Neomenthol on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Menthol is an
 In the natural compound, the
In the natural compound, the 
 The (+)- and (−)-
The (+)- and (−)-

 Menthol's ability to chemically trigger the cold-sensitive
Menthol's ability to chemically trigger the cold-sensitive

Image:Menthol synthesis.png,
rect 6 14 131 92
This image editor
was used.
The process begins by forming an allylic amine from 
Ryoji Noyori Nobel lecture (2001)
A review of menthol
from the Science Creative Quarterly {{Authority control Analgesics Antipruritics Cooling flavors Kappa-opioid receptor agonists GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators Cyclohexanols Monoterpenes Isopropyl compounds
organic compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The ...
, more specifically a monoterpenoid
Monoterpenes are a class of terpenes that consist of two isoprene units and have the molecular formula C10H16. Monoterpenes may be linear (acyclic) or contain rings (monocyclic and bicyclic). Modified terpenes, such as those containing oxygen funct ...
, made synthetically or obtained from the oils of corn mint
''Mentha arvensis'', the corn mint, field mint, or wild mint, is a species of flowering plant in the mint family Lamiaceae. It has a circumboreal distribution, being native to the temperate regions of Europe and western and central Asia, east t ...
, peppermint
Peppermint (''Mentha'' × ''piperita'') is a hybrid species of mint, a cross between watermint and spearmint. Indigenous to Europe and the Middle East, the plant is now widely spread and cultivated in many regions of the world.Euro+Med Plantbas ...
, or other mints
A mint or breath mint is a food item often consumed as an after-meal refreshment or before business and social engagements to improve breath odor. Mints are commonly believed to soothe the stomach given their association with natural byproducts ...
. It is a waxy, clear or white crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
line substance, which is solid at room temperature
Colloquially, "room temperature" is a range of air temperatures that most people prefer for indoor settings. It feels comfortable to a person when they are wearing typical indoor clothing. Human comfort can extend beyond this range depending on ...
and melts slightly above.
The main form of menthol occurring in nature is (−)-menthol, which is assigned the (1''R'',2''S'',5''R'') configuration. Menthol has local anesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of pain sensation. In the context of surgery, a local anesthetic creates an absence of pain in a specific location of the body without a loss of consciousness, as opposed to a general an ...
and counterirritant
A counterirritant is a substance which creates irritation or mild inflammation in one location with the goal of lessening discomfort and/or inflammation in another location. This strategy falls into the more general category of counterstimulation ...
qualities, and it is widely used to relieve minor throat irritation
Throat irritation can refer to a dry cough, a scratchy feeling at the back of the throat, a sensation of a lumpy feeling, something stuck at the back of the throat, or possibly a feeling of dust in the throat. The symptoms are unpleasant and usuall ...
. Menthol also acts as a weak κ-opioid receptor
The κ-opioid receptor or kappa opioid receptor, abbreviated KOR or KOP, is a G protein-coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''OPRK1'' gene. The KOR is coupled to the G protein Gi/G0 and is one of four related receptors that bind op ...
agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the ago ...
.
Structure
Natural menthol exists as one purestereoisomer
In stereochemistry, stereoisomerism, or spatial isomerism, is a form of isomerism in which molecules have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution), but differ in the three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in ...
, nearly always the (1''R'',2''S'',5''R'') form (bottom left corner of the diagram below). The eight possible stereoisomers are:
:isopropyl
In organic chemistry, propyl is a three-carbon alkyl substituent with chemical formula for the linear form. This substituent form is obtained by removing one hydrogen atom attached to the terminal carbon of propane. A propyl substituent is ofte ...
group is in the ''trans
Trans- is a Latin prefix meaning "across", "beyond", or "on the other side of".
Used alone, trans may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Trans (festival), a former festival in Belfast, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom
* ''Trans'' (fil ...
'' orientation to both the methyl
In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula . In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many ...
and hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ...
groups. Thus, it can be drawn in any of the ways shown:
: The (+)- and (−)-
The (+)- and (−)-enantiomer
In chemistry, an enantiomer ( /ɪˈnænti.əmər, ɛ-, -oʊ-/ ''ih-NAN-tee-ə-mər''; from Ancient Greek ἐνάντιος ''(enántios)'' 'opposite', and μέρος ''(méros)'' 'part') – also called optical isomer, antipode, or optical ant ...
s of menthol are the most stable among these based on their cyclohexane conformation
In organic chemistry, cyclohexane conformations are any of several three-dimensional shapes adopted by molecules of cyclohexane. Because many compounds feature structurally similar six-membered rings, the structure and dynamics of cyclohexane ...
s. With the ring itself in a chair conformation, all three bulky groups can orient in equatorial positions.
