Natal Drakensberg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Drakensberg ( Afrikaans: Drakensberge, Zulu: uKhahlambha,  The Drakensberg escarpment stretches for more than from the Eastern Cape Province in the South, then successively forms, in order from south to north, the border between
The Drakensberg escarpment stretches for more than from the Eastern Cape Province in the South, then successively forms, in order from south to north, the border between
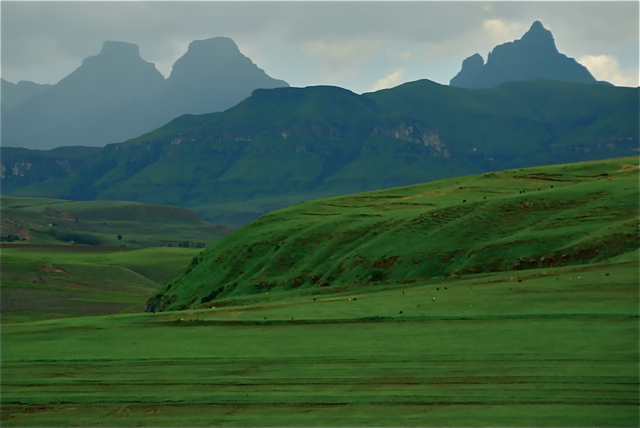
 The escarpment seen from below resembles a range of mountains. The Limpopo, Mpumalanga, and Lesotho Drakensberg have hard erosion-resistant upper surfaces and therefore have a very rugged appearance, combining steep-sided blocks and pinnacles (giving rise to the Zulu name "Barrier of up-pointed spears"). Who first gave these mountains their Afrikaans or Dutch name ''Drakensberg'', and why, is unknown.). The KwaZulu-Natal – Free State Drakensberg are composed of softer rocks and therefore have a more rounded, softer appearance from below. Generally, the top of the escarpment is almost table-top flat and smooth, even in Lesotho. The "Lesotho Mountains" are formed away from the Drakensberg escarpment by erosion gulleys which turn into deep valleys which contain tributaries of the Orange River. The large number of tributaries give the Lesotho Highlands a very rugged mountainous appearance, both from the ground and from the air.
The higher parts of Drakensberg has a mildly periglacial environment. It is possible that recent climate change has diminished the intensity of periglaciation.
Knight and Grab mapped out the distribution of lightning strikes in the Drakensburg and discovered that lightning significantly controls the evolution of the mountain landscapes because it helps to shape the summit areas – the highest areas – with this blasting effect. Previously, angular debris was presumed to have been created by changes typical of cold, periglacial environments, such as fracturing due to frost.
The escarpment seen from below resembles a range of mountains. The Limpopo, Mpumalanga, and Lesotho Drakensberg have hard erosion-resistant upper surfaces and therefore have a very rugged appearance, combining steep-sided blocks and pinnacles (giving rise to the Zulu name "Barrier of up-pointed spears"). Who first gave these mountains their Afrikaans or Dutch name ''Drakensberg'', and why, is unknown.). The KwaZulu-Natal – Free State Drakensberg are composed of softer rocks and therefore have a more rounded, softer appearance from below. Generally, the top of the escarpment is almost table-top flat and smooth, even in Lesotho. The "Lesotho Mountains" are formed away from the Drakensberg escarpment by erosion gulleys which turn into deep valleys which contain tributaries of the Orange River. The large number of tributaries give the Lesotho Highlands a very rugged mountainous appearance, both from the ground and from the air.
The higher parts of Drakensberg has a mildly periglacial environment. It is possible that recent climate change has diminished the intensity of periglaciation.
Knight and Grab mapped out the distribution of lightning strikes in the Drakensburg and discovered that lightning significantly controls the evolution of the mountain landscapes because it helps to shape the summit areas – the highest areas – with this blasting effect. Previously, angular debris was presumed to have been created by changes typical of cold, periglacial environments, such as fracturing due to frost.

 The high treeless peaks of the Drakensberg (from upward) have been described by the World Wide Fund for Nature as the ''Drakensberg alti-montane grasslands and woodlands'' ecoregion. These steep slopes are the most southerly high mountains in Africa, and being farther from the equator provide cooler habitats at lower elevations than most mountain ranges on the continent. High rainfall generates many mountain streams and rivers, including the sources of the Orange River, southern Africa's longest, and the Tugela River. These mountains also have the world's second-highest waterfall, the Tugela Falls (Thukela Falls), which has a total drop of . The rivers that run from the Drakensberg are an essential resource for South Africa's economy, providing water for the industrial provinces of Mpumalanga and Gauteng, which contains the city of Johannesburg. The climate is wet and cool at the high elevations, which experience snowfall in winter.
The grassy lower slopes (from ) of the Drakensberg in
The high treeless peaks of the Drakensberg (from upward) have been described by the World Wide Fund for Nature as the ''Drakensberg alti-montane grasslands and woodlands'' ecoregion. These steep slopes are the most southerly high mountains in Africa, and being farther from the equator provide cooler habitats at lower elevations than most mountain ranges on the continent. High rainfall generates many mountain streams and rivers, including the sources of the Orange River, southern Africa's longest, and the Tugela River. These mountains also have the world's second-highest waterfall, the Tugela Falls (Thukela Falls), which has a total drop of . The rivers that run from the Drakensberg are an essential resource for South Africa's economy, providing water for the industrial provinces of Mpumalanga and Gauteng, which contains the city of Johannesburg. The climate is wet and cool at the high elevations, which experience snowfall in winter.
