Neuchâtel Young Sprinters HC Players on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
, neighboring_municipalities= Auvernier,
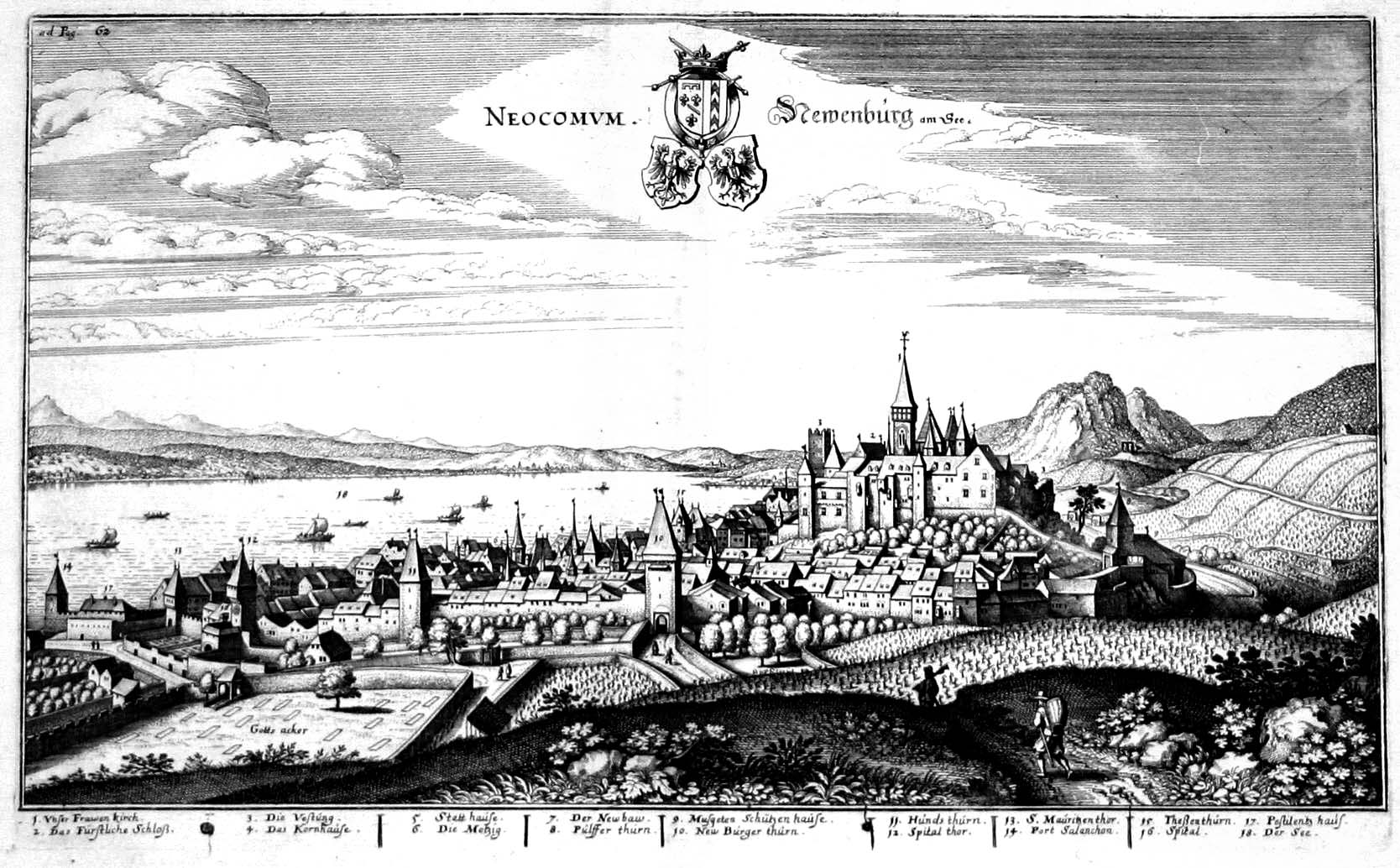 The New Latin name for Neuchâtel is the Greek-derived ''Neocomum'', and this gives the adjective ''neocomensis'' which appears on the seal of the University of Neuchâtel (in ''Universitas Neocomensis Helvetiorum'') and the English adjective Neocomian, a term for a former stratigraphic stage of the
The New Latin name for Neuchâtel is the Greek-derived ''Neocomum'', and this gives the adjective ''neocomensis'' which appears on the seal of the University of Neuchâtel (in ''Universitas Neocomensis Helvetiorum'') and the English adjective Neocomian, a term for a former stratigraphic stage of the
 The oldest traces of humans in the municipal area are the remains of a
The oldest traces of humans in the municipal area are the remains of a
 At Les Favarger a Gallo-Roman and at André Fontaine a small coin depot were discovered. In 1908, an excavation at the mouth of the discovered Gallo-Roman baths from the 2nd and 3rd Centuries AD.
At Les Favarger a Gallo-Roman and at André Fontaine a small coin depot were discovered. In 1908, an excavation at the mouth of the discovered Gallo-Roman baths from the 2nd and 3rd Centuries AD.
 Before the 2021 merger of municipalities, Neuchâtel had an area, , of . Of this area, or 10.2% was used for agricultural purposes, while or 53.8% was forested. Of the rest of the land, or 35.5% was settled (buildings or roads), or 0.2% was either rivers or lakes and or 0.1% was unproductive land.Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Land Use Statistics
Before the 2021 merger of municipalities, Neuchâtel had an area, , of . Of this area, or 10.2% was used for agricultural purposes, while or 53.8% was forested. Of the rest of the land, or 35.5% was settled (buildings or roads), or 0.2% was either rivers or lakes and or 0.1% was unproductive land.Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Land Use Statistics
2009 data accessed 25 March 2010 Of the built up area, industrial buildings made up 2.2% of the total area while housing and buildings made up 18.0% and transportation infrastructure made up 10.1%. while parks, green belts and sports fields made up 4.3%. Out of the forested land, 51.8% of the total land area was heavily forested and 2.0% is covered with orchards or small clusters of trees. Of the agricultural land, 1.4% was used for growing crops and 8.0% was pastures. All the water in the municipality is in lakes. The city is located on the northwestern shore of Lake Neuchâtel, a few kilometers east of Peseux and west of Saint-Blaise. Above Neuchâtel, roads and train tracks rise steeply into the folds and ridges of the Jura range—known within the canton as the ''Montagnes neuchâteloises''. Like the continuation of the mountains on either side, this is wild and hilly country, not exactly mountainous compared with the high Alps further south but still characterized by remote, windswept settlements and deep, rugged valleys. It is also the heartland of the celebrated Swiss watchmaking industry, centered on the once-famous towns of La Chaux-de-Fonds and Le Locle, which both rely heavily on their horological past to draw in visitors. The river Doubs marks for a part the border with France, set down in a gorge and forming along its path an impressive waterfall, the , and lake, the
 The blazon of the municipal coat of arms is ''Or, an Eagle displayed Sable beaked, langued and membered Gules, escutcheon Or, on a pale Gules three Chevrons Argent.''
The blazon of the municipal coat of arms is ''Or, an Eagle displayed Sable beaked, langued and membered Gules, escutcheon Or, on a pale Gules three Chevrons Argent.''
accessed 19 June 2010 Over the last 10 years (2000–2010) the population has changed at a rate of 3.9%. It has changed at a rate of 2.4% due to migration and at a rate of 1% due to births and deaths.
accessed 25-October-2011 , the population was 47.7% male and 52.3% female. The population was made up of 10,371 Swiss men (31.5% of the population) and 5,344 (16.2%) non-Swiss men. There were 12,366 Swiss women (37.5%) and 4,892 (14.8%) non-Swiss women.Canton of Neuchâtel Statistics
, ''République et canton de Neuchâtel - Recensement annuel de la population'' accessed 13 October 2011 Of the population in the municipality, 8,558 or about 26.0% were born in Neuchâtel and lived there in 2000. There were 5,134 or 15.6% who were born in the same canton, while 7,744 or 23.5% were born somewhere else in Switzerland, and 10,349 or 31.4% were born outside of Switzerland. , children and teenagers (0–19 years old) make up 19.3% of the population, while adults (20–64 years old) make up 63.1% and seniors (over 64 years old) make up 17.6%. , there were 14,143 people who were single and never married in the municipality. There were 14,137 married individuals, 2,186 widows or widowers and 2,448 individuals who are divorced.STAT-TAB Datenwürfel für Thema 40.3 - 2000
accessed 2 February 2011 , there were 15,937 private households in the municipality, and an average of 2. persons per household. There were 7,348 households that consist of only one person and 547 households with five or more people. , a total of 15,447 apartments (89.9% of the total) were permanently occupied, while 1,429 apartments (8.3%) were seasonally occupied and 311 apartments (1.8%) were empty.Swiss Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB - Datenwürfel für Thema 09.2 - Gebäude und Wohnungen
accessed 28 January 2011 , the construction rate of new housing units was 2.5 new units per 1000 residents. the average price to rent an average apartment in Neuchâtel was 921.35
2003 data accessed 26 May 2010 The vacancy rate for the municipality, , was 0.53%.