The two crystal forms for racemic
In chemistry, a racemic mixture, or racemate (), is one that has equal amounts of left- and right-handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule or salt. Racemic mixtures are rare in nature, but many compounds are produced industrially as racemates. ...
menthol have melting points of 28 °C and 38 °C. Pure (−)-menthol has four crystal forms, of which the most stable is the α form, the familiar broad needles.
Biological properties

 Menthol's ability to chemically trigger the cold-sensitive
Menthol's ability to chemically trigger the cold-sensitive TRPM8
Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M (melastatin) member 8 (TRPM8), also known as the cold and menthol receptor 1 (CMR1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TRPM8'' gene. The TRPM8 channel is the primary molecular ...
receptors in the skin is responsible for the well-known cooling sensation it provokes when inhaled, eaten, or applied to the skin. In this sense, it is similar to capsaicin
Capsaicin (8-methyl-''N''-vanillyl-6-nonenamide) ( or ) is an active component of chili peppers, which are plants belonging to the genus ''Capsicum''. It is a chemical irritant for mammals, including humans, and produces a sensation of burnin ...
, the chemical responsible for the spiciness of hot chilis (which stimulates heat sensors, also without causing an actual change in temperature).
Menthol's analgesic
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic (British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). It ...
properties are mediated through a selective activation of κ- opioid receptors. Menthol blocks calcium channels and voltage-sensitive sodium channels
Sodium channels are integral membrane proteins that form ion channels, conducting sodium ions (Na+) through a cell's membrane. They belong to the superfamily of cation channels and can be classified according to the trigger that opens the chann ...
, reducing neural activity that may stimulate muscles.
Some studies show that menthol acts as GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator and increases Gabaergic transmission in PAG neurons. Menthol also shares anaesthetic
An anesthetic (American English) or anaesthetic (British English; see spelling differences) is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into two ...
properties similar to propofol, by modulating the same sites of the GABAA receptor.
Menthol is widely used in dental care as a topical antibacterial agent, effective against several types of streptococci and lactobacilli
The ''Lactobacillaceae'' are a family of lactic acid bacteria. It is the only family in the lactic acid bacteria which includes homofermentative and heterofermentative organisms; in the ''Lactobacillaceae,'' the pathway used for hexose fermentati ...
. Menthol also lowers blood pressure and antagonizes vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of the blood vessels resulting from contraction of the muscular wall of the vessels, in particular the large arteries and small arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasodilation, the widening of blood vessel ...
through TRPM8 activation.
Occurrence
''Mentha arvensis
''Mentha arvensis'', the corn mint, field mint, or wild mint, is a species of flowering plant in the mint family Lamiaceae. It has a circumboreal distribution, being native to the temperate regions of Europe and western and central Asia, east to ...
'' (wild mint) is the primary species of mint
MiNT is Now TOS (MiNT) is a free software alternative operating system kernel for the Atari ST system and its successors. It is a multi-tasking alternative to TOS and MagiC. Together with the free system components fVDI device drivers, XaA ...
used to make natural menthol crystals
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macrosc ...
and natural menthol flakes. This species is primarily grown in the Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 1950 ...
region in India.
Menthol occurs naturally in peppermint oil (along with a little menthone
Menthone is a monoterpene with a minty flavor that occurs naturally in a number of essential oils. ''l''-Menthone (or (2''S'',5''R'')-''trans''-2-isopropyl-5-methylcyclohexanone), shown at right, is the most abundant in nature of the four possible ...
, the ester menthyl acetate
Menthyl acetate is a natural monoterpene which contributes to the smell and flavor of peppermint. It is the acetate ester of menthol. Menthyl acetate constitutes 3–5% of the volatile oil of ''mentha piperita'', contributing to its smell and f ...
and other compounds), obtained from ''Mentha × piperita
Peppermint (''Mentha'' × ''piperita'') is a hybrid species of mint, a cross between watermint and spearmint. Indigenous to Europe and the Middle East, the plant is now widely spread and cultivated in many regions of the world.Euro+Med Plantba ...