The grassy lower slopes (from ) of the Drakensberg in
 The mountains are rich in plant life, including a large number of species listed in the Red Data Book of threatened plants, with 119 species listed as globally endangered and "of the 2 153 plant species in the park, a remarkable 98 are endemic or near-endemic".
The ''flora of the high alti-montane grasslands'' is mainly tussock grass, creeping plants, and small shrubs such as ericas. These include the rare Spiral Aloe ''(
The mountains are rich in plant life, including a large number of species listed in the Red Data Book of threatened plants, with 119 species listed as globally endangered and "of the 2 153 plant species in the park, a remarkable 98 are endemic or near-endemic".
The ''flora of the high alti-montane grasslands'' is mainly tussock grass, creeping plants, and small shrubs such as ericas. These include the rare Spiral Aloe ''(
 The lower slopes of the Drakensberg support much wildlife, perhaps most importantly the rare southern white rhinoceros (which was nurtured here when facing extinction) and the
The lower slopes of the Drakensberg support much wildlife, perhaps most importantly the rare southern white rhinoceros (which was nurtured here when facing extinction) and the
 The high slopes are hard to reach so the environment is fairly undamaged. However, tourism in the Drakensberg is developing, with a variety of hiking trails, hotels, and resorts appearing on the slopes. Much of the higher South African parts of the range have been designated as game reserves or wilderness areas. 7% of the Drakensberg alti-montane grasslands and woodlands ecoregion is in protected areas. These include
The high slopes are hard to reach so the environment is fairly undamaged. However, tourism in the Drakensberg is developing, with a variety of hiking trails, hotels, and resorts appearing on the slopes. Much of the higher South African parts of the range have been designated as game reserves or wilderness areas. 7% of the Drakensberg alti-montane grasslands and woodlands ecoregion is in protected areas. These include  The
The
 There are numerous caves in the easily eroded sandstone of Clarens Formation, the layer below the thick, hard basalt layer on the KwaZulu Natal-Lesotho border. Many of these caves have paintings by the San (Bushmen). This portion of the Drakensberg has between 35,000 and 40,000 works of
There are numerous caves in the easily eroded sandstone of Clarens Formation, the layer below the thick, hard basalt layer on the KwaZulu Natal-Lesotho border. Many of these caves have paintings by the San (Bushmen). This portion of the Drakensberg has between 35,000 and 40,000 works of
KZN Drakensberg Homepage
– Official Website for the KwaZulu Natal Drakensberg
Southern Drakensberg Tourism
– Southern Drakensberg Tourism
Nature – Drakensberg: Barrier of Spears
– PBS Nature episode covering the eland (largest member of antelope family) of the Drakensberg.
Drakensberg hiking trails
Maloti-Drakensberg
{{Authority control Afromontane ecoregions Climbing areas of South Africa Ecoregions of Africa Escarpments of Africa Extinct volcanism Great Escarpment, Southern Africa Landforms of KwaZulu-Natal Landforms of Mpumalanga Landforms of the Free State (province) Large igneous provinces Lesotho–South Africa border Montane grasslands and shrublands Mountain ranges of Lesotho Mountain ranges of Limpopo Mountain ranges of South Africa Mountain ranges of the Eastern Cape Precambrian volcanism Prehistoric Africa Triassic volcanism Volcanism of Lesotho Volcanism of South Africa World Heritage Sites in South Africa
Sotho Sotho may refer to:
*Sotho people (or ''Basotho''), an African ethnic group principally resident in South Africa, Lesotho and southern Botswana
* Sotho language (''Sesotho'' or ''Southern Sotho''), a Bantu language spoken in southern Africa, an off ...
: Maluti) is the eastern portion of the Great Escarpment
The Great Escarpment is a major topographical feature in Africa that consists of steep slopes from the high central Southern African plateauAtlas of Southern Africa. (1984). p. 13. Reader's Digest Association, Cape Town downward in the directio ...
, which encloses the central Southern African
Southern Africa is the southernmost subregion of the African continent, south of the Congo and Tanzania. The physical location is the large part of Africa to the south of the extensive Congo River basin. Southern Africa is home to a number of ...
plateau. The Great Escarpment reaches its greatest elevation – within the border region of South Africa and Lesotho
Lesotho ( ), officially the Kingdom of Lesotho, is a country landlocked country, landlocked as an Enclave and exclave, enclave in South Africa. It is situated in the Maloti Mountains and contains the Thabana Ntlenyana, highest mountains in Sou ...
.
 The Drakensberg escarpment stretches for more than from the Eastern Cape Province in the South, then successively forms, in order from south to north, the border between
The Drakensberg escarpment stretches for more than from the Eastern Cape Province in the South, then successively forms, in order from south to north, the border between Lesotho
Lesotho ( ), officially the Kingdom of Lesotho, is a country landlocked country, landlocked as an Enclave and exclave, enclave in South Africa. It is situated in the Maloti Mountains and contains the Thabana Ntlenyana, highest mountains in Sou ...
and the Eastern Cape
The Eastern Cape is one of the provinces of South Africa. Its capital is Bhisho, but its two largest cities are East London and Gqeberha.