Colors=
id:lightgrey value:gray(0.9)
id:darkgrey value:gray(0.8)
ImageSize = width:1100 height:500
PlotArea = height:350 left: 100 bottom:90 right:100
Legend = columns:3 left:220 top:70 columnwidth:160
AlignBars = justify
DateFormat = x.y
Period = from:0 till:39000
TimeAxis = orientation:vertical
AlignBars = justify
ScaleMajor = gridcolor:darkgrey increment:8000 start:0
ScaleMinor = gridcolor:lightgrey increment:1600 start:0
Colors=
id:TO value:yellowgreen legend:Total
id:FR value:teal legend:French_Speaking
id:GE value:green legend:German_Speaking
id:PR value:lightpurple legend:Protestant
id:CA value:oceanblue legend:Catholic
id:SW value:red legend:Swiss
PlotData=
color:yellowgreen width:40 mark:(line,white) align:center
bar:1850 from:start till:7901 text:"7,901" color:TO
bar:1870 from:start till:12934 text:"12,934" color:TO
bar:1888 from:start till:16565 text:"16,565" color:TO
bar:1900 from:start till:21195 text:"21,195" color:TO
bar:1910 from:start till:24171 text:"24,171" color:TO
bar:1930 from:start till:22668 text:"22,668" color:TO
bar:1950 from:start till:27998 text:"27,998" color:TO
bar:1970 from:start till:38784 text:"38,784" color:TO
bar:1990 from:start till:33579 text:"33,579" color:TO
bar:2000 from:start till:32914 text:"32,914" color:TO
LineData =
points:(300,193)(400,230) color:FR
points:(400,230)(500,247) color:FR
points:(500,247)(600,243) color:FR
points:(600,243)(700,287) color:FR
points:(700,287)(800,325) color:FR
points:(800,325)(900,311) color:FR
points:(900,311)(1000,322) color:FR
points:(300,132)(400,131) color:GE
points:(400,131)(500,136) color:GE
points:(500,136)(600,131) color:GE
points:(600,131)(700,133) color:GE
points:(700,133)(800,136) color:GE
points:(800,136)(900,112) color:GE
points:(900,112)(1000,107) color:GE
points:(100,154)(200,189) color:PR
points:(200,189)(300,215) color:PR
points:(300,215)(400,247) color:PR
points:(400,247)(500,267) color:PR
points:(500,267)(600,257) color:PR
points:(600,257)(700,282) color:PR
points:(700,282)(800,286) color:PR
points:(800,286)(900,208) color:PR
points:(900,208)(1000,182) color:PR
points:(100,97)(200,111) color:CA
points:(200,111)(300,111) color:CA
points:(300,111)(400,121) color:CA
points:(400,121)(500,125) color:CA
points:(500,125)(600,123) color:CA
points:(600,123)(700,143) color:CA
points:(700,143)(800,227) color:CA
points:(800,227)(900,209) color:CA
points:(900,209)(1000,187) color:CA
points:(100,153)(200,191) color:SW
points:(200,191)(300,220) color:SW
points:(300,220)(400,253) color:SW
points:(400,253)(500,275) color:SW
points:(500,275)(600,275) color:SW
points:(600,275)(700,326) color:SW
points:(700,326)(800,359) color:SW
points:(800,359)(900,308) color:SW
points:(900,308)(1000,295) color:SW
accessed 24 June 2010 Of the working population, 33.7% used public transportation to get to work, and 43.4% used a private car.
 Neuchâtel is home to the French-speaking University of Neuchâtel. The university has five faculties and more than a dozen institutes, including arts and human sciences, natural sciences, law, economics and theology. For the 2005–2006 academic year, 3,595 students (1,987 women and 1,608 men) were enrolled. The Faculty of Arts and Human Sciences is the largest school of those that comprise the university of Neuchâtel with 1,500 students. Some courses at the University are taught in English.
Neuchâtel is home to eight libraries: the Bibliothèque de la Faculté des Lettres, the ''Bibliothèque de l'Institut d'ethnologie et du Musée d'ethnographie'', the ''Bibliothèque de la Faculté des Sciences'', the ''Bibliothèque de droit'', the ''Bibliothèque des sciences économiques'', the ''Bibliothèque de la Faculté de théologie'', the ''Service de coordination des bibliothèques'' and the ''Haute école Arc - Santé''. There was a combined total () of 736,773 books or other media in the libraries, and in the same year a total of 58,427 items were loaned out.
In Neuchâtel about 11,076 or (33.7%) of the population have completed non-mandatory
Neuchâtel is home to the French-speaking University of Neuchâtel. The university has five faculties and more than a dozen institutes, including arts and human sciences, natural sciences, law, economics and theology. For the 2005–2006 academic year, 3,595 students (1,987 women and 1,608 men) were enrolled. The Faculty of Arts and Human Sciences is the largest school of those that comprise the university of Neuchâtel with 1,500 students. Some courses at the University are taught in English.
Neuchâtel is home to eight libraries: the Bibliothèque de la Faculté des Lettres, the ''Bibliothèque de l'Institut d'ethnologie et du Musée d'ethnographie'', the ''Bibliothèque de la Faculté des Sciences'', the ''Bibliothèque de droit'', the ''Bibliothèque des sciences économiques'', the ''Bibliothèque de la Faculté de théologie'', the ''Service de coordination des bibliothèques'' and the ''Haute école Arc - Santé''. There was a combined total () of 736,773 books or other media in the libraries, and in the same year a total of 58,427 items were loaned out.
In Neuchâtel about 11,076 or (33.7%) of the population have completed non-mandatory
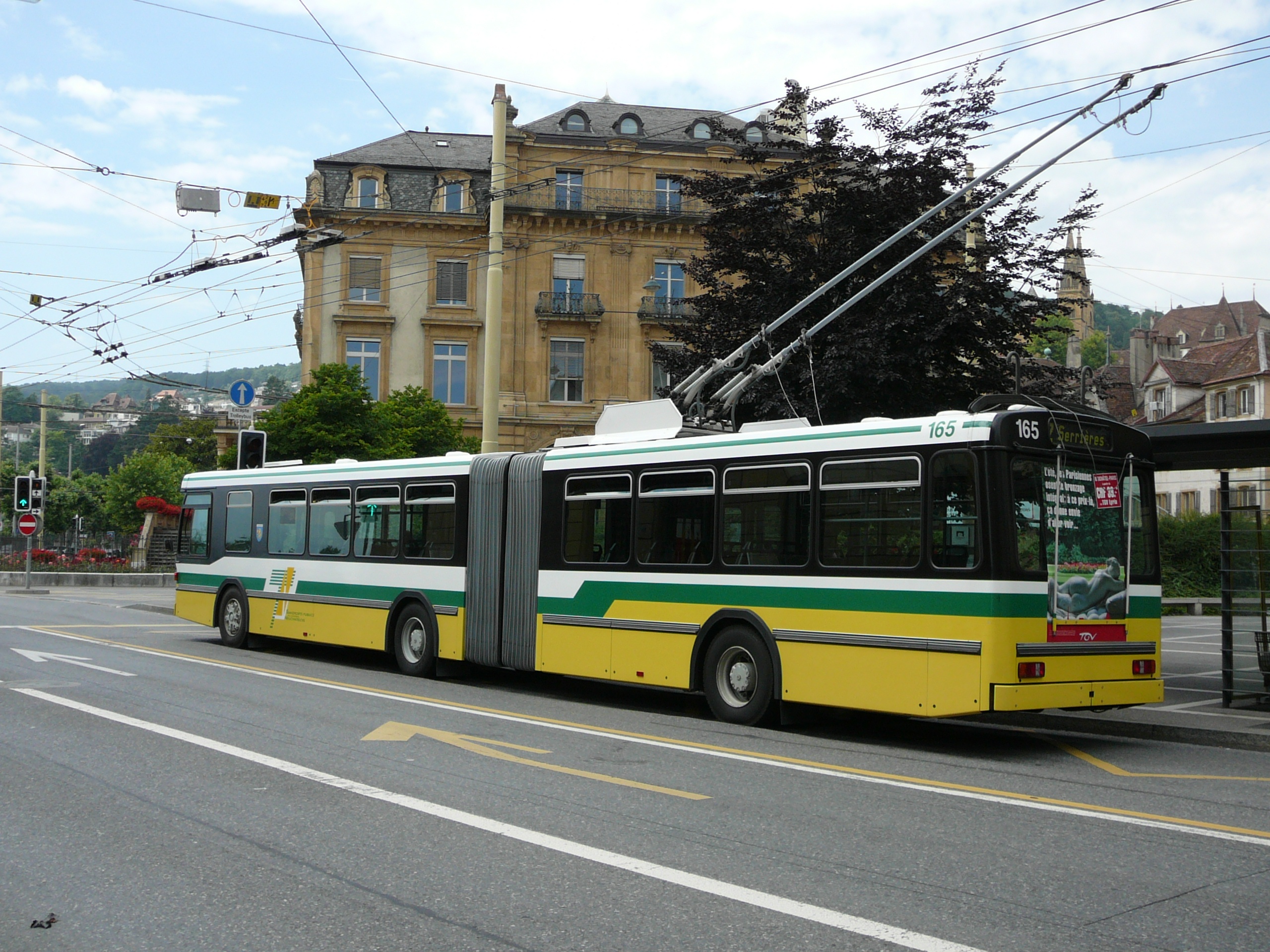 Neuchâtel has local public transport provided by Les Transports Publics du Littoral Neuchâtelois (TN), which operates the Neuchâtel trolleybus system, a funicular, and an interurban light rail line to Boudry. The total length of the TN network is . It serves 78,400 people (more than half using it on a daily basis) and in 2007 transported 17,670,000 travelers.
