Needle Gun (other) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
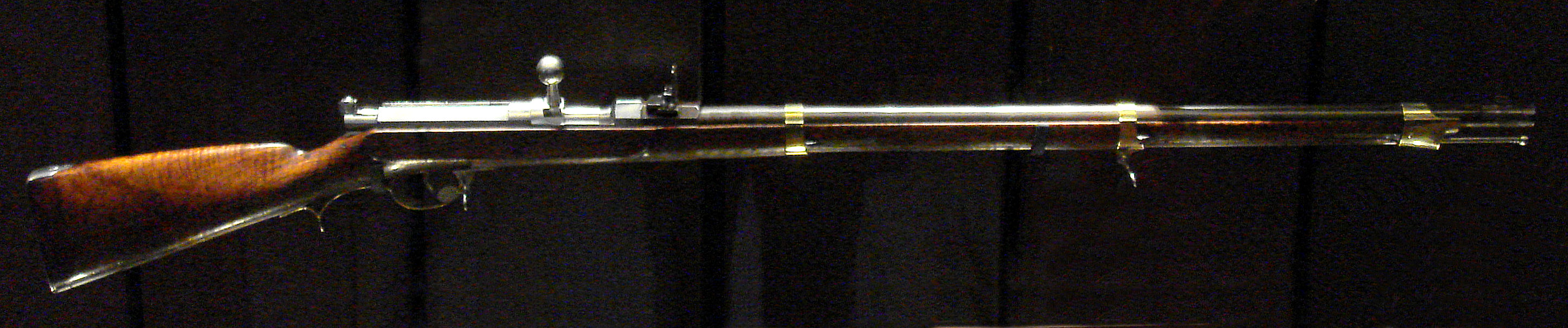 A needle gun (or needle rifle for varieties with
A needle gun (or needle rifle for varieties with
 The first mass-produced needle gun was invented by the German gunsmith Johann Nicolaus von Dreyse, who, beginning in 1824, had conducted multiple experiments, and in 1836 produced the first viable breech loading gun model using a complete cartridge.
The early Dreyse needle guns were smooth-bore. Later Dreyse guns adopted by the Prussian army were rifles using self-contained combustible cartridges holding oblong lead balls held in a papier-mâché "sabot".
From 1848 onwards the new weapon was gradually introduced into Prussian service. The Dreyse rifle became widely used during the
The first mass-produced needle gun was invented by the German gunsmith Johann Nicolaus von Dreyse, who, beginning in 1824, had conducted multiple experiments, and in 1836 produced the first viable breech loading gun model using a complete cartridge.
The early Dreyse needle guns were smooth-bore. Later Dreyse guns adopted by the Prussian army were rifles using self-contained combustible cartridges holding oblong lead balls held in a papier-mâché "sabot".
From 1848 onwards the new weapon was gradually introduced into Prussian service. The Dreyse rifle became widely used during the
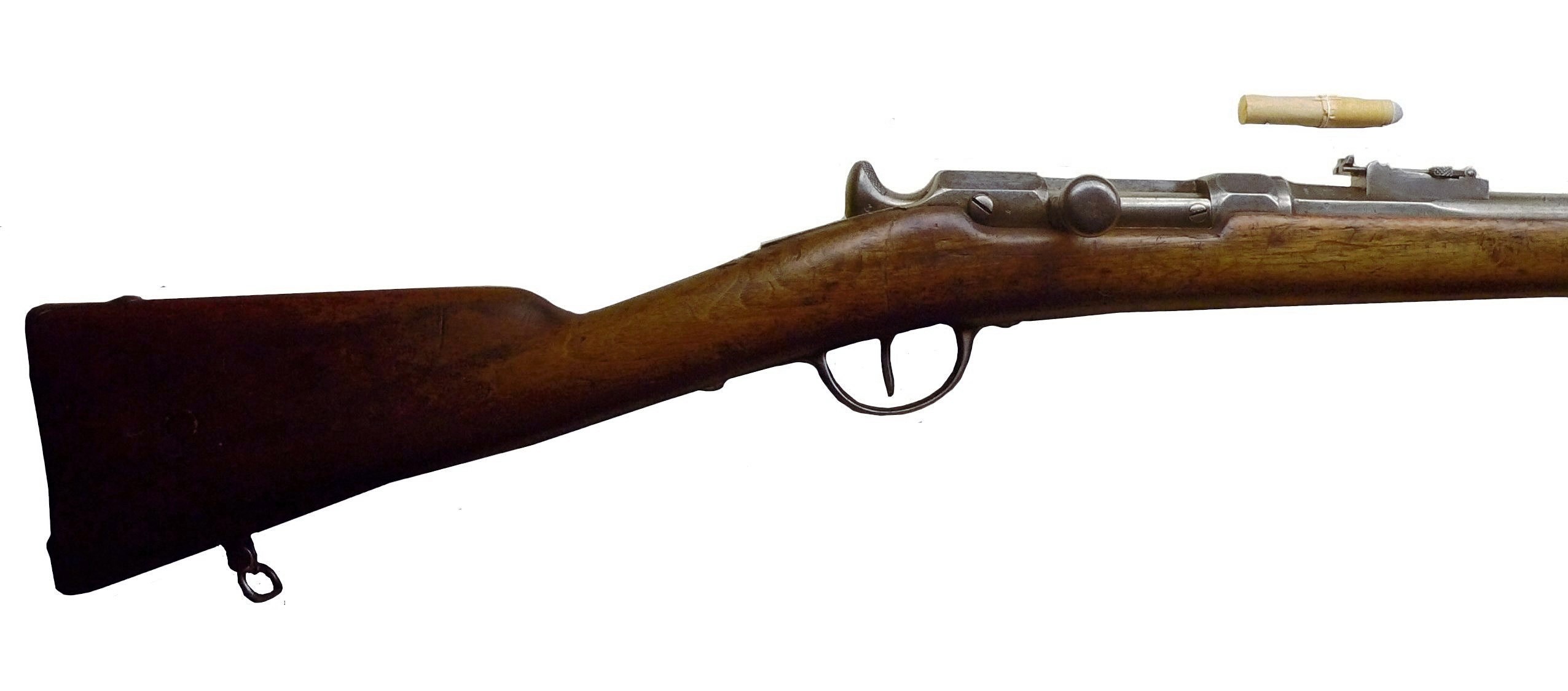

 The Chassepot was named after its inventor, Antoine Alphonse Chassepot (1833–1905), who, from 1857 onwards, had constructed various experimental forms of breechloader, and the rifle became the French service weapon in 1866. In the following year it made its first appearance on the battlefield at Mentana on 3 November 1867, where it inflicted severe losses upon
The Chassepot was named after its inventor, Antoine Alphonse Chassepot (1833–1905), who, from 1857 onwards, had constructed various experimental forms of breechloader, and the rifle became the French service weapon in 1866. In the following year it made its first appearance on the battlefield at Mentana on 3 November 1867, where it inflicted severe losses upon
 A needle gun (or needle rifle for varieties with