The second largest province in the country (at 168,966 km2) after Northern Cape, it was formed in ...
and the border between Lesotho and KwaZulu-Natal Province
KwaZulu-Natal (, also referred to as KZN and known as "the garden province") is a province of South Africa that was created in 1994 when the Zulu bantustan of KwaZulu ("Place of the Zulu" in Zulu) and Natal Province were merged. It is locat ...
. Thereafter it forms the border between KwaZulu-Natal and the Free State, and next as the border between KwaZulu-Natal and Mpumalanga Province
Mpumalanga () is a province of South Africa. The name means "East", or literally "The Place Where the Sun Rises" in the Swazi, Xhosa, Ndebele and Zulu languages. Mpumalanga lies in eastern South Africa, bordering Eswatini and Mozambique. It ...
. The escarpment winds north from there, through Mpumalanga, where it includes features such as the Blyde River Canyon, Three Rondavels
Blyde River Canyon Nature Reserve (or Motlatse Canyon Provincial Nature Reserve) is situated in the Drakensberg escarpment region of eastern Mpumalanga, South Africa. The reserve protects the Blyde River Canyon, including sections of the Ohrig ...
, and God's Window
Blyde River Canyon Nature Reserve (or Motlatse Canyon Provincial Nature Reserve) is situated in the Drakensberg escarpment region of eastern Mpumalanga, South Africa. The reserve protects the Blyde River Canyon, including sections of the Ohrig ...
. It then extends farther north to Hoedspruit in southeastern Limpopo where it is known as 'Klein Drakensberg' by the Afrikaner
Afrikaners () are a South African ethnic group descended from Free Burghers, predominantly Dutch settlers first arriving at the Cape of Good Hope in the 17th and 18th centuries.Entry: Cape Colony. ''Encyclopædia Britannica Volume 4 Part 2: ...
. From Hoedspruit it extends west to Tzaneen, also in Limpopo Province, where it is known as the Wolkberg
The Wolkberg is a mountain range in Tzaneen, Limpopo Province, South Africa. It is a northern termination and a subrange of the Drakensberg mountain range which lines up from Eastern Cape, Lesotho, Kwazulu Natal and Mpumalanga. At 2200 m (7 ...
Mountains
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher th ...
and Iron Crown Mountain. At above sea level, the Wolkberg is the highest elevation in Limpopo. The escarpment extends west again and at Mokopane
Mokopane, also known as Potgietersrus, is a town in the Limpopo province of South Africa.
The town name was changed to Mokopane in 2003 in honour of a local Ma Nrebele leader, King Mghombane Gheghana , who ruled the area before being conquered ...
it is known as the Strydpoort Mountains.
Etymology
The Afrikaans name ''Drakensberge'' comes from the name the earliest Dutch settlers gave to the escarpment, namely ''Drakensbergen'', or ''Dragons' Mountains''. The highest portion of the Great Escarpment is known in Zulu as ''uKhahlamba'' and as ''Maluti'' inSotho Sotho may refer to:
*Sotho people (or ''Basotho''), an African ethnic group principally resident in South Africa, Lesotho and southern Botswana
* Sotho language (''Sesotho'' or ''Southern Sotho''), a Bantu language spoken in southern Africa, an off ...
("Barrier of up-pointed spears").
Geology
Origins
The Great Escarpment is composed of steep rift valley walls formed around a bulging of continental crust during the breakup of southernGondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages ...
that have since eroded inland from their original positions near the southern African coast, and its entire eastern portion (see the accompanying map) constitutes the Drakensberg. The Drakensberg terminate in the north near Tzaneen at about the 22° S parallel. The absence of the Great Escarpment for approximately to the north of Tzaneen (to reappear on the border between Zimbabwe and Mozambique in the Chimanimani Mountains
The Chimanimani Mountains are a mountain range on the border of Zimbabwe and Mozambique. The mountains are in the southern portion of the Eastern Highlands, or Manica Highlands, a belt of highlands that extend north and south along the internatio ...
) is due to a failed westerly branch of the main rift that caused Antarctica to start drifting away from southern Africa during the breakup of Gondwana about 150 million years ago. The lower Limpopo River and Save River drain into the Indian Ocean through what remains of this relict incipient rift valley, which now forms part of the South African Lowveld
Veld ( or ), also spelled veldt, is a type of wide open rural landscape in :Southern Africa. Particularly, it is a flat area covered in grass or low scrub, especially in the countries of South Africa, Lesotho, Eswatini, Zimbabwe and Botswa ...
.
During the past 20 million years, southern Africa has experienced massive uplifting, especially in the east, with the result that most of the plateau lies above despite extensive erosion. The plateau is tilted such that it is highest in the east and slopes gently downward toward the west and south. Typically, the elevation of the edge of the eastern escarpments is in excess of . It reaches its highest point of over where the escarpment forms part of the international border between Lesotho
Lesotho ( ), officially the Kingdom of Lesotho, is a country landlocked country, landlocked as an Enclave and exclave, enclave in South Africa. It is situated in the Maloti Mountains and contains the Thabana Ntlenyana, highest mountains in Sou ...
and the South African province of KwaZulu-Natal
KwaZulu-Natal (, also referred to as KZN and known as "the garden province") is a province of South Africa that was created in 1994 when the Zulu bantustan of KwaZulu ("Place of the Zulu" in Zulu) and Natal Province were merged. It is locate ...
.
