NetFlow Architecture 2012 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 NetFlow is a feature that was introduced on
NetFlow is a feature that was introduced on
NetFlow Security Event Logging
utilizes NetFlow v9 fields and templates in order to efficiently deliver security telemetry in high performance environments. NetFlow Security Event Logging scales better than
 NetFlow collection using standalone NetFlow probes is an alternative to flow collection from routers and switches. This approach can overcome some limitations of router-based NetFlow monitoring. The probes are transparently connected to the monitored link as a passive appliance using the TAP or SPAN port of the appliance.
Historically, NetFlow monitoring is easier to implement in a dedicated probe than in a router. However, this approach also has some drawbacks:
* probes must be deployed on every link that must be observed, causing additional hardware, setup and maintenance costs.
* probes will not report separate input and output interface information like a report from a router would.
* probes may have problems reporting reliably the NetFlow fields related to routing, like AS Numbers or IP masks, because they can hardly be expected to use exactly the same routing information as a router.
The easiest way to address the above drawbacks is to use a
NetFlow collection using standalone NetFlow probes is an alternative to flow collection from routers and switches. This approach can overcome some limitations of router-based NetFlow monitoring. The probes are transparently connected to the monitored link as a passive appliance using the TAP or SPAN port of the appliance.
Historically, NetFlow monitoring is easier to implement in a dedicated probe than in a router. However, this approach also has some drawbacks:
* probes must be deployed on every link that must be observed, causing additional hardware, setup and maintenance costs.
* probes will not report separate input and output interface information like a report from a router would.
* probes may have problems reporting reliably the NetFlow fields related to routing, like AS Numbers or IP masks, because they can hardly be expected to use exactly the same routing information as a router.
The easiest way to address the above drawbacks is to use a
patent # 6,243,667
). The idea was that the first packet of a flow would create a NetFlow switching record. This record would then be used for all later packets of the same flow, until the expiration of the flow. Only the first packet of a flow would require an investigation of the route table to find the most specific matching route. This is an expensive operation in software implementations, especially the old ones without
/ref> NetFlow switching soon turned out to be unsuitable for big routers, especially Internet backbone routers, where the number of simultaneous flows was much more important than those on local networks, and where some traffic causes many short-lived flows, like
RFC 3334 - Policy-Based Accounting
RFC 3917 - Requirements for IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX)
RFC 3954 - NetFlow Version 9
RFC 3955 - Evaluation of Candidate Protocols for IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX)
RFC 3917 - Requirements for IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX)
RFC 3955 - Candidate Protocols for IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX)
RFC 5101 - Specification of the IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Protocol for the Exchange of IP Traffic Flow Information
RFC 5102 - Information Model for IP Flow Information Export
RFC 5103 - Bidirectional Flow Export Using IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX)
RFC 5153 - IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Implementation Guidelines
RFC 5470 - Architecture for IP Flow Information Export
RFC 5471 - Guidelines for IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Testing
RFC 5472 - IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Applicability
RFC 5473 - Reducing Redundancy in IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) and Packet Sampling (PSAMP) Reports
RFC 5476 - Packet Sampling (PSAMP) Protocol Specifications
RFC 5477 - Information Model for Packet Sampling Exports
RFC 5610 - Exporting Type Information for IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Information Elements
RFC 5655 - Specification of the IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) File Format
RFC 5815 - Definitions of Managed Objects for IP Flow Information Export
RFC 5982 - IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Mediation: Problem Statement
RFC 6183 - IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Mediation: Framework
RFC 6235 - IP Flow Anonymization Support
RFC 6313 - Export of Structured Data in IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX)
RFC 6526 - IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Per Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) Stream
RFC 6615 - Definitions of Managed Objects for IP Flow Information Export
RFC 6645 - IP Flow Information Accounting and Export Benchmarking Methodology
RFC 6727 - Definitions of Managed Objects for Packet Sampling
RFC 6728 - Configuration Data Model for the IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) and Packet Sampling (PSAMP) Protocols
RFC 6759 - Cisco Systems Export of Application Information in IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX)
RFC 7011 - Specification of the IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Protocol for the Exchange of Flow Information
RFC 7012 - Information Model for IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX)
RFC 7013 - Guidelines for Authors and Reviewers of IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Information Elements
RFC 7015 - Flow Aggregation for the IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Protocol
RFC 7119 - Operation of the IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Protocol on IPFIX Mediators
RFC 7125 - Revision of the tcpControlBits IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Information Element
RFC 7133 - Information Elements for Data Link Layer Traffic Measurement
RFC 7270 - Cisco-Specific Information Elements Reused in IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX)
RFC 7373 - Textual Representation of IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Abstract Data Types
RFC 8038 - Exporting MIB Variables Using the IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Protocol
RFC 8158 - IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Information Elements for Logging NAT Events
RFC 8272 - TinyIPFIX for Smart Meters in Constrained Networks
RFC 8549 - Export of BGP Community Information in IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX)
NetFlow/FloMA: Pointers and Software Provided by SWITCH.