'' (peppermint). Japanese menthol also contains a small percentage of the 1-epimer
In stereochemistry, an epimer is one of a pair of diastereomers. The two epimers have opposite configuration at only one stereogenic center out of at least two. All other stereogenic centers in the molecules are the same in each. Epimerization i ...
neomenthol.
Biosynthesis
The biosynthesis of menthol has been investigated in ''Mentha × piperita
Peppermint (''Mentha'' × ''piperita'') is a hybrid species of mint, a cross between watermint and spearmint. Indigenous to Europe and the Middle East, the plant is now widely spread and cultivated in many regions of the world.Euro+Med Plantba ...
'' and the enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
s involved in have been identified and characterized. It begins with the synthesis of the terpene limonene
Limonene is a colorless liquid aliphatic hydrocarbon classified as a cyclic monoterpene, and is the major component in the oil of citrus fruit peels. The -isomer, occurring more commonly in nature as the fragrance of oranges, is a flavoring ag ...
, followed by hydroxylation
In chemistry, hydroxylation can refer to:
*(i) most commonly, hydroxylation describes a chemical process that introduces a hydroxyl group () into an organic compound.
*(ii) the ''degree of hydroxylation'' refers to the number of OH groups in a ...
, and then several reduction and isomerization
In chemistry, isomerization or isomerisation is the process in which a molecule, polyatomic ion or molecular fragment is transformed into an isomer with a different chemical structure. Enolization is an example of isomerization, as is tautomeriz ...
steps.
More specifically, the biosynthesis of (−)-menthol takes place in the secretory gland cells of the peppermint plant. Geranyl diphosphate synthase (GPPS), first catalyzes the reaction of IPP and DMAPP
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP; or alternatively, dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMADP); also isoprenyl pyrophosphate) is an isoprenoid precursor. It is a product of both the mevalonate pathway and the MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynt ...
into geranyl diphosphate
Geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP), also known as geranyl diphosphate (GDP), is the pyrophosphate ester of the terpenoid geraniol. Its salts are colorless. It is a precursor to many natural products.
Occurrence
GPP is an intermediate in the isoprenoid ...
. Next (−)-limonene synthase (LS) catalyzes the cyclization of geranyl diphosphate to (−)-limonene
Limonene is a colorless liquid aliphatic hydrocarbon classified as a cyclic monoterpene, and is the major component in the oil of citrus fruit peels. The -isomer, occurring more commonly in nature as the fragrance of oranges, is a flavoring ag ...
. (−)-Limonene-3-hydroxylase (L3OH), using O2 and NADPH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NAD ...
, then catalyzes the allylic hydroxylation of (−)-limonene at the 3 position to (−)-trans-isopiperitenol. (−)-''trans''-Isopiperitenol dehydrogenase (iPD) further oxidizes the hydroxyl group on the 3 position using NAD+ to make (−)-isopiperitenone. (−)-Isopiperitenone reductase (iPR) then reduces the double bond between carbons 1 and 2 using NADPH to form (+)-''cis''-isopulegone. (+)-''cis''-Isopulegone isomerase (iPI) then isomerizes the remaining double bond to form (+)-pulegone. (+)-Pulegone reductase (PR) then reduces this double bond using NADPH to form (−)-menthone. (−)-Menthone reductase (MR) then reduces the carbonyl group using NADPH to form (−)-menthol.
:
Production
Natural menthol is obtained by freezingpeppermint oil Peppermint extract is an herbal extract of peppermint (''Mentha × piperita'') made from the essential oils of peppermint leaves. Peppermint is a hybrid of water mint and spearmint and was indigenous to Europe and the Middle East before it became c ...
. The resultant crystals of menthol are then separated by filtration.
Total world production of menthol in 1998 was 12,000 tonnes of which 2,500 tonnes was synthetic. In 2005, the annual production of synthetic menthol was almost double. Prices are in the $10–20/kg range with peaks in the $40/kg region but have reached as high as $100/kg. In 1985, it was estimated that China produced most of the world's supply of natural menthol, although it appears that India has pushed China into second place.
Menthol is manufactured as a single enantiomer
In chemistry, an enantiomer ( /ɪˈnænti.əmər, ɛ-, -oʊ-/ ''ih-NAN-tee-ə-mər''; from Ancient Greek ἐνάντιος ''(enántios)'' 'opposite', and μέρος ''(méros)'' 'part') – also called optical isomer, antipode, or optical ant ...
