Natural predator on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
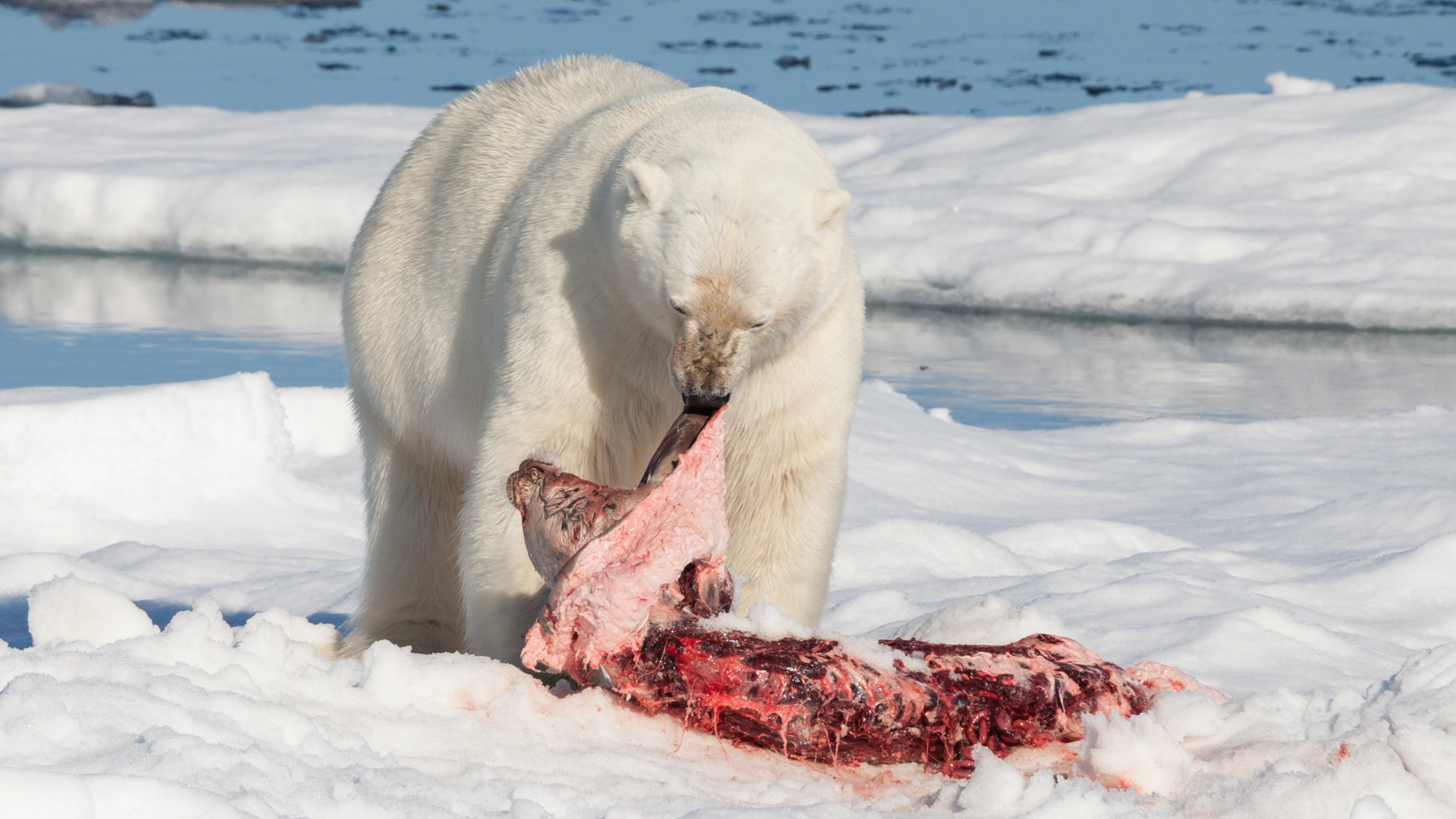

 Predation is a
Predation is a
 At the most basic level, predators kill and eat other organisms. However, the concept of predation is broad, defined differently in different contexts, and includes a wide variety of feeding methods; and some relationships that result in the prey's death are not generally called predation. A parasitoid, such as an
At the most basic level, predators kill and eat other organisms. However, the concept of predation is broad, defined differently in different contexts, and includes a wide variety of feeding methods; and some relationships that result in the prey's death are not generally called predation. A parasitoid, such as an  There are other difficult and borderline cases.
There are other difficult and borderline cases.
 To feed, a predator must search for, pursue and kill its prey. These actions form a
To feed, a predator must search for, pursue and kill its prey. These actions form a
 Prey distributions are often clumped, and predators respond by looking for ''patches'' where prey is dense and then searching within patches. Where food is found in patches, such as rare shoals of fish in a nearly empty ocean, the search stage requires the predator to travel for a substantial time, and to expend a significant amount of energy, to locate each food patch. For example, the
Prey distributions are often clumped, and predators respond by looking for ''patches'' where prey is dense and then searching within patches. Where food is found in patches, such as rare shoals of fish in a nearly empty ocean, the search stage requires the predator to travel for a substantial time, and to expend a significant amount of energy, to locate each food patch. For example, the
 Having found prey, a predator must decide whether to pursue it or keep searching. The decision depends on the costs and benefits involved. A bird foraging for insects spends a lot of time searching but capturing and eating them is quick and easy, so the efficient strategy for the bird is to eat every palatable insect it finds. By contrast, a predator such as a lion or falcon finds its prey easily but capturing it requires a lot of effort. In that case, the predator is more selective.
One of the factors to consider is size. Prey that is too small may not be worth the trouble for the amount of energy it provides. Too large, and it may be too difficult to capture. For example, a mantid captures prey with its forelegs and they are optimized for grabbing prey of a certain size. Mantids are reluctant to attack prey that is far from that size. There is a positive correlation between the size of a predator and its prey.
A predator may also assess a patch and decide whether to spend time searching for prey in it. This may involve some knowledge of the preferences of the prey; for example, ladybirds can choose a patch of vegetation suitable for their
Having found prey, a predator must decide whether to pursue it or keep searching. The decision depends on the costs and benefits involved. A bird foraging for insects spends a lot of time searching but capturing and eating them is quick and easy, so the efficient strategy for the bird is to eat every palatable insect it finds. By contrast, a predator such as a lion or falcon finds its prey easily but capturing it requires a lot of effort. In that case, the predator is more selective.
One of the factors to consider is size. Prey that is too small may not be worth the trouble for the amount of energy it provides. Too large, and it may be too difficult to capture. For example, a mantid captures prey with its forelegs and they are optimized for grabbing prey of a certain size. Mantids are reluctant to attack prey that is far from that size. There is a positive correlation between the size of a predator and its prey.
A predator may also assess a patch and decide whether to spend time searching for prey in it. This may involve some knowledge of the preferences of the prey; for example, ladybirds can choose a patch of vegetation suitable for their
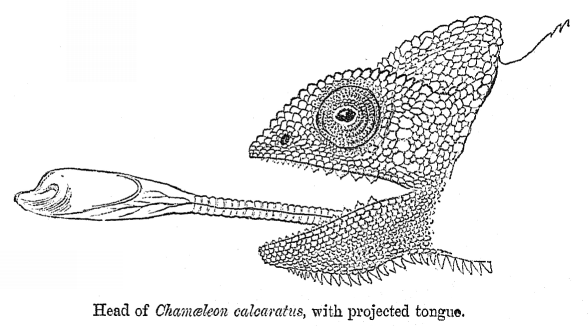 Ballistic interception is the strategy where a predator observes the movement of a prey, predicts its motion, works out an interception path, and then attacks the prey on that path. This differs from ambush predation in that the predator adjusts its attack according to how the prey is moving. Ballistic interception involves a brief period for planning, giving the prey an opportunity to escape. Some frogs wait until snakes have begun their strike before jumping, reducing the time available to the snake to recalibrate its attack, and maximising the angular adjustment that the snake would need to make to intercept the frog in real time. Ballistic predators include insects such as dragonflies, and vertebrates such as archerfish (attacking with a jet of water), chameleons (attacking with their tongues), and some Colubridae, colubrid snakes.
Ballistic interception is the strategy where a predator observes the movement of a prey, predicts its motion, works out an interception path, and then attacks the prey on that path. This differs from ambush predation in that the predator adjusts its attack according to how the prey is moving. Ballistic interception involves a brief period for planning, giving the prey an opportunity to escape. Some frogs wait until snakes have begun their strike before jumping, reducing the time available to the snake to recalibrate its attack, and maximising the angular adjustment that the snake would need to make to intercept the frog in real time. Ballistic predators include insects such as dragonflies, and vertebrates such as archerfish (attacking with a jet of water), chameleons (attacking with their tongues), and some Colubridae, colubrid snakes.
 Predators of different species sometimes cooperate to catch prey. In coral reefs, when fish such as the grouper and coral trout spot prey that is inaccessible to them, they signal to Giant moray, giant moray eels, Humphead wrasse, Napoleon wrasses or octopuses. These predators are able to access small crevices and flush out the prey. Killer whales have been known to help whalers hunt baleen whales. ISBN R-105732-9.
Social hunting allows predators to tackle a wider range of prey, but at the risk of competition for the captured food. Solitary predators have more chance of eating what they catch, at the price of increased expenditure of energy to catch it, and increased risk that the prey will escape. Ambush predators are often solitary to reduce the risk of becoming prey themselves. Of 245 terrestrial members of the Carnivora (the group that includes the cats, dogs, and bears), 177 are solitary; and 35 of the 37 Felidae, wild cats are solitary, including the cougar and cheetah. However, the solitary cougar does allow other cougars to share in a kill, and the coyote can be either solitary or social. Other solitary predators include the northern pike, wolf spiders and all the thousands of species of solitary wasps among arthropods, and many microorganisms and
Predators of different species sometimes cooperate to catch prey. In coral reefs, when fish such as the grouper and coral trout spot prey that is inaccessible to them, they signal to Giant moray, giant moray eels, Humphead wrasse, Napoleon wrasses or octopuses. These predators are able to access small crevices and flush out the prey. Killer whales have been known to help whalers hunt baleen whales. ISBN R-105732-9.