- One of the most comprehensive list including all the open source and research works.
FloCon
- The Annual Conference put on by CERT/CC dealing with network flow data and analysis.
Basic NetFlow information on the Cisco Site
Paessler IT Explained - NetFlow
Using Netflow to store re-aggregated inbound and outbound flows
AppFlow specifications and standards track discussion
Understanding NetFlow Principle Animation
Basics of NetFlow & Flow Cache
List of Netflow Analyzers and Collectors
Computer network analysis Internet Protocol based network software Cisco protocols
 NetFlow is a feature that was introduced on
NetFlow is a feature that was introduced on Cisco
Cisco Systems, Inc., commonly known as Cisco, is an American-based multinational corporation, multinational digital communications technology conglomerate (company), conglomerate corporation headquartered in San Jose, California. Cisco develo ...
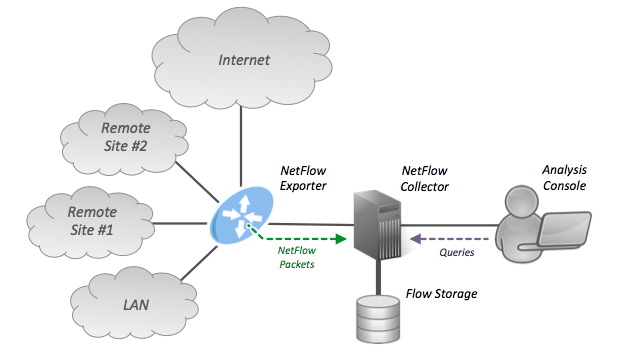
routers around 1996 that provides the ability to collect IP network traffic as it enters or exits an interface. By analyzing the data provided by NetFlow, a network administrator can determine things such as the source and destination of traffic, class of service, and the causes of congestion. A typical flow monitoring setup (using NetFlow) consists of three main components:
* Flow exporter: aggregates packets into flows and exports flow records towards one or more flow collectors.
* Flow collector: responsible for reception, storage and pre-processing of flow data received from a flow exporter.
* Analysis application: analyzes received flow data in the context of intrusion detection or traffic profiling, for example.
Protocol description
Routers and switches that support NetFlow can collect IP traffic statistics on all interfaces where NetFlow is enabled, and later export those statistics as NetFlow records toward at least one NetFlow collector—typically a server that does the actual traffic analysis.Network flows
Cisco standard NetFlow version 5 defines a ''flow'' as a unidirectional sequence of packets that all share seven values which define a unique key for the flow: # Ingress interface (SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an Internet Standard protocol for collecting and organizing information about managed devices on IP networks and for modifying that information to change device behaviour. Devices that typically ...
ifIndex)
# Source IP address
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label such as that is connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication.. Updated by . An IP address serves two main functions: network interface ident ...
# Destination IP address
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label such as that is connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication.. Updated by . An IP address serves two main functions: network interface ident ...
# IP protocol
The Internet Protocol (IP) is the network layer communications protocol in the Internet protocol suite for relaying datagrams across network boundaries. Its routing function enables internetworking, and essentially establishes the Internet.
IP h ...
# Source port for UDP or TCP, 0 for other protocols
# Destination port for UDP or TCP, type and code for ICMP, or 0 for other protocols
# IP Type of Service
Note that the Egress interface, IP Nexthop or BGP Nexthops are not part of the key, and may not be accurate if the route changes before the expiration of the flow, or if load-balancing is done per-packet.
