Nazi Soldiers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified
 In January 1919, after
In January 1919, after
 Recruitment for the ''Wehrmacht'' was accomplished through voluntary enlistment and conscription, with 1.3 million being drafted and 2.4 million volunteering in the period 1935–1939. The total number of soldiers who served in the ''Wehrmacht'' during its existence from 1935 to 1945 is believed to have approached 18.2 million. The German military leadership originally aimed at a homogeneous military, possessing traditional Prussian military values. However, with Hitler's constant wishes to increase the ''Wehrmacht''s size, the Army was forced to accept citizens of lower class and education, decreasing internal cohesion and appointing officers who lacked real-war experience from previous conflicts, especially
Recruitment for the ''Wehrmacht'' was accomplished through voluntary enlistment and conscription, with 1.3 million being drafted and 2.4 million volunteering in the period 1935–1939. The total number of soldiers who served in the ''Wehrmacht'' during its existence from 1935 to 1945 is believed to have approached 18.2 million. The German military leadership originally aimed at a homogeneous military, possessing traditional Prussian military values. However, with Hitler's constant wishes to increase the ''Wehrmacht''s size, the Army was forced to accept citizens of lower class and education, decreasing internal cohesion and appointing officers who lacked real-war experience from previous conflicts, especially  As the Second World War intensified, ''
As the Second World War intensified, ''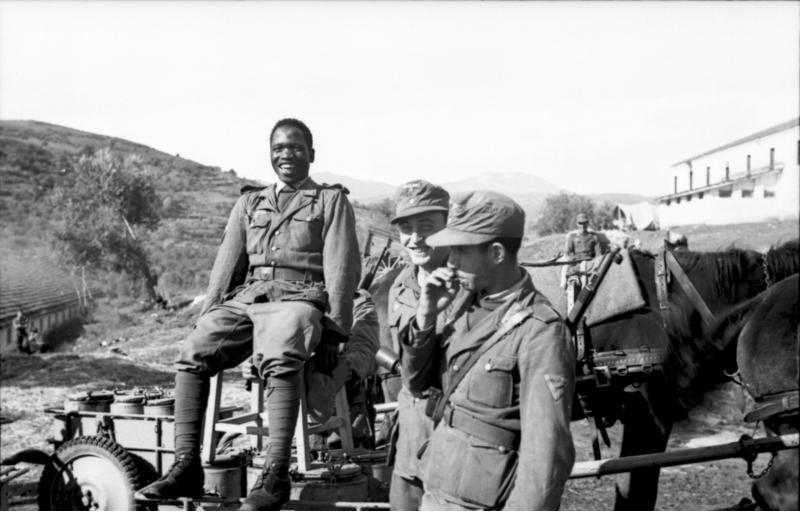 Prior to World War II, the ''Wehrmacht'' strove to remain a purely ethnic German force; as such, minorities within and outside of Germany, such as the Czechs in annexed
Prior to World War II, the ''Wehrmacht'' strove to remain a purely ethnic German force; as such, minorities within and outside of Germany, such as the Czechs in annexed
 In the beginning, women in Nazi Germany were not involved in the ''Wehrmacht'', as Hitler ideologically opposed conscription for women, stating that Germany would "''not form any section of women grenade throwers or any corps of women elite snipers.''" However, with many men going to the front, women were placed in auxiliary positions within the ''Wehrmacht'', called ''Wehrmachtshelferinnen'' (), participating in tasks as:
* telephone, telegraph and transmission operators,
* administrative clerks, typists and messengers,
* operators of listening equipment, in anti-aircraft defense, operating projectors for anti-aircraft defense, employees within
In the beginning, women in Nazi Germany were not involved in the ''Wehrmacht'', as Hitler ideologically opposed conscription for women, stating that Germany would "''not form any section of women grenade throwers or any corps of women elite snipers.''" However, with many men going to the front, women were placed in auxiliary positions within the ''Wehrmacht'', called ''Wehrmachtshelferinnen'' (), participating in tasks as:
* telephone, telegraph and transmission operators,
* administrative clerks, typists and messengers,
* operators of listening equipment, in anti-aircraft defense, operating projectors for anti-aircraft defense, employees within

 Legally, the commander-in-chief of the ''Wehrmacht'' was Adolf Hitler in his capacity as Germany's head of state, a position he gained after the death of President
Legally, the commander-in-chief of the ''Wehrmacht'' was Adolf Hitler in his capacity as Germany's head of state, a position he gained after the death of President
 The German Army furthered concepts pioneered during
The German Army furthered concepts pioneered during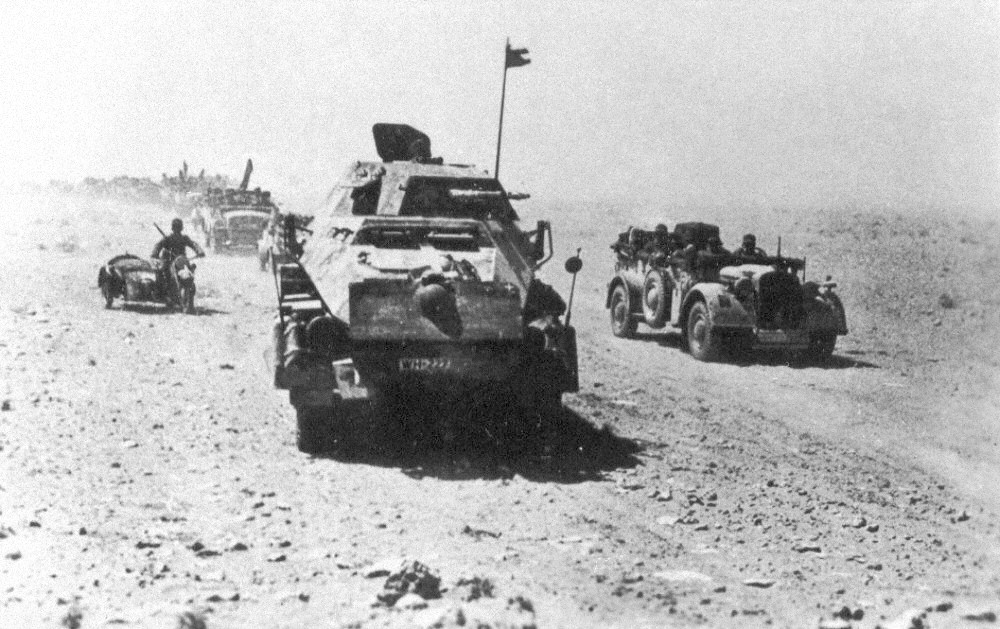  The German Army was managed through Mission-type tactics, mission-based tactics (rather than order-based tactics) which was intended to give commanders greater freedom to act on events and exploit opportunities. In public opinion, the German Army was, and sometimes still is, seen as a high-tech army. However, such modern equipment, while featured much in propaganda, was often only available in relatively small numbers. Only 40% to 60% of all units in the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front were motorized, baggage trains often relied on horse-drawn trailers due to poor roads and weather conditions in the Soviet Union, and for the same reasons many soldiers marched on foot or used bicycles as bicycle infantry. As the fortunes of war turned against them, the Germans were in constant retreat from 1943 and onward.
The Panzer divisions were vital to the German army's early success. In the strategies of the ''Blitzkrieg'', the ''Wehrmacht'' combined the mobility of light tanks with airborne assault to quickly progress through weak enemy lines, enabling the German army to quickly and brutally take over Poland and France. These tanks were used to break through enemy lines, isolating regiments from the main force so that the infantry behind the tanks could quickly kill or capture the enemy troops.
The German Army was managed through Mission-type tactics, mission-based tactics (rather than order-based tactics) which was intended to give commanders greater freedom to act on events and exploit opportunities. In public opinion, the German Army was, and sometimes still is, seen as a high-tech army. However, such modern equipment, while featured much in propaganda, was often only available in relatively small numbers. Only 40% to 60% of all units in the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front were motorized, baggage trains often relied on horse-drawn trailers due to poor roads and weather conditions in the Soviet Union, and for the same reasons many soldiers marched on foot or used bicycles as bicycle infantry. As the fortunes of war turned against them, the Germans were in constant retreat from 1943 and onward.
The Panzer divisions were vital to the German army's early success. In the strategies of the ''Blitzkrieg'', the ''Wehrmacht'' combined the mobility of light tanks with airborne assault to quickly progress through weak enemy lines, enabling the German army to quickly and brutally take over Poland and France. These tanks were used to break through enemy lines, isolating regiments from the main force so that the infantry behind the tanks could quickly kill or capture the enemy troops.
 Originally outlawed by the Treaty of Versailles, the ''
Originally outlawed by the Treaty of Versailles, the ''
 The Treaty of Versailles disallowed submarines, while limiting the size of the ''Reichsmarine'' to six battleships, six cruisers, and twelve destroyers. Following the creation of the ''Wehrmacht'', the navy was renamed the ''Kriegsmarine''.
With the signing of the Anglo-German Naval Agreement, Germany was allowed to increase its navy's size to be 35:100 tonnage of the Royal Navy, and allowed for the construction of U-boats. This was partly done to appease Germany, and because Britain believed the ''Kriegsmarine'' would not be able to reach the 35% limit until 1942. The navy was also prioritized last in the German rearmament scheme, making it the smallest of the branches.
In the Battle of the Atlantic, the initially successful German U-boat fleet arm was eventually defeated due to Allied technological innovations like sonar, radar, and the breaking of the Enigma machine, Enigma code.
Large surface vessels were few in number due to construction limitations by international treaties prior to 1935. The "pocket battleships" and were important as commerce raiders only in the opening year of the war. No aircraft carrier was operational, as German leadership lost interest in the which had been launched in 1938.
Following the loss of the in 1941, with Allied air-superiority threatening the remaining battle-cruisers in French Atlantic harbors, the ships were ordered to make the Channel Dash back to German ports. Operating from fjords along the coast of Norway, which had been occupied since 1940, Arctic convoys of World War II, convoys from North America to the Soviet port of Murmansk could be intercepted though the spent most of her career as fleet in being. After the appointment of Karl Dönitz as Grand Admiral of the ''Kriegsmarine'' (in the aftermath of the Battle of the Barents Sea), Germany stopped constructing battleships and cruisers in favor of U-boats. Though by 1941, the navy had already lost a number of its large surface ships, which could not be replenished during the war.
The ''Kriegsmarine''s most significant contribution to the German war effort was the deployment of its nearly 1,000 U-boats to strike at Allied convoys. The German naval strategy was to attack the convoys in an attempt to prevent the United States from interfering in Europe and to starve out the British. Karl Doenitz, the U-Boat Chief, began unrestricted submarine warfare which cost the Allies 22,898 men and 1,315 ships. The U-boat war remained costly for the Allies until early spring of 1943 when the Allies began to use countermeasures against U-Boats such as the use of Hunter-Killer groups, airborne radar, torpedoes and mines like the Mark 24 mine, FIDO. The submarine war cost the ''Kriegsmarine'' 757 U-boats, with more than 30,000 U-boat crewmen killed.
The Treaty of Versailles disallowed submarines, while limiting the size of the ''Reichsmarine'' to six battleships, six cruisers, and twelve destroyers. Following the creation of the ''Wehrmacht'', the navy was renamed the ''Kriegsmarine''.
With the signing of the Anglo-German Naval Agreement, Germany was allowed to increase its navy's size to be 35:100 tonnage of the Royal Navy, and allowed for the construction of U-boats. This was partly done to appease Germany, and because Britain believed the ''Kriegsmarine'' would not be able to reach the 35% limit until 1942. The navy was also prioritized last in the German rearmament scheme, making it the smallest of the branches.
In the Battle of the Atlantic, the initially successful German U-boat fleet arm was eventually defeated due to Allied technological innovations like sonar, radar, and the breaking of the Enigma machine, Enigma code.
Large surface vessels were few in number due to construction limitations by international treaties prior to 1935. The "pocket battleships" and were important as commerce raiders only in the opening year of the war. No aircraft carrier was operational, as German leadership lost interest in the which had been launched in 1938.