Social hunting allows predators to tackle a wider range of prey, but at the risk of competition for the captured food. Solitary predators have more chance of eating what they catch, at the price of increased expenditure of energy to catch it, and increased risk that the prey will escape. Ambush predators are often solitary to reduce the risk of becoming prey themselves. Of 245 terrestrial members of the Carnivora (the group that includes the cats, dogs, and bears), 177 are solitary; and 35 of the 37 Felidae, wild cats are solitary, including the cougar and cheetah. However, the solitary cougar does allow other cougars to share in a kill, and the coyote can be either solitary or social. Other solitary predators include the northern pike, wolf spiders and all the thousands of species of solitary wasps among arthropods, and many microorganisms and
File:Ursus arctos 01 MWNH 145 (cropped).JPG, Skull of brown bear has large pointed canine tooth, canines for killing prey, and self-sharpening carnassial teeth at rear for cutting flesh with a scissor-like action
File:Myrmecia pilosula specimen mandibles.jpg, Large compound eyes, sensitive antenna (biology), antennae, and powerful jaws (mandible (insect), mandibles) of Myrmecia pilosula, jack jumper ant
File:Crab spider seizes field digger wasp.jpg, Crab spider, an ambush predator with forward-facing eyes, catching another predator, a Mellinus arvensis, field digger wasp
File:Hawk eating prey (cropped).jpg, Red-tailed hawk uses sharp hooked claws and beak to kill and tear up its prey
File:GreatBlueHeronTampaFL.JPG, Specialist: a great blue heron with a speared fish
File:MNP Python at Moyer.jpg, Python molurus, Indian python unhinges its jaw to swallow large prey like this chital
 Several groups of predatory fish have the ability to detect, track, and sometimes, as in the electric ray, to incapacitate their prey by Electroreception and electrogenesis, sensing and generating electric fields. The electric organ is derived from modified nerve or muscle tissue.
Several groups of predatory fish have the ability to detect, track, and sometimes, as in the electric ray, to incapacitate their prey by Electroreception and electrogenesis, sensing and generating electric fields. The electric organ is derived from modified nerve or muscle tissue.
 Predators and prey are natural enemies, and many of their adaptations seem designed to counter each other. For example, bats have sophisticated Animal echolocation, echolocation systems to detect insects and other prey, and insects have developed a variety of defences including the ability to hear the echolocation calls. Many pursuit predators that run on land, such as wolves, have evolved long limbs in response to the increased speed of their prey. Their adaptations have been characterized as an
Predators and prey are natural enemies, and many of their adaptations seem designed to counter each other. For example, bats have sophisticated Animal echolocation, echolocation systems to detect insects and other prey, and insects have developed a variety of defences including the ability to hear the echolocation calls. Many pursuit predators that run on land, such as wolves, have evolved long limbs in response to the increased speed of their prey. Their adaptations have been characterized as an  The metaphor of an arms race implies ever-escalating advances in attack and defence. However, these adaptations come with a cost; for instance, longer legs have an increased risk of breaking, while the specialized tongue of the chameleon, with its ability to act like a projectile, is useless for lapping water, so the chameleon must drink dew off vegetation.
The "life-dinner" principle has been criticized on multiple grounds. The extent of the asymmetry in natural selection depends in part on the heritability of the adaptive traits. Also, if a predator loses enough dinners, it too will lose its life. On the other hand, the fitness cost of a given lost dinner is unpredictable, as the predator may quickly find better prey. In addition, most predators are generalists, which reduces the impact of a given prey adaption on a predator. Since specialization is caused by predator-prey coevolution, the rarity of specialists may imply that predator-prey arms races are rare.
It is difficult to determine whether given adaptations are truly the result of coevolution, where a prey adaptation gives rise to a predator adaptation that is countered by further adaptation in the prey. An alternative explanation is ''escalation'', where predators are adapting to competitors, their own predators or dangerous prey. Apparent adaptations to predation may also have arisen for other reasons and then been co-opted for attack or defence. In some of the insects preyed on by bats, hearing evolved before bats appeared and was used to hear signals used for territorial defence and mating. Their hearing evolved in response to bat predation, but the only clear example of reciprocal adaptation in bats is stealth echolocation.
A more symmetric arms race may occur when the prey are dangerous, having spines, quills, toxins or venom that can harm the predator. The predator can respond with avoidance, which in turn drives the evolution of mimicry. Avoidance is not necessarily an evolutionary response as it is generally learned from bad experiences with prey. However, when the prey is capable of killing the predator (as can a coral snake with its venom), there is no opportunity for learning and avoidance must be inherited. Predators can also respond to dangerous prey with counter-adaptations. In western North America, the common garter snake has developed a resistance to the toxin in the skin of the rough-skinned newt.
The metaphor of an arms race implies ever-escalating advances in attack and defence. However, these adaptations come with a cost; for instance, longer legs have an increased risk of breaking, while the specialized tongue of the chameleon, with its ability to act like a projectile, is useless for lapping water, so the chameleon must drink dew off vegetation.
The "life-dinner" principle has been criticized on multiple grounds. The extent of the asymmetry in natural selection depends in part on the heritability of the adaptive traits. Also, if a predator loses enough dinners, it too will lose its life. On the other hand, the fitness cost of a given lost dinner is unpredictable, as the predator may quickly find better prey. In addition, most predators are generalists, which reduces the impact of a given prey adaption on a predator. Since specialization is caused by predator-prey coevolution, the rarity of specialists may imply that predator-prey arms races are rare.
It is difficult to determine whether given adaptations are truly the result of coevolution, where a prey adaptation gives rise to a predator adaptation that is countered by further adaptation in the prey. An alternative explanation is ''escalation'', where predators are adapting to competitors, their own predators or dangerous prey. Apparent adaptations to predation may also have arisen for other reasons and then been co-opted for attack or defence. In some of the insects preyed on by bats, hearing evolved before bats appeared and was used to hear signals used for territorial defence and mating. Their hearing evolved in response to bat predation, but the only clear example of reciprocal adaptation in bats is stealth echolocation.
A more symmetric arms race may occur when the prey are dangerous, having spines, quills, toxins or venom that can harm the predator. The predator can respond with avoidance, which in turn drives the evolution of mimicry. Avoidance is not necessarily an evolutionary response as it is generally learned from bad experiences with prey. However, when the prey is capable of killing the predator (as can a coral snake with its venom), there is no opportunity for learning and avoidance must be inherited. Predators can also respond to dangerous prey with counter-adaptations. In western North America, the common garter snake has developed a resistance to the toxin in the skin of the rough-skinned newt.
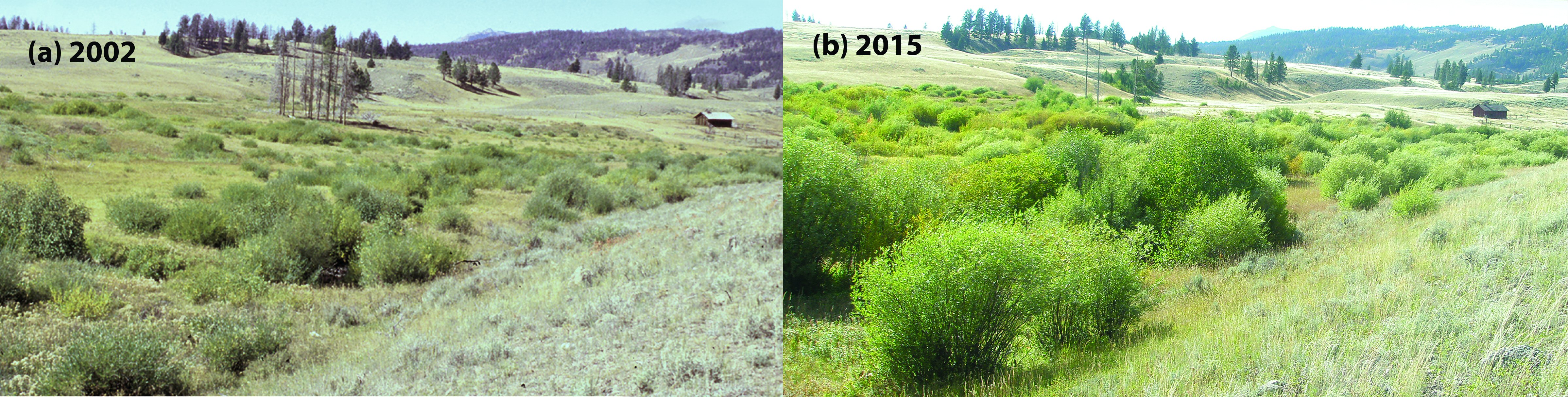 The elimination of wolves from Yellowstone National Park had profound impacts on the trophic pyramid. In that area, wolves are both keystone species and apex predators. Without predation, herbivores began to over-graze many woody browse species, affecting the area's plant populations. In addition, wolves often kept animals from grazing near streams, protecting the beavers' food sources. The removal of wolves had a direct effect on the beaver population, as their habitat became territory for grazing. Increased browsing on willows and conifers along Blacktail Creek due to a lack of predation caused channel incision because the reduced beaver population was no longer able to slow the water down and keep the soil in place. The predators were thus demonstrated to be of vital importance in the ecosystem.
