Nazi Germany Invaded Poland on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by
 On 22 August, just over a week before the onset of war, Hitler delivered a speech to his military commanders at the
On 22 August, just over a week before the onset of war, Hitler delivered a speech to his military commanders at the  However, there was one exception: on the night of 25–26 August, a German sabotage group which had not heard anything about a delay of the invasion made an attack on the
However, there was one exception: on the night of 25–26 August, a German sabotage group which had not heard anything about a delay of the invasion made an attack on the 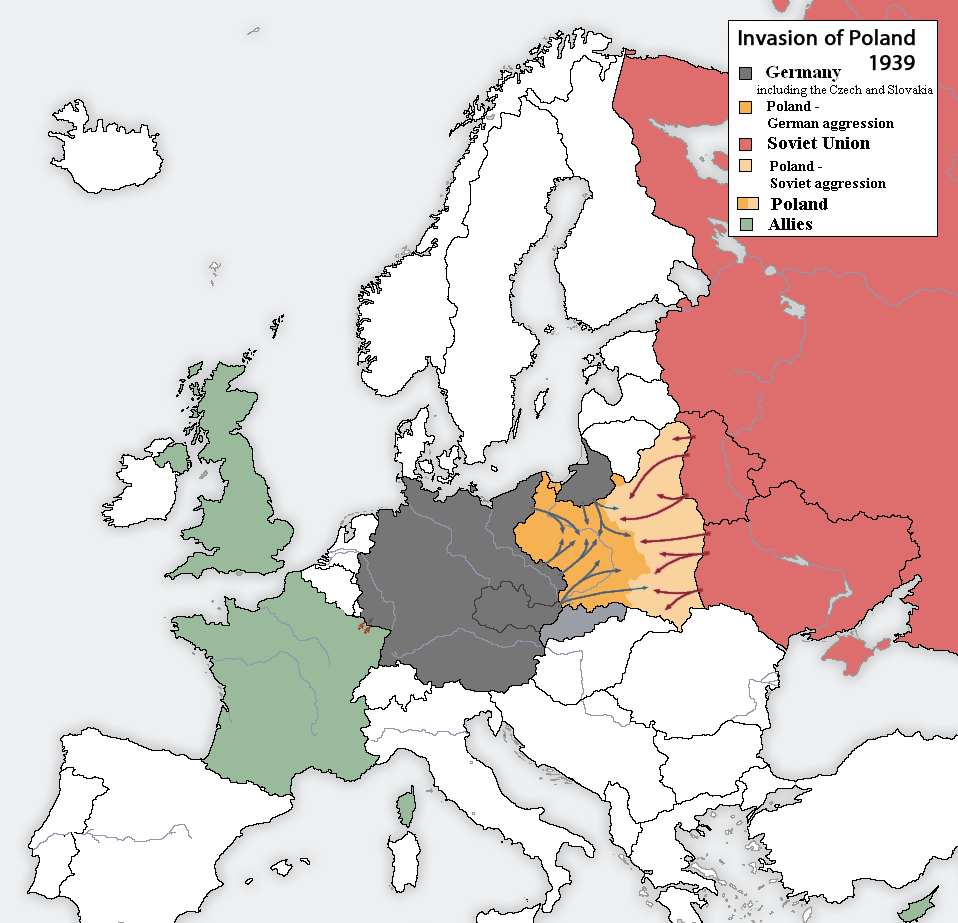 On 29 August, prompted by the British, Germany issued one last diplomatic offer, with ''Fall Weiss'' yet to be rescheduled. That evening, the German government responded in a communication that it aimed not only for the restoration of Danzig but also the Polish Corridor (which had not previously been part of Hitler's demands) in addition to the safeguarding of the
On 29 August, prompted by the British, Germany issued one last diplomatic offer, with ''Fall Weiss'' yet to be rescheduled. That evening, the German government responded in a communication that it aimed not only for the restoration of Danzig but also the Polish Corridor (which had not previously been part of Hitler's demands) in addition to the safeguarding of the
 Emerging in 1918 as an independent country after 123 years after the Partitions of Poland, the
Emerging in 1918 as an independent country after 123 years after the Partitions of Poland, the  An average Polish infantry division consisted of 16,492 soldiers and was equipped with 326 light and medium machine guns, 132 heavy machine guns, 92 anti-tank rifles and several dozen light, medium, heavy, anti-tank and anti-airplane field artillery. Contrary to the 1,009 cars and trucks and 4,842 horses in the average German infantry division, the average Polish infantry division had 76 cars and trucks and 6,939 horses.
The Polish Air Force (''Lotnictwo Wojskowe'') was at a severe disadvantage against the German ''Luftwaffe'' due to inferiority in numbers and the obsolescence of its fighter planes. However, contrary to German propaganda, it was not destroyed on the ground—in fact it was successfully dispersed before the conflict started and not a single one of its combat planes was destroyed on the ground in the first days of the conflict.Michael Alfred Peszke, ''Poland's Preparation for World War II'', ''Military Affairs'' 43 (Feb 1979): 18–24 In the era of fast progress in aviation the Polish Air Force lacked modern fighters, vastly due to the cancellation of many advanced projects, such as the PZL.38 Wilk and a delay in the introduction of a completely new modern Polish fighter PZL.50 Jastrząb. However, its pilots were among the world's best trained, as proven a year later in the Battle of Britain, in which the Poles played a notable part.Michael Alfred Peszke, ''Polish Underground Army, the Western Allies, and the Failure of Strategic Unity in World War II'', McFarland & Company, 2004,
An average Polish infantry division consisted of 16,492 soldiers and was equipped with 326 light and medium machine guns, 132 heavy machine guns, 92 anti-tank rifles and several dozen light, medium, heavy, anti-tank and anti-airplane field artillery. Contrary to the 1,009 cars and trucks and 4,842 horses in the average German infantry division, the average Polish infantry division had 76 cars and trucks and 6,939 horses.
The Polish Air Force (''Lotnictwo Wojskowe'') was at a severe disadvantage against the German ''Luftwaffe'' due to inferiority in numbers and the obsolescence of its fighter planes. However, contrary to German propaganda, it was not destroyed on the ground—in fact it was successfully dispersed before the conflict started and not a single one of its combat planes was destroyed on the ground in the first days of the conflict.Michael Alfred Peszke, ''Poland's Preparation for World War II'', ''Military Affairs'' 43 (Feb 1979): 18–24 In the era of fast progress in aviation the Polish Air Force lacked modern fighters, vastly due to the cancellation of many advanced projects, such as the PZL.38 Wilk and a delay in the introduction of a completely new modern Polish fighter PZL.50 Jastrząb. However, its pilots were among the world's best trained, as proven a year later in the Battle of Britain, in which the Poles played a notable part.Michael Alfred Peszke, ''Polish Underground Army, the Western Allies, and the Failure of Strategic Unity in World War II'', McFarland & Company, 2004,
Google Print, p. 2
/ref>
 Overall, the Germans enjoyed numerical and qualitative aircraft superiority. Poland had only about 600 aircraft, of which only PZL.37 Łoś heavy bombers were modern and comparable to their German counterparts. The Polish Air Force had roughly 185 PZL P.11 and some 95 PZL P.7 fighters, 175 PZL.23 Karaś, PZL.23 ''Karaś'' Bs, 35 ''Karaś'' as light bombers. However, for the September Campaign, not all of those aircraft were mobilized. By 1 September, out of about 120 heavy bombers PZL.37s produced, only 36 PZL.37s were deployed, the rest being mostly in training units. All those aircraft were of indigenous Polish design, with the bombers being more modern than fighters, according to the Ludomił Rayski air force expansion plan, which relied on a strong bomber force. The Polish Air Force consisted of a 'Bomber Brigade', 'Pursuit Brigade' and aircraft assigned to the various ground armies. The Polish fighters were older than their German counterparts; the PZL P.11 fighter—produced in the early 1930s—had a top speed of only , far less than German bombers. To compensate, the pilots relied on its maneuverability and high diving speed. The Polish Air Force's decisions to strengthen its resources came too late, mostly due to budget limitations. As a "last minute" order in the summer of 1939, Poland bought 160 French Morane-Saulnier M.S.406 fighters and 111 English airplanes (100 light bombers Fairey Battle, 10 Hawker Hurricane, Hurricanes and 1 Supermarine Spitfire; the sale of 150 Spitfires asked by the Polish government was rejected by the Air Ministry). Despite the fact that some of the airplanes had been shipped to Poland (the first transport of purchased aircraft on the ship "Lassel" sailed from Liverpool on 28 August), none of them would take part in combat. In late 1938, the Polish Air Force also ordered 300 advanced PZL.46 Sum light bombers, but due to a delay in starting mass production, none of them were delivered before 1 September. When in the spring of 1939 it turned out that there were problems with the implementation of the new PZL.50 Jastrząb fighter, it was decided to temporarily implement the production of the fighter PZL P 11.G Kobuz. Nevertheless, due to the outbreak of the war, not one of the ordered 90 aircraft of this type were delivered to the army.
Overall, the Germans enjoyed numerical and qualitative aircraft superiority. Poland had only about 600 aircraft, of which only PZL.37 Łoś heavy bombers were modern and comparable to their German counterparts. The Polish Air Force had roughly 185 PZL P.11 and some 95 PZL P.7 fighters, 175 PZL.23 Karaś, PZL.23 ''Karaś'' Bs, 35 ''Karaś'' as light bombers. However, for the September Campaign, not all of those aircraft were mobilized. By 1 September, out of about 120 heavy bombers PZL.37s produced, only 36 PZL.37s were deployed, the rest being mostly in training units. All those aircraft were of indigenous Polish design, with the bombers being more modern than fighters, according to the Ludomił Rayski air force expansion plan, which relied on a strong bomber force. The Polish Air Force consisted of a 'Bomber Brigade', 'Pursuit Brigade' and aircraft assigned to the various ground armies. The Polish fighters were older than their German counterparts; the PZL P.11 fighter—produced in the early 1930s—had a top speed of only , far less than German bombers. To compensate, the pilots relied on its maneuverability and high diving speed. The Polish Air Force's decisions to strengthen its resources came too late, mostly due to budget limitations. As a "last minute" order in the summer of 1939, Poland bought 160 French Morane-Saulnier M.S.406 fighters and 111 English airplanes (100 light bombers Fairey Battle, 10 Hawker Hurricane, Hurricanes and 1 Supermarine Spitfire; the sale of 150 Spitfires asked by the Polish government was rejected by the Air Ministry). Despite the fact that some of the airplanes had been shipped to Poland (the first transport of purchased aircraft on the ship "Lassel" sailed from Liverpool on 28 August), none of them would take part in combat. In late 1938, the Polish Air Force also ordered 300 advanced PZL.46 Sum light bombers, but due to a delay in starting mass production, none of them were delivered before 1 September. When in the spring of 1939 it turned out that there were problems with the implementation of the new PZL.50 Jastrząb fighter, it was decided to temporarily implement the production of the fighter PZL P 11.G Kobuz. Nevertheless, due to the outbreak of the war, not one of the ordered 90 aircraft of this type were delivered to the army.
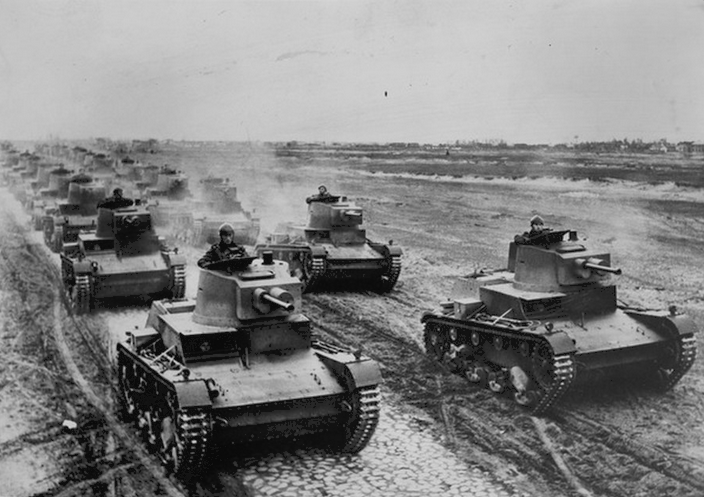 The tank force consisted of two armored brigades, four independent tank battalions and some 30 companies of TKS tankettes attached to infantry divisions and cavalry brigades. A standard tank of the Polish Army during the invasion of 1939 was the 7TP light tank. It was the first tank in the world to be equipped with a diesel engine and Vickers Tank Periscope MK.IV, 360° Gundlach periscope. The 7TP was significantly better armed than its most common opponents, the German Panzer I, ''Panzer'' I and Panzer II, II, but only 140 tanks were produced between 1935 and the outbreak of the war. Poland had also a few relatively modern imported designs, such as 50 Renault R35 tanks and 38 Vickers E tanks.
The Polish Navy was a small fleet of destroyers, submarines and smaller support vessels. Most Polish surface units followed Operation Peking, leaving Polish ports on 20 August and escaping by way of the North Sea to join with the British Royal Navy. Submarine forces participated in Worek Plan, Operation Worek, with the goal of engaging and damaging German shipping in the Baltic Sea, but they had much less success. In addition, many Ship transport, merchant marine ships joined the British merchant fleet and took part in wartime convoys.
The tank force consisted of two armored brigades, four independent tank battalions and some 30 companies of TKS tankettes attached to infantry divisions and cavalry brigades. A standard tank of the Polish Army during the invasion of 1939 was the 7TP light tank. It was the first tank in the world to be equipped with a diesel engine and Vickers Tank Periscope MK.IV, 360° Gundlach periscope. The 7TP was significantly better armed than its most common opponents, the German Panzer I, ''Panzer'' I and Panzer II, II, but only 140 tanks were produced between 1935 and the outbreak of the war. Poland had also a few relatively modern imported designs, such as 50 Renault R35 tanks and 38 Vickers E tanks.
The Polish Navy was a small fleet of destroyers, submarines and smaller support vessels. Most Polish surface units followed Operation Peking, leaving Polish ports on 20 August and escaping by way of the North Sea to join with the British Royal Navy. Submarine forces participated in Worek Plan, Operation Worek, with the goal of engaging and damaging German shipping in the Baltic Sea, but they had much less success. In addition, many Ship transport, merchant marine ships joined the British merchant fleet and took part in wartime convoys.
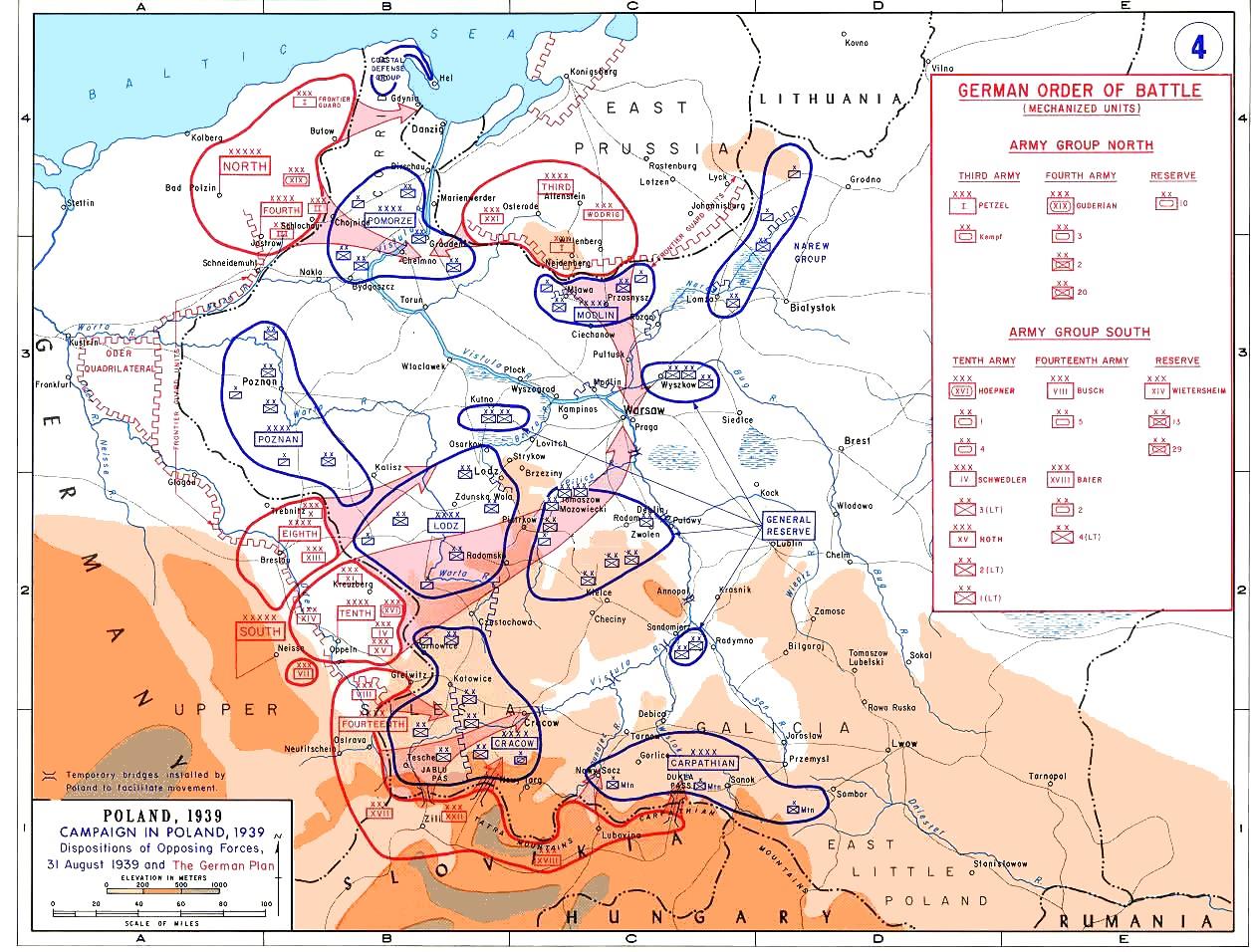 The September Campaign was devised by General Franz Halder, the Chief of the General Staff (Germany), chief of the general staff, and directed by General Walther von Brauchitsch, the commander in chief of the upcoming campaign. It called for the start of hostilities before a declaration of war, and pursued a doctrine of mass encirclement and destruction of enemy forces. The infantry, far from completely mechanized but fitted with fast-moving artillery and logistic support, was to be supported by ''Panzers'' and small numbers of truck-mounted infantry (the ''Schützen'' regiments, forerunners of the ''panzergrenadiers'') to assist the rapid movement of troops and concentrate on Schwerpunkt, localized parts of the enemy military front, front, eventually isolating segments of the enemy, surrounding, and destroying them. The prewar "armoured idea", which an American journalist in 1939 dubbed ''Blitzkrieg'', which was advocated by some generals, including Heinz Guderian, would have had the armour punching holes in the enemy's front and ranging deep into rear areas, but the campaign in Poland would be fought along more traditional lines. That stemmed from conservatism on the part of the German High Command, which mainly restricted the role of armour and mechanized forces to supporting the conventional infantry divisions.
Poland's terrain was well suited for mobile operations when the weather co-operated; the country had flat plains, with long frontiers totalling almost , Poland's long border with Germany on the west and north, facing East Prussia, extended . They had been lengthened by another on the southern side in the aftermath of the 1938 Munich Agreement. The German incorporation of Bohemia and Moravia and creation of the German
The September Campaign was devised by General Franz Halder, the Chief of the General Staff (Germany), chief of the general staff, and directed by General Walther von Brauchitsch, the commander in chief of the upcoming campaign. It called for the start of hostilities before a declaration of war, and pursued a doctrine of mass encirclement and destruction of enemy forces. The infantry, far from completely mechanized but fitted with fast-moving artillery and logistic support, was to be supported by ''Panzers'' and small numbers of truck-mounted infantry (the ''Schützen'' regiments, forerunners of the ''panzergrenadiers'') to assist the rapid movement of troops and concentrate on Schwerpunkt, localized parts of the enemy military front, front, eventually isolating segments of the enemy, surrounding, and destroying them. The prewar "armoured idea", which an American journalist in 1939 dubbed ''Blitzkrieg'', which was advocated by some generals, including Heinz Guderian, would have had the armour punching holes in the enemy's front and ranging deep into rear areas, but the campaign in Poland would be fought along more traditional lines. That stemmed from conservatism on the part of the German High Command, which mainly restricted the role of armour and mechanized forces to supporting the conventional infantry divisions.