Following the loss of the in 1941, with Allied air-superiority threatening the remaining battle-cruisers in French Atlantic harbors, the ships were ordered to make the Channel Dash back to German ports. Operating from fjords along the coast of Norway, which had been occupied since 1940, Arctic convoys of World War II, convoys from North America to the Soviet port of Murmansk could be intercepted though the spent most of her career as fleet in being. After the appointment of Karl Dönitz as Grand Admiral of the ''Kriegsmarine'' (in the aftermath of the Battle of the Barents Sea), Germany stopped constructing battleships and cruisers in favor of U-boats. Though by 1941, the navy had already lost a number of its large surface ships, which could not be replenished during the war.
The ''Kriegsmarine''s most significant contribution to the German war effort was the deployment of its nearly 1,000 U-boats to strike at Allied convoys. The German naval strategy was to attack the convoys in an attempt to prevent the United States from interfering in Europe and to starve out the British. Karl Doenitz, the U-Boat Chief, began unrestricted submarine warfare which cost the Allies 22,898 men and 1,315 ships. The U-boat war remained costly for the Allies until early spring of 1943 when the Allies began to use countermeasures against U-Boats such as the use of Hunter-Killer groups, airborne radar, torpedoes and mines like the Mark 24 mine, FIDO. The submarine war cost the ''Kriegsmarine'' 757 U-boats, with more than 30,000 U-boat crewmen killed.
 In the beginning, there was friction between the ''SS'' and the army, as the army feared the ''SS'' would attempt to become a legitimate part of the armed forces of Nazi Germany, partly due to the fighting between the limited armaments, and the perceived fanaticism towards Nazism. However, on 17 August 1938, Hitler codified the role of the ''SS'' and the army in order to end the feud between the two. The arming of the ''SS'' was to be "procured from the ''Wehrmacht'' upon payment", however "in peacetime, no organizational connection with the ''Wehrmacht'' exists." The army was however allowed to check the budget of the ''SS'' and inspect the combat readiness of the ''SS'' troops. In the event of mobilization, the ''Waffen-SS'' field units could be placed under the operational control of the OKW or the OKH. All decisions regarding this would be at Hitler's personal discretion.
Though there existed conflict between the ''SS'' and ''Wehrmacht'', many ''SS'' officers were former army officers, which ensured continuity and understanding between the two. Throughout the war, army and ''SS'' soldiers worked together in various combat situations, creating bonds between the two groups. Heinz Guderian, Guderian noted that every day the war continued the Army and the ''SS'' became closer together. Towards the end of the war, army units would even be placed under the command of the ''SS'', in Italy and the Netherlands. The relationship between the ''Wehrmacht'' and the ''SS'' improved; however, the ''Waffen-SS'' was never considered "the fourth branch of the ''Wehrmacht''.”
In the beginning, there was friction between the ''SS'' and the army, as the army feared the ''SS'' would attempt to become a legitimate part of the armed forces of Nazi Germany, partly due to the fighting between the limited armaments, and the perceived fanaticism towards Nazism. However, on 17 August 1938, Hitler codified the role of the ''SS'' and the army in order to end the feud between the two. The arming of the ''SS'' was to be "procured from the ''Wehrmacht'' upon payment", however "in peacetime, no organizational connection with the ''Wehrmacht'' exists." The army was however allowed to check the budget of the ''SS'' and inspect the combat readiness of the ''SS'' troops. In the event of mobilization, the ''Waffen-SS'' field units could be placed under the operational control of the OKW or the OKH. All decisions regarding this would be at Hitler's personal discretion.
Though there existed conflict between the ''SS'' and ''Wehrmacht'', many ''SS'' officers were former army officers, which ensured continuity and understanding between the two. Throughout the war, army and ''SS'' soldiers worked together in various combat situations, creating bonds between the two groups. Heinz Guderian, Guderian noted that every day the war continued the Army and the ''SS'' became closer together. Towards the end of the war, army units would even be placed under the command of the ''SS'', in Italy and the Netherlands. The relationship between the ''Wehrmacht'' and the ''SS'' improved; however, the ''Waffen-SS'' was never considered "the fourth branch of the ''Wehrmacht''.”
 Major campaigns and battles in Eastern and Central Europe included:
* Occupation of Czechoslovakia by Nazi Germany, Czechoslovakian campaign (1938–1945)
*Invasion of Poland (1939), Invasion of Poland (''Fall Weiss'')
*
Major campaigns and battles in Eastern and Central Europe included:
* Occupation of Czechoslovakia by Nazi Germany, Czechoslovakian campaign (1938–1945)
*Invasion of Poland (1939), Invasion of Poland (''Fall Weiss'')
*
 * Phoney War (''Sitzkrieg'', September 1939 to May 1940) between the invasion of Poland and the Battle of France
* Operation Weserübung
** German invasion of Denmark (1940), German invasion of Denmark – 9 April 1940
** The Norwegian Campaign – 9 April to 10 June 1940
* ''Fall Gelb''
**Battle of Belgium 10 to 28 May 1940
**German invasion of Luxembourg 10 May 1940
**Battle of the Netherlands – 10 to 17 May 1940
**Battle of France – 10 May to 25 June 1940
* Battle of Britain (1940)
* Battle of the Atlantic (1939–1945)
* Operation Overlord, Battle of Normandy (1944)
* Operation Dragoon, Allied invasion of southern France (1944)
* Ardennes Offensive (1944–1945)
* Defense of the Reich air-campaign, 1939 to 1945
* Phoney War (''Sitzkrieg'', September 1939 to May 1940) between the invasion of Poland and the Battle of France
* Operation Weserübung
** German invasion of Denmark (1940), German invasion of Denmark – 9 April 1940
** The Norwegian Campaign – 9 April to 10 June 1940
* ''Fall Gelb''
**Battle of Belgium 10 to 28 May 1940
**German invasion of Luxembourg 10 May 1940
**Battle of the Netherlands – 10 to 17 May 1940
**Battle of France – 10 May to 25 June 1940
* Battle of Britain (1940)
* Battle of the Atlantic (1939–1945)
* Operation Overlord, Battle of Normandy (1944)
* Operation Dragoon, Allied invasion of southern France (1944)
* Ardennes Offensive (1944–1945)
* Defense of the Reich air-campaign, 1939 to 1945
 For a time, the Battle of the Mediterranean, Axis Mediterranean Theatre and the North African Campaign were conducted as a Military campaign, joint campaign with the Regio Esercito, Italian Army, and may be considered a separate Theater (warfare), theatre.
* Balkans Campaign (World War II), Invasion of the Balkans and Greece (Operation Marita) (1940–1941)
* Battle of Crete (1941)
* The North African Campaign in Libya, Tunisia and Egypt between the UK and Commonwealth (and later, U.S.) forces and the Axis forces
* The Italian Campaign (World War II), Italian Theatre was a continuation of the Axis defeat in North Africa, and was a campaign for defence of Italy
For a time, the Battle of the Mediterranean, Axis Mediterranean Theatre and the North African Campaign were conducted as a Military campaign, joint campaign with the Regio Esercito, Italian Army, and may be considered a separate Theater (warfare), theatre.
* Balkans Campaign (World War II), Invasion of the Balkans and Greece (Operation Marita) (1940–1941)
* Battle of Crete (1941)
* The North African Campaign in Libya, Tunisia and Egypt between the UK and Commonwealth (and later, U.S.) forces and the Axis forces
* The Italian Campaign (World War II), Italian Theatre was a continuation of the Axis defeat in North Africa, and was a campaign for defence of Italy
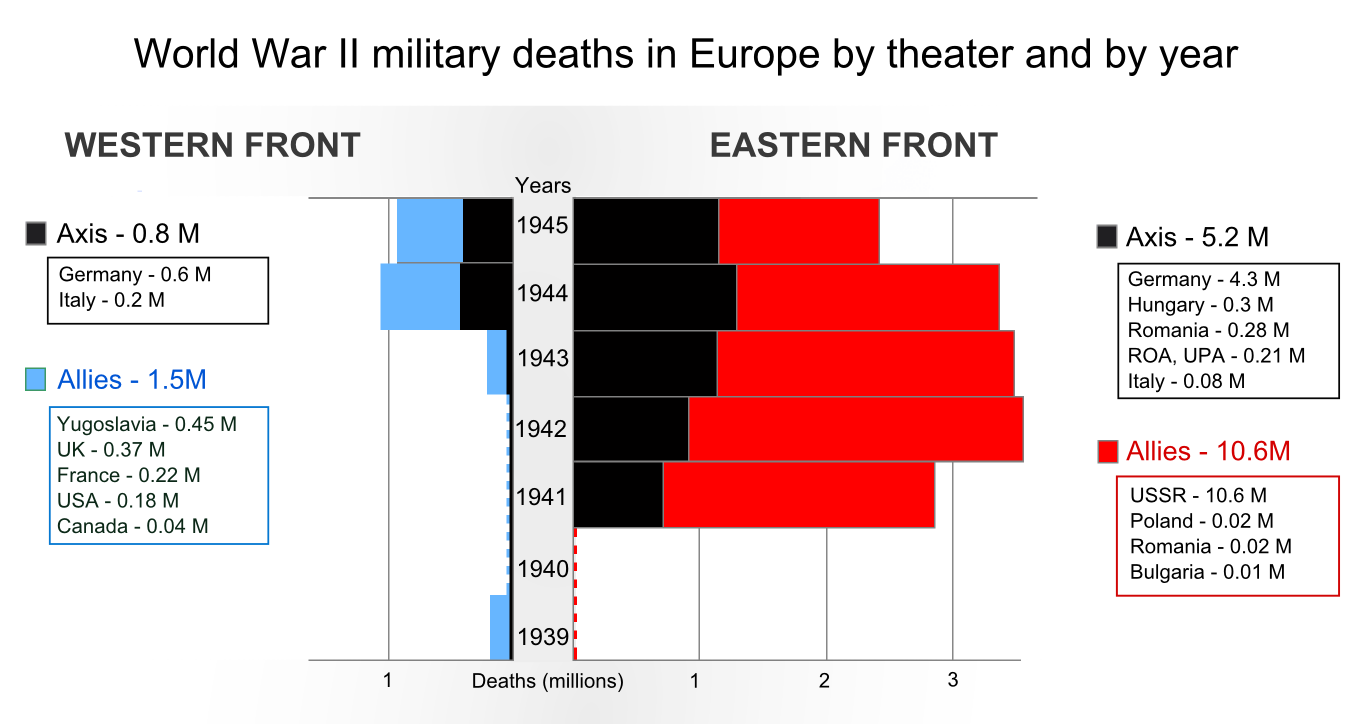
 More than 6,000,000 soldiers were wounded during the conflict, while more than 11,000,000 became prisoners. In all, approximately 5,318,000 soldiers from Germany and other nationalities fighting for the German armed forces—including the ''Waffen-SS'', ''Volkssturm'' and foreign collaborationist units—are estimated to have been killed in action, died of wounds, died in custody or gone missing in World War II. Included in this number are 215,000 Soviet citizens conscripted by Germany.
According to Frank Biess,
Jeffrey Herf wrote that:
In addition to the losses, at the hands of the elements and enemy fighting, at least 20,000 soldiers were executed as sentences by the military court. In comparison, the Red Army executed 135,000, France 102, the US 146 and the UK 40.
More than 6,000,000 soldiers were wounded during the conflict, while more than 11,000,000 became prisoners. In all, approximately 5,318,000 soldiers from Germany and other nationalities fighting for the German armed forces—including the ''Waffen-SS'', ''Volkssturm'' and foreign collaborationist units—are estimated to have been killed in action, died of wounds, died in custody or gone missing in World War II. Included in this number are 215,000 Soviet citizens conscripted by Germany.
According to Frank Biess,
Jeffrey Herf wrote that:
In addition to the losses, at the hands of the elements and enemy fighting, at least 20,000 soldiers were executed as sentences by the military court. In comparison, the Red Army executed 135,000, France 102, the US 146 and the UK 40.

 During the war, the ''Wehrmacht'' committed numerous war crimes against the civilian population in occupied countries. This includes massacres of civilians and running forced brothels in occupied areas.
Massacres would in many cases come as reprisals for acts of resistance. With these reprisals, the ''Wehrmacht''s response would vary in severity and method, depending on the scale of resistance and whether it was in East or West Europe. Often, the number of hostages to be shot was calculated based on a ratio of 100 hostages executed for every German soldier killed and 50 hostages executed for every German soldier wounded. Other times civilians would be rounded up and shot with machine guns.
