Native States on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the
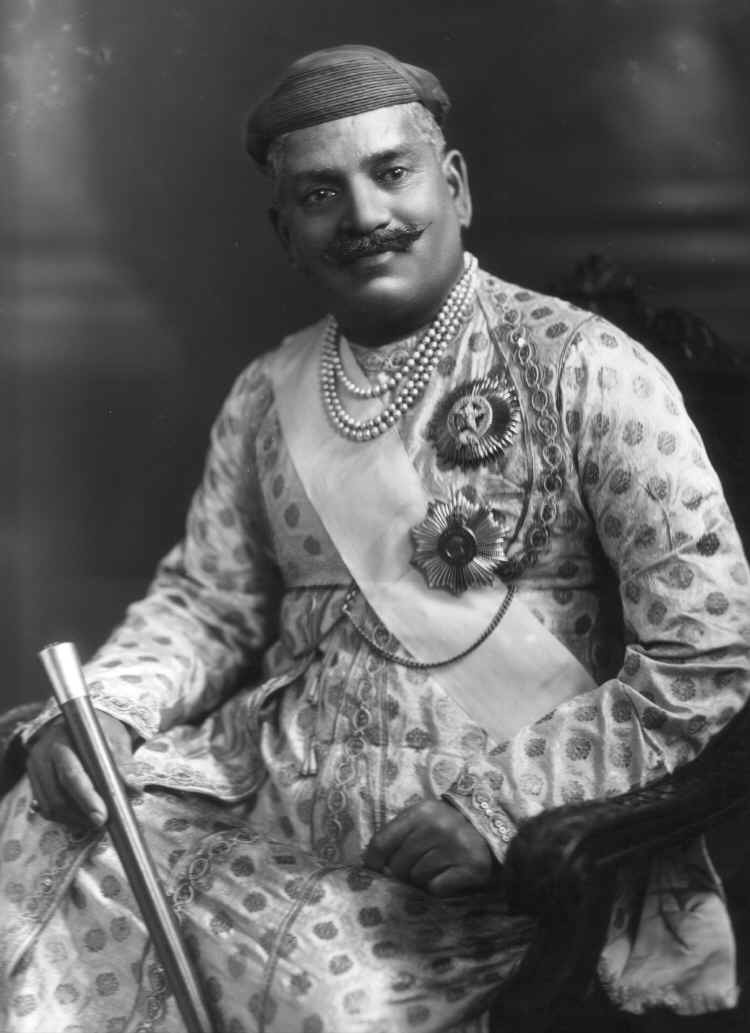 The Indian rulers bore various titles – including
The Indian rulers bore various titles – including  More prestigious Hindu rulers (mostly existing before the Mughal Empire, or having split from such old states) often used the title "
More prestigious Hindu rulers (mostly existing before the Mughal Empire, or having split from such old states) often used the title "
 In addition to their titles all princely rulers were eligible to be appointed to certain British orders of chivalry associated with India, the
In addition to their titles all princely rulers were eligible to be appointed to certain British orders of chivalry associated with India, the
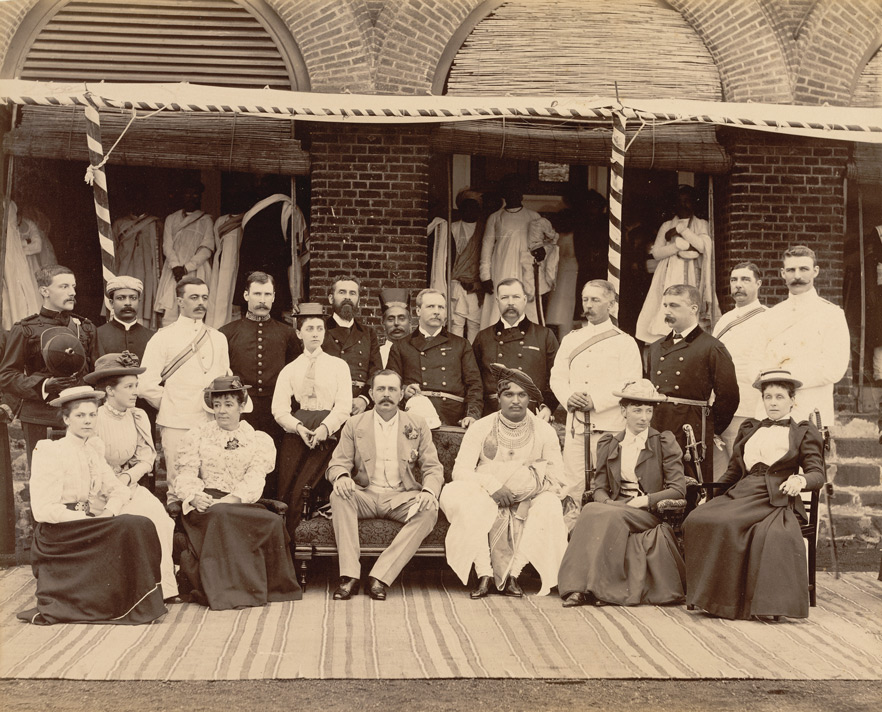 By treaty, the British controlled the external affairs of the princely states absolutely. As the states were not British possessions, they retained control over their own internal affairs, subject to a degree of British influence which in many states was substantial.
By the beginning of the 20th century, relations between the British and the four largest states –
By treaty, the British controlled the external affairs of the princely states absolutely. As the states were not British possessions, they retained control over their own internal affairs, subject to a degree of British influence which in many states was substantial.
By the beginning of the 20th century, relations between the British and the four largest states –  The Chamber of Princes (''Narender Mandal'' or ''Narendra Mandal'') was an institution established in 1920 by a Proclamation, royal proclamation of the George V of the United Kingdom, King-Emperor to provide a forum in which the rulers could voice their needs and aspirations to the government. It survived until the end of the British Raj in 1947.
By the early 1930s, most of the princely states whose agencies were under the authority of India's provinces were organised into new Agencies, answerable directly to the governor-general, on the model of the Central India and Rajputana agencies: the Eastern States Agency, Punjab States Agency, Baluchistan Agency, Deccan States Agency, Madras States Agency and the Northwest Frontier States Agency. The Baroda Residency was combined with the princely states of northern Bombay Presidency into the Baroda, Western India and Gujarat States Agency.
The Chamber of Princes (''Narender Mandal'' or ''Narendra Mandal'') was an institution established in 1920 by a Proclamation, royal proclamation of the George V of the United Kingdom, King-Emperor to provide a forum in which the rulers could voice their needs and aspirations to the government. It survived until the end of the British Raj in 1947.
By the early 1930s, most of the princely states whose agencies were under the authority of India's provinces were organised into new Agencies, answerable directly to the governor-general, on the model of the Central India and Rajputana agencies: the Eastern States Agency, Punjab States Agency, Baluchistan Agency, Deccan States Agency, Madras States Agency and the Northwest Frontier States Agency. The Baroda Residency was combined with the princely states of northern Bombay Presidency into the Baroda, Western India and Gujarat States Agency.
in JSTOR
* Bhagavan, Manu. ''Sovereign Spheres: Princes, Education and Empire in Colonial India'' (2003) * . * Ernst, W. and B. Pati, eds. ''India’s Princely States: People, Princes, and Colonialism'' (2007) * * Jeffrey, Robin. ''People, Princes and Paramount Power: Society and Politics in the Indian Princely States'' (1979) 396pp * Kooiman, Dick. ''Communalism and Indian Princely States: Travancore, Baroda & Hyderabad in the 1930s'' (2002), 249pp * * * Pochhammer, Wilhelm von ''India's Road to Nationhood: A Political History of the Subcontinent'' (1973) ch 5
excerpt
*
online
*
online
*
online
and heads of government, and some biographies. {{DEFAULTSORT:Princely State Princely states of India, 1721 establishments in India 1949 disestablishments in India Types of administrative division Client state Hindu dynasties Former British protectorates
British Indian Empire
The British Raj (; from Hindi language, Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Q ...
that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule
Indirect rule was a system of governance used by the British and others to control parts of their colonial empires, particularly in Africa and Asia, which was done through pre-existing indigenous power structures. Indirect rule was used by variou ...