This definition of flows is also used for IPv6, and a similar definition is used for MPLS
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a routing technique in telecommunications networks that directs data from one node to the next based on labels rather than network addresses. Whereas network addresses identify endpoints the labels identif ...
and Ethernet
Ethernet () is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in ...
flows.
Advanced NetFlow or IPFIX implementations like Cisco Flexible NetFlow allow user-defined flow keys.
A typical output of a NetFlow command line tool (nfdump in this case) when printing the stored flows may look as follows:
Date flow start Duration Proto Src IP Addr:Port Dst IP Addr:Port Packets Bytes Flows
2010-09-01 00:00:00.459 0.000 UDP 127.0.0.1:24920 -> 192.168.0.1:22126 1 46 1
2010-09-01 00:00:00.363 0.000 UDP 192.168.0.1:22126 -> 127.0.0.1:24920 1 80 1
Export of records
The router will output a flow record when it determines that the flow is finished. It does this by flow aging: when the router sees new traffic for an existing flow it resets the aging counter. Also,TCP session
TCP may refer to:
Science and technology
* Transformer coupled plasma
* Tool Center Point, see Robot end effector
Computing
* Transmission Control Protocol, a fundamental Internet standard
* Telephony control protocol, a Bluetooth communicati ...
termination in a TCP flow causes the router to expire the flow. Routers can also be configured to output a flow record at a fixed interval even if the flow is still ongoing.
Packet transport protocol
NetFlow records are traditionally exported using User Datagram Protocol ( UDP) and collected using a NetFlow collector. The IP address of the NetFlow collector and the destination UDP port must be configured on the sending router. A common value is UDP port 2055, but other values like 9555 or 9995, 9025, 9026 etc. can also be used. For efficiency reasons, the router traditionally does not keep track of flow records already exported, so if a NetFlow packet is dropped due tonetwork congestion
Network congestion in data networking and queueing theory is the reduced quality of service that occurs when a network node or link is carrying more data than it can handle. Typical effects include queueing delay, packet loss or the blocking ...
or packet corruption, all contained records are lost forever. The UDP protocol does not inform the router of the loss so it can send the packets again.
This can be a real problem, especially with NetFlow v8 or v9 that can aggregate a lot of packets or flows into a single record. A single UDP packet loss can cause a huge impact on the statistics of some flows.
That is why some modern implementations of NetFlow use the Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP
The Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) is a computer networking communications protocol in the transport layer of the Internet protocol suite. Originally intended for Signaling System 7 (SS7) message transport in telecommunication, the p ...
) to export packets so as to provide some protection against packet loss, and make sure that NetFlow v9 templates are received before any related record is exported. Note that TCP would not be suitable for NetFlow because a strict ordering of packets would cause excessive buffering and delays.
The problem with SCTP is that it requires interaction between each NetFlow collector and each router exporting NetFlow. There may be performance limitations if a router has to deal with many NetFlow collectors, and a NetFlow collector has to deal with many routers, especially when some of them are unavailable due to failure or maintenance.
SCTP may not be efficient if NetFlow must be exported toward several independent collectors, some of which may be test servers that can go down at any moment.
UDP allows simple replication of NetFlow packets using Network taps or L2 or L3 Mirroring. Simple stateless equipment can also filter or change the destination address of NetFlow UDP packets if necessary. Since NetFlow export almost only use network backbone links, packet loss will often be negligible. If it happens, it will mostly be on the link between the network and the NetFlow collectors.
Packet headers
All NetFlow packets begin with version-dependent header, that contains at least these fields: *Version number (v1, v5, v7, v8, v9) *Sequence number to detect loss and duplication *Timestamps at the moment of export, as system uptime or absolute time. *Number of records (v5 or v8) or list of templates and records (v9)Records
A NetFlow record can contain a wide variety of information about the traffic in a given flow. NetFlow version 5 (one of the most commonly used versions, followed by version 9) contains the following: *Input interface index used bySNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an Internet Standard protocol for collecting and organizing information about managed devices on IP networks and for modifying that information to change device behaviour. Devices that typically ...
(ifIndex in IF-MIB).
