National Trails System Act on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
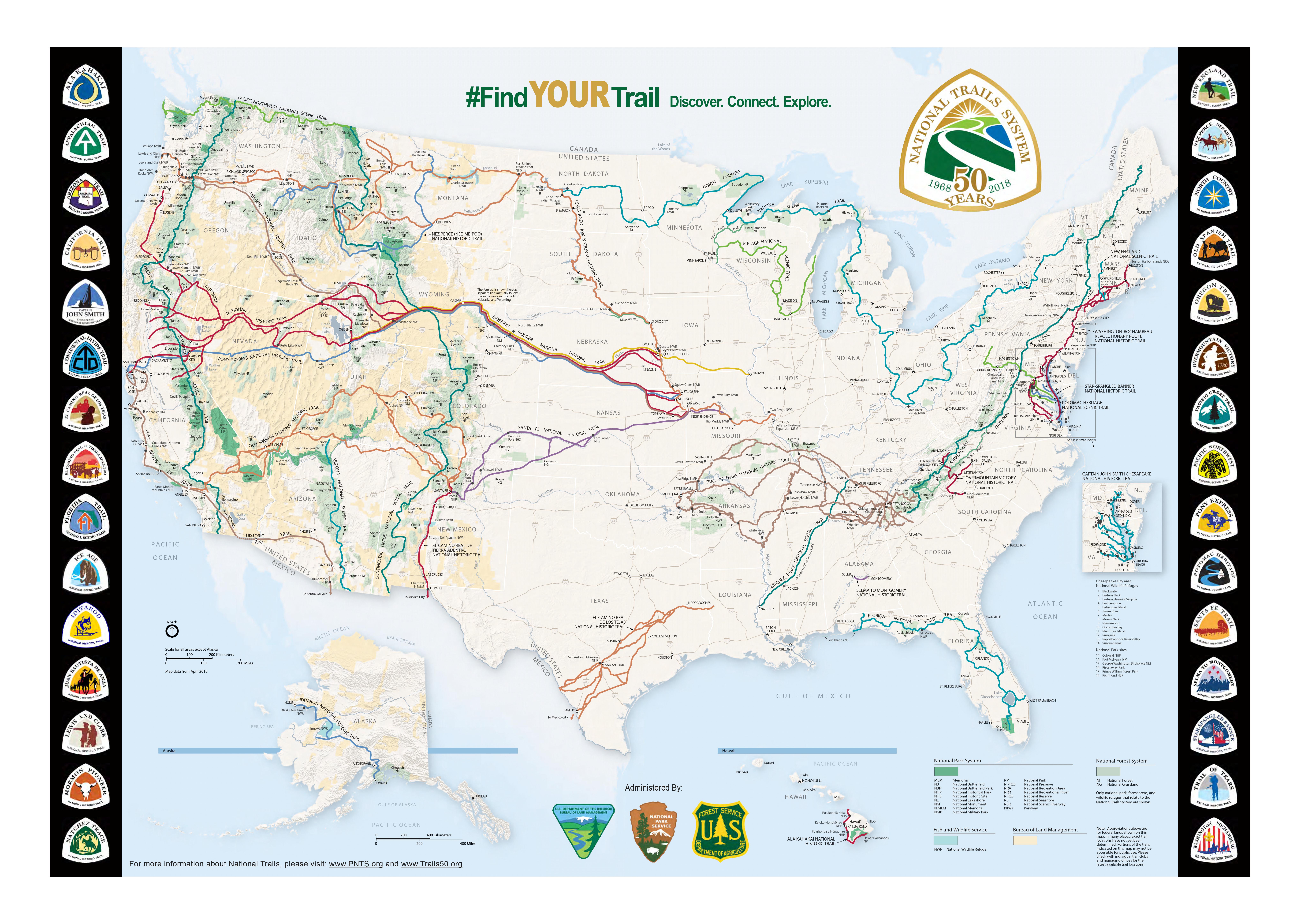
 The National Trails System is a series of
The National Trails System is a series of
/ref> *Chester River Component Connecting Trail – , extends the Captain John Smith Chesapeake National Historic Trail up the
 National recreation trail (NRT) is a designation given to existing trails that contribute to the recreational and conservation goals of a national network of trails. Over 1,300 trails over all fifty states have been designated as NRTs on
National recreation trail (NRT) is a designation given to existing trails that contribute to the recreational and conservation goals of a national network of trails. Over 1,300 trails over all fifty states have been designated as NRTs on
Partnership for National Trails System
– National Park Service
America's National Trails
– U.S. Forest Service
National Scenic and Historic Trails
– Bureau of Land Management
National Recreation Trails Program
– American Trails
National Recreation Trails databaseThe National Trails System: A Brief Overview
– Congressional Research Service {{Authority control 01 Trails Hiking trails in the United States Scenic highways in the United States United States federal public land legislation 1968 in law 1968 in the United States

trail
A trail, also known as a path or track, is an unpaved lane or small road usually passing through a natural area. In the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland, a path or footpath is the preferred term for a pedestrian or hiking trail. Th ...