Neuchâtel railway station forms part of one of Switzerland's most important railway lines, the Jura foot railway (Olten–Genève-Aéroport), which is operated by the
Neuchâtel has local public transport provided by Les Transports Publics du Littoral Neuchâtelois (TN), which operates the Neuchâtel trolleybus system, a funicular, and an interurban light rail line to Boudry. The total length of the TN network is . It serves 78,400 people (more than half using it on a daily basis) and in 2007 transported 17,670,000 travelers.
Neuchâtel railway station forms part of one of Switzerland's most important railway lines, the Jura foot railway (Olten–Genève-Aéroport), which is operated by the
 Neuchâtel's Old Town has about 140 street fountains, a handful of which date from the 16th century. The Place des Halles is overlooked by Louis XIV architecture – shuttered façades and the turreted orioles of the 16th-century Maison des Halles. To the east, on Rue de l’Hôpital, is the grand 1790 Hôtel de Ville (Town Hall), designed by Louis XVI's chief architect Pierre-Adrien Paris.
The center of the Old Town is located at the top of the hill, accessed by the steeply winding Rue du Château. The Collégiale church, begun in 1185 and consecrated in 1276, is an example of early Gothic. The east end of the church has three Norman apses. The main entrance, to the west, is crowned by a giant rose window of stained glass. Within the vaulted interior, the transept is lit by a lantern tower. The Cenotaph of the Counts of Neuchâtel is located on the north wall of the choir. Begun in 1372, and the only artwork of its kind to survive north of the Alps, the monument comprises fifteen near-life-size painted statues of various knights and ladies from Neuchâtel's past, framed by 15th-century arches and gables. Beside the church is the Castle, begun in the 12th century and still in use as the offices of the cantonal government. The nearby turreted Prison Tower, which is the remains of a medieval bastion, has panoramic views over the town, along with models of Neuchâtel in different eras.
Neuchâtel's Old Town has about 140 street fountains, a handful of which date from the 16th century. The Place des Halles is overlooked by Louis XIV architecture – shuttered façades and the turreted orioles of the 16th-century Maison des Halles. To the east, on Rue de l’Hôpital, is the grand 1790 Hôtel de Ville (Town Hall), designed by Louis XVI's chief architect Pierre-Adrien Paris.
The center of the Old Town is located at the top of the hill, accessed by the steeply winding Rue du Château. The Collégiale church, begun in 1185 and consecrated in 1276, is an example of early Gothic. The east end of the church has three Norman apses. The main entrance, to the west, is crowned by a giant rose window of stained glass. Within the vaulted interior, the transept is lit by a lantern tower. The Cenotaph of the Counts of Neuchâtel is located on the north wall of the choir. Begun in 1372, and the only artwork of its kind to survive north of the Alps, the monument comprises fifteen near-life-size painted statues of various knights and ladies from Neuchâtel's past, framed by 15th-century arches and gables. Beside the church is the Castle, begun in the 12th century and still in use as the offices of the cantonal government. The nearby turreted Prison Tower, which is the remains of a medieval bastion, has panoramic views over the town, along with models of Neuchâtel in different eras.

 Neuchâtel has several museums, including the
Neuchâtel has several museums, including the
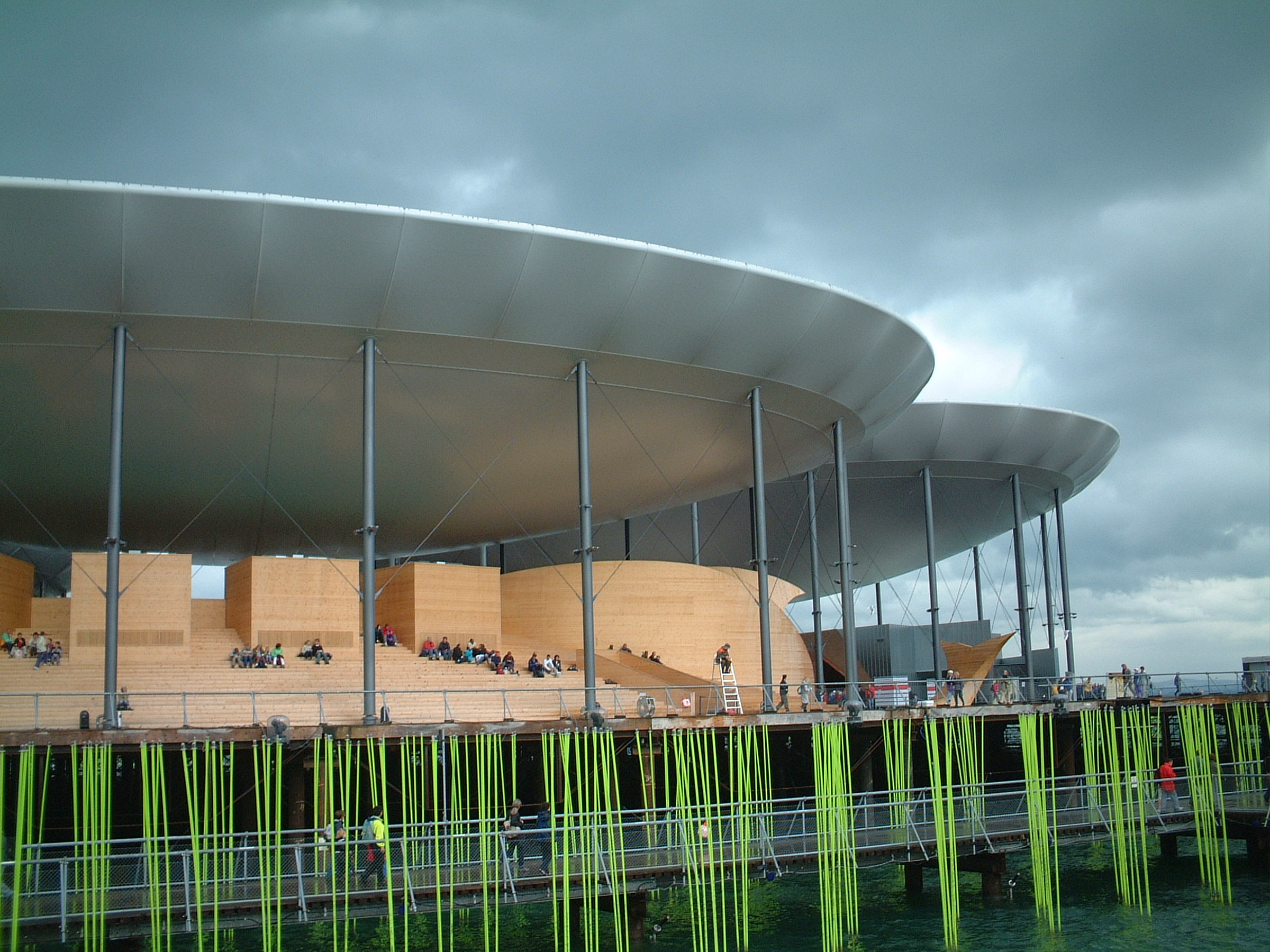 During the summer of 2002, Neuchâtel was one of five sites which held Expo.02, the sixth Swiss national exhibition, which was subject to financial controversy. The Neuchâtel International Fantastic Film Festival is held every year to celebrate fantastic cinema from around the world. The festival of the Fête des Vendanges, representing the wine harvest, is held traditionally in late September.
During the summer of 2002, Neuchâtel was one of five sites which held Expo.02, the sixth Swiss national exhibition, which was subject to financial controversy. The Neuchâtel International Fantastic Film Festival is held every year to celebrate fantastic cinema from around the world. The festival of the Fête des Vendanges, representing the wine harvest, is held traditionally in late September.
 Neuchâtel Xamax is the most important
Neuchâtel Xamax is the most important
File:Lac de Neuchatel depuis la Neuchatel (ville suisse) dscn0660.jpg, Lake Neuchâtel, seen from the castle
File:Neuchatel (ville suisse) statue dscn0647.jpg, The statue of the justice fountain
File:Collégiale Neuchâtel Vue Ouest 03.02.06.jpg, The collegiale by night
File:Collégiale_Neuchâtel_Vue_Nord_03.03.06.JPG, The collegiale by night, north view
File:David de Pury Neuchatel.jpg, Bronze statue of David de Pury, Baron de Pury in Neuchâtel, sculpted by David d'Angers.
File:Littorail in Neuchatel.jpg, Littorail train at Neuchâtel
File:Neuchatel2009-sm.jpg, Aerial view of Neuchâtel and Lake Neuchâtel, looking to the north-east.
File:Urne-IMG 4613-black.jpg, Ballot box used to elect members of the Grand Conseil of the city of Neuchâtel. Made during the 18th century, used until 1848. Walnut and brass.
City of Neuchâtel official website
Transports Publics du Littoral Neuchâtelois
*Museums
Archeology museum
Ethnography museum
Art and history museum
Museum of natural historyNeuchâtel Tourism OfficeNeuchâtel Junior CollegeHotel Beaulac on Lake Neuchâtel
{{DEFAULTSORT:Neuchatel Archaeological sites in Switzerland Cities in Switzerland Cantonal capitals of Switzerland Municipalities of the canton of Neuchâtel Neuchatel (capital) Cultural property of national significance in the canton of Neuchâtel Populated places on Lake Neuchâtel 1011 establishments
Boudry
Boudry a municipality in the canton of Neuchâtel in Switzerland.
History
Boudry is first mentioned in 1278 as ''Baudri''.
There are numerous prehistoric settlements around Boudry. These include the neolithic stilt houses on the banks of ...