*Output interface index or zero if the packet is dropped.
*Timestamps for the flow start and finish time, in milliseconds since the last boot.
*Number of bytes and packets observed in the flow
*Layer 3
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the network layer is layer 3. The network layer is responsible for packet forwarding including routing through intermediate routers.
Functions
The network layer provides the means of transf ...
headers:
**Source & destination IP addresses
** ICMP Type and Code.
**IP protocol
** Type of Service (ToS) value
*Source and destination port numbers for TCP, UDP, SCTP
*For TCP flows, the union of all TCP flags observed over the life of the flow.
*Layer 3 Routing
Routing is the process of selecting a path for traffic in a network or between or across multiple networks. Broadly, routing is performed in many types of networks, including circuit-switched networks, such as the public switched telephone netw ...
information:
**IP address of the immediate next-hop (not the BGP nexthop) along the route to the destination
**Source & destination IP masks (prefix lengths in the CIDR notation)
For ICMP flows, the Source Port is zero, and the Destination Port number field codes ICMP message Type and Code (port = ICMP-Type * 256 + ICMP-Code) .
The source and destination Autonomous System Autonomous system may refer to:
* Autonomous system (Internet), a collection of IP networks and routers under the control of one entity
* Autonomous system (mathematics), a system of ordinary differential equations which does not depend on the inde ...
(AS) number fields can report the destination AS (last AS of AS-Path) or the immediate neighbor AS (first AS of AS-Path) depending on the router configuration. But the AS number will be zero if the feature is not supported, the route is unknown or not announced by BGP, or the AS is the local AS. There is no explicit way to distinguish between these cases.
NetFlow version 9 can include all of these fields and can optionally include additional information such as Multiprotocol Label Switching
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a routing technique in telecommunications networks that directs data from one node to the next based on labels rather than network addresses. Whereas network addresses identify endpoints the labels identi ...
(MPLS) labels and IPv6
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol (IP), the communications protocol that provides an identification and location system for computers on networks and routes traffic across the Internet. I ...
addresses and ports,
By analyzing flow data, a picture of traffic flow and traffic volume in a network can be built. The NetFlow record format has evolved over time, hence the inclusion of version numbers. Cisco maintains details of the different version numbers and the layout of the packets for each version.
Interfaces
NetFlow is usually enabled on a per-interface basis to limit load on the router components involved in NetFlow, or to limit the amount of NetFlow records exported. NetFlow usually captures all packets received by an ingress IP interface, but some NetFlow implementations use IP filters to decide if a packet can be observed by NetFlow. Some NetFlow implementations also allow the observation of packets on the egress IP interface, but this must be used with care: all flows from any ingress interface with NetFlow enabled to any interface with NetFlow enabled could be counted twice.Sampled NetFlow
Standard NetFlow was designed to process all IP packets on an interface. But in some environments, e.g. on Internet backbones, that was too costly, due to the extra processing required for each packet, and large number of simultaneous flows. So Cisco introduced sampled NetFlow on Cisco 12000, and that is now used in all high-end routers that implement NetFlow. Only one packet out of ''n'' is processed, where ''n'', the sampling rate, is determined by the router configuration. The exact selection process depends on the implementation: * One packet every ''n'' packet, in Deterministic NetFlow, as used on Cisco's 12000. * One packet randomly selected in an interval of ''n'' packet, in Random Sampled NetFlow, used on modern Cisco routers. Some implementations have more complex methods to sample packets, like per-flow sampling on Cisco Martinez Catalysts. The sampling rate is often the same for all interfaces, but can be adjusted per interface for some routers. When Sampled NetFlow is used, the NetFlow records must be adjusted for the effect of sampling - traffic volumes, in particular, are now an estimate rather than the actual measured flow volume. The sampling rate is indicated in a header field of NetFlow version 5 (same sampling rate for all interfaces) or in option records of NetFlow version 9 (sampling rate per interface)Versions
NetFlow and IPFIX
NetFlow was initially implemented by Cisco, and described in an "informational" document that was not on the standards track: RFC 3954 – Cisco Systems NetFlow Services Export Version 9. The NetFlow protocol itself has been superseded by Internet Protocol Flow Information eXport (IPFIX
Internet Protocol Flow Information Export (IPFIX) is an IETF protocol, as well as the name of the IETF working group defining the protocol. It was created based on the need for a common, universal standard of export for Internet Protocol flow infor ...
