neurogenic bladder dysfunction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Neurogenic bladder dysfunction, often called by the shortened term neurogenic bladder, was technically termed neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction by the International Continence Society. It refers to

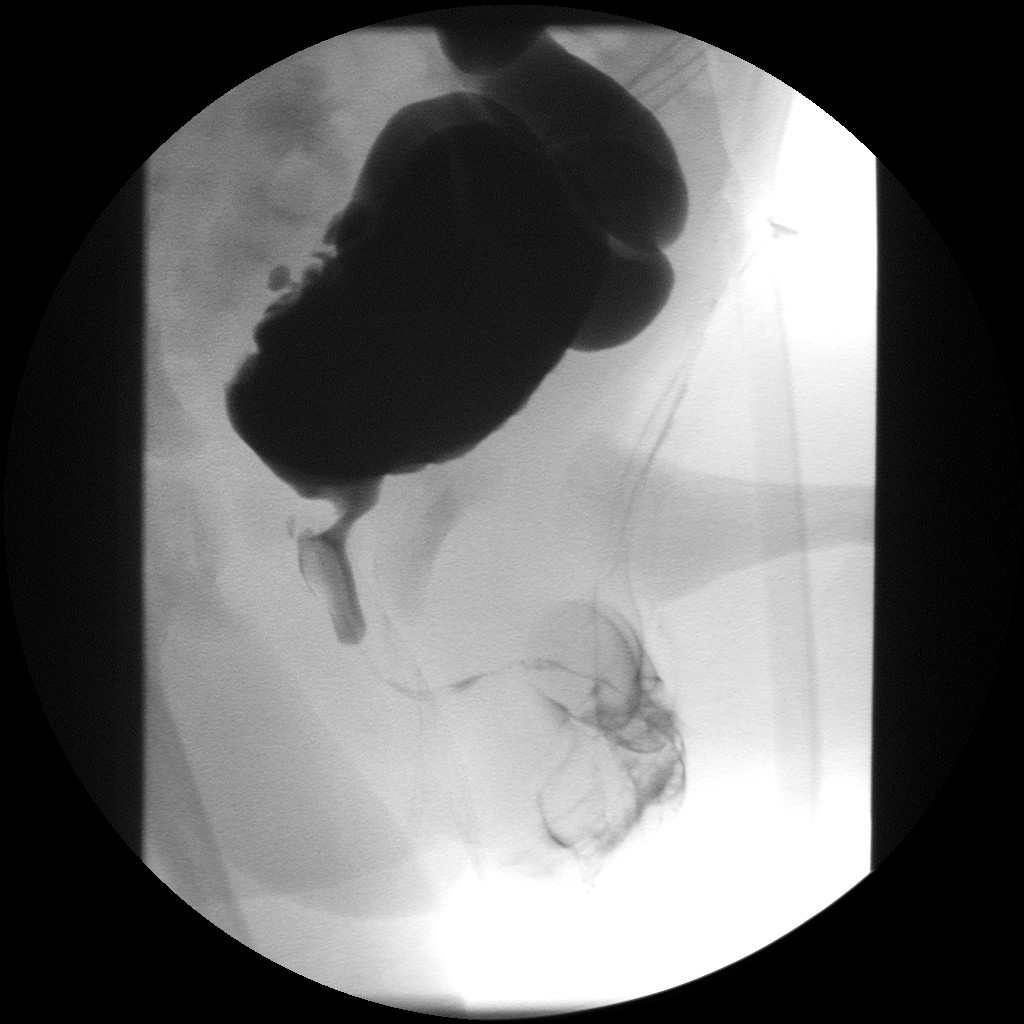 The diagnosis of neurogenic bladder is made based on a complete history and physical examination and may require imaging and specialized studies. History should include information on the onset, duration, triggers, severity, other medical conditions and medications (including
The diagnosis of neurogenic bladder is made based on a complete history and physical examination and may require imaging and specialized studies. History should include information on the onset, duration, triggers, severity, other medical conditions and medications (including
urinary bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the ...
problems due to disease or injury of the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
or peripheral nerves involved in the control of urination
Urination is the release of urine from the bladder through the urethra in Placentalia, placental mammals, or through the cloaca in other vertebrates. It is the urinary system's form of excretion. It is also known medically as micturition, v ...