, Chabrey (VD), Colombier, Cressier, Cudrefin (VD), Delley-Portalban (FR), Enges, Fenin-Vilars-Saules, Hauterive, Saint-Blaise, Savagnier
, twintowns = Aarau
Aarau (, ) is a List of towns in Switzerland, town, a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality, and the capital of the northern Swiss Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Aargau. The List of towns in Switzerland, town is also the capital of the dis ...
(Switzerland), Besançon (France), Sansepolcro (Italy)
Neuchâtel (, , ; german: Neuenburg) is the capital of the Swiss canton
The 26 cantons of Switzerland (german: Kanton; french: canton ; it, cantone; Sursilvan and Surmiran: ; Vallader and Puter: ; Sutsilvan: ; Rumantsch Grischun: ) are the member states of the Swiss Confederation. The nucleus of the Swiss Conf ...
of Neuchâtel
, neighboring_municipalities= Auvernier, Boudry, Chabrey (VD), Colombier, Cressier, Cudrefin (VD), Delley-Portalban (FR), Enges, Fenin-Vilars-Saules, Hauterive, Saint-Blaise, Savagnier
, twintowns = Aarau (Switzerland), Besançon (France), ...
, situated on the shoreline of Lake Neuchâtel. Since the fusion in 2021 of the municipalities of Neuchâtel, Corcelles-Cormondrèche, Peseux, and Valangin, the city has approximately 45,000 inhabitants (80,000 in the metropolitan area). The city is sometimes referred to historically by the German name ; both the French and German names mean "New Castle". It was originally part of the Kingdom of Burgundy, then part of the Holy Roman Empire and later under Prussian control from 1707 until 1848, with an interruption during the Napoleonic Wars from 1802 to 1814. In 1848, Neuchâtel became a republic and a canton of Switzerland.
Neuchâtel is a centre of the Swiss watch industry, the site of micro-technology and high-tech industries, and home to research centres and organizations such as the Swiss Center for Electronics and Microtechnology
The CSEM is a Swiss research and development centre (R&D) active in the fields of precision manufacturing, digitalization, and renewable energy. It follows a public-private not-for-profit partnership model. CSEM develops and transfers technolo ...
(CSEM), and Philip Morris International's ''Cube''. The apparel
Clothing (also known as clothes, apparel, and attire) are items worn on the body. Typically, clothing is made of fabrics or textiles, but over time it has included garments made from animal skin and other thin sheets of materials and natural ...
company heidi.com
heidi.com was a Neuchâtel, Switzerland-based company specialized in ready-to-wear apparel. Its name and logo are directly inspired from Heidi, the main character in Johanna Spyri's 1880 novel. The brand officially equipped all members of the Swiss ...
established its headquarters in the city.
The official language of Neuchâtel is French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
. Neuchâtel is a pilot of the Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold European Convention on Human Rights, human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. ...
and the European Commission Intercultural Cities programme.
Names and etymology
''Neuchâtel'' is a medieval toponym derived from the fro, neu "new" ( Modern French ''neuf'') and "castle" (now ''château'') in reference to the 10th century Neuchâtel Castle. In French, most adjectives, when used attributively, appear after their nouns; however, the leading position of the adjective is a phenomenon widely attested in the north and east of France, as well as in Belgium and in French-speaking Switzerland ( Romandy). As with the various other places namedNeuchâtel
, neighboring_municipalities= Auvernier, Boudry, Chabrey (VD), Colombier, Cressier, Cudrefin (VD), Delley-Portalban (FR), Enges, Fenin-Vilars-Saules, Hauterive, Saint-Blaise, Savagnier
, twintowns = Aarau (Switzerland), Besançon (France), ...
, Neufchâtel, Neufchâteau of northern France and Belgium, this reflects the Germanic influence on Gallo-Romance languages retained in the toponymy today. This contrasts with the Occitan Castelnaus (and the Frenchified Châteauneufs) in the south of France.
Of the other three national languages of Switzerland
The four national languages of Switzerland are German, French, Italian, and Romansh. German, French, and Italian maintain equal status as official languages at the national level within the Federal Administration of the Swiss Confederation, w ...
, the German name for the town is ''Neuenburg'' , which also translates roughly as "new castle". The longer form ''Neuenburg am See'' ("Newcastle by the lake") is sometimes used to disambiguate it from the numerous other Neuenburgs, especially Neuenburg am Rhein. The Romansh language uses the French ''Neuchâtel'', and occasionanally ''Neuschatel'' and ''Neufchâtel''; contemporary Italian largely uses the French name as well, but occasionally the historic ''Neocastello'' is seen.
Regionally, the Romand (Arpitan) name for the town is ''Nôchâtél'' in the broad '' Orthographe de référence B'' and is pronounced ''N'tchati'' locally, ''N'tchatai'' in La Sagne, ''N'tchaté'' in Les Planchettes and ''Nchaté'' or ''Ntchaté'' in .
Historic names
 The New Latin name for Neuchâtel is the Greek-derived ''Neocomum'', and this gives the adjective ''neocomensis'' which appears on the seal of the University of Neuchâtel (in ''Universitas Neocomensis Helvetiorum'') and the English adjective Neocomian, a term for a former stratigraphic stage of the
The New Latin name for Neuchâtel is the Greek-derived ''Neocomum'', and this gives the adjective ''neocomensis'' which appears on the seal of the University of Neuchâtel (in ''Universitas Neocomensis Helvetiorum'') and the English adjective Neocomian, a term for a former stratigraphic stage of the Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma.
Geology
Pro ...
. Other Latin names seen historically include ''Novum castellum'' in 1011 (upon the presentation of Neuchâtel Castle by Rudolph III of Burgundy to his wife Ermengarde Ermengarde or Ermengard or Ermingarde or Irmingard or Irmgard is a feminine given name of Germanic origin derived from the Germanic words "ermen/irmin," meaning "whole, universal" and "gard" meaning "enclosure, protection". Armgarð is a Faroese ver ...
) and ''Novum Castrum'' in 1143.
Historic French names included ''Nuefchastel'' (attested in 1251), ''Neufchastel'' (1338), and ''Neufchatel'', with modern ''Neuchâtel'' in use by 1750. In the Franche-Comté
Franche-Comté (, ; ; Frainc-Comtou: ''Fraintche-Comtè''; frp, Franche-Comtât; also german: Freigrafschaft; es, Franco Condado; all ) is a cultural and historical region of eastern France. It is composed of the modern departments of Doubs, ...
, the city was also called ''Neuchâtel-outre-Joux'' ("Neuchâtel beyond Joux
Joux () is a commune in the Rhône department in eastern France.
See also
*Communes of the Rhône department
The following is a list of the 208 communes of the Rhône department of France. This list does not includes the Lyon Metropolis wh ...
") to distinguish it from another Neuchâtel in that region, now called Neuchâtel-Urtière.
German names of the town included ''Nienburg'', ''Nuvenburch'' (attested in 1033) ''Nüwenburg'', ''Welschen Nüwenburg'', ''Newenburg am See'' ("Newcastle by the lake") and ''Welschneuburg'', with modern ''Neuenburg'' established by 1725.
Italian names included ''Neocastello''
(which is occasionally seen in contemporary contexts) and ''Nuovo Castello''.
History
Prehistory
 The oldest traces of humans in the municipal area are the remains of a
The oldest traces of humans in the municipal area are the remains of a Magdalenian
The Magdalenian cultures (also Madelenian; French: ''Magdalénien'') are later cultures of the Upper Paleolithic and Mesolithic in western Europe. They date from around 17,000 to 12,000 years ago. It is named after the type site of La Madele ...
hunting camp, which was dated to 13,000 BC. It was discovered in 1990 during construction of the A5 motorway at Monruz (La Coudre). The site was about below the main road. Around the fire pits carved flints and bones were found. In addition to the flint and bone artifacts three tiny earrings from lignite
Lignite, often referred to as brown coal, is a soft, brown, combustible, sedimentary rock formed from naturally compressed peat. It has a carbon content around 25–35%, and is considered the lowest rank of coal due to its relatively low heat ...
were found. The earrings may have served as symbols of fertility and represent the oldest known art in Switzerland. This first camp was used by Cro-Magnon
Early European modern humans (EEMH), or Cro-Magnons, were the first early modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') to settle in Europe, migrating from Western Asia, continuously occupying the continent possibly from as early as 56,800 years ago. They ...
s to hunt horse and reindeer in the area. Azilian hunters had a camp at the same site at about 11,000 BC. Since the climate had changed, their prey was now deer and wild boar.
During the 19th century, traces of some stilt house
Stilt houses (also called pile dwellings or lake dwellings) are houses raised on stilts (or piles) over the surface of the soil or a body of water. Stilt houses are built primarily as a protection against flooding; they also keep out vermin. The ...
s were found in Le Cret near the red church. However, their location was not well documented and the site was lost. In 1999, during construction of the lower station of the funicular railway, which connects the railway station and university, the settlement was rediscovered. It was later determined to be a Cortaillod culture (middle Neolithic) village. According to dendrochronological
Dendrochronology (or tree-ring dating) is the scientific method of dating tree rings (also called growth rings) to the exact year they were formed. As well as dating them, this can give data for dendroclimatology, the study of climate and at ...
studies, some of the piles were from 3571 BC.
A Hallstatt grave (early Iron Age) was found in the forest of Les Cadolles.
