Nature Magazine (US) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Nature'' is a British weekly
 Not long after the conclusion of ''The Reader'', a former editor, Norman Lockyer, decided to create a new scientific journal titled ''Nature'', taking its name from a line by William Wordsworth: "To the solid ground of nature trusts the Mind that builds for aye". First owned and published by Alexander Macmillan, ''Nature'' was similar to its predecessors in its attempt to "provide cultivated readers with an accessible forum for reading about advances in scientific knowledge." Janet Browne has proposed that "far more than any other science journal of the period, ''Nature'' was conceived, born, and raised to serve polemic purpose." Many of the early editions of ''Nature'' consisted of articles written by members of a group that called itself the X Club, a group of scientists known for having liberal, progressive, and somewhat controversial scientific beliefs relative to the time period. Initiated by Thomas Henry Huxley, the group consisted of such important scientists as Joseph Dalton Hooker, Herbert Spencer, and
Not long after the conclusion of ''The Reader'', a former editor, Norman Lockyer, decided to create a new scientific journal titled ''Nature'', taking its name from a line by William Wordsworth: "To the solid ground of nature trusts the Mind that builds for aye". First owned and published by Alexander Macmillan, ''Nature'' was similar to its predecessors in its attempt to "provide cultivated readers with an accessible forum for reading about advances in scientific knowledge." Janet Browne has proposed that "far more than any other science journal of the period, ''Nature'' was conceived, born, and raised to serve polemic purpose." Many of the early editions of ''Nature'' consisted of articles written by members of a group that called itself the X Club, a group of scientists known for having liberal, progressive, and somewhat controversial scientific beliefs relative to the time period. Initiated by Thomas Henry Huxley, the group consisted of such important scientists as Joseph Dalton Hooker, Herbert Spencer, and
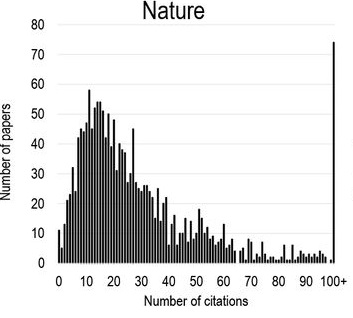 According to '' Science'', another academic journal, being published in ''Nature'' has been known to carry a certain level of prestige in academia. In particular, empirical papers are often highly cited, which can lead to promotions, grant funding, and attention from the mainstream media. Because of these positive feedback effects, competition among scientists to publish in high-level journals like ''Nature'' and its closest competitor, '' Science'', can be very fierce. ''Nature''s impact factor, a measure of how many citations a journal generates in other works, was 42.778 in 2019 (as measured by
According to '' Science'', another academic journal, being published in ''Nature'' has been known to carry a certain level of prestige in academia. In particular, empirical papers are often highly cited, which can lead to promotions, grant funding, and attention from the mainstream media. Because of these positive feedback effects, competition among scientists to publish in high-level journals like ''Nature'' and its closest competitor, '' Science'', can be very fierce. ''Nature''s impact factor, a measure of how many citations a journal generates in other works, was 42.778 in 2019 (as measured by
 ''Nature'' is edited and published in the United Kingdom by a division of the international
''Nature'' is edited and published in the United Kingdom by a division of the international
Freely available scans of volumes: 1–112 (1869–1923)
''Nature'' Index
For €9500, ''Nature'' journals will now make your paper free to read
{{DEFAULTSORT:Nature (Journal) 1869 establishments in England English-language journals Multidisciplinary scientific journals Natural sciences Nature Research academic journals Publications established in 1869 Weekly journals
scientific journal
In academic publishing, a scientific journal is a periodical publication intended to further the progress of science, usually by reporting new research.
Content
Articles in scientific journals are mostly written by active scientists such as s ...
founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed
Peer review is the evaluation of work by one or more people with similar competencies as the producers of the work (peers). It functions as a form of self-regulation by qualified members of a profession within the relevant field. Peer review ...
research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature
Springer Nature or the Springer Nature Group is a German-British academic publishing company created by the May 2015 merger of Springer Science+Business Media and Holtzbrinck Publishing Group's Nature Publishing Group, Palgrave Macmillan, and Macm ...
. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 '' Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 42.778), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month.