Poland's terrain was well suited for mobile operations when the weather co-operated; the country had flat plains, with long frontiers totalling almost , Poland's long border with Germany on the west and north, facing East Prussia, extended . They had been lengthened by another on the southern side in the aftermath of the 1938 Munich Agreement. The German incorporation of Bohemia and Moravia and creation of the German
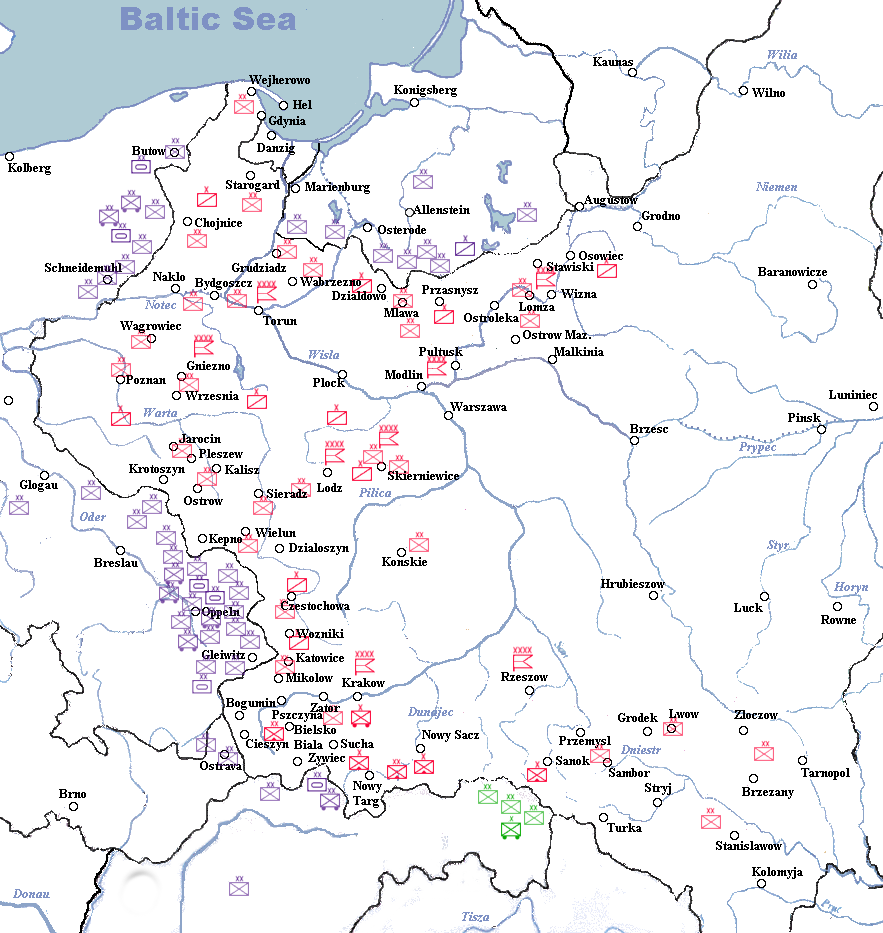 The Polish determination to deploy forces directly at the German-Polish border, prompted by the
The Polish determination to deploy forces directly at the German-Polish border, prompted by the  The Polish General Staff had not begun elaborating the "West" defence plan until 4 March 1939. It was assumed that the Polish Army, fighting in the initial phase of the war alone, would have to defend the western regions of the country. The plan of operations took into account the numerical and material superiority of the enemy and, also assumed the defensive character of Polish operations. The Polish intentions were defending the western regions that were judged as indispensable for waging the war, taking advantage of the propitious conditions for counterattacks by reserve units and avoiding it from being smashed before the beginning of Franco-British operations in Western Europe. The operation plan had not been elaborated in detail and concerned only the first stage of operations.
The British and the French estimated that Poland would be able to defend itself for two to three months, and Poland estimated it could do so for at least six months. While Poland drafted its estimates based upon the expectation that the Western Allies would honor their treaty obligations and quickly start an offensive of their own, the French and the British expected the war to develop into trench warfare, much like World War I. The Polish government was not notified of the strategy and based all of its defence plans on promises of quick relief by the Western Allies.
Polish forces were stretched thinly along the Polish-German border and lacked compact defence lines and good defence positions along disadvantageous terrain. That strategy also left supply lines poorly protected. One-third of Poland's forces were massed in or near the Polish Corridor, making them vulnerable to a pincer movement, double envelopment from East Prussia and the west. Another third was concentrated in the north-central part of the country, between the major cities of Łódź and Warsaw. The forward positioning of Polish forces vastly increased the difficulty of carrying out strategic maneuvres, compounded by inadequate mobility, as Polish units often lacked the ability to retreat from their defensive positions, as they were being overrun by more mobile German mechanized formations.
The Polish General Staff had not begun elaborating the "West" defence plan until 4 March 1939. It was assumed that the Polish Army, fighting in the initial phase of the war alone, would have to defend the western regions of the country. The plan of operations took into account the numerical and material superiority of the enemy and, also assumed the defensive character of Polish operations. The Polish intentions were defending the western regions that were judged as indispensable for waging the war, taking advantage of the propitious conditions for counterattacks by reserve units and avoiding it from being smashed before the beginning of Franco-British operations in Western Europe. The operation plan had not been elaborated in detail and concerned only the first stage of operations.
The British and the French estimated that Poland would be able to defend itself for two to three months, and Poland estimated it could do so for at least six months. While Poland drafted its estimates based upon the expectation that the Western Allies would honor their treaty obligations and quickly start an offensive of their own, the French and the British expected the war to develop into trench warfare, much like World War I. The Polish government was not notified of the strategy and based all of its defence plans on promises of quick relief by the Western Allies.
Polish forces were stretched thinly along the Polish-German border and lacked compact defence lines and good defence positions along disadvantageous terrain. That strategy also left supply lines poorly protected. One-third of Poland's forces were massed in or near the Polish Corridor, making them vulnerable to a pincer movement, double envelopment from East Prussia and the west. Another third was concentrated in the north-central part of the country, between the major cities of Łódź and Warsaw. The forward positioning of Polish forces vastly increased the difficulty of carrying out strategic maneuvres, compounded by inadequate mobility, as Polish units often lacked the ability to retreat from their defensive positions, as they were being overrun by more mobile German mechanized formations.
 As the prospect of conflict increased, the British government pressed Marshal Edward Śmigły-Rydz to evacuate the most modern elements of the Polish Navy from the Baltic Sea. In the event of war, the Polish military leaders realized that the ships that remained in the Baltic were likely to be quickly sunk by the Germans. Furthermore, since the Danish Straits were well within operating range of the German ''Kriegsmarine'' and ''Luftwaffe'', there was little chance of an evacuation plan succeeding if it were implemented after hostilities began. Four days after the signing of the Polish-British Common Defence Pact, three destroyers of the Polish Navy executed the Peking Plan and so evacuated to Great Britain.
Although the Polish military had prepared for conflict, the civilian population remained largely unprepared. Polish prewar propaganda emphasized that any German invasion would be easily repelled. That made Polish defeats during the German invasion come as a shock to the civilian population. Lacking training for such a disaster, the civilian population panicked and retreated east, spreading chaos, lowering the troops' morale and making road transportation for Polish troops very difficult. The propaganda also had some negative consequences for the Polish troops themselves, whose communications, disrupted by German mobile units operating in the rear and civilians blocking roads, were further thrown into chaos by bizarre reports from Polish radio stations and newspapers, which often reported imaginary victories and other military operations. That led to some Polish troops being encircled or taking a stand against overwhelming odds when they thought they were actually counterattacking or would soon receive reinforcements from other victorious areas.
As the prospect of conflict increased, the British government pressed Marshal Edward Śmigły-Rydz to evacuate the most modern elements of the Polish Navy from the Baltic Sea. In the event of war, the Polish military leaders realized that the ships that remained in the Baltic were likely to be quickly sunk by the Germans. Furthermore, since the Danish Straits were well within operating range of the German ''Kriegsmarine'' and ''Luftwaffe'', there was little chance of an evacuation plan succeeding if it were implemented after hostilities began. Four days after the signing of the Polish-British Common Defence Pact, three destroyers of the Polish Navy executed the Peking Plan and so evacuated to Great Britain.
Although the Polish military had prepared for conflict, the civilian population remained largely unprepared. Polish prewar propaganda emphasized that any German invasion would be easily repelled. That made Polish defeats during the German invasion come as a shock to the civilian population. Lacking training for such a disaster, the civilian population panicked and retreated east, spreading chaos, lowering the troops' morale and making road transportation for Polish troops very difficult. The propaganda also had some negative consequences for the Polish troops themselves, whose communications, disrupted by German mobile units operating in the rear and civilians blocking roads, were further thrown into chaos by bizarre reports from Polish radio stations and newspapers, which often reported imaginary victories and other military operations. That led to some Polish troops being encircled or taking a stand against overwhelming odds when they thought they were actually counterattacking or would soon receive reinforcements from other victorious areas.
 Following several German-staged incidents, such as the
Following several German-staged incidents, such as the  France and Britain declared war on Germany on 3 September, but Western betrayal, failed to provide any meaningful support. The German-French border Saar Offensive, saw only a few minor skirmishes, and most German forces, including 85% of armoured forces, were engaged in Poland. Despite some Polish successes in minor border battles, the German technical, operational and numerical superiority forced the Polish armies to retreat from the borders towards Warsaw and Lwów. The ''Luftwaffe'' gained air superiority early in the campaign. By destroying communications, the ''Luftwaffe'' increased the pace of the advance which overran Polish airstrips and early warning sites, causing logistical problems for the Poles. Many Polish Air Force units ran low on supplies, and 98 of their number withdrew into neutral Romania. The Polish initial strength of 400 was reduced to 54 by 14 September and air opposition virtually ceased, with the main Polish air bases destroyed during the first 48 hours of the war.
France and Britain declared war on Germany on 3 September, but Western betrayal, failed to provide any meaningful support. The German-French border Saar Offensive, saw only a few minor skirmishes, and most German forces, including 85% of armoured forces, were engaged in Poland. Despite some Polish successes in minor border battles, the German technical, operational and numerical superiority forced the Polish armies to retreat from the borders towards Warsaw and Lwów. The ''Luftwaffe'' gained air superiority early in the campaign. By destroying communications, the ''Luftwaffe'' increased the pace of the advance which overran Polish airstrips and early warning sites, causing logistical problems for the Poles. Many Polish Air Force units ran low on supplies, and 98 of their number withdrew into neutral Romania. The Polish initial strength of 400 was reduced to 54 by 14 September and air opposition virtually ceased, with the main Polish air bases destroyed during the first 48 hours of the war.
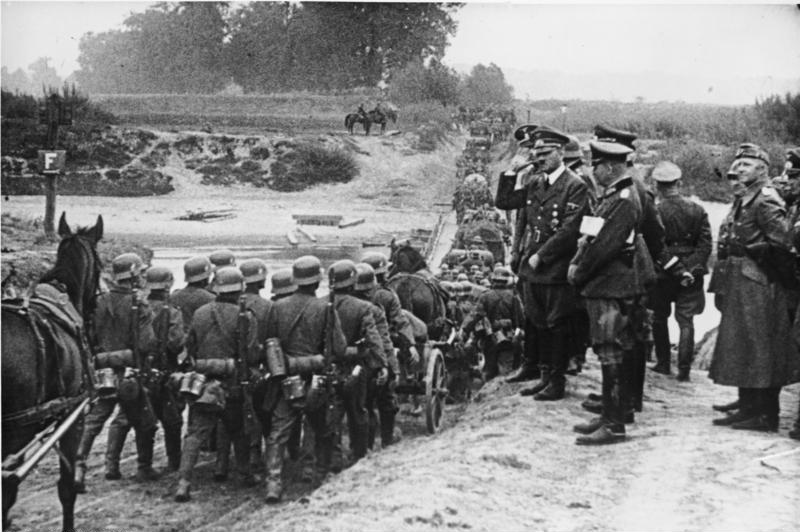 Germany attacked from three directions on land. Günther von Kluge led 20 divisions that entered the Polish Corridor and met a second force heading to Warsaw from East Prussia. Gerd von Rundstedt's 35 divisions attacked southern Poland. By 3 September, when von Kluge in the north had reached the Vistula River, then some from the German border, and Georg von Küchler was approaching the Narew River, Walther von Reichenau's armour was already beyond the Warta river. Two days later, his left wing was well to the rear of Łódź and his right wing at the town of Kielce. On 7 September, the defenders of Warsaw had fallen back to a line paralleling the Vistula River, where they rallied against German tank thrusts. The defensive line ran between Płońsk and Pułtusk, respectively north-west and north-east of Warsaw. The right wing of the Poles had been hammered back from Ciechanów, about north-west of Pułtusk, and was pivoting on Płońsk. At one stage, the Poles were driven from Pułtusk, and the Germans threatened to turn the Polish flank and thrust on to the Vistula and Warsaw. Pułtusk, however, was regained in the face of withering German fire. Many German tanks were captured after a German attack had pierced the line, but the Polish defenders outflanked them. By 8 September, one of Reichenau's armoured corps, having advanced during the first week of the campaign, reached the outskirts of Warsaw. Light divisions on Reichenau's right were on the Vistula between Warsaw and the town of Sandomierz by 9 September, and List, in the south, was on the San River north and south of the town of Przemyśl. At the same time, Guderian led his 3rd Army tanks across the Narew, attacking the line of the Bug River that had already encircled Warsaw. All of the German armies made progress in fulfilling their parts of the plan. The Polish armies split up into uncoordinated fragments, some of which were retreating while others were launching disjointed attacks on the nearest German columns.
Germany attacked from three directions on land. Günther von Kluge led 20 divisions that entered the Polish Corridor and met a second force heading to Warsaw from East Prussia. Gerd von Rundstedt's 35 divisions attacked southern Poland. By 3 September, when von Kluge in the north had reached the Vistula River, then some from the German border, and Georg von Küchler was approaching the Narew River, Walther von Reichenau's armour was already beyond the Warta river. Two days later, his left wing was well to the rear of Łódź and his right wing at the town of Kielce. On 7 September, the defenders of Warsaw had fallen back to a line paralleling the Vistula River, where they rallied against German tank thrusts. The defensive line ran between Płońsk and Pułtusk, respectively north-west and north-east of Warsaw. The right wing of the Poles had been hammered back from Ciechanów, about north-west of Pułtusk, and was pivoting on Płońsk. At one stage, the Poles were driven from Pułtusk, and the Germans threatened to turn the Polish flank and thrust on to the Vistula and Warsaw. Pułtusk, however, was regained in the face of withering German fire. Many German tanks were captured after a German attack had pierced the line, but the Polish defenders outflanked them. By 8 September, one of Reichenau's armoured corps, having advanced during the first week of the campaign, reached the outskirts of Warsaw. Light divisions on Reichenau's right were on the Vistula between Warsaw and the town of Sandomierz by 9 September, and List, in the south, was on the San River north and south of the town of Przemyśl. At the same time, Guderian led his 3rd Army tanks across the Narew, attacking the line of the Bug River that had already encircled Warsaw. All of the German armies made progress in fulfilling their parts of the plan. The Polish armies split up into uncoordinated fragments, some of which were retreating while others were launching disjointed attacks on the nearest German columns.

 Polish forces abandoned the regions of Pomerelia (the Polish Corridor), Greater Poland and Silesian Voivodeship (1920–1939), Polish Upper Silesia in the first week. The Polish plan for border defence was a dismal failure. The German advance, as a whole, was not slowed. On 10 September, the Polish commander-in-chief, Marshal Edward Rydz-Śmigły, ordered a general withdrawal (military), retreat to the south-east, towards the Romanian Bridgehead. Meanwhile, the Germans were tightening their encirclement of the Polish forces west of the Vistula (in the Łódź area and, still farther west, around Poznań) and penetrating deeply into eastern Poland. Warsaw, which had undergone heavy aerial bombardment since the first hours of the war, was attacked on 9 September and was Siege of Warsaw (1939), put under siege on 13 September. Around then, advanced German forces also reached Lwów, a major city in eastern Poland, and 1,150 German aircraft bombed Warsaw on 24 September.
The Polish defensive plan called for a strategy of encirclement. It would allow the Germans to advance in between two Polish Army groups in the line between Berlin and Warsaw-Lodz, and Armia Prusy would then move in and repulse the German spearhead, trapping it. For that to happen, Armia Prusy needed to be fully mobilized by 3 September. However, Polish military planners failed to foresee the speed of the German advance and assumed that Armia Prusy would need to be fully mobilized by 16 September.
Polish forces abandoned the regions of Pomerelia (the Polish Corridor), Greater Poland and Silesian Voivodeship (1920–1939), Polish Upper Silesia in the first week. The Polish plan for border defence was a dismal failure. The German advance, as a whole, was not slowed. On 10 September, the Polish commander-in-chief, Marshal Edward Rydz-Śmigły, ordered a general withdrawal (military), retreat to the south-east, towards the Romanian Bridgehead. Meanwhile, the Germans were tightening their encirclement of the Polish forces west of the Vistula (in the Łódź area and, still farther west, around Poznań) and penetrating deeply into eastern Poland. Warsaw, which had undergone heavy aerial bombardment since the first hours of the war, was attacked on 9 September and was Siege of Warsaw (1939), put under siege on 13 September. Around then, advanced German forces also reached Lwów, a major city in eastern Poland, and 1,150 German aircraft bombed Warsaw on 24 September.
The Polish defensive plan called for a strategy of encirclement. It would allow the Germans to advance in between two Polish Army groups in the line between Berlin and Warsaw-Lodz, and Armia Prusy would then move in and repulse the German spearhead, trapping it. For that to happen, Armia Prusy needed to be fully mobilized by 3 September. However, Polish military planners failed to foresee the speed of the German advance and assumed that Armia Prusy would need to be fully mobilized by 16 September.
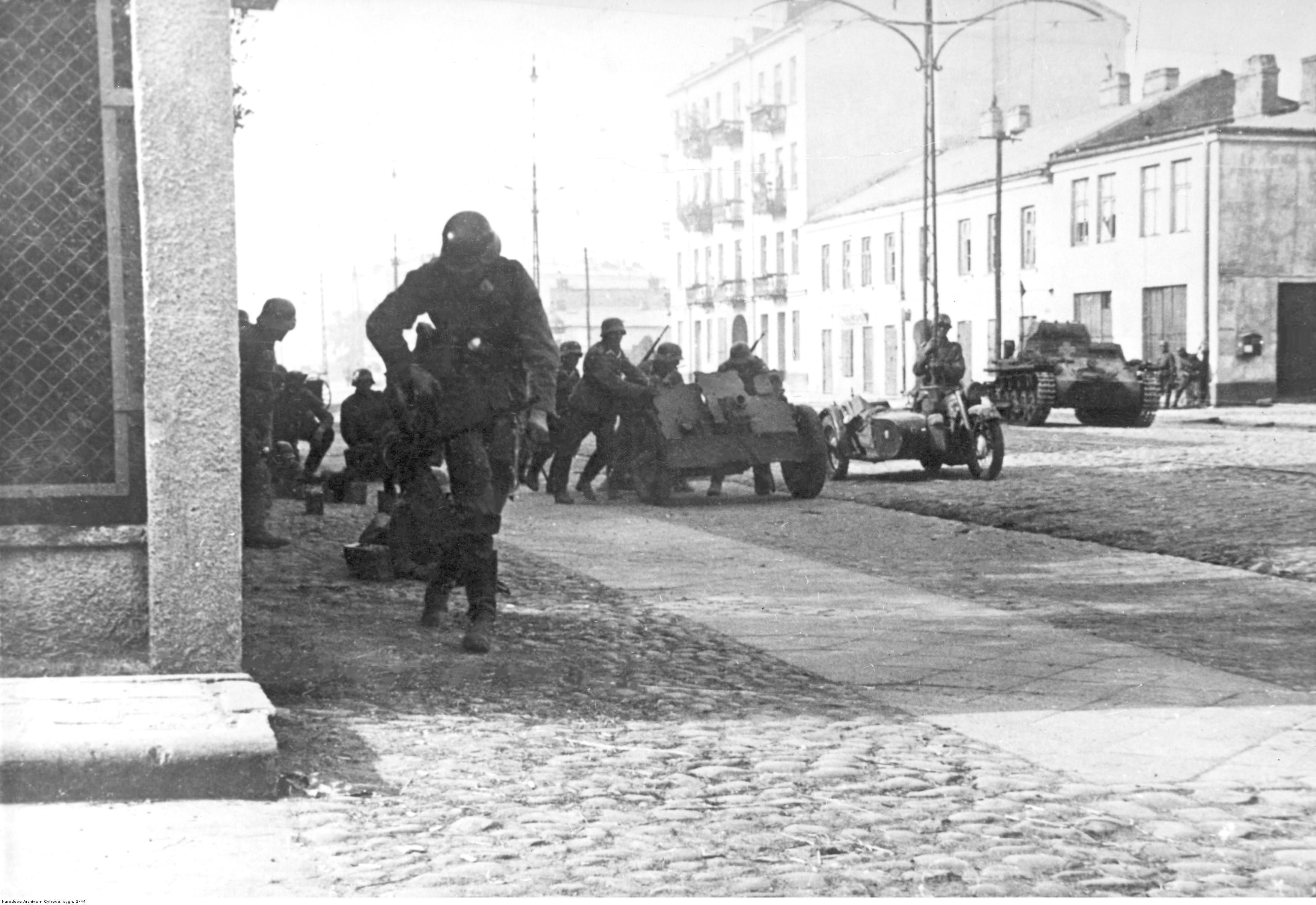
 The largest battle during this campaign, the Battle of Bzura, took place near the Bzura River, west of Warsaw, and lasted from 9 to 19 September. The Polish armies ''Poznań'' and ''Pomorze'', retreating from the border area of the Polish Corridor, attacked the flank of the advancing German 8th Army, but the counterattack failed despite initial success. After the defeat, Poland lost its ability to take the initiative and counterattack on a large scale. The German air power was instrumental during the battle. The offensive of the ''Luftwaffe'' broke what remained of the Polish resistance in an "awesome demonstration of air power". The ''Luftwaffe'' quickly destroyed the bridges across the Bzura River. Then, the Polish forces were trapped out in the open and were attacked by wave after wave of ''Stukas'', dropping light bombs, which caused huge numbers of casualties. The Polish anti-aircraft warfare, anti-aircraft batteries ran out of ammunition and retreated to the forests but were then smoked out by the
The largest battle during this campaign, the Battle of Bzura, took place near the Bzura River, west of Warsaw, and lasted from 9 to 19 September. The Polish armies ''Poznań'' and ''Pomorze'', retreating from the border area of the Polish Corridor, attacked the flank of the advancing German 8th Army, but the counterattack failed despite initial success. After the defeat, Poland lost its ability to take the initiative and counterattack on a large scale. The German air power was instrumental during the battle. The offensive of the ''Luftwaffe'' broke what remained of the Polish resistance in an "awesome demonstration of air power". The ''Luftwaffe'' quickly destroyed the bridges across the Bzura River. Then, the Polish forces were trapped out in the open and were attacked by wave after wave of ''Stukas'', dropping light bombs, which caused huge numbers of casualties. The Polish anti-aircraft warfare, anti-aircraft batteries ran out of ammunition and retreated to the forests but were then smoked out by the
 From the beginning, the German government repeatedly asked Molotov whether the Soviet Union would keep to its side of the partition bargain. The Soviet forces were holding fast along their designated invasion points pending finalization of the five-month-long undeclared war with Japan in the Far East, successful end of the conflict for the Soviet Union, which occurred in the Battles of Khalkhin Gol. On 15 September 1939, Molotov and Shigenori Tōgō completed their agreement that ended the conflict, and the Nomonhan ceasefire went into effect on 16 September 1939. Now cleared of any "second front" threat from the Japanese, Soviet Premier Joseph Stalin ordered his forces into Poland on 17 September.Goldman pp. 163, 164 It was agreed that the Soviets would relinquish its interest in the territories between the new border and Warsaw in exchange for inclusion of Lithuania in the Soviet "zone of interest".
