understood. It is unlikely to server to territorial, as the animals only establish territories in the water. They may be used as trails between the water and grazing areas. "Yawning" serves as a threat display. When fighting, bulls use their incisors to block each other's attacks and their large canines as offensive weapons. When hippos become over-populated or a habitat shrinks, bulls sometimes attempt infanticide, but this behaviour is not common under normal conditions.
The most common hippo vocalisation is the "wheeze honk", which can travel over long distances in air. This call starts as a high-pitched squeal followed by a deeper, resonant call. The animals can recognise the calls of other individuals. Hippos are more likely to react to the wheeze honks of strangers than those they are more familiar with. When threatened or alarmed, they produce exhalations, and fighting bulls will bellow loudly. Hippos are recorded to produce clicks underwater which may have echolocative properties. They have the unique ability to hold their heads partially above the water and send out a cry that travels through both water and air; individuals respond both above and below water.
 Cows reach sexual maturity at five to six years of age and have a gestation period of eight months. A study of
Cows reach sexual maturity at five to six years of age and have a gestation period of eight months. A study of 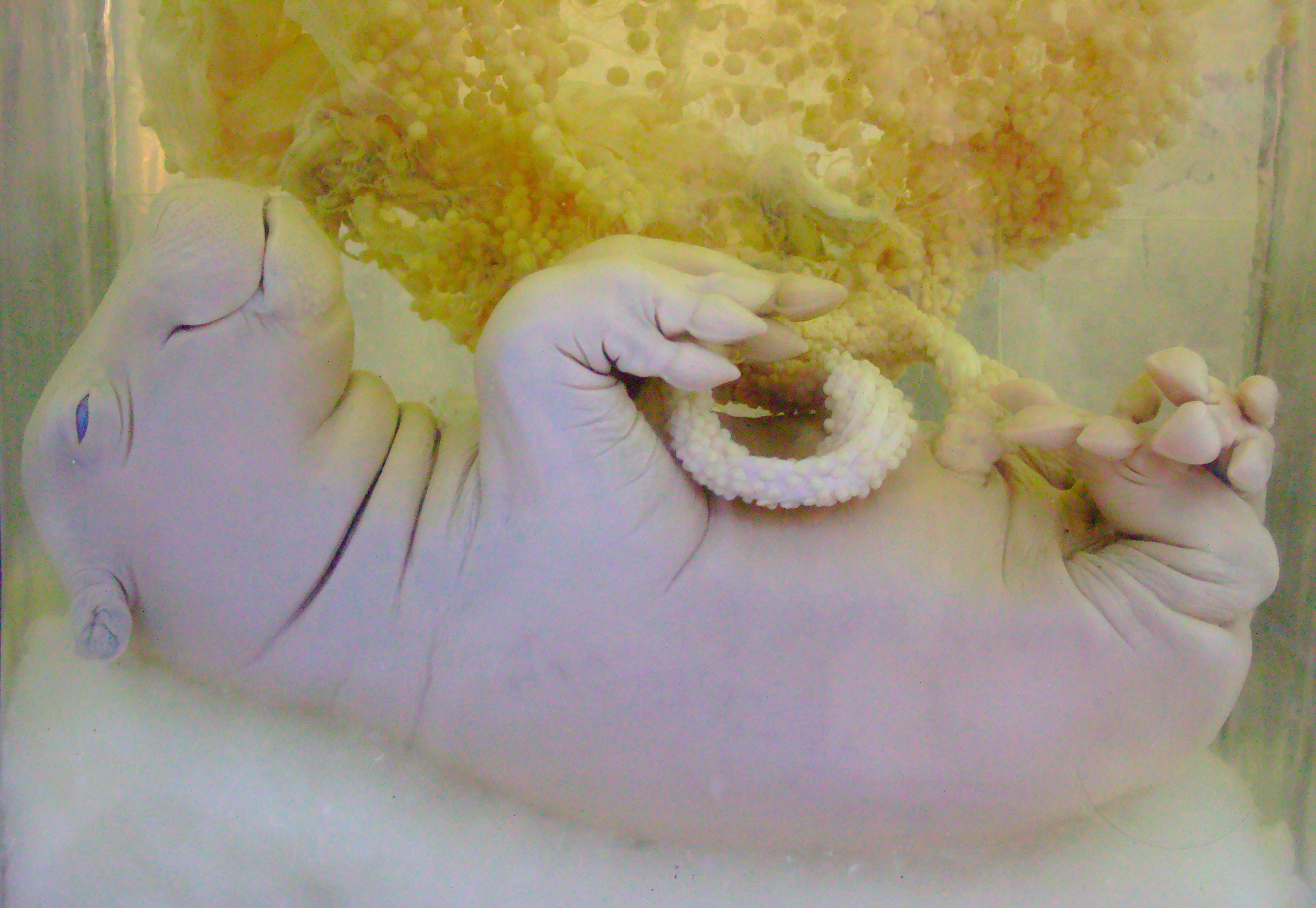 Hippos mate in the water, with the cow remaining under the surface, her head emerging periodically to draw breath. Cows give birth in seclusion and return within 10 to 14 days. Calves are born on land or shallow water weighing on average and at an average length of around . The female lays on her side when nursing, which can occur underwater or on land. The young are carried on their mothers' backs in deep water.
Mother hippos are very protective of their young, not allowing others to get too close. One cow was recorded protecting a calf's carcass after it had died. Calves may be temporarily kept in nurseries, guarded by one or more adults, and will play amongst themselves. Like many other large mammals, hippos are described as K-strategists, in this case typically producing just one large, well-developed infant every couple of years (rather than many small, poorly developed young several times per year, as is common among small mammals such as rodents). Calves no longer need to suckle when they are a year old.