Appearance
 The escarpment seen from below resembles a range of mountains. The Limpopo, Mpumalanga, and Lesotho Drakensberg have hard erosion-resistant upper surfaces and therefore have a very rugged appearance, combining steep-sided blocks and pinnacles (giving rise to the Zulu name "Barrier of up-pointed spears"). Who first gave these mountains their Afrikaans or Dutch name ''Drakensberg'', and why, is unknown.). The KwaZulu-Natal – Free State Drakensberg are composed of softer rocks and therefore have a more rounded, softer appearance from below. Generally, the top of the escarpment is almost table-top flat and smooth, even in Lesotho. The "Lesotho Mountains" are formed away from the Drakensberg escarpment by erosion gulleys which turn into deep valleys which contain tributaries of the Orange River. The large number of tributaries give the Lesotho Highlands a very rugged mountainous appearance, both from the ground and from the air.
The higher parts of Drakensberg has a mildly periglacial environment. It is possible that recent climate change has diminished the intensity of periglaciation.
Knight and Grab mapped out the distribution of lightning strikes in the Drakensburg and discovered that lightning significantly controls the evolution of the mountain landscapes because it helps to shape the summit areas – the highest areas – with this blasting effect. Previously, angular debris was presumed to have been created by changes typical of cold, periglacial environments, such as fracturing due to frost.
The escarpment seen from below resembles a range of mountains. The Limpopo, Mpumalanga, and Lesotho Drakensberg have hard erosion-resistant upper surfaces and therefore have a very rugged appearance, combining steep-sided blocks and pinnacles (giving rise to the Zulu name "Barrier of up-pointed spears"). Who first gave these mountains their Afrikaans or Dutch name ''Drakensberg'', and why, is unknown.). The KwaZulu-Natal – Free State Drakensberg are composed of softer rocks and therefore have a more rounded, softer appearance from below. Generally, the top of the escarpment is almost table-top flat and smooth, even in Lesotho. The "Lesotho Mountains" are formed away from the Drakensberg escarpment by erosion gulleys which turn into deep valleys which contain tributaries of the Orange River. The large number of tributaries give the Lesotho Highlands a very rugged mountainous appearance, both from the ground and from the air.
The higher parts of Drakensberg has a mildly periglacial environment. It is possible that recent climate change has diminished the intensity of periglaciation.
Knight and Grab mapped out the distribution of lightning strikes in the Drakensburg and discovered that lightning significantly controls the evolution of the mountain landscapes because it helps to shape the summit areas – the highest areas – with this blasting effect. Previously, angular debris was presumed to have been created by changes typical of cold, periglacial environments, such as fracturing due to frost.
Composition
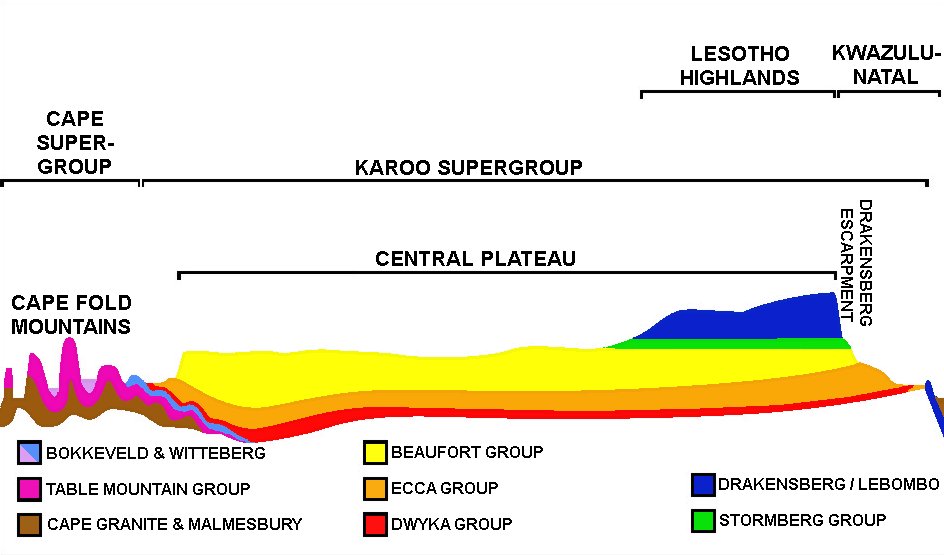
The geological composition of Drakensberg (escarpment wall) varies considerably along its more than 1000 km length. The Limpopo and Mpumalanga Drakensberg are capped by an erosion resistant quartzite layer that is part of the Transvaal Supergroup, which also forms the Magaliesberg to the north and northwest of Pretoria. These rocks are more than 2000 million years old. South of the 26°S parallel the Drakensberg escarpment is composed of Ecca shales, which belong to theKaroo Supergroup
The Karoo Supergroup is the most widespread stratigraphic unit in Africa south of the Kalahari Desert. The supergroup consists of a sequence of units, mostly of nonmarine origin, deposited between the Late Carboniferous and Early Jurassic, a perio ...
, and they are 300 million years old.''Geological map of South Africa, Lesotho and Swaziland ''(1970). Council for Geoscience, Geological Survey of South Africa. The portion of the Drakensberg that forms the KwaZulu-Natal – Free State border is formed by slightly younger Beaufort rocks (250 million years old) that also are part of the Karoo Supergroup. The Ecca and Beaufort groups are composed of sedimentary rocks that are less erosion resistant than the other rocks that make up the Drakensberg escarpment. Therefore, this portion of escarpment is not so impressive as the Mpumalanga and Lesotho stretches of the Drakensberg. The Drakensberg that form the northeastern and eastern borders of Lesotho, as well as the Eastern Cape Drakensberg, are composed of a thick layer of basalt (lava) that erupted 180 million years ago. That layer rests on the youngest of the Karoo Supergroup sediments, the Clarens sandstone, which was laid down under desert conditions, about 200 million years ago.