By 17 September, the Polish defence had already been broken and the only hope was to retreat and reorganize along the Romanian Bridgehead. However, the plans were rendered obsolete nearly overnight when the over 800,000-strong Soviet
From the beginning, the German government repeatedly asked Molotov whether the Soviet Union would keep to its side of the partition bargain. The Soviet forces were holding fast along their designated invasion points pending finalization of the five-month-long undeclared war with Japan in the Far East, successful end of the conflict for the Soviet Union, which occurred in the Battles of Khalkhin Gol. On 15 September 1939, Molotov and Shigenori Tōgō completed their agreement that ended the conflict, and the Nomonhan ceasefire went into effect on 16 September 1939. Now cleared of any "second front" threat from the Japanese, Soviet Premier Joseph Stalin ordered his forces into Poland on 17 September.Goldman pp. 163, 164 It was agreed that the Soviets would relinquish its interest in the territories between the new border and Warsaw in exchange for inclusion of Lithuania in the Soviet "zone of interest".
By 17 September, the Polish defence had already been broken and the only hope was to retreat and reorganize along the Romanian Bridgehead. However, the plans were rendered obsolete nearly overnight when the over 800,000-strong Soviet  The Polish border defence forces in the east, known as the ''Korpus Ochrony Pogranicza'', had about 25 battalions. Rydz-Śmigły ordered them to fall back and not to engage the Soviets. That, however, did not prevent some clashes and small battles, such as the Battle of Grodno (1939), Battle of Grodno, as soldiers and locals attempted to defend the city. The Soviets executed numerous Polish officers, including prisoner of war, prisoners of war like General Józef Olszyna-Wilczyński. The Organization of Ukrainian Nationalists rose against the Poles, and communist partisans organized local revolts, robbing and killing civilians. Those movements were quickly disciplined by the NKVD. The Soviet invasion was one of the decisive factors that convinced the Polish government that the war in Poland was lost. Before the Soviet attack from the east, the Polish military's plan had called for long-term defence against Germany in south-eastern Poland and to await relief from an attack by the Western Allies on Germany's western border. However, the Polish government refused to surrender or to negotiate peace with Germany. Instead, it ordered all units to evacuate Poland and to reorganize in France.
The Polish border defence forces in the east, known as the ''Korpus Ochrony Pogranicza'', had about 25 battalions. Rydz-Śmigły ordered them to fall back and not to engage the Soviets. That, however, did not prevent some clashes and small battles, such as the Battle of Grodno (1939), Battle of Grodno, as soldiers and locals attempted to defend the city. The Soviets executed numerous Polish officers, including prisoner of war, prisoners of war like General Józef Olszyna-Wilczyński. The Organization of Ukrainian Nationalists rose against the Poles, and communist partisans organized local revolts, robbing and killing civilians. Those movements were quickly disciplined by the NKVD. The Soviet invasion was one of the decisive factors that convinced the Polish government that the war in Poland was lost. Before the Soviet attack from the east, the Polish military's plan had called for long-term defence against Germany in south-eastern Poland and to await relief from an attack by the Western Allies on Germany's western border. However, the Polish government refused to surrender or to negotiate peace with Germany. Instead, it ordered all units to evacuate Poland and to reorganize in France.
 Meanwhile, Polish forces tried to move towards the Romanian Bridgehead area, still actively resisting the German invasion. From 17 to 20 September, Polish armies ''Kraków'' and ''Lublin'' were crippled at the Battle of Tomaszów Lubelski, the second-largest battle of the campaign. Lwów capitulated on 22 September because of the Soviet intervention; the city had been attacked by the Germans over a week earlier, and in the middle of the siege, the German troops handed operations over to their Soviet allies. Despite a series of intensifying German attacks, Warsaw, defended by quickly-reorganized retreating units, civilian volunteers and militias, held out until 28 September. The Modlin Fortress north of Warsaw capitulated on 29 September, after Battle of Modlin, an intense 16-day battle. Some isolated Polish garrisons managed to hold their positions long after they had been surrounded by German forces. The enclave of Westerplatte's tiny garrison capitulated on 7 September and the Oksywie garrison Battle of Kępa Oksywska, held until 19 September; the Hel Fortified Area Battle of Hel, was defended until 2 October. In the last week of September, Hitler made a speech in Danzig and said:
Despite a Polish victory at the Battle of Szack (the Soviets later executed all the officers and non-commissioned officer, NCOs they had captured), the Red Army reached the line of rivers Narew, Bug, Vistula and San by 28 September, in many cases meeting German units advancing from the other direction. Polish defenders on the Hel Peninsula on the shore of the Baltic Sea held out until 2 October. The last operational unit of the Polish Army, General Franciszek Kleeberg's ''Independent Operational Group Polesie, Samodzielna Grupa Operacyjna "Polesie"'', surrendered after the four-day Battle of Kock near Lublin on 6 October, marking the end of the September Campaign.
Meanwhile, Polish forces tried to move towards the Romanian Bridgehead area, still actively resisting the German invasion. From 17 to 20 September, Polish armies ''Kraków'' and ''Lublin'' were crippled at the Battle of Tomaszów Lubelski, the second-largest battle of the campaign. Lwów capitulated on 22 September because of the Soviet intervention; the city had been attacked by the Germans over a week earlier, and in the middle of the siege, the German troops handed operations over to their Soviet allies. Despite a series of intensifying German attacks, Warsaw, defended by quickly-reorganized retreating units, civilian volunteers and militias, held out until 28 September. The Modlin Fortress north of Warsaw capitulated on 29 September, after Battle of Modlin, an intense 16-day battle. Some isolated Polish garrisons managed to hold their positions long after they had been surrounded by German forces. The enclave of Westerplatte's tiny garrison capitulated on 7 September and the Oksywie garrison Battle of Kępa Oksywska, held until 19 September; the Hel Fortified Area Battle of Hel, was defended until 2 October. In the last week of September, Hitler made a speech in Danzig and said:
Despite a Polish victory at the Battle of Szack (the Soviets later executed all the officers and non-commissioned officer, NCOs they had captured), the Red Army reached the line of rivers Narew, Bug, Vistula and San by 28 September, in many cases meeting German units advancing from the other direction. Polish defenders on the Hel Peninsula on the shore of the Baltic Sea held out until 2 October. The last operational unit of the Polish Army, General Franciszek Kleeberg's ''Independent Operational Group Polesie, Samodzielna Grupa Operacyjna "Polesie"'', surrendered after the four-day Battle of Kock near Lublin on 6 October, marking the end of the September Campaign.
 The Polish Campaign was the first action by Hitler in his attempt to create ''Lebensraum'' (living space) for Germans. Nazi propaganda was one of the factors behind the German brutality directed at civilians that had worked relentlessly to convince the Germans into believing that Jews and Slavs were ''Untermenschen'' (subhumans).
The Polish Campaign was the first action by Hitler in his attempt to create ''Lebensraum'' (living space) for Germans. Nazi propaganda was one of the factors behind the German brutality directed at civilians that had worked relentlessly to convince the Germans into believing that Jews and Slavs were ''Untermenschen'' (subhumans).
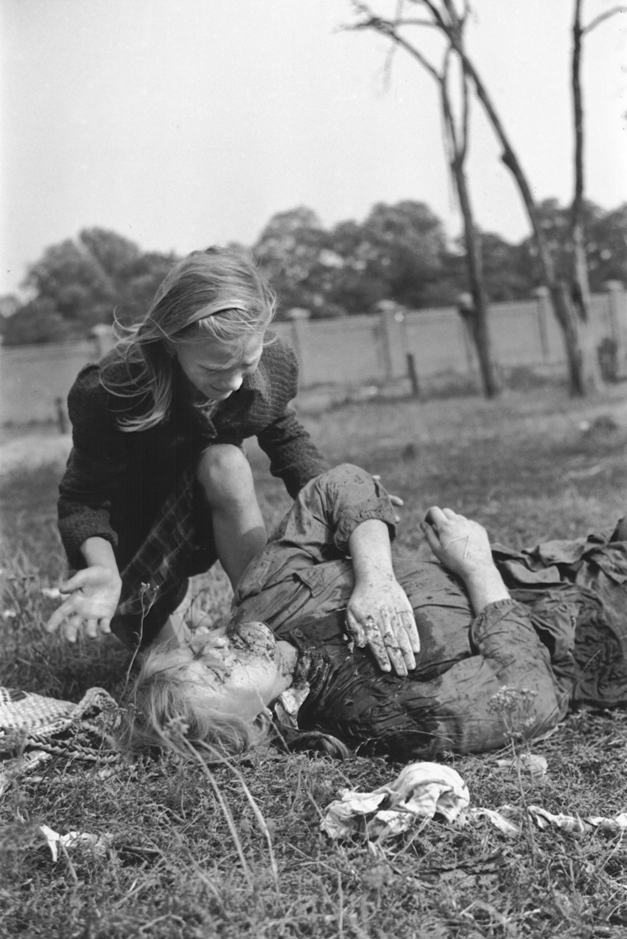 From the first day of invasion, the German air force (the ''Luftwaffe'') attacked civilian targets and columns of refugees along the roads to terrorize the Polish people, disrupt communications and target Polish morale. The ''Luftwaffe'' killed 6,000 to 7,000 Polish civilians during the Bombing of Warsaw in World War II, bombing of Warsaw.
The German invasion saw atrocities committed against Polish men, women and children. The German forces (both SS and the regular ''Wehrmacht'') murdered tens of thousands of Polish civilians (such as the Leibstandarte SS Adolf Hitler was notorious throughout the campaign for burning villages and committing atrocities in numerous Polish towns, including massacres in Błonie, Złoczew, Bolesławiec, Łódź Voivodeship, Bolesławiec, Torzeniec, Goworowo, Mława and Włocławek).
During Operation Tannenberg, a campaign of ethnic cleansing organized by multiple elements of the German government, tens of thousands of Polish civilians were shot at 760 mass execution sites by the ''Einsatzgruppen''.
Altogether, the civilian losses of Polish population amounted to about 150,000 to 200,000. Roughly 1,250 German civilians were also killed during the invasion. (Also, 2,000 died fighting Polish troops as members of ethnic German militia forces such as the ''Volksdeutscher Selbstschutz'', which was a fifth column during the invasion.)
From the first day of invasion, the German air force (the ''Luftwaffe'') attacked civilian targets and columns of refugees along the roads to terrorize the Polish people, disrupt communications and target Polish morale. The ''Luftwaffe'' killed 6,000 to 7,000 Polish civilians during the Bombing of Warsaw in World War II, bombing of Warsaw.
The German invasion saw atrocities committed against Polish men, women and children. The German forces (both SS and the regular ''Wehrmacht'') murdered tens of thousands of Polish civilians (such as the Leibstandarte SS Adolf Hitler was notorious throughout the campaign for burning villages and committing atrocities in numerous Polish towns, including massacres in Błonie, Złoczew, Bolesławiec, Łódź Voivodeship, Bolesławiec, Torzeniec, Goworowo, Mława and Włocławek).
During Operation Tannenberg, a campaign of ethnic cleansing organized by multiple elements of the German government, tens of thousands of Polish civilians were shot at 760 mass execution sites by the ''Einsatzgruppen''.
Altogether, the civilian losses of Polish population amounted to about 150,000 to 200,000. Roughly 1,250 German civilians were also killed during the invasion. (Also, 2,000 died fighting Polish troops as members of ethnic German militia forces such as the ''Volksdeutscher Selbstschutz'', which was a fifth column during the invasion.)
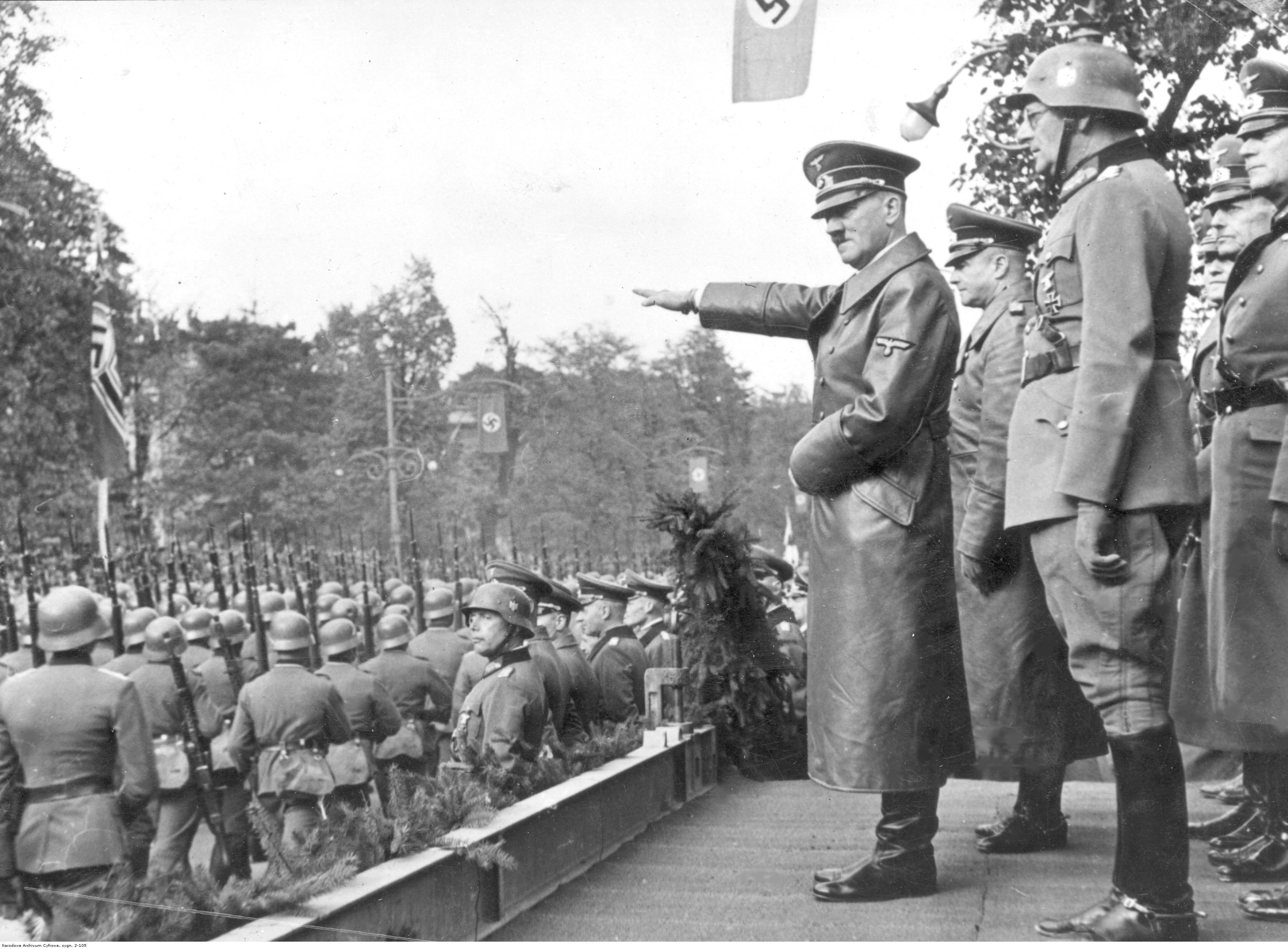 John Gunther wrote in December 1939 that "the German campaign was a masterpiece. Nothing quite like it has been seen in military history". The country was divided between Germany and the Soviet Union. Slovak Republic (WWII), Slovakia gained back those territories taken by Poland in autumn 1938. Lithuania Vilnius#World War II, received the city of Vilnius and its environs on 28 October 1939 from the Soviet Union. On 8 and 13 September 1939, the German military district in the area of Poznań, Posen, commanded by general , and West Prussia, commanded by general Walter Heitz, were established in conquered Greater Poland and Pomerelia, respectively. Based on laws of 21 May 1935 and 1 June 1938, the German military delegated civil administrative powers to Chiefs of Civil Administration (''CdZ''). Hitler appointed Arthur Greiser to become the CdZ of the Posen military district, and Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia, Danzig's Gauleiter Albert Forster to become the CdZ of the West Prussian military district. On 3 October 1939, the military districts centered on and named "Lodz" and "Krakow, Krakau" were set up under command of major generals Gerd von Rundstedt and Wilhelm List, and Hitler appointed Hans Frank and Arthur Seyß-Inquart as civil heads, respectively. Thus the entirety of occupied Poland was divided into four military districts (West Prussia, Posen, Lodz, and Krakau). Frank was at the same time appointed "supreme chief administrator" for all occupied territories. On 28 September, another German–Soviet Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Demarcation, secret German–Soviet protocol modified the arrangements of August: all of Lithuania was shifted to the Soviet sphere of influence; in exchange, the dividing line in Poland was moved in Germany's favour, eastwards towards the Bug River. On 8 October, Germany formally Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany, annexed the western parts of Poland with Greiser and Forster as ''Reichsstatthalter'', while the south-central parts were administered as the General Government led by Frank.
John Gunther wrote in December 1939 that "the German campaign was a masterpiece. Nothing quite like it has been seen in military history". The country was divided between Germany and the Soviet Union. Slovak Republic (WWII), Slovakia gained back those territories taken by Poland in autumn 1938. Lithuania Vilnius#World War II, received the city of Vilnius and its environs on 28 October 1939 from the Soviet Union. On 8 and 13 September 1939, the German military district in the area of Poznań, Posen, commanded by general , and West Prussia, commanded by general Walter Heitz, were established in conquered Greater Poland and Pomerelia, respectively. Based on laws of 21 May 1935 and 1 June 1938, the German military delegated civil administrative powers to Chiefs of Civil Administration (''CdZ''). Hitler appointed Arthur Greiser to become the CdZ of the Posen military district, and Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia, Danzig's Gauleiter Albert Forster to become the CdZ of the West Prussian military district. On 3 October 1939, the military districts centered on and named "Lodz" and "Krakow, Krakau" were set up under command of major generals Gerd von Rundstedt and Wilhelm List, and Hitler appointed Hans Frank and Arthur Seyß-Inquart as civil heads, respectively. Thus the entirety of occupied Poland was divided into four military districts (West Prussia, Posen, Lodz, and Krakau). Frank was at the same time appointed "supreme chief administrator" for all occupied territories. On 28 September, another German–Soviet Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Demarcation, secret German–Soviet protocol modified the arrangements of August: all of Lithuania was shifted to the Soviet sphere of influence; in exchange, the dividing line in Poland was moved in Germany's favour, eastwards towards the Bug River. On 8 October, Germany formally Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany, annexed the western parts of Poland with Greiser and Forster as ''Reichsstatthalter'', while the south-central parts were administered as the General Government led by Frank.