Founded in autumn 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander Macmillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the journal; ''Nature'' redoubled its efforts in explanatory and scientific journalism
Science journalism conveys reporting about science to the public. The field typically involves interactions between scientists, journalists, and the public.
Origins
Modern science journalism dates back to '' Digdarshan'' (means showing the d ...
. The late 1980s and early 1990s saw the creation of a network of editorial offices outside of Britain and the establishment of ten new supplementary, speciality publications (e.g. '' Nature Materials''). Since the late 2000s, dedicated editorial and current affairs columns are created weekly, and electoral endorsements are featured. The primary source of the journal remains, as established at its founding, research scientists; editing standards are primarily concerned with technical readability. Each issue also features articles that are of general interest to the scientific community, namely business, funding, scientific ethics, and research breakthroughs. There are also sections on books, arts, and short science fiction stories.
The main research published in ''Nature'' consists mostly of papers (articles or letters) in lightly edited form. They are highly technical and dense, but, due to imposed text limits, they are typically summaries of larger work. Innovations or breakthroughs in any scientific or technological field are featured in the journal as either letters or news articles. The papers that have been published in this journal are internationally acclaimed for maintaining high research standards. Conversely, due to the journal's exposure, it has at various times been a subject of controversy for its handling of academic dishonesty, the scientific method, and news coverage. Fewer than 8% of submitted papers are accepted for publication. In 2007, ''Nature'' (together with '' Science'') received the Prince of Asturias Award for Communications and Humanity.
Nature mostly publishes research articles. Spotlight articles are not research papers but mostly news or magazine style papers and hence do not count towards impact factor nor receive similar recognition as research articles. Some spotlight articles are also paid by partners or sponsors.
History
Background
The enormous progress in science and mathematics during the 19th century was recorded in journals written mostly inGerman
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
or French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, as well as in English. Britain underwent enormous technological and industrial changes and advances particularly in the latter half of the 19th century. The most respected scientific journals of this time were the refereed journals of the Royal Society, which had published many of the great works from Isaac Newton and Michael Faraday to Charles Darwin. In addition, the number of popular science periodicals doubled from the 1850s to the 1860s. According to the editors of these popular science magazines, the publications were designed to serve as "organs of science", in essence, a means of connecting the public to the scientific world.
''Nature'', first created in 1869, was not the first magazine of its kind in Britain. One journal to precede ''Nature'' was ''Recreative Science: A Record and Remembrancer of Intellectual Observation'', which, created in 1859, began as a natural history magazine and progressed to include more physical observational science and technical subjects and less natural history. The journal's name changed from its original title to ''Intellectual Observer: A Review of Natural History, Microscopic Research, and Recreative Science'' and then to the ''Student and Intellectual Observer of Science, Literature, and Art''. While ''Recreative Science'' had attempted to include more physical sciences such as astronomy and archaeology, the ''Intellectual Observer'' broadened itself further to include literature and art as well. Similar to ''Recreative Science'' was the scientific journal ''Popular Science Review'', created in 1862, which covered different fields of science by creating subsections titled "Scientific Summary" or "Quarterly Retrospect", with book reviews and commentary on the latest scientific works and publications. Two other journals produced in England prior to the development of ''Nature'' were the ''Quarterly Journal of Science
''Quarterly Journal of Science'' was the title of two British scientific periodicals of the 19th century.
The first was established in 1816 by William Thomas Brande, as the ''Quarterly Journal of Science, Literature and the Arts''. He edited it w ...
'' and ''Scientific Opinion'', established in 1864 and 1868, respectively. The journal most closely related to ''Nature'' in its editorship and format was ''The Reader
''The Reader'' (german: Der Vorleser) is a novel by German law professor and judge Bernhard Schlink, published in Germany in 1995 and in the United States in 1997. The story is a parable, dealing with the difficulties post-war German generations ...
'', created in 1863; the publication mixed science with literature and art in an attempt to reach an audience outside of the scientific community, similar to ''Popular Science Review''.
These similar journals all ultimately failed. The ''Popular Science Review'' survived longest, lasting 20 years and ending its publication in 1881; ''Recreative Science'' ceased publication as the ''Student and Intellectual Observer'' in 1871. The ''Quarterly Journal'', after undergoing a number of editorial changes, ceased publication in 1885. ''The Reader'' terminated in 1867, and finally, ''Scientific Opinion'' lasted a mere 2 years, until June 1870.