Hippos mate in the water, with the cow remaining under the surface, her head emerging periodically to draw breath. Cows give birth in seclusion and return within 10 to 14 days. Calves are born on land or shallow water weighing on average and at an average length of around . The female lays on her side when nursing, which can occur underwater or on land. The young are carried on their mothers' backs in deep water.
Mother hippos are very protective of their young, not allowing others to get too close. One cow was recorded protecting a calf's carcass after it had died. Calves may be temporarily kept in nurseries, guarded by one or more adults, and will play amongst themselves. Like many other large mammals, hippos are described as K-strategists, in this case typically producing just one large, well-developed infant every couple of years (rather than many small, poorly developed young several times per year, as is common among small mammals such as rodents). Calves no longer need to suckle when they are a year old.
 Hippos coexist alongside a variety of large predators in their habitats.
Hippos coexist alongside a variety of large predators in their habitats.
 The earliest evidence of human interaction with hippos comes from butchery cut marks on hippo bones found at the Bouri Formation and dated to around 160,000 years ago. 4,000–5,000 year art showing hippos being hunted have been found in the Tassili n'Ajjer, Tassili n'Ajjer Mountains of the central Sahara near Djanet. The ancient Egyptians recognised the hippo as a ferocious denizen of the
The earliest evidence of human interaction with hippos comes from butchery cut marks on hippo bones found at the Bouri Formation and dated to around 160,000 years ago. 4,000–5,000 year art showing hippos being hunted have been found in the Tassili n'Ajjer, Tassili n'Ajjer Mountains of the central Sahara near Djanet. The ancient Egyptians recognised the hippo as a ferocious denizen of the
sister taxon
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and ...
to Hippopotamidae suggests that hippo ancestors likely entered Africa from Asia around . An early hippopotamid is the genus ''Kenyapotamus
''Kenyapotamus'' is a possible ancestor of living hippopotamuses that lived roughly 16 million to 8 million years ago during the Miocene epoch. Its name reflects that its fossils were first found in modern-day Kenya.
Although little is known a ...
'', which lived in Africa from 15 to . Hippopotamid species would spread across Africa and Eurasia, including the modern pygmy hippo. From 7.5 to , a possible ancestor to the modern hippo, ''Archaeopotamus
''Archaeopotamus'' is an extinct genus of Hippopotamidae that lived between 7.5 and 2.58 million years ago in Africa and the Middle East. The genus was described in 2005 to encompass species of hippos that were previously grouped in ''Hexaprot ...
'', lived in Africa and the Middle East.

Extinct species
Three species of Malagasy hippopotamus became extinct during theHolocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
on Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
, the last of them within the past 1,000 years. The Malagasy hippos were smaller than the modern hippo, a likely result of the process of insular dwarfism
Insular dwarfism, a form of phyletic dwarfism, is the process and condition of large animals evolving or having a reduced body size when their population's range is limited to a small environment, primarily islands. This natural process is disti ...
. Fossil evidence indicates many Malagasy hippos were hunted by humans, a factor in their eventual extinction. Isolated individual Malagasy hippos may have survived in remote pockets; in 1976, villagers described a living animal called the ''kilopilopitsofy'', which may have been a Malagasy hippo.
An extinct species, ''Hippopotamus antiquus
''Hippopotamus antiquus'', sometimes called the European hippopotamus, is an extinct species of ''Hippopotamus'' that ranged across Europe during the Early and Middle Pleistocene.
Chronology
In Italy, the first appearance of the taxon is durin ...
,'' ranged throughout Europe, extending as far north as Britain during the Early and Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, widely known by its previous designation of Middle Pleistocene, is an age in the international geologic timescale or a stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. Th ...
epochs, before being replaced by the modern ''H. amphibius'' during the latter part of the Middle Pleistocene. The Pleistocene also saw a number of dwarf species evolve on several Mediterranean islands, including Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, ...
('' Hippopotamus creutzburgi''), Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ge ...
(the Cyprus dwarf hippopotamus, ''Hippopotamus minor''), Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
(''Hippopotamus melitensis
''Hippopotamus melitensis'' is an extinct hippopotamus from Malta. It arrived after the Messinian salinity crisisHunt, Christopher O., Schembri, Patrick J.Quaternary Environments and Biogeography of the Maltese Islands, page 31, access in 13/03/ ...
''), and Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
(''Hippopotamus pentlandi
''Hippopotamus pentlandi'' is an extinct hippopotamus from Sicily. It arrived during the Pleistocene. It is the largest of the insular dwarf hippos known from the Pleistocene of the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to ...
''). Of these, the Cyprus dwarf hippo survived until the end of the Pleistocene or early Holocene. Evidence from the archaeological site Aetokremnos continues to cause debate on whether or not the species was driven to extinction, or even encountered, by man. Across Eurasia, the hippopotamus became extinct between 50,000 and 16,000 years ago.
Characteristics and adaptations
 The hippopotamus is a
The hippopotamus is a megaherbivore
Megaherbivores (Greek μέγας megas "large" and Latin ''herbivora'' "herbivore") are large terrestrial herbivores that can exceed in weight. This polyphyletic group of megafauna includes elephants, rhinos, hippos, and giraffes. The largest ...
and is exceeded in size among land animals only by elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae ...
s and some rhinoceros
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct species ...
species. The mean adult weight is around for bulls and for cows. Exceptionally large males have been recorded reaching . Male hippos appear to continue growing throughout their lives, while females reach maximum weight at around age 25. Hippos measure long, including a tail of about in length and tall at the shoulder, with males and females ranging and tall at the shoulder respectively. The species has a typical head-body length of and an average standing height of at the shoulder.