The elimination of wolves from Yellowstone National Park had profound impacts on the trophic pyramid. In that area, wolves are both keystone species and apex predators. Without predation, herbivores began to over-graze many woody browse species, affecting the area's plant populations. In addition, wolves often kept animals from grazing near streams, protecting the beavers' food sources. The removal of wolves had a direct effect on the beaver population, as their habitat became territory for grazing. Increased browsing on willows and conifers along Blacktail Creek due to a lack of predation caused channel incision because the reduced beaver population was no longer able to slow the water down and keep the soil in place. The predators were thus demonstrated to be of vital importance in the ecosystem.
 In the absence of predators, the population of a species can grow exponentially until it approaches the carrying capacity of the environment. Predators limit the growth of prey both by consuming them and by changing their behavior. Increases or decreases in the prey population can also lead to increases or decreases in the number of predators, for example, through an increase in the number of young they bear.
Cyclical fluctuations have been seen in populations of predator and prey, often with offsets between the predator and prey cycles. A well-known example is that of the snowshoe hare and lynx. Over a broad span of boreal forests in Alaska and Canada, the hare populations fluctuate in near synchrony with a 10-year period, and the lynx populations fluctuate in response. This was first seen in historical records of animals caught by Fur trade, fur hunters for the Hudson Bay Company over more than a century.
In the absence of predators, the population of a species can grow exponentially until it approaches the carrying capacity of the environment. Predators limit the growth of prey both by consuming them and by changing their behavior. Increases or decreases in the prey population can also lead to increases or decreases in the number of predators, for example, through an increase in the number of young they bear.
Cyclical fluctuations have been seen in populations of predator and prey, often with offsets between the predator and prey cycles. A well-known example is that of the snowshoe hare and lynx. Over a broad span of boreal forests in Alaska and Canada, the hare populations fluctuate in near synchrony with a 10-year period, and the lynx populations fluctuate in response. This was first seen in historical records of animals caught by Fur trade, fur hunters for the Hudson Bay Company over more than a century.
 A simple model of a system with one species each of predator and prey, the Lotka–Volterra equations, predicts population cycles. However, attempts to reproduce the predictions of this model in the laboratory have often failed; for example, when the protozoan ''Didinium#Didinium nasutum, Didinium nasutum'' is added to a culture containing its prey, ''Paramecium caudatum'', the latter is often driven to extinction.
The Lotka-Volterra equations rely on several simplifying assumptions, and they are structural stability, structurally unstable, meaning that any change in the equations can stabilize or destabilize the dynamics. For example, one assumption is that predators have a linear functional response to prey: the rate of kills increases in proportion to the rate of encounters. If this rate is limited by time spent handling each catch, then prey populations can reach densities above which predators cannot control them. Another assumption is that all prey individuals are identical. In reality, predators tend to select young, weak, and ill individuals, leaving prey populations able to regrow.
Many factors can stabilize predator and prey populations. One example is the presence of multiple predators, particularly generalists that are attracted to a given prey species if it is abundant and look elsewhere if it is not. As a result, population cycles tend to be found in northern temperate and subarctic ecosystems because the food webs are simpler. The snowshoe hare-lynx system is subarctic, but even this involves other predators, including coyotes, goshawks and great horned owls, and the cycle is reinforced by variations in the food available to the hares.
A range of mathematical models have been developed by relaxing the assumptions made in the Lotka-Volterra model; these variously allow animals to have spatial distribution, geographic distributions, or to animal migration, migrate; to have differences between individuals, such as sexes and an age structure, so that only some individuals reproduce; to live in a varying environment, such as with changing seasons; and analysing the interactions of more than just two species at once. Such models predict widely differing and often chaos theory, chaotic predator-prey population dynamics. The presence of refuge (ecology), refuge areas, where prey are safe from predators, may enable prey to maintain larger populations but may also destabilize the dynamics.
A simple model of a system with one species each of predator and prey, the Lotka–Volterra equations, predicts population cycles. However, attempts to reproduce the predictions of this model in the laboratory have often failed; for example, when the protozoan ''Didinium#Didinium nasutum, Didinium nasutum'' is added to a culture containing its prey, ''Paramecium caudatum'', the latter is often driven to extinction.
The Lotka-Volterra equations rely on several simplifying assumptions, and they are structural stability, structurally unstable, meaning that any change in the equations can stabilize or destabilize the dynamics. For example, one assumption is that predators have a linear functional response to prey: the rate of kills increases in proportion to the rate of encounters. If this rate is limited by time spent handling each catch, then prey populations can reach densities above which predators cannot control them. Another assumption is that all prey individuals are identical. In reality, predators tend to select young, weak, and ill individuals, leaving prey populations able to regrow.
Many factors can stabilize predator and prey populations. One example is the presence of multiple predators, particularly generalists that are attracted to a given prey species if it is abundant and look elsewhere if it is not. As a result, population cycles tend to be found in northern temperate and subarctic ecosystems because the food webs are simpler. The snowshoe hare-lynx system is subarctic, but even this involves other predators, including coyotes, goshawks and great horned owls, and the cycle is reinforced by variations in the food available to the hares.
A range of mathematical models have been developed by relaxing the assumptions made in the Lotka-Volterra model; these variously allow animals to have spatial distribution, geographic distributions, or to animal migration, migrate; to have differences between individuals, such as sexes and an age structure, so that only some individuals reproduce; to live in a varying environment, such as with changing seasons; and analysing the interactions of more than just two species at once. Such models predict widely differing and often chaos theory, chaotic predator-prey population dynamics. The presence of refuge (ecology), refuge areas, where prey are safe from predators, may enable prey to maintain larger populations but may also destabilize the dynamics.
File:Auroralumina attenboroughii reconstruction.jpg, ''Auroralumina attenboroughii'', an Ediacaran predator (c. 560 mya). It was a stem-group cnidarian, catching prey with its nematocysts.
File:Cambrian substrate revolution 02.png, The Cambrian substrate revolution saw life on the sea floor change from minimal burrowing (left) to a diverse burrowing fauna (right), probably to avoid new Cambrian predators.
File:20191021 Peytoia nathorsti Laggania cambria.png, The anomalocaridid ''Peytoia'', a Cambrian invertebrate, probably an apex predator
File:D Terrelli.png, ''Dunkleosteus'', a Devonian placoderm, perhaps the world's first vertebrate superpredator, reconstruction
File:Meganeura monyi au Museum de Toulouse.jpg, ''Meganeura monyi'', a predatory Carboniferous insect related to

 In film, the idea of the predator as a dangerous if humanoid enemy is used in the 1987 science fiction horror film, horror action film Predator (film), ''Predator'' and Predator (franchise), its three sequels. A terrifying predator, a gigantic Man-eater, man-eating great white shark, is central, too, to Steven Spielberg's 1974 thriller ''Jaws (film), Jaws''.
Among poetry on the theme of predation, a predator's consciousness might be explored, such as in Ted Hughes's ''Pike''. The phrase "Nature, red in tooth and claw" from Alfred, Lord Tennyson's 1849 poem "In Memoriam A.H.H." has been interpreted as referring to the struggle between predators and prey.
In mythology and folk fable, predators such as the fox and wolf have mixed reputations. translated from Wallner, A. (1998) ''Die Bedeutung der Raubtiere in der Mythologie: Ergebnisse einer Literaturstudie''. – Inf.bl. Forsch.bereiches Landsch.ökol. 39: 4–5. The fox was a symbol of fertility in ancient Greece, but a weather demon in northern Europe, and a creature of the devil in early Christianity; the fox is presented as sly, greedy, and cunning in fables from Aesop's Fables, Aesop onwards. The big bad wolf is known to children in tales such as ''Little Red Riding Hood'', but is a demonic figure in the Icelandic Edda sagas, where the wolf Fenrir appears in the apocalyptic Ragnarok, ending of the world. In the Middle Ages, belief spread in werewolf, werewolves, men transformed into wolves. In ancient Rome, and in ancient Egypt, the wolf was worshipped, the she-wolf appearing in the founding myth of Rome, suckling Romulus and Remus. More recently, in Rudyard Kipling's 1894 ''The Jungle Book'', Mowgli is raised by the wolf pack. Attitudes to large predators in North America, such as wolf, grizzly bear and cougar, have shifted from hostility or ambivalence, accompanied by active persecution, towards positive and protective in the second half of the 20th century.
In film, the idea of the predator as a dangerous if humanoid enemy is used in the 1987 science fiction horror film, horror action film Predator (film), ''Predator'' and Predator (franchise), its three sequels. A terrifying predator, a gigantic Man-eater, man-eating great white shark, is central, too, to Steven Spielberg's 1974 thriller ''Jaws (film), Jaws''.
Among poetry on the theme of predation, a predator's consciousness might be explored, such as in Ted Hughes's ''Pike''. The phrase "Nature, red in tooth and claw" from Alfred, Lord Tennyson's 1849 poem "In Memoriam A.H.H." has been interpreted as referring to the struggle between predators and prey.
In mythology and folk fable, predators such as the fox and wolf have mixed reputations. translated from Wallner, A. (1998) ''Die Bedeutung der Raubtiere in der Mythologie: Ergebnisse einer Literaturstudie''. – Inf.bl. Forsch.bereiches Landsch.ökol. 39: 4–5. The fox was a symbol of fertility in ancient Greece, but a weather demon in northern Europe, and a creature of the devil in early Christianity; the fox is presented as sly, greedy, and cunning in fables from Aesop's Fables, Aesop onwards. The big bad wolf is known to children in tales such as ''Little Red Riding Hood'', but is a demonic figure in the Icelandic Edda sagas, where the wolf Fenrir appears in the apocalyptic Ragnarok, ending of the world. In the Middle Ages, belief spread in werewolf, werewolves, men transformed into wolves. In ancient Rome, and in ancient Egypt, the wolf was worshipped, the she-wolf appearing in the founding myth of Rome, suckling Romulus and Remus. More recently, in Rudyard Kipling's 1894 ''The Jungle Book'', Mowgli is raised by the wolf pack. Attitudes to large predators in North America, such as wolf, grizzly bear and cougar, have shifted from hostility or ambivalence, accompanied by active persecution, towards positive and protective in the second half of the 20th century.