s in the United States designated "to promote the preservation of, public access to, travel within, and enjoyment and appreciation of the open-air, outdoor areas and historic resources of the Nation". There are four types of trails: the national scenic trails, national historic trails, national recreation trails, and connecting or side trails. The national trails provide opportunities for hiking
Hiking is a long, vigorous walk, usually on trails or footpaths in the countryside. Walking for pleasure developed in Europe during the eighteenth century.AMATO, JOSEPH A. "Mind over Foot: Romantic Walking and Rambling." In ''On Foot: A Histor ...
and historic education, as well as horseback riding
Equestrianism (from Latin , , , 'horseman', 'horse'), commonly known as horse riding (Commonwealth English) or horseback riding (American English), includes the disciplines of riding, driving, and vaulting. This broad description includes the ...
, biking, camping
Camping is an outdoor activity involving overnight stays away from home, either without shelter or using basic shelter such as a tent, or a recreational vehicle. Typically, participants leave developed areas to spend time outdoors in more nat ...
, scenic driving, water sports, and other activities. The National Trails System consists of 11 national scenic trails, 19 national historic trails, over 1,300 national recreation trails, and seven connecting and side trails, as well as one national geologic trail, with a total length of more than . The scenic and historic trails are in every state, and Virginia and Wyoming have the most running through them, with six.
In response to a call by President Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
to have a cooperative program to build public trails for "the forgotten outdoorsmen of today" in both urban and backcountry areas, the Bureau of Outdoor Recreation
The Bureau of Outdoor Recreation (BOR) was an agency of the United States Department of the Interior with the mission of planning outdoor recreation opportunities for the Interior Department and assisting private, local, and state organizations w ...
released a report in 1966 entitled ''Trails for America''. The study made recommendations for a network of national scenic trails, park and forest trails, and metropolitan area trails to provide recreational opportunities, with evaluations of several possible trails, both scenic and historic. The program for long-distance natural trails was created on October 2, 1968, by the National Trails System Act, which also designated two national scenic trails, the Appalachian Trail
The Appalachian Trail (also called the A.T.), is a hiking trail in the Eastern United States, extending almost between Springer Mountain in Georgia and Mount Katahdin in Maine, and passing through 14 states.Gailey, Chris (2006)"Appalachian Tr ...
and the Pacific Crest Trail
The Pacific Crest Trail (PCT), officially designated as the Pacific Crest National Scenic Trail, is a long-distance hiking and equestrian trail closely aligned with the highest portion of the Cascade and Sierra Nevada mountain ranges, which lie ...
, and requested that an additional fourteen trail routes be studied for possible inclusion. Sponsored by Senators Henry M. Jackson
Henry Martin "Scoop" Jackson (May 31, 1912 – September 1, 1983) was an American lawyer and politician who served as a U.S. representative (1941–1953) and U.S. senator (1953–1983) from the state of Washington. A Cold War liberal and a ...
and Gaylord Nelson
Gaylord Anton Nelson (June 4, 1916July 3, 2005) was an American politician and environmentalist from Wisconsin who served as a United States senator and governor. He was a member of the Democratic Party and the founder of Earth Day, which launch ...
and Representative Roy A. Taylor
Roy Arthur Taylor (January 31, 1910 – November 28, 1995) was a U.S. Representative from North Carolina.
Born in Vader, Washington, Taylor graduated from Asheville-Biltmore College, Asheville, North Carolina, 1929.
He graduated from Maryvill ...
, part of the bill's impetus was threats of development along the Appalachian Trail, which was at risk of losing its wilderness character, and the Land and Water Conservation Fund
The United States' Land and Water Conservation Fund (LWCF) is a federal program that was established by Act of Congress in 1965 to provide funds and matching grants to federal, state and local governments for the acquisition of land and water, and ...
was used to acquire lands. In 1978, as a result of the study of trails that were most significant for their historic associations, national historic trails were created as a new category with four trails designated that year. Since 1968, over forty trail routes have been studied for inclusion in the system.