Hippos have barrel-shaped bodies with short tails and legs, and an hourglass-shaped skull with a long snout. Their skeletal structures are graviportal, adapted to carrying their enormous weight, and their dense bones and low centre of gravity
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the balance point) is the unique point where the weighted relative position of the distributed mass sums to zero. This is the point to which a force ma ...
allows them to sink and move along the bottom of the water. Hippopotamuses have small legs (relative to other megafauna) because the water in which they live reduces the weight burden. The pelvis rests at an angle of 45 degrees. Hippos usually trot to move quickly on land and can gallop at when needed. They are incapable of jumping but can walk up steep banks. Despite their rounded appearance, hippos have little fat.
The eyes, ears, and nostrils of hippos are placed high on the roof of their skulls. This allows these organs to remain above the surface while the rest of the body is submerged. The nostrils and ears can close when underwater while nictitating membranes cover the eyes. Despite being semiaquatic and having webbed feet, an adult hippo is not a particularly good swimmer, nor can it float. It rarely enters deep water; when does, the animal moves by bouncing off the bottom. An adult hippo surfaces every four to six minutes, while young need to breathe every two to three minutes. The hippopotamus sleeps with both hemispheres of the brain resting, as in all land mammals, and usually sleeps on land or in water with the nostrils exposed. Despite this, it may be capable of sleeping while submerged, intermittently surfacing to breathe without waking. They appear to transition between different phases of sleep more quickly than other mammals.
The hippo's jaw is powered by huge masseter
In human anatomy, the masseter is one of the muscles of mastication. Found only in mammals, it is particularly powerful in herbivores to facilitate chewing of plant matter. The most obvious muscle of mastication is the masseter muscle, since it ...
and digastric
The digastric muscle (also digastricus) (named ''digastric'' as it has two 'bellies') is a small muscle located under the jaw. The term "digastric muscle" refers to this specific muscle. However, other muscles that have two separate muscle belli ...
muscles which give them large, droopy cheeks. The jaw hinge allows the animal to open its mouth at almost 180°. A folded orbicularis oris muscle
In human anatomy, the orbicularis oris muscle is a complex of muscles in the lips that encircles the mouth.
It is a sphincter, or circular muscle, but it is actually composed of four independent quadrants that interlace and give only an appearance ...
allows the hippo to attain an extreme gape without tearing any tissue. On the lower jaw, the incisor
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, wher ...
s and canines
Canine may refer to:
Zoology and anatomy
* a dog-like Canid animal in the subfamily Caninae
** ''Canis'', a genus including dogs, wolves, coyotes, and jackals
** Dog, the domestic dog
* Canine tooth, in mammalian oral anatomy
People with the surn ...
grow continuously, the former reaching , while the latter can grow to up to . The lower canines are sharpened through contact with the smaller upper canines. The canines and incisors are used mainly for combat instead of feeding. Hippos rely on their flattened, horny lips to grasp and pull grasses which are then ground by the molars
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone to ...
. The hippo is considered to be a pseudoruminant
Pseudoruminant is a classification of animals based on their digestive tract differing from the ruminants. Hippopotami and camels are ungulate mammals with a three-chambered stomach (ruminants have a four-chambered stomach) while equids (horses, ...
; it has a complex three-chambered stomach, but does not "chew cud
Cud is a portion of food that returns from a ruminant's stomach to the mouth to be chewed for the second time. More precisely, it is a bolus of semi-degraded food regurgitated from the reticulorumen of a ruminant. Cud is produced during the phy ...
".
 Hippo skin is thick across much of its body with little hair. The animal is mostly purplish-grey or blue-black, but brownish-pink on the underside and around the eyes and ears. Their skin secretes a natural, red-coloured sunscreen substance that is sometimes referred to as "blood sweat" but is neither blood nor sweat. This secretion is initially colourless and turns red-orange within minutes, eventually becoming brown. Two highly acidic pigments have been identified in the secretions; one red ( hipposudoric acid) and one orange (norhipposudoric acid), which inhibit the growth of disease-causing bacteria and their light-absorption profile peaks in the
Hippo skin is thick across much of its body with little hair. The animal is mostly purplish-grey or blue-black, but brownish-pink on the underside and around the eyes and ears. Their skin secretes a natural, red-coloured sunscreen substance that is sometimes referred to as "blood sweat" but is neither blood nor sweat. This secretion is initially colourless and turns red-orange within minutes, eventually becoming brown. Two highly acidic pigments have been identified in the secretions; one red ( hipposudoric acid) and one orange (norhipposudoric acid), which inhibit the growth of disease-causing bacteria and their light-absorption profile peaks in the ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
range, creating a sunscreen effect. Regardless of diet, all hippos secrete these pigments so food does not appear to be their source; rather, they may be synthesised from precursors such as the amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha a ...
tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the G ...
. This natural sunscreen cannot prevent the animal's skin from cracking if it stays out of water too long.
The testes of the males do not fully descend and a scrotum is not present. In addition, the penis retracts into the body when not erect. The genitals of the female hippos are unusual in that the vagina is ridged and the vulval vestibule
The vulval vestibule (or vulvar vestibule or vestibule of vagina) is a part of the vulva between the labia minora into which the urinary meatus (urethral opening) and the vaginal opening open. Its edge is marked by Hart's line. It represents the ...
has two large, protruding diverticula
In medicine or biology, a diverticulum is an outpouching of a hollow (or a fluid-filled) structure in the body. Depending upon which layers of the structure are involved, diverticula are described as being either true or false.
In medicine, t ...
. Both of these have an unknown function.
A hippo's lifespan is typically 40 to 50 years. Donna the Hippo was one of the oldest living hippos in captivity. She lived at the Mesker Park Zoo
The Mesker Park Zoo and Botanic Garden is a zoo that opened in 1928 in Evansville, Indiana, United States. It is located in Mesker Park on Evansville's northwest side and is run by the City of Evansville.
The Mesker Park Zoo and Botanic Garden ...
in Evansville, Indiana
Evansville is a city in, and the county seat of, Vanderburgh County, Indiana, United States. The population was 118,414 at the 2020 census, making it the state's third-most populous city after Indianapolis and Fort Wayne, the largest city in ...