 Predation is a
Predation is a biological interaction
In ecology, a biological interaction is the effect that a pair of organisms living together in a community have on each other. They can be either of the same species (intraspecific interactions), or of different species (interspecific interaction ...
where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
(which usually do not kill the host
A host is a person responsible for guests at an event or for providing hospitality during it.
Host may also refer to:
Places
* Host, Pennsylvania, a village in Berks County
People
*Jim Host (born 1937), American businessman
* Michel Host ...
) and parasitoidism (which always does, eventually). It is distinct from scavenging
Scavengers are animals that consume dead organisms that have died from causes other than predation or have been killed by other predators. While scavenging generally refers to carnivores feeding on carrion, it is also a herbivorous feeding ...
on dead prey, though many predators also scavenge; it overlaps with herbivory
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
, as seed predator
Seed predation, often referred to as granivory, is a type of plant-animal interaction in which granivores (seed predators) feed on the seeds of plants as a main or exclusive food source,Hulme, P.E. and Benkman, C.W. (2002) "Granivory", pp. 13 ...
s and destructive frugivores are predators.
Predators may actively search for or pursue prey or wait for it, often concealed. When prey is detected, the predator assesses whether to attack it. This may involve ambush
An ambush is a long-established military tactic in which a combatant uses an advantage of concealment or the element of surprise to attack unsuspecting enemy combatants from concealed positions, such as among dense underbrush or behind mo ...
or pursuit predation
Pursuit predation is a form of predation in which predators actively give chase to their prey, either solitarily or as a group. It is an alternate predation strategy to ambush predation — pursuit predators rely on superior speed, endurance a ...
, sometimes after stalking the prey. If the attack is successful, the predator kills the prey, removes any inedible parts like the shell or spines, and eats it.
Predators are adapted and often highly specialized for hunting, with acute senses such as vision
Vision, Visions, or The Vision may refer to:
Perception Optical perception
* Visual perception, the sense of sight
* Visual system, the physical mechanism of eyesight
* Computer vision, a field dealing with how computers can be made to gain und ...
, hearing
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is audit ...
, or smell. Many predatory animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
s, both vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
and invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
, have sharp claw
A claw is a curved, pointed appendage found at the end of a toe or finger in most amniotes (mammals, reptiles, birds). Some invertebrates such as beetles and spiders have somewhat similar fine, hooked structures at the end of the leg or tarsus ...
s or jaw
The jaw is any opposable articulated structure at the entrance of the mouth, typically used for grasping and manipulating food. The term ''jaws'' is also broadly applied to the whole of the structures constituting the vault of the mouth and serv ...
s to grip, kill, and cut up their prey. Other adaptations include stealth and aggressive mimicry
Aggressive mimicry is a form of mimicry in which predators, parasites, or parasitoids share similar signals, using a harmless model, allowing them to avoid being correctly identified by their prey or host. Zoologists have repeatedly compare ...
that improve hunting efficiency.
Predation has a powerful selective effect on prey, and the prey develop antipredator adaptation
Anti-predator adaptations are mechanisms developed through evolution that assist prey organisms in their constant struggle against predators. Throughout the animal kingdom, adaptations have evolved for every stage of this struggle, namely by avo ...
s such as warning coloration
Aposematism is the advertising by an animal to potential predators that it is not worth attacking or eating. This unprofitability may consist of any defences which make the prey difficult to kill and eat, such as toxicity, venom, foul taste ...
, alarm call
In animal communication, an alarm signal is an antipredator adaptation in the form of signals emitted by social animals in response to danger. Many primates and birds have elaborate alarm calls for warning conspecifics of approaching predator ...
s and other signals
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The ''IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' ...
, camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the b ...
, mimicry of well-defended species, and defensive spines and chemicals. Sometimes predator and prey find themselves in an evolutionary arms race
In evolutionary biology, an evolutionary arms race is an ongoing struggle between competing sets of co-evolving genes, phenotypic and behavioral traits that develop escalating adaptations and counter-adaptations against each other, resembling an ...
, a cycle of adaptations and counter-adaptations. Predation has been a major driver of evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
since at least the Cambrian period.
Definition
ichneumon wasp
The Ichneumonidae, also known as the ichneumon wasps, Darwin wasps, or ichneumonids, are a family of parasitoid wasps of the insect order Hymenoptera. They are one of the most diverse groups within the Hymenoptera with roughly 25,000 species cu ...
, lays its eggs in or on its host; the eggs hatch into larvae, which eat the host, and it inevitably dies. Zoologists generally call this a form of parasitism, though conventionally parasites are thought not to kill their hosts. A predator can be defined to differ from a parasitoid in that it has many prey, captured over its lifetime, where a parasitoid's larva has just one, or at least has its food supply provisioned for it on just one occasion.
Micropredator
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
s are small animals that, like predators, feed entirely on other organisms; they include flea
Flea, the common name for the order Siphonaptera, includes 2,500 species of small flightless insects that live as external parasites of mammals and birds. Fleas live by ingesting the blood of their hosts. Adult fleas grow to about long, a ...
s and mosquito
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning " gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish for "li ...
es that consume blood from living animals, and aphid
Aphids are small sap-sucking insects and members of the superfamily Aphidoidea. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white woolly aphids. A t ...
s that consume sap from living plants. However, since they typically do not kill their hosts, they are now often thought of as parasites. Animals that graze on phytoplankton or mats of microbes are predators, as they consume and kill their food organisms; but herbivores that browse leaves are not, as their food plants usually survive the assault. When animals eat seeds (''seed predation
Seed predation, often referred to as granivory, is a type of plant-animal interaction in which granivores (seed predators) feed on the seeds of plants as a main or exclusive food source,Hulme, P.E. and Benkman, C.W. (2002) "Granivory", pp. 13 ...
'' or ''granivory'') or eggs (''egg predation
Egg predation is a feeding strategy in many groups of animals (ovivores) in which they consume eggs. Since an egg represents a complete organism at one stage of its Biological life cycle, life cycle, eating an egg is a form of predation, the kill ...
''), they are consuming entire living organisms, which by definition makes them predators.
Scavengers, organisms that only eat organisms found already dead, are not predators, but many predators such as the jackal
Jackals are medium-sized canids native to Africa and Eurasia. While the word "jackal" has historically been used for many canines of the subtribe canina, in modern use it most commonly refers to three species: the closely related black-backed ...
and the hyena scavenge when the opportunity arises. Among invertebrates, social wasp
A wasp is any insect of the narrow-waisted suborder Apocrita of the order Hymenoptera which is neither a bee nor an ant; this excludes the broad-waisted sawflies (Symphyta), which look somewhat like wasps, but are in a separate suborder. Th ...
s (yellowjackets) are both hunters and scavengers of other insects.
Taxonomic range
While examples of predators among mammals and birds are well known, predators can be found in a broad range of taxa including arthropods. They are common among insects, including mantids,dragonflies
A dragonfly is a flying insect belonging to the infraorder Anisoptera below the order Odonata. About 3,000 extant species of true dragonfly are known. Most are tropical, with fewer species in temperate regions. Loss of wetland habitat threa ...
, lacewings
The insect order Neuroptera, or net-winged insects, includes the lacewings, mantidflies, antlions, and their relatives. The order consists of some 6,000 species. Neuroptera can be grouped together with the Megaloptera and Raphidioptera in the ...
and scorpionflies. In some species such as the alderfly
Alderflies are megalopteran insects of the family Sialidae. They are closely related to the dobsonflies and fishflies as well as to the prehistoric Euchauliodidae. All living alderflies – about 66 species all together – are part of the s ...
, only the larvae are predatory (the adults do not eat). Spiders are predatory, as well as other terrestrial invertebrates such as scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arachnids of the order Scorpiones. They have eight legs, and are easily recognized by a pair of grasping pincers and a narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back and always en ...
s; centipedes; some mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods). Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari, but genetic analysis does not show clear e ...
s, snail
A snail is, in loose terms, a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class G ...
s and slugs; nematodes; and planarian worms. In marine environments, most cnidaria
Cnidaria () is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter.
Their distinguishing feature is cnidocytes, specialized cells that ...
ns (e.g., jellyfish
Jellyfish and sea jellies are the informal common names given to the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animals with umbrell ...
, hydroids
Hydroids are a life stage for most animals of the class Hydrozoa, small predators related to jellyfish.
Some hydroids such as the freshwater '' Hydra'' are solitary, with the polyp attached directly to the substrate. When these produce buds ...
), ctenophora
Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and ...
(comb jellies), echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any member of the phylum Echinodermata (). The adults are recognisable by their (usually five-point) radial symmetry, and include starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers, as well as the s ...
s (e.g., sea stars
Starfish or sea stars are star-shaped echinoderms belonging to the class Asteroidea (). Common usage frequently finds these names being also applied to ophiuroids, which are correctly referred to as brittle stars or basket stars. Starfish ar ...
, sea urchins, sand dollar
Sand dollars (also known as a sea cookie or snapper biscuit in New Zealand, or pansy shell in South Africa) are species of flat, burrowing sea urchins belonging to the order Clypeasteroida. Some species within the order, not quite as flat, are k ...
s, and sea cucumbers) and flatworms are predatory. Among crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can ...
s, lobsters, crabs, shrimps and barnacles are predators, and in turn crustaceans are preyed on by nearly all cephalopods (including octopuses, squid and cuttlefish).
Seed predation is restricted to mammals, birds, and insects but is found in almost all terrestrial ecosystems. Egg predation includes both specialist egg predators such as some colubrid
Colubridae (, commonly known as colubrids , from la, coluber, 'snake') is a family of snakes. With 249 genera, it is the largest snake family. The earliest species of the family date back to the Oligocene epoch. Colubrid snakes are found on ev ...
snake
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more j ...
s and generalists such as foxes and badgers that opportunistically take eggs when they find them.