Antiquity
 At Les Favarger a Gallo-Roman and at André Fontaine a small coin depot were discovered. In 1908, an excavation at the mouth of the discovered Gallo-Roman baths from the 2nd and 3rd Centuries AD.
At Les Favarger a Gallo-Roman and at André Fontaine a small coin depot were discovered. In 1908, an excavation at the mouth of the discovered Gallo-Roman baths from the 2nd and 3rd Centuries AD.
Middle Ages
One of the most important Merovingian cemeteries in the canton was discovered at Les Battieux in . In 1982, 38 graves dating from the 7th century were excavated many of which contained silver-inlaid or silver-plated belt buckles. Also in Serrières at the church of Saint-Jean, the remains of a 7th-century shrine were excavated. In 1011, Rudolph III of Burgundy presented a ''Novum castellum'' or ''new castle'' on the lake shore to his wife,Ermengarde Ermengarde or Ermengard or Ermingarde or Irmingard or Irmgard is a feminine given name of Germanic origin derived from the Germanic words "ermen/irmin," meaning "whole, universal" and "gard" meaning "enclosure, protection". Armgarð is a Faroese ver ...
. It was long assumed that this new castle replaced an older one, but nothing about its location or design is known. At the time of this gift Neuchâtel was probably the center of a newly created royal court, which was recently developed to complement the other royal estates which managed western estates of the kings of Burgundy.
The first counts of Neuchâtel were named shortly afterwards, and in 1214 their domain was officially dubbed a city.
Early modern era
For three centuries, the County of Neuchâtel flourished, and in 1530, the people of Neuchâtel accepted the Reformation, and their city and territory were proclaimed to be indivisible from then on. Future rulers were required to seek investiture from the citizens. With increasing power and prestige, Neuchâtel was raised to the level of aprincipality
A principality (or sometimes princedom) can either be a monarchical feudatory or a sovereign state, ruled or reigned over by a regnant-monarch with the title of prince and/or princess, or by a monarch with another title considered to fall under ...
at the beginning of the 17th century. On the death in 1707 Marie d'Orleans-Longueville, duchess de Nemours
Marie de Nemours, originally known as Marie d'Orléans-Longueville (1625–1707), was Princess of Neuchâtel from 1694 to 1707. She was the daughter of Henri II d'Orléans, duc de Longueville and Louise de Bourbon. After the death of her brother ...
and Princess of Neuchâtel
Princess is a regal rank and the feminine equivalent of prince (from Latin '' princeps'', meaning principal citizen). Most often, the term has been used for the consort of a prince, or for the daughter of a king or prince.
Princess as a s ...
, the people had to choose her successor from among fifteen claimants. They wanted their new prince first and foremost to be a Protestant, and also to be strong enough to protect their territory but based far enough away to leave them to their own devices. Louis XIV actively promoted the many French pretenders to the title, but the Neuchâtelois people passed them over in favour of King Frederick I of Prussia, who claimed his entitlement in a rather complicated fashion through the Houses of Orange and Nassau. With the requisite stability assured, Neuchâtel entered its golden age, with commerce and industry (including watchmaking and lace) and banking undergoing steady expansion.
Modern Neuchâtel
At the turn of the 19th century, the King of Prussia was defeated byNapoleon I
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
and was forced to give up Neuchâtel in order to keep Hanover. Napoleon's field marshal, Berthier, became Prince of Neuchâtel, building roads and restoring infrastructure, but never actually setting foot in his domain. After the fall of Napoleon, Frederick William III of Prussia
Frederick William III (german: Friedrich Wilhelm III.; 3 August 1770 – 7 June 1840) was King of Prussia from 16 November 1797 until his death in 1840. He was concurrently Elector of Brandenburg in the Holy Roman Empire until 6 August 1806, wh ...
reasserted his rights by proposing that Neuchâtel be linked with the other Swiss cantons (to exert better influence over all of them). On September 12, 1814, Neuchâtel became the capital of the 21st canton, but also remained a Prussian principality. It took a bloodless revolution in the decades following for Neuchâtel to shake off its princely past and declare itself, on March 1, 1848, a republic within the Swiss Confederation. Prussia yielded its claim to the canton following the 1856–1857 Neuchâtel Crisis.
On 1 January 2021 the former municipalities of Corcelles-Cormondrèche, Peseux and Valangin merged into the municipality of Neuchâtel. Corcelles-Cormondrèche was first mentioned in the historical record in 1092 as ''Curcellis''. Around 1220 it was mentioned as ''Cormundreschi''. Peseux was first mentioned in 1195 as ''apud Pusoz'' though this comes from a 15th-century copy of an earlier document. In 1278 it was mentioned as ''de Posoys''. Valangin was first mentioned in 1241 as ''de Valengiz''.
Geography
 Before the 2021 merger of municipalities, Neuchâtel had an area, , of . Of this area, or 10.2% was used for agricultural purposes, while or 53.8% was forested. Of the rest of the land, or 35.5% was settled (buildings or roads), or 0.2% was either rivers or lakes and or 0.1% was unproductive land.Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Land Use Statistics
Before the 2021 merger of municipalities, Neuchâtel had an area, , of . Of this area, or 10.2% was used for agricultural purposes, while or 53.8% was forested. Of the rest of the land, or 35.5% was settled (buildings or roads), or 0.2% was either rivers or lakes and or 0.1% was unproductive land.Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Land Use Statistics2009 data accessed 25 March 2010 Of the built up area, industrial buildings made up 2.2% of the total area while housing and buildings made up 18.0% and transportation infrastructure made up 10.1%. while parks, green belts and sports fields made up 4.3%. Out of the forested land, 51.8% of the total land area was heavily forested and 2.0% is covered with orchards or small clusters of trees. Of the agricultural land, 1.4% was used for growing crops and 8.0% was pastures. All the water in the municipality is in lakes. The city is located on the northwestern shore of Lake Neuchâtel, a few kilometers east of Peseux and west of Saint-Blaise. Above Neuchâtel, roads and train tracks rise steeply into the folds and ridges of the Jura range—known within the canton as the ''Montagnes neuchâteloises''. Like the continuation of the mountains on either side, this is wild and hilly country, not exactly mountainous compared with the high Alps further south but still characterized by remote, windswept settlements and deep, rugged valleys. It is also the heartland of the celebrated Swiss watchmaking industry, centered on the once-famous towns of La Chaux-de-Fonds and Le Locle, which both rely heavily on their horological past to draw in visitors. The river Doubs marks for a part the border with France, set down in a gorge and forming along its path an impressive waterfall, the , and lake, the
Lac des Brenets
__NOTOC__
Lac des Brenets (Swiss name) or Lac de Chaillexon (French name) is a lake on the river Doubs on the border of Switzerland and France.
Characteristics
The depression in which the lake lies was formed by the movements of a glacier, whi ...
.
The municipality was the capital of Neuchâtel District, until the district level of administration was eliminated on 1 January 2018.
Climate
Politics
Coat of arms
Administrative divisions
Government
The Municipal Council (, CC) constitutes the executive government of the City of Neuchâtel and operates as acollegiate authority
Collegiate may refer to:
* College
* Webster's Dictionary, a dictionary with editions referred to as a "Collegiate"
* ''Collegiate'' (1926 film), 1926 American silent film directed by Del Andrews
* ''Collegiate'' (1936 film), 1936 American musi ...
. It is composed of five councillors (french: Conseiller communal/ Conseillère communale), each presiding over administrational sections and services comprising the related commissions. The president of the executive department acts as mayor (') and is nominated annually in a tournus by the collegiate itself. In the mandate period January 2021 – June 2022 (') the Municipal Council is presided by ' Violaine Blétry-de Montmollin. Departmental tasks, coordination measures and implementation of laws decreed by the General Council (parliament) are carried by the Municipal Council. The regular election of the Municipal Council by any inhabitant valid to vote is held every four years. Any resident of Neuchâtel allowed to vote can be elected as a member of the Municipal Council. Due to the constitution by canton of Neuchâtel not only Swiss citizens have the right to vote and elect and being elected on communal and cantonal level, but also foreigners with a residence in the canton of Neuchâtel and being resident in the canton of Neuchâtel for at least one year for communal elections and votes, and at least five years of residence in the canton for cantonal elections and votes. The current mandate period is from 2021 to 2024. The delegates are selected by means of a system of proportional representation.
, Neuchâtel's Municipal Council is made up of two representatives of the PS/SP ( Social Democratic Party), two representatives of the PLR/FDP (), and one member of the PES/GPS ( Green Party). The last regular election was held on 25 October 2020.
Daniel Veuve is Town Chancellor (') since 2021 for the City Council.