). Based on the NetFlow Version 9 implementation, IPFIX is on the IETF standards track with RFC 5101 (obsoleted by RFC 7011), RFC 5102 (obsoleted by RFC 7012), etc. which were published in 2008.
Equivalents
Many vendors other thanCisco
Cisco Systems, Inc., commonly known as Cisco, is an American-based multinational corporation, multinational digital communications technology conglomerate (company), conglomerate corporation headquartered in San Jose, California. Cisco develo ...
provide similar network flow monitoring technology. NetFlow may be a prevalent name in the area of flow monitoring, because of Cisco
Cisco Systems, Inc., commonly known as Cisco, is an American-based multinational corporation, multinational digital communications technology conglomerate (company), conglomerate corporation headquartered in San Jose, California. Cisco develo ...
dominant market share in the networking industry. NetFlow is thought to be a Cisco trademark (even though as of March 2012 it is not listed in Cisco Trademarks):
* Argus - Audit Record Generation and Utilization System
* Jflow or cflowd for Juniper Networks
Juniper Networks, Inc. is an American multinational corporation headquartered in Sunnyvale, California. The company develops and markets networking products, including routers, switches, network management software, network security products, ...
* NetStream for 3Com/HP
* NetStream for Huawei Technologies
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ( ; ) is a Chinese multinational technology corporation headquartered in Shenzhen, Guangdong, China. It designs, develops, produces and sells telecommunications equipment, consumer electronics and various s ...
* Cflowd for Nokia
Nokia Corporation (natively Nokia Oyj, referred to as Nokia) is a Finnish multinational telecommunications, information technology, and consumer electronics corporation, established in 1865. Nokia's main headquarters are in Espoo, Finlan ...
* Rflow for Ericsson
(lit. "Telephone Stock Company of LM Ericsson"), commonly known as Ericsson, is a Sweden, Swedish multinational networking and telecommunications company headquartered in Stockholm. The company sells infrastructure, software, and services in ...
* AppFlow Citrix
Citrix Systems, Inc. is an American multinational cloud computing and virtualization technology company that provides server, application and desktop virtualization, networking, software as a service (SaaS), and cloud computing technologies. C ...
* sFlow
sFlow, short for "sampled flow", is an industry standard for packet export at Layer 2 of the OSI model. sFlow was originally developed by InMon Corp. It provides a means for exporting truncated packets, together with interface counters for the purp ...
vendors include: Alaxala
, commonly known as its brand Alaxala, is a Japanese company headquartered in Kawasaki, Kanagawa, Japan, that offers networking hardware products.
Overview
Originally, in 2004, Alaxala Networks Corp. was established, as the merger between Hitach ...
, Alcatel Lucent, Allied Telesis
is a network infrastructure/telecommunications company, formerly Allied Telesyn. Headquartered in Japan, their North American headquarters are in San Jose, California. Founded in 1987, the company is a global provider of secure Ethernet & IP ...
, Arista Networks
Arista Networks (formerly Arastra) is an American computer networking company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. The company designs and sells multilayer network switches to deliver software-defined networking (SDN) for large datacenter ...
, Brocade
Brocade is a class of richly decorative shuttle-woven fabrics, often made in colored silks and sometimes with gold and silver threads. The name, related to the same root as the word " broccoli", comes from Italian ''broccato'' meaning "em ...
, Cisco
Cisco Systems, Inc., commonly known as Cisco, is an American-based multinational corporation, multinational digital communications technology conglomerate (company), conglomerate corporation headquartered in San Jose, California. Cisco develo ...
, Dell
Dell is an American based technology company. It develops, sells, repairs, and supports computers and related products and services. Dell is owned by its parent company, Dell Technologies.
Dell sells personal computers (PCs), servers, data ...
, D-Link
D-Link Corporation is a Taiwanese multinational networking equipment manufacturing corporation headquartered in Taipei, Taiwan. It was founded in March 1986 in Taipei as ''Datex Systems Inc.''
History
D-Link Corporation changed its name f ...