(94% e.e.) on the scale of 3,000 tonnes per year by Takasago International Corporation
is a major international producer of flavours and fragrances headquartered in Japan, with presence in 27 countries and regions worldwide. Takasago ranked 8th overall and 1st in Asia on the Global Top Food Flavours and Fragrances Companies list ...
. The process involves an asymmetric synthesis developed by a team led by Ryōji Noyori
is a Japanese chemist. He won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2001, Noyori shared a half of the prize with William S. Knowles for the study of chirally catalyzed hydrogenations; the second half of the prize went to K. Barry Sharpless for his st ...
, who won the 2001 Nobel Prize for Chemistry
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "M ...
in recognition of his work on this process:
:myrcene
Myrcene, or β-myrcene, is a monoterpene. A colorless oil, it occurs widely in essential oils. It is produced mainly semi-synthetically from '' Myrcia'', from which it gets its name. It is an intermediate in the production of several fragrances. ...
rect 136 46 201 63 diethylamine
Diethylamine is an organic compound with the formula (CH3CH2)2NH. It is a secondary amine. It is a flammable, weakly alkaline liquid that is miscible with most solvents. It is a colorless liquid, but commercial samples often appear brown due to im ...
rect 468 110 628 180 citronellal
Citronellal or rhodinal ( C10 H18 O) is a monoterpenoid aldehyde, the main component in the mixture of terpenoid chemical compounds that give citronella oil its distinctive lemon scent.
Citronellal is a main isolate in distilled oils from the p ...
rect 387 112 458 135 zinc bromide
Zinc bromide ( Zn Br2) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Zn Br2. It is a colourless salt that shares many properties with zinc chloride (ZnCl2), namely a high solubility in water forming acidic solutions, and good solubility in o ...
desc bottom-left
#Notes:
#Details on the new coding for clickable images is here: mw:Extension:ImageMapThis image editor
was used.
myrcene
Myrcene, or β-myrcene, is a monoterpene. A colorless oil, it occurs widely in essential oils. It is produced mainly semi-synthetically from '' Myrcia'', from which it gets its name. It is an intermediate in the production of several fragrances. ...
, which undergoes asymmetric isomerisation in the presence of a BINAP
BINAP (2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthyl) is an organophosphorus compound. This chiral diphosphine ligand is widely used in asymmetric synthesis. It consists of a pair of 2-diphenylphosphinonaphthyl groups linked at the 1 and ...
rhodium
Rhodium is a chemical element with the symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is a very rare, silvery-white, hard, corrosion-resistant transition metal. It is a noble metal and a member of the platinum group. It has only one naturally occurring isoto ...
complex to give (after hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
) enantiomerically pure ''R''-citronellal
Citronellal or rhodinal ( C10 H18 O) is a monoterpenoid aldehyde, the main component in the mixture of terpenoid chemical compounds that give citronella oil its distinctive lemon scent.
Citronellal is a main isolate in distilled oils from the p ...
. This is cyclised by a carbonyl-ene-reaction
In organic chemistry, the ene reaction (also known as the Alder-ene reaction by its discoverer Kurt Alder in 1943) is a chemical reaction between an alkene with an allylic hydrogen (the ene) and a compound containing a multiple bond (the enophile ...
initiated by zinc bromide
Zinc bromide ( Zn Br2) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Zn Br2. It is a colourless salt that shares many properties with zinc chloride (ZnCl2), namely a high solubility in water forming acidic solutions, and good solubility in o ...
to , which is then hydrogenated to give pure (1''R'',2''S'',5''R'')-menthol.
Another commercial process is the Haarmann–Reimer process (after the company Haarmann & Reimer, now part of Symrise) This process starts from ''m''-cresol which is alkylated with propene
Propylene, also known as propene, is an unsaturated organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CH=CH2. It has one double bond, and is the second simplest member of the alkene class of hydrocarbons. It is a colorless gas with a faint petro ...
to thymol
Thymol (also known as 2-isopropyl-5-methylphenol, IPMP), , is a natural monoterpenoid phenol derivative of ''p''-Cymene, isomeric with carvacrol, found in oil of thyme, and extracted from ''Thymus vulgaris'' (common thyme), ajwain, and vari ...
. This compound is hydrogenated
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic ...
in the next step. Racemic menthol is isolated by fractional distillation
Fractional distillation is the separation of a mixture into its component parts, or fractions. Chemical compounds are separated by heating them to a temperature at which one or more fractions of the mixture will vaporize. It uses distillation to ...