, in the US until her death in 2012 at the age of 61. The oldest hippo ever recorded was called Bertha; she had lived in the Manila Zoo
The Manila Zoo, formally known as the Manila Zoological and Botanical Garden, is a zoo located in Malate, Manila, Philippines.
History
The Manila Zoological and Botanical Garden first opened to the public on July 25, 1959, during the tenure ...
in the Philippines since it first opened in 1959. When she died in 2017, her age was estimated to be 65.
Distribution and status
 ''Hippopotamus amphibius'' was widespread in
''Hippopotamus amphibius'' was widespread in North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
and Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
during the Eemian (130–115,000 years ago), with remains found as far north as England. Archaeological evidence exists of its presence in the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
, dating to less than 3,000 years ago. The species was common in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
's Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest ...
region during antiquity, but it has since been driven out. According to Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
, in his time, the best location in Egypt for capturing this animal was in the Saite nome;English translation
Damietta
Damietta ( arz, دمياط ' ; cop, ⲧⲁⲙⲓⲁϯ, Tamiati) is a port city and the capital of the Damietta Governorate in Egypt, a former bishopric and present multiple Catholic titular see. It is located at the Damietta branch, an easter ...
branch of the Nile after the Arab Conquest in 639. Reports of the slaughter of the last hippo in Natal Province were made at the end of the 19th century. Hippos are still found in the rivers and lakes of the northern Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
, Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa. The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The sou ...
, Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
, and Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
...
, north through to Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constituti ...
, and Sudan, west to The Gambia
The Gambia,, ff, Gammbi, ar, غامبيا officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. It is the smallest country within mainland AfricaHoare, Ben. (2002) ''The Kingfisher A-Z Encyclopedia'', Kingfisher Publicatio ...
, and south to South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
.
Genetic evidence suggests common hippos in Africa experienced a marked population expansion during or after the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
, attributed to an increase in water bodies at the end of the era. These findings have important conservation implications, as hippo populations across the continent are currently threatened by loss of access to fresh water. Hippos are also subject to unregulated hunting and poaching
Poaching has been defined as the illegal hunting or capturing of wild animals, usually associated with land use rights.
Poaching was once performed by impoverished peasants for subsistence purposes and to supplement meager diets. It was set a ...
. The species is included in Appendix II of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species
CITES (shorter name for the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, also known as the Washington Convention) is a multilateral treaty to protect endangered plants and animals from the threats of interna ...
(CITES) meaning international export/import (including in parts and derivatives) requires CITES documentation to be obtained and presented to border authorities.
As of 2017, the IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biol ...
drawn up by the International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of nat ...
(IUCN) lists the species as vulnerable, with a stable population estimated between 115,000 and 130,000 animals. The hippo population has declined most dramatically in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. By 2005, the population in Virunga National Park
, iucn_category = II
, iucn_ref =
, location = Democratic Republic of the Congo
, map = Democratic Republic of the Congo
, relief = 1
, coordinates =
, area =
, established =
, nearest_city = Goma
, photo =Virunga National Park-107997 ...
had dropped to 800 or 900 from around 29,000 in the mid-1970s. This decline is attributed to the disruptions caused by the Second Congo War. The poachers are believed to be Mai-Mai
The term Mai-Mai or Mayi-Mayi refers to any kind of community-based militia group active in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) that is formed to defend local communities and territory against other armed groups. Most were formed to resis ...
rebels, underpaid Congolese soldiers, and local militia groups. Reasons for poaching include the belief hippos are harmful to society, as well as financial gain. As of 2016, the Virunga hippo population appears to have increased again, possibly due to better protection from park rangers, who have worked with local fishermen. The sale of hippo meat is illegal, but black-market sales are difficult for Virunga National Park officers to track. Hippo meat is highly valued in some areas of central Africa and the teeth may be used as a replacement for elephant ivory.
A population of hippos exists in Colombia, descended from captive individuals that escaped from Pablo Escobar's estate after this death in 1993. Their numbers grew to 100 by the 2020s and ecologists believe the population should be eradicated, as they are breeding rapidly and are an increasing menace to humans and the environment. Attempts to control them include sterilisation and culling
In biology, culling is the process of segregating organisms from a group according to desired or undesired characteristics. In animal breeding, it is the process of removing or segregating animals from a breeding stock based on a specific tr ...
.
Behaviour and ecology
Hippos aresemiaquatic
In biology, semiaquatic can refer to various types of animals that spend part of their time in water, or plants that naturally grow partially submerged in water. Examples are given below.
Semiaquatic animals
Semi aquatic animals include:
* Ve ...
and require enough water to immerse in, while being close to grass. They prefer relatively still waters with gently sloping shores though, male hippos may also be found in very small numbers in more rapid waters with rocky slopes. Hippos mostly live in freshwater habitat, but can be found in estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environmen ...
.
Hippos spend most the day in water to stay cool and hydrated. Just before night begins, they leave the water to foraging on land. Like most herbivores, hippos will consume a variety of plants if presented with them in captivity, but their diet in nature consists almost entirely of grass, with only minimal consumption of aquatic plants. A hippo will travel per night, eating around of grass. By dawn, they are back in the water. On occasion, hippos have been filmed eating carrion, usually near the water. There are other reports of meat-eating and even cannibalism and predation
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill th ...
. The stomach anatomy of lacks adaptions to carnivory, and meat-eating is likely caused by not having enough nutrients or just an abnormal behaviour.
Because of their size and their habit of taking the same paths to feed, hippos can have a significant impact on the land across which they walk, keeping the land clear of vegetation and depressing the ground. Over prolonged periods, hippos can divert the paths of swamps and channels. By defecating in the water, the animals also appear to pass on microbes from their gut, affecting the biogeochemical cycle.