Geography
Peaks
The highest peak is Thabana Ntlenyana, at . Other notable peaks include Mafadi (), Makoaneng at , Njesuthi at ,Champagne Castle
Champagne Castle is a mountain in the central Drakensberg range, and is the second highest peak in South Africa. It contains a series of subsidiary peaks, amongst them, Cathkin Peak (3149 m), Sterkhorn (previously called Mount Memory), Monk's C ...
at , Giant's Castle at , Ben Macdhui at , and Popple Peak
Popple Peak ( af, Popplepiek) is a mountain in the Drakensberg range, South Africa. It is located on the border between South Africa and Lesotho, on the watershed that forms the border between the two countries. Popple peak is 3331 m above sea le ...
at , all of these are in the area bordering on Lesotho, which contains an area popular for hikers, Cathedral Peak Cathedral Peak may be any of several mountains, typically those with steep sides and towers reminiscent of a cathedral. In the United States alone, the USGS identifies 17 summits named "Cathedral Peak".
In other countries:
*Cathedr ...
. North of Lesotho the range becomes lower and less rugged until entering Mpumalanga where the quartzite mountains of the Transvaal Drakensberg are loftier and more broken and they form the eastern rim of the Transvaal Basin, the Blyde River Canyon lying within this stretch. The geology of this section is the same as, and continuous with, that of the Magaliesberg.
Mountain passes
Ecology

 The high treeless peaks of the Drakensberg (from upward) have been described by the World Wide Fund for Nature as the ''Drakensberg alti-montane grasslands and woodlands'' ecoregion. These steep slopes are the most southerly high mountains in Africa, and being farther from the equator provide cooler habitats at lower elevations than most mountain ranges on the continent. High rainfall generates many mountain streams and rivers, including the sources of the Orange River, southern Africa's longest, and the Tugela River. These mountains also have the world's second-highest waterfall, the Tugela Falls (Thukela Falls), which has a total drop of . The rivers that run from the Drakensberg are an essential resource for South Africa's economy, providing water for the industrial provinces of Mpumalanga and Gauteng, which contains the city of Johannesburg. The climate is wet and cool at the high elevations, which experience snowfall in winter.
The grassy lower slopes (from ) of the Drakensberg in
The high treeless peaks of the Drakensberg (from upward) have been described by the World Wide Fund for Nature as the ''Drakensberg alti-montane grasslands and woodlands'' ecoregion. These steep slopes are the most southerly high mountains in Africa, and being farther from the equator provide cooler habitats at lower elevations than most mountain ranges on the continent. High rainfall generates many mountain streams and rivers, including the sources of the Orange River, southern Africa's longest, and the Tugela River. These mountains also have the world's second-highest waterfall, the Tugela Falls (Thukela Falls), which has a total drop of . The rivers that run from the Drakensberg are an essential resource for South Africa's economy, providing water for the industrial provinces of Mpumalanga and Gauteng, which contains the city of Johannesburg. The climate is wet and cool at the high elevations, which experience snowfall in winter.
The grassy lower slopes (from ) of the Drakensberg in Eswatini
Eswatini ( ; ss, eSwatini ), officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and formerly named Swaziland ( ; officially renamed in 2018), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. It is bordered by Mozambique to its northeast and South Africa to its no ...
, South Africa and Lesotho constitute the ''Drakensberg montane grasslands, woodlands, and forests'' ecoregion.
Flora
 The mountains are rich in plant life, including a large number of species listed in the Red Data Book of threatened plants, with 119 species listed as globally endangered and "of the 2 153 plant species in the park, a remarkable 98 are endemic or near-endemic".
The ''flora of the high alti-montane grasslands'' is mainly tussock grass, creeping plants, and small shrubs such as ericas. These include the rare Spiral Aloe ''(
The mountains are rich in plant life, including a large number of species listed in the Red Data Book of threatened plants, with 119 species listed as globally endangered and "of the 2 153 plant species in the park, a remarkable 98 are endemic or near-endemic".
The ''flora of the high alti-montane grasslands'' is mainly tussock grass, creeping plants, and small shrubs such as ericas. These include the rare Spiral Aloe ''(Aloe polyphylla
''Aloe polyphylla'', the spiral aloe, ''kroonaalwyn'', ''lekhala kharetsa'', or many-leaved aloe, is a species of flowering plant in the genus '' Aloe'' that is endemic to the Kingdom of Lesotho in the Drakensberg mountains. An evergreen succul ...
)'', which as its name suggests, has leaves with a spiral shape.
Meanwhile, the ''lower slopes'' are mainly grassland, but are also home to conifer
Conifers are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single ...
s, which are rare in Africa, the species of conifer found in the Drakensberg belong to the genus Podocarpus. The grassland is of interest as it contains a great number of endemic plants. Grasses found here include oat grass ''Monocymbium ceresiiforme
''Monocymbium'' is a genus of African plants in the grass family.