. The enantiomers are separated by chiral resolution
Chiral resolution, or enantiomeric resolution, is a process in stereochemistry for the separation of racemic compounds into their enantiomers. It is an important tool in the production of optically active compounds, including drugs. Another term wi ...
in reaction with methyl benzoate
Methyl benzoate is an organic compound. It is an ester with the chemical formula C6H5CO2CH3. It is a colorless liquid that is poorly soluble in water, but miscible with organic solvents. Methyl benzoate has a pleasant smell, strongly reminisce ...
, selective crystallisation followed by hydrolysis.
:Racemic
In chemistry, a racemic mixture, or racemate (), is one that has equal amounts of left- and right-handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule or salt. Racemic mixtures are rare in nature, but many compounds are produced industrially as racemates. ...
menthol can also be formed by hydrogenation of thymol
Thymol (also known as 2-isopropyl-5-methylphenol, IPMP), , is a natural monoterpenoid phenol derivative of ''p''-Cymene, isomeric with carvacrol, found in oil of thyme, and extracted from ''Thymus vulgaris'' (common thyme), ajwain, and vari ...
, menthone
Menthone is a monoterpene with a minty flavor that occurs naturally in a number of essential oils. ''l''-Menthone (or (2''S'',5''R'')-''trans''-2-isopropyl-5-methylcyclohexanone), shown at right, is the most abundant in nature of the four possible ...
, or pulegone
Pulegone is a naturally occurring organic compound obtained from the essential oils of a variety of plants such as ''Nepeta cataria'' (catnip), ''Mentha piperita'', and pennyroyal. It is classified as a monoterpene.
Pulegone is a clear colorles ...
. In both cases with further processing (crystallizative entrainment resolution of the menthyl benzoate conglomerate) it is possible to concentrate the L-enantiomer, however this tends to be less efficient, although the higher processing costs may be offset by lower raw material costs. A further advantage of this process is that D-menthol becomes inexpensively available for use as a chiral auxiliary, along with the more usual L-antipode.
Applications
Menthol is included in many products, and for a variety of reasons. These include: *In nonprescription products for short-term relief of minor sore throat and minor mouth or throat irritation. **Examples:lip balm
Lip balm or lip salve is a wax-like substance applied topically to the lips to moisturize and relieve chapped or dry lips, angular cheilitis, stomatitis, or cold sores. Lip balm often contains beeswax or carnauba wax, camphor, cetyl alcohol, l ...
s and cough medicine
Cold medicines are a group of medications taken individually or in combination as a treatment for the symptoms of the common cold and similar conditions of the upper respiratory tract. The term encompasses a broad array of drugs, including ...
s.
*As an antipruritic to reduce itching.
* As a topical analgesic, it is used to relieve minor aches and pains, such as muscle cramps, sprains, headaches and similar conditions, alone or combined with chemicals such as camphor, eucalyptus oil
Eucalyptus oil is the generic name for distilled oil from the leaf of ''Eucalyptus'', a genus of the plant family Myrtaceae native to Australia and cultivated worldwide. Eucalyptus oil has a history of wide application, as a pharmaceutical, ant ...
or capsaicin
Capsaicin (8-methyl-''N''-vanillyl-6-nonenamide) ( or ) is an active component of chili peppers, which are plants belonging to the genus ''Capsicum''. It is a chemical irritant for mammals, including humans, and produces a sensation of burnin ...
. In Europe, it tends to appear as a gel or a cream, while in the U.S., patches and body sleeves are very frequently used.
** Examples: Tiger Balm
Tiger Balm () is an analgesic heat rub manufactured and distributed by Singaporean company Haw Par Healthcare. It is used for external pain relief.
History
A precursor to Tiger Balm called Ban Kin Yu ( zh, t=萬金油, l=Ten Thousand Gol ...
, or IcyHot
Liniment (from la, linere, meaning "to anoint"), also called embrocation and heat rub, is a medicated topical preparation for application to the skin. Some liniments have viscosity similar to that of water; others are lotion or balm; still other ...
patches or knee/elbow sleeve
A sleeve ( ang, slīef, a word allied to ''slip'', cf. Dutch ) is the part of a garment that covers the arm, or through which the arm passes or slips.
The sleeve is a characteristic of fashion seen in almost every country and time period, acro ...
s.
* As a penetration enhancer in transdermal drug delivery.