Social interaction
 It is challenging to study the interaction of bulls and cows because hippos are not
It is challenging to study the interaction of bulls and cows because hippos are not sexually dimorphic
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most ani ...
, so cows and young bulls are almost indistinguishable in the field. Hippo pods fluctuate but can contain over 100 hippos. Although they lie close together, adults develop almost no social bonds. Males establish territories
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or a ...
in water but not land, and these may range in lakes and in rivers. Territories are abandoned when the water dries up. The bull has breeding access to all the cows in his territory. Younger bachelors are allowed to stay as long as they defer to him. A younger male may challenge the old bull for control of the territory. Within the pods, the hippos tend to segregate by sex and status. Bachelor males lounge near other bachelors, females with other females, and the territorial male is on his own. When hippos emerge from the water to graze, they do so individually.
 Hippos engage in "muck-spreading" which involves defecating while spinning their tails to distribute the faeces over a greater area. Muck-spreading occurs both on land and in water and its function is not well understood. It is unlikely to server to territorial, as the animals only establish territories in the water. They may be used as trails between the water and grazing areas. "Yawning" serves as a threat display. When fighting, bulls use their incisors to block each other's attacks and their large canines as offensive weapons. When hippos become over-populated or a habitat shrinks, bulls sometimes attempt infanticide, but this behaviour is not common under normal conditions.
The most common hippo vocalisation is the "wheeze honk", which can travel over long distances in air. This call starts as a high-pitched squeal followed by a deeper, resonant call. The animals can recognise the calls of other individuals. Hippos are more likely to react to the wheeze honks of strangers than those they are more familiar with. When threatened or alarmed, they produce exhalations, and fighting bulls will bellow loudly. Hippos are recorded to produce clicks underwater which may have echolocative properties. They have the unique ability to hold their heads partially above the water and send out a cry that travels through both water and air; individuals respond both above and below water.
Hippos engage in "muck-spreading" which involves defecating while spinning their tails to distribute the faeces over a greater area. Muck-spreading occurs both on land and in water and its function is not well understood. It is unlikely to server to territorial, as the animals only establish territories in the water. They may be used as trails between the water and grazing areas. "Yawning" serves as a threat display. When fighting, bulls use their incisors to block each other's attacks and their large canines as offensive weapons. When hippos become over-populated or a habitat shrinks, bulls sometimes attempt infanticide, but this behaviour is not common under normal conditions.
The most common hippo vocalisation is the "wheeze honk", which can travel over long distances in air. This call starts as a high-pitched squeal followed by a deeper, resonant call. The animals can recognise the calls of other individuals. Hippos are more likely to react to the wheeze honks of strangers than those they are more familiar with. When threatened or alarmed, they produce exhalations, and fighting bulls will bellow loudly. Hippos are recorded to produce clicks underwater which may have echolocative properties. They have the unique ability to hold their heads partially above the water and send out a cry that travels through both water and air; individuals respond both above and below water.
Reproduction
 Cows reach sexual maturity at five to six years of age and have a gestation period of eight months. A study of
Cows reach sexual maturity at five to six years of age and have a gestation period of eight months. A study of endocrine system
The endocrine system is a messenger system comprising feedback loops of the hormones released by internal glands of an organism directly into the circulatory system, regulating distant target organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neu ...
s revealed cows may begin puberty at as early as three or four years. Males reach maturity at around 7.5 years. Both conceptions and births are highest during the wet season
The wet season (sometimes called the Rainy season) is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs. It is the time of year where the majority of a country's or region's annual precipitation occurs. Generally, the sea ...
. Male hippo always have mobile spermatozoa
A spermatozoon (; also spelled spermatozoön; ; ) is a motile sperm cell, or moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete. A spermatozoon joins an ovum to form a zygote. (A zygote is a single cell, with a complete set of chromos ...
and can breed year-round. After becoming pregnant, a female hippo will typically not begin ovulation again for 17 months.
 Hippos mate in the water, with the cow remaining under the surface, her head emerging periodically to draw breath. Cows give birth in seclusion and return within 10 to 14 days. Calves are born on land or shallow water weighing on average and at an average length of around . The female lays on her side when nursing, which can occur underwater or on land. The young are carried on their mothers' backs in deep water.
Mother hippos are very protective of their young, not allowing others to get too close. One cow was recorded protecting a calf's carcass after it had died. Calves may be temporarily kept in nurseries, guarded by one or more adults, and will play amongst themselves. Like many other large mammals, hippos are described as K-strategists, in this case typically producing just one large, well-developed infant every couple of years (rather than many small, poorly developed young several times per year, as is common among small mammals such as rodents). Calves no longer need to suckle when they are a year old.
Hippos mate in the water, with the cow remaining under the surface, her head emerging periodically to draw breath. Cows give birth in seclusion and return within 10 to 14 days. Calves are born on land or shallow water weighing on average and at an average length of around . The female lays on her side when nursing, which can occur underwater or on land. The young are carried on their mothers' backs in deep water.
Mother hippos are very protective of their young, not allowing others to get too close. One cow was recorded protecting a calf's carcass after it had died. Calves may be temporarily kept in nurseries, guarded by one or more adults, and will play amongst themselves. Like many other large mammals, hippos are described as K-strategists, in this case typically producing just one large, well-developed infant every couple of years (rather than many small, poorly developed young several times per year, as is common among small mammals such as rodents). Calves no longer need to suckle when they are a year old.
Interspecies interactions
 Hippos coexist alongside a variety of large predators in their habitats.