To combat German officials' fear of Sexually transmitted disease, venereal disease and masturbation, the ''Wehrmacht'' established numerous brothels throughout Nazi Germany and its occupied territories. Women would often be kidnapped off the streets and forced to work in the brothels, with an estimated minimum of 34,140 women being forced to serve as prostitutes.
During the war, the ''Wehrmacht'' committed numerous war crimes against the civilian population in occupied countries. This includes massacres of civilians and running forced brothels in occupied areas.
Massacres would in many cases come as reprisals for acts of resistance. With these reprisals, the ''Wehrmacht''s response would vary in severity and method, depending on the scale of resistance and whether it was in East or West Europe. Often, the number of hostages to be shot was calculated based on a ratio of 100 hostages executed for every German soldier killed and 50 hostages executed for every German soldier wounded. Other times civilians would be rounded up and shot with machine guns.
To combat German officials' fear of Sexually transmitted disease, venereal disease and masturbation, the ''Wehrmacht'' established numerous brothels throughout Nazi Germany and its occupied territories. Women would often be kidnapped off the streets and forced to work in the brothels, with an estimated minimum of 34,140 women being forced to serve as prostitutes.
 While the ''Wehrmacht''s prisoner-of-war camps for inmates from the west generally satisfied the humanitarian requirement prescribed by international law, prisoners from Poland and the USSR were incarcerated under significantly worse conditions. Between the launching of Operation Barbarossa in the summer of 1941 and the following spring, 2.8 million of the 3.2 million Nazi crimes against Soviet POWs, Soviet prisoners taken died while in German hands.
While the ''Wehrmacht''s prisoner-of-war camps for inmates from the west generally satisfied the humanitarian requirement prescribed by international law, prisoners from Poland and the USSR were incarcerated under significantly worse conditions. Between the launching of Operation Barbarossa in the summer of 1941 and the following spring, 2.8 million of the 3.2 million Nazi crimes against Soviet POWs, Soviet prisoners taken died while in German hands.
 Originally, there was little German resistance to Nazism, resistance within the ''Wehrmacht'', as Hitler actively went against the Treaty of Versailles and attempted to recover the army's honor. The first major resistance began in 1938 with the Oster conspiracy, where several members of the military wanted to remove Hitler from power, as they feared a war with
Originally, there was little German resistance to Nazism, resistance within the ''Wehrmacht'', as Hitler actively went against the Treaty of Versailles and attempted to recover the army's honor. The first major resistance began in 1938 with the Oster conspiracy, where several members of the military wanted to remove Hitler from power, as they feared a war with
 Following the German Instrument of Surrender, unconditional surrender of the ''Wehrmacht'', which went into effect on 8 May 1945, some ''Wehrmacht'' units remained active, either independently (e.g. in Norway), or under Allied command as police forces. The last ''Wehrmacht'' unit to come under Allied control was an isolated weather station in Svalbard, which formally surrendered to a Norwegian relief ship on 4 September.
On 20 September 1945, with Proclamation No. 2 of the Allied Control Council (ACC), "[a]ll German land, naval and air forces, the S.S., S.A., S.D. and Gestapo, with all their organizations, staffs and institution, including the General Staff, the Officers' corps, the Reserve Corps, military schools, war veterans' organizations, and all other military and quasi-military organizations, together with all clubs and associations which serve to keep alive the military tradition in Germany, shall be completely and finally abolished in accordance with the methods and procedures to be laid down by the Allied Representatives." The ''Wehrmacht'' was officially dissolved by the ACC Law 34 on 20 August 1946, which proclaimed the OKW, OKH, the Ministry of Aviation (Nazi Germany), Ministry of Aviation and the OKM to be "disbanded, completely liquidated and declared illegal".
Following the German Instrument of Surrender, unconditional surrender of the ''Wehrmacht'', which went into effect on 8 May 1945, some ''Wehrmacht'' units remained active, either independently (e.g. in Norway), or under Allied command as police forces. The last ''Wehrmacht'' unit to come under Allied control was an isolated weather station in Svalbard, which formally surrendered to a Norwegian relief ship on 4 September.
On 20 September 1945, with Proclamation No. 2 of the Allied Control Council (ACC), "[a]ll German land, naval and air forces, the S.S., S.A., S.D. and Gestapo, with all their organizations, staffs and institution, including the General Staff, the Officers' corps, the Reserve Corps, military schools, war veterans' organizations, and all other military and quasi-military organizations, together with all clubs and associations which serve to keep alive the military tradition in Germany, shall be completely and finally abolished in accordance with the methods and procedures to be laid down by the Allied Representatives." The ''Wehrmacht'' was officially dissolved by the ACC Law 34 on 20 August 1946, which proclaimed the OKW, OKH, the Ministry of Aviation (Nazi Germany), Ministry of Aviation and the OKM to be "disbanded, completely liquidated and declared illegal".
 Following the division of Germany, many former ''Wehrmacht'' and ''SS'' officers in West Germany feared a Soviet invasion of the country. To combat this, several prominent officers created a Schnez-Truppe, secret army, unknown to the general public and without mandate from the Allied Control Authority or the West German government.
By the mid-1950s, tensions of the Cold War led to the creation of separate military forces in the West Germany, Federal Republic of Germany and the socialist German Democratic Republic. The West German military, officially created on 5 May 1955, took the name ''Bundeswehr'' (). Its East German counterpart—created on 1 March 1956—took the name National People's Army (german: Nationale Volksarmee). Both organizations employed many former ''Wehrmacht'' members, particularly in their formative years, though neither organization considered themselves successors to the ''Wehrmacht''. However, according to historian Hannes Heer "Germans still have a hard time, when it comes to openly dealing with their Nazi past", as such of the 50 military bases named after ''Wehrmacht'' soldiers, only 16 bases have changed names.
''Wehrmacht'' veterans in West Germany have received pensions through the ''War Victims' Assistance Act'' (german: Bundesversorgungsgesetz) from the government. According to ''The Times of Israel'', "The benefits come through the Federal Pension Act, which was passed in 1950 to support war victims, whether civilians or veterans of the ''Wehrmacht'' or ''Waffen-SS''."
Following the division of Germany, many former ''Wehrmacht'' and ''SS'' officers in West Germany feared a Soviet invasion of the country. To combat this, several prominent officers created a Schnez-Truppe, secret army, unknown to the general public and without mandate from the Allied Control Authority or the West German government.
By the mid-1950s, tensions of the Cold War led to the creation of separate military forces in the West Germany, Federal Republic of Germany and the socialist German Democratic Republic. The West German military, officially created on 5 May 1955, took the name ''Bundeswehr'' (). Its East German counterpart—created on 1 March 1956—took the name National People's Army (german: Nationale Volksarmee). Both organizations employed many former ''Wehrmacht'' members, particularly in their formative years, though neither organization considered themselves successors to the ''Wehrmacht''. However, according to historian Hannes Heer "Germans still have a hard time, when it comes to openly dealing with their Nazi past", as such of the 50 military bases named after ''Wehrmacht'' soldiers, only 16 bases have changed names.
''Wehrmacht'' veterans in West Germany have received pensions through the ''War Victims' Assistance Act'' (german: Bundesversorgungsgesetz) from the government. According to ''The Times of Israel'', "The benefits come through the Federal Pension Act, which was passed in 1950 to support war victims, whether civilians or veterans of the ''Wehrmacht'' or ''Waffen-SS''."
''The Wehrmacht: A Criminal Organization?''
Review of Hannes Heer and Klaus Naumann's 1995 work ''Vernichtungskrieg – Verbrechen der Wehrmacht 1941–1944'' by Jörg Bottger
''Wehrmacht Propaganda Troops and the Jews''
– an article by Daniel Uziel
The Nazi German Army 1935–1945
"A Blind Eye and Dirty Hands: The Wehrmacht's Crimes"
– lecture by the historian Geoffrey P. Megargee, via the YouTube channel of the Wiener Library for the Study of the Holocaust and Genocide {{Authority control Wehrmacht, Disbanded armed forces 1935 establishments in Germany 1946 disestablishments in Germany Military of Nazi Germany Military units and formations established in 1935 Military units and formations disestablished in 1946
armed forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine
The (, ) was the navy of Germany from 1935 to 1945. It superseded the Imperial German Navy of the German Empire (1871–1918) and the inter-war (1919–1935) of the Weimar Republic. The was one of three official branches, along with the a ...
'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabtei ...
'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previously used term and was the manifestation of the Nazi regime's efforts to rearm Germany to a greater extent than the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June ...
permitted.
After the Nazi rise to power
Adolf Hitler's rise to power began in the newly established Weimar Republic in September 1919 when Hitler joined the '' Deutsche Arbeiterpartei'' (DAP; German Workers' Party). He rose to a place of prominence in the early years of the party. Be ...
in 1933, one of Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
's most overt and audacious moves was to establish the ''Wehrmacht'', a modern offensively-capable armed force, fulfilling the Nazi régime's long-term goals of regaining lost territory as well as gaining new territory and dominating its neighbours. This required the reinstatement of conscription and massive investment and defense spending
A military budget (or military expenditure), also known as a defense budget, is the amount of financial resources dedicated by a state to raising and maintaining an armed forces or other methods essential for defense purposes.
Financing militar ...
on the arms industry
The arms industry, also known as the arms trade, is a global industry which manufactures and sells weapons and military technology. It consists of a commercial industry involved in the research and development, engineering, production, and servi ...
.
The ''Wehrmacht'' formed the heart of Germany's politico-military power. In the early part of the Second World War, the ''Wehrmacht'' employed combined arms
Combined arms is an approach to warfare
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme vio ...
tactics (close-cover air-support, tanks and infantry) to devastating effect in what became known as ''Blitzkrieg
Blitzkrieg ( , ; from 'lightning' + 'war') is a word used to describe a surprise attack using a rapid, overwhelming force concentration that may consist of armored and motorized or mechanized infantry formations, together with close air su ...
'' (lightning war). Its campaigns in France (1940), the Soviet Union (1941) and North Africa (1941/42) are regarded by historians as acts of boldness. At the same time, the far-flung advances strained the ''Wehrmacht's'' capacity to the breaking point, culminating in its first major defeat in the Battle of Moscow
The Battle of Moscow was a military campaign that consisted of two periods of strategically significant fighting on a sector of the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front during World War II. It took place between September 1941 and January ...
(1941); by late 1942, Germany was losing the initiative in all theatres. The German operational art proved no match to the war-making abilities of the Allied coalition, making the ''Wehrmacht's'' weaknesses in strategy, doctrine and logistics readily apparent.
Closely cooperating with the ''SS'' and the , the German armed forces committed numerous war crimes (despite later denials and promotion of the myth of the clean ''Wehrmacht''). The majority of the war crimes took place in the Soviet Union, Poland, Yugoslavia, Greece and Italy, as part of the war of annihilation
A war of annihilation (german: Vernichtungskrieg) or war of extermination is a type of war in which the goal is the complete annihilation of a state, a people or an ethnic minority through genocide or through the destruction of their livelihood. ...
against the Soviet Union, the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; a ...
and Nazi security warfare
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Na ...
.
During World War II about 18 million men served in the ''Wehrmacht''. By the time the war ended in Europe in May 1945, German forces (consisting of the ''Heer'', the ''Kriegsmarine
The (, ) was the navy of Germany from 1935 to 1945. It superseded the Imperial German Navy of the German Empire (1871–1918) and the inter-war (1919–1935) of the Weimar Republic. The was one of three official branches, along with the a ...
'', the ''Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabtei ...
'', the ''Waffen-SS
The (, "Armed SS") was the combat branch of the Nazi Party's ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) organisation. Its formations included men from Nazi Germany, along with Waffen-SS foreign volunteers and conscripts, volunteers and conscripts from both occup ...
'', the ''Volkssturm
The (; "people's storm") was a levée en masse national militia established by Nazi Germany during the last months of World War II. It was not set up by the German Army, the ground component of the combined German ''Wehrmacht'' armed forces, ...