, subject to a subsidiary alliance
A subsidiary alliance, in South Asian history, was a tributary alliance between a South Asian state and a European East India Company.
Under this system, an Indian ruler who formed a treaty with the company in question would be provided wi ...
and the suzerainty
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is cal ...
or paramountcy
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is calle ...
of the British crown
The Crown is the state (polity), state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, British Overseas Territories, overseas territories, Provinces and territorie ...
.
There were officially 565 princely states when India and Pakistan became independent in 1947, but the great majority had contracted with the viceroy to provide public services and tax collection. Only 21 had actual state governments, and only four were large (Hyderabad State
Hyderabad State () was a princely state located in the south-central Deccan region of India with its capital at the city of Hyderabad. It is now divided into the present-day state of Telangana, the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka, and t ...
, Mysore State
Mysore State, colloquially Old Mysore, was a state within the Dominion of India and the later Republic of India from 1947 until 1956. The state was formed by renaming the Kingdom of Mysore, and Bangalore replaced Mysore as the state's capital. ...
, Jammu and Kashmir State
Jammu and Kashmir was a region formerly administered by India as a state from 1952 to 2019, constituting the southern and southeastern portion of the larger Kashmir region, which has been the subject of a dispute between India, Pakistan an ...
, and Baroda State
Baroda State was a state in present-day Gujarat, ruled by the Gaekwad dynasty of the Maratha Confederacy from its formation in 1721 until its accession to the newly formed Dominion of India in 1949. With the city of Baroda (Vadodara) as its c ...
). They acceded to one of the two new independent nations between 1947 and 1949. All the princes were eventually pensioned off.
At the time of the British withdrawal, 565 princely states were officially recognised in the Indian subcontinent, apart from thousands of zamindari estates
A zamindar ( Hindustani: Devanagari: , ; Persian: , ) in the Indian subcontinent was an autonomous or semiautonomous ruler of a province. The term itself came into use during the reign of Mughals and later the British had begun using it as a ...
and jagir
A jagir ( fa, , translit=Jāgir), also spelled as jageer, was a type of feudal land grant in the Indian subcontinent at the foundation of its Jagirdar (Zamindar) system. It developed during the Islamic rule era of the Indian subcontinent, start ...
s. In 1947, princely states covered 40% of the area of pre-independence India and constituted 23% of its population. The most important states had their own British political residencies: Hyderabad
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River (India), Musi River, in the northern part ...
of the Nizam
The Nizams were the rulers of Hyderabad from the 18th through the 20th century. Nizam of Hyderabad (Niẓām ul-Mulk, also known as Asaf Jah) was the title of the monarch of the Hyderabad State ( divided between the state of Telangana, Mar ...
s, Mysore
Mysore (), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern part of the state of Karnataka, India. Mysore city is geographically located between 12° 18′ 26″ north latitude and 76° 38′ 59″ east longitude. It is located at an altitude of ...
and Travancore
The Kingdom of Travancore ( /ˈtrævənkɔːr/), also known as the Kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor, was an Indian kingdom from c. 1729 until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At ...
in the South, followed by Jammu and Kashmir Jammu and Kashmir may refer to:
* Kashmir, the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent
* Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), a region administered by India as a union territory
* Jammu and Kashmir (state), a region administered ...
, and Sikkim
Sikkim (; ) is a state in Northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Province No. 1 of Nepal in the west and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Siligur ...
in the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 ...
, and Indore
Indore () is the largest and most populous Cities in India, city in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It serves as the headquarters of both Indore District and Indore Division. It is also considered as an education hub of the state and is t ...
in Central India. The most prominent among those – roughly a quarter of the total – had the status of a salute state
A salute state was a princely state under the British Raj that had been granted a gun salute by the British Crown (as paramount ruler); i.e., the protocolary privilege for its ruler to be greeted—originally by Royal Navy ships, later also ...
, one whose ruler was entitled to a set number of gun salute
A gun salute or cannon salute is the use of a piece of artillery to fire shots, often 21 in number (''21-gun salute''), with the aim of marking an honor or celebrating a joyful event. It is a tradition in many countries around the world.
Histo ...
s on ceremonial occasions.
The princely states varied greatly in status, size, and wealth; the premier 21-gun salute states of Hyderabad and Jammu and Kashmir were each over in size. In 1941, Hyderabad had a population of over 16 million, while Jammu and Kashmir had a population of slightly over 4 million. At the other end of the scale, the non-salute principality of Lawa
Los Angeles World Airports (LAWA) is the airport authority that owns and operates Los Angeles International Airport (LAX) and Van Nuys Airport (VNY) for the city of Los Angeles, California. LAWA also owns and manages aviation-related property n ...
covered an area of , with a population of just below 3,000. Some two hundred of the lesser states even had an area of less than .
The era of the princely states effectively ended with Indian independence in 1947; by 1950, almost all of the principalities had acceded to either India or Pakistan. The accession process was largely peaceful, except in the cases of Jammu and Kashmir Jammu and Kashmir may refer to:
* Kashmir, the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent
* Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), a region administered by India as a union territory
* Jammu and Kashmir (state), a region administered ...
(whose ruler decided to accede to India following an invasion
An invasion is a military offensive in which large numbers of combatants of one geopolitical entity aggressively enter territory owned by another such entity, generally with the objective of either: conquering; liberating or re-establishing con ...
by Pakistan-based forces, resulting in a long-standing dispute
Dispute may refer to:
* an act of physical violence; combat
* Controversy
** Lawsuit
** Dispute resolution
* Dispute (credit card)
* ''La Dispute'', a 1744 prose comedy by Pierre de Marivaux
* La Dispute (band)
La Dispute is an American pos ...
between the two countries), Hyderabad State
Hyderabad State () was a princely state located in the south-central Deccan region of India with its capital at the city of Hyderabad. It is now divided into the present-day state of Telangana, the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka, and t ...
(whose ruler opted for independence in 1947, followed a year later by the invasion and annexation of the state by India), Junagarh and its vassal Bantva Manavadar
Bantva-Manavadar or Manavadar State was a princely state during the era of the British Raj in India. It was located on the Kathiawar peninsula in Gujarat.
See also
*Political integration of India
*Bantva Memons
*Bantva
References
External l ...
(whose rulers acceded to Pakistan, but were annexed
Annexation (Latin ''ad'', to, and ''nexus'', joining), in international law, is the forcible acquisition of one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. It is generally held to be an illegal act ...
by India), and Kalat (whose ruler declared independence in 1947, followed in 1948 by the state's accession to Pakistan).
As per the terms of accession, the erstwhile Indian princes received privy purses (government allowances), and initially retained their statuses, privileges, and autonomy in internal matters during a transitional period which lasted until 1956. During this time, the former princely states were merged into unions, each of which was headed by a former ruling prince with the title of ''Rajpramukh'' (ruling chief), equivalent to a state governor. In 1956, the position of ''Rajpramukh'' was abolished and the federations dissolved, the former principalities becoming part of Indian states. The states which acceded to Pakistan retained their status until the promulgation of a new constitution in 1956, when most became part of the province of West Pakistan
West Pakistan ( ur, , translit=Mag̱ẖribī Pākistān, ; bn, পশ্চিম পাকিস্তান, translit=Pôścim Pakistan) was one of the two Provincial exclaves created during the One Unit Scheme in 1955 in Pakistan. It was d ...
; a few of the former states retained their autonomy until 1969 when they were fully integrated into Pakistan. The Indian government abolished the privy purses in 1971, followed by the government of Pakistan in 1972.
History
Though principalities and chiefdoms existed on the Indian subcontinent from at least theIron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
, the history of princely states on the Indian subcontinent dates to at least the fifth or sixth century C.E., during the rise of the middle kingdoms of India
The middle kingdoms of India were the political entities in the Indian subcontinent from 200 BCE to 1200 CE. The period begins after the decline of the Maurya Empire and the corresponding rise of the Satavahana dynasty, starting with Simuka, ...
following the collapse of the Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Gol ...