; Species
* '' Monocymbium ceresiiforme'' (Nees) Stapf - widespread in sub-Saharan Africa from Liberia to Ethiopia to Cape Province
* '' Monocymbium deightonii'' C.E.Hubb. - G ...
'', '' Diheteropogon filifolius'', '' Sporobolus centrifugus'', caterpillar grass ''(Harpochloa falx
''Harpochloa falx'', caterpillar grass, is a species of flowering plant in the family Poaceae, native to all of South Africa, Lesotho, and Eswatini. Although fire-adapted, in the absence of regular burns it comes to dominate its competitors.
Re ...
)'', ''Cymbopogon
''Cymbopogon'', also known as lemongrass, barbed wire grass, silky heads, Cochin grass, Malabar grass, oily heads, citronella grass or fever grass, is a genus of Asian, African, Australian, and tropical island plants in the grass family.
Some ...
dieterlenii'', and Eulalia villosa.
In the highest part of Drakensberg the composition of the flora is independent on slope aspect
In mathematics, the slope or gradient of a line is a number that describes both the ''direction'' and the ''steepness'' of the line. Slope is often denoted by the letter ''m''; there is no clear answer to the question why the letter ''m'' is used ...
(direction) and varies, depending on the hardness of the rock clasts. This hardness is related to weathering and is variable even within a single landform
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, ...
.
Fauna
The Drakensberg area is "home to 299 recorded bird species"' making up "37% of all non-marine avian species in southern Africa". There are 24 species of snakes in the Drakensberg, two of which are highly venomous. One bird is endemic to the high peaks, themountain pipit
The mountain pipit (''Anthus hoeschi'') is a species of bird in the family Motacillidae.
It is found in Lesotho, South Africa, possibly Botswana, possibly Democratic Republic of the Congo, possibly Namibia, and possibly Zambia.
Its natural habi ...
''(Anthus hoeschi)'', and another six species are found mainly here: Bush blackcap
The bush blackcap (''Sylvia nigricapillus'') is a species of bird in the family Sylviidae. It is endemic to South Africa and Eswatini. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist montane forests and subtropical or tropical high-altitu ...
''(Lioptilus nigricapillus)'', buff-streaked chat
The buff-streaked chat or buff-streaked bushchat (''Campicoloides bifasciatus'') is a species of bird in the family Muscicapidae. It is found in Lesotho, South Africa, and Eswatini.
Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry lowland gra ...
''(Oenanthe bifasciata)'', Rudd's lark
Rudd's lark (''Heteromirafra ruddi'') is a species of lark in the family Alaudidae. It is endemic to South Africa. Its natural habitat is high-altitude grassland. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Taxonomy and systematics
left, Bird in flight a ...
''(Heteromirafra ruddi)'', Drakensberg rockjumper ''(Chaetops aurantius)'', yellow-breasted pipit
The yellow-breasted pipit (''Anthus chloris'') is a species of bird in the pipit and wagtail family Motacillidae.
It is found in Lesotho and South Africa.
Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical high-altitude grassland, arable land, and ...
''(Anthus chloris)'', and Drakensberg siskin
The Drakensberg siskin (''Crithagra symonsi'') is a small passerine bird in the finch family. It is an endemic resident breeder in the eastern Cape Province Transkei and western Natal in South Africa, and in Lesotho.
This species is sometimes co ...
''(Serinus symonsi)''. The endangered Cape vulture and lesser kestrel are two of the birds of prey that hunt in the mountains. Mammals include klipspringer
The klipspringer (; ''Oreotragus oreotragus'') is a small antelope found in eastern and southern Africa. The sole member of its genus and subfamily/tribe, the klipspringer was first described by German zoologist Eberhard August Wilhelm von Zimm ...
''(Oreotragus oreotragus)'', eland
Eland may refer to:
Animals
*''Taurotragus'', a genus of antelope
** Common eland of East and Southern Africa
** Giant eland of Central and Western Africa
Places
* Eland, Wisconsin, United States
* An old spelling of Elland, West Yorkshire
* Ela ...
''(Taurotragus oryx)'', and mountain reedbuck
The mountain reedbuck (''Redunca fulvorufula'') is an antelope found in mountainous areas of much of sub-Saharan Africa.
Subspecies
There are three recognized subspecies.
* ''Redunca fulvorufula adamauae'' - Adamawa mountain reedbuck
* ''Redunc ...
''(Redunca fulvorufula)''. Other endemic species include three frogs found in the mountain streams, Drakensberg river frog ''(Amietia dracomontana)'', Phofung river frog ''(Amietia vertebralis
''Amietia vertebralis'', also known as Maluti river frog, aquatic river frog, ice frog, large-mouthed frog, or water frog, is a species of frogs in the family Pyxicephalidae. It is an aquatic high-altitude species found in Lesotho and neighbour ...
)'', and Maluti river frog
''Amietia vertebralis'', also known as Maluti river frog, aquatic river frog, ice frog, large-mouthed frog, or water frog, is a species of frogs in the family Pyxicephalidae. It is an aquatic high-altitude species found in Lesotho and neighbour ...
''(Amietia umbraculata)''. Fish are found in the many rivers and streams, including the Maluti redfin (''Pseudobarbus quathlambae'') that was thought to be extinct before being found in the Senqunyane River
The Senqunyane River is a river of central Lesotho. The river rises in the Maluti Mountains in northwest Lesotho, and flows southwards and then westwards for 120 kilometres before joining the Senqu River (Orange River) in the southwest.Fitzpatri ...
in Lesotho.