Parliament
The General Council (, CG), the city parliament, holds legislative power. It is made up of 41 members, with elections held every four years. The General Council decrees regulations and by-laws that are executed by the Municipal Council and the administration. The delegates are selected by means of a system of proportional representation. The sessions of the General Council are public. Unlike members of the Municipal Council, members of the General Council are not politicians by profession, and they are paid a fee based on their attendance. Any resident of Neuchâtel allowed to vote can be elected as a member of the General Council. Due to the constitution of the canton of Neuchâtel not only Swiss citizen have the right to vote and elect and be elected on the communal level, but also foreigners in the canton of Neuchâtel having been resident in the canton of Neuchâtel for at least one year for communal elections and votes, and at least five years of residence in the canton for cantonal elections and votes. The CG holds its meetings in the Town Hall ('), in the old city on '. The last regular election of the General Council was held on 25 October 2020 for the mandate period (') from 2020 to 2024. Currently the General Council consist of 12 members of The Liberals (PLR/FDP), 11 ' members (an alliance of the Green Party (PES/GPS) and others), 10 Social Democratic Party (PS/SP), 5 members of the Green Liberals (pvl/glp), 2 members of the left party ', and one of the Swiss Party of Labour (PST-POP/PdA) (').Elections
National Council
In the 2015 federal election the most popular party was the PS which received 29.3% of the vote. The next four most popular parties were the PLR (22.8%), the UDC (13.6%), the Green Party (12.1%), and the Swiss Party of Labour (10.1%). In the federal election, a total of 8,136 voters were cast, and the voter turnout was 41.4%.International relations
* Neuchâtel is a pilot city of the Council of Europe and the European Commission Intercultural cities programme.Twin towns – Sister cities
Neuchâtel istwinned
Twinning (making a twin of) may refer to:
* In biology and agriculture, producing two offspring (i.e., twins) at a time, or having a tendency to do so;
* Twin towns and sister cities, towns and cities involved in town twinning
* Twinning inst ...
with:
* Aarau
Aarau (, ) is a List of towns in Switzerland, town, a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality, and the capital of the northern Swiss Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Aargau. The List of towns in Switzerland, town is also the capital of the dis ...
, Switzerland, 1997
* Besançon, France, 1975
* Sansepolcro, Italy, 1997
Namesakes
Neuchâtel was part of the 1998summit
A summit is a point on a surface that is higher in elevation than all points immediately adjacent to it. The topography, topographic terms acme, apex, peak (mountain peak), and zenith are synonymous.
The term (mountain top) is generally used ...
of worldwide cities named "New Castle" with:
Demographics
Population
Neuchâtel has a population () of . , 32.1% of the population are resident foreign nationals.Swiss Federal Statistical Office - Superweb database - Gemeinde Statistics 1981-2008accessed 19 June 2010 Over the last 10 years (2000–2010) the population has changed at a rate of 3.9%. It has changed at a rate of 2.4% due to migration and at a rate of 1% due to births and deaths.
accessed 25-October-2011 , the population was 47.7% male and 52.3% female. The population was made up of 10,371 Swiss men (31.5% of the population) and 5,344 (16.2%) non-Swiss men. There were 12,366 Swiss women (37.5%) and 4,892 (14.8%) non-Swiss women.Canton of Neuchâtel Statistics
, ''République et canton de Neuchâtel - Recensement annuel de la population'' accessed 13 October 2011 Of the population in the municipality, 8,558 or about 26.0% were born in Neuchâtel and lived there in 2000. There were 5,134 or 15.6% who were born in the same canton, while 7,744 or 23.5% were born somewhere else in Switzerland, and 10,349 or 31.4% were born outside of Switzerland. , children and teenagers (0–19 years old) make up 19.3% of the population, while adults (20–64 years old) make up 63.1% and seniors (over 64 years old) make up 17.6%. , there were 14,143 people who were single and never married in the municipality. There were 14,137 married individuals, 2,186 widows or widowers and 2,448 individuals who are divorced.STAT-TAB Datenwürfel für Thema 40.3 - 2000
accessed 2 February 2011 , there were 15,937 private households in the municipality, and an average of 2. persons per household. There were 7,348 households that consist of only one person and 547 households with five or more people. , a total of 15,447 apartments (89.9% of the total) were permanently occupied, while 1,429 apartments (8.3%) were seasonally occupied and 311 apartments (1.8%) were empty.Swiss Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB - Datenwürfel für Thema 09.2 - Gebäude und Wohnungen
accessed 28 January 2011 , the construction rate of new housing units was 2.5 new units per 1000 residents. the average price to rent an average apartment in Neuchâtel was 921.35
Swiss franc
The Swiss franc is the currency and legal tender of Switzerland and Liechtenstein. It is also legal tender in the Italian exclave of Campione d'Italia which is surrounded by Swiss territory. The Swiss National Bank (SNB) issues banknotes and the f ...
s (CHF) per month (US$740, £410, €590 approx. exchange rate from 2003). The average rate for a one-room apartment was 451.40 CHF (US$360, £200, €290), a two-room apartment was about 675.66 CHF (US$540, £300, €430), a three-room apartment was about 825.15 CHF (US$660, £370, €530) and a six or more room apartment cost an average of 1647.88 CHF (US$1320, £740, €1050). The average apartment price in Neuchâtel was 82.6% of the national average of 1116 CHF.Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Rental prices2003 data accessed 26 May 2010 The vacancy rate for the municipality, , was 0.53%.
Historical population
The historical population is given in the following chart:Language
Most of the population () speaksFrench
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
(25,881 or 78.6%) as their first language, German is the second most common (1,845 or 5.6%) and Italian is the third (1,421 or 4.3%). There are about six people who speak Romansh.
Religion
Neuchâtel was historically Protestant, but Catholics have since formed a plurality due to immigration. From the , 10,809 or 32.8% were Roman Catholic, while 9,443 or 28.7% belonged to theSwiss Reformed Church
The Protestant Church in Switzerland (PCS), (EKS); french: Église évangélique réformée de Suisse (EERS); it, Chiesa evangelica riformata in Svizzera (CERiS); rm, Baselgia evangelica refurmada da la Svizra (BRRS) formerly named Federation o ...
. Of the rest of the population, there were 374 members of an Orthodox church (or about 1.14% of the population), there were 80 individuals (or about 0.24% of the population) who belonged to the Christian Catholic Church, and there were 1,756 individuals (or about 5.34% of the population) who belonged to another Christian church. There were 58 individuals (or about 0.18% of the population) who were Jewish, and 1,723 (or about 5.23% of the population) who were Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
. There were 99 individuals who were Buddhist, 100 individuals who were Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
and 59 individuals who belonged to another church. 7,549 (or about 22.94% of the population) belonged to no church, are agnostic
Agnosticism is the view or belief that the existence of God, of the divine or the supernatural is unknown or unknowable. (page 56 in 1967 edition) Another definition provided is the view that "human reason is incapable of providing sufficient ...
or atheist
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no ...
, and 1,717 individuals (or about 5.22% of the population) did not answer the question.
Crime
In 2014 the crime rate, of crimes listed in the Swiss Criminal Code, in Neuchâtel was 140.4 per thousand residents. During the same period, the rate of drug crimes was 16.3 per thousand residents. The rate of violations of immigration, visa and work permit laws was 5.7 per thousand residents.Economy
Neuchâtel is a centre of the watch industry, and is also the site of micro-technology and high-tech industries. It is home to research centres and organizations such as theSwiss Center for Electronics and Microtechnology
The CSEM is a Swiss research and development centre (R&D) active in the fields of precision manufacturing, digitalization, and renewable energy. It follows a public-private not-for-profit partnership model. CSEM develops and transfers technolo ...
(CSEM), Microcity innovation pole, University of applied Sciences HE-Arc in Engineering and also Philip Morris International's ''Cube''. The apparel
Clothing (also known as clothes, apparel, and attire) are items worn on the body. Typically, clothing is made of fabrics or textiles, but over time it has included garments made from animal skin and other thin sheets of materials and natural ...
company heidi.com
heidi.com was a Neuchâtel, Switzerland-based company specialized in ready-to-wear apparel. Its name and logo are directly inspired from Heidi, the main character in Johanna Spyri's 1880 novel. The brand officially equipped all members of the Swiss ...
also established its headquarters in the city.
, Neuchâtel had an unemployment rate of 7.5%. , there were 46 people employed in the primary economic sector and about 14 businesses involved in this sector. 5,658 people were employed in the secondary sector and there were 261 businesses in this sector. 20,472 people were employed in the tertiary sector, with 1,955 businesses in this sector. There were 16,353 residents of the municipality who were employed in some capacity, of which women made up 45.4% of the workforce.
the total number of full-time equivalent jobs was 21,624. The number of jobs in the primary sector was 38, of which 20 were in agriculture and 18 were in forestry or lumber production. The number of jobs in the secondary sector was 5,433 of which 4,234 or (77.9%) were in manufacturing, 9 or (0.2%) were in mining and 1,022 (18.8%) were in construction. The number of jobs in the tertiary sector was 16,153. In the tertiary sector; 2,397 or 14.8% were in wholesale or retail sales or the repair of motor vehicles, 796 or 4.9% were in the movement and storage of goods, 919 or 5.7% were in a hotel or restaurant, 766 or 4.7% were in the information industry, 1,077 or 6.7% were the insurance or financial industry, 1,897 or 11.7% were technical professionals or scientists, 1,981 or 12.3% were in education and 2,633 or 16.3% were in health care.
, there were 15,535 workers who commuted into the municipality and 6,056 workers who commuted away. The municipality is a net importer of workers, with about 2.6 workers entering the municipality for every one leaving.Swiss Federal Statistical Office - Statwebaccessed 24 June 2010 Of the working population, 33.7% used public transportation to get to work, and 43.4% used a private car.
Education
 Neuchâtel is home to the French-speaking University of Neuchâtel. The university has five faculties and more than a dozen institutes, including arts and human sciences, natural sciences, law, economics and theology. For the 2005–2006 academic year, 3,595 students (1,987 women and 1,608 men) were enrolled. The Faculty of Arts and Human Sciences is the largest school of those that comprise the university of Neuchâtel with 1,500 students. Some courses at the University are taught in English.