, Enterasys
Enterasys Networks, Inc. was an American networking company. Enterasys products included networking equipment ranging from routers, switches, and IEEE 802.11 wireless access points and controllers. The company formed in March 2000 as a spin-off ...
, Extreme
Extreme may refer to:
Science and mathematics Mathematics
*Extreme point, a point in a convex set which does not lie in any open line segment joining two points in the set
*Maxima and minima, extremes on a mathematical function
Science
*Extremop ...
, F5 BIG-IP, Fortinet
Fortinet is an American multinational corporation headquartered in Sunnyvale, California. The company develops and sells cybersecurity solutions, such as physical firewalls, antivirus software, intrusion prevention systems, and endpoint secu ...
, Hewlett-Packard, Hitachi
() is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate corporation headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo, Japan. It is the parent company of the Hitachi Group (''Hitachi Gurūpu'') and had formed part of the Ni ...
, Huawei
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ( ; ) is a Chinese multinational technology corporation headquartered in Shenzhen, Guangdong, China. It designs, develops, produces and sells telecommunications equipment, consumer electronics and various smart ...
, IBM, Juniper
Junipers are coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Juniperus'' () of the cypress family Cupressaceae. Depending on the taxonomy, between 50 and 67 species of junipers are widely distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere, from the Arcti ...
, LG-Ericsson
Ericsson-LG is a joint venture company owned by the Swedish group Ericsson (75%) and the South Korean group LG Electronics (25%). Founded in November 2005, it engineers and designs telecommunications equipment, with LG providing distribution and ...
, Mellanox
Mellanox Technologies Ltd. ( he, מלאנוקס טכנולוגיות בע"מ) was an Israeli-American multinational supplier of computer networking products based on InfiniBand and Ethernet technology. Mellanox offered adapters, switches, softwa ...
, MRV, NEC
is a Japanese multinational information technology and electronics corporation, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. The company was known as the Nippon Electric Company, Limited, before rebranding in 1983 as NEC. It provides IT and network soluti ...
, Netgear, Proxim Wireless, Quanta Computer
Quanta Computer Incorporated () () is a Taiwan-based manufacturer of notebook computers and other electronic hardware. Its customers include Apple Inc., Dell, Hewlett-Packard Inc., Acer Inc., Alienware, Amazon.com, Cisco, Fujitsu, Gericom, Le ...
, Vyatta
Vyatta is a software-based virtual router, virtual firewall and VPN products for Internet Protocol networks (IPv4 and IPv6). A free download of Vyatta has been available since March 2006. The system is a specialized Debian-based Linux distribut ...
, Telesoft, ZTE
ZTE Corporation is a Chinese partially state-owned technology company that specializes in telecommunication. Founded in 1985, ZTE is listed on both the Hong Kong and Shenzhen Stock Exchanges.
ZTE's core business is wireless, exchange, opt ...
and ZyXEL
Also flow-tools collection of software allows to process and manage NetFlow exports from Cisco and Juniper routers.
Support
Variants
Cisco's NetFlow Security Event Logging
Introduced with the launch of theCisco ASA In computer networking, Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliances, or simply Cisco ASA, is Cisco's line of network security devices introduced in May 2005. It succeeded three existing lines of popular Cisco products:
* Cisco PIX, which prov ...
5580 productsNetFlow Security Event Logging
utilizes NetFlow v9 fields and templates in order to efficiently deliver security telemetry in high performance environments. NetFlow Security Event Logging scales better than
syslog
In computing, syslog is a standard for message logging. It allows separation of the software that generates messages, the system that stores them, and the software that reports and analyzes them. Each message is labeled with a facility code, i ...
while offering the same level of detail and granularity in logged events.
Monitoring based on standalone probes
 NetFlow collection using standalone NetFlow probes is an alternative to flow collection from routers and switches. This approach can overcome some limitations of router-based NetFlow monitoring. The probes are transparently connected to the monitored link as a passive appliance using the TAP or SPAN port of the appliance.
Historically, NetFlow monitoring is easier to implement in a dedicated probe than in a router. However, this approach also has some drawbacks:
* probes must be deployed on every link that must be observed, causing additional hardware, setup and maintenance costs.
* probes will not report separate input and output interface information like a report from a router would.