A needle gun (or needle rifle for varieties with rifling
In firearms, rifling is machining helical grooves into the internal (bore) surface of a gun's barrel for the purpose of exerting torque and thus imparting a spin to a projectile around its longitudinal axis during shooting to stabilize the pro ...
) is a firearm
A firearm is any type of gun designed to be readily carried and used by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see Legal definitions).
The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes ...
that has a needle-like firing pin, which can pass through the paper cartridge case to strike a percussion cap at the bullet
A bullet is a kinetic projectile, a component of firearm ammunition that is shot from a gun barrel. Bullets are made of a variety of materials, such as copper, lead, steel, polymer, rubber and even wax. Bullets are made in various shapes and co ...
base.
Types
Pauly
A diagram of a needle-gun cartridge, showing the paper cartridge case, the sabot, and acorn-shaped bullet. The first experimental needle gun was designed by Jean Samuel Pauly, a Swiss gunsmith. In Paris in 1808, in association with French gunsmith François Prélat, Pauly created the first fully self-contained cartridges: the cartridges incorporated a copper base with integrated mercury fulminate primer powder (the major innovation of Pauly), a round bullet and either brass or paper casing. The cartridge was loaded through the breech and fired with a needle. The needle-activated central-firebreech-loading
A breechloader is a firearm in which the user loads the ammunition (cartridge or shell) via the rear (breech) end of its barrel, as opposed to a muzzleloader, which loads ammunition via the front ( muzzle).
Modern firearms are generally breech ...
gun became a major feature of firearms thereafter. The corresponding firearm was also developed by Pauly. Pauly made an improved version which was protected by a patent on 29 September 1812. The cartridge was further improved by the French gunsmith Casimir Lefaucheux in 1836.
In 1809 Pauly employed the German Johann Nicolaus von Dreyse, who later invented the famous Dreyse rifle.