.Agarwal, Ashvini (1989). ''Rise and Fall of the Imperial Guptas'', Delhi:Motilal Banarsidass, , pp.264–9 Many of the future ruling clan groups – notably the Rajputs
Rajput (from Sanskrit ''raja-putra'' 'son of a king') is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating from the Indian subcontinent. The term Ra ...
– began to emerge during this period; by the 13th–14th centuries, many of the Rajput clans had firmly established semi-independent principalities in the north-west, along with several in the north-east. The widespread expansion of Islam during this time brought many principalities into tributary relations with Islamic sultanates, notably with the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
. In the south, however, the Hindu Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also called the Karnata Kingdom, was a Hinduism, Hindu empire based in the region of South India, which consisted the modern states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Goa and some parts of Telangana an ...
remained dominant until the mid-17th century; among its tributaries was the future Mysore Kingdom
The Kingdom of Mysore was a realm in southern India, traditionally believed to have been founded in 1399 in the vicinity of the modern city of Mysore. From 1799 until 1950, it was a princely state, until 1947 in a subsidiary alliance with Brit ...
.
The Turco-Mongol Mughal Empire brought a majority of the existing Indian kingdoms and principalities under its suzerainty by the 17th century, beginning with its foundation in the early 16th century. Despite the difference in religion, the Mughal emperors also contracted a series of marriages with Rajput
Rajput (from Sanskrit ''raja-putra'' 'son of a king') is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating from the Indian subcontinent. The term Ra ...
princesses, and Rajput forces and generals became an important part of their military power. The advent of Sikhism
Sikhism (), also known as Sikhi ( pa, ਸਿੱਖੀ ', , from pa, ਸਿੱਖ, lit=disciple', 'seeker', or 'learner, translit=Sikh, label=none),''Sikhism'' (commonly known as ''Sikhī'') originated from the word ''Sikh'', which comes fro ...
resulted in the creation of the Sikh Empire
The Sikh Empire was a state originating in the Indian subcontinent, formed under the leadership of Maharaja Ranjit Singh, who established an empire based in the Punjab. The empire existed from 1799, when Maharaja Ranjit Singh captured Lahor ...
in the north by the early 18th century, by which time the Mughal Empire was in full decline. The Muslim nawab
Nawab (Balochi language, Balochi: نواب; ar, نواب;
bn, নবাব/নওয়াব;
hi, नवाब;
Punjabi language, Punjabi : ਨਵਾਬ;
Persian language, Persian,
Punjabi language, Punjabi ,
Sindhi language, Sindhi,
Urd ...
s had begun as appointed governors of territories conquered by the Mughals, in theory a non-hereditary title, with obligations to pay a large share of their revenues to the emperor. As the emperors became too weak to enforce their power, the nawabs stopped paying, and passed on their realms to their sons.
At the same time, the Maratha
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
s carved out their own states to form the Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern Indian confederation that came to dominate much of the Indian subcontinent in the 18th century. Maratha rule formally began in 1674 with the coronation of Shi ...
. Through the 18th century, former Mughal governors formed their own independent states. In the north-west, some of those – such as Tonk – allied themselves with various groups, including the Marathas and the Durrani Empire
The Durrani Empire ( ps, د درانيانو ټولواکمني; fa, امپراتوری درانیان) or the Afghan Empire ( ps, د افغانان ټولواکمني, label=none; fa, امپراتوری افغان, label=none), also know ...
, itself formed in 1747 from a loose agglomeration of tribal chiefdoms that composed former Mughal territories. In the south, the principalities of Hyderabad and Arcot were fully established by the 1760s, though they nominally remained vassals of the Mughal emperor.
The largest Muslim-ruled state was Hyderabad State
Hyderabad State () was a princely state located in the south-central Deccan region of India with its capital at the city of Hyderabad. It is now divided into the present-day state of Telangana, the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka, and t ...
, which was also the first to sign a treaty with the British, in 1798, when it was caught between them and the Marathas. The treaties of 1817 and 1818 concluding the decisive Third Anglo-Maratha War
The Third Anglo-Maratha War (1817–1819) was the final and decisive conflict between the English East India Company and the Maratha Empire in India. The war left the Company in control of most of India. It began with an invasion of Maratha te ...
left the remaining Maratha territories as princely states, with treaties with the British, and the Rajput states resumed their subordinate status, now with the British.
British relationship with the princely states
India under the British ''Raj'' (the "Indian Empire") consisted of two types of territory:British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
and the ''native states'' or ''princely states''. In its Interpretation Act 1889
The Interpretation Act 1889 (52 & 53 Vict c 63) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom.
In Northern IrelandSection 48(2)of the Interpretation Act (Northern Ireland) 1954 provided that without prejudice to 48(1) of that Act, the Inte ...
, the British Parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative supremacy ...
adopted the following definitions:
(4.) The expression "British India" shall mean all territories and places within Her Majesty's dominions which are for the time being governed by Her Majesty through the Governor-General of India or through any governor or other officer subordinate to the Governor-General of India.In general the term "
(5.) The expression "India" shall mean British India together with any territories of any native prince or chief under the suzerainty of Her Majesty exercised through the Governor-General of India, or through any governor or other officer subordinate to the Governor-General of India.
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
" had been used (and is still used) also to refer to the regions under the rule of the East India Company in India from 1774 to 1858.
The British Crown
The Crown is the state (polity), state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, British Overseas Territories, overseas territories, Provinces and territorie ...
's suzerainty over 175 princely states, generally the largest and most important, was exercised in the name of the British Crown by the central government of British India under the Viceroy; the remaining approximately 400 states were influenced by Agents answerable to the provincial governments of British India under a governor, lieutenant-governor, or chief commissioner. A clear distinction between "dominion" and "suzerainty" was supplied by the jurisdiction of the courts of law: the law of British India rested upon the legislation enacted by the British Parliament, and the legislative powers those laws vested in the various governments of British India, both central and local; in contrast, the courts of the princely states existed under the authority of the respective rulers of those states.
Princely status and titles
 The Indian rulers bore various titles – including
The Indian rulers bore various titles – including Chhatrapati
Chhatrapati is a royal title from Sanskrit language.The word ‘Chhatrapati’ is a Sanskrit language compound word (tatpurusha in Sanskrit) of ''Chatra (umbrella), chhatra'' (''parasol'' or ''umbrella'') and ''pati'' (''master/lord/ruler''). Th ...
(exclusively used by the three Bhonsle
The Bhonsle (or Bhonsale, Bhosale, Bhosle) are a prominent group within the Maratha clan system of kunbi origin. They claimed descent from the Sisodia Rajputs but were likely Kunbi tiller-plainsmen.
History Earliest members
The earliest a ...
dynasty of the Maratha
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
s) ("emperor"), Maharaja
Mahārāja (; also spelled Maharajah, Maharaj) is a Sanskrit title for a "great ruler", "great king" or " high king".
A few ruled states informally called empires, including ruler raja Sri Gupta, founder of the ancient Indian Gupta Empire, an ...
or Raja
''Raja'' (; from , IAST ') is a royal title used for South Asian monarchs. The title is equivalent to king or princely ruler in South Asia and Southeast Asia.
The title has a long history in South Asia and Southeast Asia, being attested f ...
("king"), Sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it ...
, Nawab
Nawab (Balochi language, Balochi: نواب; ar, نواب;
bn, নবাব/নওয়াব;
hi, नवाब;
Punjabi language, Punjabi : ਨਵਾਬ;
Persian language, Persian,
Punjabi language, Punjabi ,
Sindhi language, Sindhi,
Urd ...
, Emir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cerem ...
, Raje
*In Maharashtra, Chatrapati Shivaji Raje was addressed as ''King'' or ''Raje''. Also, other clans of the Maratha community put Raje before their original clan name; Raje Shirke, Raje Mahadik, Raje Kadam, Raje Chalukya, Raje Jadhavrao etc or used ...
, Nizam
The Nizams were the rulers of Hyderabad from the 18th through the 20th century. Nizam of Hyderabad (Niẓām ul-Mulk, also known as Asaf Jah) was the title of the monarch of the Hyderabad State ( divided between the state of Telangana, Mar ...