 The lower slopes of the Drakensberg support much wildlife, perhaps most importantly the rare southern white rhinoceros (which was nurtured here when facing extinction) and the
The lower slopes of the Drakensberg support much wildlife, perhaps most importantly the rare southern white rhinoceros (which was nurtured here when facing extinction) and the black wildebeest
The black wildebeest or white-tailed gnu (''Connochaetes gnou'') is one of the two closely related wildebeest species. It is a member of the genus '' Connochaetes'' and family Bovidae. It was first described in 1780 by Eberhard August Wilhelm ...
(''Connochaetes gnou'', which only thrives in protected areas and game reserves). The area is home to large herds of grazing fauna and antelopes such as eland
Eland may refer to:
Animals
*''Taurotragus'', a genus of antelope
** Common eland of East and Southern Africa
** Giant eland of Central and Western Africa
Places
* Eland, Wisconsin, United States
* An old spelling of Elland, West Yorkshire
* Ela ...
''(Taurotragus oryx)'', reedbuck ''(Redunca arundinum)'', mountain reedbuck
The mountain reedbuck (''Redunca fulvorufula'') is an antelope found in mountainous areas of much of sub-Saharan Africa.
Subspecies
There are three recognized subspecies.
* ''Redunca fulvorufula adamauae'' - Adamawa mountain reedbuck
* ''Redunc ...
''(Redunca fulvorufula)'', grey rhebok ''(Pelea capreolus)'', and even some oribi ''(Ourebia ourebi)''. Chacma baboons also are present. Endemic species include a large number of chameleon
Chameleons or chamaeleons (family Chamaeleonidae) are a distinctive and highly specialized clade of Old World lizards with 202 species described as of June 2015. The members of this family are best known for their distinct range of colors, bein ...
s and other reptiles. There is one endemic frog, the forest rain frog ''(Breviceps sylvestris
The forest rain frog (''Breviceps sylvestris'') is a species of frog in the family Brevicipitidae. It is endemic to Limpopo, South Africa. Two allopatric subspecies are recognized: the nominate one, ''Breviceps sylvestris sylvestris'', and ''Br ...
)'', and four more species that are found mainly in these mountains; long-toed tree frog ''( Leptopelis xenodactylus)'', plaintive rain frog ''(Breviceps maculatus
The plaintive rain frog or rough rain frog (''Breviceps verrucosus'') is a species of frog in the family Brevicipitidae.
It is found in Lesotho, South Africa, and Eswatini.
Its natural habitats are temperate forests, dry savanna, temperate shrubl ...
)'', rough rain frog ''( Breviceps verrucosus)'', and Poynton's caco ''(Cacosternum poyntoni
Poynton's caco or Poynton's dainty frog (''Cacosternum poyntoni'') is a species of frog in the family Pyxicephalidae, endemic to South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmo ...
)''.
Conservation
 The high slopes are hard to reach so the environment is fairly undamaged. However, tourism in the Drakensberg is developing, with a variety of hiking trails, hotels, and resorts appearing on the slopes. Much of the higher South African parts of the range have been designated as game reserves or wilderness areas. 7% of the Drakensberg alti-montane grasslands and woodlands ecoregion is in protected areas. These include
The high slopes are hard to reach so the environment is fairly undamaged. However, tourism in the Drakensberg is developing, with a variety of hiking trails, hotels, and resorts appearing on the slopes. Much of the higher South African parts of the range have been designated as game reserves or wilderness areas. 7% of the Drakensberg alti-montane grasslands and woodlands ecoregion is in protected areas. These include Golden Gate Highlands National Park
Golden Gate Highlands National Park is located in Free State, South Africa, near the Lesotho border. It covers an area of . The park's most notable features are its golden, ochre, and orange-hued, deeply eroded sandstone cliffs and outcrops, es ...
, Sehlabathebe National Park
The Sehlabathebe National Park is located in the Maloti Mountains in Qacha's Nek District, Lesotho and is part of the Maloti-Drakensberg World Heritage Site. The park was first established on May 8. 1969 and since then, it is recognized importa ...
, Tsehlanyane National Park
Ts'ehlanyane National Park is a National Park in Lesotho. It is located in the Maloti Mountains in Leribe District, and is part of the larger Maloti-Drakensberg Transfrontier Conservation Area. This Lesotho northern park protects a high-altitude, ...
, Malekgalonyane Nature Reserve, Giant's Castle Game Reserve, Loteni Nature Reserve, Natal National Park
Royal Natal National Park is a park in KwaZulu-Natal province, South Africa and forms part of the uKhahlamba Drakensberg Park World Heritage Site. Notwithstanding the name, it is actually not a South African National Park managed by the South A ...
, Vergelegen Nature Reserve, Beaumont Nature Reserve
Beaumont may refer to:
Places Canada
* Beaumont, Alberta
* Beaumont, Quebec
England
* Beaumont, Cumbria
* Beaumont, Essex
**Beaumont Cut, a canal closed in the 1930s
* Beaumont Street, Oxford
France (communes)
* Beaumont, Ardèche
* Be ...
, and Lammergeier Highlands Nature Reserve.