The scenic and historic trails are congressionally established long-distance trails, administered by the National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational propertie ...
(NPS), United States Forest Service
The United States Forest Service (USFS) is an agency of the U.S. Department of Agriculture that administers the nation's 154 national forests and 20 national grasslands. The Forest Service manages of land. Major divisions of the agency inc ...
(USFS), and/or Bureau of Land Management
The Bureau of Land Management (BLM) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior responsible for administering federal lands. Headquartered in Washington DC, and with oversight over , it governs one eighth of the country's la ...
(BLM). These agencies may acquire lands to protect key rights of way
Right of way is the legal right, established by grant from a landowner or long usage (i.e. by prescription), to pass along a specific route through property belonging to another.
A similar ''right of access'' also exists on land held by a gov ...
, sites, resources and viewshed
A viewshed is the geographical area that is visible from a location. It includes all surrounding points that are in line-of-sight with that location and excludes points that are beyond the horizon or obstructed by terrain and other features (e.g. ...
s, though the trails do not have fixed boundaries. They work in cooperation with each other, states, local governments, land trust
Land trusts are nonprofit organizations which own and manage land, and sometimes waters. There are three common types of land trust, distinguished from one another by the ways in which they are legally structured and by the purposes for which th ...
s, and private landowners to coordinate and protect lands and structures along these trails, enabling them to be accessible to the public. These partnerships between the agency administrators and local site managers are vital for resource protection and the visitor experience. The Federal Interagency Council on the National Trails System promotes collaboration and standardization in trail development and protection. National recreation trails and connecting and side trails do not require congressional action, but are recognized by actions of the secretary of the interior Secretary of the Interior may refer to:
* Secretary of the Interior (Mexico)
* Interior Secretary of Pakistan
* Secretary of the Interior and Local Government (Philippines)
* United States Secretary of the Interior
See also
*Interior ministry ...
or the secretary of agriculture. The national trails are supported by volunteers at private non-profit organizations that work with the federal agencies under the Partnership for the National Trails System and other trail type-specific advocacy groups.
For fiscal year 2021, the 24 trails administered by the NPS received a budget of $15.4 million.
National Scenic Trails
The eleven national scenic trails were established to provide outdoor recreation opportunities and to conserve portions of the natural landscape with significant scenic, natural, cultural, or historic importance. These trails are continuous non-motorized long-distance trails that can be backpacked from end-to-end or hiked for short segments, except for Natchez Trace NST, which consists of five shorter, disconnected trail segments. The ''Trails for America'' report said, "Each National Scenic Trail should stand out in its own right as a recreation resource of superlative quality and of physical challenge." Most notably, the national scenic trail system provides access to the crest of theAppalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
in the east via the Appalachian Trail
The Appalachian Trail (also called the A.T.), is a hiking trail in the Eastern United States, extending almost between Springer Mountain in Georgia and Mount Katahdin in Maine, and passing through 14 states.Gailey, Chris (2006)"Appalachian Tr ...
, of the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
in the west on the Continental Divide Trail
The Continental Divide National Scenic Trail (in short Continental Divide Trail (CDT)) is a United States National Scenic Trail with a length measured by the Continental Divide Trail Coalition of between the U.S. border with Chihuahua, Mexico ...
, and of the Cascade
Cascade, Cascades or Cascading may refer to:
Science and technology Science
*Cascade waterfalls, or series of waterfalls
* Cascade, the CRISPR-associated complex for antiviral defense (a protein complex)
* Cascade (grape), a type of fruit
* Bioc ...
and Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada () is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primarily ...
ranges on the Pacific Crest Trail
The Pacific Crest Trail (PCT), officially designated as the Pacific Crest National Scenic Trail, is a long-distance hiking and equestrian trail closely aligned with the highest portion of the Cascade and Sierra Nevada mountain ranges, which lie ...
, which make up the Triple Crown of Hiking
The Triple Crown of Hiking informally refers to the three major U.S. long-distance hiking trails:
* Appalachian Trail – , between Springer Mountain in Georgia and Mount Katahdin in Maine and traversing North Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia, Wes ...
. Other places of note include the southern wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The ...
s and Gulf Coast
The Gulf Coast of the United States, also known as the Gulf South, is the coastline along the Southern United States where they meet the Gulf of Mexico. The coastal states that have a shoreline on the Gulf of Mexico are Texas, Louisiana, Mississ ...
on the Florida Trail
The Florida Trail is one of eleven National Scenic Trails in the United States. It currently runs , from Big Cypress National Preserve (between Miami and Naples, Florida along the Tamiami Trail) to Fort Pickens at Gulf Islands National Seashore, ...