. There are multiple types of neurogenic bladder depending on the underlying cause and the symptoms. Symptoms include overactive bladder
Overactive bladder (OAB) is a common condition where there is a frequent feeling of needing to urinate to a degree that it negatively affects a person's life. The frequent need to urinate may occur during the day, at night, or both. Loss of bl ...
, urinary urgency, frequency, incontinence or difficulty passing urine. A range of diseases or conditions can cause neurogenic bladder including spinal cord injury
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. It is a destructive neurological and pathological state that causes major motor, sensory and autonomic dysfunctions.
Symptoms of ...
, multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit ...
, stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
, brain injury, spina bifida, peripheral nerve damage, Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
, multiple system atrophy or other neurodegenerative diseases. Neurogenic bladder can be diagnosed through a history and physical as well as imaging and more specialized testing. In addition to symptomatic treatment, treatment depends on the nature of the underlying disease and can be managed with behavioral changes, medications, surgeries, or other procedures. The symptoms of neurogenic bladder, especially incontinence, can severely degrade a person's quality of life.
Classification
There are different types of neurogenic bladder depending on the underlying cause. Many of these types may have similar symptoms.
Uninhibited
Uninhibited bladder is usually due to damage to the brain from astroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
or brain tumor
A brain tumor (sometimes referred to as brain cancer) occurs when a group of cells within the Human brain, brain turn cancerous and grow out of control, creating a mass. There are two main types of tumors: malignant (cancerous) tumors and benign ...
. This can cause reduced sensation of bladder fullness, low capacity bladder and urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence (UI), also known as involuntary urination, is any uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a significant effect on quality of life. Urinary incontinence is common in older women ...
. Unlike other forms of neurogenic bladder, it does not lead to high bladder pressures that can cause kidney damage.
Spastic
In spastic neurogenic bladder (also known asupper motor neuron
Upper motor neurons (UMNs) is a term introduced by William Gowers in 1886. They are found in the cerebral cortex and brainstem and carry information down to activate interneurons and lower motor neurons, which in turn directly signal muscles ...
or hyper-reflexive bladder), the muscle of the bladder ( detrusor) and urethral sphincter
The urethral sphincters are two muscles used to control the exit of urine in the urinary bladder through the urethra. The two muscles are either the external sphincter muscle of male urethra, male or external sphincter muscle of female urethra, fe ...
do not work together and are usually tightly contracted at the same time. This phenomenon is also called detrusor external sphincter dyssynergia (DESD). This leads to urinary retention
Urinary retention is an inability to completely empty the bladder. Onset can be sudden or gradual. When of sudden onset, symptoms include an inability to urinate and lower abdominal pain. When of gradual onset, symptoms may include urinary incont ...
with high pressures in the bladder that can damage the kidneys. The bladder volume is usually smaller than normal due to increased muscle tone in the bladder. Spastic neurogenic bladder is usually caused by damage to the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
above the level of the 10th thoracic vertebrae
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebra (anatomy), vertebrae of intermediate size between the ce ...
(T10).
Flaccid
In flaccid bladder (also known aslower motor neuron
Lower motor neurons (LMNs) are motor neurons located in either the anterior grey column, anterior nerve roots (spinal lower motor neurons) or the cranial nerve nuclei of the brainstem and cranial nerves with motor function (cranial nerve lower ...
or hypotonic bladder), the muscles of the bladder lose ability to contract normally. This can cause the inability to void urine even if the bladder is full and cause a large bladder capacity. The internal urinary sphincter can contract normally, however urinary incontinence is common. This type of neurogenic bladder is caused by damage to the peripheral nerves that travel from the spinal cord to the bladder.