Some plants, like the pitcher plant
Pitcher plants are several different carnivorous plants which have modified leaves known as pitfall traps—a prey-trapping mechanism featuring a deep cavity filled with digestive liquid. The traps of what are considered to be "true" pitcher p ...
, the Venus fly trap
The Venus flytrap (''Dionaea muscipula'') is a carnivorous plant native to subtropical wetlands on the East Coast of the United States in North Carolina and South Carolina. It catches its prey—chiefly insects and arachnids—with a trapping ...
and the sundew
''Drosera'', which is commonly known as the sundews, is one of the largest genera of carnivorous plants, with at least 194 species. 2 volumes. These members of the family Droseraceae lure, capture, and digest insects using stalked mucilaginou ...
, are carnivorous and consume insects. Methods of predation by plants varies greatly but often involves a food trap, mechanical stimulation, and electrical impulses to eventually catch and consume its prey. Some carnivorous fungi
Carnivorous fungi or predaceous fungi are fungi that derive some or most of their nutrients from trapping and eating microscopic or other minute animals. More than 200 species have been described, belonging to the phyla Ascomycota, Mucoromycotina, ...
catch nematodes using either active traps in the form of constricting rings, or passive traps with adhesive structures.
Many species of protozoa ( eukaryotes) and bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometr ...
(prokaryote
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Conne ...
s) prey on other microorganisms; the feeding mode is evidently ancient, and evolved many times in both groups. Among freshwater and marine zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by ...
, whether single-celled or multi-cellular, predatory grazing on phytoplankton and smaller zooplankton is common, and found in many species of nanoflagellates, dinoflagellates, ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a differen ...
s, rotifers, a diverse range of meroplankton
Meroplankton are a wide variety of aquatic organisms which have both planktonic and benthic stages in their life cycles. Much of the meroplankton consists of larval stages of larger organism. Meroplankton can be contrasted with holoplankton, whi ...
animal larvae, and two groups of crustaceans, namely copepods and cladocera
The Diplostraca or Cladocera, commonly known as water fleas, are a superorder of small crustaceans that feed on microscopic chunks of organic matter (excluding some predatory forms).
Over 1000 species have been recognised so far, with many more ...
ns. summarizes findings from many authors.
Foraging
foraging
Foraging is searching for wild food resources. It affects an animal's fitness because it plays an important role in an animal's ability to survive and reproduce. Foraging theory is a branch of behavioral ecology that studies the foraging behavi ...
cycle. The predator must decide where to look for prey based on its geographical distribution; and once it has located prey, it must assess whether to pursue it or to wait for a better choice. If it chooses pursuit, its physical capabilities determine the mode of pursuit (e.g., ambush or chase). Having captured the prey, it may also need to expend energy ''handling'' it (e.g., killing it, removing any shell or spines, and ingesting it).
Search
Predators have a choice of search modes ranging from ''sit-and-wait'' to ''active'' or ''widely foraging''. The sit-and-wait method is most suitable if the prey are dense and mobile, and the predator has low energy requirements. Wide foraging expends more energy, and is used when prey is sedentary or sparsely distributed. There is a continuum of search modes with intervals between periods of movement ranging from seconds to months. Sharks, sunfish, Insectivorous birds andshrew
Shrews (family Soricidae) are small mole-like mammals classified in the order Eulipotyphla. True shrews are not to be confused with treeshrews, otter shrews, elephant shrews, West Indies shrews, or marsupial shrews, which belong to differ ...
s are almost always moving while web-building spiders, aquatic invertebrates, praying mantises and kestrel
The term kestrel (from french: crécerelle, derivative from , i.e. ratchet) is the common name given to several species of predatory birds from the falcon genus ''Falco''. Kestrels are most easily distinguished by their typical hunting behaviou ...
s rarely move. In between, plover
Plovers ( , ) are a widely distributed group of wading birds belonging to the subfamily Charadriinae.
Description
There are about 66 species in the subfamily, most of them called "plover" or "dotterel". The closely related lapwing subf ...
s and other shorebirds, freshwater fish including crappies, and the larvae of coccinellid beetles (ladybirds), alternate between actively searching and scanning the environment.
 Prey distributions are often clumped, and predators respond by looking for ''patches'' where prey is dense and then searching within patches. Where food is found in patches, such as rare shoals of fish in a nearly empty ocean, the search stage requires the predator to travel for a substantial time, and to expend a significant amount of energy, to locate each food patch. For example, the
Prey distributions are often clumped, and predators respond by looking for ''patches'' where prey is dense and then searching within patches. Where food is found in patches, such as rare shoals of fish in a nearly empty ocean, the search stage requires the predator to travel for a substantial time, and to expend a significant amount of energy, to locate each food patch. For example, the black-browed albatross
The black-browed albatross (''Thalassarche melanophris''), also known as the black-browed mollymawk,Robertson, C. J. R. (2003) is a large seabird of the albatross family Diomedeidae; it is the most widespread and common member of its family.
T ...
regularly makes foraging flights to a range of around , up to a maximum foraging range of for breeding birds gathering food for their young. With static prey, some predators can learn suitable patch locations and return to them at intervals to feed. The optimal foraging
Optimal foraging theory (OFT) is a behavioral ecology model that helps predict how an animal behaves when searching for food. Although obtaining food provides the animal with energy, searching for and capturing the food require both energy and t ...
strategy for search has been modelled using the marginal value theorem.
Search patterns often appear random. One such is the Lévy walk, that tends to involve clusters of short steps with occasional long steps. It is a good fit to the behaviour of a wide variety of organisms including bacteria, honeybees, sharks and human hunter-gatherers.
Assessment
aphid
Aphids are small sap-sucking insects and members of the superfamily Aphidoidea. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white woolly aphids. A t ...
prey.
Capture
To capture prey, predators have a spectrum of pursuit modes that range from overt chase (''pursuit predation
Pursuit predation is a form of predation in which predators actively give chase to their prey, either solitarily or as a group. It is an alternate predation strategy to ambush predation — pursuit predators rely on superior speed, endurance a ...
'') to a sudden strike on nearby prey (''ambush predation
Ambush predators or sit-and-wait predators are carnivorous animals that capture or trap prey via stealth, luring or by (typically instinctive) strategies utilizing an element of surprise. Unlike pursuit predators, who chase to capture prey ...
''). Another strategy in between ambush and pursuit is ''ballistic interception'', where a predator observes and predicts a prey's motion and then launches its attack accordingly.
Ambush
Ambush or sit-and-wait predators are carnivorous animals that capture prey by stealth or surprise. In animals, ambush predation is characterized by the predator's scanning the environment from a concealed position until a prey is spotted, and then rapidly executing a fixed surprise attack. Vertebrate ambush predators include frogs, fish such as theangel shark
The angelsharks are a group of sharks in the genus ''Squatina'' of the family Squatinidae. They commonly inhabit sandy seabeds close to in depth. Many species are now classified as critically endangered by the International Union for Conservat ...
, the northern pike
The northern pike (''Esox lucius'') is a species of carnivorous fish of the genus ''Esox'' (the pikes). They are typical of brackish and fresh waters of the Northern Hemisphere (''i.e.'' holarctic in distribution). They are known simply as a p ...
and the eastern frogfish. Among the many invertebrate ambush predators are trapdoor spiders and Thomisus spectabilis, Australian Crab spiders on land and mantis shrimps in the sea. Ambush predators often construct a burrow in which to hide, improving concealment at the cost of reducing their field of vision. Some ambush predators also use lures to attract prey within striking range. The capturing movement has to be rapid to trap the prey, given that the attack is not modifiable once launched.
Ballistic interception
 Ballistic interception is the strategy where a predator observes the movement of a prey, predicts its motion, works out an interception path, and then attacks the prey on that path. This differs from ambush predation in that the predator adjusts its attack according to how the prey is moving. Ballistic interception involves a brief period for planning, giving the prey an opportunity to escape. Some frogs wait until snakes have begun their strike before jumping, reducing the time available to the snake to recalibrate its attack, and maximising the angular adjustment that the snake would need to make to intercept the frog in real time. Ballistic predators include insects such as dragonflies, and vertebrates such as archerfish (attacking with a jet of water), chameleons (attacking with their tongues), and some Colubridae, colubrid snakes.
Ballistic interception is the strategy where a predator observes the movement of a prey, predicts its motion, works out an interception path, and then attacks the prey on that path. This differs from ambush predation in that the predator adjusts its attack according to how the prey is moving. Ballistic interception involves a brief period for planning, giving the prey an opportunity to escape. Some frogs wait until snakes have begun their strike before jumping, reducing the time available to the snake to recalibrate its attack, and maximising the angular adjustment that the snake would need to make to intercept the frog in real time. Ballistic predators include insects such as dragonflies, and vertebrates such as archerfish (attacking with a jet of water), chameleons (attacking with their tongues), and some Colubridae, colubrid snakes.