, Wadiyar (used only by the Maharajas of Mysore
Mysore (), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern part of the state of Karnataka, India. Mysore city is geographically located between 12° 18′ 26″ north latitude and 76° 38′ 59″ east longitude. It is located at an altitude of ...
, meaning "lord"), Agniraj Maharaj for the rulers of Bhaddaiyan Raj, Chogyal
The Chogyal ("Dharma Kings", ) were the monarchs of the former Kingdom of Sikkim, which belonged to the Namgyal dynasty. The Chogyal was the absolute monarch of Sikkim from 1642 to 1975, when the monarchy was abolished and the Sikkimese people ...
, Nawab
Nawab (Balochi language, Balochi: نواب; ar, نواب;
bn, নবাব/নওয়াব;
hi, नवाब;
Punjabi language, Punjabi : ਨਵਾਬ;
Persian language, Persian,
Punjabi language, Punjabi ,
Sindhi language, Sindhi,
Urd ...
("governor"), Nayak, Wāli
''Wāli'', ''Wā'lī'' or ''vali'' (from ar, والي ''Wālī'') is an administrative title that was used in the Muslim World (including the Caliphate and Ottoman Empire) to designate governors of administrative divisions. It is still in us ...
, Inamdar, Saranjamdar
A Saranjam is a grant of land (initially non-hereditary) for maintenance of troops or for military service found among the Maratha, Rajput, Chandraseniya Kayastha Prabhu, Pathare Prabhu, and Kunbi communities in Maharashtra and the former Maratha ...
and many others. Whatever the literal meaning and traditional prestige of the ruler's actual title, the British government translated them all as "prince", to avoid the implication that the native rulers could be "kings" with status equal to that of the British monarch.
 More prestigious Hindu rulers (mostly existing before the Mughal Empire, or having split from such old states) often used the title "
More prestigious Hindu rulers (mostly existing before the Mughal Empire, or having split from such old states) often used the title "Raja
''Raja'' (; from , IAST ') is a royal title used for South Asian monarchs. The title is equivalent to king or princely ruler in South Asia and Southeast Asia.
The title has a long history in South Asia and Southeast Asia, being attested f ...
", Raje
*In Maharashtra, Chatrapati Shivaji Raje was addressed as ''King'' or ''Raje''. Also, other clans of the Maratha community put Raje before their original clan name; Raje Shirke, Raje Mahadik, Raje Kadam, Raje Chalukya, Raje Jadhavrao etc or used ...
" or a variant such as Rai
RAI – Radiotelevisione italiana (; commercially styled as Rai since 2000; known until 1954 as Radio Audizioni Italiane) is the national public broadcasting company of Italy, owned by the Ministry of Economy and Finance. RAI operates many terr ...
, Rana
Rana may refer to:
Astronomy
* Rana (crater), a crater on Mars
* Delta Eridani or Rana, a star
People, groups and titles
* Rana (name), a given name and surname (including a list of people and characters with the name)
* Rana (title), a histori ...
, "Rao", "Rawat" or Rawal
Rawal (also spelled Raval) or Raol originally is a regional variation of the Hindi princely ruler title Raja/Radjah (literally "king") used in some princely states in Rajputana and Western India (notably Gujarat), and is now also used as a caste ...
. Also in this 'class' were several Thakurs or Thai ores and a few particular titles, such as Sardar
Sardar, also spelled as Sardaar/Sirdar ( fa, سردار, , 'commander', literally 'headmaster'), is a title of royalty and nobility that was originally used to denote princes, noblemen, chiefs, kings and other aristocrats. It has also been u ...
, Mankari
Mankari (Mānkari or Maankari) is a hereditary title used by Maratha nobles and troops from the Indian subcontinent who held land grants, and cash allowances. They held an official position at the Darbar (court) and were entitled to certain cer ...
(or Mānkari/Maankari), Deshmukh
Deshmukh (IAST:Dēśamukh), is a historical title conferred to the rulers of a . It is used as a surname in certain regions of India, specifically in the states of Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh whose family received it as a ...
, Sar Desai, Istamuradar, Saranjamdar
A Saranjam is a grant of land (initially non-hereditary) for maintenance of troops or for military service found among the Maratha, Rajput, Chandraseniya Kayastha Prabhu, Pathare Prabhu, and Kunbi communities in Maharashtra and the former Maratha ...
, Raja Inamdar etc.
The most prestigious Hindu rulers usually had the prefix "maha" ("great", compare for example Grand Duke) in their titles, as in ''Maharaja, Maharana, Maharao'', etc. This was used in many princely states, including Mewar
Mewar or Mewad is a region in the south-central part of Rajasthan state of India. It includes the present-day districts of Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Udaipur, Pirawa Tehsil of Jhalawar District of Rajasthan, Neemuch and Man ...
, Travancore
The Kingdom of Travancore ( /ˈtrævənkɔːr/), also known as the Kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor, was an Indian kingdom from c. 1729 until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At ...
and Cochin
Kochi (), also known as Cochin ( ) ( the official name until 1996) is a major port city on the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea, which is a part of the Arabian Sea. It is part of the district of Ernakulam in the state of K ...
. The state of Travancore
The Kingdom of Travancore ( /ˈtrævənkɔːr/), also known as the Kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor, was an Indian kingdom from c. 1729 until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At ...
also had queens regent styled Maharani, applied only to sister of king in Kerala.
There were also compound titles, such as (Maha)rajadhiraj, Raj-i-rajgan, often relics from an elaborate system of hierarchical titles under the Mughal emperors
The Mughal emperors ( fa, , Pādishāhān) were the supreme heads of state of the Mughal Empire on the Indian subcontinent, mainly corresponding to the modern countries of India, Pakistan, Afghanistan and Bangladesh. The Mughal rulers styled t ...
. For example, the addition of the adjective ''Bahadur'' raised the status of the titleholder one level.
Furthermore, most dynasties used a variety of additional titles, such as Varma in South India. This should not be confused with various titles and suffixes not specific to princes but used by entire (sub)castes. This is almost analogous to Singh
Singh (Help:IPA, IPA: ) is a title, middle name or surname that means "lion" in various South Asian and Southeast Asian communities. Traditionally used by the Hindu Kshatriya community, it eventually became a common surname adopted by different ...
title in North India.
The Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Gu ...
princes concentrated at Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
usually adopted Hindu type titles when attaining princely rank; at a lower level Sardar
Sardar, also spelled as Sardaar/Sirdar ( fa, سردار, , 'commander', literally 'headmaster'), is a title of royalty and nobility that was originally used to denote princes, noblemen, chiefs, kings and other aristocrats. It has also been u ...
was used.
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
rulers almost all used the title "Nawab
Nawab (Balochi language, Balochi: نواب; ar, نواب;
bn, নবাব/নওয়াব;
hi, नवाब;
Punjabi language, Punjabi : ਨਵਾਬ;
Persian language, Persian,
Punjabi language, Punjabi ,
Sindhi language, Sindhi,
Urd ...
" (the Arabic honorific of ''naib'', "deputy", used of the Mughal governors, who became de facto autonomous with the decline of the Mughal Empire), with the prominent exceptions of the Nizam
The Nizams were the rulers of Hyderabad from the 18th through the 20th century. Nizam of Hyderabad (Niẓām ul-Mulk, also known as Asaf Jah) was the title of the monarch of the Hyderabad State ( divided between the state of Telangana, Mar ...
of Hyderabad & Berar, the Wāli
''Wāli'', ''Wā'lī'' or ''vali'' (from ar, والي ''Wālī'') is an administrative title that was used in the Muslim World (including the Caliphate and Ottoman Empire) to designate governors of administrative divisions. It is still in us ...
/Khan
Khan may refer to:
*Khan (inn), from Persian, a caravanserai or resting-place for a travelling caravan
*Khan (surname), including a list of people with the name
*Khan (title), a royal title for a ruler in Mongol and Turkic languages and used by ...
of Kalat and the Wāli of Swat
The Wāli of Swat ( ur, ) was the official title of the leader (wāli) of the erstwhile princely state of Swat and also the nomenclature of the Miangul dynasty that ruled there from 1926 to 1969.