Mixed
Mixed type of neurogenic bladder can cause a combination of the above presentations. In mixed type A, the bladder muscle is flaccid but the sphincter is overactive. This creates a large, low pressure bladder and inability to void, but does not carry as much risk for kidney damage as a spastic bladder. Mixed type B is characterized by a flaccid external sphincter and a spastic bladder causing problems with incontinence.Signs and symptoms
Neurogenic bladder can cause a range of urinary symptoms including urinary urgency,urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence (UI), also known as involuntary urination, is any uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a significant effect on quality of life. Urinary incontinence is common in older women ...
or difficulty urinating (urinary retention
Urinary retention is an inability to completely empty the bladder. Onset can be sudden or gradual. When of sudden onset, symptoms include an inability to urinate and lower abdominal pain. When of gradual onset, symptoms may include urinary incont ...
). The first sign of bladder dysfunction may be recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs).
Complications
Neurogenic bladder can cause hydronephrosis (swelling of a kidney due to a build-up of urine), recurrent urinary tract infections, and recurrent kidney stones which may compromise kidney function. This is especially significant in spastic neurogenic bladder that leads to high bladder pressures. Kidney failure was previously a leading cause of mortality in patients with spinal cord injury but is now dramatically less common due to improvements in bladder management.Causes
Urine storage and elimination (urination) requires coordination between the bladder emptying muscle (detrusor) and the external sphincter of the bladder. This coordination can be disrupted by damage or diseases of the central nervous system, peripheral nerves orautonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), sometimes called the visceral nervous system and formerly the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the nervous system that operates viscera, internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervo ...
. Any trauma or disease impairing the voluntary micturition process' components, e.g., spinal cord, peripheral nerves, bladder sphincter or the urethral internal and external sphincters, can cause bladder dysfunction.
Central nervous system
Damage to the brain or spinal cord is the most common cause of neurogenic bladder. Damage to the brain can be caused bystroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
, brain tumors, multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit ...
, Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
, multiple system atrophy or other neurodegenerative conditions. Bladder involvement is more likely if the damage is in the area of the pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other mammals, lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of ...
. Damage to the spinal cord can be caused by traumatic injury, demyelinating disease, meningitis-retention syndrome, vitamin B12 deficiency, syringomyelia, cauda equina syndrome, or spina bifida. Spinal cord compression from herniated disk
A disc herniation or spinal disc herniation is an injury to the intervertebral disc between two vertebrae, usually caused by excessive Strain (injury), strain or trauma to the Vertebral column, spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensatio ...
s, tumor, or spinal stenosis can also result in neurogenic bladder.
Peripheral nervous system
Damage to the nerves that travel from the spinal cord to the bladder (peripheral nerves) can cause neurogenic bladder, usually the flaccid type. Nerve damage can be caused bydiabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
, alcoholism
Alcoholism is the continued drinking of alcohol despite it causing problems. Some definitions require evidence of dependence and withdrawal. Problematic use of alcohol has been mentioned in the earliest historical records. The World He ...
, vitamin B12 deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency, also known as cobalamin deficiency, is the medical condition in which the blood and tissue have a lower than normal level of Vitamin B12, vitamin B12. Symptoms can vary from none to severe. Mild deficiency may have fe ...
, or genital herpes. Peripheral nerves can also be damaged as a complication of major surgery of the pelvis, such as for removal of tumors or as collateral damage from pelvic radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), ...
or chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
, e.g., cytotoxic chemotherapy involving doxorubicin.
Diagnosis
 The diagnosis of neurogenic bladder is made based on a complete history and physical examination and may require imaging and specialized studies. History should include information on the onset, duration, triggers, severity, other medical conditions and medications (including
The diagnosis of neurogenic bladder is made based on a complete history and physical examination and may require imaging and specialized studies. History should include information on the onset, duration, triggers, severity, other medical conditions and medications (including anticholinergic
Anticholinergics (anticholinergic agents) are substances that block the action of the acetylcholine (ACh) neurotransmitter at synapses in the central nervous system, central and peripheral nervous system.