'', and foreign collaborator units) had lost approximately 11,300,000 men, about half of whom were missing or killed during the war. Only a few of the ''Wehrmacht''s upper leadership went on trial for war crimes, despite evidence suggesting that more were involved in illegal actions. According to Ian Kershaw
Sir Ian Kershaw (born 29 April 1943) is an English historian whose work has chiefly focused on the social history of 20th-century Germany. He is regarded by many as one of the world's leading experts on Adolf Hitler and Nazi Germany, and is pa ...
, most of the three million ''Wehrmacht'' soldiers who invaded the USSR participated in committing war crimes.
Origin
Etymology
The German term ''"Wehrmacht''" stems from the compound word of german: wehren, "to defend" and , "power, force". It has been used to describe any nation's armed forces; for example, meaning "British Armed Forces". TheFrankfurt Constitution
The Frankfurt Constitution (german: Frankfurter Reichsverfassung, FRV) or Constitution of St. Paul's Church (''Paulskirchenverfassung''), officially named the Constitution of the German Empire (''Verfassung des Deutschen Reiches'') of 28 March 18 ...
of 1849 designated all German military forces as the "German ''Wehrmacht''", consisting of the (sea force) and the (land force). In 1919, the term ''Wehrmacht'' also appears in Article 47 of the Weimar Constitution
The Constitution of the German Reich (german: Die Verfassung des Deutschen Reichs), usually known as the Weimar Constitution (''Weimarer Verfassung''), was the constitution that governed Germany during the Weimar Republic era (1919–1933). The c ...
, establishing that: "The Reich's President holds supreme command of all armed forces .e. the ''Wehrmacht''of the Reich". From 1919, Germany's national defense force was known as the , a name that was dropped in favor of ''Wehrmacht'' on 21 May 1935.
Background
 In January 1919, after
In January 1919, after World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
ended with the signing of the armistice of 11 November 1918
The Armistice of 11 November 1918 was the armistice signed at Le Francport near Compiègne that ended fighting on land, sea, and air in World War I between the Entente and their last remaining opponent, Germany. Previous armistices ...
, the armed forces were dubbed (peace army). In March 1919, the national assembly passed a law founding a 420,000-strong preliminary army, the . The terms of the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June ...
were announced in May, and in June, Germany signed the treaty that, among other terms, imposed severe constraints on the size of Germany's armed forces. The army was limited to one hundred thousand men with an additional fifteen thousand in the navy. The fleet was to consist of at most six battleship
A battleship is a large armored warship with a main battery consisting of large caliber guns. It dominated naval warfare in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
The term ''battleship'' came into use in the late 1880s to describe a type of ...
s, six cruiser
A cruiser is a type of warship. Modern cruisers are generally the largest ships in a fleet after aircraft carriers and amphibious assault ships, and can usually perform several roles.
The term "cruiser", which has been in use for several hu ...
s, and twelve destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in ...
s. Submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
s, tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and good battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engin ...
s and heavy artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during siege ...
were forbidden and the air-force was dissolved. A new post-war military, the ''Reichswehr
''Reichswehr'' () was the official name of the German armed forces during the Weimar Republic and the first years of the Third Reich. After Germany was defeated in World War I, the Imperial German Army () was dissolved in order to be reshaped ...
'', was established on 23 March 1921. General conscription was abolished under another mandate of the Versailles treaty.
The ''Reichswehr'' was limited to 115,000 men, and thus the armed forces, under the leadership of Hans von Seeckt
Johannes "Hans" Friedrich Leopold von Seeckt (22 April 1866 – 27 December 1936) was a German military officer who served as Chief of Staff to August von Mackensen and was a central figure in planning the victories Mackensen achieved for Germany ...
, retained only the most capable officers. The American historians Alan Millet and Williamson Murray
Williamson Murray (born November 23, 1941) is an American historian and author. He has authored numerous works on history and strategic studies, and served as an editor on other projects extensively. As of 2012, he is professor emeritus of histo ...
wrote "In reducing the officers corps, Seeckt chose the new leadership from the best men of the general staff with ruthless disregard for other constituencies, such as war heroes and the nobility." Seeckt's determination that the ''Reichswehr'' be an elite cadre force that would serve as the nucleus of an expanded military when the chance for restoring conscription came essentially led to the creation of a new army, based upon, but very different from, the army that existed in World War I. In the 1920s, Seeckt and his officers developed new doctrines that emphasized speed, aggression, combined arms and initiative on the part of lower officers to take advantage of momentary opportunities. Though Seeckt retired in 1926, his influence on the army was still apparent when it went to war in 1939.
Germany was forbidden to have an air force by the Versailles treaty; nonetheless, Seeckt created a clandestine cadre of air force officers in the early 1920s. These officers saw the role of an air force as winning air superiority, strategic bombing, and close air support. That the ''Luftwaffe'' did not develop a strategic bombing force in the 1930s was not due to a lack of interest, but because of economic limitations. The leadership of the Navy led by Grand Admiral Erich Raeder
Erich Johann Albert Raeder (24 April 1876 – 6 November 1960) was a German admiral who played a major role in the naval history of World War II. Raeder attained the highest possible naval rank, that of grand admiral, in 1939, becoming the fir ...
, a close protégé of Alfred von Tirpitz
Alfred Peter Friedrich von Tirpitz (19 March 1849 – 6 March 1930) was a German grand admiral, Secretary of State of the German Imperial Naval Office, the powerful administrative branch of the German Imperial Navy from 1897 until 1916. Prussi ...
, was dedicated to the idea of reviving Tirpitz's High Seas Fleet. Officers who believed in submarine warfare led by Admiral Karl Dönitz
Karl Dönitz (sometimes spelled Doenitz; ; 16 September 1891 24 December 1980) was a German admiral who briefly succeeded Adolf Hitler as head of state in May 1945, holding the position until the dissolution of the Flensburg Government follo ...
were in a minority before 1939.
By 1922, Germany had begun covertly circumventing the conditions of the Versailles treaty. A secret collaboration with the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
began after the Treaty of Rapallo Following World War I there were two Treaties of Rapallo, both named after Rapallo, a resort on the Ligurian coast of Italy:
* Treaty of Rapallo, 1920, an agreement between Italy and the Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (the later Yugoslav ...
. Major-General Otto Hasse traveled to Moscow in 1923 to further negotiate the terms. Germany helped the Soviet Union with industrialization and Soviet officers were to be trained in Germany. German tank and air-force specialists could exercise in the Soviet Union and German chemical weapons research and manufacture would be carried out there along with other projects. In 1924 a fighter-pilot school was established at Lipetsk
Lipetsk ( rus, links=no, Липецк, p=ˈlʲipʲɪtsk), also romanized as Lipeck, is a city and the administrative center of Lipetsk Oblast, Russia, located on the banks of the Voronezh River in the Don basin, southeast of Moscow. Populatio ...
, where several hundred German air force personnel received instruction in operational maintenance, navigation, and aerial combat training over the next decade until the Germans finally left in September 1933. However, the arms buildup was done in secrecy, until Hitler came to power and it received broad political support.
Nazi rise to power
After the death of PresidentPaul von Hindenburg
Paul Ludwig Hans Anton von Beneckendorff und von Hindenburg (; abbreviated ; 2 October 1847 – 2 August 1934) was a German field marshal and statesman who led the Imperial German Army during World War I and later became President of Germany fro ...
on 2 August 1934, Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
assumed the office of President of Germany
The president of Germany, officially the Federal President of the Federal Republic of Germany (german: link=no, Bundespräsident der Bundesrepublik Deutschland),The official title within Germany is ', with ' being added in international corres ...
, and thus became commander in chief. In February 1934, the Defence Minister Werner von Blomberg
Werner Eduard Fritz von Blomberg (2 September 1878 – 13 March 1946) was a German General Staff officer and the first Minister of War in Adolf Hitler's government. After serving on the Western Front in World War I, Blomberg was appointed chi ...
, acting on his own initiative, had all of the Jews serving in the ''Reichswehr'' given an automatic and immediate dishonorable discharge
A military discharge is given when a member of the armed forces is released from their obligation to serve. Each country's military has different types of discharge. They are generally based on whether the persons completed their training and the ...
. Again, on his own initiative Blomberg had the armed forces adopt Nazi symbols
The 20th-century German Nazi Party made extensive use of graphic symbols, especially the ''swastika'', notably in the form of the swastika flag, which became the co-national flag of Nazi Germany in 1933, and the sole national flag in 1935. A ...
into their uniforms in May 1934. In August of the same year, on Blomberg's initiative and that of the ''Ministeramt'' chief General Walther von Reichenau
Walter Karl Ernst August von Reichenau (8 October 1884 – 17 January 1942) was a field marshal in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany during World War II. Reichenau commanded the 6th Army, during the invasions of Belgium and France. During Operation ...
, the entire military took the Hitler oath
The Hitler Oath (German: or Führer Oath)—also referred in English as the Soldier's Oath—refers to the oaths of allegiance sworn by the officers and soldiers of the German Armed Forces and civil servants of Nazi Germany between the years 193 ...
, an oath of personal loyalty to Hitler. Hitler was most surprised at the offer; the popular view that Hitler imposed the oath on the military is false. The oath read: "I swear by God this sacred oath that to the Leader of the German empire and people, Adolf Hitler, supreme commander of the armed forces, I shall render unconditional obedience and that as a brave soldier I shall at all times be prepared to give my life for this oath".
By 1935, Germany was openly flouting the military restrictions set forth in the Versailles Treaty: German rearmament
German rearmament (''Aufrüstung'', ) was a policy and practice of rearmament carried out in Germany during the interwar period (1918–1939), in violation of the Treaty of Versailles which required German disarmament after WWI to prevent Germa ...
was announced on 16 March with the "Edict for the Buildup of the ''Wehrmacht''" (german: Gesetz für den Aufbau der Wehrmacht) and the reintroduction of conscription. While the size of the standing army was to remain at about the 100,000-man mark decreed by the treaty, a new group of conscripts equal to this size would receive training each year. The conscription law introduced the name "''Wehrmacht''"; the ''Reichswehr'' was officially renamed the ''Wehrmacht'' on 21 May 1935. Hitler's proclamation of the ''Wehrmacht''s existence included a total of no less than 36 divisions in its original projection, contravening the Treaty of Versailles in grandiose fashion. In December 1935, General Ludwig Beck
Ludwig August Theodor Beck (; 29 June 1880 – 20 July 1944) was a German general and Chief of the German General Staff during the early years of the Nazi regime in Germany before World War II. Although Beck never became a member of the Na ...
added 48 tank battalions to the planned rearmament program. Hitler originally set a time frame of 10 years for remilitarization, but soon shortened it to four years. With the remilitarization of the Rhineland
The remilitarization of the Rhineland () began on 7 March 1936, when German military forces entered the Rhineland, which directly contravened the Treaty of Versailles and the Locarno Treaties. Neither France nor Britain was prepared for a milit ...
and the ''Anschluss
The (, or , ), also known as the (, en, Annexation of Austria), was the annexation of the Federal State of Austria into the German Reich on 13 March 1938.
The idea of an (a united Austria and Germany that would form a " Greater Germany ...
'', the German Reich's territory increased significantly, providing a larger population pool for conscription.
Personnel and recruitment
 Recruitment for the ''Wehrmacht'' was accomplished through voluntary enlistment and conscription, with 1.3 million being drafted and 2.4 million volunteering in the period 1935–1939. The total number of soldiers who served in the ''Wehrmacht'' during its existence from 1935 to 1945 is believed to have approached 18.2 million. The German military leadership originally aimed at a homogeneous military, possessing traditional Prussian military values. However, with Hitler's constant wishes to increase the ''Wehrmacht''s size, the Army was forced to accept citizens of lower class and education, decreasing internal cohesion and appointing officers who lacked real-war experience from previous conflicts, especially
Recruitment for the ''Wehrmacht'' was accomplished through voluntary enlistment and conscription, with 1.3 million being drafted and 2.4 million volunteering in the period 1935–1939. The total number of soldiers who served in the ''Wehrmacht'' during its existence from 1935 to 1945 is believed to have approached 18.2 million. The German military leadership originally aimed at a homogeneous military, possessing traditional Prussian military values. However, with Hitler's constant wishes to increase the ''Wehrmacht''s size, the Army was forced to accept citizens of lower class and education, decreasing internal cohesion and appointing officers who lacked real-war experience from previous conflicts, especially World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and the Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebelión, lin ...
.