Neuchâtel is home to eight libraries: the Bibliothèque de la Faculté des Lettres, the ''Bibliothèque de l'Institut d'ethnologie et du Musée d'ethnographie'', the ''Bibliothèque de la Faculté des Sciences'', the ''Bibliothèque de droit'', the ''Bibliothèque des sciences économiques'', the ''Bibliothèque de la Faculté de théologie'', the ''Service de coordination des bibliothèques'' and the ''Haute école Arc - Santé''. There was a combined total () of 736,773 books or other media in the libraries, and in the same year a total of 58,427 items were loaned out.
In Neuchâtel about 11,076 or (33.7%) of the population have completed non-mandatory
Neuchâtel is home to the French-speaking University of Neuchâtel. The university has five faculties and more than a dozen institutes, including arts and human sciences, natural sciences, law, economics and theology. For the 2005–2006 academic year, 3,595 students (1,987 women and 1,608 men) were enrolled. The Faculty of Arts and Human Sciences is the largest school of those that comprise the university of Neuchâtel with 1,500 students. Some courses at the University are taught in English.
Neuchâtel is home to eight libraries: the Bibliothèque de la Faculté des Lettres, the ''Bibliothèque de l'Institut d'ethnologie et du Musée d'ethnographie'', the ''Bibliothèque de la Faculté des Sciences'', the ''Bibliothèque de droit'', the ''Bibliothèque des sciences économiques'', the ''Bibliothèque de la Faculté de théologie'', the ''Service de coordination des bibliothèques'' and the ''Haute école Arc - Santé''. There was a combined total () of 736,773 books or other media in the libraries, and in the same year a total of 58,427 items were loaned out.
In Neuchâtel about 11,076 or (33.7%) of the population have completed non-mandatory upper secondary education
Secondary education or post-primary education covers two phases on the International Standard Classification of Education scale. Level 2 or lower secondary education (less commonly junior secondary education) is considered the second and final ph ...
, and 5,948 or (18.1%) have completed additional higher education (either university or a ''Fachhochschule
A ''Fachhochschule'' (; plural ''Fachhochschulen''), abbreviated FH, is a university of applied sciences (UAS), in other words a German tertiary education institution that provides professional education in many applied sciences and applied arts ...
''). Of the 5,948 who completed tertiary schooling, 43.6% were Swiss men, 28.4% were Swiss women, 16.4% were non-Swiss men and 11.6% were non-Swiss women.
In the canton of Neuchâtel most municipalities provide two years of non-mandatory kindergarten, followed by five years of mandatory primary education. The next four years of mandatory secondary education is provided at thirteen larger secondary schools, which many students travel out of their home municipality to attend. During the 2010–11 school year, there were 27 kindergarten classes with a total of 527 students in Neuchâtel. In the same year, there were 78 primary classes with a total of 1,424 students. Secondary schools include the Lycée Jean-Piaget Lycée Jean-Piaget is an institution in Neuchâtel, Switzerland offering secondary education, tertiary education and language education
Language education – the process and practice of teaching a second or foreign language – is primarily ...
.
Apart from one International Montessori school for kids up to age 11 offering an English and a French class there is no international school in Neuchâtel. Neuchâtel Junior College was founded in 1956 as a non-profit foundation of the Ville de Neuchâtel to provide a unique international education. Neuchâtel Junior College
Neuchâtel Junior College (or NJC) is a private international school located in the French-speaking town of Neuchâtel, Switzerland. It is a member of Canadian Accredited Independent Schools.
History
NJC was founded in 1956 by Leonard Wilde, an E ...
is a one-year school annually welcoming over 100 students in their final pre-university year to study the Ontario Grade 12 curriculum as well as Advanced Placement.
, there were 3,859 students in Neuchâtel who came from another municipality, while 346 residents attended schools outside the municipality.
Transport
Swiss Federal Railways
Swiss Federal Railways (german: link=no, Schweizerische Bundesbahnen, ''SBB''; french: link=no, Chemins de fer fédéraux suisses, ''CFF''; it, Ferrovie federali svizzere, ''FFS'') is the national railway company of Switzerland. It is usuall ...
. The station is also a junction for several other lines, including a cross-border line served by the TGV (High Speed Train), with direct trains linking Neuchâtel to Paris in four hours.
Neuchâtel's airport is about away from the center of the city and it takes 9 minutes to get into town with the direct tramway. It is a small airport that does not offer commercial flights. Neuchâtel is also linked to four international airports: Bern, Geneva, Basel and Zürich which are respectively , , and away by car. Geneva and Zürich airports both have direct trains to Neuchâtel, connecting the cities respectively in 1h 17min and 1h 49min.
Three funiculars serve the city:
* The Funambule, linking the lower part of the town, near the University, to the railway station
* The Funiculaire Ecluse Plan
A funicular (, , ) is a type of cable railway system that connects points along a railway track laid on a steep slope. The system is characterized by two counterbalanced carriages (also called cars or trains) permanently attached to opposite en ...
* The Funiculaire La Coudre Chaumont
The Société de Navigation sur les Lacs de Neuchâtel et Morat SA is the boat company which serves 17 towns on Lake Neuchâtel, 6 towns on Lake Murten and 7 towns on Lake Bienne
__NOTOC__
Lake Bienne or Lake Biel (french: Lac de Bienne ; german: Bielersee) is a lake in western Switzerland. Together with Lake Morat and Lake Neuchâtel, it is one of the three large lakes in the Jura region of Switzerland. It lies approxima ...
from 6:30am to 9pm. Some boats offer free wireless internet connections.
Sights
Heritage sites of national significance
There are 34 sites in Neuchâtel that are listed as Swiss heritage site of national significance. The entire old city of Neuchâtel, the urban village of Corcelles the small city of Valangin, the Bussy/Le Sorgereux region and the La Borcarderie region are part of theInventory of Swiss Heritage Sites
The Federal Inventory of Heritage Sites (ISOS) is part of a 1981 Ordinance of the Swiss Federal Council implementing the Federal Law on the Protection of Nature and Cultural Heritage.
Sites of national importance
Types
The types are based on t ...
.
Architecture
 Neuchâtel's Old Town has about 140 street fountains, a handful of which date from the 16th century. The Place des Halles is overlooked by Louis XIV architecture – shuttered façades and the turreted orioles of the 16th-century Maison des Halles. To the east, on Rue de l’Hôpital, is the grand 1790 Hôtel de Ville (Town Hall), designed by Louis XVI's chief architect Pierre-Adrien Paris.
The center of the Old Town is located at the top of the hill, accessed by the steeply winding Rue du Château. The Collégiale church, begun in 1185 and consecrated in 1276, is an example of early Gothic. The east end of the church has three Norman apses. The main entrance, to the west, is crowned by a giant rose window of stained glass. Within the vaulted interior, the transept is lit by a lantern tower. The Cenotaph of the Counts of Neuchâtel is located on the north wall of the choir. Begun in 1372, and the only artwork of its kind to survive north of the Alps, the monument comprises fifteen near-life-size painted statues of various knights and ladies from Neuchâtel's past, framed by 15th-century arches and gables. Beside the church is the Castle, begun in the 12th century and still in use as the offices of the cantonal government. The nearby turreted Prison Tower, which is the remains of a medieval bastion, has panoramic views over the town, along with models of Neuchâtel in different eras.
Neuchâtel's Old Town has about 140 street fountains, a handful of which date from the 16th century. The Place des Halles is overlooked by Louis XIV architecture – shuttered façades and the turreted orioles of the 16th-century Maison des Halles. To the east, on Rue de l’Hôpital, is the grand 1790 Hôtel de Ville (Town Hall), designed by Louis XVI's chief architect Pierre-Adrien Paris.
The center of the Old Town is located at the top of the hill, accessed by the steeply winding Rue du Château. The Collégiale church, begun in 1185 and consecrated in 1276, is an example of early Gothic. The east end of the church has three Norman apses. The main entrance, to the west, is crowned by a giant rose window of stained glass. Within the vaulted interior, the transept is lit by a lantern tower. The Cenotaph of the Counts of Neuchâtel is located on the north wall of the choir. Begun in 1372, and the only artwork of its kind to survive north of the Alps, the monument comprises fifteen near-life-size painted statues of various knights and ladies from Neuchâtel's past, framed by 15th-century arches and gables. Beside the church is the Castle, begun in the 12th century and still in use as the offices of the cantonal government. The nearby turreted Prison Tower, which is the remains of a medieval bastion, has panoramic views over the town, along with models of Neuchâtel in different eras.
Museums

 Neuchâtel has several museums, including the
Neuchâtel has several museums, including the Laténium
The Laténium is an archeology museum located in Hauterive, a suburb of Neuchâtel, Switzerland. Its name refers to the famous nearby site of La Tène which gave its name to the Second European Iron age. The Laténium is composed of a park an ...
, an archeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
museum focusing on the prehistorical times in the region of Neuchâtel and Hauterive, particularly the La Tène culture, with the eponym site being a few kilometers away; the Musée d'ethnographie de Neuchâtel (MEN), an ethnography museum; and the Musée d'Art et d'Histoire, which houses the Automates Jaquet-Droz (Jaquet-Droz Mechanical Figurines).
Culture
Sport
football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
club based in Neuchâtel. It was created in 1970 through a merger between FC Cantonal (1906) and FC Xamax
FC may refer to:
Businesses, organisations, and schools
* Fergusson College, a science and arts college in Pune, India
* Finncomm Airlines (IATA code)
* FranklinCovey company, NYSE stock symbol FC
* Frontier Corps, a paramilitary force in Pakist ...
(1916). The club plays in Swiss Super League
The Swiss Super League (known as the Credit Suisse Super League for sponsorship reasons) is a Swiss professional league in the top tier of the Swiss football league system and has been played in its current format since the 2003–04 season ...