, the North Woods
The Laurentian Mixed Forest Province, also known as the North Woods, is a forested ecoregion in eastern North America. Among others, this terminology has been adopted by the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources. Similar, though not n ...
on the North Country Trail
The North Country National Scenic Trail, generally known as the North Country Trail or simply the NCT, is a footpath stretching over from Middlebury in central Vermont to Lake Sakakawea State Park in central North Dakota in the United States; ...
, the variety of southwestern mountains and ecosystems on the Arizona Trail
The Arizona National Scenic Trail is a National Scenic Trail from Mexico to Utah that traverses the whole north–south length of the U.S. state of Arizona. The trail begins at the Coronado National Memorial near the US–Mexico border and moves ...
, and the remote high-mountain landscape near the Canadian border on the Pacific Northwest Trail
The Pacific Northwest Trail (PNT) is a 1200-mile hiking trail running from the Continental Divide in Montana to the Pacific Ocean on Washington's Olympic Coast. Along the way, the PNT crosses three national parks, seven national forests, and two ...
.
They have a total length of approximately . Due to the extent of construction of route realignments, segment alternatives, and measurement methods, some sources vary in their distances reported and values may be rounded.
Of the eleven national scenic trails, Appalachian, Natchez Trace, and Potomac Heritage are official units of the NPS; though their enabling legislation does not distinguish them, these have more direct administration. The NPS manages its other three trails more as a coordinator with local partners than as an administrator. The NPS manages its scenic trails like its other areas, as long, linear parks. Five trails are overseen by the U.S. Forest Service.
In 2022 Arlette Laan, whose trail name was "Apple Pie," became the first woman known to have completely hiked all eleven of the national scenic trails.
National Historic Trails
The 19 national historic trails are designated to protect the courses of significant overland or water routes that reflect the history of the nation. They represent the earliest European travels in the country in Chesapeake Bay and on Spanish royal roads; the nation's struggle for independence on theOvermountain Victory National Historic Trail
The Overmountain Victory National Historic Trail (OVHT) is part of the U.S. National Trails System, and N.C. State Trail System. It recognizes the Revolutionary War Overmountain Men, Patriots from what is now East Tennessee who crossed the Un ...
and Washington–Rochambeau Revolutionary Route
The Washington–Rochambeau Revolutionary Route is a series of roads used in 1781 by the Continental Army under the command of George Washington and the Expédition Particulière under the command of Jean-Baptiste de Rochambeau during their 1 ...
; westward migrations on the Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
, California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
, and Mormon Trails, which traverse some of the same route; and the development of continental commerce on the Santa Fe Trail
The Santa Fe Trail was a 19th-century route through central North America that connected Franklin, Missouri, with Santa Fe, New Mexico. Pioneered in 1821 by William Becknell, who departed from the Boonslick region along the Missouri River, th ...
, Old Spanish Trail, and Pony Express
The Pony Express was an American express mail service that used relays of horse-mounted riders. It operated from April 3, 1860, to October 26, 1861, between Missouri and California. It was operated by the Central Overland California and Pik ...
. They also memorialize the forced displacement and hardships of the Native Americans on the Trail of Tears
The Trail of Tears was an ethnic cleansing and forced displacement of approximately 60,000 people of the "Five Civilized Tribes" between 1830 and 1850 by the United States government. As part of the Indian removal, members of the Cherokee, ...
and Nez Perce National Historic Trail
The Nez Perce (Nee-Me-Poo) National Historic Trail follows the route taken by a large group of the Nez Perce tribe in 1877 to avoid being forced onto a reservation. The 1,170-mile (1,883 km) trail was created in 1986 as part of the National ...
.
Their routes follow the nationally significant, documented historical journeys of notable individuals or groups but are not necessarily meant to be continuously traversed today; they are largely networks of partner sites along marked auto routes rather than the exact non-motorized trails as originally used. Interpretative sites are often at other areas of the National Park System along the trails, as well as locally operated museums and sites. The National Historic Trails Interpretive Center
The National Historic Trails Interpretive Center (NHTIC) is an interpretive center about several of the National Historic Trails and is located northwest of Casper, Wyoming on Interstate 25. It is operated through a partnership between the Bur ...
in Wyoming is on the Oregon, California, Mormon Pioneer, and Pony Express National Historic Trails and has exhibits on Western emigration. Nine are administered by the NPS National Trails Office in Santa Fe and Salt Lake City.