Creation
 Not long after the conclusion of ''The Reader'', a former editor, Norman Lockyer, decided to create a new scientific journal titled ''Nature'', taking its name from a line by William Wordsworth: "To the solid ground of nature trusts the Mind that builds for aye". First owned and published by Alexander Macmillan, ''Nature'' was similar to its predecessors in its attempt to "provide cultivated readers with an accessible forum for reading about advances in scientific knowledge." Janet Browne has proposed that "far more than any other science journal of the period, ''Nature'' was conceived, born, and raised to serve polemic purpose." Many of the early editions of ''Nature'' consisted of articles written by members of a group that called itself the X Club, a group of scientists known for having liberal, progressive, and somewhat controversial scientific beliefs relative to the time period. Initiated by Thomas Henry Huxley, the group consisted of such important scientists as Joseph Dalton Hooker, Herbert Spencer, and
Not long after the conclusion of ''The Reader'', a former editor, Norman Lockyer, decided to create a new scientific journal titled ''Nature'', taking its name from a line by William Wordsworth: "To the solid ground of nature trusts the Mind that builds for aye". First owned and published by Alexander Macmillan, ''Nature'' was similar to its predecessors in its attempt to "provide cultivated readers with an accessible forum for reading about advances in scientific knowledge." Janet Browne has proposed that "far more than any other science journal of the period, ''Nature'' was conceived, born, and raised to serve polemic purpose." Many of the early editions of ''Nature'' consisted of articles written by members of a group that called itself the X Club, a group of scientists known for having liberal, progressive, and somewhat controversial scientific beliefs relative to the time period. Initiated by Thomas Henry Huxley, the group consisted of such important scientists as Joseph Dalton Hooker, Herbert Spencer, and John Tyndall
John Tyndall FRS (; 2 August 1820 – 4 December 1893) was a prominent 19th-century Irish physicist. His scientific fame arose in the 1850s from his study of diamagnetism. Later he made discoveries in the realms of infrared radiation and the p ...
, along with another five scientists and mathematicians; these scientists were all avid supporters of Darwin's theory of evolution
Darwinism is a theory of biological evolution developed by the English naturalist Charles Darwin (1809–1882) and others, stating that all species of organisms arise and develop through the natural selection of small, inherited variations that ...
as common descent
Common descent is a concept in evolutionary biology applicable when one species is the ancestor of two or more species later in time. All living beings are in fact descendants of a unique ancestor commonly referred to as the last universal comm ...
, a theory which, during the latter half of the 19th century, received a great deal of criticism among more conservative groups of scientists. Perhaps it was in part its scientific liberality that made ''Nature'' a longer-lasting success than its predecessors. John Maddox, editor of ''Nature'' from 1966 to 1973 and from 1980 to 1995, suggested at a celebratory dinner for the journal's centennial edition that perhaps it was the journalistic qualities of Nature that drew readers in; "journalism" Maddox states, "is a way of creating a sense of community among people who would otherwise be isolated from each other. This is what Lockyer's journal did from the start." In addition, Maddox mentions that the financial backing of the journal in its first years by the Macmillan family also allowed the journal to flourish and develop more freely than scientific journals before it.
Editors
Norman Lockyer, the founder of ''Nature'', was a professor atImperial College
Imperial College London (legally Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine) is a public research university in London, United Kingdom. Its history began with Prince Albert, consort of Queen Victoria, who developed his vision for a cu ...
. He was succeeded as editor in 1919 by Sir Richard Gregory. Gregory helped to establish ''Nature'' in the international scientific community. His obituary by the Royal Society stated: "Gregory was always very interested in the international contacts of science, and in the columns of ''Nature'' he always gave generous space to accounts of the activities of the International Scientific Unions." During the years 1945 to 1973, editorship of ''Nature'' changed three times, first in 1945 to A. J. V. Gale and L. J. F. Brimble
Lionel John Farnham Brimble (16 January 1904 in Radstock, Somerset – 15 November 1965 in London) was a botanist, author, Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh and editor of the journal ''Nature''.
Early life
He was born in 1904, the son ...