Hippos coexist alongside a variety of large predators in their habitats. Nile crocodile
The Nile crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'') is a large crocodilian native to freshwater habitats in Africa, where it is present in 26 countries. It is widely distributed throughout sub-Saharan Africa, occurring mostly in the central, eastern, ...
s, lions, and spotted hyenas are known to prey on young hippos. Beyond these, adult hippos are not usually preyed upon by other animals due to their aggression and size. Cases where large lion prides have successfully preyed on adult hippos have been reported, but it is generally rare. Lions occasionally prey on adults at Gorongosa National Park and calves are sometimes taken at Virunga. Crocodiles are frequent targets of hippo aggression, probably because they often inhabit the same riparian habitats; crocodiles may be either aggressively displaced or killed by hippos. In turn, very large Nile crocodiles have been observed preying occasionally on calves, "half-grown" hippos, and possibly also adult female hippos. Groups of crocodiles have also been observed finishing off still-living male hippos that were previously injured in mating battles with other males.
Hippos occasionally visit cleaning stations in order to be cleaned of parasites by certain species of fishes. They signal their readiness for this service by opening their mouths wide. This is an example of Mutualism (biology), mutualism, in which the hippo benefits from the cleaning while the fish receive food. Hippo defecation creates allochthonous deposits of organic matter along the river beds. These deposits have an unclear ecological function. A 2015 study concluded hippo dung provides nutrients from terrestrial material for fish and aquatic invertebrates, while a 2018 study found that their dung can be toxic to aquatic life in large quantities, due to absorption of dissolved oxygen in water bodies.
The parasitic monogenean flatworm'' Oculotrema hippopotami'' infests hippopotamus eyes, mainly the nictitating membrane. It is the only monogenean species (which normally live on fish) documented to live on a mammal.
Hippos and humans
 The earliest evidence of human interaction with hippos comes from butchery cut marks on hippo bones found at the Bouri Formation and dated to around 160,000 years ago. 4,000–5,000 year art showing hippos being hunted have been found in the Tassili n'Ajjer, Tassili n'Ajjer Mountains of the central Sahara near Djanet. The ancient Egyptians recognised the hippo as a ferocious denizen of the
The earliest evidence of human interaction with hippos comes from butchery cut marks on hippo bones found at the Bouri Formation and dated to around 160,000 years ago. 4,000–5,000 year art showing hippos being hunted have been found in the Tassili n'Ajjer, Tassili n'Ajjer Mountains of the central Sahara near Djanet. The ancient Egyptians recognised the hippo as a ferocious denizen of the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest ...
and representations on the tombs of nobles show the animals were hunted by humans.
The hippo was also known to the Ancient Greece, Greeks and Ancient Rome, Romans. The Greek historian Herodotus described the hippo in ''Histories (Herodotus), The Histories'' (written ''Wiktionary:circa, circa'' 440 BC) and the Roman naturalist Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
wrote about the hippo in his encyclopedia ''Naturalis Historia'' (written ''circa'' 77 AD). The Yoruba people called the hippo ''erinmi'', which means "elephant of the water". Some individual hippos have achieved international fame. Huberta (hippopotamus), Huberta became a celebrity during the Great Depression for trekking a great distance across South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
.
Attacks on humans
The hippo is considered to be extremely aggressive and has frequently been reported charging and attacking boats. Small boats can easily be capsized by hippos and passengers can be injured or killed by the animals, or drown in the water. In one 2014 case inNiger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languages
Hippos have long been popular zoo animals. The first record of hippos taken into captivity for display is dated to 3500 BC in Hierakonpolis, Egypt. The first zoo hippo in modern history was Obaysch, who arrived at the London Zoo on 25 May 1850, where he attracted up to 10,000 visitors a day and inspired a popular song, the "Hippopotamus Polka".
Hippos generally breed well in captivity; birth rates are lower than in the wild, but this can be attributed to zoos' desire to limit births, since hippos are relatively expensive to maintain. Starting in 2015, the Cincinnati Zoo built a US$73 million exhibit to house three adult hippos, featuring a tank. Modern hippo enclosures also have a complex filtration system for the animal's waste, an underwater viewing area for the visitors, and glass that may be up to thick and capable of holding water under pressures of . In 1987, the Toledo Zoo saw the first underwater birth by a captive hippo. The exhibit was so popular, the logo of the Toledo Zoo was updated to feature the hippos.
 In Egyptian mythology, the god Set (deity), Set takes the form of a red hippopotamus and fights Horus for control of the land, but is defeated. The goddess Tawaret is depicted as a pregnant woman with a hippo head, representing fierce maternal love. The Ijaw people of the Niger Delta wore masks of aquatic animals like the hippo when practising their water spirit cults, and hippo ivory was used in the divination rituals of the Yoruba. Hippo masks were also used in Nyau funerary rituals of the Chewa people, Chewa of Southern Africa. According to Robert Baden-Powell, 1st Baron Baden-Powell, Robert Baden-Powell, Zulu people, Zulu warriors referred to hippos in war chants. The Behemoth from the Book of Job, 40:15–24 is thought to be based on the hippo.
Hippos have been the subjects of various African folklore, African folktales. According to a San people, San story, when the Creator deity, Creator assigned each animal its place in nature, the hippos wanted to live in the water, but were refused out of fear they might eat all the fish. After begging and pleading, the hippos were finally allowed to live in the water on the condition they would eat grass instead of fish, and fling their dung so it can be inspected for fish bones. In a Ndebele tale, the hippo originally had long, beautiful hair, but it was set on fire by a jealous hare and the hippo had to jump into a nearby pool. The hippo lost most of his hair and was too embarrassed to leave the water.
In Egyptian mythology, the god Set (deity), Set takes the form of a red hippopotamus and fights Horus for control of the land, but is defeated. The goddess Tawaret is depicted as a pregnant woman with a hippo head, representing fierce maternal love. The Ijaw people of the Niger Delta wore masks of aquatic animals like the hippo when practising their water spirit cults, and hippo ivory was used in the divination rituals of the Yoruba. Hippo masks were also used in Nyau funerary rituals of the Chewa people, Chewa of Southern Africa. According to Robert Baden-Powell, 1st Baron Baden-Powell, Robert Baden-Powell, Zulu people, Zulu warriors referred to hippos in war chants. The Behemoth from the Book of Job, 40:15–24 is thought to be based on the hippo.