Pursuit
In pursuit predation, predators chase fleeing prey. If the prey flees in a straight line, capture depends only on the predator's being faster than the prey. If the prey manoeuvres by turning as it flees, the predator must react in real time to calculate and follow a new intercept path, such as by parallel navigation, as it closes on the prey. Many pursuit predators use camouflage to approach the prey as close as possible unobserved (''stalking'') before starting the pursuit. Pursuit predators include terrestrial mammals such as humans, African wild dogs, spotted hyenas and wolves; marine predators such as dolphins, orcas and many predatory fishes, such as tuna; predatory birds (raptors) such as falcons; and insects such as dragonfly, dragonflies. An extreme form of pursuit is Persistence hunting, endurance or persistence hunting, in which the predator tires out the prey by following it over a long distance, sometimes for hours at a time. The method is used by human hunter-gatherers and by Canidae, canids such as African wild dogs and domestic hounds. The African wild dog is an extreme persistence predator, tiring out individual prey by following them for many miles at relatively low speed. A specialised form of pursuit predation is the lunge feeding of baleen whales. These very large marine predators feed on plankton, especially krill, diving and actively swimming into concentrations of plankton, and then taking a huge gulp of water and Filter feeder, filtering it through their feathery baleen plates. Pursuit predators may be Social predator, social, like the lion and wolf that hunt in groups, or solitary.Handling
Once the predator has captured the prey, it has to handle it: very carefully if the prey is dangerous to eat, such as if it possesses sharp or poisonous spines, as in many prey fish. Some catfish such as the Ictaluridae have fish fin, spines on the back (dorsal) and belly (pectoral) which lock in the erect position; as the catfish thrashes about when captured, these could pierce the predator's mouth, possibly fatally. Some fish-eating birds like the osprey avoid the danger of spines by tearing up their prey before eating it.Solitary versus social predation
In social predation, a group of predators cooperates to kill prey. This makes it possible to kill creatures larger than those they could overpower singly; for example, hyenas, and Wolf, wolves collaborate to catch and kill herbivores as large as buffalo, and lions even hunt elephants. It can also make prey more readily available through strategies like flushing of prey and herding it into a smaller area. For example, when mixed flocks of birds forage, the birds in front flush out insects that are caught by the birds behind. Spinner dolphins form a circle around a school of fish and move inwards, concentrating the fish by a factor of 200. By hunting socially Common chimpanzee, chimpanzees can catch colobus monkeys that would readily escape an individual hunter, while cooperating Harris hawks can trap rabbits. Predators of different species sometimes cooperate to catch prey. In coral reefs, when fish such as the grouper and coral trout spot prey that is inaccessible to them, they signal to Giant moray, giant moray eels, Humphead wrasse, Napoleon wrasses or octopuses. These predators are able to access small crevices and flush out the prey. Killer whales have been known to help whalers hunt baleen whales. ISBN R-105732-9.
Social hunting allows predators to tackle a wider range of prey, but at the risk of competition for the captured food. Solitary predators have more chance of eating what they catch, at the price of increased expenditure of energy to catch it, and increased risk that the prey will escape. Ambush predators are often solitary to reduce the risk of becoming prey themselves. Of 245 terrestrial members of the Carnivora (the group that includes the cats, dogs, and bears), 177 are solitary; and 35 of the 37 Felidae, wild cats are solitary, including the cougar and cheetah. However, the solitary cougar does allow other cougars to share in a kill, and the coyote can be either solitary or social. Other solitary predators include the northern pike, wolf spiders and all the thousands of species of solitary wasps among arthropods, and many microorganisms and
Predators of different species sometimes cooperate to catch prey. In coral reefs, when fish such as the grouper and coral trout spot prey that is inaccessible to them, they signal to Giant moray, giant moray eels, Humphead wrasse, Napoleon wrasses or octopuses. These predators are able to access small crevices and flush out the prey. Killer whales have been known to help whalers hunt baleen whales. ISBN R-105732-9.
Social hunting allows predators to tackle a wider range of prey, but at the risk of competition for the captured food. Solitary predators have more chance of eating what they catch, at the price of increased expenditure of energy to catch it, and increased risk that the prey will escape. Ambush predators are often solitary to reduce the risk of becoming prey themselves. Of 245 terrestrial members of the Carnivora (the group that includes the cats, dogs, and bears), 177 are solitary; and 35 of the 37 Felidae, wild cats are solitary, including the cougar and cheetah. However, the solitary cougar does allow other cougars to share in a kill, and the coyote can be either solitary or social. Other solitary predators include the northern pike, wolf spiders and all the thousands of species of solitary wasps among arthropods, and many microorganisms and zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by ...
.
Specialization
Physical adaptations
Under the pressure of natural selection, predators have evolved a variety of physical adaptations for detecting, catching, killing, and digesting prey. These include speed, agility, stealth, sharp senses, claws, teeth, filters, and suitable digestive systems. For Prey detection, detecting prey, predators have well-developedvision
Vision, Visions, or The Vision may refer to:
Perception Optical perception
* Visual perception, the sense of sight
* Visual system, the physical mechanism of eyesight
* Computer vision, a field dealing with how computers can be made to gain und ...
, smell, or hearing
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is audit ...
. Predators as diverse as owls and jumping spiders have forward-facing eyes, providing accurate binocular vision over a relatively narrow field of view, whereas prey animals often have less acute all-round vision. Animals such as foxes can smell their prey even when it is concealed under of snow or earth. Many predators have acute hearing, and some such as animal echolocation, echolocating bats hunt exclusively by active or passive use of sound.
Predators including big cats, bird of prey, birds of prey, and ants share powerful jaws, sharp teeth, or claws which they use to seize and kill their prey. Some predators such as snake
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more j ...
s and fish-eating birds like herons and cormorants swallow their prey whole; some snakes can unhinge their jaws to allow them to swallow large prey, while fish-eating birds have long spear-like beaks that they use to stab and grip fast-moving and slippery prey. Fish and other predators have developed the ability to crush or open the armoured shells of molluscs.
Many predators are powerfully built and can catch and kill animals larger than themselves; this applies as much to small predators such as ants and shrew
Shrews (family Soricidae) are small mole-like mammals classified in the order Eulipotyphla. True shrews are not to be confused with treeshrews, otter shrews, elephant shrews, West Indies shrews, or marsupial shrews, which belong to differ ...
s as to big and visibly muscular carnivores like the cougar and lion.
Diet and behaviour
Predators are often highly specialized in their diet and hunting behaviour; for example, the Eurasian lynx only hunts small ungulates. Others such as leopards are more opportunistic generalists, preying on at least 100 species. The specialists may be highly adapted to capturing their preferred prey, whereas generalists may be better able to switch to other prey when a preferred target is scarce. When prey have a clumped (uneven) distribution, the optimal strategy for the predator is predicted to be more specialized as the prey are more conspicuous and can be found more quickly; this appears to be correct for predators of immobile prey, but is doubtful with mobile prey. In size-selective predation, predators select prey of a certain size. Large prey may prove troublesome for a predator, while small prey might prove hard to find and in any case provide less of a reward. This has led to a correlation between the size of predators and their prey. Size may also act as a refuge (ecology), refuge for large prey. For example, adult elephants are relatively safe from predation by lions, but juveniles are vulnerable.Camouflage and mimicry
Members of the Felidae, cat family such as the snow leopard (treeless highlands), tiger (grassy plains, reed swamps), ocelot (forest), fishing cat (waterside thickets), and lion (open plains) are camouflaged with coloration and disruptive patterns suiting their habitats. Inaggressive mimicry
Aggressive mimicry is a form of mimicry in which predators, parasites, or parasitoids share similar signals, using a harmless model, allowing them to avoid being correctly identified by their prey or host. Zoologists have repeatedly compare ...
, certain predators, including insects and fishes, make use of coloration and behaviour to attract prey. Female ''Photuris (genus), Photuris'' Firefly, fireflies, for example, copy the light signals of other species, thereby attracting male fireflies, which they capture and eat. Flower mantises are ambush predators; camouflaged as flowers, such as orchids, they attract prey and seize it when it is close enough. Frogfishes are extremely well camouflaged, and actively lure their prey to approach using an esca, a bait on the end of a rod-like appendage on the head, which they wave gently to mimic a small animal, gulping the prey in an extremely rapid movement when it is within range.
Venom
Many smaller predators such as the box jellyfish use venom to subdue their prey, and venom can also aid in digestion (as is the case for rattlesnakes and some spiders). The marbled sea snake that has adapted to egg predation has atrophied venom glands, and the gene for its three finger toxin contains a mutation (the deletion of two nucleotides) that inactives it. These changes are explained by the fact that its prey does not need to be subdued.Electric fields
 Several groups of predatory fish have the ability to detect, track, and sometimes, as in the electric ray, to incapacitate their prey by Electroreception and electrogenesis, sensing and generating electric fields. The electric organ is derived from modified nerve or muscle tissue.
Several groups of predatory fish have the ability to detect, track, and sometimes, as in the electric ray, to incapacitate their prey by Electroreception and electrogenesis, sensing and generating electric fields. The electric organ is derived from modified nerve or muscle tissue.
Physiology
Physiological adaptations to predation include the ability of predatory bacteria to digest the complex peptidoglycan polymer from the cell walls of the bacteria that they prey upon. Carnivorous vertebrates of all five major classes (fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals) have lower relative rates of sugar to amino acid transport than either herbivores or omnivores, presumably because they acquire plenty of amino acids from the animal proteins in their diet.Antipredator adaptations
To counter predation, prey have evolved defences for use at each stage of an attack. They can try to avoid detection, such as by usingcamouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the b ...
and mimicry. They can detect predators and warn others of their presence.
If detected, they can try to avoid being the target of an attack, for example, by Aposematism, signalling that they are toxic or unpalatable, by signalling that a chase would be unprofitable, or by forming groups. If they become a target, they can try to fend off the attack with defences such as armour, Spine (zoology), quills, unpalatability, or mobbing; and they can often escape an attack in progress by deimatic behaviour, startling the predator, Thanatosis, playing dead, shedding body parts such as tails, or simply fleeing.
Coevolution
 Predators and prey are natural enemies, and many of their adaptations seem designed to counter each other. For example, bats have sophisticated Animal echolocation, echolocation systems to detect insects and other prey, and insects have developed a variety of defences including the ability to hear the echolocation calls. Many pursuit predators that run on land, such as wolves, have evolved long limbs in response to the increased speed of their prey. Their adaptations have been characterized as an
Predators and prey are natural enemies, and many of their adaptations seem designed to counter each other. For example, bats have sophisticated Animal echolocation, echolocation systems to detect insects and other prey, and insects have developed a variety of defences including the ability to hear the echolocation calls. Many pursuit predators that run on land, such as wolves, have evolved long limbs in response to the increased speed of their prey. Their adaptations have been characterized as an evolutionary arms race
In evolutionary biology, an evolutionary arms race is an ongoing struggle between competing sets of co-evolving genes, phenotypic and behavioral traits that develop escalating adaptations and counter-adaptations against each other, resembling an ...