(who in 1958 became the sole editor), then to John Maddox in 1965, and finally to David Davies in 1973. In 1980, Maddox returned as editor and retained his position until 1995. Philip Campbell became Editor-in-chief of all ''Nature'' publications until 2018. Magdalena Skipper
Magdalena Skipper is a British geneticist and the editor-in-chief of the journal ''Nature''. She previously served as an editor of ''Nature Reviews Genetics'' and the open access journal ''Nature Communications''.
Education
Skipper obtained a ...
has since become Editor-in-chief.
Expansion and development
In 1970, ''Nature'' first opened its Washington office; other branches opened in New York in 1985, Tokyo and Munich in 1987, Paris in 1989, San Francisco in 2001, Boston in 2004, and Hong Kong in 2005. In 1971, under John Maddox's editorship, the journal split into ''Nature Physical Sciences'' (published on Mondays), ''Nature New Biology'' (published on Wednesdays), and ''Nature'' (published on Fridays). In 1974, Maddox was no longer editor, and the journals were merged into ''Nature''. Starting in the 1980s, the journal underwent a great deal of expansion, launching over ten new journals. These new journals comprise Nature Research, which was created in 1999 under the name Nature Publishing Group and includes ''Nature'', Nature Research Journals, Stockton Press Specialist Journals and Macmillan Reference (renamed NPG Reference). In 1996, ''Nature'' created its own website and in 1999 Nature Publishing Group began its series of ''Nature Reviews''. Some articles and papers are available for free on the Nature website, while others require the purchase of premium access to the site. , ''Nature'' claimed an online readership of about 3 million unique readers per month. On 30 October 2008, ''Nature'' endorsed an American presidential candidate for the first time when it supported Barack Obama during his campaign in America's 2008 presidential election. In October 2012, an Arabic edition of the magazine was launched in partnership withKing Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology
King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (KACST; ar, مدينة الملك عبدالعزيز للعلوم والتقنية) in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia is an organization established in 1977 as the Saudi Arabian National Center for Science & ...
. As of the time it was released, it had about 10,000 subscribers. On 2 December 2014, ''Nature'' announced that it would allow its subscribers and a group of selected media outlets to share links allowing free, "read-only" access to content from its journals. These articles are presented using the digital rights management
Digital rights management (DRM) is the management of legal access to digital content. Various tools or technological protection measures (TPM) such as access control technologies can restrict the use of proprietary hardware and copyrighted works. ...
system ReadCube
ReadCube is a technology company developing software for researchers, publishers, academic and commercial organizations. ReadCube’s product line includes the reference manager ReadCube Papers, Anywhere Access and custom services for publishers ...
(which is funded by the Macmillan subsidiary Digital Science), and does not allow readers to download, copy, print, or otherwise distribute the content. While it does, to an extent, provide free online access to articles, it is not a true open access
Open access (OA) is a set of principles and a range of practices through which research outputs are distributed online, free of access charges or other barriers. With open access strictly defined (according to the 2001 definition), or libre op ...
scheme due to its restrictions on re-use and distribution. On 15 January 2015, details of a proposed merger with Springer Science+Business Media were announced.
In May 2015 it came under the umbrella of Springer Nature
Springer Nature or the Springer Nature Group is a German-British academic publishing company created by the May 2015 merger of Springer Science+Business Media and Holtzbrinck Publishing Group's Nature Publishing Group, Palgrave Macmillan, and Macm ...
, by the merger of Springer Science+Business Media and Holtzbrinck Publishing Group's Nature Publishing Group, Palgrave Macmillan, and Macmillan Education. Since 2011, the journal has published Nature's 10
''Nature'' 10 is an annual listicle of ten "people who mattered" in science, produced by the scientific journal ''Nature (journal), Nature''. Nominees have made a significant impact in science either for good or for bad. Reporters and editorial s ...
"people who mattered" during the year, as part of their annual review.