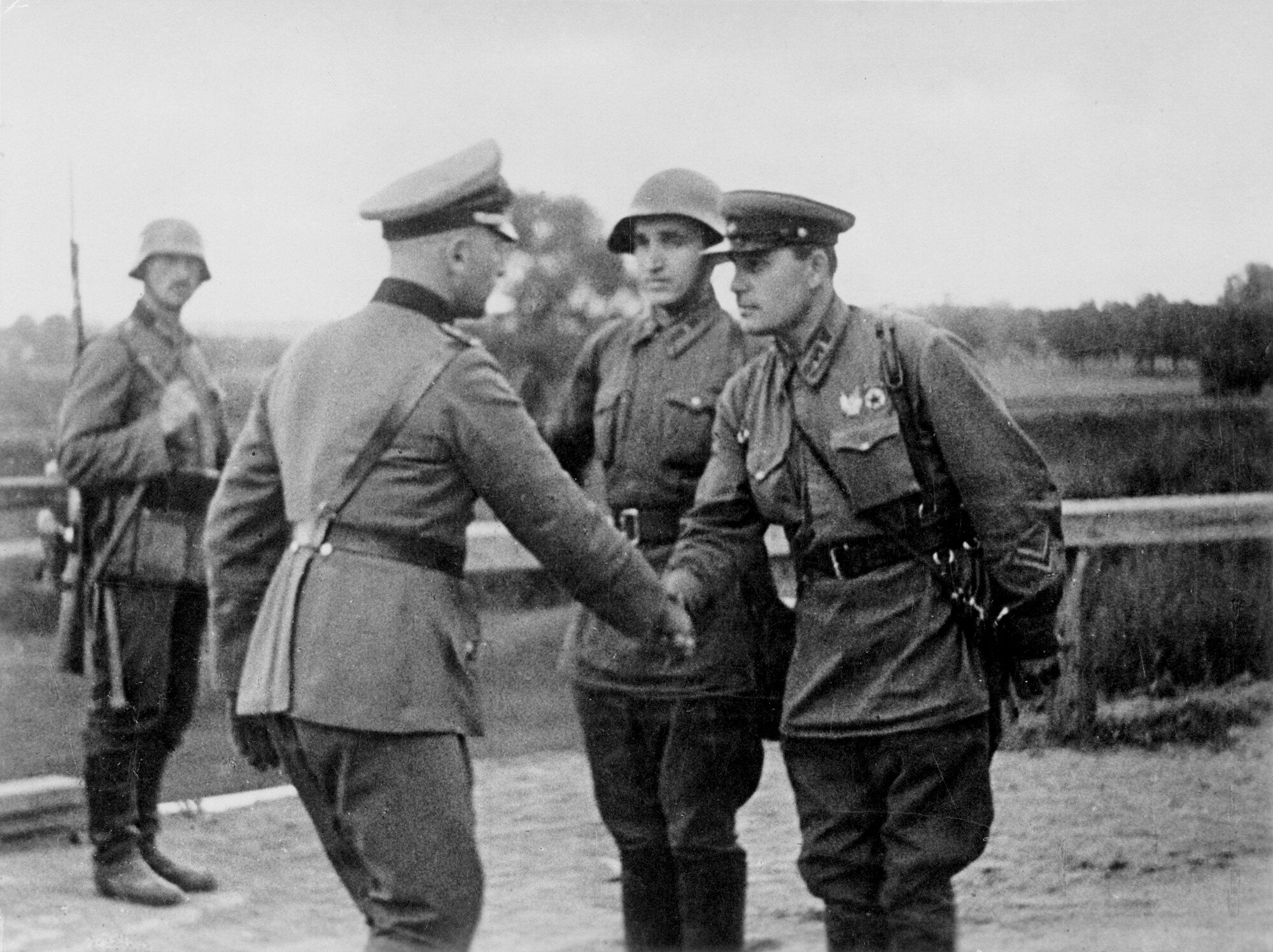 Even though water barriers separated most of the spheres of interest, the Soviet and German troops met on numerous occasions. The most remarkable event of this kind occurred at Brest-Litovsk on 22 September. The German 19th ''Panzer'' Corps—commanded by General Heinz Guderian—had occupied the city, which lay within the Soviet sphere of interest. When the Soviet 29th Tank Brigade (commanded by Semyon Krivoshein) approached, the commanders agreed that the German troops would withdraw and the Soviet troops would enter the city, saluting each other. At Brest-Litovsk, Soviet and German commanders held a joint Nazi–Soviet military parade in Brest-Litovsk, victory parade before German forces withdrew westward behind a new demarcation line. Just three days earlier, however, the parties had a more hostile encounter near Lwów (''Lviv, Lemberg''), when the German 137th ''Gebirgsjägerregimenter'' (mountain infantry regiment) attacked a reconnaissance detachment of the Soviet 24th Tank Brigade; after a few casualties on both sides, the parties turned to negotiations. The German troops left the area, and the Red Army troops entered Lwów on 22 September.
The Molotov–Ribbentrop pact and the invasion of Poland marked the beginning of a period during which the government of the Soviet Union increasingly tried to convince itself that the actions of Germany were reasonable, and were not developments to be worried about, despite evidence to the contrary. On 7 September 1939, just a few days after France and Britain joined the war against Germany, Stalin explained to a colleague that the war was to the advantage of the Soviet Union, as follows:Clark, Lloyd, ''Kursk: The greatest battle: Eastern Front 1943'', 2011, p. 62
About 65,000 Polish troops were killed in the fighting, with 420,000 others being captured by the Germans and 240,000 more by the Soviets (for a total of 660,000 prisoners). Up to 120,000 Polish troops escaped to Neutral country, neutral Romania (through the Romanian Bridgehead and Hungary), and another 20,000 to Latvia and Lithuania, with the majority eventually making their way to France or Britain. Most of the Polish Navy succeeded in evacuating to Britain as well. German personnel losses were less than their enemies (c. 16,000 killed).
Even though water barriers separated most of the spheres of interest, the Soviet and German troops met on numerous occasions. The most remarkable event of this kind occurred at Brest-Litovsk on 22 September. The German 19th ''Panzer'' Corps—commanded by General Heinz Guderian—had occupied the city, which lay within the Soviet sphere of interest. When the Soviet 29th Tank Brigade (commanded by Semyon Krivoshein) approached, the commanders agreed that the German troops would withdraw and the Soviet troops would enter the city, saluting each other. At Brest-Litovsk, Soviet and German commanders held a joint Nazi–Soviet military parade in Brest-Litovsk, victory parade before German forces withdrew westward behind a new demarcation line. Just three days earlier, however, the parties had a more hostile encounter near Lwów (''Lviv, Lemberg''), when the German 137th ''Gebirgsjägerregimenter'' (mountain infantry regiment) attacked a reconnaissance detachment of the Soviet 24th Tank Brigade; after a few casualties on both sides, the parties turned to negotiations. The German troops left the area, and the Red Army troops entered Lwów on 22 September.
The Molotov–Ribbentrop pact and the invasion of Poland marked the beginning of a period during which the government of the Soviet Union increasingly tried to convince itself that the actions of Germany were reasonable, and were not developments to be worried about, despite evidence to the contrary. On 7 September 1939, just a few days after France and Britain joined the war against Germany, Stalin explained to a colleague that the war was to the advantage of the Soviet Union, as follows:Clark, Lloyd, ''Kursk: The greatest battle: Eastern Front 1943'', 2011, p. 62
About 65,000 Polish troops were killed in the fighting, with 420,000 others being captured by the Germans and 240,000 more by the Soviets (for a total of 660,000 prisoners). Up to 120,000 Polish troops escaped to Neutral country, neutral Romania (through the Romanian Bridgehead and Hungary), and another 20,000 to Latvia and Lithuania, with the majority eventually making their way to France or Britain. Most of the Polish Navy succeeded in evacuating to Britain as well. German personnel losses were less than their enemies (c. 16,000 killed).
 None of the parties to the conflict—Germany, the Western Allies or the Soviet Union—expected that the German invasion of Poland would lead to a war that would surpass World War I in its scale and cost. It would be months before Hitler would see the futility of his peace negotiation attempts with the United Kingdom and France, but the culmination of combined European and Pacific conflicts would result in what was truly a "world war". Thus, what was not seen by most politicians and generals in 1939 is clear from the historical perspective: The Polish September Campaign marked the beginning of a pan-European war, which combined with the Second Sino-Japanese War, Japanese invasion of China in 1937 and the Pacific War in 1941 to form the global conflict known as World War II.
The invasion of Poland led Britain and France to declare war on Germany on 3 September. However, they did little to affect the outcome of the September Campaign. No declaration of war was issued by Britain and France against the Soviet Union. This lack of direct help led many Poles to believe that they had been Western betrayal#Up to 1939, betrayed by their Western allies. British Foreign Secretary
None of the parties to the conflict—Germany, the Western Allies or the Soviet Union—expected that the German invasion of Poland would lead to a war that would surpass World War I in its scale and cost. It would be months before Hitler would see the futility of his peace negotiation attempts with the United Kingdom and France, but the culmination of combined European and Pacific conflicts would result in what was truly a "world war". Thus, what was not seen by most politicians and generals in 1939 is clear from the historical perspective: The Polish September Campaign marked the beginning of a pan-European war, which combined with the Second Sino-Japanese War, Japanese invasion of China in 1937 and the Pacific War in 1941 to form the global conflict known as World War II.
The invasion of Poland led Britain and France to declare war on Germany on 3 September. However, they did little to affect the outcome of the September Campaign. No declaration of war was issued by Britain and France against the Soviet Union. This lack of direct help led many Poles to believe that they had been Western betrayal#Up to 1939, betrayed by their Western allies. British Foreign Secretary  Since October 1939, the Polish army that could escape imprisonment from the Soviets or Nazis were mainly heading for British and French territories. These places were considered safe, because of the pre-war alliance between Great-Britain, France and Poland. Not only did the government escape, but also the national gold supply was evacuated via Romania and brought to the West, notably London and Ottawa. The approximately of gold was considered sufficient to field an army for the duration of the war.
Since October 1939, the Polish army that could escape imprisonment from the Soviets or Nazis were mainly heading for British and French territories. These places were considered safe, because of the pre-war alliance between Great-Britain, France and Poland. Not only did the government escape, but also the national gold supply was evacuated via Romania and brought to the West, notably London and Ottawa. The approximately of gold was considered sufficient to field an army for the duration of the war.

 Polish cavalry units did not engage German tanks with lances and swords. At the Battle of Tuchola Forest on 1 September 1939 the 18th Pomeranian Uhlan Regiment had been tasked to cover the retreat of Polish infantry. In the evening the Pomeranian Uhlans encountered contingents of the advancing German 20th Infantry Division of Heinz Guderian's XIX Army. Commander Kazimierz Mastalerz ordered an attack, forcing the 20th infantry to withdraw and disperse. The engagement proved to be successful as the German advance had been delayed. However, upon redeployment, the 18th Pomeranians came under sudden and intense machine gun fire of German armored reconnaissance vehicles. Despite their quick retreat, nearly a third of the Uhlans were killed or wounded.
A group of German and Italian war correspondents, who visited the battlefield noticed the dead cavalry men and horses among the armored vehicles. Italian reporter Indro Montanelli promptly published an article in the ''Corriere della Sera'', on the brave and heroic Polish cavalry men, who charged German tanks with sabres and lances.
Historian Steven Zaloga in ''Poland 1939: The Birth of Blitzkrieg'' (2004):
In 1939, only 10% of the Polish army was made up of cavalry units.
Polish cavalry units did not engage German tanks with lances and swords. At the Battle of Tuchola Forest on 1 September 1939 the 18th Pomeranian Uhlan Regiment had been tasked to cover the retreat of Polish infantry. In the evening the Pomeranian Uhlans encountered contingents of the advancing German 20th Infantry Division of Heinz Guderian's XIX Army. Commander Kazimierz Mastalerz ordered an attack, forcing the 20th infantry to withdraw and disperse. The engagement proved to be successful as the German advance had been delayed. However, upon redeployment, the 18th Pomeranians came under sudden and intense machine gun fire of German armored reconnaissance vehicles. Despite their quick retreat, nearly a third of the Uhlans were killed or wounded.
A group of German and Italian war correspondents, who visited the battlefield noticed the dead cavalry men and horses among the armored vehicles. Italian reporter Indro Montanelli promptly published an article in the ''Corriere della Sera'', on the brave and heroic Polish cavalry men, who charged German tanks with sabres and lances.
Historian Steven Zaloga in ''Poland 1939: The Birth of Blitzkrieg'' (2004):
In 1939, only 10% of the Polish army was made up of cavalry units.


online review
* * * * * * * * * *
The Conquest of Poland and the Beginnings of Jewish Persecution
on the Yad Vashem website
German invasion of Poland
Original reports from The Times
Blitzkrieg Unleashed: The German Invasion of Poland, 1939
History of the invasion with focus on precise locations and events, as experienced by real people.
The Campaign in Poland at WorldWar2 Database
German Statistics including September Campaign losses
Radio reports on the German invasion of Poland
an
Nazi broadcast claiming that Germany's action is an act of defence
Headline story on BBC: Germany invades Poland
1 September 1939.
An essay describing the Polish Campaign in a larger strategic context of the war
schemas by Dr. Leo Niehorster
schemas by Dr. Leo Niehorster
* [http://www.polishnews.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&catid=93%3Ahistoriapolish-history&id=402%3Athe-polish-campaign-of-september-1939-in-perspective&Itemid=329&showall=1 "The Polish Campaign of September 1939 in Perspective" ''Polish News'', 24 September 2008]
Invasion of Poland
by Bradley Lightbody, Last updated 2011-03-30
Polish forces in the West
. A website describing the Polish forces in France, UK and the Netherlands War propaganda newsreel * ''Advance into Poland''. National Archives and Records Administration (German. Series: Motion Picture Films. G-2 Army Military Intelligence Division). Internet Archive
Reel 1 of 4Reel 2 of 4Reel 3 of 4Reel 4 of 4
''Invasion of Poland in 1939 by German Army''
(1943). Film Bulletin n. 48 US Department of the Army, Signal Corps Photographic Center. Internet Archive.
''Special Release – Europe At War!''
(1939). Universal Studios. Internet Archive. {{DEFAULTSORT:Invasion Of Poland Invasion of Poland, 1939 in Poland Conflicts in 1939, Poland World War II invasions, Poland Invasions of Poland September 1939 events October 1939 events
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
which marked the beginning of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week after the signing of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact
, long_name = Treaty of Non-Aggression between Germany and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics
, image = Bundesarchiv Bild 183-H27337, Moskau, Stalin und Ribbentrop im Kreml.jpg
, image_width = 200
, caption = Stalin and Ribbentrop shaking ...
between Germany and the Soviet Union, and one day after the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union had approved the pact. The Soviets invaded Poland on 17 September. The campaign ended on 6 October with Germany and the Soviet Union dividing and annexing the whole of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
under the terms of the German–Soviet Frontier Treaty. The invasion is also known in Poland as the September campaign ( pl, kampania wrześniowa) or 1939 defensive war ( pl, wojna obronna 1939 roku, links=no) and known in Germany as the Poland campaign (german: Überfall auf Polen, Polenfeldzug).
German forces invaded Poland from the north, south, and west the morning after the Gleiwitz incident
The Gleiwitz incident (german: Überfall auf den Sender Gleiwitz; ) was a false flag attack on the radio station ''Sender Gleiwitz'' in Gleiwitz (then Germany and now Gliwice, Poland) staged by Nazi Germany on the night of 31 August 1939. Along ...
. Slovak military forces advanced alongside the Germans in northern Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
. As the Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previous ...
advanced, Polish forces withdrew from their forward bases of operation close to the Germany–Poland border
The Germany–Poland border (german: Grenze zwischen Deutschland und Polen, pl, Granica polsko-niemiecka), the state international border, border between Poland and Germany, is currently the Oder–Neisse line. It has a total length of (Downl ...
to more established defense line
A defense line or fortification line is a geographically-recognizable line of troops and armament, fortified and set up to protect a high-value location or defend territory.
A defense line may be based on natural difficult terrain features, s ...
s to the east. After the mid-September Polish defeat in the Battle of the Bzura
The Battle of the Bzura (or the Battle of Kutno) was the largest Polish counter-attack of the German invasion of Poland and was fought from 9 to 19 September.''The Second World War: An Illustrated History '', Putnam, 1975, Google Print snippet ...
, the Germans gained an undisputed advantage. Polish forces then withdrew to the southeast where they prepared for a long defence of the Romanian Bridgehead
__NOTOC__
The Romanian Bridgehead ( pl, Przedmoście rumuńskie; ro, Capul de pod român) was an area in southeastern Poland that is now located in Ukraine. During the invasion of Poland in 1939 at the start of the Second World War), the Polish ...
and awaited expected support and relief from France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
and the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
. On 3 September, based on their alliance agreements with Poland, the United Kingdom and France declared war on Germany; in the end their aid to Poland was very limited. France invaded a small part of Germany in the Saar Offensive
The Saar Offensive was a French invasion of Saarland, Germany, in the first stages of World War II, from 7 to 16 September 1939. The original plans called for 40 divisions, and one armored division, three mechanised divisions, 78 artillery r ...
, and the Polish army was effectively defeated even before the British Expeditionary Force could be transported to Europe, with the bulk of the BEF in France by the end of September.
On 17 September, the Soviet Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after ...
invaded
An invasion is a military offensive in which large numbers of combatants of one geopolitical entity aggressively enter territory owned by another such entity, generally with the objective of either: conquering; liberating or re-establishing con ...
Eastern Poland
Eastern Poland is a macroregion in Poland comprising the Lublin, Podkarpackie, Podlaskie, Świętokrzyskie, and Warmian-Masurian voivodeships.
The make-up of the distinct macroregion is based not only of geographical criteria, but also econo ...
, the territory beyond the Curzon Line
The Curzon Line was a proposed demarcation line between the Second Polish Republic and the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Soviet Union, two new states emerging after World War I. It was first proposed by George Curzon, 1st Marque ...
that fell into the Soviet "sphere of influence
In the field of international relations, a sphere of influence (SOI) is a spatial region or concept division over which a state or organization has a level of cultural, economic, military or political exclusivity.
While there may be a formal al ...
" according to the secret protocol of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact; this rendered the Polish plan of defence obsolete. Facing a second front, the Polish government concluded the defence of the Romanian Bridgehead was no longer feasible and ordered an emergency evacuation of all troops to neutral Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
. On 6 October, following the Polish defeat at the Battle of Kock, German and Soviet forces gained full control over Poland. The success of the invasion marked the end of the Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of ...
, though Poland never formally surrendered.
On 8 October, after an initial period of military administration, Germany directly annexed western Poland and the former Free City of Danzig
The Free City of Danzig (german: Freie Stadt Danzig; pl, Wolne Miasto Gdańsk; csb, Wòlny Gard Gduńsk) was a city-state under the protection of the League of Nations between 1920 and 1939, consisting of the Baltic Sea port of Danzig (now Gda ...
and placed the remaining block of territory under the administration of the newly established General Government
The General Government (german: Generalgouvernement, pl, Generalne Gubernatorstwo, uk, Генеральна губернія), also referred to as the General Governorate for the Occupied Polish Region (german: Generalgouvernement für die be ...
. The Soviet Union incorporated its newly acquired areas into its constituent Byelorussian and Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
republics
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th ...
, and immediately started a campaign of Sovietization
Sovietization (russian: Советизация) is the adoption of a political system based on the model of soviets (workers' councils) or the adoption of a way of life, mentality, and culture modelled after the Soviet Union. This often included ...
. In the aftermath of the invasion, a collective of underground resistance organizations formed the Polish Underground State
The Polish Underground State ( pl, Polskie Państwo Podziemne, also known as the Polish Secret State) was a single political and military entity formed by the union of resistance organizations in occupied Poland that were loyal to the Gover ...
within the territory of the former Polish state. Many of the military exiles who escaped Poland joined the Polish Armed Forces in the West
The Polish Armed Forces in the West () refers to the Polish military formations formed to fight alongside the Western Allies against Nazi Germany and its allies during World War II. Polish forces were also raised within Soviet territories; thes ...
, an armed force loyal to the Polish government-in-exile
The Polish government-in-exile, officially known as the Government of the Republic of Poland in exile ( pl, Rząd Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej na uchodźstwie), was the government in exile of Poland formed in the aftermath of the Invasion of Pola ...
.
Background
On 30 January 1933, theNational Socialist German Workers' Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported t ...
, under its leader Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
, came to power in Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
. While some dissident elements within the Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic (german: link=no, Weimarer Republik ), officially named the German Reich, was the government of Germany from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional federal republic for the first time in history; hence it is al ...
had long sought to annex territories belonging to Poland, it was Hitler's own idea and not a realization of any pre-1933 Weimar plans to invade and partition Poland, annex Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
and Austria, and create satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotope ...
or puppet state
A puppet state, puppet régime, puppet government or dummy government, is a State (polity), state that is ''de jure'' independent but ''de facto'' completely dependent upon an outside Power (international relations), power and subject to its o ...
s economically subordinate to Germany. As part of this long-term policy, Hitler at first pursued a policy of rapprochement
In international relations, a rapprochement, which comes from the French word ''rapprocher'' ("to bring together"), is a re-establishment of cordial relations between two countries. This may be done due to a mutual enemy, as was the case with Germ ...
with Poland, trying to improve opinion in Germany, culminating in the German–Polish Non-Aggression Pact of 1934. Earlier, Hitler's foreign policy worked to weaken ties between Poland and France and attempted to manoeuvre Poland into the Anti-Comintern Pact
The Anti-Comintern Pact, officially the Agreement against the Communist International was an anti-Communist pact concluded between Nazi Germany and the Empire of Japan on 25 November 1936 and was directed against the Communist International (Com ...
, forming a cooperative front against the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
. Poland would be granted territory to its northeast in Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
and Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by R ...
if it agreed to wage war against the Soviet Union, but the concessions the Poles were expected to make meant that their homeland would become largely dependent on Germany, functioning as little more than a client state
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite state, ...
. The Poles feared that their independence would eventually be threatened altogether; historically Hitler had already denounced the right of Poland to independence in 1930, writing that Poles and Czechs were a "rabble not worth a penny more than the inhabitants of Sudan or India. How can they demand the rights of independent states?"
The population of the Free City of Danzig
The Free City of Danzig (german: Freie Stadt Danzig; pl, Wolne Miasto Gdańsk; csb, Wòlny Gard Gduńsk) was a city-state under the protection of the League of Nations between 1920 and 1939, consisting of the Baltic Sea port of Danzig (now Gda ...
was strongly in favour of annexation by Germany, as were many of the ethnic German inhabitants of the Polish territory that separated the German exclave
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
of East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label=Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 187 ...
from the rest of the Reich. The Polish Corridor
The Polish Corridor (german: Polnischer Korridor; pl, Pomorze, Polski Korytarz), also known as the Danzig Corridor, Corridor to the Sea or Gdańsk Corridor, was a territory located in the region of Pomerelia (Pomeranian Voivodeship, eastern ...
constituted land long disputed by Poland and Germany, and was inhabited by a Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
majority. The Corridor had become a part of Poland after the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June ...
. Many Germans also wanted the urban port city of Danzig and its environs (comprising the Free City of Danzig) to be reincorporated into Germany. Danzig city had a German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
majority, and had been separated from Germany after Versailles and made into the nominally independent Free City. Hitler sought to use this as ''casus belli
A (; ) is an act or an event that either provokes or is used to justify a war. A ''casus belli'' involves direct offenses or threats against the nation declaring the war, whereas a ' involves offenses or threats against its ally—usually one b ...
'', a reason for war, reverse the post-1918 territorial losses, and on many occasions had appealed to German nationalism
German nationalism () is an ideological notion that promotes the unity of Germans and German-speakers into one unified nation state. German nationalism also emphasizes and takes pride in the patriotism and national identity of Germans as one na ...
, promising to "liberate" the German minority still in the Corridor, as well as Danzig.