, an example of the coevolution of two species. In a gene centered view of evolution, the genes of predator and prey can be thought of as Competition (biology), competing for the prey's body. However, the "life-dinner" principle of Dawkins and Krebs predicts that this arms race is asymmetric: if a predator fails to catch its prey, it loses its dinner, while if it succeeds, the prey loses its life.
 The metaphor of an arms race implies ever-escalating advances in attack and defence. However, these adaptations come with a cost; for instance, longer legs have an increased risk of breaking, while the specialized tongue of the chameleon, with its ability to act like a projectile, is useless for lapping water, so the chameleon must drink dew off vegetation.
The "life-dinner" principle has been criticized on multiple grounds. The extent of the asymmetry in natural selection depends in part on the heritability of the adaptive traits. Also, if a predator loses enough dinners, it too will lose its life. On the other hand, the fitness cost of a given lost dinner is unpredictable, as the predator may quickly find better prey. In addition, most predators are generalists, which reduces the impact of a given prey adaption on a predator. Since specialization is caused by predator-prey coevolution, the rarity of specialists may imply that predator-prey arms races are rare.
It is difficult to determine whether given adaptations are truly the result of coevolution, where a prey adaptation gives rise to a predator adaptation that is countered by further adaptation in the prey. An alternative explanation is ''escalation'', where predators are adapting to competitors, their own predators or dangerous prey. Apparent adaptations to predation may also have arisen for other reasons and then been co-opted for attack or defence. In some of the insects preyed on by bats, hearing evolved before bats appeared and was used to hear signals used for territorial defence and mating. Their hearing evolved in response to bat predation, but the only clear example of reciprocal adaptation in bats is stealth echolocation.
A more symmetric arms race may occur when the prey are dangerous, having spines, quills, toxins or venom that can harm the predator. The predator can respond with avoidance, which in turn drives the evolution of mimicry. Avoidance is not necessarily an evolutionary response as it is generally learned from bad experiences with prey. However, when the prey is capable of killing the predator (as can a coral snake with its venom), there is no opportunity for learning and avoidance must be inherited. Predators can also respond to dangerous prey with counter-adaptations. In western North America, the common garter snake has developed a resistance to the toxin in the skin of the rough-skinned newt.
The metaphor of an arms race implies ever-escalating advances in attack and defence. However, these adaptations come with a cost; for instance, longer legs have an increased risk of breaking, while the specialized tongue of the chameleon, with its ability to act like a projectile, is useless for lapping water, so the chameleon must drink dew off vegetation.
The "life-dinner" principle has been criticized on multiple grounds. The extent of the asymmetry in natural selection depends in part on the heritability of the adaptive traits. Also, if a predator loses enough dinners, it too will lose its life. On the other hand, the fitness cost of a given lost dinner is unpredictable, as the predator may quickly find better prey. In addition, most predators are generalists, which reduces the impact of a given prey adaption on a predator. Since specialization is caused by predator-prey coevolution, the rarity of specialists may imply that predator-prey arms races are rare.
It is difficult to determine whether given adaptations are truly the result of coevolution, where a prey adaptation gives rise to a predator adaptation that is countered by further adaptation in the prey. An alternative explanation is ''escalation'', where predators are adapting to competitors, their own predators or dangerous prey. Apparent adaptations to predation may also have arisen for other reasons and then been co-opted for attack or defence. In some of the insects preyed on by bats, hearing evolved before bats appeared and was used to hear signals used for territorial defence and mating. Their hearing evolved in response to bat predation, but the only clear example of reciprocal adaptation in bats is stealth echolocation.
A more symmetric arms race may occur when the prey are dangerous, having spines, quills, toxins or venom that can harm the predator. The predator can respond with avoidance, which in turn drives the evolution of mimicry. Avoidance is not necessarily an evolutionary response as it is generally learned from bad experiences with prey. However, when the prey is capable of killing the predator (as can a coral snake with its venom), there is no opportunity for learning and avoidance must be inherited. Predators can also respond to dangerous prey with counter-adaptations. In western North America, the common garter snake has developed a resistance to the toxin in the skin of the rough-skinned newt.
Role in ecosystems
Predators affect their ecosystems not only directly by eating their own prey, but by indirect means such as reducing predation by other species, or altering the foraging behaviour of a herbivore, as with the biodiversity effect of wolves on riverside vegetation or sea otters on kelp forests. This may explain population dynamics effects such as the cycles observed in lynx and snowshoe hares.Trophic level
One way of classifying predators is by trophic level. Carnivores that feed on herbivores are secondary consumers; their predators are tertiary consumers, and so forth. At the top of this food chain are apex predators such as lions. Many predators however eat from multiple levels of the food chain; a carnivore may eat both secondary and tertiary consumers. This means that many predators must contend with intraguild predation, where other predators kill and eat them. For example, coyotes compete with and sometimes kill gray foxes and bobcats.Biodiversity maintained by apex predation
Predators may increase the biodiversity of communities by preventing a single species from becoming dominant. Such predators are known as keystone species and may have a profound influence on the balance of organisms in a particular ecosystem. Introduction or removal of this predator, or changes in its population density, can have drastic cascading effects on the equilibrium of many other populations in the ecosystem. For example, grazers of a grassland may prevent a single dominant species from taking over. The elimination of wolves from Yellowstone National Park had profound impacts on the trophic pyramid. In that area, wolves are both keystone species and apex predators. Without predation, herbivores began to over-graze many woody browse species, affecting the area's plant populations. In addition, wolves often kept animals from grazing near streams, protecting the beavers' food sources. The removal of wolves had a direct effect on the beaver population, as their habitat became territory for grazing. Increased browsing on willows and conifers along Blacktail Creek due to a lack of predation caused channel incision because the reduced beaver population was no longer able to slow the water down and keep the soil in place. The predators were thus demonstrated to be of vital importance in the ecosystem.
The elimination of wolves from Yellowstone National Park had profound impacts on the trophic pyramid. In that area, wolves are both keystone species and apex predators. Without predation, herbivores began to over-graze many woody browse species, affecting the area's plant populations. In addition, wolves often kept animals from grazing near streams, protecting the beavers' food sources. The removal of wolves had a direct effect on the beaver population, as their habitat became territory for grazing. Increased browsing on willows and conifers along Blacktail Creek due to a lack of predation caused channel incision because the reduced beaver population was no longer able to slow the water down and keep the soil in place. The predators were thus demonstrated to be of vital importance in the ecosystem.
Population dynamics
 In the absence of predators, the population of a species can grow exponentially until it approaches the carrying capacity of the environment. Predators limit the growth of prey both by consuming them and by changing their behavior. Increases or decreases in the prey population can also lead to increases or decreases in the number of predators, for example, through an increase in the number of young they bear.
Cyclical fluctuations have been seen in populations of predator and prey, often with offsets between the predator and prey cycles. A well-known example is that of the snowshoe hare and lynx. Over a broad span of boreal forests in Alaska and Canada, the hare populations fluctuate in near synchrony with a 10-year period, and the lynx populations fluctuate in response. This was first seen in historical records of animals caught by Fur trade, fur hunters for the Hudson Bay Company over more than a century.
In the absence of predators, the population of a species can grow exponentially until it approaches the carrying capacity of the environment. Predators limit the growth of prey both by consuming them and by changing their behavior. Increases or decreases in the prey population can also lead to increases or decreases in the number of predators, for example, through an increase in the number of young they bear.
Cyclical fluctuations have been seen in populations of predator and prey, often with offsets between the predator and prey cycles. A well-known example is that of the snowshoe hare and lynx. Over a broad span of boreal forests in Alaska and Canada, the hare populations fluctuate in near synchrony with a 10-year period, and the lynx populations fluctuate in response. This was first seen in historical records of animals caught by Fur trade, fur hunters for the Hudson Bay Company over more than a century.
 A simple model of a system with one species each of predator and prey, the Lotka–Volterra equations, predicts population cycles. However, attempts to reproduce the predictions of this model in the laboratory have often failed; for example, when the protozoan ''Didinium#Didinium nasutum, Didinium nasutum'' is added to a culture containing its prey, ''Paramecium caudatum'', the latter is often driven to extinction.
The Lotka-Volterra equations rely on several simplifying assumptions, and they are structural stability, structurally unstable, meaning that any change in the equations can stabilize or destabilize the dynamics. For example, one assumption is that predators have a linear functional response to prey: the rate of kills increases in proportion to the rate of encounters. If this rate is limited by time spent handling each catch, then prey populations can reach densities above which predators cannot control them. Another assumption is that all prey individuals are identical. In reality, predators tend to select young, weak, and ill individuals, leaving prey populations able to regrow.
Many factors can stabilize predator and prey populations. One example is the presence of multiple predators, particularly generalists that are attracted to a given prey species if it is abundant and look elsewhere if it is not. As a result, population cycles tend to be found in northern temperate and subarctic ecosystems because the food webs are simpler. The snowshoe hare-lynx system is subarctic, but even this involves other predators, including coyotes, goshawks and great horned owls, and the cycle is reinforced by variations in the food available to the hares.
A range of mathematical models have been developed by relaxing the assumptions made in the Lotka-Volterra model; these variously allow animals to have spatial distribution, geographic distributions, or to animal migration, migrate; to have differences between individuals, such as sexes and an age structure, so that only some individuals reproduce; to live in a varying environment, such as with changing seasons; and analysing the interactions of more than just two species at once. Such models predict widely differing and often chaos theory, chaotic predator-prey population dynamics. The presence of refuge (ecology), refuge areas, where prey are safe from predators, may enable prey to maintain larger populations but may also destabilize the dynamics.