Publication in Nature
 According to '' Science'', another academic journal, being published in ''Nature'' has been known to carry a certain level of prestige in academia. In particular, empirical papers are often highly cited, which can lead to promotions, grant funding, and attention from the mainstream media. Because of these positive feedback effects, competition among scientists to publish in high-level journals like ''Nature'' and its closest competitor, '' Science'', can be very fierce. ''Nature''s impact factor, a measure of how many citations a journal generates in other works, was 42.778 in 2019 (as measured by
According to '' Science'', another academic journal, being published in ''Nature'' has been known to carry a certain level of prestige in academia. In particular, empirical papers are often highly cited, which can lead to promotions, grant funding, and attention from the mainstream media. Because of these positive feedback effects, competition among scientists to publish in high-level journals like ''Nature'' and its closest competitor, '' Science'', can be very fierce. ''Nature''s impact factor, a measure of how many citations a journal generates in other works, was 42.778 in 2019 (as measured by Thomson ISI
The Institute for Scientific Information (ISI) was an academic publishing service, founded by Eugene Garfield in Philadelphia in 1956. ISI offered scientometric and bibliographic database services. Its specialty was citation indexing and analysis, ...
). However, as with many journals, most papers receive far fewer citations than the impact factor would indicate. ''Nature''mission statement
A mission statement is a short statement of why an organization exists, what its overall goal is, the goal of its operations: what kind of product or service it provides, its primary customers or market, and its geographical region of operation ...
:
This was later revised to:
Landmark papers
Many of the most significant scientific breakthroughs in modern history have been first published in ''Nature''. The following is a selection of scientific breakthroughs published in ''Nature'', all of which had far-reaching consequences, and the citation for the article in which they were published. *Wave nature
In physics, mathematics, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from equilibrium) of one or more quantities. Waves can be periodic, in which case those quantities oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium (re ...
of particles —
* The neutron —
* Nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radio ...
—
* The structure of DNA —
* First molecular protein structure (myoglobin
Myoglobin (symbol Mb or MB) is an iron- and oxygen-binding protein found in the cardiac and skeletal muscle tissue of vertebrates in general and in almost all mammals. Myoglobin is distantly related to hemoglobin. Compared to hemoglobin, myoglobi ...
) —
* Plate tectonics —
* Pulsars —
* The ozone hole —
* First cloning of a mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
( Dolly the sheep) —
* The human genome —
Controversies
In 2017, ''Nature'' published an editorial entitled "Removing Statues of Historical figures risks whitewashing history: Science must acknowledge mistakes as it marks its past". The article commented on the placement and maintenance of statues honouring scientists with known unethical, abusive and torturous histories. Specifically, the editorial called on examples of J. Marion Sims, the 'Father of gynecology' who experimented on African American female slaves who were unable to give informed consent, andThomas Parran Jr.
Thomas Parran (September 28, 1892 – February 16, 1968) was an American physician and Public Health Service officer. He was appointed the sixth Surgeon General of the United States from 1936 to 1948, and oversaw the notorious Tuskegee syphilis e ...
who oversaw the Tuskegee Syphilis Experiment. The editorial as written made the case that removing such statues, and erasing names, runs the risk of "whitewashing history", and stated "Instead of removing painful reminders, perhaps these should be supplemented". The article caused a large outcry and was quickly modified by Nature. The article was largely seen as offensive, inappropriate, and by many, racist. ''Nature'' acknowledged that the article as originally written was "offensive and poorly worded" and published selected letters of response. The editorial came just weeks after hundreds of white supremacists marched in Charlottesville, Virginia
Charlottesville, colloquially known as C'ville, is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia. It is the county seat of Albemarle County, which surrounds the city, though the two are separate legal entities. It is named after Queen Ch ...
in the Unite the Right rally to oppose the removal of a statue of Robert E. Lee, setting off violence in the streets and killing a young woman. When Nature posted a link to the editorial on Twitter, the thread quickly exploded with criticisms. In response, several scientists called for a boycott. On 18 September 2017, the editorial was updated and edited by Philip Campbell, the editor of the journal.
When Paul Lauterbur and Peter Mansfield won a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for research initially rejected by ''Nature'' and published only after Lauterbur appealed against the rejection, ''Nature'' acknowledged more of its own missteps in rejecting papers in an editorial titled, "Coping with Peer Rejection":
In June 1988, after nearly a year of guided scrutiny from its editors, ''Nature'' published a controversial and seemingly anomalous paper detailing Jacques Benveniste
Jacques Benveniste (; 12 March 1935 – 3 October 2004) was a French immunology, immunologist born in Paris. In 1979, he published a well-known paper on the structure of platelet-activating factor and its relationship with histamine. He was head of ...