The invasion was referred to by Germany as the 1939 Defensive War
A defensive war (german: Verteidigungskrieg) is one of the causes that justify war by the criteria of the Just War tradition. It means a war where at least one nation is mainly trying to defend itself from another, as opposed to a war where both s ...
(''Verteidigungskrieg'') since Hitler proclaimed that Poland had attacked Germany and that "Germans in Poland are persecuted with a bloody terror and are driven from their homes. The series of border violations, which are unbearable to a great power, prove that the Poles no longer are willing to respect the German frontier."
Poland participated with Germany in the partition of Czechoslovakia that followed the Munich Agreement
The Munich Agreement ( cs, Mnichovská dohoda; sk, Mníchovská dohoda; german: Münchner Abkommen) was an agreement concluded at Munich on 30 September 1938, by Nazi Germany, Germany, the United Kingdom, French Third Republic, France, and Fa ...
, although they were not part of the agreement. It coerced Czechoslovakia to surrender the region of Český Těšín
Český Těšín (; pl, Czeski Cieszyn ; german: Tschechisch-Teschen) is a town in the Karviná District in the Moravian-Silesian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 24,000 inhabitants.
Český Těšín lies on the west bank of the Olza r ...
by issuing an ultimatum to that effect on 30 September 1938, which was accepted by Czechoslovakia on 1 October. This region had a Polish majority and had been disputed between Czechoslovakia and Poland in the aftermath of World War I. The Polish annexation of Slovak territory (several villages in the regions of Čadca
Čadca (; until 1918 Čatca, Czača, hu, Csaca, pl, Czadca) is a district town in northern Slovakia, near the border with Poland and the Czech Republic.
Etymology
The name is derived from a word ''čad'' (smoke, soot; Proto-Slavic: ''čadъ'', ...
, Orava and Spiš
Spiš (Latin: ''Cips/Zepus/Scepus/Scepusia'', german: Zips, hu, Szepesség/Szepes, pl, Spisz) is a region in north-eastern Slovakia, with a very small area in south-eastern Poland (14 villages). Spiš is an informal designation of the territory ...
) later served as the justification for the Slovak state
Slovak may refer to:
* Something from, related to, or belonging to Slovakia (''Slovenská republika'')
* Slovaks, a Western Slavic ethnic group
* Slovak language, an Indo-European language that belongs to the West Slavic languages
* Slovak, Arka ...
to join the German invasion.
By 1937, Germany began to increase its demands for Danzig, while proposing that an extraterritorial
In international law, extraterritoriality is the state of being exempted from the jurisdiction of local law, usually as the result of diplomatic negotiations.
Historically, this primarily applied to individuals, as jurisdiction was usually cla ...
roadway, part of the Reichsautobahn
The ''Reichsautobahn'' system was the beginning of the German autobahns under Nazi Germany. There had been previous plans for controlled-access highways in Germany under the Weimar Republic, and two had been constructed, but work had yet to st ...
system, be built in order to connect East Prussia with Germany proper, running through the Polish Corridor. Poland rejected this proposal, fearing that after accepting these demands, it would become increasingly subject to the will of Germany and eventually lose its independence as the Czechs had. Polish leaders also distrusted Hitler. The British were also wary of Germany's increasing strength and assertiveness threatening its balance of power strategy. On 31 March 1939, Poland formed a military alliance
A military alliance is a formal Alliance, agreement between nations concerning national security. Nations in a military alliance agree to active participation and contribution to the defense of others in the alliance in the event of a crisis. ...
with the United Kingdom and with France, believing that Polish independence and territorial integrity would be defended with their support if it were to be threatened by Germany. On the other hand, British Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
Neville Chamberlain
Arthur Neville Chamberlain (; 18 March 18699 November 1940) was a British politician of the Conservative Party who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from May 1937 to May 1940. He is best known for his foreign policy of appeasemen ...
and his Foreign Secretary
The secretary of state for foreign, Commonwealth and development affairs, known as the foreign secretary, is a minister of the Crown of the Government of the United Kingdom and head of the Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office. Seen as ...
, Lord Halifax
Edward Frederick Lindley Wood, 1st Earl of Halifax, (16 April 1881 – 23 December 1959), known as The Lord Irwin from 1925 until 1934 and The Viscount Halifax from 1934 until 1944, was a senior British Conservative politician of the 19 ...
, still hoped to strike a deal with Hitler regarding Danzig (and possibly the Polish Corridor). Chamberlain and his supporters believed war could be avoided and hoped Germany would agree to leave the rest of Poland alone. German hegemony
Hegemony (, , ) is the political, economic, and military predominance of one State (polity), state over other states. In Ancient Greece (8th BC – AD 6th ), hegemony denoted the politico-military dominance of the ''hegemon'' city-state over oth ...
over Central Europe was also at stake. In private, Hitler said in May that Danzig was not the important issue to him, but pursuit of ''Lebensraum
(, ''living space'') is a German concept of settler colonialism, the philosophy and policies of which were common to German politics from the 1890s to the 1940s. First popularized around 1901, '' lso in:' became a geopolitical goal of Imperi ...
'' for Germany.
Breakdown of talks
With tensions mounting, Germany turned to aggressive diplomacy. On 28 April 1939, Hitlerunilateral
__NOTOC__
Unilateralism is any doctrine or agenda that supports one-sided action. Such action may be in disregard for other parties, or as an expression of a commitment toward a direction which other parties may find disagreeable. As a word, ''un ...
ly withdrew from both the German-Polish Non-Aggression Pact of 1934 and the Anglo-German Naval Agreement
The Anglo-German Naval Agreement (AGNA) of 18 June 1935 was a naval agreement between the United Kingdom and Germany regulating the size of the '' Kriegsmarine'' in relation to the Royal Navy.
The Anglo-German Naval Agreement fixed a ratio whe ...
of 1935. Talks over Danzig and the Corridor broke down and months passed without diplomatic interaction between Germany and Poland. During this interim period, the Germans learned that France and Britain had failed to secure an alliance with the Soviet Union against Germany, and that the Soviet Union was interested in an alliance with Germany against Poland. Hitler had already issued orders to prepare for a possible "solution of the Polish problem by military means" through the Case White
Case White (german: Fall Weiss), also known as the Fourth Enemy Offensive ( sh, Četvrta neprijateljska ofenziva/ofanziva), was a combined Axis strategic offensive launched against the Yugoslav Partisans throughout occupied Yugoslavia during W ...
scenario.
In May, in a statement to his generals while they were in the midst of planning the invasion of Poland, Hitler made it clear that the invasion would not come without resistance as it had in Czechoslovakia:Clark, Lloyd, ''Kursk: The Greatest Battle: Eastern Front 1943'', 2011, p. 26
 On 22 August, just over a week before the onset of war, Hitler delivered a speech to his military commanders at the
On 22 August, just over a week before the onset of war, Hitler delivered a speech to his military commanders at the Obersalzberg
Obersalzberg is a mountainside retreat situated above the market town of Berchtesgaden in Bavaria, Germany. Located about south-east of Munich, close to the border with Austria, it is best known as the site of Adolf Hitler's former mountain resi ...
:
With the surprise signing of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact on 23 August, the result of secret Nazi–Soviet talks held in Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
, Germany neutralized the possibility of Soviet opposition to a campaign against Poland and war became imminent. In fact, the Soviets agreed not to aid France or the UK in the event of their going to war with Germany over Poland and, in a secret protocol of the pact, the Germans and the Soviets agreed to divide Eastern Europe, including Poland, into two spheres of influence
In the field of international relations, a sphere of influence (SOI) is a spatial region or concept division over which a state or organization has a level of cultural, economic, military or political exclusivity.
While there may be a formal al ...
; the western one-third of the country was to go to Germany and the eastern two-thirds to the Soviet Union.
The German assault was originally scheduled to begin at 4:00 a.m. on 26 August. However, on 25 August, the Polish-British Common Defence Pact
The military alliance between the United Kingdom and Poland was formalised by the Anglo-Polish Agreement in 1939, with subsequent addenda of 1940 and 1944, for mutual assistance in case of a military invasion from Nazi Germany, as specified in ...
was signed as an annex to the Franco-Polish alliance (1921)
The Franco-Polish Alliance was the military alliance between Poland and France that was active between the early 1920s and the outbreak of the Second World War. The initial agreements were signed in February 1921 and formally took effect in 1923 ...
. In this accord, Britain committed itself to the defence of Poland, guaranteeing to preserve Polish independence. At the same time, the British and the Poles were hinting to Berlin that they were willing to resume discussions—not at all how Hitler hoped to frame the conflict. Thus, he wavered and postponed his attack until 1 September, managing to in effect halt the entire invasion "in mid-leap".
Jablunkov Pass
Jablunkov Pass ( cs, , pl, ) is a mountain pass in the Western Beskids at above sea level. It is located in the municipality of Mosty u Jablunkova in the Czech Republic, near the border with Poland and Slovakia.
Geography
The pass separat ...
and Mosty railway station in Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
. On the morning of 26 August, this group was repelled by Polish troops. The German side described all this as an incident "caused by an insane individual" (see Jabłonków incident).
On 26 August, Hitler tried to dissuade the British and the French from interfering in the upcoming conflict, even pledging that the ''Wehrmacht'' forces would be made available to Britain's empire in the future. The negotiations convinced Hitler that there was little chance the Western Allies would declare war on Germany, and even if they did, because of the lack of "territorial guarantees" to Poland, they would be willing to negotiate a compromise favourable to Germany after its conquest of Poland. Meanwhile, the increased number of overflights by high-altitude reconnaissance aircraft
A reconnaissance aircraft (colloquially, a spy plane) is a military aircraft designed or adapted to perform aerial reconnaissance with roles including collection of imagery intelligence (including using photography), signals intelligence, as ...
and cross-border troop movements signaled that war was imminent.
 On 29 August, prompted by the British, Germany issued one last diplomatic offer, with ''Fall Weiss'' yet to be rescheduled. That evening, the German government responded in a communication that it aimed not only for the restoration of Danzig but also the Polish Corridor (which had not previously been part of Hitler's demands) in addition to the safeguarding of the
On 29 August, prompted by the British, Germany issued one last diplomatic offer, with ''Fall Weiss'' yet to be rescheduled. That evening, the German government responded in a communication that it aimed not only for the restoration of Danzig but also the Polish Corridor (which had not previously been part of Hitler's demands) in addition to the safeguarding of the German minority in Poland
The registered German minority in Poland at the 2011 national census consisted of 148,000 people, of whom 64,000 declared both German and Polish ethnicities and 45,000 solely German ethnicity.Przynależność narodowo-etniczna ludności – wyni ...
. It said that they were willing to commence negotiations, but indicated that a Polish representative with the power to sign an agreement had to arrive in Berlin the next day while in the meantime it would draw up a set of proposals. The British Cabinet was pleased that negotiations had been agreed to but, mindful of how Emil Hácha
Emil Dominik Josef Hácha (12 July 1872 – 27 June 1945) was a Czech lawyer, the president of Czechoslovakia from November 1938 to March 1939. In March 1939, after the breakup of Czechoslovakia, Hácha was the nominal president of the newly pro ...
had been forced to sign his country away under similar circumstances just months earlier, regarded the requirement for an immediate arrival of a Polish representative with full signing powers as an unacceptable ultimatum
An ultimatum (; ) is a demand whose fulfillment is requested in a specified period of time and which is backed up by a threat to be followed through in case of noncompliance (open loop). An ultimatum is generally the final demand in a series o ...
. On the night of 30/31 August, German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ribbentrop
Ulrich Friedrich Wilhelm Joachim von Ribbentrop (; 30 April 1893 – 16 October 1946) was a German politician and diplomat who served as Minister of Foreign Affairs of Nazi Germany from 1938 to 1945.
Ribbentrop first came to Adolf Hitler's not ...
read a 16-point German proposal to ambassador Nevile Henderson
Sir Nevile Meyrick Henderson (10 June 1882 – 30 December 1942) was a British diplomat who served as the ambassador of the United Kingdom to Germany from 1937 to 1939.
Early life and education
Henderson was born at Sedgwick Park, near Horsha ...
. When the ambassador requested a copy of the proposals for transmission to the Polish government, Ribbentrop refused, on the grounds that the requested Polish representative had failed to arrive by midnight. When Polish Ambassador Lipski went to see Ribbentrop later on 31 August to indicate that Poland was favorably disposed to negotiations, he announced that he did not have the full power to sign, and Ribbentrop dismissed him. It was then broadcast that Poland had rejected Germany's offer, and negotiations with Poland came to an end. Hitler issued orders for the invasion to commence soon afterwards.
On 29 August, Polish Minister of Foreign Affairs, Józef Beck
Józef Beck (; 4 October 1894 – 5 June 1944) was a Poles, Polish statesman who served the Second Republic of Poland as a diplomat and military officer. A close associate of Józef Piłsudski, Beck is most famous for being Polish foreign minist ...
ordered military mobilization
Mobilization is the act of assembling and readying military troops and supplies for war. The word ''mobilization'' was first used in a military context in the 1850s to describe the preparation of the Prussian Army. Mobilization theories and ...
, but under the pressure from Great Britain and France, the mobilization was cancelled. When the final mobilization started, it added to the confusion.
On 30 August, the Polish Navy sent its destroyer flotilla
A flotilla (from Spanish, meaning a small ''flota'' (fleet) of ships), or naval flotilla, is a formation of small warships that may be part of a larger fleet.
Composition
A flotilla is usually composed of a homogeneous group of the same class ...
to Britain, executing the Peking Plan
The Peking Plan"Peking" was one contemporary spelling for the city now spelled 'Beijing' in English. In modern Polish the name is written as "Pekin". Some modern Polish works refer to the "Pekin Plan". The original orders used the spelling " ...
. On the same day, Marshal of Poland
Marshal of Poland ( pl, Marszałek Polski) is the highest rank in the Polish Army. It has been granted to only six officers. At present, Marshal is equivalent to a Field Marshal or General of the Army (OF-10) in other NATO armies.
History
To ...
Edward Rydz-Śmigły
Marshal Edward Rydz-Śmigły (11 March 1886 – 2 December 1941; nom de guerre ''Śmigły, Tarłowski, Adam Zawisza''), also called Edward Śmigły-Rydz, was a Polish politician, statesman, Marshal of Poland and Commander-in-Chief of Poland ...
announced the mobilization of Polish troops. However, he was pressured into revoking the order by the French, who apparently still hoped for a diplomatic settlement, failing to realize that the Germans were fully mobilized and concentrated at the Polish border. During the night of 31 August, the Gleiwitz incident
The Gleiwitz incident (german: Überfall auf den Sender Gleiwitz; ) was a false flag attack on the radio station ''Sender Gleiwitz'' in Gleiwitz (then Germany and now Gliwice, Poland) staged by Nazi Germany on the night of 31 August 1939. Along ...
, a false flag
A false flag operation is an act committed with the intent of disguising the actual source of responsibility and pinning blame on another party. The term "false flag" originated in the 16th century as an expression meaning an intentional misr ...
attack on the radio station, was staged near the border city of Gleiwitz
Gliwice (; german: Gleiwitz) is a city in Upper Silesia, in southern Poland. The city is located in the Silesian Highlands, on the Kłodnica river (a tributary of the Oder River, Oder). It lies approximately 25 km west from Katowice, the re ...
in Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( pl, Górny Śląsk; szl, Gůrny Ślůnsk, Gōrny Ślōnsk; cs, Horní Slezsko; german: Oberschlesien; Silesian German: ; la, Silesia Superior) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located ...
by German units posing as Polish troops, as part of the wider Operation Himmler
Operation or Operations may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* ''Operation'' (game), a battery-operated board game that challenges dexterity
* Operation (music), a term used in musical set theory
* ''Operations'' (magazine), Multi-Ma ...
. On 31 August, Hitler ordered hostilities against Poland to start at 4:45 the next morning. However, partly because of the earlier stoppage, Poland finally managed to mobilize only about 70% of its planned forces (only about 900,000 of 1,350,000 soldiers planned to mobilize in first order), and because of that many units were still forming or moving to their designated frontline positions. The late mobilization reduced combat capability of the Polish Army by about 1/3.
Opposing forces
Germany
Germany had a substantial numeric advantage over Poland and had developed a significant military before the conflict. The '' Heer'' (army) had 3,472tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and good battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engin ...
s in its inventory, of which 2,859 were with the Field Army and 408 with the Replacement Army
The Replacement Army () was part of the Imperial German Army during World War I and part of the Wehrmacht during World War II. It was based within Germany proper and included command and administrative units as well as training and guard troops. It ...
. 453 tanks were assigned into four light divisions, while another 225 tanks were in detached regiments and companies. Most notably, the Germans had seven ''Panzer
This article deals with the tanks (german: panzer) serving in the German Army (''Deutsches Heer'') throughout history, such as the World War I tanks of the Imperial German Army, the interwar and World War II tanks of the Nazi German Wehrmacht, ...
'' divisions, with 2,009 tanks between them, using a new operational doctrine
Military doctrine is the expression of how military forces contribute to campaigns, major operations, battles, and engagements.
It is a guide to action, rather than being hard and fast rules. Doctrine provides a common frame of reference acros ...
. It held that these divisions should act in coordination with other elements of the military, punching holes in the enemy line and isolating selected units, which would be encircled and destroyed. This would be followed up by less-mobile mechanized infantry and foot soldiers. The ''Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabtei ...
'' (air force) provided both tactical and strategic air power
Airpower or air power consists of the application of military aviation, military strategy and strategic theory to the realm of aerial warfare and close air support. Airpower began in the advent of powered flight early in the 20th century. Airpo ...
, particularly dive bomber
A dive bomber is a bomber aircraft that dives directly at its targets in order to provide greater accuracy for the bomb it drops. Diving towards the target simplifies the bomb's trajectory and allows the pilot to keep visual contact througho ...
s that disrupted lines of supply and communications. Together, the new methods were nicknamed "''Blitzkrieg
Blitzkrieg ( , ; from 'lightning' + 'war') is a word used to describe a surprise attack using a rapid, overwhelming force concentration that may consist of armored and motorized or mechanized infantry formations, together with close air su ...
''" (lightning war). While historian Basil Liddell Hart
Sir Basil Henry Liddell Hart (31 October 1895 – 29 January 1970), commonly known throughout most of his career as Captain B. H. Liddell Hart, was a British soldier, military historian and military theorist. He wrote a series of military histo ...
claimed "Poland was a full demonstration of the ''Blitzkrieg'' theory", some other historians disagree.
Aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines ...
played a major role in the campaign. Bombers
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped from an aircraf ...
also attacked cities, causing huge losses amongst the civilian population through terror bombing
Strategic bombing is a military strategy used in total war with the goal of defeating the enemy by destroying its morale, its economic ability to produce and transport materiel to the theatres of military operations, or both. It is a systematic ...
and strafing. The ''Luftwaffe'' forces consisted of 1,180 fighters
Fighter(s) or The Fighter(s) may refer to:
Combat and warfare
* Combatant, an individual legally entitled to engage in hostilities during an international armed conflict
* Fighter aircraft, a warplane designed to destroy or damage enemy warplan ...
, 290 Ju 87 ''Stuka'' dive bomber
A dive bomber is a bomber aircraft that dives directly at its targets in order to provide greater accuracy for the bomb it drops. Diving towards the target simplifies the bomb's trajectory and allows the pilot to keep visual contact througho ...
s, 1,100 conventional bombers (mainly Heinkel He 111
The Heinkel He 111 is a German airliner and bomber designed by Siegfried and Walter Günter at Heinkel Flugzeugwerke in 1934. Through development, it was described as a "wolf in sheep's clothing". Due to restrictions placed on Germany after th ...
s and Dornier Do 17s), and an assortment of 550 transport and 350 reconnaissance aircraft. In total, Germany had close to 4,000 aircraft, most of them modern. A force of 2,315 aircraft was assigned to ''Weiss''. Due to its earlier participation in the Spanish Civil War, the ''Luftwaffe'' was probably the most experienced, best-trained and best-equipped air force in the world in 1939.
Poland
 Emerging in 1918 as an independent country after 123 years after the Partitions of Poland, the
Emerging in 1918 as an independent country after 123 years after the Partitions of Poland, the Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of ...
, when compared with countries such as United Kingdom or Germany, was a relatively indigent and mostly agricultural country. The partitioning powers did not invest in the development of industry, especially in the armaments industry in ethnically Polish areas. Moreover, Poland had to deal with damage caused by World War I. This resulted in the need to build a defense industry from scratch. Between 1936 and 1939, Poland invested heavily in the newly created Centralny Okręg Przemysłowy, Central Industrial Region. Preparations for a defensive war with Germany were ongoing for many years, but most plans assumed fighting would not begin before 1942. To raise funds for industrial development, Poland sold much of the modern equipment it produced. In 1936, a Fundusz Obrony Narodowej, National Defence Fund was set up to collect funds necessary for strengthening the Polish Armed forces. The Polish Army had approximately a million soldiers, but not all were mobilized by 1 September. Latecomers sustained significant casualties when public transport became targets of the ''Luftwaffe''. The Polish military had fewer armored forces than the Germans, and these units, dispersed within the infantry, were unable to effectively engage the Germans.
Experiences in the Polish–Soviet War shaped Polish Army organizational and operational doctrine. Unlike the trench warfare of World War I, the Polish–Soviet War was a conflict in which the cavalry's mobility played a decisive role. Poland acknowledged the benefits of mobility but was unable to invest heavily in many of the expensive, unproven inventions since then. In spite of this, Polish cavalry brigades were used as mobile mounted infantry and had some successes against both German infantry and cavalry.
 An average Polish infantry division consisted of 16,492 soldiers and was equipped with 326 light and medium machine guns, 132 heavy machine guns, 92 anti-tank rifles and several dozen light, medium, heavy, anti-tank and anti-airplane field artillery. Contrary to the 1,009 cars and trucks and 4,842 horses in the average German infantry division, the average Polish infantry division had 76 cars and trucks and 6,939 horses.