A simple model of a system with one species each of predator and prey, the Lotka–Volterra equations, predicts population cycles. However, attempts to reproduce the predictions of this model in the laboratory have often failed; for example, when the protozoan ''Didinium#Didinium nasutum, Didinium nasutum'' is added to a culture containing its prey, ''Paramecium caudatum'', the latter is often driven to extinction.
The Lotka-Volterra equations rely on several simplifying assumptions, and they are structural stability, structurally unstable, meaning that any change in the equations can stabilize or destabilize the dynamics. For example, one assumption is that predators have a linear functional response to prey: the rate of kills increases in proportion to the rate of encounters. If this rate is limited by time spent handling each catch, then prey populations can reach densities above which predators cannot control them. Another assumption is that all prey individuals are identical. In reality, predators tend to select young, weak, and ill individuals, leaving prey populations able to regrow.
Many factors can stabilize predator and prey populations. One example is the presence of multiple predators, particularly generalists that are attracted to a given prey species if it is abundant and look elsewhere if it is not. As a result, population cycles tend to be found in northern temperate and subarctic ecosystems because the food webs are simpler. The snowshoe hare-lynx system is subarctic, but even this involves other predators, including coyotes, goshawks and great horned owls, and the cycle is reinforced by variations in the food available to the hares.
A range of mathematical models have been developed by relaxing the assumptions made in the Lotka-Volterra model; these variously allow animals to have spatial distribution, geographic distributions, or to animal migration, migrate; to have differences between individuals, such as sexes and an age structure, so that only some individuals reproduce; to live in a varying environment, such as with changing seasons; and analysing the interactions of more than just two species at once. Such models predict widely differing and often chaos theory, chaotic predator-prey population dynamics. The presence of refuge (ecology), refuge areas, where prey are safe from predators, may enable prey to maintain larger populations but may also destabilize the dynamics.
Evolutionary history
Predation dates from before the rise of commonly recognized carnivores by hundreds of millions (perhaps billions) of years. Predation has evolved repeatedly in different groups of organisms. The rise of eukaryotic cells at around 2.7 Gya, the rise of multicellular organisms at about 2 Gya, and the rise of mobile predators (around 600 Mya - 2 Gya, probably around 1 Gya) have all been attributed to early predatory behavior, and many very early remains show evidence of boreholes or other markings attributed to small predator species. It likely triggered major evolutionary transitions including the arrival of Cell (biology), cells, eukaryotes, sexual reproduction, multicellularity, increased size, mobility (including insect flight) and armoured shells and exoskeletons. The earliest predators were microbial organisms, which engulfed or grazed on others. Because the fossil record is poor, these first predators could date back anywhere between 1 and over 2.7 Gya (billion years ago). Predation visibly became important shortly before the Cambrian period—around —as evidenced by the almost simultaneous development of calcification in animals and algae, and predation-avoiding burrowing. However, predators had been grazing on micro-organisms since at least , with evidence of selective (rather than random) predation from a similar time. ''Auroralumina attenboroughii'' is an Ediacaran crown-groupcnidaria
Cnidaria () is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter.
Their distinguishing feature is cnidocytes, specialized cells that ...
n (557–562 mya, some 20 million years before the Cambrian explosion) from Charnwood Forest, England. It is thought to be one of the earliest predatory animals, catching small prey with its nematocysts as modern cnidarians do.
The fossil record demonstrates a long history of interactions between predators and their prey from the Cambrian period onwards, showing for example that some predators drilled through the shells of bivalve and gastropod molluscs, while others ate these organisms by breaking their shells.
Among the Cambrian predators were invertebrates like the anomalocaridids with appendages suitable for grabbing prey, large compound eyes and jaws made of a hard material like that in the exoskeleton of an insect.
Some of the first jawed fish, fish to have jaws were the armoured and mainly predatory placoderms of the Silurian to Devonian periods, one of which, the ''Dunkleosteus'', is considered the world's first vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
"superpredator", preying upon other predators.
Insects developed the ability to fly in the Early Carboniferous or Late Devonian, enabling them among other things to escape from predators.
Among the largest predators that have ever lived were the theropod dinosaurs such as ''Tyrannosaurus'' from the Cretaceous period. They preyed upon herbivorous dinosaurs such as hadrosaurs, ceratopsians and ankylosaurs.
dragonflies
A dragonfly is a flying insect belonging to the infraorder Anisoptera below the order Odonata. About 3,000 extant species of true dragonfly are known. Most are tropical, with fewer species in temperate regions. Loss of wetland habitat threa ...
, could fly to escape terrestrial predators. Its large size, with a wingspan of , may reflect the lack of vertebrate aerial predators at that time.
File:Tyrannosaurus rex Reconstruction by Nobu Tamura.jpg, ''Tyrannosaurus'', a large theropod dinosaur of the Cretaceous, reconstruction
In human society

Practical uses
Humans, as omnivores, are to some extent predatory, using weapons and tools to fishing, fish, hunting, hunt and animal trapping, trap animals. They also use other predatory species such as Hunting dog, dogs, cormorants, and falcons to catch prey for food or for sport. Two mid-sized predators, dogs and cats, are the animals most often kept as pets in western societies. Human hunters, including the San people, San of southern Africa, use persistence hunting, a form of pursuit predation where the pursuer may be slower than prey such as a kudu antelope over short distances, but follows it in the midday heat until it is exhausted, a pursuit that can take up to five hours. In biological pest control, predators (and parasitoids) from a pest's natural range are introduced to control populations, at the risk of causing unforeseen problems. Natural predators, provided they do no harm to non-pest species, are an environmentally friendly and sustainable way of reducing damage to crops and an alternative to the use of chemical agents such as pesticides.Symbolic uses
 In film, the idea of the predator as a dangerous if humanoid enemy is used in the 1987 science fiction horror film, horror action film Predator (film), ''Predator'' and Predator (franchise), its three sequels. A terrifying predator, a gigantic Man-eater, man-eating great white shark, is central, too, to Steven Spielberg's 1974 thriller ''Jaws (film), Jaws''.
Among poetry on the theme of predation, a predator's consciousness might be explored, such as in Ted Hughes's ''Pike''. The phrase "Nature, red in tooth and claw" from Alfred, Lord Tennyson's 1849 poem "In Memoriam A.H.H." has been interpreted as referring to the struggle between predators and prey.
In mythology and folk fable, predators such as the fox and wolf have mixed reputations. translated from Wallner, A. (1998) ''Die Bedeutung der Raubtiere in der Mythologie: Ergebnisse einer Literaturstudie''. – Inf.bl. Forsch.bereiches Landsch.ökol. 39: 4–5. The fox was a symbol of fertility in ancient Greece, but a weather demon in northern Europe, and a creature of the devil in early Christianity; the fox is presented as sly, greedy, and cunning in fables from Aesop's Fables, Aesop onwards. The big bad wolf is known to children in tales such as ''Little Red Riding Hood'', but is a demonic figure in the Icelandic Edda sagas, where the wolf Fenrir appears in the apocalyptic Ragnarok, ending of the world. In the Middle Ages, belief spread in werewolf, werewolves, men transformed into wolves. In ancient Rome, and in ancient Egypt, the wolf was worshipped, the she-wolf appearing in the founding myth of Rome, suckling Romulus and Remus. More recently, in Rudyard Kipling's 1894 ''The Jungle Book'', Mowgli is raised by the wolf pack. Attitudes to large predators in North America, such as wolf, grizzly bear and cougar, have shifted from hostility or ambivalence, accompanied by active persecution, towards positive and protective in the second half of the 20th century.
In film, the idea of the predator as a dangerous if humanoid enemy is used in the 1987 science fiction horror film, horror action film Predator (film), ''Predator'' and Predator (franchise), its three sequels. A terrifying predator, a gigantic Man-eater, man-eating great white shark, is central, too, to Steven Spielberg's 1974 thriller ''Jaws (film), Jaws''.
Among poetry on the theme of predation, a predator's consciousness might be explored, such as in Ted Hughes's ''Pike''. The phrase "Nature, red in tooth and claw" from Alfred, Lord Tennyson's 1849 poem "In Memoriam A.H.H." has been interpreted as referring to the struggle between predators and prey.
In mythology and folk fable, predators such as the fox and wolf have mixed reputations. translated from Wallner, A. (1998) ''Die Bedeutung der Raubtiere in der Mythologie: Ergebnisse einer Literaturstudie''. – Inf.bl. Forsch.bereiches Landsch.ökol. 39: 4–5. The fox was a symbol of fertility in ancient Greece, but a weather demon in northern Europe, and a creature of the devil in early Christianity; the fox is presented as sly, greedy, and cunning in fables from Aesop's Fables, Aesop onwards. The big bad wolf is known to children in tales such as ''Little Red Riding Hood'', but is a demonic figure in the Icelandic Edda sagas, where the wolf Fenrir appears in the apocalyptic Ragnarok, ending of the world. In the Middle Ages, belief spread in werewolf, werewolves, men transformed into wolves. In ancient Rome, and in ancient Egypt, the wolf was worshipped, the she-wolf appearing in the founding myth of Rome, suckling Romulus and Remus. More recently, in Rudyard Kipling's 1894 ''The Jungle Book'', Mowgli is raised by the wolf pack. Attitudes to large predators in North America, such as wolf, grizzly bear and cougar, have shifted from hostility or ambivalence, accompanied by active persecution, towards positive and protective in the second half of the 20th century.
See also
* Ecology of fear (concept), Ecology of fear * Predation problem * Predator–prey reversal * Wa-TorNotes
References
Sources
* * * * * * *External links
* * {{good article Ecology Predation, Biological pest control