* In decongestant
A decongestant, or nasal decongestant, is a type of pharmaceutical drug that is used to relieve nasal congestion in the upper respiratory tract. The active ingredient in most decongestants is either pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine (the latter ...
s for chest and sinuses (cream, patch or nose inhaler).
** Examples: Vicks VapoRub
Vicks VapoRub is a mentholated topical ointment, part of the Vicks brand of over-the-counter medications owned by the American consumer goods company Procter & Gamble.
VapoRub is intended for use on the chest, back and throat for cough suppres ...
, Mentholatum
The Mentholatum Company, Inc. is a maker of non-prescription health care products founded in 1889 by Albert Alexander Hyde in the United States. It was bought out by Rohto Pharmaceutical Co., a Japanese health care company, in 1988. The Ment ...
, Axe Brand, VapoRem, Mentisan.
* In certain medications used to treat sunburn
Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, usually from the Sun. Common symptoms in humans and animals include: red or reddish skin that is ho ...
s, as it provides a cooling sensation (then often associated with aloe
''Aloe'' (; also written ''Aloë'') is a genus containing over 650 species of flowering succulent plants.WFO (2022): Aloe L. Published on the Internet;http://www.worldfloraonline.org/taxon/wfo-4000001341. Accessed on: 06 Nov 2022 The most wid ...
).
* In aftershave products to relieve razor burn.
* As a smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is burned and the resulting smoke is typically breathed in to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, which have bee ...
tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
additive
Additive may refer to:
Mathematics
* Additive function, a function in number theory
* Additive map, a function that preserves the addition operation
* Additive set-functionn see Sigma additivity
* Additive category, a preadditive category with f ...
in some cigarette
A cigarette is a narrow cylinder containing a combustible material, typically tobacco, that is rolled into thin paper for smoking. The cigarette is ignited at one end, causing it to smolder; the resulting smoke is orally inhaled via the opp ...
brands, for flavor, and to reduce throat and sinus irritation caused by smoking. Menthol also increases nicotine receptor density, increasing the addictive potential of tobacco products.
* Commonly used in oral hygiene
Oral hygiene is the practice of keeping one's mouth clean and free of disease and other problems (e.g. bad breath) by regular brushing of the teeth (dental hygiene) and cleaning between the teeth. It is important that oral hygiene be carried out ...
products and bad-breath remedies, such as mouthwash
Mouthwash, mouth rinse, oral rinse, or mouth bath is a liquid which is held in the mouth passively or swilled around the mouth by contraction of the perioral muscles and/or movement of the head, and may be gargling, gargled, where the head is ti ...
, toothpaste
Toothpaste is a paste or gel dentifrice used with a toothbrush to clean and maintain the aesthetics and health of teeth. Toothpaste is used to promote oral hygiene: it is an abrasive that aids in removing dental plaque and food from the teeth, a ...
, mouth and tongue sprays, and more generally as a food flavor agent; such as in chewing gum
Chewing gum is a soft, cohesive substance designed to be chewed without being swallowed. Modern chewing gum is composed of gum base, sweeteners, softeners/ plasticizers, flavors, colors, and, typically, a hard or powdered polyol coating. Its t ...
and candy
Candy, also called sweets (British English) or lollies (Australian English
Australian English (AusE, AusEng, AuE, AuEng, en-AU) is the set of varieties of the English language native to Australia. It is the country's common language an ...
.
* As a pesticide against tracheal mites of honey bee
A honey bee (also spelled honeybee) is a eusocial flying insect within the genus ''Apis'' of the bee clade, all native to Afro-Eurasia. After bees spread naturally throughout Africa and Eurasia, humans became responsible for the current co ...
s.
* In perfumery
Perfume (, ; french: parfum) is a mixture of fragrant essential oils or aroma compounds (fragrances), fixatives and solvents, usually in liquid form, used to give the human body, animals, food, objects, and living-spaces an agreeable scent. Th ...
, menthol is used to prepare menthyl esters to emphasize floral notes (especially rose).
* In first aid products such as "mineral ice" to produce a cooling effect as a substitute for real ice in the absence of water or electricity (pouch, body patch/sleeve or cream).
* In various patches ranging from fever-reducing patches applied to children's foreheads to "foot patches" to relieve numerous ailments (the latter being much more frequent and elaborate in Asia, especially Japan: some varieties use "functional protrusions", or small bumps to massage one's feet as well as soothing them and cooling them down).
* In some beauty products such as hair conditioners, based on natural ingredients (e.g., St. Ives).