The Polish Air Force (''Lotnictwo Wojskowe'') was at a severe disadvantage against the German ''Luftwaffe'' due to inferiority in numbers and the obsolescence of its fighter planes. However, contrary to German propaganda, it was not destroyed on the ground—in fact it was successfully dispersed before the conflict started and not a single one of its combat planes was destroyed on the ground in the first days of the conflict.Michael Alfred Peszke, ''Poland's Preparation for World War II'', ''Military Affairs'' 43 (Feb 1979): 18–24 In the era of fast progress in aviation the Polish Air Force lacked modern fighters, vastly due to the cancellation of many advanced projects, such as the PZL.38 Wilk and a delay in the introduction of a completely new modern Polish fighter PZL.50 Jastrząb. However, its pilots were among the world's best trained, as proven a year later in the Battle of Britain, in which the Poles played a notable part.Michael Alfred Peszke, ''Polish Underground Army, the Western Allies, and the Failure of Strategic Unity in World War II'', McFarland & Company, 2004,
An average Polish infantry division consisted of 16,492 soldiers and was equipped with 326 light and medium machine guns, 132 heavy machine guns, 92 anti-tank rifles and several dozen light, medium, heavy, anti-tank and anti-airplane field artillery. Contrary to the 1,009 cars and trucks and 4,842 horses in the average German infantry division, the average Polish infantry division had 76 cars and trucks and 6,939 horses.
The Polish Air Force (''Lotnictwo Wojskowe'') was at a severe disadvantage against the German ''Luftwaffe'' due to inferiority in numbers and the obsolescence of its fighter planes. However, contrary to German propaganda, it was not destroyed on the ground—in fact it was successfully dispersed before the conflict started and not a single one of its combat planes was destroyed on the ground in the first days of the conflict.Michael Alfred Peszke, ''Poland's Preparation for World War II'', ''Military Affairs'' 43 (Feb 1979): 18–24 In the era of fast progress in aviation the Polish Air Force lacked modern fighters, vastly due to the cancellation of many advanced projects, such as the PZL.38 Wilk and a delay in the introduction of a completely new modern Polish fighter PZL.50 Jastrząb. However, its pilots were among the world's best trained, as proven a year later in the Battle of Britain, in which the Poles played a notable part.Michael Alfred Peszke, ''Polish Underground Army, the Western Allies, and the Failure of Strategic Unity in World War II'', McFarland & Company, 2004, Google Print, p. 2
/ref>

 Overall, the Germans enjoyed numerical and qualitative aircraft superiority. Poland had only about 600 aircraft, of which only PZL.37 Łoś heavy bombers were modern and comparable to their German counterparts. The Polish Air Force had roughly 185 PZL P.11 and some 95 PZL P.7 fighters, 175 PZL.23 Karaś, PZL.23 ''Karaś'' Bs, 35 ''Karaś'' as light bombers. However, for the September Campaign, not all of those aircraft were mobilized. By 1 September, out of about 120 heavy bombers PZL.37s produced, only 36 PZL.37s were deployed, the rest being mostly in training units. All those aircraft were of indigenous Polish design, with the bombers being more modern than fighters, according to the Ludomił Rayski air force expansion plan, which relied on a strong bomber force. The Polish Air Force consisted of a 'Bomber Brigade', 'Pursuit Brigade' and aircraft assigned to the various ground armies. The Polish fighters were older than their German counterparts; the PZL P.11 fighter—produced in the early 1930s—had a top speed of only , far less than German bombers. To compensate, the pilots relied on its maneuverability and high diving speed. The Polish Air Force's decisions to strengthen its resources came too late, mostly due to budget limitations. As a "last minute" order in the summer of 1939, Poland bought 160 French Morane-Saulnier M.S.406 fighters and 111 English airplanes (100 light bombers Fairey Battle, 10 Hawker Hurricane, Hurricanes and 1 Supermarine Spitfire; the sale of 150 Spitfires asked by the Polish government was rejected by the Air Ministry). Despite the fact that some of the airplanes had been shipped to Poland (the first transport of purchased aircraft on the ship "Lassel" sailed from Liverpool on 28 August), none of them would take part in combat. In late 1938, the Polish Air Force also ordered 300 advanced PZL.46 Sum light bombers, but due to a delay in starting mass production, none of them were delivered before 1 September. When in the spring of 1939 it turned out that there were problems with the implementation of the new PZL.50 Jastrząb fighter, it was decided to temporarily implement the production of the fighter PZL P 11.G Kobuz. Nevertheless, due to the outbreak of the war, not one of the ordered 90 aircraft of this type were delivered to the army.
Overall, the Germans enjoyed numerical and qualitative aircraft superiority. Poland had only about 600 aircraft, of which only PZL.37 Łoś heavy bombers were modern and comparable to their German counterparts. The Polish Air Force had roughly 185 PZL P.11 and some 95 PZL P.7 fighters, 175 PZL.23 Karaś, PZL.23 ''Karaś'' Bs, 35 ''Karaś'' as light bombers. However, for the September Campaign, not all of those aircraft were mobilized. By 1 September, out of about 120 heavy bombers PZL.37s produced, only 36 PZL.37s were deployed, the rest being mostly in training units. All those aircraft were of indigenous Polish design, with the bombers being more modern than fighters, according to the Ludomił Rayski air force expansion plan, which relied on a strong bomber force. The Polish Air Force consisted of a 'Bomber Brigade', 'Pursuit Brigade' and aircraft assigned to the various ground armies. The Polish fighters were older than their German counterparts; the PZL P.11 fighter—produced in the early 1930s—had a top speed of only , far less than German bombers. To compensate, the pilots relied on its maneuverability and high diving speed. The Polish Air Force's decisions to strengthen its resources came too late, mostly due to budget limitations. As a "last minute" order in the summer of 1939, Poland bought 160 French Morane-Saulnier M.S.406 fighters and 111 English airplanes (100 light bombers Fairey Battle, 10 Hawker Hurricane, Hurricanes and 1 Supermarine Spitfire; the sale of 150 Spitfires asked by the Polish government was rejected by the Air Ministry). Despite the fact that some of the airplanes had been shipped to Poland (the first transport of purchased aircraft on the ship "Lassel" sailed from Liverpool on 28 August), none of them would take part in combat. In late 1938, the Polish Air Force also ordered 300 advanced PZL.46 Sum light bombers, but due to a delay in starting mass production, none of them were delivered before 1 September. When in the spring of 1939 it turned out that there were problems with the implementation of the new PZL.50 Jastrząb fighter, it was decided to temporarily implement the production of the fighter PZL P 11.G Kobuz. Nevertheless, due to the outbreak of the war, not one of the ordered 90 aircraft of this type were delivered to the army.
 The tank force consisted of two armored brigades, four independent tank battalions and some 30 companies of TKS tankettes attached to infantry divisions and cavalry brigades. A standard tank of the Polish Army during the invasion of 1939 was the 7TP light tank. It was the first tank in the world to be equipped with a diesel engine and Vickers Tank Periscope MK.IV, 360° Gundlach periscope. The 7TP was significantly better armed than its most common opponents, the German Panzer I, ''Panzer'' I and Panzer II, II, but only 140 tanks were produced between 1935 and the outbreak of the war. Poland had also a few relatively modern imported designs, such as 50 Renault R35 tanks and 38 Vickers E tanks.
The Polish Navy was a small fleet of destroyers, submarines and smaller support vessels. Most Polish surface units followed Operation Peking, leaving Polish ports on 20 August and escaping by way of the North Sea to join with the British Royal Navy. Submarine forces participated in Worek Plan, Operation Worek, with the goal of engaging and damaging German shipping in the Baltic Sea, but they had much less success. In addition, many Ship transport, merchant marine ships joined the British merchant fleet and took part in wartime convoys.
The tank force consisted of two armored brigades, four independent tank battalions and some 30 companies of TKS tankettes attached to infantry divisions and cavalry brigades. A standard tank of the Polish Army during the invasion of 1939 was the 7TP light tank. It was the first tank in the world to be equipped with a diesel engine and Vickers Tank Periscope MK.IV, 360° Gundlach periscope. The 7TP was significantly better armed than its most common opponents, the German Panzer I, ''Panzer'' I and Panzer II, II, but only 140 tanks were produced between 1935 and the outbreak of the war. Poland had also a few relatively modern imported designs, such as 50 Renault R35 tanks and 38 Vickers E tanks.
The Polish Navy was a small fleet of destroyers, submarines and smaller support vessels. Most Polish surface units followed Operation Peking, leaving Polish ports on 20 August and escaping by way of the North Sea to join with the British Royal Navy. Submarine forces participated in Worek Plan, Operation Worek, with the goal of engaging and damaging German shipping in the Baltic Sea, but they had much less success. In addition, many Ship transport, merchant marine ships joined the British merchant fleet and took part in wartime convoys.
Details
German plan
 The September Campaign was devised by General Franz Halder, the Chief of the General Staff (Germany), chief of the general staff, and directed by General Walther von Brauchitsch, the commander in chief of the upcoming campaign. It called for the start of hostilities before a declaration of war, and pursued a doctrine of mass encirclement and destruction of enemy forces. The infantry, far from completely mechanized but fitted with fast-moving artillery and logistic support, was to be supported by ''Panzers'' and small numbers of truck-mounted infantry (the ''Schützen'' regiments, forerunners of the ''panzergrenadiers'') to assist the rapid movement of troops and concentrate on Schwerpunkt, localized parts of the enemy military front, front, eventually isolating segments of the enemy, surrounding, and destroying them. The prewar "armoured idea", which an American journalist in 1939 dubbed ''Blitzkrieg'', which was advocated by some generals, including Heinz Guderian, would have had the armour punching holes in the enemy's front and ranging deep into rear areas, but the campaign in Poland would be fought along more traditional lines. That stemmed from conservatism on the part of the German High Command, which mainly restricted the role of armour and mechanized forces to supporting the conventional infantry divisions.
Poland's terrain was well suited for mobile operations when the weather co-operated; the country had flat plains, with long frontiers totalling almost , Poland's long border with Germany on the west and north, facing East Prussia, extended . They had been lengthened by another on the southern side in the aftermath of the 1938 Munich Agreement. The German incorporation of Bohemia and Moravia and creation of the German
The September Campaign was devised by General Franz Halder, the Chief of the General Staff (Germany), chief of the general staff, and directed by General Walther von Brauchitsch, the commander in chief of the upcoming campaign. It called for the start of hostilities before a declaration of war, and pursued a doctrine of mass encirclement and destruction of enemy forces. The infantry, far from completely mechanized but fitted with fast-moving artillery and logistic support, was to be supported by ''Panzers'' and small numbers of truck-mounted infantry (the ''Schützen'' regiments, forerunners of the ''panzergrenadiers'') to assist the rapid movement of troops and concentrate on Schwerpunkt, localized parts of the enemy military front, front, eventually isolating segments of the enemy, surrounding, and destroying them. The prewar "armoured idea", which an American journalist in 1939 dubbed ''Blitzkrieg'', which was advocated by some generals, including Heinz Guderian, would have had the armour punching holes in the enemy's front and ranging deep into rear areas, but the campaign in Poland would be fought along more traditional lines. That stemmed from conservatism on the part of the German High Command, which mainly restricted the role of armour and mechanized forces to supporting the conventional infantry divisions.
Poland's terrain was well suited for mobile operations when the weather co-operated; the country had flat plains, with long frontiers totalling almost , Poland's long border with Germany on the west and north, facing East Prussia, extended . They had been lengthened by another on the southern side in the aftermath of the 1938 Munich Agreement. The German incorporation of Bohemia and Moravia and creation of the German puppet state
A puppet state, puppet régime, puppet government or dummy government, is a State (polity), state that is ''de jure'' independent but ''de facto'' completely dependent upon an outside Power (international relations), power and subject to its o ...
of History of Slovakia#World War II, Slovakia meant that Poland's southern flank was also exposed.
Hitler demanded that Poland be conquered in six weeks, but German planners thought that it would require three months. They intended to exploit their long border fully with the great enveloping manoeuver of ''Fall Weiss''. German units were to invade Poland from three directions:
* A main attack over the western Polish border, which was to be carried out by Army Group South, commanded by Colonel General Gerd von Rundstedt, attacking from German Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
and from the Moravian and Slovak border. General Johannes Blaskowitz's 8th Army was to drive eastward against Łódź. General Wilhelm List's 14th Army was to push on toward Kraków and to turn the Poles' Carpathian Mountains, Carpathian flank. General Walter von Reichenau's 10th Army, in the centre with Army Group South's armour, was to deliver the decisive blow with a northeastward thrust into the heart of Poland.
* A second route of attack from northern Prussia. Colonel General Fedor von Bock commanded Army Group North, comprising General Georg von Küchler's 3rd Army, which was to strike southward from East Prussia, and General Günther von Kluge's 4th Army, which was to attack eastward across the base of the Polish Corridor
The Polish Corridor (german: Polnischer Korridor; pl, Pomorze, Polski Korytarz), also known as the Danzig Corridor, Corridor to the Sea or Gdańsk Corridor, was a territory located in the region of Pomerelia (Pomeranian Voivodeship, eastern ...
.
* A tertiary attack by part of Army Group South's allied Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak units from Slovakia.
* From within Poland, the German minority would assist by engaging in diversion and sabotage operations by ''Volksdeutscher Selbstschutz'' units that had been prepared before the war.
All three assaults were to converge on Warsaw, and the main Polish army was to be encircled and destroyed west of the Vistula. ''Fall Weiss'' was initiated on 1 September 1939 and was the first operation of European Theatre of World War II, Second World War in Europe.
Polish defence plan
 The Polish determination to deploy forces directly at the German-Polish border, prompted by the
The Polish determination to deploy forces directly at the German-Polish border, prompted by the Polish-British Common Defence Pact
The military alliance between the United Kingdom and Poland was formalised by the Anglo-Polish Agreement in 1939, with subsequent addenda of 1940 and 1944, for mutual assistance in case of a military invasion from Nazi Germany, as specified in ...
, shaped the country's defence plan, "Plan West". Poland's most valuable natural resources, industry and population were along the western border in Silesian Voivodeship (1920–1939), Eastern Upper Silesia. Polish policy centred on their protection, especially since many politicians feared that if Poland retreated from the regions disputed by Germany, Britain and France would sign a separate peace treaty with Germany like the 1938 Munich Agreement and allow Germany to stay in those regions. The fact that none of Poland's allies had specifically guaranteed Polish borders or territorial integrity was another Polish concern. These reasons made the Polish government disregarded French advice to deploy the bulk of its forces behind natural barriers, such as the Vistula and San (river), San Rivers, despite some Polish generals supported the idea to be a better strategy. The West Plan allowed the Polish armies to retreat inside the country, but that was supposed to be a slow retreat behind prepared positions intended to give the armed forces time to complete its mobilization and execute a general counteroffensive with the support of the Allies of World War II, Western Allies.
In case of a failure to defend most of the territory, the army was to retreat to the south-east of the country, where the rough terrain, the Stryi River, Stryj and Dniestr rivers, valleys, hills and swamps would provide natural lines of defence against the German advance, and the Romanian Bridgehead
__NOTOC__
The Romanian Bridgehead ( pl, Przedmoście rumuńskie; ro, Capul de pod român) was an area in southeastern Poland that is now located in Ukraine. During the invasion of Poland in 1939 at the start of the Second World War), the Polish ...
could be created.
 The Polish General Staff had not begun elaborating the "West" defence plan until 4 March 1939. It was assumed that the Polish Army, fighting in the initial phase of the war alone, would have to defend the western regions of the country. The plan of operations took into account the numerical and material superiority of the enemy and, also assumed the defensive character of Polish operations. The Polish intentions were defending the western regions that were judged as indispensable for waging the war, taking advantage of the propitious conditions for counterattacks by reserve units and avoiding it from being smashed before the beginning of Franco-British operations in Western Europe. The operation plan had not been elaborated in detail and concerned only the first stage of operations.
The British and the French estimated that Poland would be able to defend itself for two to three months, and Poland estimated it could do so for at least six months. While Poland drafted its estimates based upon the expectation that the Western Allies would honor their treaty obligations and quickly start an offensive of their own, the French and the British expected the war to develop into trench warfare, much like World War I. The Polish government was not notified of the strategy and based all of its defence plans on promises of quick relief by the Western Allies.
Polish forces were stretched thinly along the Polish-German border and lacked compact defence lines and good defence positions along disadvantageous terrain. That strategy also left supply lines poorly protected. One-third of Poland's forces were massed in or near the Polish Corridor, making them vulnerable to a pincer movement, double envelopment from East Prussia and the west. Another third was concentrated in the north-central part of the country, between the major cities of Łódź and Warsaw. The forward positioning of Polish forces vastly increased the difficulty of carrying out strategic maneuvres, compounded by inadequate mobility, as Polish units often lacked the ability to retreat from their defensive positions, as they were being overrun by more mobile German mechanized formations.
The Polish General Staff had not begun elaborating the "West" defence plan until 4 March 1939. It was assumed that the Polish Army, fighting in the initial phase of the war alone, would have to defend the western regions of the country. The plan of operations took into account the numerical and material superiority of the enemy and, also assumed the defensive character of Polish operations. The Polish intentions were defending the western regions that were judged as indispensable for waging the war, taking advantage of the propitious conditions for counterattacks by reserve units and avoiding it from being smashed before the beginning of Franco-British operations in Western Europe. The operation plan had not been elaborated in detail and concerned only the first stage of operations.
The British and the French estimated that Poland would be able to defend itself for two to three months, and Poland estimated it could do so for at least six months. While Poland drafted its estimates based upon the expectation that the Western Allies would honor their treaty obligations and quickly start an offensive of their own, the French and the British expected the war to develop into trench warfare, much like World War I. The Polish government was not notified of the strategy and based all of its defence plans on promises of quick relief by the Western Allies.
Polish forces were stretched thinly along the Polish-German border and lacked compact defence lines and good defence positions along disadvantageous terrain. That strategy also left supply lines poorly protected. One-third of Poland's forces were massed in or near the Polish Corridor, making them vulnerable to a pincer movement, double envelopment from East Prussia and the west. Another third was concentrated in the north-central part of the country, between the major cities of Łódź and Warsaw. The forward positioning of Polish forces vastly increased the difficulty of carrying out strategic maneuvres, compounded by inadequate mobility, as Polish units often lacked the ability to retreat from their defensive positions, as they were being overrun by more mobile German mechanized formations.
 As the prospect of conflict increased, the British government pressed Marshal Edward Śmigły-Rydz to evacuate the most modern elements of the Polish Navy from the Baltic Sea. In the event of war, the Polish military leaders realized that the ships that remained in the Baltic were likely to be quickly sunk by the Germans. Furthermore, since the Danish Straits were well within operating range of the German ''Kriegsmarine'' and ''Luftwaffe'', there was little chance of an evacuation plan succeeding if it were implemented after hostilities began. Four days after the signing of the Polish-British Common Defence Pact, three destroyers of the Polish Navy executed the Peking Plan and so evacuated to Great Britain.
Although the Polish military had prepared for conflict, the civilian population remained largely unprepared. Polish prewar propaganda emphasized that any German invasion would be easily repelled. That made Polish defeats during the German invasion come as a shock to the civilian population. Lacking training for such a disaster, the civilian population panicked and retreated east, spreading chaos, lowering the troops' morale and making road transportation for Polish troops very difficult. The propaganda also had some negative consequences for the Polish troops themselves, whose communications, disrupted by German mobile units operating in the rear and civilians blocking roads, were further thrown into chaos by bizarre reports from Polish radio stations and newspapers, which often reported imaginary victories and other military operations. That led to some Polish troops being encircled or taking a stand against overwhelming odds when they thought they were actually counterattacking or would soon receive reinforcements from other victorious areas.
As the prospect of conflict increased, the British government pressed Marshal Edward Śmigły-Rydz to evacuate the most modern elements of the Polish Navy from the Baltic Sea. In the event of war, the Polish military leaders realized that the ships that remained in the Baltic were likely to be quickly sunk by the Germans. Furthermore, since the Danish Straits were well within operating range of the German ''Kriegsmarine'' and ''Luftwaffe'', there was little chance of an evacuation plan succeeding if it were implemented after hostilities began. Four days after the signing of the Polish-British Common Defence Pact, three destroyers of the Polish Navy executed the Peking Plan and so evacuated to Great Britain.
Although the Polish military had prepared for conflict, the civilian population remained largely unprepared. Polish prewar propaganda emphasized that any German invasion would be easily repelled. That made Polish defeats during the German invasion come as a shock to the civilian population. Lacking training for such a disaster, the civilian population panicked and retreated east, spreading chaos, lowering the troops' morale and making road transportation for Polish troops very difficult. The propaganda also had some negative consequences for the Polish troops themselves, whose communications, disrupted by German mobile units operating in the rear and civilians blocking roads, were further thrown into chaos by bizarre reports from Polish radio stations and newspapers, which often reported imaginary victories and other military operations. That led to some Polish troops being encircled or taking a stand against overwhelming odds when they thought they were actually counterattacking or would soon receive reinforcements from other victorious areas.
German invasion
 Following several German-staged incidents, such as the
Following several German-staged incidents, such as the Gleiwitz incident
The Gleiwitz incident (german: Überfall auf den Sender Gleiwitz; ) was a false flag attack on the radio station ''Sender Gleiwitz'' in Gleiwitz (then Germany and now Gliwice, Poland) staged by Nazi Germany on the night of 31 August 1939. Along ...
, part of Operation Himmler
Operation or Operations may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* ''Operation'' (game), a battery-operated board game that challenges dexterity
* Operation (music), a term used in musical set theory
* ''Operations'' (magazine), Multi-Ma ...