National historic trails were authorized under the National Parks and Recreation Act of 1978 (), amending the National Trails System Act of 1968. They have a total length of approximately ; many trails include several branches making them much longer than a single end-to-end distance.
Connecting or side trails
The act also established a category of trails known as connecting or side trails. Though there are no guidelines for how these are managed, these have been designated by the secretary of the interior to extend trails beyond the original congressionally established route. Seven side trails have been designated: * Timms Hill Trail – , connects theIce Age Trail
The Ice Age Trail is a National Scenic Trail stretching in the state of Wisconsin in the United States. The trail is administered by the National Park Service, and is constructed and maintained by private and public agencies including the Ice ...
to Wisconsin's highest point, Timms Hill
Timms Hill or Timm's Hill is the highest natural point in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and is located in north-central Wisconsin in Timms Hill County Park in the Town of Hill in Price County. After being surveyed by Quentin Stevens of Ogema Tele ...
(1990)
* Anvik Connector – , joins the Iditarod Trail
The Iditarod Trail, also known historically as the Seward-to-Nome Trail, is a thousand-plus mile (1,600 km) historic and contemporary trail system in the US state of Alaska. The trail began as a composite of trails established by Alaskan ...
to the village of Anvik, Alaska
Anvik ( Deg Xinag: ) is a city, home to the Deg Hit'an people, in the Yukon-Koyukuk Census Area, Alaska, United States. The name Anvik, meaning "exit" in the Central Alaskan Yup'ik language, became the common usage despite multiple names at the ...
(1990)
*Susquehanna River Component Connecting Trail – , extends the Captain John Smith Chesapeake National Historic Trail
The Captain John Smith Chesapeake National Historic Trail is a series of water routes in the United States extending approximately along the Chesapeake Bay, the nation's largest estuary, and its tributaries in Virginia, Maryland, Delaware, ...
up the Susquehanna River
The Susquehanna River (; Lenape: Siskëwahane) is a major river located in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, overlapping between the lower Northeast and the Upland South. At long, it is the longest river on the East Coast of the ...
in Pennsylvania and New York (2012)Map/ref> *Chester River Component Connecting Trail – , extends the Captain John Smith Chesapeake National Historic Trail up the
Chester River
The Chester River is a major tributary of the Chesapeake Bay on the Delmarva Peninsula. It is about long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed April 1, 2011 and its watershe ...
in Maryland (2012)
*Upper Nanticoke River Component Connecting Trail – , extends the Captain John Smith Chesapeake National Historic Trail up the Nanticoke River in Delaware (2012)
*Upper James River Component Connecting Trail – , extends the Captain John Smith Chesapeake National Historic Trail up the James River in Virginia (2012)
*Marion to Selma Connecting Trail – , connects the Selma to Montgomery National Historic Trail to Marion, Alabama
Marion is a city in, and the county seat of, Perry County, Alabama, United States. As of the 2010 census, the population of the city is 3,686, up 4.8% over 2000. First known as Muckle Ridge, the city was renamed for a hero of the American Revolu ...
, where Jimmie Lee Jackson was murdered in 1965 (2015)
National Recreation Trails
 National recreation trail (NRT) is a designation given to existing trails that contribute to the recreational and conservation goals of a national network of trails. Over 1,300 trails over all fifty states have been designated as NRTs on
National recreation trail (NRT) is a designation given to existing trails that contribute to the recreational and conservation goals of a national network of trails. Over 1,300 trails over all fifty states have been designated as NRTs on federal
Federal or foederal (archaic) may refer to:
Politics
General
*Federal monarchy, a federation of monarchies
*Federation, or ''Federal state'' (federal system), a type of government characterized by both a central (federal) government and states or ...
, state, municipal, tribal and private lands that are available for public use and are less than a mile to more than in length. They have a combined length of more than .
Most NRTs are hiking trails
A trail, also known as a path or track, is an unpaved lane or small road usually passing through a natural area. In the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland, a path or footpath is the preferred term for a pedestrian or hiking trail. Th ...
, but a significant number are multi-use trails or bike paths
A bike path is a bikeway separated from motorized traffic and dedicated to cycling or shared with pedestrians or other non-motorized users. In the US a bike path sometimes encompasses ''shared use paths'', "multi-use path", or "Class III bikewa ...