Of these the uKhahlamba Drakensberg Park
The uKhahlamba-Drakensberg Park is a protected area in the KwaZulu-Natal province of South Africa, covering , and is part of a world heritage site. The park includes Royal Natal National Park, a provincial park, and covers part of the Drakensberg ...
was listed by UNESCO in 2000 as a World Heritage site. The park also is in the List of Wetlands of International Importance (under the Ramsar Convention). The Royal Natal National Park
Royal Natal National Park is a park in KwaZulu-Natal province, South Africa and forms part of the uKhahlamba Drakensberg Park World Heritage Site. Notwithstanding the name, it is actually not a South African National Park managed by the SANPark ...
, which contains some of the higher peaks, is part of this large park complex. Adjacent to the Ukhahlamba Drakensberg World Heritage Site is the 1900 ha Allendale Mountain Reserve, which is the largest private reserve adjoining the World Heritage Site and is found in the accessible Kamberg area, the heart of the historic San (Bushman) painting region of the Ukhahlamba.
The grassland of the ''lower slopes'' has been greatly affected by agriculture, however, especially by overgrazing. Nearly all of the original grassland and forest has disappeared and more protection is needed, although the Giant's Castle reserve is a haven for the eland
Eland may refer to:
Animals
*''Taurotragus'', a genus of antelope
** Common eland of East and Southern Africa
** Giant eland of Central and Western Africa
Places
* Eland, Wisconsin, United States
* An old spelling of Elland, West Yorkshire
* Ela ...
and also is a breeding ground for the bearded vulture. 5.81% of the Drakensberg montane grasslands, woodlands and forests ecoregion is in protected areas. These include Kruger National Park
Kruger National Park is a South African National Park and one of the largest game reserves in Africa. It covers an area of in the provinces of Limpopo and Mpumalanga in northeastern South Africa, and extends from north to south and from ea ...
, Mountain Zebra National Park
Mountain Zebra National Park is a national park in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa proclaimed in July 1937 for the purpose of providing a nature reserve for the endangered Cape mountain zebra.
History
In the early 1930s, the Cape mou ...
, Golden Gate Highlands National Park National Park, Camdeboo National Park, Sehlabathebe National Park, and Tsehlanyane National Park.
 The
The Maloti-Drakensberg Transfrontier Conservation Area
Maloti-Drakensberg Park was established on 11 June 2001 by linking the Sehlabathebe National Park in the Kingdom of Lesotho and the uKhahlamba Drakensberg Park in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. The highest peak is Thaba Ntlenyana rising to 3.482 m. ...
was established to preserve some of the high mountain areas of the range.
Human habitation
Towns and cities in the Drakensberg area include, from south to north,Matatiele
Matatiele is a town located in the northern part of the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. According to the South African National Census of 2011, its 12,466 residents (1,113.44 per km²) and 4,107 households (366.83 per km²) make Matatiel ...
and Barkly East in the Kwa-Zulu Natal Province; Ladysmith, Newcastle, Ulundi – the former Zulu capital, Dundee
Dundee (; sco, Dundee; gd, Dùn Dè or ) is Scotland's fourth-largest city and the 51st-most-populous built-up area in the United Kingdom. The mid-year population estimate for 2016 was , giving Dundee a population density of 2,478/km2 or ...
, and Ixopo in KwaZulu-Natal; all of Lesotho, whose capital is Maseru; and Tzaneen in Limpopo Province.
San cave paintings
San rock art
The San, or Bushmen, are indigenous people in Southern Africa particularly in what is now South Africa and Botswana. Their ancient rock paintings and carvings (collectively called rock art) are found in caves and on rock shelters. The artwork depi ...
, and is the largest collection of such parietal work in the world. Some 20,000 individual rock paintings have been recorded at 500 different caves and overhanging sites between the Drakensberg Royal Natal National Park and Bushman's Nek. Due to the materials used in their production, these paintings are difficult to date, but there is anthropological evidence, including many hunting implements, that the San people existed in the Drakensberg at least 40,000 years ago, and possibly more than 100,000 years ago. According to mountainsides.co.za, " Nd edema Gorge in the Central Ginsberg 3,900 paintings have been recorded at 17 sites. One of them, Sebaayeni Cave, contains 1,146 individual paintings." The website, south Africa.info, indicates that although "the oldest painting on a rock shelter wall in the Ginsberg dates back about 2400 years... paint chips at least a thousand years older have also been found." The site also indicates that " e rock art of the Drakensberg is the largest and most concentrated group of rock paintings in Africa south of the Sahara, and is outstanding both in quality and diversity of subject."
See also
* List of mountains in South Africa * Maloti MountainsReferences
Further reading
*External links
*KZN Drakensberg Homepage
– Official Website for the KwaZulu Natal Drakensberg
Southern Drakensberg Tourism
– Southern Drakensberg Tourism
Nature – Drakensberg: Barrier of Spears
– PBS Nature episode covering the eland (largest member of antelope family) of the Drakensberg.
Drakensberg hiking trails
Maloti-Drakensberg
{{Authority control Afromontane ecoregions Climbing areas of South Africa Ecoregions of Africa Escarpments of Africa Extinct volcanism Great Escarpment, Southern Africa Landforms of KwaZulu-Natal Landforms of Mpumalanga Landforms of the Free State (province) Large igneous provinces Lesotho–South Africa border Montane grasslands and shrublands Mountain ranges of Lesotho Mountain ranges of Limpopo Mountain ranges of South Africa Mountain ranges of the Eastern Cape Precambrian volcanism Prehistoric Africa Triassic volcanism Volcanism of Lesotho Volcanism of South Africa World Heritage Sites in South Africa