, which German propaganda used as a pretext to claim that German forces were acting in self-defence, one of the first acts of war took place on 1 September 1939. At 04:45, the old German pre-dreadnought battleship ''German battleship Schleswig-Holstein, Schleswig-Holstein'' opened fire on the Polish military transit depot at Battle of Westerplatte, Westerplatte, in the Free City of Danzig, on the Baltic Sea. However, in many places, German units crossed the Polish border even before that time. Around then, the Luftwaffe attacked a number of military and civilian targets, bombing of Wieluń, including Wieluń, the first large-scale city bombing of the war. At 08:00, German troops, still without a formal declaration of war issued, Battle of Mokra, attacked near the Polish village of Mokra. The Battle of the Border had begun. Later that day, the Germans attacked Poland's western, southern and northern borders, and German aircraft began raids on Polish cities. The main axis of attack led eastwards from Germany through the western Polish border. Supporting attacks came from East Prussia, in the north, and a joint German-Slovak tertiary attack by units (Field Army Bernolák, Field Army "Bernolák") from the German-allied Slovak Republic, in the south. All three assaults converged on the Polish capital, Warsaw.
 France and Britain declared war on Germany on 3 September, but Western betrayal, failed to provide any meaningful support. The German-French border Saar Offensive, saw only a few minor skirmishes, and most German forces, including 85% of armoured forces, were engaged in Poland. Despite some Polish successes in minor border battles, the German technical, operational and numerical superiority forced the Polish armies to retreat from the borders towards Warsaw and Lwów. The ''Luftwaffe'' gained air superiority early in the campaign. By destroying communications, the ''Luftwaffe'' increased the pace of the advance which overran Polish airstrips and early warning sites, causing logistical problems for the Poles. Many Polish Air Force units ran low on supplies, and 98 of their number withdrew into neutral Romania. The Polish initial strength of 400 was reduced to 54 by 14 September and air opposition virtually ceased, with the main Polish air bases destroyed during the first 48 hours of the war.
France and Britain declared war on Germany on 3 September, but Western betrayal, failed to provide any meaningful support. The German-French border Saar Offensive, saw only a few minor skirmishes, and most German forces, including 85% of armoured forces, were engaged in Poland. Despite some Polish successes in minor border battles, the German technical, operational and numerical superiority forced the Polish armies to retreat from the borders towards Warsaw and Lwów. The ''Luftwaffe'' gained air superiority early in the campaign. By destroying communications, the ''Luftwaffe'' increased the pace of the advance which overran Polish airstrips and early warning sites, causing logistical problems for the Poles. Many Polish Air Force units ran low on supplies, and 98 of their number withdrew into neutral Romania. The Polish initial strength of 400 was reduced to 54 by 14 September and air opposition virtually ceased, with the main Polish air bases destroyed during the first 48 hours of the war.
 Germany attacked from three directions on land. Günther von Kluge led 20 divisions that entered the Polish Corridor and met a second force heading to Warsaw from East Prussia. Gerd von Rundstedt's 35 divisions attacked southern Poland. By 3 September, when von Kluge in the north had reached the Vistula River, then some from the German border, and Georg von Küchler was approaching the Narew River, Walther von Reichenau's armour was already beyond the Warta river. Two days later, his left wing was well to the rear of Łódź and his right wing at the town of Kielce. On 7 September, the defenders of Warsaw had fallen back to a line paralleling the Vistula River, where they rallied against German tank thrusts. The defensive line ran between Płońsk and Pułtusk, respectively north-west and north-east of Warsaw. The right wing of the Poles had been hammered back from Ciechanów, about north-west of Pułtusk, and was pivoting on Płońsk. At one stage, the Poles were driven from Pułtusk, and the Germans threatened to turn the Polish flank and thrust on to the Vistula and Warsaw. Pułtusk, however, was regained in the face of withering German fire. Many German tanks were captured after a German attack had pierced the line, but the Polish defenders outflanked them. By 8 September, one of Reichenau's armoured corps, having advanced during the first week of the campaign, reached the outskirts of Warsaw. Light divisions on Reichenau's right were on the Vistula between Warsaw and the town of Sandomierz by 9 September, and List, in the south, was on the San River north and south of the town of Przemyśl. At the same time, Guderian led his 3rd Army tanks across the Narew, attacking the line of the Bug River that had already encircled Warsaw. All of the German armies made progress in fulfilling their parts of the plan. The Polish armies split up into uncoordinated fragments, some of which were retreating while others were launching disjointed attacks on the nearest German columns.
Germany attacked from three directions on land. Günther von Kluge led 20 divisions that entered the Polish Corridor and met a second force heading to Warsaw from East Prussia. Gerd von Rundstedt's 35 divisions attacked southern Poland. By 3 September, when von Kluge in the north had reached the Vistula River, then some from the German border, and Georg von Küchler was approaching the Narew River, Walther von Reichenau's armour was already beyond the Warta river. Two days later, his left wing was well to the rear of Łódź and his right wing at the town of Kielce. On 7 September, the defenders of Warsaw had fallen back to a line paralleling the Vistula River, where they rallied against German tank thrusts. The defensive line ran between Płońsk and Pułtusk, respectively north-west and north-east of Warsaw. The right wing of the Poles had been hammered back from Ciechanów, about north-west of Pułtusk, and was pivoting on Płońsk. At one stage, the Poles were driven from Pułtusk, and the Germans threatened to turn the Polish flank and thrust on to the Vistula and Warsaw. Pułtusk, however, was regained in the face of withering German fire. Many German tanks were captured after a German attack had pierced the line, but the Polish defenders outflanked them. By 8 September, one of Reichenau's armoured corps, having advanced during the first week of the campaign, reached the outskirts of Warsaw. Light divisions on Reichenau's right were on the Vistula between Warsaw and the town of Sandomierz by 9 September, and List, in the south, was on the San River north and south of the town of Przemyśl. At the same time, Guderian led his 3rd Army tanks across the Narew, attacking the line of the Bug River that had already encircled Warsaw. All of the German armies made progress in fulfilling their parts of the plan. The Polish armies split up into uncoordinated fragments, some of which were retreating while others were launching disjointed attacks on the nearest German columns.

 Polish forces abandoned the regions of Pomerelia (the Polish Corridor), Greater Poland and Silesian Voivodeship (1920–1939), Polish Upper Silesia in the first week. The Polish plan for border defence was a dismal failure. The German advance, as a whole, was not slowed. On 10 September, the Polish commander-in-chief, Marshal Edward Rydz-Śmigły, ordered a general withdrawal (military), retreat to the south-east, towards the Romanian Bridgehead. Meanwhile, the Germans were tightening their encirclement of the Polish forces west of the Vistula (in the Łódź area and, still farther west, around Poznań) and penetrating deeply into eastern Poland. Warsaw, which had undergone heavy aerial bombardment since the first hours of the war, was attacked on 9 September and was Siege of Warsaw (1939), put under siege on 13 September. Around then, advanced German forces also reached Lwów, a major city in eastern Poland, and 1,150 German aircraft bombed Warsaw on 24 September.
The Polish defensive plan called for a strategy of encirclement. It would allow the Germans to advance in between two Polish Army groups in the line between Berlin and Warsaw-Lodz, and Armia Prusy would then move in and repulse the German spearhead, trapping it. For that to happen, Armia Prusy needed to be fully mobilized by 3 September. However, Polish military planners failed to foresee the speed of the German advance and assumed that Armia Prusy would need to be fully mobilized by 16 September.
Polish forces abandoned the regions of Pomerelia (the Polish Corridor), Greater Poland and Silesian Voivodeship (1920–1939), Polish Upper Silesia in the first week. The Polish plan for border defence was a dismal failure. The German advance, as a whole, was not slowed. On 10 September, the Polish commander-in-chief, Marshal Edward Rydz-Śmigły, ordered a general withdrawal (military), retreat to the south-east, towards the Romanian Bridgehead. Meanwhile, the Germans were tightening their encirclement of the Polish forces west of the Vistula (in the Łódź area and, still farther west, around Poznań) and penetrating deeply into eastern Poland. Warsaw, which had undergone heavy aerial bombardment since the first hours of the war, was attacked on 9 September and was Siege of Warsaw (1939), put under siege on 13 September. Around then, advanced German forces also reached Lwów, a major city in eastern Poland, and 1,150 German aircraft bombed Warsaw on 24 September.
The Polish defensive plan called for a strategy of encirclement. It would allow the Germans to advance in between two Polish Army groups in the line between Berlin and Warsaw-Lodz, and Armia Prusy would then move in and repulse the German spearhead, trapping it. For that to happen, Armia Prusy needed to be fully mobilized by 3 September. However, Polish military planners failed to foresee the speed of the German advance and assumed that Armia Prusy would need to be fully mobilized by 16 September.

 The largest battle during this campaign, the Battle of Bzura, took place near the Bzura River, west of Warsaw, and lasted from 9 to 19 September. The Polish armies ''Poznań'' and ''Pomorze'', retreating from the border area of the Polish Corridor, attacked the flank of the advancing German 8th Army, but the counterattack failed despite initial success. After the defeat, Poland lost its ability to take the initiative and counterattack on a large scale. The German air power was instrumental during the battle. The offensive of the ''Luftwaffe'' broke what remained of the Polish resistance in an "awesome demonstration of air power". The ''Luftwaffe'' quickly destroyed the bridges across the Bzura River. Then, the Polish forces were trapped out in the open and were attacked by wave after wave of ''Stukas'', dropping light bombs, which caused huge numbers of casualties. The Polish anti-aircraft warfare, anti-aircraft batteries ran out of ammunition and retreated to the forests but were then smoked out by the
The largest battle during this campaign, the Battle of Bzura, took place near the Bzura River, west of Warsaw, and lasted from 9 to 19 September. The Polish armies ''Poznań'' and ''Pomorze'', retreating from the border area of the Polish Corridor, attacked the flank of the advancing German 8th Army, but the counterattack failed despite initial success. After the defeat, Poland lost its ability to take the initiative and counterattack on a large scale. The German air power was instrumental during the battle. The offensive of the ''Luftwaffe'' broke what remained of the Polish resistance in an "awesome demonstration of air power". The ''Luftwaffe'' quickly destroyed the bridges across the Bzura River. Then, the Polish forces were trapped out in the open and were attacked by wave after wave of ''Stukas'', dropping light bombs, which caused huge numbers of casualties. The Polish anti-aircraft warfare, anti-aircraft batteries ran out of ammunition and retreated to the forests but were then smoked out by the Heinkel He 111
The Heinkel He 111 is a German airliner and bomber designed by Siegfried and Walter Günter at Heinkel Flugzeugwerke in 1934. Through development, it was described as a "wolf in sheep's clothing". Due to restrictions placed on Germany after th ...
and Dornier Do 17s dropping incendiaries. The ''Luftwaffe'' left the army with the task of mopping up survivors. The ''Stukageschwaders'' alone dropped of bombs during the battle.
By 12 September, all of Poland west of the Vistula had been conquered except for the isolated Warsaw. The Polish government, led by President Ignacy Mościcki, and the high command, led by Marshal Edward Rydz-Śmigły, left Warsaw in the first days of the campaign and headed southeast, reaching Lublin on 6 September. From there, it moved on 9 September to Kremenez and, on 13 September to Zaleshiki, on the Romanian border. Rydz-Śmigły ordered the Polish forces to retreat in the same direction, behind the Vistula and San Rivers, beginning the preparations for the defence of the Romanian Bridgehead area.
Soviet invasion
 From the beginning, the German government repeatedly asked Molotov whether the Soviet Union would keep to its side of the partition bargain. The Soviet forces were holding fast along their designated invasion points pending finalization of the five-month-long undeclared war with Japan in the Far East, successful end of the conflict for the Soviet Union, which occurred in the Battles of Khalkhin Gol. On 15 September 1939, Molotov and Shigenori Tōgō completed their agreement that ended the conflict, and the Nomonhan ceasefire went into effect on 16 September 1939. Now cleared of any "second front" threat from the Japanese, Soviet Premier Joseph Stalin ordered his forces into Poland on 17 September.Goldman pp. 163, 164 It was agreed that the Soviets would relinquish its interest in the territories between the new border and Warsaw in exchange for inclusion of Lithuania in the Soviet "zone of interest".
By 17 September, the Polish defence had already been broken and the only hope was to retreat and reorganize along the Romanian Bridgehead. However, the plans were rendered obsolete nearly overnight when the over 800,000-strong Soviet
From the beginning, the German government repeatedly asked Molotov whether the Soviet Union would keep to its side of the partition bargain. The Soviet forces were holding fast along their designated invasion points pending finalization of the five-month-long undeclared war with Japan in the Far East, successful end of the conflict for the Soviet Union, which occurred in the Battles of Khalkhin Gol. On 15 September 1939, Molotov and Shigenori Tōgō completed their agreement that ended the conflict, and the Nomonhan ceasefire went into effect on 16 September 1939. Now cleared of any "second front" threat from the Japanese, Soviet Premier Joseph Stalin ordered his forces into Poland on 17 September.Goldman pp. 163, 164 It was agreed that the Soviets would relinquish its interest in the territories between the new border and Warsaw in exchange for inclusion of Lithuania in the Soviet "zone of interest".
By 17 September, the Polish defence had already been broken and the only hope was to retreat and reorganize along the Romanian Bridgehead. However, the plans were rendered obsolete nearly overnight when the over 800,000-strong Soviet Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after ...
entered and created the Belarusian and Ukrainian Front (1939), Ukrainian Front (Soviet Army), fronts after they had invaded the eastern regions of Poland, in violation of the Riga Peace Treaty, the Soviet–Polish Non-Aggression Pact, and other international treaties, both bilateral and multilateral. Soviet diplomacy had lied that they were "protecting the Ukrainians, Ukrainian and Belarusians, Belarusian minorities of eastern Poland since the Polish government had abandoned the country and the Polish state ceased to exist".
 The Polish border defence forces in the east, known as the ''Korpus Ochrony Pogranicza'', had about 25 battalions. Rydz-Śmigły ordered them to fall back and not to engage the Soviets. That, however, did not prevent some clashes and small battles, such as the Battle of Grodno (1939), Battle of Grodno, as soldiers and locals attempted to defend the city. The Soviets executed numerous Polish officers, including prisoner of war, prisoners of war like General Józef Olszyna-Wilczyński. The Organization of Ukrainian Nationalists rose against the Poles, and communist partisans organized local revolts, robbing and killing civilians. Those movements were quickly disciplined by the NKVD. The Soviet invasion was one of the decisive factors that convinced the Polish government that the war in Poland was lost. Before the Soviet attack from the east, the Polish military's plan had called for long-term defence against Germany in south-eastern Poland and to await relief from an attack by the Western Allies on Germany's western border. However, the Polish government refused to surrender or to negotiate peace with Germany. Instead, it ordered all units to evacuate Poland and to reorganize in France.
The Polish border defence forces in the east, known as the ''Korpus Ochrony Pogranicza'', had about 25 battalions. Rydz-Śmigły ordered them to fall back and not to engage the Soviets. That, however, did not prevent some clashes and small battles, such as the Battle of Grodno (1939), Battle of Grodno, as soldiers and locals attempted to defend the city. The Soviets executed numerous Polish officers, including prisoner of war, prisoners of war like General Józef Olszyna-Wilczyński. The Organization of Ukrainian Nationalists rose against the Poles, and communist partisans organized local revolts, robbing and killing civilians. Those movements were quickly disciplined by the NKVD. The Soviet invasion was one of the decisive factors that convinced the Polish government that the war in Poland was lost. Before the Soviet attack from the east, the Polish military's plan had called for long-term defence against Germany in south-eastern Poland and to await relief from an attack by the Western Allies on Germany's western border. However, the Polish government refused to surrender or to negotiate peace with Germany. Instead, it ordered all units to evacuate Poland and to reorganize in France.
 Meanwhile, Polish forces tried to move towards the Romanian Bridgehead area, still actively resisting the German invasion. From 17 to 20 September, Polish armies ''Kraków'' and ''Lublin'' were crippled at the Battle of Tomaszów Lubelski, the second-largest battle of the campaign. Lwów capitulated on 22 September because of the Soviet intervention; the city had been attacked by the Germans over a week earlier, and in the middle of the siege, the German troops handed operations over to their Soviet allies. Despite a series of intensifying German attacks, Warsaw, defended by quickly-reorganized retreating units, civilian volunteers and militias, held out until 28 September. The Modlin Fortress north of Warsaw capitulated on 29 September, after Battle of Modlin, an intense 16-day battle. Some isolated Polish garrisons managed to hold their positions long after they had been surrounded by German forces. The enclave of Westerplatte's tiny garrison capitulated on 7 September and the Oksywie garrison Battle of Kępa Oksywska, held until 19 September; the Hel Fortified Area Battle of Hel, was defended until 2 October. In the last week of September, Hitler made a speech in Danzig and said:
Despite a Polish victory at the Battle of Szack (the Soviets later executed all the officers and non-commissioned officer, NCOs they had captured), the Red Army reached the line of rivers Narew, Bug, Vistula and San by 28 September, in many cases meeting German units advancing from the other direction. Polish defenders on the Hel Peninsula on the shore of the Baltic Sea held out until 2 October. The last operational unit of the Polish Army, General Franciszek Kleeberg's ''Independent Operational Group Polesie, Samodzielna Grupa Operacyjna "Polesie"'', surrendered after the four-day Battle of Kock near Lublin on 6 October, marking the end of the September Campaign.
Meanwhile, Polish forces tried to move towards the Romanian Bridgehead area, still actively resisting the German invasion. From 17 to 20 September, Polish armies ''Kraków'' and ''Lublin'' were crippled at the Battle of Tomaszów Lubelski, the second-largest battle of the campaign. Lwów capitulated on 22 September because of the Soviet intervention; the city had been attacked by the Germans over a week earlier, and in the middle of the siege, the German troops handed operations over to their Soviet allies. Despite a series of intensifying German attacks, Warsaw, defended by quickly-reorganized retreating units, civilian volunteers and militias, held out until 28 September. The Modlin Fortress north of Warsaw capitulated on 29 September, after Battle of Modlin, an intense 16-day battle. Some isolated Polish garrisons managed to hold their positions long after they had been surrounded by German forces. The enclave of Westerplatte's tiny garrison capitulated on 7 September and the Oksywie garrison Battle of Kępa Oksywska, held until 19 September; the Hel Fortified Area Battle of Hel, was defended until 2 October. In the last week of September, Hitler made a speech in Danzig and said:
Despite a Polish victory at the Battle of Szack (the Soviets later executed all the officers and non-commissioned officer, NCOs they had captured), the Red Army reached the line of rivers Narew, Bug, Vistula and San by 28 September, in many cases meeting German units advancing from the other direction. Polish defenders on the Hel Peninsula on the shore of the Baltic Sea held out until 2 October. The last operational unit of the Polish Army, General Franciszek Kleeberg's ''Independent Operational Group Polesie, Samodzielna Grupa Operacyjna "Polesie"'', surrendered after the four-day Battle of Kock near Lublin on 6 October, marking the end of the September Campaign.
Civilian deaths
 The Polish Campaign was the first action by Hitler in his attempt to create ''Lebensraum'' (living space) for Germans. Nazi propaganda was one of the factors behind the German brutality directed at civilians that had worked relentlessly to convince the Germans into believing that Jews and Slavs were ''Untermenschen'' (subhumans).
The Polish Campaign was the first action by Hitler in his attempt to create ''Lebensraum'' (living space) for Germans. Nazi propaganda was one of the factors behind the German brutality directed at civilians that had worked relentlessly to convince the Germans into believing that Jews and Slavs were ''Untermenschen'' (subhumans).
 From the first day of invasion, the German air force (the ''Luftwaffe'') attacked civilian targets and columns of refugees along the roads to terrorize the Polish people, disrupt communications and target Polish morale. The ''Luftwaffe'' killed 6,000 to 7,000 Polish civilians during the Bombing of Warsaw in World War II, bombing of Warsaw.
The German invasion saw atrocities committed against Polish men, women and children. The German forces (both SS and the regular ''Wehrmacht'') murdered tens of thousands of Polish civilians (such as the Leibstandarte SS Adolf Hitler was notorious throughout the campaign for burning villages and committing atrocities in numerous Polish towns, including massacres in Błonie, Złoczew, Bolesławiec, Łódź Voivodeship, Bolesławiec, Torzeniec, Goworowo, Mława and Włocławek).
During Operation Tannenberg, a campaign of ethnic cleansing organized by multiple elements of the German government, tens of thousands of Polish civilians were shot at 760 mass execution sites by the ''Einsatzgruppen''.
Altogether, the civilian losses of Polish population amounted to about 150,000 to 200,000. Roughly 1,250 German civilians were also killed during the invasion. (Also, 2,000 died fighting Polish troops as members of ethnic German militia forces such as the ''Volksdeutscher Selbstschutz'', which was a fifth column during the invasion.)
From the first day of invasion, the German air force (the ''Luftwaffe'') attacked civilian targets and columns of refugees along the roads to terrorize the Polish people, disrupt communications and target Polish morale. The ''Luftwaffe'' killed 6,000 to 7,000 Polish civilians during the Bombing of Warsaw in World War II, bombing of Warsaw.
The German invasion saw atrocities committed against Polish men, women and children. The German forces (both SS and the regular ''Wehrmacht'') murdered tens of thousands of Polish civilians (such as the Leibstandarte SS Adolf Hitler was notorious throughout the campaign for burning villages and committing atrocities in numerous Polish towns, including massacres in Błonie, Złoczew, Bolesławiec, Łódź Voivodeship, Bolesławiec, Torzeniec, Goworowo, Mława and Włocławek).
During Operation Tannenberg, a campaign of ethnic cleansing organized by multiple elements of the German government, tens of thousands of Polish civilians were shot at 760 mass execution sites by the ''Einsatzgruppen''.