History
The earlier titles of the rulers of Sw ...
.
Other less usual titles included Darbar Sahib, Dewan
''Dewan'' (also known as ''diwan'', sometimes spelled ''devan'' or ''divan'') designated a powerful government official, minister, or ruler. A ''dewan'' was the head of a state institution of the same name (see Divan). Diwans belonged to the el ...
, Jam, Mehtar (unique to Chitral
Chitral ( khw, , lit=field, translit=ćhitrār; ur, , translit=ćitrāl) is situated on the Chitral River in northern Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. It serves as the capital of the Chitral District and before that as the capital of Chitral ...
) and Mir (from Emir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cerem ...
).
Precedence and prestige
However, the actual importance of a princely state cannot be read from the title of its ruler, which was usually ''granted'' (or at least recognised) as a favour, often in recognition for loyalty and services rendered to theMughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
. Although some titles were raised once or even repeatedly, there was no automatic updating when a state gained or lost real power. In fact, princely titles were even awarded to holders of domains (mainly jagir
A jagir ( fa, , translit=Jāgir), also spelled as jageer, was a type of feudal land grant in the Indian subcontinent at the foundation of its Jagirdar (Zamindar) system. It developed during the Islamic rule era of the Indian subcontinent, start ...
s) and even taluqdar
Taluqdars or Talukdar ( Hindustani: Devanagari: ; Perso-Arabic: , ; from ''taluq'' "estate/attachment" + '' dar'' "owner"), were aristocrats who formed the ruling class during the Delhi Sultanate, Bengal Sultanate, Mughal Empire and British Raj ...
s and zamindar
A zamindar ( Hindustani: Devanagari: , ; Persian: , ) in the Indian subcontinent was an autonomous or semiautonomous ruler of a province. The term itself came into use during the reign of Mughals and later the British had begun using it as a ...
s, which were not states at all. Most of the zamindar who hold the princely titles were in fact erstwhile princely and royal states reduced to zamindari by the British EIC. Various sources give significantly different numbers of states and domains of the various types. Even in general, the definition of titles and domains are clearly not well-established.
 In addition to their titles all princely rulers were eligible to be appointed to certain British orders of chivalry associated with India, the
In addition to their titles all princely rulers were eligible to be appointed to certain British orders of chivalry associated with India, the Most Exalted Order of the Star of India
The Most Exalted Order of the Star of India is an order of chivalry founded by Queen Victoria in 1861. The Order includes members of three classes:
# Knight Grand Commander (GCSI)
# Knight Commander ( KCSI)
# Companion ( CSI)
No appointments ...
and the Most Eminent Order of the Indian Empire. Women could be appointed as "Knights" (instead of Dames) of these orders. Rulers entitled to 21-gun and 19-gun salutes were normally appointed to the highest rank, Knight Grand Commander of the Order of the Star of India.
Many Indian princes served in the British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurk ...
, the Indian Army
The Indian Army is the land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head is the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), who is a four- ...
, or in local guard or police forces, often rising to high ranks; some even served while on the throne. Many of these were appointed as an Aide de camp, either to the ruling prince of their own house (in the case of relatives of such rulers) or indeed to the British monarchs. Many saw active service
Active may refer to:
Music
* ''Active'' (album), a 1992 album by Casiopea
* Active Records, a record label
Ships
* ''Active'' (ship), several commercial ships by that name
* HMS ''Active'', the name of various ships of the British Royal ...
, both on the subcontinent and on other fronts, during both World Wars.
Apart from those members of the princely houses who entered military service and who distinguished themselves, a good number of princes received honorary ranks as officers in the British and Indian Armed Forces. Those ranks were conferred based on several factors, including their heritage, lineage, gun-salute (or lack of one) as well as personal character or martial traditions. After the First and Second World Wars, the princely rulers of several of the major states, including Gwalior
Gwalior() is a major city in the central Indian state of Madhya Pradesh; it lies in northern part of Madhya Pradesh and is one of the Counter-magnet cities. Located south of Delhi, the capital city of India, from Agra and from Bhopal, the s ...
, Patiala
Patiala () is a city in southeastern Punjab, India, Punjab, northwestern India. It is the fourth largest city in the state and is the administrative capital of Patiala district. Patiala is located around the ''Qila Mubarak, Patiala, Qila Mubarak ...
, Nabha
Nabha is a city and municipal council in the Patiala district in the south-west of the Indian state of Punjab. It was the capital of the former Nabha State. Nabha is also a sub-division city which comes under Patiala district.
Geography
Nabha ...
, Faridkort, Bikaner
Bikaner () is a city in the northwest of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is located northwest of the state capital, Jaipur. Bikaner city is the administrative headquarters of Bikaner District and Bikaner division.
Formerly the capital of ...
, Jaipur
Jaipur (; Hindi Language, Hindi: ''Jayapura''), formerly Jeypore, is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and largest city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Rajasthan. , the city had a pop ...
, Jodhpur
Jodhpur (; ) is the second-largest city in the Indian state of Rajasthan and officially the second metropolitan city of the state. It was formerly the seat of the princely state of Jodhpur State. Jodhpur was historically the capital of the Ki ...
, Jammu and Kashmir Jammu and Kashmir may refer to:
* Kashmir, the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent
* Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), a region administered by India as a union territory
* Jammu and Kashmir (state), a region administered ...
and Hyderabad, were given honorary general officer ranks as a result of their states' contributions to the war effort.
* Lieutenant/Captain/Flight Lieutenant or Lieutenant-Commander/Major/Squadron Leader (for junior members of princely houses or for minor princes)
* Commander/Lieutenant-Colonel/Wing Commander or Captain/Colonel/Group Captain (granted to princes of salute states, often to those entitled to 15-guns or more)
* Commodore/Brigadier/Air Commodore (conferred upon princes of salute states entitled to gun salutes of 15-guns or more)
* Major-General/Air Vice-Marshal (conferred upon princes of salute states entitled to 15-guns or more; conferred upon rulers of the major princely states, including Baroda, Kapurthala
Kapurthala is a city in Punjab state of India. It is the administrative headquarters of Kapurthala District. It was the capital of the Kapurthala State, a princely state in British India. The aesthetic mix of the city with its prominent build ...
, Travancore, Bhopal
Bhopal (; ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and the administrative headquarters of both Bhopal district and Bhopal division. It is known as the ''City of Lakes'' due to its various natural and artificial lakes. It i ...
and Mysore
Mysore (), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern part of the state of Karnataka, India. Mysore city is geographically located between 12° 18′ 26″ north latitude and 76° 38′ 59″ east longitude. It is located at an altitude of ...
)
* Lieutenant-General (conferred upon the rulers of the largest and most prominent princely houses after the First and Second World Wars for their states' contributions to the war effort.)
* General (very rarely awarded; the Maharajas of Gwalior and Jammu & Kashmir were created honorary Generals in the British Army in 1877, the Maharaja of Bikaner was made one in 1937, and the Nizam of Hyderabad in 1941)
It was also not unusual for members of princely houses to be appointed to various colonial offices, often far from their native state, or to enter the diplomatic corps.
Salute states
Thegun salute
A gun salute or cannon salute is the use of a piece of artillery to fire shots, often 21 in number (''21-gun salute''), with the aim of marking an honor or celebrating a joyful event. It is a tradition in many countries around the world.
Histo ...
system was used to set unambiguously the precedence of the major rulers in the area in which the British East India Company was active, or generally of the states and their dynasties. As heads of a state, certain princely rulers were entitled to be saluted by the firing of an odd number of guns between three and 21, with a greater number of guns indicating greater prestige. Generally, the number of guns remained the same for all successive rulers of a particular state, but individual princes were sometimes granted additional guns on a personal basis. Furthermore, rulers were sometimes granted additional gun salutes within their own territories only, constituting a semi-promotion. The states of all these rulers (about 120) were known as salute states
A salute state was a princely state under the British Raj that had been granted a gun salute by the British Crown (as paramount ruler); i.e., the protocolary privilege for its ruler to be greeted—originally by Royal Navy ships, later also ...