These agents inhibit the parasympatheti ...
s, calcium channel blocker
Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium () through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as ...
s, diuretics, sedatives, alpha-adrenergic agonist, alpha 1 antagonists). Urinary symptoms may include frequency, urgency, incontinence or recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs). Questionnaires can be helpful in quantifying symptom burden. In children it is important to obtain a prenatal
Prenatal development () involves the embryonic development, development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparity, viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic develop ...
and developmental history.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
imaging can give information on the shape of the bladder, post-void residual volume, and evidence of kidney damage such as kidney size, thickness or ureter
The ureters are tubes composed of smooth muscle that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In an adult human, the ureters typically measure 20 to 30 centimeters in length and about 3 to 4 millimeters in diameter. They are lin ...
al dilation. Trabeculated bladder on ultrasound indicates high risk of developing urinary tract abnormalities such as hydronephrosis and stones. A voiding cystourethrography study uses contrast dye to obtain images of the bladder both when it is full and after urination which can show changes in bladder shape consistent with neurogenic bladder.
Urodynamic studies are an important component of the evaluation for neurogenic bladder. Urodynamics refers to the measurement of the pressure-volume relationship in the bladder. The bladder usually stores urine at low pressure and urination can be completed without a dramatic pressure rise. Damage to the kidneys is probable if the pressure rises above 40 cm of water during filling. Bladder pressure can be measured by cystometry, during which the bladder is artificially filled with a catheter and bladder pressures and detrusor activity are monitored. Patterns of involuntary detrusor activity as well as bladder flexibility, or compliance, can be evaluated. The most valuable test to test for detrusor sphincter dyssynergia (DESD) is to perform cystometry simultaneously with external sphincter electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyo ...
(EMG). Uroflowmetry is a less-invasive study that can measure urine flow rate and use it to estimate detrusor strength and sphincter resistance. Urethral pressure monitoring is another less-invasive approach to assessing detrusor sphincter dyssynergia. These studies can be repeated at regular intervals, especially if symptoms worsen or to measure response to therapies.
Evaluation of kidney function through blood tests such as serum creatinine should be obtained.
Sustained post-voiding high bladder pressures indicate a potential obstruction and typically recommend pelvic imaging with CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
or cystoscopy
Cystoscopy is endoscopy of the urinary bladder via the urethra. It is carried out with a cystoscope.
The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
The cystoscope has lenses like a telescope or microscop ...
to rule out tumor obstruction or urethral strictures. The inside of the bladder can be visualized during a cystoscopic pathological exam, but the procedure is not recommended for routine follow-up due to low observed incidence rates.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the type of neurogenic bladder and other medical problems. Treatment strategies include catheterization, medications, surgeries or other procedures. The goals of treatment focus on preserving the structure and function of the upper urinary tract, and on improving the quality of life for patients with neurogenic bladder.Medications
The first-line therapy for most patients is ananticholinergic
Anticholinergics (anticholinergic agents) are substances that block the action of the acetylcholine (ACh) neurotransmitter at synapses in the central nervous system, central and peripheral nervous system.
These agents inhibit the parasympatheti ...
medication. These are used for patients with over-active bladder muscles, who have lost the ability to hold their urine in. Oxybutynin is a common anti-cholinergic medication used to reduce bladder contractions by blocking M3 muscarinic receptors in the detrusor muscle. Its use is limited by side effects such as dry mouth, constipation and decreased sweating. Patients must also be monitored for newly-developed difficulty emptying the bladder, which may result from excessive effects of the drug. Tolterodine is a longer acting anticholinergic that may have fewer side effects.
For urinary retention, cholinergics (muscarinic agonists) like bethanechol can improve the squeezing ability of the bladder. Alpha blockers can also reduce outlet resistance and allow complete emptying if there is adequate bladder muscle function.