, including rail trails
A rail trail is a shared-use path on railway right of way. Rail trails are typically constructed after a railway has been abandoned and the track has been removed, but may also share the right of way with active railways, light rail, or streetca ...
and greenways
Greenway or Greenways may refer to:
* Greenway (landscape), a linear park focused on a trail or bike path
* Another term for bicycle boulevards in some jurisdictions
People
* Greenway (surname)
Places
Australia
* Electoral Division of Greenwa ...
. Some are intended for use with watercraft, horses, cross-country skis
Cross-country skiing is a form of skiing where skiers rely on their own locomotion to move across snow-covered terrain, rather than using ski lifts or other forms of assistance. Cross-country skiing is widely practiced as a sport and recreation ...
, or off-road recreational vehicles. There are a number of water trails
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
that make up the National Water Trails System subprogram. Eligible trails must be complete, well designed and maintained, and open to the public.
The NPS and the USFS jointly administer the National Recreation Trails Program with help from other federal and nonprofit partners, notably American Trails, the lead nonprofit
A nonprofit organization (NPO) or non-profit organisation, also known as a non-business entity, not-for-profit organization, or nonprofit institution, is a legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public or social benefit, in co ...
for developing and promoting NRTs. The secretary of interior or the secretary of agriculture (if on USFS land) designates national recreation trails that are of local and regional significance. Managers of eligible trails can apply for designation with the support of all landowners and their state's trail coordinator (if on non-federal land). Designated trails become part of the National Trails System and receive promotional benefits, use of the NRT logo, technical and networking assistance, and preference for funding through the Department of Transportation's Recreational Trails Program
The Recreational Trails Program (RTP) is a federal assistance program of the United States Department of Transportation's Federal Highway Administration (FHWA). It provides funds to the States to develop and maintain recreational trails and trail ...
.
American Trails sponsors an annual NRT photo contest and a biennial symposium and maintains the NRT database.
National Geologic Trail
The first national geologic trail was established by theOmnibus Public Land Management Act of 2009
The Omnibus Public Land Management Act of 2009 (, ) is a land management law passed in the 111th United States Congress and signed into law by President Barack Obama on March 30, 2009. The bill designates millions of acres in the US as protected a ...
, though it did not amend the National Trails System Act to create an official category.
See also
*Protected areas of the United States
The protected areas of the United States are managed by an array of different federal, state, tribal and local level authorities and receive widely varying levels of protection. Some areas are managed as wilderness, while others are operated wi ...
*List of long-distance footpaths
This is a list of some long-distance footpaths used for walking and hiking.
Africa
Namibia
* Fish River Canyon: route in the ǀAi-ǀAis/Richtersveld Transfrontier Park
South Africa
* Otter Trail: section of the Garden Route along the Cape ...
*Long-distance trails in the United States
This is a list of notable long-distance trails in the United States, with a minimum length of 30 miles.
See also
* National Trails System
* National Millennium Trail project – 16 long-distance trails selected in 2000 as visionary trails th ...
References
Further reading
*Karen Berger
Karen Berger (; born February 26, 1958) is an American comic book editor. She is best known for her role in helping create DC Comics' Vertigo imprint in 1993 and serving as the line's Executive Editor until 2013. She currently oversees Berger B ...
, Bart Smith
Bart Smith (born 1959) is an outdoor photographer who concentrates on documenting America's National Trails System. Over the course of more than 25 years, he became the first person to hike and photograph all of the 11 national scenic trails and t ...
(photography), and Bill McKibben (foreword): ''America's Great Hiking Trails''. Rizzoli, 2014,
* Karen Berger, Bart Smith (photography), and Ken Burns
Kenneth Lauren Burns (born July 29, 1953) is an American filmmaker known for his documentary film, documentary films and television series, many of which chronicle United States, American History of the United States, history and Culture of the ...
& Dayton Duncan
Dayton Duncan (born September 3, 1949) is an American screenwriter, producer and former political aide.
He is best known for his collaborations with documentary maker Ken Burns.
Early life and education
Born and raised in Indianola, Iowa, Du ...
(foreword) (2014), ''America's National Historic Trails: Walking the Trails of History''. Rizzoli, 2020,
External links
Partnership for National Trails System
– National Park Service
– U.S. Forest Service
National Scenic and Historic Trails
– Bureau of Land Management
National Recreation Trails Program
– American Trails
National Recreation Trails database
– Congressional Research Service {{Authority control 01 Trails Hiking trails in the United States Scenic highways in the United States United States federal public land legislation 1968 in law 1968 in the United States