.
After Indian Independence, the Maharana of Udaipur
Udaipur () (ISO 15919: ''Udayapura''), historically named as Udayapura, is a city and municipal corporation in Udaipur district of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is the administrative headquarter of Udaipur district. It is the historic capit ...
displaced the Nizam
The Nizams were the rulers of Hyderabad from the 18th through the 20th century. Nizam of Hyderabad (Niẓām ul-Mulk, also known as Asaf Jah) was the title of the monarch of the Hyderabad State ( divided between the state of Telangana, Mar ...
of Hyderabad as the most senior prince in India, because Hyderabad State
Hyderabad State () was a princely state located in the south-central Deccan region of India with its capital at the city of Hyderabad. It is now divided into the present-day state of Telangana, the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka, and t ...
had not acceded to the new Dominion of India
The Dominion of India, officially the Union of India,* Quote: “The first collective use (of the word "dominion") occurred at the Colonial Conference (April to May 1907) when the title was conferred upon Canada and Australia. New Zealand and N ...
, and the style ''Highness'' was extended to all rulers entitled to 9-gun salutes. When the princely states had been integrated into the Indian Union their rulers were promised continued privileges and an income (known as the Privy Purse
The Privy Purse is the British Sovereign's private income, mostly from the Duchy of Lancaster. This amounted to £20.1 million in net income for the year to 31 March 2018.
Overview
The Duchy is a landed estate of approximately 46,000 acres (200 ...
) for their upkeep. Subsequently, when the Indian government abolished the Privy Purse in 1971, the whole princely order ceased to be recognised under Indian law, although many families continue to retain their social prestige informally; some descendants of the rulers are still prominent in regional or national politics, diplomacy, business and high society.
At the time of Indian independence, only five rulers – the Nizam
The Nizams were the rulers of Hyderabad from the 18th through the 20th century. Nizam of Hyderabad (Niẓām ul-Mulk, also known as Asaf Jah) was the title of the monarch of the Hyderabad State ( divided between the state of Telangana, Mar ...
of Hyderabad
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River (India), Musi River, in the northern part ...
, the Maharaja of Mysore
Mysore (), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern part of the state of Karnataka, India. Mysore city is geographically located between 12° 18′ 26″ north latitude and 76° 38′ 59″ east longitude. It is located at an altitude of ...
, the Maharaja of Jammu and Kashmir state
Jammu and Kashmir was a region formerly administered by India as a state from 1952 to 2019, constituting the southern and southeastern portion of the larger Kashmir region, which has been the subject of a dispute between India, Pakistan an ...
, the Maharaja Gaekwad
Gaekwad (also spelt Gaikwar and Gaikwad; mr, Gāyǎkǎvāḍǎ) is a surname native to the Indian state of Maharashtra. The surname is found among the Marathas, Kolis and in Scheduled castes. It is also a common surname among Bharadis, Dhor, an ...
of Baroda
Vadodara (), also known as Baroda, is the second largest city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Vadodara district and is situated on the banks of the Vishwamitri River, from the state capital ...
and the Maharaja Scindia
The Scindia dynasty (anglicized from Shinde) is a Hindu Maratha dynasty of maratha origin that ruled the erstwhile State of Gwalior. It had the Patil-ship of Kumberkerrab in Wai. It was founded by Ranoji Scindia, who started as a personal servan ...
of Gwalior
Gwalior() is a major city in the central Indian state of Madhya Pradesh; it lies in northern part of Madhya Pradesh and is one of the Counter-magnet cities. Located south of Delhi, the capital city of India, from Agra and from Bhopal, the s ...
– were entitled to a 21-gun salute. Six more – the Nawab of Bhopal
Bhopal (; ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and the administrative headquarters of both Bhopal district and Bhopal division. It is known as the ''City of Lakes'' due to its various natural and artificial lakes. It i ...
, the Maharaja Holkar
The Holkar (Pronunciation: �o(ː)ɭkəɾ dynasty was a Maratha clan of Dhangar origin in India. The Holkars were generals under Peshwa Baji Rao I, and later became Maharajas of Indore in Central India as an independent member of the Marath ...
of Indore
Indore () is the largest and most populous Cities in India, city in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It serves as the headquarters of both Indore District and Indore Division. It is also considered as an education hub of the state and is t ...
, the Maharaja of Bharatpur, the Maharana of Udaipur
Udaipur () (ISO 15919: ''Udayapura''), historically named as Udayapura, is a city and municipal corporation in Udaipur district of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is the administrative headquarter of Udaipur district. It is the historic capit ...
, the Maharaja of Kolhapur
Kolhapur () is a city on the banks of the Panchganga River in the southern part of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the administrative headquarter of the Kolhapur district. In, around 2 C.E. Kolapur's name was 'Kuntal'.
Kolhapur is kn ...
, the Maharaja
Mahārāja (; also spelled Maharajah, Maharaj) is a Sanskrit title for a "great ruler", "great king" or " high king".
A few ruled states informally called empires, including ruler raja Sri Gupta, founder of the ancient Indian Gupta Empire, an ...
of Patiala
Patiala () is a city in southeastern Punjab, India, Punjab, northwestern India. It is the fourth largest city in the state and is the administrative capital of Patiala district. Patiala is located around the ''Qila Mubarak, Patiala, Qila Mubarak ...
and the Maharaja of Travancore
The Kingdom of Travancore ( /ˈtrævənkɔːr/), also known as the Kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor, was an Indian kingdom from c. 1729 until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At ...
– were entitled to 19-gun salutes. The most senior princely ruler was the Nizam of Hyderabad
The Nizams were the rulers of Hyderabad from the 18th through the 20th century. Nizam of Hyderabad (Niẓām ul-Mulk, also known as Asaf Jah) was the title of the monarch of the Hyderabad State ( divided between the state of Telangana, Mar ...
, who was entitled to the unique style ''Exalted Highness
His Exalted Highness is a rare hybrid of the title style Highness. It is used as a salutation style ''only'' for the Nizams of Hyderabad and Berar conferred by the British Government.
See also
*Mir Osman Ali Khan
Mir Osman Ali Khan, Asaf Jah ...
'' and 21-gun salute
A 21-gun salute is the most commonly recognized of the customary gun salutes that are performed by the firing of cannons or artillery as a military honor. As naval customs evolved, 21 guns came to be fired for heads of state, or in exceptiona ...
. Other princely rulers entitled to salutes of 11 guns (soon 9 guns too) or more were entitled to the style ''Highness''. No special style was used by rulers entitled to lesser gun salutes.
As ''paramount ruler'', and successor to the Mughals, the British ''King-Emperor
A king-emperor (the female equivalent being queen-empress) is a sovereign ruler who is simultaneously a king of one territory and emperor of another. This title usually results from a merger of a royal and imperial crown, but recognises that the ...
'' of India, for whom the style of Majesty
Majesty (abbreviated HM for His Majesty or Her Majesty, oral address Your Majesty; from the Latin ''maiestas'', meaning "greatness") is used as a manner of address by many monarchs, usually kings or queens. Where used, the style outranks the st ...
was reserved, was entitled to an 'imperial' 101-gun salute—in the European tradition also the number of guns fired to announce the birth of an heir (male) to the throne.
Non-salute states
There was no strict correlation between the levels of the titles and the classes of gun salutes, the real measure of precedence, but merely a growing percentage of higher titles in classes with more guns. As a rule the majority of gun-salute princes had at least nine, with numbers below that usually the prerogative of Arab Sheikhs of theAden protectorate
The Aden Protectorate ( ar, محمية عدن ') was a British protectorate in South Arabia which evolved in the hinterland of the port of Aden and in the Hadhramaut following the conquest of Aden by the Bombay Presidency of British India ...
, also under British protection.
There were many so-called non-salute states of lower prestige. Since the total of salute states was 117 and there were more than 500 princely states, most rulers were not entitled to any gun salute. Not all of these were minor rulers – Surguja State
Surguja State, was one of the main princely states of Central India during the period of the British Raj, even though it was not entitled to any gun salute. Formerly it was placed under the Central India Agency, but in 1905 it was transferred t ...