Catheterization
Use of acatheter
In medicine, a catheter ( ) is a thin tubing (material), tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. ...
is a standard approach for patients with difficulty voiding (emptying) the bladder. For most patients, this can be accomplished with intermittent catherization which involves no surgery or permanently attached appliances. Intermittent catheterization involves using straight catheters (which are usually disposable or single-use products) several times a day to empty the bladder. This can be done independently or with assistance. For people who are unable to use disposable straight catheters, a Foley catheter
In urology, a Foley catheter is one of many types of urinary catheters (UC). The Foley UC was named after Frederic Foley, who produced the original design in 1929. Foleys are indwelling UC, often referred to as an IDCs (sometimes IDUCs). This dif ...
allows continuous drainage of urine into a sterile drainage bag that is worn by the patient, but such catheters are associated with higher rates of complications.
Catheters are preferred over externally-applied pressure (such as with hands) or straining of the abdomen, even when these methods succeed in completely emptying the bladder. Those techniques can elevate the pressure inside the detrusor muscle of the bladder and cause additional bladder dysfunction, or even rupture the bladder.
Botulinum Toxin
Botulinum toxin
Botulinum toxin, or botulinum neurotoxin (commonly called botox), is a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium ''Clostridium botulinum'' and related species. It prevents the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine from axon en ...
(Botox) can be used through two different approaches. For spastic neurogenic bladder, the bladder muscle (detrusor) can be injected which will cause it to be flaccid for 6–9 months. This prevents high bladder pressures and intermittent catherization must be used during this time.
Botox can also be injected into the external sphincter to paralyze a spastic sphincter in patients with detrusor sphincter dyssynergia.
Neuromodulation
There are various strategies to alter the interaction between the nerves and muscles of the bladder, including nonsurgical therapies (transurethral electrical bladder stimulation), minimally invasive procedures (sacral neuromodulation pacemaker), and operative (reconfiguration of sacral nerve root anatomy).Surgery
Surgical interventions may be pursued if medical approaches have been maximized. Surgical options depend on the type of dysfunction observed on urodynamic testing, and may include: * Urinary Diversion: Creation of astoma
In botany, a stoma (: stomata, from Greek language, Greek ''στόμα'', "mouth"), also called a stomate (: stomates), is a pore found in the Epidermis (botany), epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exc ...
(from the intestines, called "conduit") on the skin of the abdomen that bypasses the urethra to empty the bladder directly through the skin opening. Several techniques may be used. One technique is the Mitrofanoff
The Mitrofanoff procedure, also known as the Mitrofanoff appendicovesicostomy, is a surgical procedure in which the appendix (anatomy), appendix is used to create a conduit, or channel, between the skin surface and the urinary bladder. The small o ...
stoma, where the appendix or a portion of the ileum ('Yang-Monti' conduit) are used to create the diversion. The ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine may ...
and ascending colon can also be used to create a pouch accessible for catheter
In medicine, a catheter ( ) is a thin tubing (material), tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. ...
ization ( Indiana pouch).
* Urethral stents or urethral sphincterotomy are other surgical approaches that can reduce bladder pressures but require use of an external urinary collection device.
* Urethral slings may be used in both adults and children
* Artificial Urinary Sphincters have shown good term outcomes in adults and pediatric patients. An artificial urinary sphincter has three components: a control pump, an inflatable cuff that goes around the urethra, and a pressure regulating balloon. One study on 97 patients followed for a mean duration of 4 years found that 92% percent were continent at day and night during follow up. However, patients in this study who had intermediate-type bladders underwent adjuvant cystoplasty. Additionally, one study showed that there was no significant difference in success rates between artificial urinary sphincters and sling procedures, however patients tended to need more additional surgeries with the artificial sphincter versus a sling.
* Bladder Neck Closure is a major surgical procedure which can be a last resort treatment for incontinence, a Mitrofanoff stoma is necessary to empty the bladder.