* probes may have problems reporting reliably the NetFlow fields related to routing, like AS Numbers or IP masks, because they can hardly be expected to use exactly the same routing information as a router.
The easiest way to address the above drawbacks is to use a
NetFlow collection using standalone NetFlow probes is an alternative to flow collection from routers and switches. This approach can overcome some limitations of router-based NetFlow monitoring. The probes are transparently connected to the monitored link as a passive appliance using the TAP or SPAN port of the appliance.
Historically, NetFlow monitoring is easier to implement in a dedicated probe than in a router. However, this approach also has some drawbacks:
* probes must be deployed on every link that must be observed, causing additional hardware, setup and maintenance costs.
* probes will not report separate input and output interface information like a report from a router would.
* probes may have problems reporting reliably the NetFlow fields related to routing, like AS Numbers or IP masks, because they can hardly be expected to use exactly the same routing information as a router.
The easiest way to address the above drawbacks is to use a packet capture appliance
A packet capture appliance is a standalone device that performs packet capture. Packet capture appliances may be deployed anywhere on a network, however, most commonly are placed at the entrances to the network (i.e. the internet connections) and i ...
inline in front of the router and capture all of the NetFlow output from the router. This method allows for storage of large amount of NetFlow data (typically many years worth of data) and does not require reconfiguration of the network.
NetFlow collection from dedicated probes is well suited for observation of critical links, whereas NetFlow on routers provides a Network-wide view of the traffic that can be used for capacity planning, accounting, performance monitoring, and security.
History
NetFlow was originally a Cisco packet switching technology for Cisco routers, implemented inIOS
iOS (formerly iPhone OS) is a mobile operating system created and developed by Apple Inc. exclusively for its hardware. It is the operating system that powers many of the company's mobile devices, including the iPhone; the term also include ...
11.x around 1996.
It was originally a software implementation for the Cisco 7000, 7200 and 7500, where it was thought as an improvement over the then current Cisco Fast Switching. Netflow was invented by Darren Kerr and Barry Bruin from Cisco (U.Spatent # 6,243,667
). The idea was that the first packet of a flow would create a NetFlow switching record. This record would then be used for all later packets of the same flow, until the expiration of the flow. Only the first packet of a flow would require an investigation of the route table to find the most specific matching route. This is an expensive operation in software implementations, especially the old ones without
Forwarding information base
A forwarding information base (FIB), also known as a forwarding table or MAC table, is most commonly used in network bridging, routing, and similar functions to find the proper output network interface controller to which the input interface shou ...
. The NetFlow switching record was actually some kind of route cache record, and old versions of IOS still refer to the NetFlow cache as ip route-cache.
This technology was advantageous for local networks. This was especially true if some of the traffic had to be filtered by an ACL as only the first packet of a flow had to be evaluated by the ACL.NetFlow, sFlow, and Flow Extensibility, Part 1/ref> NetFlow switching soon turned out to be unsuitable for big routers, especially Internet backbone routers, where the number of simultaneous flows was much more important than those on local networks, and where some traffic causes many short-lived flows, like
Domain Name System
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical and distributed naming system for computers, services, and other resources in the Internet or other Internet Protocol (IP) networks. It associates various information with domain names assigned ...
requests (whose source port is random for security reasons).
As a switching technology, NetFlow was replaced around 1995 by Cisco Express Forwarding {{Short description, Layer 3 switching technology
Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) is an advanced layer 3 switching technology used mainly in large core networks or the Internet to enhance the overall network performance. Although CEF is a Cisco propr ...
. This first appeared on Cisco 12000 routers, and later replaced NetFlow switching on advanced IOS for the Cisco 7200 and Cisco 7500.
As of 2012, technologies similar to NetFlow switching are still in use in most firewalls and software-based IP routers. For instance the conntrack feature of the Netfilter
Netfilter is a framework provided by the Linux kernel that allows various networking-related operations to be implemented in the form of customized handlers. Netfilter offers various functions and operations for packet filtering, network addr ...
framework used by Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which i ...
.