, for example, was both larger and more populous than Karauli State
Karauli State was a princely state in India from 1348 to 1949. It is located in the Braj region. Karauli city was the capital while Mandrayal or Mandrail was another important town.
Geography
The state had an area of . In 1901, the population ...
, but the Maharaja of Karauli was entitled to a 17-gun salute and the Maharaja of Surguja was not entitled to any gun salute at all.
A number of princes, in the broadest sense of the term, were not even acknowledged as such. On the other hand, the dynasties of certain defunct states were allowed to keep their princely status – they were known as political pensioner
A political pensioner enjoys a pension awarded due to his or political career or significance.
UK domestic politicians
By the Political Offices Pension Act 1869, pensions were instituted for those who had held political office. For the purpos ...
s, such as the Nawab of Oudh
The Oudh State (, also Kingdom of Awadh, Kingdom of Oudh, or Awadh State) was a princely state in the Awadh region of North India until its annexation by the British in 1856. The name Oudh, now obsolete, was once the anglicized name of ...
. There were also certain estates of British India which were rendered as political saranjam
A Saranjam is a grant of land (initially non-hereditary) for maintenance of troops or for military service found among the Maratha, Rajput, Chandraseniya Kayastha Prabhu, Pathare Prabhu, and Kunbi communities in Maharashtra and the former Marath ...
s, having equal princely status. Though none of these princes were awarded gun salutes, princely titles in this category were recognised as a form of vassals
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain. W ...
of salute states, and were not even in direct relation with the paramount power.
Largest princely states by area
Doctrine of lapse
A controversial aspect of East India Company rule was thedoctrine of lapse
The doctrine of lapse was a policy of annexation initiated by the East India Company in the Indian subcontinent about the princely states, and applied until the year 1858, the year after Company rule was succeeded by the British Raj under the ...
, a policy under which lands whose feudal ruler died (or otherwise became unfit to rule) without a male biological heir (as opposed to an adopted son) would become directly controlled by the company and an adopted son would not become the ruler of the princely state. This policy went counter to Indian tradition where, unlike Europe, it was far more the accepted norm for a ruler to appoint his own heir.
The doctrine of lapse was pursued most vigorously by the Governor-General Sir James Ramsay, 10th Earl (later 1st Marquess) of Dalhousie. Dalhousie annexed seven states, including Awadh
Awadh (), known in British historical texts as Avadh or Oudh, is a region in the modern Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, which was before independence known as the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh. It is synonymous with the Kośāla region of ...
(Oudh), whose Nawabs he had accused of misrule, and the Maratha
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
states of Nagpur
Nagpur (pronunciation: Help:IPA/Marathi, aːɡpuːɾ is the third largest city and the winter capital of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the 13th largest city in India by population and according to an Oxford's Economics report, Nag ...
, Jhansi
Jhansi (; Hindi: झांसी, Urdu: ) is a historic city in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It lies in the region of Bundelkhand on the banks of the Pahuj River, in the extreme south of Uttar Pradesh. Jhansi is the administrative hea ...
, Satara, Sambalpur
Sambalpur () is the fifth largest city in the Indian State of Odisha. It is located on the banks of river Mahanadi, with a population of 335,761 (as per 2011 census). Prehistoric settlements have been recorded there. It is the home of the Samb ...
, and Thanjavur
Thanjavur (), also Tanjore, Pletcher 2010, p. 195 is a city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. Thanjavur is the 11th biggest city in Tamil Nadu. Thanjavur is an important center of South Indian religion, art, and architecture. Most of the Gr ...
. Resentment over the annexation of these states turned to indignation when the heirlooms of the Maharajas of Nagpur were auctioned off in Calcutta. Dalhousie's actions contributed to the rising discontent amongst the upper castes which played a large part in the outbreak of the Indian mutiny of 1857. The last Mughal Badshah (emperor), whom many of the mutineers saw as a figurehead to rally around, was deposed following its suppression.
In response to the unpopularity of the doctrine, it was discontinued with the end of Company rule and the British Parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative supremacy ...
's assumption of direct power over India.
Imperial governance
 By treaty, the British controlled the external affairs of the princely states absolutely. As the states were not British possessions, they retained control over their own internal affairs, subject to a degree of British influence which in many states was substantial.
By the beginning of the 20th century, relations between the British and the four largest states –
By treaty, the British controlled the external affairs of the princely states absolutely. As the states were not British possessions, they retained control over their own internal affairs, subject to a degree of British influence which in many states was substantial.
By the beginning of the 20th century, relations between the British and the four largest states – Hyderabad
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River (India), Musi River, in the northern part ...
, Mysore
Mysore (), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern part of the state of Karnataka, India. Mysore city is geographically located between 12° 18′ 26″ north latitude and 76° 38′ 59″ east longitude. It is located at an altitude of ...
, Jammu and Kashmir, and Baroda
Vadodara (), also known as Baroda, is the second largest city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Vadodara district and is situated on the banks of the Vishwamitri River, from the state capital ...
– were directly under the control of the governor-general of India, in the person of a British Resident minister#Residents in Asia, resident. Two agencies, for Rajputana and Central India Agency, Central India, oversaw twenty and 148 princely states respectively. The remaining princely states had their own British political officers, or Agents, who answered to the administrators of India's provinces. The agents of five princely states were then under the authority of Madras Presidency, Madras, 354 under Bombay Presidency, Bombay, 26 of Bengal Presidency, Bengal, two under Assam, 34 under Punjab (British India), Punjab, fifteen under the Central Provinces and Berar and two under the Uttar Pradesh, United Provinces.
 The Chamber of Princes (''Narender Mandal'' or ''Narendra Mandal'') was an institution established in 1920 by a Proclamation, royal proclamation of the George V of the United Kingdom, King-Emperor to provide a forum in which the rulers could voice their needs and aspirations to the government. It survived until the end of the British Raj in 1947.
By the early 1930s, most of the princely states whose agencies were under the authority of India's provinces were organised into new Agencies, answerable directly to the governor-general, on the model of the Central India and Rajputana agencies: the Eastern States Agency, Punjab States Agency, Baluchistan Agency, Deccan States Agency, Madras States Agency and the Northwest Frontier States Agency. The Baroda Residency was combined with the princely states of northern Bombay Presidency into the Baroda, Western India and Gujarat States Agency.
The Chamber of Princes (''Narender Mandal'' or ''Narendra Mandal'') was an institution established in 1920 by a Proclamation, royal proclamation of the George V of the United Kingdom, King-Emperor to provide a forum in which the rulers could voice their needs and aspirations to the government. It survived until the end of the British Raj in 1947.
By the early 1930s, most of the princely states whose agencies were under the authority of India's provinces were organised into new Agencies, answerable directly to the governor-general, on the model of the Central India and Rajputana agencies: the Eastern States Agency, Punjab States Agency, Baluchistan Agency, Deccan States Agency, Madras States Agency and the Northwest Frontier States Agency. The Baroda Residency was combined with the princely states of northern Bombay Presidency into the Baroda, Western India and Gujarat States Agency. Gwalior
Gwalior() is a major city in the central Indian state of Madhya Pradesh; it lies in northern part of Madhya Pradesh and is one of the Counter-magnet cities. Located south of Delhi, the capital city of India, from Agra and from Bhopal, the s ...
was separated from the Central India Agency and given its own Resident, and the states of Rampur, Uttar Pradesh, Rampur and Benares, formerly with Agents under the authority of the United Provinces, were placed under the Gwalior Residency in 1936. The princely states of Sandur, India, Sandur and Banganapalle in Mysore Presidency were transferred to the agency of the Mysore Resident in 1939.