Dreyse
 The first mass-produced needle gun was invented by the German gunsmith Johann Nicolaus von Dreyse, who, beginning in 1824, had conducted multiple experiments, and in 1836 produced the first viable breech loading gun model using a complete cartridge.
The early Dreyse needle guns were smooth-bore. Later Dreyse guns adopted by the Prussian army were rifles using self-contained combustible cartridges holding oblong lead balls held in a papier-mâché "sabot".
From 1848 onwards the new weapon was gradually introduced into Prussian service. The Dreyse rifle became widely used during the
The first mass-produced needle gun was invented by the German gunsmith Johann Nicolaus von Dreyse, who, beginning in 1824, had conducted multiple experiments, and in 1836 produced the first viable breech loading gun model using a complete cartridge.
The early Dreyse needle guns were smooth-bore. Later Dreyse guns adopted by the Prussian army were rifles using self-contained combustible cartridges holding oblong lead balls held in a papier-mâché "sabot".
From 1848 onwards the new weapon was gradually introduced into Prussian service. The Dreyse rifle became widely used during the Austro-Prussian War
The Austro-Prussian War, also by many variant names such as Seven Weeks' War, German Civil War, Brothers War or Fraternal War, known in Germany as ("German War"), (; "German war of brothers") and by a variety of other names, was fought in 186 ...
of 1866 when it played a decisive role at the Battle of Königgrätz.
Doersch and von Baumgarten
This Model 1861 rifle was an improvement of the Dreyse rifle by Johannes Doersch and Cramer von Baumgarten. They shortened the needle mechanism and moved the handle to the rear of the bolt. The rifle was officially adopted in the Principality of Schaumburg-Lippe. More than one thousand rifles were produced until the principality was forced to join the German Empire in 1871.Carl
In 1865, Johannes Friedrich Christian Carl (also known as Carlé or Karl), a ship- and insurance broker of Hamburg, patented a needle gun which was an improvement on the Dreyse gun. Sohs (Zons), a Hamburg citizen, participated in the design and development of it. The Carl system was officially adopted by the Russian Empire in 1867. Only 215,500 Carl rifles were manufactured in Russia, because a short time later, needle rifles were replaced by rifles with metal cartridges, such as the Berdan rifle.Chassepot

 The Chassepot was named after its inventor, Antoine Alphonse Chassepot (1833–1905), who, from 1857 onwards, had constructed various experimental forms of breechloader, and the rifle became the French service weapon in 1866. In the following year it made its first appearance on the battlefield at Mentana on 3 November 1867, where it inflicted severe losses upon
The Chassepot was named after its inventor, Antoine Alphonse Chassepot (1833–1905), who, from 1857 onwards, had constructed various experimental forms of breechloader, and the rifle became the French service weapon in 1866. In the following year it made its first appearance on the battlefield at Mentana on 3 November 1867, where it inflicted severe losses upon Giuseppe Garibaldi
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi ( , ;In his native Ligurian language, he is known as ''Gioxeppe Gaibado''. In his particular Niçard dialect of Ligurian, he was known as ''Jousé'' or ''Josep''. 4 July 1807 – 2 June 1882) was an Italian general, patr ...
's troops. It was reported at the French Parliament that "", or loosely translated: "The Chassepots have done wonderfully!" The undisguised truth is that the heavy cylindrical lead bullets fired at high velocity by the Chassepot rifle inflicted wounds that were even worse than those of the earlier Minié rifle.
In the Franco-Prussian War (1870–71) it proved greatly superior to the German Dreyse needle gun, outranging it by 2 to 1.
The Chassepot used a paper cartridge, that many refer to as being 'combustible', whereas in reality it was quite the opposite. It held an round-headed cylindro-conoidal lead bullet that was wax paper patched. An inverted standard percussion cap was at the rear of the paper cartridge and hidden inside. It was fired by the Chassepot's needle (a sharply pointed firing pin) upon pressing the trigger.
Carcano
The Carcano Fucile di Fanteria Modello 1860/67 needle gun was developed by Salvatore Carcano, an Italian technician. This rifle was operated by pulling a cocking knob on the back of the action, retracting the needle and allowing the bolt handle to be lifted. It was adopted in 1867 in Italy. The Carcano Modello 1868 needle fire rifle had very few differences from the 1860/1867 model.References
Further reading
* John Walter. The German Rifle pages 20–46 Arms & Armour Press/London 1979External links
* {{Cite EB1911, wstitle=Needle-Gun, volume=19, page=339 Early rifles