Pediatric Surgical Care
* Mitrofanoff Surgery: A surgery in which a conduit, such as the small intestine or appendix, is used to divert urine from a high pressure bladder to the skin to create a stoma, where the bladder can be catheterized via the stoma. This surgery is indicated in spina bifida, urethral strictures, urogenital anomalies, and worsening bladder dysfunction that is refractory to medical treatment. Some providers have begun performing these surgery with a minimally invasive robot. ** Mitrofanoff using the appendix: The appendix is mobilized from the cecum, while still being connected to its blood source (mesentery). A catheter is passed through the appendix to ensure it is patent. The appendix is then connected to the bladder on one side and to the skin of the abdomen on the other side, creating a stoma. ** Yang-Monti Mitrofanoff: A 2-3 cm segment of the small intestine (ileum) is used. The ileum is then mobilized to the bladder and connected to the bladder on one side and to the skin of the abdomen on the other side, creating a stoma using the intestine. * Augmentation Cytoplasty: A class of surgery in which a segment of intestine is used to increase the capacity of the bladder. This surgery is indicated in patients who have low capacity bladders, poorly compliant bladders, and overactive bladder that is refractory to medical treatment. ** Ileocystoplasty (Most common): A segment of small intestine (ileum) is isolated and disconnected from the rest of the bowel. The rest of the bowel is reconnected. The removed segment is opened up and is attached to the bladder to increase bladder capacity. ** Stomach, cecum, and sigmoid colon have been used for augmentation, however it is much less commonly used. ** Detrusorectomy: part of the detrusor muscle of the bladder is stripped away from the bladder to increase capacity. * Sling: A class of surgery that is often done for patients who have paralyzed pelvic floors and urinary incontinence ** Sling suspension in boys: A plane is created between the bladder neck/prostate and rectum to allow a sling to be passed through in order to assist with continence. ** Sling suspension in girls: A plane is created between the bladder neck and anterior vaginal wall to allow a sling to be passed in order to assist with continence.Epidemiology
The overall prevalence of neurogenic bladder is limited due to the broad range of conditions that can lead to urinary dysfunction. Neurogenic bladder is common with spinal cord injury and multiple sclerosis. Rates of some type of urinary dysfunction surpass 80% one year after spinal cord injury. Among patients with multiple sclerosis, 20–25% will develop neurogenic bladder although the type and severity bladder dysfunction is variable.Incidence
In the United States, 40-90% of patients withmultiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit ...
, 37-72% of patients with Parkinsonism, and 15% of patients with stroke have neurogenic bladder. Dysfunction of the bladder is also frequently seen in patients with Spina Bifida, which affects 1 in 2700 births in the United States. It has been documented that about 61% of adult patients with Spina Bifida have some form of urinary incontinence. Around 70-80% of US patients with spinal cord injury have degrees of bladder dysfunction.
Worldwide annual spinal cord injuries result in neurogenic bladder dysfunction occurrences between 12 - 65+ cases/million population.
Society and culture
Burden
The burden of neurogenic bladder dysfunction on individuals and health care systems is substantial, but the actual costs of care are less understood. A recent systematic review of the literature assessed the global costs associated with the current state of care for neurogenic bladder and found that the annual costs of routine care can range from $2,039.69 to $12,219.07, with lifetime costs reaching up to $112,774 when complications are considered. Catheters and absorbent aids are among the costliest categories of expenditure during routine care. More invasive and reconstructive treatments were found to be even more costly, with costs ranging from $18,057 to $55,873.See also
* Bladder sphincter dyssynergia *Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit ...
* Pseudodyssynergia
* Spinal cord injury
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. It is a destructive neurological and pathological state that causes major motor, sensory and autonomic dysfunctions.
Symptoms of ...
* Urinary retention
Urinary retention is an inability to completely empty the bladder. Onset can be sudden or gradual. When of sudden onset, symptoms include an inability to urinate and lower abdominal pain. When of gradual onset, symptoms may include urinary incont ...
* Neurogenic bowel dysfunction
References
External links
{{Urinary tract disease Urinary bladder disorders