The effectiveness of officer training and recruitment by the ''Wehrmacht'' has been identified as a major factor in its early victories as well as its ability to keep the war going as long as it did even as the war turned against Germany.
 As the Second World War intensified, ''
As the Second World War intensified, ''Kriegsmarine
The (, ) was the navy of Germany from 1935 to 1945. It superseded the Imperial German Navy of the German Empire (1871–1918) and the inter-war (1919–1935) of the Weimar Republic. The was one of three official branches, along with the a ...
'' and ''Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabtei ...
'' personnel were increasingly transferred to the army, and "voluntary" enlistments in the ''SS'' were stepped up as well. Following the Battle of Stalingrad
The Battle of Stalingrad (23 August 19422 February 1943) was a major battle on the Eastern Front of World War II where Nazi Germany and its allies unsuccessfully fought the Soviet Union for control of the city of Stalingrad (later re ...
in 1943, fitness and physical health standards for ''Wehrmacht'' recruits were drastically lowered, with the regime going so far as to create "special diet" battalions for men with severe stomach ailments. Rear-echelon personnel were more often sent to front-line duty wherever possible, especially during the final two years of the war where, inspired by constant propaganda, the oldest and youngest were being recruited and driven by instilled fear and fanaticism to serve on the fronts and, often, to fight to the death, whether judged to be cannon fodder or elite troops.
 Prior to World War II, the ''Wehrmacht'' strove to remain a purely ethnic German force; as such, minorities within and outside of Germany, such as the Czechs in annexed
Prior to World War II, the ''Wehrmacht'' strove to remain a purely ethnic German force; as such, minorities within and outside of Germany, such as the Czechs in annexed Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
, were exempted from military service after Hitler's takeover in 1938. Foreign volunteers were generally not accepted in the German armed forces prior to 1941. With the invasion of the Soviet Union
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named afte ...
in 1941, the government's positions changed. German propagandists wanted to present the war not as a purely German concern, but as a multi-national crusade
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were i ...
against the so-called Jewish Bolshevism
Jewish Bolshevism, also Judeo–Bolshevism, is an anti-communist and antisemitic canard, which alleges that the Jews were the originators of the Russian Revolution in 1917, and that they held primary power among the Bolsheviks who led the revo ...
. Hence, the ''Wehrmacht'' and the ''SS'' began to seek out recruits from occupied and neutral countries across Europe: the Germanic populations of the Netherlands and Norway were recruited largely into the ''SS'', while "non-Germanic" people were recruited into the ''Wehrmacht''. The "voluntary" nature of such recruitment was often dubious, especially in the later years of the war when even Poles living in the Polish Corridor
The Polish Corridor (german: Polnischer Korridor; pl, Pomorze, Polski Korytarz), also known as the Danzig Corridor, Corridor to the Sea or Gdańsk Corridor, was a territory located in the region of Pomerelia (Pomeranian Voivodeship, eastern ...
were declared "ethnic Germans" and drafted.
After Germany's defeat in the Battle of Stalingrad
The Battle of Stalingrad (23 August 19422 February 1943) was a major battle on the Eastern Front of World War II where Nazi Germany and its allies unsuccessfully fought the Soviet Union for control of the city of Stalingrad (later re ...
, the ''Wehrmacht'' also made substantial use of personnel from the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
, including the Caucasian Muslim Legion
The Caucasian-Mohammedan Legion (German: ''Kaukasisch-Mohammedanische Legion'') was a volunteer unit of the German Army during World War II. The Legion was created on 13 January 1942 by order of General of the Infantry Friedrich Olbricht. The Le ...
, Turkestan Legion
The Turkestan Legion (german: Turkistanische Legion) was the name for the military units composed of the Turkic peoples who served in the Wehrmacht during World War II. Most of these troops were Red Army POWs who formed a common cause with the G ...
, Crimean Tatars, ethnic Ukrainians and Russians, Cossack
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
s, and others who wished to fight against the Soviet regime or who were otherwise induced to join. Between 15,000 and 20,000 anti-communist White émigrés
White is the lightness, lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully diffuse reflection, reflect and scattering, scatter all the ...
who had left Russia after the Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and ad ...
joined the ranks of the ''Wehrmacht'' and ''Waffen-SS'', with 1,500 acting as interpreters
Interpreting is a translational activity in which one produces a first and final target-language output on the basis of a one-time exposure to an expression in a source language.
The most common two modes of interpreting are simultaneous inter ...
and more than 10,000 serving in the guard force of the Russian Protective Corps
The Russian Protective Corps (german: Russisches Schutzkorps, russian: Русский охранный корпус, sr, Руски заштитни корпус / Ruski zaštitni korpus) was an armed force composed of anti-communist White Russi ...
.
Women in the ''Wehrmacht''
 In the beginning, women in Nazi Germany were not involved in the ''Wehrmacht'', as Hitler ideologically opposed conscription for women, stating that Germany would "''not form any section of women grenade throwers or any corps of women elite snipers.''" However, with many men going to the front, women were placed in auxiliary positions within the ''Wehrmacht'', called ''Wehrmachtshelferinnen'' (), participating in tasks as:
* telephone, telegraph and transmission operators,
* administrative clerks, typists and messengers,
* operators of listening equipment, in anti-aircraft defense, operating projectors for anti-aircraft defense, employees within
In the beginning, women in Nazi Germany were not involved in the ''Wehrmacht'', as Hitler ideologically opposed conscription for women, stating that Germany would "''not form any section of women grenade throwers or any corps of women elite snipers.''" However, with many men going to the front, women were placed in auxiliary positions within the ''Wehrmacht'', called ''Wehrmachtshelferinnen'' (), participating in tasks as:
* telephone, telegraph and transmission operators,
* administrative clerks, typists and messengers,
* operators of listening equipment, in anti-aircraft defense, operating projectors for anti-aircraft defense, employees within meteorology
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not ...
services, and auxiliary civil defense personnel
* volunteer nurses in military health service, as the German Red Cross
The German Red Cross (german: Deutsches Rotes Kreuz ; DRK) is the national Red Cross Society in Germany.
With 4 million members, it is the third largest Red Cross society in the world. The German Red Cross offers a wide range of services within ...
or other voluntary organizations.
They were placed under the same authority as (Hiwis
Hiwi (), the German abbreviation of the word ''Hilfswilliger'' or, in English, auxiliary volunteer, designated, during World War II, a member of different kinds of voluntary auxiliary forces made up of recruits indigenous to the territories of Ea ...
), auxiliary personnel of the army (german: Behelfspersonal) and they were assigned to duties within the Reich, and to a lesser extent, in the occupied territories, for example in the general government of occupied Poland, in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, and later in Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
, in Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
and in Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
.
By 1945, 500,000 women were serving as ''Wehrmachtshelferinnen'', half of whom were volunteers, while the other half performed obligatory services connected to the war effort (german: Kriegshilfsdienst).
Command structure
Paul von Hindenburg
Paul Ludwig Hans Anton von Beneckendorff und von Hindenburg (; abbreviated ; 2 October 1847 – 2 August 1934) was a German field marshal and statesman who led the Imperial German Army during World War I and later became President of Germany fro ...
in August 1934. With the creation of the ''Wehrmacht'' in 1935, Hitler elevated himself to Supreme Commander of the Armed Forces, retaining the position until his suicide on 30 April 1945. The title of Commander-in-Chief was given to the Minister of the ''Reichswehr'' Werner von Blomberg
Werner Eduard Fritz von Blomberg (2 September 1878 – 13 March 1946) was a German General Staff officer and the first Minister of War in Adolf Hitler's government. After serving on the Western Front in World War I, Blomberg was appointed chi ...
, who was simultaneously renamed the Reich Minister of War. Following the Blomberg-Fritsch Affair, Blomberg resigned and Hitler abolished the Ministry of War. As a replacement for the ministry, the ''Wehrmacht'' High Command '' Oberkommando der Wehrmacht'' (OKW), under Field Marshal Wilhelm Keitel
Wilhelm Bodewin Johann Gustav Keitel (; 22 September 188216 October 1946) was a German field marshal and war criminal who held office as chief of the '' Oberkommando der Wehrmacht'' (OKW), the high command of Nazi Germany's Armed Forces, duri ...
, was put in its place.
Placed under the OKW were the three branch High Commands: ''Oberkommando des Heeres
The (; abbreviated OKH) was the Command (military formation), high command of the German Army (1935–1945), Army of Nazi Germany. It was founded in 1935 as part of Adolf Hitler's German rearmament, rearmament of Germany. OKH was ''de facto'' t ...
'' (OKH), ''Oberkommando der Marine
The (; abbreviated OKM) was the high command and the highest administrative and command authority of the ''Kriegsmarine''. It was officially formed from the ''Marineleitung'' ("Naval Command") of the ''Reichswehr'' on 11 January 1936. In 1937 ...
'' (OKM), and ''Oberkommando der Luftwaffe
The (; abbreviated OKL) was the high command of the air force () of Nazi Germany.
History
The was organized in a large and diverse structure led by Reich minister and supreme commander of the Air force (german: Oberbefehlshaber der Luftwaf ...
'' (OKL). The OKW was intended to serve as a joint command and coordinate all military activities, with Hitler at the top. Though many senior officers, such as von Manstein, had advocated for a real tri-service Joint Command, or appointment of a single Joint Chief of Staff, Hitler refused. Even after the defeat at Stalingrad, Hitler refused, stating that Göring as ''Reichsmarschall
(german: Reichsmarschall des Großdeutschen Reiches; ) was a rank and the highest military office in the ''Wehrmacht'' specially created for Hermann Göring during World War II. It was senior to the rank of , which was previously the highes ...
'' and Hitler's deputy, would not submit to someone else or see himself as an equal to other service commanders. However, a more likely reason was Hitler feared it would break his image of having the "Midas touch" concerning military strategy.
With the creation of the OKW, Hitler solidified his control over the ''Wehrmacht''. Showing restraint at the beginning of the war, Hitler also became increasingly involved in military operations at every scale.
Additionally, there was a clear lack of cohesion between the three High Commands and the OKW, as senior generals were unaware of the needs, capabilities and limitations of the other branches. With Hitler serving as Supreme Commander, branch commands were often forced to fight for influence with Hitler. However, influence with Hitler not only came from rank and merit but also who Hitler perceived as loyal, leading to inter-service rivalry, rather than cohesion between his military advisers.
Branches
Army
 The German Army furthered concepts pioneered during
The German Army furthered concepts pioneered during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, combining ground (''Heer'') and air force (''Luftwaffe'') assets into combined arms
Combined arms is an approach to warfare
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme vio ...
teams. Coupled with traditional war fighting methods such as encirclement
Encirclement is a military term for the situation when a force or target is isolated and surrounded by enemy forces. The situation is highly dangerous for the encircled force. At the strategic level, it cannot receive supplies or reinforceme ...
s and the "battle of annihilation
Annihilation is a military strategy in which an attacking army seeks to entirely destroy the military capacity of the opposing army. This strategy can be executed in a single planned pivotal battle, called a "battle of annihilation". A succes ...
", the ''Wehrmacht'' managed many lightning quick victories in the first year of World War II, prompting foreign journalists to create a new word for what they witnessed: ''Blitzkrieg
Blitzkrieg ( , ; from 'lightning' + 'war') is a word used to describe a surprise attack using a rapid, overwhelming force concentration that may consist of armored and motorized or mechanized infantry formations, together with close air su ...
''. Germany's immediate military success on the field at the start of the Second World War coincides the favorable beginning they achieved during the First World War, a fact which some attribute to their superior officer corps.
The ''Heer'' entered the war with a minority of its formations motorized; infantry remained approximately 90% foot-borne throughout the war, and artillery was primarily horse-drawn
A horse-drawn vehicle is a mechanized piece of equipment pulled by one horse or by a team of horses. These vehicles typically had two or four wheels and were used to carry passengers and/or a load. They were once common worldwide, but they have m ...
. The motorized formations received much attention in the world press in the opening years of the war, and were cited as the reason for the success of the invasions of Poland
An invasion is a military offensive in which large numbers of combatants of one geopolitical entity aggressively enter territory owned by another such entity, generally with the objective of either: conquering; liberating or re-establishing con ...