and his team's work studying human basophil degranulation
Degranulation is a cellular process that releases antimicrobial cytotoxic or other molecules from secretory vesicles called granules found inside some cells. It is used by several different cells involved in the immune system, including granulo ...
in the presence of extremely dilute antibody serum. The paper concluded that less than a single molecule of antibody could trigger an immune response in human basophils, defying the physical law of mass action. The paper excited substantial media attention in Paris, chiefly because their research sought funding from homeopathic medicine companies. Public inquiry prompted ''Nature'' to mandate an extensive and stringent experimental replication
Replication may refer to:
Science
* Replication (scientific method), one of the main principles of the scientific method, a.k.a. reproducibility
** Replication (statistics), the repetition of a test or complete experiment
** Replication crisi ...
in Benveniste's lab, through which his team's results were refuted.
Before publishing one of its most famous discoveries, Watson
Watson may refer to:
Companies
* Actavis, a pharmaceutical company formerly known as Watson Pharmaceuticals
* A.S. Watson Group, retail division of Hutchison Whampoa
* Thomas J. Watson Research Center, IBM research center
* Watson Systems, make ...
and Crick
Crick may refer to:
Places
* Crick, Monmouthshire, Wales
* Crick, Northamptonshire, England
* Crick Road, Oxford, England
People with the name
* Crick (surname)
Other uses
* Crick, the cricket from ''Beat Bugs''
* Francis Crick Institute
...
's 1953 paper on the structure of DNA, ''Nature'' did not send the paper out for peer review. John Maddox, ''Nature''s editor, stated: "the Watson and Crick paper was not peer-reviewed by ''Nature'' ... the paper could not have been refereed: its correctness is self-evident. No referee working in the field ... could have kept his mouth shut once he saw the structure".
An earlier error occurred when Enrico Fermi
Enrico Fermi (; 29 September 1901 – 28 November 1954) was an Italian (later naturalized American) physicist and the creator of the world's first nuclear reactor, the Chicago Pile-1. He has been called the "architect of the nuclear age" and ...
submitted his breakthrough paper on the weak interaction theory Interaction theory (IT) is an approach to questions about social cognition, or how one understands other people, that focuses on bodily behaviors and environmental contexts rather than on mental processes. IT argues against two other contemporary a ...
of beta decay. ''Nature'' rejected the paper because it was considered too remote from reality. Fermi's paper was published by ''Zeitschrift für Physik
''Zeitschrift für Physik'' (English: ''Journal for Physics'') is a defunct series of German peer-reviewed physics journals established in 1920 by Springer Berlin Heidelberg. The series stopped publication in 1997, when it merged with other journ ...
'' in 1934.
The journal apologised for its initial coverage of the COVID-19 pandemic in which it linked China and Wuhan with the outbreak, which may have led to racist attacks.
Retractions
A paper was published with important figure anomalies from an author with a past of publishing figure anomalies. A 2013 fraudulent paper was also published in ''Nature''. From 2000 to 2001, a series of five fraudulent papers by Jan Hendrik Schön was published in ''Nature''. The papers, aboutsemiconductors
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical conductivity value falling between that of a electrical conductor, conductor, such as copper, and an insulator (electricity), insulator, such as glas ...
, were revealed to contain falsified data and other scientific fraud. In 2003, ''Nature'' retracted the papers. The Schön scandal was not limited to ''Nature''; other prominent journals, such as '' Science'' and ''Physical Review
''Physical Review'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal established in 1893 by Edward Nichols. It publishes original research as well as scientific and literature reviews on all aspects of physics. It is published by the American Physical S ...
'', also retracted papers by Schön.
Science fiction
In 1999, ''Nature'' began publishing science fiction short stories. The brief "vignettes
Vignette may refer to:
* Vignette (entertainment), a sketch in a sketch comedy
* Vignette (graphic design), decorative designs in books (originally in the form of leaves and vines) to separate sections or chapters
* Vignette (literature), short, i ...
" are printed in a series called "Futures". The stories appeared in 1999 and 2000, again in 2005 and 2006, and have appeared weekly since July 2007. Sister publication ''Nature Physics
''Nature Physics'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Nature Portfolio. It was first published in October 2005 (volume 1, issue 1). The chief editor is Andrea Taroni, who is a full-time professional editor employed by this ...