Principal princely states in 1947
The native states in 1947 included five large states that were in "direct political relations" with the Government of India. For the complete list of princely states in 1947, see List of princely states of India.In direct relations with the central government
Central India Agency, Gwalior Residency, Baluchistan Agency, Rajputana Agency, Eastern States Agency Gwalior Residency (two states) Other states under provincial governments Madras Presidency, Madras (5 States) Bombay Presidency, Bombay (354 States) Central Provinces and Berar, Central Provinces (15 States) Punjab (British India), Punjab (45 States) Assam#British Assam, Assam (26 states)Burma
;Burma#Colonial era (1886–1948), Burma (52 states)State military forces
The armies of the Native States were bound by many restrictions that were imposed bysubsidiary alliance
A subsidiary alliance, in South Asian history, was a tributary alliance between a South Asian state and a European East India Company.
Under this system, an Indian ruler who formed a treaty with the company in question would be provided wi ...
s. They existed mainly for ceremonial use and for internal policing, although certain units designated as Imperial Service Troops, were available for service alongside the regular Indian Army upon request by the British government.
According to the , Since a chief can neither attack his neighbour nor fall out with a foreign nation, it follows that he needs no military establishment which is not required either for police purposes or personal display, or for cooperation with the Imperial Government. The treaty made with Gwalior in 1844, and the instrument of transfer given to Mysore in 1881, alike base the restriction of the forces of the State upon the broad ground of protection. The former explained in detail that unnecessary armies were embarrassing to the State itself and the cause of disquietude to others: a few months later a striking proof of this was afforded by the army of the Sikh kingdom of Lahore. The British Government has undertaken to protect the dominions of the Native princes from invasion and even from rebellion within: its army is organised for the defence not merely ofIn addition, other restrictions were imposed:British India The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ..., but of all the possessions under thesuzerainty Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is cal ...of the King-Emperor.
The treaties with most of the larger States are clear on this point. Posts in the interior must not be fortified, factories for the production of guns and ammunition must not be constructed, nor may the subject of other States be enlisted in the local forces. ... They must allow the forces that defend them to obtain local supplies, to occupy cantonments or positions, and to arrest deserters; and in addition to these services they must recognise the British Empire, Imperial control of the railways, telegraphs, and postal communications as essential not only to the common welfare but to the common defence.The Imperial Service Troops were routinely inspected by British army officers and generally had the same equipment as soldiers in the British Indian Army. Although their numbers were relatively small, the Imperial Service Troops were employed in China and British Somaliland in the first decade of the 20th century, and later saw action in the First World War and Second World War .
Political integration of princely states in 1947 and after
India
At the time of Partition of India, Indian independence on 15 August 1947, India was divided into two sets of territories, the first being the territories of "British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
", which were under the direct control of the India Office in London and the Governor-General of India, governor-general of India, and the second being the "princely states", the territories over which the Crown had suzerainty
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is cal ...
, but which were under the control of their hereditary rulers. In addition, there were several colonial enclaves controlled by France and Portugal. The integration of these territories into Dominion of India
The Dominion of India, officially the Union of India,* Quote: “The first collective use (of the word "dominion") occurred at the Colonial Conference (April to May 1907) when the title was conferred upon Canada and Australia. New Zealand and N ...
, that had been created by the Indian Independence Act 1947 by the British Parliament, was a declared objective of the Indian National Congress, which the Government of India pursued over the years 1947 to 1949. Through a combination of tactics, Sardar
Sardar, also spelled as Sardaar/Sirdar ( fa, سردار, , 'commander', literally 'headmaster'), is a title of royalty and nobility that was originally used to denote princes, noblemen, chiefs, kings and other aristocrats. It has also been u ...
Vallabhbhai Patel and V. P. Menon in the months immediately preceding and following the independence convinced the rulers of almost all of the hundreds of princely states to accede to India. In a speech in January 1948, Vallabhbhai Patel said:
Although this process successfully integrated the vast majority of princely states into India, it was not as successful in relation to a few states, notably the former princely state of Kashmir and Jammu (princely state), Kashmir, whose Maharaja delayed signing the instrument of accession into India until his territories were under the threat of invasion by Pakistan, and the state of Hyderabad
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River (India), Musi River, in the northern part ...
, whose ruler decided to remain independent and was subsequently defeated by the Operation Polo invasion.
Having secured their accession, Sardar Patel and V. P. Menon then proceeded, in a step-by-step process, to secure and extend the central government's authority over these states and to transform their administrations until, by 1956, there was little difference between the territories that had formerly been part of British India and those that had been princely states. Simultaneously, the Government of India, through a combination of diplomatic and economic pressure, acquired control over most of the remaining European colonial exclaves on the subcontinent. Fed up with the protracted and stubborn resistance of the Portuguese government; in 1961 the Indian Army Annexation of Goa, invaded and annexed Portuguese India. These territories, like the princely states, were also integrated into the Republic of India.
As the final step, in 1971, the 26th amendment to the Constitution of India withdrew recognition of the princes as rulers, took away their remaining privileges, and abolished the remuneration granted to them by privy purses. In 2012, the High Court of Kerala in a judgement on ''Mujeeba Rahman vs the State Of Kerala'' stated that, 'though by the 26th amendment of the Constitution, Article 363 was repealed whereby the rights and privileges of the rulers of Indian States were taken away, still the name and title of the rulers remained as such and unaffected in so far as names and titles were not contemplated as rights or privileges under the repealed Articles 291 and 362 of the Constitution.' So the titles were not abolished by the government; only their political powers and right to receive Privy Purse were cancelled.
Pakistan
During the period of the British Raj, there were four princely states in Balochistan: Makran (princely state), Makran, Kharan (princely state), Kharan, Las Bela (princely state), Las Bela and Kalat. The first three acceded to Pakistan. However, the ruler of the fourth princely state, the Khan of Kalat Ahmad Yar Khan, declared Kalat's independence as this was one of the options given to all princely states. The state remained independent until it was acceded on 27 March 1948. The signing of the Instrument of Accession by Ahmad Yar Khan, led his brother, Prince Abdul Karim, to revolt against his brother's decision in July 1948, causing an Balochistan conflict, ongoing and still unresolved insurgency. Bahawalpur (princely state), Bahawalpur from the Punjab Agency joined Pakistan on 5 October 1947. The princely states of the North-West Frontier States Agency, North-West Frontier States Agencies. included the Dir Swat and Chitral Agency and the Deputy Commissioner of Hazara acting as the Political Agent for Amb and Phulra. These states joined Pakistan on independence from the British.See also
* Flags of Indian princely states * Political integration of India * List of princely states of British India (by region) * List of Indian monarchs * Praja Mandal * Salute state * Indian feudalism * Indian honorifics * Ghatwals and Mulraiyats * Jagirdar * List of Maratha dynasties and states * List of Rajput dynasties and states *Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern Indian confederation that came to dominate much of the Indian subcontinent in the 18th century. Maratha rule formally began in 1674 with the coronation of Shi ...
* Maratha titles
* Oudh Bequest
* Rajputana
* Zamindar
* Vorstenlanden, ''princely states in the Netherlands Indies''
References
Bibliography
* Bangash, Yaqoob Khan (2016). "A Princely Affair: The Accession and Integration of the Princely States of Pakistan, 1947–1955". Oxford University Press Pakistan. *Bhagavan, Manu. "Princely States and the Hindu Imaginary: Exploring the Cartography of Hindu Nationalism in Colonial India" ''Journal of Asian Studies,'' (Aug 2008) 67#3 pp 881–91in JSTOR
* Bhagavan, Manu. ''Sovereign Spheres: Princes, Education and Empire in Colonial India'' (2003) * . * Ernst, W. and B. Pati, eds. ''India’s Princely States: People, Princes, and Colonialism'' (2007) * * Jeffrey, Robin. ''People, Princes and Paramount Power: Society and Politics in the Indian Princely States'' (1979) 396pp * Kooiman, Dick. ''Communalism and Indian Princely States: Travancore, Baroda & Hyderabad in the 1930s'' (2002), 249pp * * * Pochhammer, Wilhelm von ''India's Road to Nationhood: A Political History of the Subcontinent'' (1973) ch 5
excerpt
*
Gazetteers
*online
*
online
*
online
External links
*and heads of government, and some biographies. {{DEFAULTSORT:Princely State Princely states of India, 1721 establishments in India 1949 disestablishments in India Types of administrative division Client state Hindu dynasties Former British protectorates