, the highest Swiss football league. The club plays its home matches at the Stade de la Maladière
Stade de la Maladière is a multi-purpose stadium in Neuchâtel, Switzerland. It is currently used mostly for football matches and is the home ground of Neuchâtel Xamax. The stadium holds 12,000. It replaced the old Stade de la Maladière.
...
.
HC Uni Neuchâtel plays in the MySports League, the third tier of the Swiss hockey league system. Their home games are held in the 7,000-seat Littoral.
Union Neuchâtel Basket is the city's top basketball team, which plays in the Championnat LNA, Switzerland's only professional basketball league.
Notable people
William Ritter William Ritter may refer to:
*William Ritter (writer) (1867–1955), Swiss writer
* William Emerson Ritter (1856–1944), American biologist
See also
*Bill Ritter
August William Ritter Jr. (born September 6, 1956) is an American politician and ...
, Jean Piaget, Marcel Junod, Robert Miles and Yves Larock were all born in Neuchâtel. Friedrich Dürrenmatt lived in Neuchâtel the last 30 years of his life. Prens Sabahaddin, was an Ottoman sociologist and thinker of the Ottoman dynasty, lived in Neuchâtel the last 25 years of his life.
Canadian illustrator John Howe, well known for his illustrations of J. R. R. Tolkien's work and his participation in Peter Jackson
Sir Peter Robert Jackson (born 31 October 1961) is a New Zealand film director, screenwriter and producer. He is best known as the director, writer and producer of the ''Lord of the Rings'' trilogy (2001–2003) and the ''Hobbit'' trilogy ( ...
's '' The Lord of the Rings'' trilogy as chief conceptual designer, also lives in the Swiss city. It was also the site of a secret first meeting between French novelist Honoré de Balzac and the married woman who later became his wife, Eveline Hanska Eveline may refer to:
* Eveline (given name)
* Eveline (short story), "Eveline" (short story), a short story by James Joyce
* Eveline, Missouri, United States
* Eveline Street, in Windhoek, Namibia
* Eveline Township, Michigan, United States
See a ...
.
Roger Schutz, founder of the Taizé Community in France, was born on 12 May 1915 at the village of Provence near Neuchâtel. He was stabbed to death on 16 August 2005 by a mentally deranged woman during a prayer meeting in Taizé's Church of Reconciliation.
The de Pury family, a Prussian noble family, is from Neuchâtel. Swiss merchant and philanthropist David de Pury
David de Pury, Baron de Pury (19 January 1709 – 31 May 1786) was a banker, merchant, and philanthropist from the Principality of Neuchâtel, then a Kingdom of Prussia, Prussian principality and now part of Switzerland. His involvement in Trian ...
, a native of Neuchâtel, left a large fortune to the city for public works and charities. His relative, James-Ferdinand de Pury, also a merchant and philanthropist, bequest his villa to house the town's ethnography museum. Other members of the family who were born or resided in the town include explorer and colonist Jean-Pierre Pury, winemaker and diplomat Frédéric Guillaume de Pury
Baron Frédéric Guillaume de Pury (15 December 1831 – 11 November 1890) was a Swiss-Australian winemaker, farmer, statesman, and diplomat. From 1875 to 1890 he served as the Swiss Honorary Consul to Australia in Melbourne and was also a just ...
, painter Edmond Jean de Pury, and biblical scholar Albert de Pury.
The de Castello family, a French noble family, including winemakers Hubert de Castella and Paul de Castella, is from Neuchâtel. The de Montmollin family, including the Protestant minister David-François de Montmollin
David-François de Montmollin (18 March 1721 – 17 December 1803) was a Canadian colonist from the Principality of Neuchâtel (then a Prussian principality and now part of Switzerland), landowner, and Anglican priest. He was the first French-spea ...
, are also from the town. Frédéric Louis Godet (1812-1900) was another Swiss Protestant theologian who was born and died in Neuchâtel; as was Jean-Frédéric Osterwald
Jean-Frédéric Osterwald (or Ostervald) (25 November 1663 – 14 April 1747) was a Protestant pastor from Neuchâtel (now in Switzerland).
Life
He was born at Neuchâtel in 1663 in a patrician family, a son of the Reformed pastor Johann Rudolf O ...
(1663–1747), a further Protestant pastor.
French counter-revolutionary Louis Fauche-Borel was born and died in Neuchâtel, and François Bigot
François Bigot (; born Bordeaux, 30 January 1703; died Neuchâtel, Switzerland, 12 January 1778) was a French government official. He served as the Financial Commissary on Île Royale (nowadays Cape Breton Island), commissary general of the ill-f ...
, the last Intendant of New France, relocated to there after being exiled from France.
Abraham Louis Breguet
Abraham-Louis Breguet (10 January 1747 – 17 September 1823), born in Neuchâtel, then a Prussian principality, was a horologist who made many innovations in the course of a career in watchmaking industry. He was the founder of the Breguet ...
, the founder of the Breguet watch company and an esteemed inventor, often regarded as the father of modern horology, was born in Neuchâtel. The company still maintains its headquarters at L'Abbaye, about 40 km southwest of Neuchâtel.
The psychiatrist and psychoanalyst Silvio Fanti
Silvio Fanti (22 September 1919 – 26 June 1997) was a Swiss psychiatrist who founded micropsychoanalysis. He wrote several books about micropsychoanalysis and among them stand out ''J’ai peur, Docteur...'', ''Le fou est normal,'' ''Contre l ...
was born in Neuchâtel in 1919. He founded and developed Micropsychoanalysis Micropsychoanalysis is a psychotherapy method. A basic form of micropsychoanalysis was first conceived in the 1950s by Swiss psychiatrist Silvio Fanti and developed systematically by himself and his collaborators, Pierre Codoni and Daniel Lysek, fro ...
, a new school of psychoanalysis. Another important psychiatrist, Gottlieb Burckhardt, practiced in Neuchâtel. Alexander Agassiz
Alexander Emmanuel Rodolphe Agassiz (December 17, 1835March 27, 1910), son of Louis Agassiz and stepson of Elizabeth Cabot Agassiz, was an American scientist and engineer.
Biography
Agassiz was born in Neuchâtel, Switzerland and immigrated to ...
(1835–1910), was an American scientist and engineer from the town.
Didier Burkhalter, 94th President of the Swiss Confederation was born in Neuchâtel, as was Logitech founder Daniel Borel.
Footballers Max Abegglen
Max "Xam" Abegglen (11 April 1902 – 25 August 1970) was a Swiss footballer who played as a forward. Throughout his career, he played for FC Lausanne until 1923 when he transferred to Grasshopper Zurich. He was the brother of André 'Trello' ...
, Jayson Leutwiler, and Yann Kasaï
Yann Aime Kasaï (born 14 April 1998) is a Swiss football player who plays as forward for Biel-Bienne in the third-tier Swiss Promotion League.
Club career
On 5 December 2018, Kasaï joined FC Zürich. made his professional debut for Zürich in ...
, as well as Swiss Olympic field hockey player Albert Piaget
Albert Piaget (born 13 April 1928) is a Swiss former field hockey player. He competed in the men's tournament at the 1960 Summer Olympics
The 1960 Summer Olympics ( it, Giochi Olimpici estivi del 1960), officially known as the Games of the X ...
were all born in Neuchâtel. It is also the current residence of French tennis players Richard Gasquet, Gilles Simon and Florent Serra
Florent Lucien Serra (born 28 February 1981) is a French retired professional tennis player. A right-hander, he won two ATP titles during his career and achieved a career-high singles ranking of World No. 36 in June 2006.
Career Early life and ...
, as well as the Mexican Formula 1
Formula One (also known as Formula 1 or F1) is the highest class of international racing for open-wheel single-seater formula racing cars sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The World Drivers' Championship, ...
driver Sergio Pérez
Sergio Michel "Checo" Pérez Mendoza (; born 26 January 1990), is a Mexican Auto racing, racing driver who races in Formula One for Red Bull Racing, having previously driven for Sauber, McLaren, Force India, and Racing Point. He won his first ...
, and the artist and designer Ini Archibong
Inimfon “Ini” Joshua Archibong (born 23 June 1983) is an industrial designer, creative director, artist and musician who is active in product design, furniture design, environmental design, architecture, watch design, and fashion. He has said ...
. Anthropologist, artist, and filmmaker Véréna Paravel
Véréna Paravel (born 21 April 1971 in Neuchâtel, Switzerland) is a French anthropologist and artist who works in film, video, and photography.
Biography
Verena Paravel was born in 1971. She is an anthropologist, artist and filmmaker who wor ...
was also born in Neuchâtel.
Gallery
See also
*''L'Express
''L'Express'' () is a French weekly news magazine headquartered in Paris. The weekly stands at the political centre in the French media landscape, and has a lifestyle supplement, ''L'Express Styles'', and a job supplement, ''Réussir''.
History ...
''
Notes
References
Further reading
*External links
*City of Neuchâtel official website
Transports Publics du Littoral Neuchâtelois
*Museums
Archeology museum
Ethnography museum
Art and history museum
Museum of natural history
{{DEFAULTSORT:Neuchatel Archaeological sites in Switzerland Cities in Switzerland Cantonal capitals of Switzerland Municipalities of the canton of Neuchâtel Neuchatel (capital) Cultural property of national significance in the canton of Neuchâtel Populated places on Lake Neuchâtel 1011 establishments