* As an antispasmodic
An antispasmodic (synonym: spasmolytic) is a pharmaceutical drug or other agent that suppresses muscle spasms.
Smooth muscle spasm
One type of antispasmodics is used for smooth muscle relaxation, especially in tubular organs of the gastrointesti ...
and smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit mus ...
relaxant in upper gastrointestinal endoscopy
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) or oesophagogastroduodenoscopy (OGD), also called by various other names, is a diagnostic endoscopic procedure that visualizes the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract down to the duodenum. It is considere ...
.
In organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; ...
, menthol is used as a chiral auxiliary
In stereochemistry, a chiral auxiliary is a stereogenic group or unit that is temporarily incorporated into an organic compound in order to control the stereochemical outcome of the synthesis. The chirality present in the auxiliary can bias the ...
in asymmetric synthesis. For example, sulfinate ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ar ...
s made from sulfinyl chlorides and menthol can be used to make enantiomerically pure sulfoxides by reaction with organolithium reagent
In organometallic chemistry, organolithium reagents are chemical compounds that contain carbon–lithium (C–Li) bonds. These reagents are important in organic synthesis, and are frequently used to transfer the organic group or the lithium atom ...
s or Grignard reagents
A Grignard reagent or Grignard compound is a chemical compound with the general formula , where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride and phenylmagnesium bromide . ...
. Menthol reacts with chiral carboxylic acids to give diastereomic menthyl esters, which are useful for chiral resolution
Chiral resolution, or enantiomeric resolution, is a process in stereochemistry for the separation of racemic compounds into their enantiomers. It is an important tool in the production of optically active compounds, including drugs. Another term wi ...
.
*It can be used as a catalyst for sodium production for the amateur chemist via the alcohol catalysed magnesium reduction process.
*menthol is potentially ergogenic
Performance-enhancing substances, also known as performance-enhancing drugs (PEDs), are substances that are used to improve any form of activity performance in humans. A well-known example of cheating in sports involves doping in sport, where ba ...
(performance enhancing) for athletic performance in hot environments
Reactions
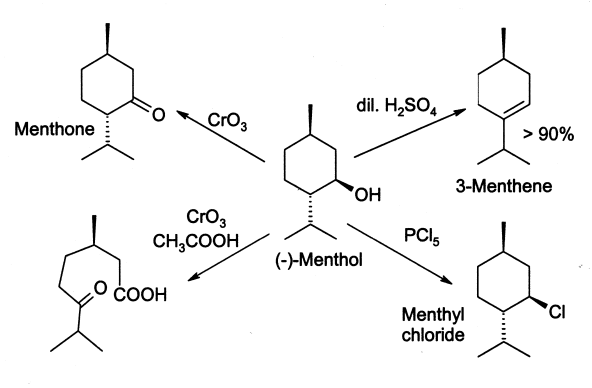
Menthol reacts in many ways like a normal secondary alcohol. It is oxidised tomenthone
Menthone is a monoterpene with a minty flavor that occurs naturally in a number of essential oils. ''l''-Menthone (or (2''S'',5''R'')-''trans''-2-isopropyl-5-methylcyclohexanone), shown at right, is the most abundant in nature of the four possible ...
by oxidising agents such as chromic acid
The term chromic acid is usually used for a mixture made by adding concentrated sulfuric acid to a dichromate, which may contain a variety of compounds, including solid chromium trioxide. This kind of chromic acid may be used as a cleaning mixtu ...
or dichromate, though under some conditions the oxidation can go further and break open the ring. Menthol is easily dehydrated to give mainly 3-menthene, by the action of 2% sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
. Phosphorus pentachloride
Phosphorus pentachloride is the chemical compound with the formula PCl5. It is one of the most important phosphorus chlorides, others being PCl3 and POCl3. PCl5 finds use as a chlorinating reagent. It is a colourless, water-sensitive and moist ...
(PCl5) gives menthyl chloride.
:
History
In theWest
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sunset, Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic languages, German ...
, menthol was first isolated in 1771, by the German, Hieronymus David Gaubius
Hieronymus David Gaubius (24 February 1705 – 29 November 1780) was a German physician and chemist.
Life
He was a native of Heidelberg. He studied medicine and sciences at the Universities of Harderwijk and Leiden, where he was a pupil of Herm ...
. Early characterizations were done by Oppenheim, Beckett, Moriya, and Atkinson. It was named by F. L. Alphons Oppenheim (1833–1877) in 1861.