(September 1939), Denmark and Norway (April 1940), Belgium, France, and Netherlands (May 1940), Yugoslavia and Greece (April 1941) and the early stage of Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after ...
in the Soviet Union (June 1941).
After Hitler declared war on the United States in December 1941, the Axis powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
found themselves engaged in campaigns against several major industrial powers while Germany was still in transition to a war economy. German units were then overextended, undersupplied, outmaneuvered, outnumbered and defeated by its enemies in decisive battles during 1941, 1942, and 1943 at the Battle of Moscow
The Battle of Moscow was a military campaign that consisted of two periods of strategically significant fighting on a sector of the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front during World War II. It took place between September 1941 and January ...
, the Siege of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad (russian: links=no, translit=Blokada Leningrada, Блокада Ленинграда; german: links=no, Leningrader Blockade; ) was a prolonged military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the Soviet city of L ...
, Stalingrad
Volgograd ( rus, Волгогра́д, a=ru-Volgograd.ogg, p=vəɫɡɐˈɡrat), geographical renaming, formerly Tsaritsyn (russian: Цари́цын, Tsarítsyn, label=none; ) (1589–1925), and Stalingrad (russian: Сталингра́д, Stal ...
, Tunis
''Tounsi'' french: Tunisois
, population_note =
, population_urban =
, population_metro = 2658816
, population_density_km2 =
, timezone1 = CET
, utc_offset1 ...
in North African Campaign, North Africa, and the Battle of Kursk.
 The German Army was managed through Mission-type tactics, mission-based tactics (rather than order-based tactics) which was intended to give commanders greater freedom to act on events and exploit opportunities. In public opinion, the German Army was, and sometimes still is, seen as a high-tech army. However, such modern equipment, while featured much in propaganda, was often only available in relatively small numbers. Only 40% to 60% of all units in the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front were motorized, baggage trains often relied on horse-drawn trailers due to poor roads and weather conditions in the Soviet Union, and for the same reasons many soldiers marched on foot or used bicycles as bicycle infantry. As the fortunes of war turned against them, the Germans were in constant retreat from 1943 and onward.
The Panzer divisions were vital to the German army's early success. In the strategies of the ''Blitzkrieg'', the ''Wehrmacht'' combined the mobility of light tanks with airborne assault to quickly progress through weak enemy lines, enabling the German army to quickly and brutally take over Poland and France. These tanks were used to break through enemy lines, isolating regiments from the main force so that the infantry behind the tanks could quickly kill or capture the enemy troops.
The German Army was managed through Mission-type tactics, mission-based tactics (rather than order-based tactics) which was intended to give commanders greater freedom to act on events and exploit opportunities. In public opinion, the German Army was, and sometimes still is, seen as a high-tech army. However, such modern equipment, while featured much in propaganda, was often only available in relatively small numbers. Only 40% to 60% of all units in the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front were motorized, baggage trains often relied on horse-drawn trailers due to poor roads and weather conditions in the Soviet Union, and for the same reasons many soldiers marched on foot or used bicycles as bicycle infantry. As the fortunes of war turned against them, the Germans were in constant retreat from 1943 and onward.
The Panzer divisions were vital to the German army's early success. In the strategies of the ''Blitzkrieg'', the ''Wehrmacht'' combined the mobility of light tanks with airborne assault to quickly progress through weak enemy lines, enabling the German army to quickly and brutally take over Poland and France. These tanks were used to break through enemy lines, isolating regiments from the main force so that the infantry behind the tanks could quickly kill or capture the enemy troops.
Air Force
 Originally outlawed by the Treaty of Versailles, the ''
Originally outlawed by the Treaty of Versailles, the ''Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabtei ...
'' was officially established in 1935, under the leadership of Hermann Göring. First gaining experience in the Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebelión, lin ...
, it was a key element in the early ''Blitzkrieg'' campaigns (Poland, France 1940, USSR 1941). The ''Luftwaffe'' concentrated production on fighters and (small) tactical bombers, like the Messerschmitt Bf 109 fighter and the Junkers Ju 87 ''Stuka'' dive bomber. The planes cooperated closely with the ground forces. Overwhelming numbers of fighters assured air-supremacy, and the bombers would attack command- and supply-lines, depots, and other support targets close to the front. The ''Luftwaffe'' would also be used to transport paratroopers, as first used during Operation Weserübung. Due to the Army's sway with Hitler, the ''Luftwaffe'' was often subordinated to the Army, resulting in it being used as a tactical support role and losing its strategic capabilities.
The Western Allies' strategic bombing campaign against German industrial targets, particularly the round the clock Combined Bomber Offensive and Defence of the Reich, deliberately forced the ''Luftwaffe'' into a war of attrition. With German fighter force destroyed the Western Allies had air supremacy over the battlefield, denying support to German forces on the ground and using its own fighter-bombers to attack and disrupt. Following the losses in Operation Bodenplatte in 1945, the ''Luftwaffe'' was no longer an effective force.
Navy
 The Treaty of Versailles disallowed submarines, while limiting the size of the ''Reichsmarine'' to six battleships, six cruisers, and twelve destroyers. Following the creation of the ''Wehrmacht'', the navy was renamed the ''Kriegsmarine''.
With the signing of the Anglo-German Naval Agreement, Germany was allowed to increase its navy's size to be 35:100 tonnage of the Royal Navy, and allowed for the construction of U-boats. This was partly done to appease Germany, and because Britain believed the ''Kriegsmarine'' would not be able to reach the 35% limit until 1942. The navy was also prioritized last in the German rearmament scheme, making it the smallest of the branches.
In the Battle of the Atlantic, the initially successful German U-boat fleet arm was eventually defeated due to Allied technological innovations like sonar, radar, and the breaking of the Enigma machine, Enigma code.
Large surface vessels were few in number due to construction limitations by international treaties prior to 1935. The "pocket battleships" and were important as commerce raiders only in the opening year of the war. No aircraft carrier was operational, as German leadership lost interest in the which had been launched in 1938.
Following the loss of the in 1941, with Allied air-superiority threatening the remaining battle-cruisers in French Atlantic harbors, the ships were ordered to make the Channel Dash back to German ports. Operating from fjords along the coast of Norway, which had been occupied since 1940, Arctic convoys of World War II, convoys from North America to the Soviet port of Murmansk could be intercepted though the spent most of her career as fleet in being. After the appointment of Karl Dönitz as Grand Admiral of the ''Kriegsmarine'' (in the aftermath of the Battle of the Barents Sea), Germany stopped constructing battleships and cruisers in favor of U-boats. Though by 1941, the navy had already lost a number of its large surface ships, which could not be replenished during the war.
The ''Kriegsmarine''s most significant contribution to the German war effort was the deployment of its nearly 1,000 U-boats to strike at Allied convoys. The German naval strategy was to attack the convoys in an attempt to prevent the United States from interfering in Europe and to starve out the British. Karl Doenitz, the U-Boat Chief, began unrestricted submarine warfare which cost the Allies 22,898 men and 1,315 ships. The U-boat war remained costly for the Allies until early spring of 1943 when the Allies began to use countermeasures against U-Boats such as the use of Hunter-Killer groups, airborne radar, torpedoes and mines like the Mark 24 mine, FIDO. The submarine war cost the ''Kriegsmarine'' 757 U-boats, with more than 30,000 U-boat crewmen killed.
The Treaty of Versailles disallowed submarines, while limiting the size of the ''Reichsmarine'' to six battleships, six cruisers, and twelve destroyers. Following the creation of the ''Wehrmacht'', the navy was renamed the ''Kriegsmarine''.
With the signing of the Anglo-German Naval Agreement, Germany was allowed to increase its navy's size to be 35:100 tonnage of the Royal Navy, and allowed for the construction of U-boats. This was partly done to appease Germany, and because Britain believed the ''Kriegsmarine'' would not be able to reach the 35% limit until 1942. The navy was also prioritized last in the German rearmament scheme, making it the smallest of the branches.
In the Battle of the Atlantic, the initially successful German U-boat fleet arm was eventually defeated due to Allied technological innovations like sonar, radar, and the breaking of the Enigma machine, Enigma code.
Large surface vessels were few in number due to construction limitations by international treaties prior to 1935. The "pocket battleships" and were important as commerce raiders only in the opening year of the war. No aircraft carrier was operational, as German leadership lost interest in the which had been launched in 1938.
Following the loss of the in 1941, with Allied air-superiority threatening the remaining battle-cruisers in French Atlantic harbors, the ships were ordered to make the Channel Dash back to German ports. Operating from fjords along the coast of Norway, which had been occupied since 1940, Arctic convoys of World War II, convoys from North America to the Soviet port of Murmansk could be intercepted though the spent most of her career as fleet in being. After the appointment of Karl Dönitz as Grand Admiral of the ''Kriegsmarine'' (in the aftermath of the Battle of the Barents Sea), Germany stopped constructing battleships and cruisers in favor of U-boats. Though by 1941, the navy had already lost a number of its large surface ships, which could not be replenished during the war.
The ''Kriegsmarine''s most significant contribution to the German war effort was the deployment of its nearly 1,000 U-boats to strike at Allied convoys. The German naval strategy was to attack the convoys in an attempt to prevent the United States from interfering in Europe and to starve out the British. Karl Doenitz, the U-Boat Chief, began unrestricted submarine warfare which cost the Allies 22,898 men and 1,315 ships. The U-boat war remained costly for the Allies until early spring of 1943 when the Allies began to use countermeasures against U-Boats such as the use of Hunter-Killer groups, airborne radar, torpedoes and mines like the Mark 24 mine, FIDO. The submarine war cost the ''Kriegsmarine'' 757 U-boats, with more than 30,000 U-boat crewmen killed.
Coexistence with the Waffen-SS
 In the beginning, there was friction between the ''SS'' and the army, as the army feared the ''SS'' would attempt to become a legitimate part of the armed forces of Nazi Germany, partly due to the fighting between the limited armaments, and the perceived fanaticism towards Nazism. However, on 17 August 1938, Hitler codified the role of the ''SS'' and the army in order to end the feud between the two. The arming of the ''SS'' was to be "procured from the ''Wehrmacht'' upon payment", however "in peacetime, no organizational connection with the ''Wehrmacht'' exists." The army was however allowed to check the budget of the ''SS'' and inspect the combat readiness of the ''SS'' troops. In the event of mobilization, the ''Waffen-SS'' field units could be placed under the operational control of the OKW or the OKH. All decisions regarding this would be at Hitler's personal discretion.
Though there existed conflict between the ''SS'' and ''Wehrmacht'', many ''SS'' officers were former army officers, which ensured continuity and understanding between the two. Throughout the war, army and ''SS'' soldiers worked together in various combat situations, creating bonds between the two groups. Heinz Guderian, Guderian noted that every day the war continued the Army and the ''SS'' became closer together. Towards the end of the war, army units would even be placed under the command of the ''SS'', in Italy and the Netherlands. The relationship between the ''Wehrmacht'' and the ''SS'' improved; however, the ''Waffen-SS'' was never considered "the fourth branch of the ''Wehrmacht''.”
In the beginning, there was friction between the ''SS'' and the army, as the army feared the ''SS'' would attempt to become a legitimate part of the armed forces of Nazi Germany, partly due to the fighting between the limited armaments, and the perceived fanaticism towards Nazism. However, on 17 August 1938, Hitler codified the role of the ''SS'' and the army in order to end the feud between the two. The arming of the ''SS'' was to be "procured from the ''Wehrmacht'' upon payment", however "in peacetime, no organizational connection with the ''Wehrmacht'' exists." The army was however allowed to check the budget of the ''SS'' and inspect the combat readiness of the ''SS'' troops. In the event of mobilization, the ''Waffen-SS'' field units could be placed under the operational control of the OKW or the OKH. All decisions regarding this would be at Hitler's personal discretion.
Though there existed conflict between the ''SS'' and ''Wehrmacht'', many ''SS'' officers were former army officers, which ensured continuity and understanding between the two. Throughout the war, army and ''SS'' soldiers worked together in various combat situations, creating bonds between the two groups. Heinz Guderian, Guderian noted that every day the war continued the Army and the ''SS'' became closer together. Towards the end of the war, army units would even be placed under the command of the ''SS'', in Italy and the Netherlands. The relationship between the ''Wehrmacht'' and the ''SS'' improved; however, the ''Waffen-SS'' was never considered "the fourth branch of the ''Wehrmacht''.”