Hippos have been the subjects of various African folklore, African folktales. According to a San people, San story, when the Creator deity, Creator assigned each animal its place in nature, the hippos wanted to live in the water, but were refused out of fear they might eat all the fish. After begging and pleading, the hippos were finally allowed to live in the water on the condition they would eat grass instead of fish, and fling their dung so it can be inspected for fish bones. In a Ndebele tale, the hippo originally had long, beautiful hair, but it was set on fire by a jealous hare and the hippo had to jump into a nearby pool. The hippo lost most of his hair and was too embarrassed to leave the water.
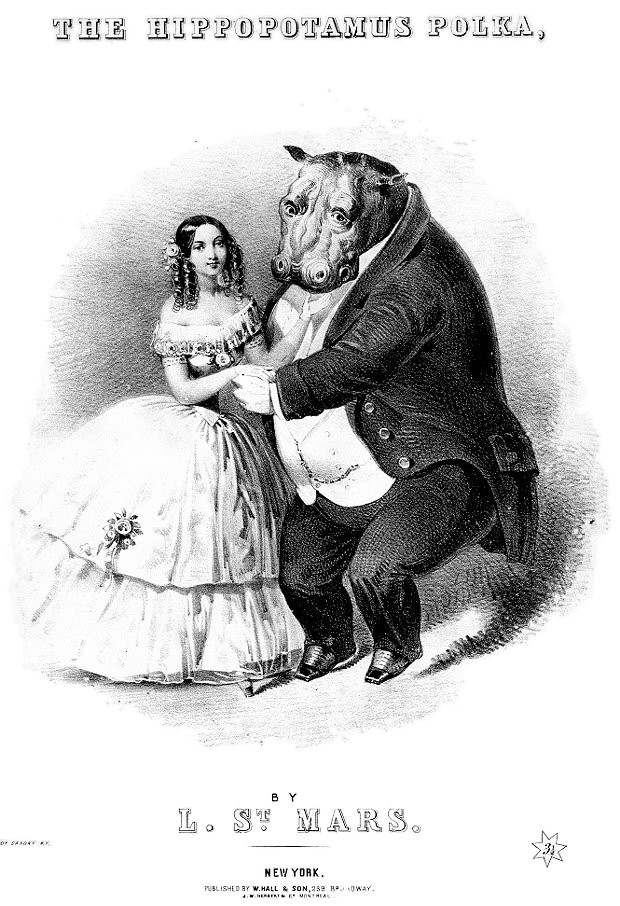 Hippopotamuses were rarely depicted in European art during the Renaissance and Baroque periods, due to less access to specimens by Europeans. One notable exception is Peter Paul Rubens' ''The Hippopotamus and Crocodile Hunt'' (1615–1616). Ever since Obaysch inspired the "Hippopotamus Polka", hippos have been popular animals in Western culture for their rotund appearance, which many consider comical. The The Walt Disney Company, Disney film ''Fantasia (1940 film), Fantasia'' featured a ballerina hippo dancing to the opera ''La Gioconda (opera), La Gioconda''. The film ''Hugo the Hippo'' is set in Tanzania and involves the title character trying to escape being slaughtered with the help of local children. The ''Madagascar (franchise), Madagascar'' films feature a hippo named List of Madagascar (franchise) characters#Gloria, Gloria. Hippos even inspired a popular board game, Hungry Hungry Hippos.
Among the most famous poems about the hippo is "The Hippopotamus" by T. S. Eliot, where he uses the animal to represent the Catholic Church. Hippos are mentioned in the novelty Christmas song "I Want a Hippopotamus for Christmas" that became a hit for child star Gayla Peevey in 1953. They also featured in the popular "The Hippopotamous Song" by Flanders and Swann.
A List of common misconceptions, popular internet myth reports that hippos have pink milk. Biologist David Wynick states, "I think this is an Internet legend that is oft repeated but without any evidence for it that I can find... Like all mammals, hippos produce white or off-white milk for their young."
Hippopotamuses were rarely depicted in European art during the Renaissance and Baroque periods, due to less access to specimens by Europeans. One notable exception is Peter Paul Rubens' ''The Hippopotamus and Crocodile Hunt'' (1615–1616). Ever since Obaysch inspired the "Hippopotamus Polka", hippos have been popular animals in Western culture for their rotund appearance, which many consider comical. The The Walt Disney Company, Disney film ''Fantasia (1940 film), Fantasia'' featured a ballerina hippo dancing to the opera ''La Gioconda (opera), La Gioconda''. The film ''Hugo the Hippo'' is set in Tanzania and involves the title character trying to escape being slaughtered with the help of local children. The ''Madagascar (franchise), Madagascar'' films feature a hippo named List of Madagascar (franchise) characters#Gloria, Gloria. Hippos even inspired a popular board game, Hungry Hungry Hippos.
Among the most famous poems about the hippo is "The Hippopotamus" by T. S. Eliot, where he uses the animal to represent the Catholic Church. Hippos are mentioned in the novelty Christmas song "I Want a Hippopotamus for Christmas" that became a hit for child star Gayla Peevey in 1953. They also featured in the popular "The Hippopotamous Song" by Flanders and Swann.
A List of common misconceptions, popular internet myth reports that hippos have pink milk. Biologist David Wynick states, "I think this is an Internet legend that is oft repeated but without any evidence for it that I can find... Like all mammals, hippos produce white or off-white milk for their young."