'' also printed stories in 2007 and 2008. In 2005, ''Nature'' was awarded the European Science Fiction Society
The European Science Fiction Society is an international organisation of professionals and fans who are committed to promoting science fiction in Europe and European science fiction worldwide.
The organisation was founded at the first Eurocon (Eu ...
's Best Publisher award for the "Futures" series. One hundred of the ''Nature'' stories between 1999 and 2006 were published as the collection ''Futures from Nature'' in 2008. Another collection, ''Futures from Nature 2'', was published in 2014.
Publication
 ''Nature'' is edited and published in the United Kingdom by a division of the international
''Nature'' is edited and published in the United Kingdom by a division of the international scientific publishing
: ''For a broader class of literature, see Academic publishing.''
Scientific literature comprises scholarly publications that report original empirical and theoretical work in the natural and social sciences. Within an academic field, scient ...
company Springer Nature
Springer Nature or the Springer Nature Group is a German-British academic publishing company created by the May 2015 merger of Springer Science+Business Media and Holtzbrinck Publishing Group's Nature Publishing Group, Palgrave Macmillan, and Macm ...
that publishes academic journals, magazine
A magazine is a periodical publication, generally published on a regular schedule (often weekly or monthly), containing a variety of content. They are generally financed by advertising, purchase price, prepaid subscriptions, or by a combinatio ...
s, online databases, and services in science and medicine. ''Nature'' has offices in London, New York City, San Francisco, Washington, D.C., Boston, Tokyo, Hong Kong, Paris, Munich, and Basingstoke
Basingstoke ( ) is the largest town in the county of Hampshire. It is situated in south-central England and lies across a valley at the source of the River Loddon, at the far western edge of The North Downs. It is located north-east of Southa ...
. Nature Research also publishes other specialized journals including '' Nature Neuroscience'', '' Nature Biotechnology,'' '' Nature Methods'', the ''Nature Clinical Practice
This is a list of journals published by Nature Research. These include the flagship ''Nature'' journal, the ''Nature Reviews'' series (which absorbed the former ''Nature Clinical Practice'' series in 2009), the ''npj'' series, ''Scientific Repor ...
'' series of journals, ''Nature Structural & Molecular Biology
''Nature Structural & Molecular Biology'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal publishing research articles, reviews, news, and commentaries in structural and molecular biology, with an emphasis on papers that further a "functional and m ...
'', '' Nature Chemistry'', and the ''Nature Reviews'' series of journals.
Since 2005, each issue of ''Nature'' has been accompanied by a ''Nature Podcast
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. ...
'' featuring highlights from the issue and interviews with the articles' authors and the journalists covering the research. It is presented by Kerri Smith and features interviews with scientists on the latest research, as well as news reports from ''Nature''The Naked Scientists
''The Naked Scientists'' is a one-hour audience-interactive science radio talk show broadcast live by the BBC in the East of England, nationally by BBC Radio 5 Live and internationally on ABC Radio National, Australia; it is also distributed g ...
''.
Nature Research actively supports the self-archiving process and in 2002 was one of the first publishers to allow authors to post their contributions on their personal websites, by requesting an exclusive licence to publish, rather than requiring authors to transfer copyright. In December 2007, Nature Publishing Group introduced the Creative Commons attribution-non-commercial-share alike unported licence for those articles in Nature journals that are publishing the primary sequence of an organism's genome for the first time.
In 2008, a collection of articles from ''Nature'' was edited by John S. Partington under the title ''H. G. Wells in Nature, 1893–1946: A Reception Reader'' and published by Peter Lang.
See also
*Open-access (publishing)
Open access (OA) is a set of principles and a range of practices through which research outputs are distributed online, free of access charges or other barriers. With open access strictly defined (according to the 2001 definition), or libre op ...
* Scientific journal
In academic publishing, a scientific journal is a periodical publication intended to further the progress of science, usually by reporting new research.
Content
Articles in scientific journals are mostly written by active scientists such as s ...
Citations
General bibliography
* * *External links
*Freely available scans of volumes: 1–112 (1869–1923)
''Nature'' Index
For €9500, ''Nature'' journals will now make your paper free to read
{{DEFAULTSORT:Nature (Journal) 1869 establishments in England English-language journals Multidisciplinary scientific journals Natural sciences Nature Research academic journals Publications established in 1869 Weekly journals