Theatres and campaigns
The ''Wehrmacht'' directed combat operations during World War II (from 1 September 19398 May 1945) as the German Reich's armed forces umbrella command-organization. After 1941 the OKH became the ''de facto'' Eastern Theatre higher-echelon command-organization for the ''Wehrmacht'', excluding ''Waffen-SS
The (, "Armed SS") was the combat branch of the Nazi Party's ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) organisation. Its formations included men from Nazi Germany, along with Waffen-SS foreign volunteers and conscripts, volunteers and conscripts from both occup ...
'' except for operational and tactical combat purposes. The OKW conducted operations in the Western Theatre. The operations by the ''Kriegsmarine'' in the North and Mid-Atlantic can also be considered as separate theatres, considering the size of the area of operations and their remoteness from other theatres.
The ''Wehrmacht'' fought on other fronts, sometimes three simultaneously; redeploying troops from the intensifying theatre in the East to the West after the Normandy landings caused tensions between the General Staffs of both the OKW and the OKHas Germany lacked sufficient materiel and manpower for a two-front war of such magnitude.
Eastern theatre
 Major campaigns and battles in Eastern and Central Europe included:
* Occupation of Czechoslovakia by Nazi Germany, Czechoslovakian campaign (1938–1945)
*Invasion of Poland (1939), Invasion of Poland (''Fall Weiss'')
*
Major campaigns and battles in Eastern and Central Europe included:
* Occupation of Czechoslovakia by Nazi Germany, Czechoslovakian campaign (1938–1945)
*Invasion of Poland (1939), Invasion of Poland (''Fall Weiss'')
* Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after ...
(1941), conducted by Army Group North, Army Group Centre, and Army Group South
* Battle of Moscow
The Battle of Moscow was a military campaign that consisted of two periods of strategically significant fighting on a sector of the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front during World War II. It took place between September 1941 and January ...
(1941)
* Battles of Rzhev (1942–1943)
* Battle of Stalingrad
The Battle of Stalingrad (23 August 19422 February 1943) was a major battle on the Eastern Front of World War II where Nazi Germany and its allies unsuccessfully fought the Soviet Union for control of the city of Stalingrad (later re ...
(1942–1943)
* Battle of the Caucasus (1942–1943)
* Battle of Kursk (Operation Citadel) (1943)
* Battle of Kiev (1943), Battle of Kiev (1943)
* Operation Bagration (1944)
* Nazi security warfare
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Na ...
– largely carried out by Security Division (Wehrmacht), security divisions of the ''Wehrmacht'', by Order Police and by ''Waffen-SS'' units in the occupied territories behind Axis front-lines.
Western theatre
 * Phoney War (''Sitzkrieg'', September 1939 to May 1940) between the invasion of Poland and the Battle of France
* Operation Weserübung
** German invasion of Denmark (1940), German invasion of Denmark – 9 April 1940
** The Norwegian Campaign – 9 April to 10 June 1940
* ''Fall Gelb''
**Battle of Belgium 10 to 28 May 1940
**German invasion of Luxembourg 10 May 1940
**Battle of the Netherlands – 10 to 17 May 1940
**Battle of France – 10 May to 25 June 1940
* Battle of Britain (1940)
* Battle of the Atlantic (1939–1945)
* Operation Overlord, Battle of Normandy (1944)
* Operation Dragoon, Allied invasion of southern France (1944)
* Ardennes Offensive (1944–1945)
* Defense of the Reich air-campaign, 1939 to 1945
* Phoney War (''Sitzkrieg'', September 1939 to May 1940) between the invasion of Poland and the Battle of France
* Operation Weserübung
** German invasion of Denmark (1940), German invasion of Denmark – 9 April 1940
** The Norwegian Campaign – 9 April to 10 June 1940
* ''Fall Gelb''
**Battle of Belgium 10 to 28 May 1940
**German invasion of Luxembourg 10 May 1940
**Battle of the Netherlands – 10 to 17 May 1940
**Battle of France – 10 May to 25 June 1940
* Battle of Britain (1940)
* Battle of the Atlantic (1939–1945)
* Operation Overlord, Battle of Normandy (1944)
* Operation Dragoon, Allied invasion of southern France (1944)
* Ardennes Offensive (1944–1945)
* Defense of the Reich air-campaign, 1939 to 1945
Mediterranean theatre
 For a time, the Battle of the Mediterranean, Axis Mediterranean Theatre and the North African Campaign were conducted as a Military campaign, joint campaign with the Regio Esercito, Italian Army, and may be considered a separate Theater (warfare), theatre.
* Balkans Campaign (World War II), Invasion of the Balkans and Greece (Operation Marita) (1940–1941)
* Battle of Crete (1941)
* The North African Campaign in Libya, Tunisia and Egypt between the UK and Commonwealth (and later, U.S.) forces and the Axis forces
* The Italian Campaign (World War II), Italian Theatre was a continuation of the Axis defeat in North Africa, and was a campaign for defence of Italy
For a time, the Battle of the Mediterranean, Axis Mediterranean Theatre and the North African Campaign were conducted as a Military campaign, joint campaign with the Regio Esercito, Italian Army, and may be considered a separate Theater (warfare), theatre.
* Balkans Campaign (World War II), Invasion of the Balkans and Greece (Operation Marita) (1940–1941)
* Battle of Crete (1941)
* The North African Campaign in Libya, Tunisia and Egypt between the UK and Commonwealth (and later, U.S.) forces and the Axis forces
* The Italian Campaign (World War II), Italian Theatre was a continuation of the Axis defeat in North Africa, and was a campaign for defence of Italy
Casualties

 More than 6,000,000 soldiers were wounded during the conflict, while more than 11,000,000 became prisoners. In all, approximately 5,318,000 soldiers from Germany and other nationalities fighting for the German armed forces—including the ''Waffen-SS'', ''Volkssturm'' and foreign collaborationist units—are estimated to have been killed in action, died of wounds, died in custody or gone missing in World War II. Included in this number are 215,000 Soviet citizens conscripted by Germany.
According to Frank Biess,
Jeffrey Herf wrote that:
In addition to the losses, at the hands of the elements and enemy fighting, at least 20,000 soldiers were executed as sentences by the military court. In comparison, the Red Army executed 135,000, France 102, the US 146 and the UK 40.
More than 6,000,000 soldiers were wounded during the conflict, while more than 11,000,000 became prisoners. In all, approximately 5,318,000 soldiers from Germany and other nationalities fighting for the German armed forces—including the ''Waffen-SS'', ''Volkssturm'' and foreign collaborationist units—are estimated to have been killed in action, died of wounds, died in custody or gone missing in World War II. Included in this number are 215,000 Soviet citizens conscripted by Germany.
According to Frank Biess,
Jeffrey Herf wrote that:
In addition to the losses, at the hands of the elements and enemy fighting, at least 20,000 soldiers were executed as sentences by the military court. In comparison, the Red Army executed 135,000, France 102, the US 146 and the UK 40.
War crimes
Nazi propaganda had told ''Wehrmacht'' soldiers to wipe out what were variously called Jewish Bolshevik subhumans, the Mongol hordes, the Asiatic flood and the red beast. While the principal perpetrators of the civil suppression behind the front lines amongst German armed forces were the Nazi German "political" armies (the ''SS-Totenkopfverbände'', the ''Waffen-SS
The (, "Armed SS") was the combat branch of the Nazi Party's ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) organisation. Its formations included men from Nazi Germany, along with Waffen-SS foreign volunteers and conscripts, volunteers and conscripts from both occup ...
'', and the ''Einsatzgruppen'', which were responsible for mass-murders, primarily by implementation of the so-called Final Solution of the Jewish Question in occupied territories), the traditional armed forces represented by the ''Wehrmacht'' committed and ordered war crimes of their own (e.g. the Commissar Order), particularly during the Invasion of Poland (1939), invasion of Poland in 1939 and later in the Operation Barbarossa, war against the Soviet Union.
Cooperation with the ''SS''
Prior to the outbreak of war, Hitler informed senior ''Wehrmacht'' officers that actions "which would not be in the taste of German generals", would take place in occupied areas and ordered them that they "should not interfere in such matters but restrict themselves to their military duties". Some ''Wehrmacht'' officers initially showed a strong dislike for the ''SS'' and objected to the army committing war crimes with the ''SS'', though these objections were not against the idea of the atrocities themselves. Later during the war, relations between the ''SS'' and ''Wehrmacht'' improved significantly. The common soldier had no qualms with the ''SS'', and often assisted them in rounding up civilians for executions. The Army's Chief of Staff General Franz Halder in a directive declared that in the event of guerrilla attacks, German troops were to impose "collective measures of force" by massacring entire villages. Cooperation between the ''SS Einsatzgruppen'' and the ''Wehrmacht'' involved supplying the death squads with weapons, ammunition, equipment, transport, and even housing. Partisan fighters, Jews, and Communists became synonymous enemies of the Nazi regime and were hunted down and exterminated by the ''Einsatzgruppen'' and ''Wehrmacht'' alike, something revealed in numerous field journal entries from German soldiers. With the implementation of the Hunger Plan, hundreds of thousands, perhaps millions, of Soviet civilians were deliberately starvation, starved to death, as the Germans seized food for their armies and fodder for their draft horses. According to Thomas Kühne: "an estimated 300,000–500,000 people were killed during the ''Wehrmacht''sNazi security warfare
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Na ...
in the Soviet Union."
While secretly listening to conversations of captured German generals, British officials became aware that the German Army had taken part in the atrocities and mass-murder of Jews and were guilty of war crimes. American officials learned of the ''Wehrmacht''s atrocities in much the same way. Taped conversations of soldiers detained as POWs revealed how some of them voluntarily participated in mass executions.
Crimes against civilians

 During the war, the ''Wehrmacht'' committed numerous war crimes against the civilian population in occupied countries. This includes massacres of civilians and running forced brothels in occupied areas.
Massacres would in many cases come as reprisals for acts of resistance. With these reprisals, the ''Wehrmacht''s response would vary in severity and method, depending on the scale of resistance and whether it was in East or West Europe. Often, the number of hostages to be shot was calculated based on a ratio of 100 hostages executed for every German soldier killed and 50 hostages executed for every German soldier wounded. Other times civilians would be rounded up and shot with machine guns.
To combat German officials' fear of Sexually transmitted disease, venereal disease and masturbation, the ''Wehrmacht'' established numerous brothels throughout Nazi Germany and its occupied territories. Women would often be kidnapped off the streets and forced to work in the brothels, with an estimated minimum of 34,140 women being forced to serve as prostitutes.
During the war, the ''Wehrmacht'' committed numerous war crimes against the civilian population in occupied countries. This includes massacres of civilians and running forced brothels in occupied areas.
Massacres would in many cases come as reprisals for acts of resistance. With these reprisals, the ''Wehrmacht''s response would vary in severity and method, depending on the scale of resistance and whether it was in East or West Europe. Often, the number of hostages to be shot was calculated based on a ratio of 100 hostages executed for every German soldier killed and 50 hostages executed for every German soldier wounded. Other times civilians would be rounded up and shot with machine guns.
To combat German officials' fear of Sexually transmitted disease, venereal disease and masturbation, the ''Wehrmacht'' established numerous brothels throughout Nazi Germany and its occupied territories. Women would often be kidnapped off the streets and forced to work in the brothels, with an estimated minimum of 34,140 women being forced to serve as prostitutes.
Crimes against POWs
 While the ''Wehrmacht''s prisoner-of-war camps for inmates from the west generally satisfied the humanitarian requirement prescribed by international law, prisoners from Poland and the USSR were incarcerated under significantly worse conditions. Between the launching of Operation Barbarossa in the summer of 1941 and the following spring, 2.8 million of the 3.2 million Nazi crimes against Soviet POWs, Soviet prisoners taken died while in German hands.
While the ''Wehrmacht''s prisoner-of-war camps for inmates from the west generally satisfied the humanitarian requirement prescribed by international law, prisoners from Poland and the USSR were incarcerated under significantly worse conditions. Between the launching of Operation Barbarossa in the summer of 1941 and the following spring, 2.8 million of the 3.2 million Nazi crimes against Soviet POWs, Soviet prisoners taken died while in German hands.