Cultural significance
 In Egyptian mythology, the god Set (deity), Set takes the form of a red hippopotamus and fights Horus for control of the land, but is defeated. The goddess Tawaret is depicted as a pregnant woman with a hippo head, representing fierce maternal love. The Ijaw people of the Niger Delta wore masks of aquatic animals like the hippo when practising their water spirit cults, and hippo ivory was used in the divination rituals of the Yoruba. Hippo masks were also used in Nyau funerary rituals of the Chewa people, Chewa of Southern Africa. According to Robert Baden-Powell, 1st Baron Baden-Powell, Robert Baden-Powell, Zulu people, Zulu warriors referred to hippos in war chants. The Behemoth from the Book of Job, 40:15–24 is thought to be based on the hippo.
Hippos have been the subjects of various African folklore, African folktales. According to a San people, San story, when the Creator deity, Creator assigned each animal its place in nature, the hippos wanted to live in the water, but were refused out of fear they might eat all the fish. After begging and pleading, the hippos were finally allowed to live in the water on the condition they would eat grass instead of fish, and fling their dung so it can be inspected for fish bones. In a Ndebele tale, the hippo originally had long, beautiful hair, but it was set on fire by a jealous hare and the hippo had to jump into a nearby pool. The hippo lost most of his hair and was too embarrassed to leave the water.
In Egyptian mythology, the god Set (deity), Set takes the form of a red hippopotamus and fights Horus for control of the land, but is defeated. The goddess Tawaret is depicted as a pregnant woman with a hippo head, representing fierce maternal love. The Ijaw people of the Niger Delta wore masks of aquatic animals like the hippo when practising their water spirit cults, and hippo ivory was used in the divination rituals of the Yoruba. Hippo masks were also used in Nyau funerary rituals of the Chewa people, Chewa of Southern Africa. According to Robert Baden-Powell, 1st Baron Baden-Powell, Robert Baden-Powell, Zulu people, Zulu warriors referred to hippos in war chants. The Behemoth from the Book of Job, 40:15–24 is thought to be based on the hippo.
Hippos have been the subjects of various African folklore, African folktales. According to a San people, San story, when the Creator deity, Creator assigned each animal its place in nature, the hippos wanted to live in the water, but were refused out of fear they might eat all the fish. After begging and pleading, the hippos were finally allowed to live in the water on the condition they would eat grass instead of fish, and fling their dung so it can be inspected for fish bones. In a Ndebele tale, the hippo originally had long, beautiful hair, but it was set on fire by a jealous hare and the hippo had to jump into a nearby pool. The hippo lost most of his hair and was too embarrassed to leave the water.
 Hippopotamuses were rarely depicted in European art during the Renaissance and Baroque periods, due to less access to specimens by Europeans. One notable exception is Peter Paul Rubens' ''The Hippopotamus and Crocodile Hunt'' (1615–1616). Ever since Obaysch inspired the "Hippopotamus Polka", hippos have been popular animals in Western culture for their rotund appearance, which many consider comical. The The Walt Disney Company, Disney film ''Fantasia (1940 film), Fantasia'' featured a ballerina hippo dancing to the opera ''La Gioconda (opera), La Gioconda''. The film ''Hugo the Hippo'' is set in Tanzania and involves the title character trying to escape being slaughtered with the help of local children. The ''Madagascar (franchise), Madagascar'' films feature a hippo named List of Madagascar (franchise) characters#Gloria, Gloria. Hippos even inspired a popular board game, Hungry Hungry Hippos.
Among the most famous poems about the hippo is "The Hippopotamus" by T. S. Eliot, where he uses the animal to represent the Catholic Church. Hippos are mentioned in the novelty Christmas song "I Want a Hippopotamus for Christmas" that became a hit for child star Gayla Peevey in 1953. They also featured in the popular "The Hippopotamous Song" by Flanders and Swann.
A List of common misconceptions, popular internet myth reports that hippos have pink milk. Biologist David Wynick states, "I think this is an Internet legend that is oft repeated but without any evidence for it that I can find... Like all mammals, hippos produce white or off-white milk for their young."
Hippopotamuses were rarely depicted in European art during the Renaissance and Baroque periods, due to less access to specimens by Europeans. One notable exception is Peter Paul Rubens' ''The Hippopotamus and Crocodile Hunt'' (1615–1616). Ever since Obaysch inspired the "Hippopotamus Polka", hippos have been popular animals in Western culture for their rotund appearance, which many consider comical. The The Walt Disney Company, Disney film ''Fantasia (1940 film), Fantasia'' featured a ballerina hippo dancing to the opera ''La Gioconda (opera), La Gioconda''. The film ''Hugo the Hippo'' is set in Tanzania and involves the title character trying to escape being slaughtered with the help of local children. The ''Madagascar (franchise), Madagascar'' films feature a hippo named List of Madagascar (franchise) characters#Gloria, Gloria. Hippos even inspired a popular board game, Hungry Hungry Hippos.
Among the most famous poems about the hippo is "The Hippopotamus" by T. S. Eliot, where he uses the animal to represent the Catholic Church. Hippos are mentioned in the novelty Christmas song "I Want a Hippopotamus for Christmas" that became a hit for child star Gayla Peevey in 1953. They also featured in the popular "The Hippopotamous Song" by Flanders and Swann.
A List of common misconceptions, popular internet myth reports that hippos have pink milk. Biologist David Wynick states, "I think this is an Internet legend that is oft repeated but without any evidence for it that I can find... Like all mammals, hippos produce white or off-white milk for their young."
See also
* American Hippo bill - 1910 bill that proposed the introduction of hippos into Louisiana * Armley Hippo * Owen and Mzee - hippo and tortoise who bonded * Fiona_(hippopotamus), Fiona - hippo born 6 weeks early at the Cincinnati Zoo and Botanical GardenReferences
External links
* * * {{Authority control Hippopotamuses, Mammals of Africa Fauna of Sub-Saharan Africa Herbivorous mammals Vulnerable animals Vulnerable biota of Africa Mammals described in 1758 Articles containing video clips Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Semiaquatic mammals