Altogether, the civilian losses of Polish population amounted to about 150,000 to 200,000. Roughly 1,250 German civilians were also killed during the invasion. (Also, 2,000 died fighting Polish troops as members of ethnic German militia forces such as the ''Volksdeutscher Selbstschutz'', which was a fifth column during the invasion.)
Aftermath
 John Gunther wrote in December 1939 that "the German campaign was a masterpiece. Nothing quite like it has been seen in military history". The country was divided between Germany and the Soviet Union. Slovak Republic (WWII), Slovakia gained back those territories taken by Poland in autumn 1938. Lithuania Vilnius#World War II, received the city of Vilnius and its environs on 28 October 1939 from the Soviet Union. On 8 and 13 September 1939, the German military district in the area of Poznań, Posen, commanded by general , and West Prussia, commanded by general Walter Heitz, were established in conquered Greater Poland and Pomerelia, respectively. Based on laws of 21 May 1935 and 1 June 1938, the German military delegated civil administrative powers to Chiefs of Civil Administration (''CdZ''). Hitler appointed Arthur Greiser to become the CdZ of the Posen military district, and Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia, Danzig's Gauleiter Albert Forster to become the CdZ of the West Prussian military district. On 3 October 1939, the military districts centered on and named "Lodz" and "Krakow, Krakau" were set up under command of major generals Gerd von Rundstedt and Wilhelm List, and Hitler appointed Hans Frank and Arthur Seyß-Inquart as civil heads, respectively. Thus the entirety of occupied Poland was divided into four military districts (West Prussia, Posen, Lodz, and Krakau). Frank was at the same time appointed "supreme chief administrator" for all occupied territories. On 28 September, another German–Soviet Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Demarcation, secret German–Soviet protocol modified the arrangements of August: all of Lithuania was shifted to the Soviet sphere of influence; in exchange, the dividing line in Poland was moved in Germany's favour, eastwards towards the Bug River. On 8 October, Germany formally Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany, annexed the western parts of Poland with Greiser and Forster as ''Reichsstatthalter'', while the south-central parts were administered as the General Government led by Frank.
John Gunther wrote in December 1939 that "the German campaign was a masterpiece. Nothing quite like it has been seen in military history". The country was divided between Germany and the Soviet Union. Slovak Republic (WWII), Slovakia gained back those territories taken by Poland in autumn 1938. Lithuania Vilnius#World War II, received the city of Vilnius and its environs on 28 October 1939 from the Soviet Union. On 8 and 13 September 1939, the German military district in the area of Poznań, Posen, commanded by general , and West Prussia, commanded by general Walter Heitz, were established in conquered Greater Poland and Pomerelia, respectively. Based on laws of 21 May 1935 and 1 June 1938, the German military delegated civil administrative powers to Chiefs of Civil Administration (''CdZ''). Hitler appointed Arthur Greiser to become the CdZ of the Posen military district, and Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia, Danzig's Gauleiter Albert Forster to become the CdZ of the West Prussian military district. On 3 October 1939, the military districts centered on and named "Lodz" and "Krakow, Krakau" were set up under command of major generals Gerd von Rundstedt and Wilhelm List, and Hitler appointed Hans Frank and Arthur Seyß-Inquart as civil heads, respectively. Thus the entirety of occupied Poland was divided into four military districts (West Prussia, Posen, Lodz, and Krakau). Frank was at the same time appointed "supreme chief administrator" for all occupied territories. On 28 September, another German–Soviet Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Demarcation, secret German–Soviet protocol modified the arrangements of August: all of Lithuania was shifted to the Soviet sphere of influence; in exchange, the dividing line in Poland was moved in Germany's favour, eastwards towards the Bug River. On 8 October, Germany formally Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany, annexed the western parts of Poland with Greiser and Forster as ''Reichsstatthalter'', while the south-central parts were administered as the General Government led by Frank.
 Even though water barriers separated most of the spheres of interest, the Soviet and German troops met on numerous occasions. The most remarkable event of this kind occurred at Brest-Litovsk on 22 September. The German 19th ''Panzer'' Corps—commanded by General Heinz Guderian—had occupied the city, which lay within the Soviet sphere of interest. When the Soviet 29th Tank Brigade (commanded by Semyon Krivoshein) approached, the commanders agreed that the German troops would withdraw and the Soviet troops would enter the city, saluting each other. At Brest-Litovsk, Soviet and German commanders held a joint Nazi–Soviet military parade in Brest-Litovsk, victory parade before German forces withdrew westward behind a new demarcation line. Just three days earlier, however, the parties had a more hostile encounter near Lwów (''Lviv, Lemberg''), when the German 137th ''Gebirgsjägerregimenter'' (mountain infantry regiment) attacked a reconnaissance detachment of the Soviet 24th Tank Brigade; after a few casualties on both sides, the parties turned to negotiations. The German troops left the area, and the Red Army troops entered Lwów on 22 September.
The Molotov–Ribbentrop pact and the invasion of Poland marked the beginning of a period during which the government of the Soviet Union increasingly tried to convince itself that the actions of Germany were reasonable, and were not developments to be worried about, despite evidence to the contrary. On 7 September 1939, just a few days after France and Britain joined the war against Germany, Stalin explained to a colleague that the war was to the advantage of the Soviet Union, as follows:Clark, Lloyd, ''Kursk: The greatest battle: Eastern Front 1943'', 2011, p. 62
About 65,000 Polish troops were killed in the fighting, with 420,000 others being captured by the Germans and 240,000 more by the Soviets (for a total of 660,000 prisoners). Up to 120,000 Polish troops escaped to Neutral country, neutral Romania (through the Romanian Bridgehead and Hungary), and another 20,000 to Latvia and Lithuania, with the majority eventually making their way to France or Britain. Most of the Polish Navy succeeded in evacuating to Britain as well. German personnel losses were less than their enemies (c. 16,000 killed).
Even though water barriers separated most of the spheres of interest, the Soviet and German troops met on numerous occasions. The most remarkable event of this kind occurred at Brest-Litovsk on 22 September. The German 19th ''Panzer'' Corps—commanded by General Heinz Guderian—had occupied the city, which lay within the Soviet sphere of interest. When the Soviet 29th Tank Brigade (commanded by Semyon Krivoshein) approached, the commanders agreed that the German troops would withdraw and the Soviet troops would enter the city, saluting each other. At Brest-Litovsk, Soviet and German commanders held a joint Nazi–Soviet military parade in Brest-Litovsk, victory parade before German forces withdrew westward behind a new demarcation line. Just three days earlier, however, the parties had a more hostile encounter near Lwów (''Lviv, Lemberg''), when the German 137th ''Gebirgsjägerregimenter'' (mountain infantry regiment) attacked a reconnaissance detachment of the Soviet 24th Tank Brigade; after a few casualties on both sides, the parties turned to negotiations. The German troops left the area, and the Red Army troops entered Lwów on 22 September.
The Molotov–Ribbentrop pact and the invasion of Poland marked the beginning of a period during which the government of the Soviet Union increasingly tried to convince itself that the actions of Germany were reasonable, and were not developments to be worried about, despite evidence to the contrary. On 7 September 1939, just a few days after France and Britain joined the war against Germany, Stalin explained to a colleague that the war was to the advantage of the Soviet Union, as follows:Clark, Lloyd, ''Kursk: The greatest battle: Eastern Front 1943'', 2011, p. 62
About 65,000 Polish troops were killed in the fighting, with 420,000 others being captured by the Germans and 240,000 more by the Soviets (for a total of 660,000 prisoners). Up to 120,000 Polish troops escaped to Neutral country, neutral Romania (through the Romanian Bridgehead and Hungary), and another 20,000 to Latvia and Lithuania, with the majority eventually making their way to France or Britain. Most of the Polish Navy succeeded in evacuating to Britain as well. German personnel losses were less than their enemies (c. 16,000 killed).
 None of the parties to the conflict—Germany, the Western Allies or the Soviet Union—expected that the German invasion of Poland would lead to a war that would surpass World War I in its scale and cost. It would be months before Hitler would see the futility of his peace negotiation attempts with the United Kingdom and France, but the culmination of combined European and Pacific conflicts would result in what was truly a "world war". Thus, what was not seen by most politicians and generals in 1939 is clear from the historical perspective: The Polish September Campaign marked the beginning of a pan-European war, which combined with the Second Sino-Japanese War, Japanese invasion of China in 1937 and the Pacific War in 1941 to form the global conflict known as World War II.
The invasion of Poland led Britain and France to declare war on Germany on 3 September. However, they did little to affect the outcome of the September Campaign. No declaration of war was issued by Britain and France against the Soviet Union. This lack of direct help led many Poles to believe that they had been Western betrayal#Up to 1939, betrayed by their Western allies. British Foreign Secretary
None of the parties to the conflict—Germany, the Western Allies or the Soviet Union—expected that the German invasion of Poland would lead to a war that would surpass World War I in its scale and cost. It would be months before Hitler would see the futility of his peace negotiation attempts with the United Kingdom and France, but the culmination of combined European and Pacific conflicts would result in what was truly a "world war". Thus, what was not seen by most politicians and generals in 1939 is clear from the historical perspective: The Polish September Campaign marked the beginning of a pan-European war, which combined with the Second Sino-Japanese War, Japanese invasion of China in 1937 and the Pacific War in 1941 to form the global conflict known as World War II.
The invasion of Poland led Britain and France to declare war on Germany on 3 September. However, they did little to affect the outcome of the September Campaign. No declaration of war was issued by Britain and France against the Soviet Union. This lack of direct help led many Poles to believe that they had been Western betrayal#Up to 1939, betrayed by their Western allies. British Foreign Secretary Lord Halifax
Edward Frederick Lindley Wood, 1st Earl of Halifax, (16 April 1881 – 23 December 1959), known as The Lord Irwin from 1925 until 1934 and The Viscount Halifax from 1934 until 1944, was a senior British Conservative politician of the 19 ...
said they were only obligated to declare war on Germany due to the first clause of the Anglo-Polish military alliance, Anglo-Polish Agreement in 1939.
The different attitude of the Anglo-French allies of Poland towards Nazi Germany and the USSR was argued at this time, for example, by the future head of the British government, Churchill:
On 23 May 1939, Hitler explained to his officers that the object of the aggression was not Danzig, but the need to obtain German ''Lebensraum
(, ''living space'') is a German concept of settler colonialism, the philosophy and policies of which were common to German politics from the 1890s to the 1940s. First popularized around 1901, '' lso in:' became a geopolitical goal of Imperi ...
'' and details of this concept would be later formulated in the infamous ''Generalplan Ost''. The invasion decimated Urban area, urban residential areas, civilians soon became indistinguishable from combatants, and the forthcoming German occupation (both on the Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany, annexed territories and in the General Government) was one of the most brutal episodes of World War II, resulting in between 5.47 million and 5.67 million Polish deaths (about one-sixth of the country's total population, and over 90% of its Jewish minority)—including the mass murder of 3 million Polish citizens (mainly Jews as part of the final solution) in extermination camps like Auschwitz, in concentration camps, and in numerous ad hoc massacres, where civilians were rounded up, taken to a nearby forest, machine-gunned, and then buried, whether they were dead or not. Among the 100,000 people murdered in the ''Intelligenzaktion'' operations in 1939–1940, approximately 61,000 were members of the Polish intelligentsia: scholars, clergy, former officers, and others, whom the Germans identified as political targets in the ''Special Prosecution Book-Poland'', compiled before the war began in September 1939.
According to the Polish Institute of National Remembrance, Polish areas annexed by the Soviet Union, Soviet occupation between 1939 and 1941 resulted in the death of 150,000 and deportation of 320,000 of Polish citizens, when all who were deemed dangerous to the Soviet regime were subject to Sovietization
Sovietization (russian: Советизация) is the adoption of a political system based on the model of soviets (workers' councils) or the adoption of a way of life, mentality, and culture modelled after the Soviet Union. This often included ...
, forced resettlement, imprisonment in labor camps (the ''Gulags'') or murdered, like the Polish officers in the Katyn massacre.
 Since October 1939, the Polish army that could escape imprisonment from the Soviets or Nazis were mainly heading for British and French territories. These places were considered safe, because of the pre-war alliance between Great-Britain, France and Poland. Not only did the government escape, but also the national gold supply was evacuated via Romania and brought to the West, notably London and Ottawa. The approximately of gold was considered sufficient to field an army for the duration of the war.
Since October 1939, the Polish army that could escape imprisonment from the Soviets or Nazis were mainly heading for British and French territories. These places were considered safe, because of the pre-war alliance between Great-Britain, France and Poland. Not only did the government escape, but also the national gold supply was evacuated via Romania and brought to the West, notably London and Ottawa. The approximately of gold was considered sufficient to field an army for the duration of the war.
Eyewitness accounts
''From Lemberg to Bordeaux'' ('Von Lemberg bis Bordeaux'), written by Leo Leixner, a journalist and war correspondent, is a first-hand account of the battles that led to the falls of Poland, the Low Countries, and France. It includes a rare eyewitness description of the Battle of Węgierska Górka. In August 1939, Leixner joined the Wehrmacht as a war reporter, was promoted to sergeant and, in 1941, published his recollections. The book was originally issued by Franz Eher Nachfolger, the central publishing house of the Nazi Party. The American journalist and filmmaker Julien Bryan came to besieged Warsaw on 7 September 1939 in the time of German bombardment. He photographed the beginning of the war by using one roll of colour film (Kodachrome) and much black-and-white film. He made one film about German crimes against civilians during the invasion. In colour, he photographed Polish soldiers, fleeing civilians, bombed houses, and a German bomber He 111 destroyed by the Polish Army in Warsaw. His photographs and film ''Siege'' are stored in the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum.Misconceptions
Combat between Polish cavalry and German tanks
 Polish cavalry units did not engage German tanks with lances and swords. At the Battle of Tuchola Forest on 1 September 1939 the 18th Pomeranian Uhlan Regiment had been tasked to cover the retreat of Polish infantry. In the evening the Pomeranian Uhlans encountered contingents of the advancing German 20th Infantry Division of Heinz Guderian's XIX Army. Commander Kazimierz Mastalerz ordered an attack, forcing the 20th infantry to withdraw and disperse. The engagement proved to be successful as the German advance had been delayed. However, upon redeployment, the 18th Pomeranians came under sudden and intense machine gun fire of German armored reconnaissance vehicles. Despite their quick retreat, nearly a third of the Uhlans were killed or wounded.
A group of German and Italian war correspondents, who visited the battlefield noticed the dead cavalry men and horses among the armored vehicles. Italian reporter Indro Montanelli promptly published an article in the ''Corriere della Sera'', on the brave and heroic Polish cavalry men, who charged German tanks with sabres and lances.
Historian Steven Zaloga in ''Poland 1939: The Birth of Blitzkrieg'' (2004):
In 1939, only 10% of the Polish army was made up of cavalry units.
Polish cavalry units did not engage German tanks with lances and swords. At the Battle of Tuchola Forest on 1 September 1939 the 18th Pomeranian Uhlan Regiment had been tasked to cover the retreat of Polish infantry. In the evening the Pomeranian Uhlans encountered contingents of the advancing German 20th Infantry Division of Heinz Guderian's XIX Army. Commander Kazimierz Mastalerz ordered an attack, forcing the 20th infantry to withdraw and disperse. The engagement proved to be successful as the German advance had been delayed. However, upon redeployment, the 18th Pomeranians came under sudden and intense machine gun fire of German armored reconnaissance vehicles. Despite their quick retreat, nearly a third of the Uhlans were killed or wounded.
A group of German and Italian war correspondents, who visited the battlefield noticed the dead cavalry men and horses among the armored vehicles. Italian reporter Indro Montanelli promptly published an article in the ''Corriere della Sera'', on the brave and heroic Polish cavalry men, who charged German tanks with sabres and lances.
Historian Steven Zaloga in ''Poland 1939: The Birth of Blitzkrieg'' (2004):
In 1939, only 10% of the Polish army was made up of cavalry units.
Polish Air Force
The Polish Air Force order of battle in 1939, Polish Air Force was not destroyed on the ground in the first days of the war. Though numerically inferior, it had been redeployed from major air bases to small camouflaged airfields shortly before the war. Only some trainer aircraft, trainers and auxiliary aircraft were destroyed on the ground. The Polish Air Force, despite being significantly outnumbered and with its fighters outmatched by more advanced German fighters, remained active until the second week of the campaign, inflicting significant damage on the ''Luftwaffe''. The ''Luftwaffe'' lost 285 aircraft to all operational causes, with 279 more damaged, and the Poles lost 333 aircraft.Polish resistance to the invasion
Another question concerns whether Poland inflicted any significant losses on the German forces and whether it surrendered too quickly. While exact estimates vary, Poland cost the Germans about 45,000 casualties and 11,000 damaged or destroyed military vehicles, including 993 tanks and armored cars, 565 to 697 airplanes and 370 artillery pieces. – lists 236 tanks as totally destroyed and 457 damaged, of which 180 were repaired and the remainder scrapped, giving 180 + 277 = 513 tanks destroyed or scrapped following damage, and 319 armoured cars lost. As for duration, the September Campaign lasted about a week and a half less than the Battle of France in 1940 even though the Anglo-French forces were much closer to parity with the Germans in numerical strength and equipment and were supported by the Maginot line.Polish to German forces in the September Campaign: 1,000,000 soldiers, 4,300 guns, 880 tanks, 435 aircraft (Poland) to 1,800,000 soldiers, 10,000 guns, 2,800 tanks, 3,000 aircraft (Germany). French and participating Allies to German forces in the Battle of France: 2,862,000 soldiers, 13,974 guns, 3,384 tanks, 3,099 aircraft 2 (Allies) to 3,350,000 soldiers, 7,378 guns, 2,445 tanks, 5,446 aircraft (Germany). Furthermore, the Polish Army was preparing theRomanian Bridgehead
__NOTOC__
The Romanian Bridgehead ( pl, Przedmoście rumuńskie; ro, Capul de pod român) was an area in southeastern Poland that is now located in Ukraine. During the invasion of Poland in 1939 at the start of the Second World War), the Polish ...
, which would have prolonged Polish defence, but the plan was invalidated by the Soviet invasion of Poland on 17 September 1939.
Poland also never officially surrendered to the Germans. Under German occupation, there was continued resistance by forces such as the ''Armia Krajowa'', Henryk Dobrzański's guerillas, and the Leśni ("forest partisans").


First use of ''Blitzkrieg'' strategy
It is often assumed that '' Blitzkrieg'' is the strategy that Germany first used in Poland. Many early post-war histories, such as Barrie Pitt's in ''The Second World War'' (BPC Publishing 1966), attribute German victory to "enormous development in military technique which occurred between 1918 and 1940", and cite that "Germany, who translated (British inter-war) theories into action... called the result ''Blitzkrieg''". That idea has been repudiated by some authors. Matthew Cooper writes: ''Vernichtungsgedanke'' was a strategy dating back to Frederick the Great, and it was applied in the Polish Campaign, little changed from the Franco-Prussian War, French campaigns in 1870 or 1914. The use oftank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and good battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engin ...
s
John Ellis, writing in ''Brute Force (Ellis book), Brute Force'', asserted that
Zaloga and Madej, in ''The Polish Campaign 1939'', also address the subject of mythical interpretations of ''Blitzkrieg'' and the importance of other arms in the campaign. Western accounts of the September campaign have stressed the shock value of the ''panzers'' and ''Stuka'' attacks, they have
See also
* Eastern Front (World War II) * Gestapo–NKVD conferences * History of Poland (1939–1945) * List of Polish divisions in World War II * Occupation of Poland (1939–1945) * Oder–Neisse line * Phoney War * Polish cavalry brigade order of battle in 1939 * Polish contribution to World War II * Polish resistance movement in World War II * Siege of Warsaw (1939) * The Black Book of Poland * Timeline of the invasion of Poland * List of World War II military equipment of Poland * List of German military equipment of World War II * List of Czechoslovakia interwar period weapons - the Slovak arsenal was inherited from Czechoslovakia * Slovak Air Force (1939–1945) * Western betrayalNotes
References
Sources and further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Moorhouse, Roger. ''Poland 1939: The Outbreak of World War II'' (Basic Books, 2020) popular historonline review
* * * * * * * * * *
Further reading
* * *External links
The Conquest of Poland and the Beginnings of Jewish Persecution
on the Yad Vashem website
German invasion of Poland
Original reports from The Times
Blitzkrieg Unleashed: The German Invasion of Poland, 1939
History of the invasion with focus on precise locations and events, as experienced by real people.
The Campaign in Poland at WorldWar2 Database
German Statistics including September Campaign losses
Radio reports on the German invasion of Poland
an
Nazi broadcast claiming that Germany's action is an act of defence
Headline story on BBC: Germany invades Poland
1 September 1939.
An essay describing the Polish Campaign in a larger strategic context of the war
schemas by Dr. Leo Niehorster
schemas by Dr. Leo Niehorster
* [http://www.polishnews.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&catid=93%3Ahistoriapolish-history&id=402%3Athe-polish-campaign-of-september-1939-in-perspective&Itemid=329&showall=1 "The Polish Campaign of September 1939 in Perspective" ''Polish News'', 24 September 2008]
Invasion of Poland
by Bradley Lightbody, Last updated 2011-03-30
Polish forces in the West
. A website describing the Polish forces in France, UK and the Netherlands War propaganda newsreel * ''Advance into Poland''. National Archives and Records Administration (German. Series: Motion Picture Films. G-2 Army Military Intelligence Division). Internet Archive
Reel 1 of 4
''Invasion of Poland in 1939 by German Army''
(1943). Film Bulletin n. 48 US Department of the Army, Signal Corps Photographic Center. Internet Archive.
''Special Release – Europe At War!''
(1939). Universal Studios. Internet Archive. {{DEFAULTSORT:Invasion Of Poland Invasion of Poland, 1939 in Poland Conflicts in 1939, Poland World War II invasions, Poland Invasions of Poland September 1939 events October 1939 events