RFCs
RFC 3334 - Policy-Based Accounting
RFC 3917 - Requirements for IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX)
RFC 3954 - NetFlow Version 9
RFC 3955 - Evaluation of Candidate Protocols for IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX)
RFC 3917 - Requirements for IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX)
RFC 3955 - Candidate Protocols for IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX)
RFC 5101 - Specification of the IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Protocol for the Exchange of IP Traffic Flow Information
RFC 5102 - Information Model for IP Flow Information Export
RFC 5103 - Bidirectional Flow Export Using IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX)
RFC 5153 - IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Implementation Guidelines
RFC 5470 - Architecture for IP Flow Information Export
RFC 5471 - Guidelines for IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Testing
RFC 5472 - IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Applicability
RFC 5473 - Reducing Redundancy in IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) and Packet Sampling (PSAMP) Reports
RFC 5476 - Packet Sampling (PSAMP) Protocol Specifications
RFC 5477 - Information Model for Packet Sampling Exports
RFC 5610 - Exporting Type Information for IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Information Elements
RFC 5655 - Specification of the IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) File Format
RFC 5815 - Definitions of Managed Objects for IP Flow Information Export
RFC 5982 - IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Mediation: Problem Statement
RFC 6183 - IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Mediation: Framework
RFC 6235 - IP Flow Anonymization Support
RFC 6313 - Export of Structured Data in IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX)
RFC 6526 - IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Per Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) Stream
RFC 6615 - Definitions of Managed Objects for IP Flow Information Export
RFC 6645 - IP Flow Information Accounting and Export Benchmarking Methodology
RFC 6727 - Definitions of Managed Objects for Packet Sampling
RFC 6728 - Configuration Data Model for the IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) and Packet Sampling (PSAMP) Protocols
RFC 6759 - Cisco Systems Export of Application Information in IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX)
RFC 7011 - Specification of the IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Protocol for the Exchange of Flow Information
RFC 7012 - Information Model for IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX)
RFC 7013 - Guidelines for Authors and Reviewers of IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Information Elements
RFC 7015 - Flow Aggregation for the IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Protocol
RFC 7119 - Operation of the IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Protocol on IPFIX Mediators
RFC 7125 - Revision of the tcpControlBits IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Information Element
RFC 7133 - Information Elements for Data Link Layer Traffic Measurement
RFC 7270 - Cisco-Specific Information Elements Reused in IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX)
RFC 7373 - Textual Representation of IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Abstract Data Types
RFC 8038 - Exporting MIB Variables Using the IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Protocol
RFC 8158 - IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX) Information Elements for Logging NAT Events
RFC 8272 - TinyIPFIX for Smart Meters in Constrained Networks
RFC 8549 - Export of BGP Community Information in IP Flow Information Export (IPFIX)
See also
*Traffic flow (computer networking)
In packet switching networks, traffic flow, packet flow or ''network flow'' is a sequence of packets from a source computer to a destination, which may be another host, a multicast group, or a broadcast domain. RFC 2722 defines traffic flow as "a ...
* IP Flow Information Export
Internet Protocol Flow Information Export (IPFIX) is an IETF protocol, as well as the name of the IETF working group defining the protocol. It was created based on the need for a common, universal standard of export for Internet Protocol flow infor ...
(IPFIX) - IETF
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is a standards organization for the Internet and is responsible for the technical standards that make up the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP). It has no formal membership roster or requirements and ...
standards-track flow export protocol, based on NetFlow version 9
* sFlow
sFlow, short for "sampled flow", is an industry standard for packet export at Layer 2 of the OSI model. sFlow was originally developed by InMon Corp. It provides a means for exporting truncated packets, together with interface counters for the purp ...
- alternative to NetFlow (mandatory sampling, no flow cache, no templates )
References
{{reflistExternal links
NetFlow/FloMA: Pointers and Software Provided by SWITCH.
- One of the most comprehensive list including all the open source and research works.
FloCon
- The Annual Conference put on by CERT/CC dealing with network flow data and analysis.
Basic NetFlow information on the Cisco Site
Paessler IT Explained - NetFlow
Using Netflow to store re-aggregated inbound and outbound flows
AppFlow specifications and standards track discussion
Understanding NetFlow Principle Animation
Basics of NetFlow & Flow Cache
List of Netflow Analyzers and Collectors
Computer network analysis Internet Protocol based network software Cisco protocols