Criminal and genocidal organization
Among German historians, the view that the ''Wehrmacht'' had participated in wartime atrocities, particularly on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front, grew in the late 1970s and the 1980s. In the 1990s, public conception in Germany was influenced by controversial reactions and debates about the Wehrmachtsausstellung, exhibition of war crime issues. The Israeli historian Omer Bartov, a leading expert on the ''Wehrmacht'' wrote in 2003 that the ''Wehrmacht'' was a willing instrument of genocide, and that it is untrue that the ''Wehrmacht'' was an apolitical, professional fighting force that had only a few "bad apples". Bartov argues that far from being the "untarnished shield", as successive German apologists stated after the war, the ''Wehrmacht'' was a criminal organization. Likewise, the historian Richard J. Evans, a leading expert on modern German history, wrote that the ''Wehrmacht'' was a genocidal organization. The historian Ben H. Shepherd writes that "There is now clear agreement amongst historians that the German ''Wehrmacht'' ... identified strongly with National Socialism and embroiled itself in the criminality of the Third Reich." British historianIan Kershaw
Sir Ian Kershaw (born 29 April 1943) is an English historian whose work has chiefly focused on the social history of 20th-century Germany. He is regarded by many as one of the world's leading experts on Adolf Hitler and Nazi Germany, and is pa ...
concludes that the ''Wehrmacht''s duty was to ensure that the people who met Hitler's requirements of being part of the Aryan race, Aryan ''Herrenvolk'' ("Aryan master race") had living space. He wrote that:
Several high-ranking ''Wehrmacht'' officers, including Hermann Hoth, Georg von Küchler, Georg-Hans Reinhardt, Karl von Roques, Walter Warlimont and others, were convicted of war crimes and crimes against humanity at the High Command Trial given sentences ranging from time served to life.
Resistance to the Nazi regime
 Originally, there was little German resistance to Nazism, resistance within the ''Wehrmacht'', as Hitler actively went against the Treaty of Versailles and attempted to recover the army's honor. The first major resistance began in 1938 with the Oster conspiracy, where several members of the military wanted to remove Hitler from power, as they feared a war with
Originally, there was little German resistance to Nazism, resistance within the ''Wehrmacht'', as Hitler actively went against the Treaty of Versailles and attempted to recover the army's honor. The first major resistance began in 1938 with the Oster conspiracy, where several members of the military wanted to remove Hitler from power, as they feared a war with Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
would ruin Germany. However, following the success of the early campaigns in Poland, Scandinavia and France, belief in Hitler was restored. With the defeat in Battle of Stalingrad, Stalingrad, trust in Hitler's leadership began to wane. This caused an increase in resistance within the military. The resistance culminated in the 20 July plot (1944), when a group of officers led by Claus von Stauffenberg attempted to assassinate Hitler. The attempt failed, resulting in the execution of 4,980 people and the standard military salute being replaced with the Hitler salute.
Some members of the ''Wehrmacht'' did save Jews and non-Jews from the concentration camps and/or mass murder. Anton Schmida sergeant in the armyhelped between 250 and 300 Jewish men, women, and children escape from the Vilna Ghetto in Lithuania. He was court-martialed and executed as a consequence. Albert Battel, a reserve officer stationed near the Przemysl ghetto, blocked an ''SS'' detachment from entering it. He then evacuated up to 100 Jews and their families to the barracks of the local military command, and placed them under his protection. Wilm Hosenfeldan army captain in Warsawhelped, hid, or rescued several Poles, including Jews, in occupied Poland. He helped the Polish-Jewish composer Władysław Szpilman, who was hiding among the city's ruins, by supplying him with food and water.
According to Wolfram Wette, only three ''Wehrmacht'' soldiers are known for being executed for rescuing Jews: Anton Schmid, Friedrich Rath and Friedrich Winking.
After World War II
 Following the German Instrument of Surrender, unconditional surrender of the ''Wehrmacht'', which went into effect on 8 May 1945, some ''Wehrmacht'' units remained active, either independently (e.g. in Norway), or under Allied command as police forces. The last ''Wehrmacht'' unit to come under Allied control was an isolated weather station in Svalbard, which formally surrendered to a Norwegian relief ship on 4 September.
On 20 September 1945, with Proclamation No. 2 of the Allied Control Council (ACC), "[a]ll German land, naval and air forces, the S.S., S.A., S.D. and Gestapo, with all their organizations, staffs and institution, including the General Staff, the Officers' corps, the Reserve Corps, military schools, war veterans' organizations, and all other military and quasi-military organizations, together with all clubs and associations which serve to keep alive the military tradition in Germany, shall be completely and finally abolished in accordance with the methods and procedures to be laid down by the Allied Representatives." The ''Wehrmacht'' was officially dissolved by the ACC Law 34 on 20 August 1946, which proclaimed the OKW, OKH, the Ministry of Aviation (Nazi Germany), Ministry of Aviation and the OKM to be "disbanded, completely liquidated and declared illegal".
Following the German Instrument of Surrender, unconditional surrender of the ''Wehrmacht'', which went into effect on 8 May 1945, some ''Wehrmacht'' units remained active, either independently (e.g. in Norway), or under Allied command as police forces. The last ''Wehrmacht'' unit to come under Allied control was an isolated weather station in Svalbard, which formally surrendered to a Norwegian relief ship on 4 September.
On 20 September 1945, with Proclamation No. 2 of the Allied Control Council (ACC), "[a]ll German land, naval and air forces, the S.S., S.A., S.D. and Gestapo, with all their organizations, staffs and institution, including the General Staff, the Officers' corps, the Reserve Corps, military schools, war veterans' organizations, and all other military and quasi-military organizations, together with all clubs and associations which serve to keep alive the military tradition in Germany, shall be completely and finally abolished in accordance with the methods and procedures to be laid down by the Allied Representatives." The ''Wehrmacht'' was officially dissolved by the ACC Law 34 on 20 August 1946, which proclaimed the OKW, OKH, the Ministry of Aviation (Nazi Germany), Ministry of Aviation and the OKM to be "disbanded, completely liquidated and declared illegal".
Military operational legacy
Immediately following the end of the war, many were quick to dismiss the ''Wehrmacht'' due to its failures and claim allied superiority. However, historians have since reevaluated the ''Wehrmacht'' in terms of fighting power and tactics, giving it a more favorable assessment, with some calling it one of the best in the world, partly due to its ability to regularly inflict higher losses than it received, while it fought outnumbered and outgunned. Israeli military historian Martin van Creveld, who attempted to examine the military force of the ''Wehrmacht'' in a purely military context, concluded: "The German army was a superb fighting organization. In point of morale, wikt:elan#Noun, elan, troop cohesion and resilience, it probably had no equal among twentieth century armies." German historian Rolf-Dieter Müller comes to the following conclusion: "In the purely military sense [...] you can indeed say that the impression of a superior fighting force rightly exists. The proverbial efficiency was even greater than previously thought, because the superiority of the opponent was much higher than at that time German officers suspected. The analysis of Russian archive files finally gives us a clear picture in this regard." Strategic thinker and professor Colin S. Gray believed that the ''Wehrmacht'' possessed outstanding tactical and operational capabilities. However, following a number of successful campaigns, German policy began to have victory disease, asking the ''Wehrmacht'' to do the impossible. The continued use of the ''Blitzkrieg'' also led to Soviets learning the tactic and using it against the ''Wehrmacht''.Historical negationism
Soon after the war ended, former ''Wehrmacht'' officers, veterans' groups and various far-right authors began to state that the ''Wehrmacht'' was an apolitical organization which was largely innocent of Nazi Germany's war crimes and crimes against humanity. Attempting to benefit from the clean ''Wehrmacht'' myth, veterans of the ''Waffen-SS
The (, "Armed SS") was the combat branch of the Nazi Party's ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) organisation. Its formations included men from Nazi Germany, along with Waffen-SS foreign volunteers and conscripts, volunteers and conscripts from both occup ...
'' declared that the organisation had virtually been a branch of the ''Wehrmacht'' and therefore had fought as "honourably" as it. Its veterans organisation, HIAG, attempted to cultivate a myth of their soldiers having been "Soldiers like any other".
Post-war militaries
 Following the division of Germany, many former ''Wehrmacht'' and ''SS'' officers in West Germany feared a Soviet invasion of the country. To combat this, several prominent officers created a Schnez-Truppe, secret army, unknown to the general public and without mandate from the Allied Control Authority or the West German government.
By the mid-1950s, tensions of the Cold War led to the creation of separate military forces in the West Germany, Federal Republic of Germany and the socialist German Democratic Republic. The West German military, officially created on 5 May 1955, took the name ''Bundeswehr'' (). Its East German counterpart—created on 1 March 1956—took the name National People's Army (german: Nationale Volksarmee). Both organizations employed many former ''Wehrmacht'' members, particularly in their formative years, though neither organization considered themselves successors to the ''Wehrmacht''. However, according to historian Hannes Heer "Germans still have a hard time, when it comes to openly dealing with their Nazi past", as such of the 50 military bases named after ''Wehrmacht'' soldiers, only 16 bases have changed names.
''Wehrmacht'' veterans in West Germany have received pensions through the ''War Victims' Assistance Act'' (german: Bundesversorgungsgesetz) from the government. According to ''The Times of Israel'', "The benefits come through the Federal Pension Act, which was passed in 1950 to support war victims, whether civilians or veterans of the ''Wehrmacht'' or ''Waffen-SS''."
Following the division of Germany, many former ''Wehrmacht'' and ''SS'' officers in West Germany feared a Soviet invasion of the country. To combat this, several prominent officers created a Schnez-Truppe, secret army, unknown to the general public and without mandate from the Allied Control Authority or the West German government.
By the mid-1950s, tensions of the Cold War led to the creation of separate military forces in the West Germany, Federal Republic of Germany and the socialist German Democratic Republic. The West German military, officially created on 5 May 1955, took the name ''Bundeswehr'' (). Its East German counterpart—created on 1 March 1956—took the name National People's Army (german: Nationale Volksarmee). Both organizations employed many former ''Wehrmacht'' members, particularly in their formative years, though neither organization considered themselves successors to the ''Wehrmacht''. However, according to historian Hannes Heer "Germans still have a hard time, when it comes to openly dealing with their Nazi past", as such of the 50 military bases named after ''Wehrmacht'' soldiers, only 16 bases have changed names.
''Wehrmacht'' veterans in West Germany have received pensions through the ''War Victims' Assistance Act'' (german: Bundesversorgungsgesetz) from the government. According to ''The Times of Israel'', "The benefits come through the Federal Pension Act, which was passed in 1950 to support war victims, whether civilians or veterans of the ''Wehrmacht'' or ''Waffen-SS''."
See also
* Bribery of senior Wehrmacht officers * German resistance to Nazism * Glossary of German military terms * Glossary of Nazi Germany * Nazism and the Wehrmacht * Wehrmacht Propaganda TroopsNotes
References
Citations
Bibliography
Printed
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Online
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
''The Wehrmacht: A Criminal Organization?''
Review of Hannes Heer and Klaus Naumann's 1995 work ''Vernichtungskrieg – Verbrechen der Wehrmacht 1941–1944'' by Jörg Bottger
''Wehrmacht Propaganda Troops and the Jews''
– an article by Daniel Uziel
The Nazi German Army 1935–1945
Videos
* "How the Red Army Defeated Germany: The Three Alibis": —lecture by Jonathan House, Jonathan M. House of the U.S. Army Command and General Staff College, via the official channel of Dole Institute of Politics. * "Fighting a Lost War: The German Army in 1943": —lecture by Robert Citino, via the official channel of the U.S. Army Heritage and Education Center. * "Mindset of WWII German Soldiers": —interview with the historian Sönke Neitzel discussing his book ''Soldaten: On Fighting, Killing and Dying'', via the official channel of The Agenda, a programme of TVOntario, a Canadian public television station."A Blind Eye and Dirty Hands: The Wehrmacht's Crimes"
– lecture by the historian Geoffrey P. Megargee, via the YouTube channel of the Wiener Library for the Study of the Holocaust and Genocide {{Authority control Wehrmacht, Disbanded armed forces 1935 establishments in Germany 1946 disestablishments in Germany Military of Nazi Germany Military units and formations established in 1935 Military units and formations disestablished in 1946