Compendial status
* ''United States Pharmacopeia
The ''United States Pharmacopeia'' (''USP'') is a pharmacopeia (compendium of drug information) for the United States published annually by the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (usually also called the USP), a nonprofit organization that ...
'' 23
* Japanese Pharmacopoeia
The is the official pharmacopoeia of Japan. It is published by the . The first edition was published on 25 June 1886, with revisions being issued from time to time. The current revision is number 18, issued electronically on 7 June 2021. An offi ...
15
* Food Chemicals Codex The Food Chemicals Codex (FCC) is a collection of internationally recognized standards for the purity and identity of food ingredients.
Scope
The FCC features more than 1,250 monographs, including food-grade chemicals, processing aids, foods (suc ...
Safety
The estimatedlethal dose
In toxicology, the lethal dose (LD) is an indication of the lethal toxicity of a given substance or type of radiation. Because resistance varies from one individual to another, the "lethal dose" represents a dose (usually recorded as dose per kilog ...
for menthol (and peppermint oil Peppermint extract is an herbal extract of peppermint (''Mentha × piperita'') made from the essential oils of peppermint leaves. Peppermint is a hybrid of water mint and spearmint and was indigenous to Europe and the Middle East before it became c ...
) in humans may be as low as 50–500 mg/kg, (LD50 Acute: 3300 mg/kg at 3400 mg/kg ouse
Ouse may refer to:
Places Rivers in England
* River Ouse, Yorkshire
* River Ouse, Sussex
* River Great Ouse, Northamptonshire and East Anglia
** River Little Ouse, a tributary of the River Great Ouse
Other places
* Ouse, Tasmania, a town in Au ...
800 mg/kg at.
Survival after doses of 8 to 9 g has been reported. Overdose effects are abdominal pain, ataxia, atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, coma, dizziness, lethargy, nausea, skin rash, tremor, vomiting, and vertigo.
See also
*Aroma compound
An aroma compound, also known as an odorant, aroma, fragrance or flavoring, is a chemical compound that has a smell or odor. For an individual chemical or class of chemical compounds to impart a smell or fragrance, it must be sufficiently vo ...
* Carvone
Carvone is a member of a family of chemicals called terpenoids. Carvone is found naturally in many essential oils, but is most abundant in the oils from seeds of caraway (''Carum carvi''), spearmint (''Mentha spicata''), and dill.
Uses
Both c ...
* Chlorobutanol
Chlorobutanol (trichloro-2-methyl-2-propanol) is a preservative, sedative, hypnotic and weak local anesthetic similar in nature to chloral hydrate. It has antibacterial and antifungal properties. Chlorobutanol is typically used at a concentratio ...
* Ethyl benzoate
Ethyl benzoate, C9H10O2, is the ester formed by the condensation of benzoic acid and ethanol. It is a colorless liquid that is almost insoluble in water, but miscible with most organic solvents.
As with many volatile esters, ethyl benzoate has a ...
* Ethyl salicylate
* Menthoxypropanediol
* Methyl salicylate
Methyl salicylate (oil of wintergreen or wintergreen oil) is an organic compound with the formula C8H8O3. It is the methyl ester of salicylic acid. It is a colorless, viscous liquid with a sweet, fruity odor reminiscent of root beer, but often a ...
* Menthol cigarette
A menthol cigarette is a cigarette flavored with the compound menthol.
Menthol cigarettes have been banned in several countries, including Brazil, Canada, Ethiopia, Turkey, Moldova, the European Union, the United Kingdom and the US states o ...
s
* Menthyl isovalerate
* Menthyl nicotinate
* ''p''-Menthane-3,8-diol
* Thujone
Thujone () is a ketone and a monoterpene that occurs predominantly in two diastereomeric (epimeric) forms: (−)-α-thujone and (+)-β-thujone.
Though it is best known as a chemical compound in the spirit absinthe, it is unlikely to be responsib ...
* Vapor pressure
Vapor pressure (or vapour pressure in English-speaking countries other than the US; see spelling differences) or equilibrium vapor pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases ...
References
Further reading
* * * * *External links
*Ryoji Noyori Nobel lecture (2001)
A review of menthol
from the Science Creative Quarterly {{Authority control Analgesics Antipruritics Cooling flavors Kappa-opioid receptor agonists GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators Cyclohexanols Monoterpenes Isopropyl compounds