Nasal Surgery on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Nasal surgery is a medical procedure designed to treat various conditions that cause nasal blockages in the upper respiratory tract, for example
'' , initiated the second period of nasal surgery. Under the ideologies of


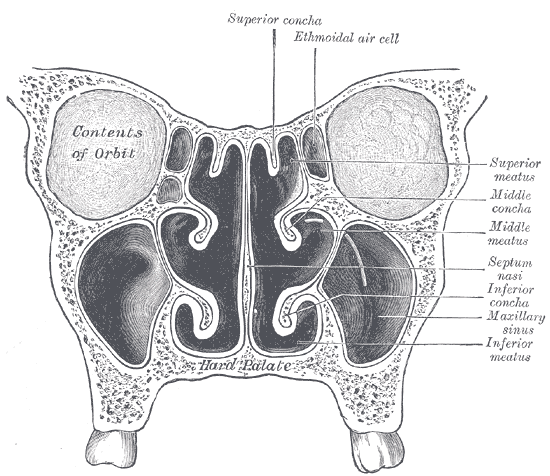 Ethmoidectomy treats ethmoid sinusitis through removing the
Ethmoidectomy treats ethmoid sinusitis through removing the

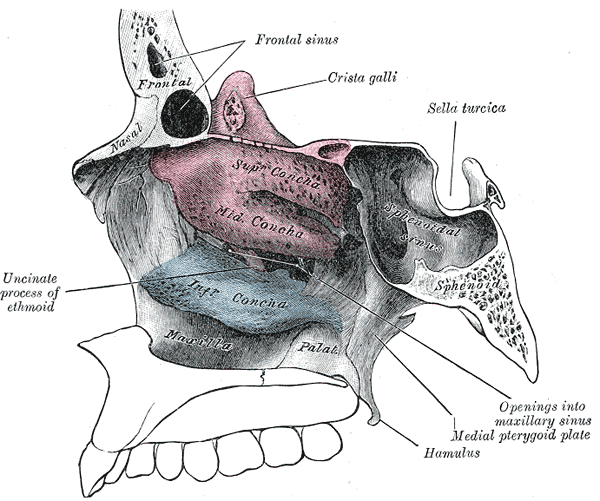 Turbinoplasty is an intervention aiming to treat turbinate hypertrophy by reducing turbinate volume. Turbinate hypertrophy is commonly characterised by enlarged nasal turbinates arising from
Turbinoplasty is an intervention aiming to treat turbinate hypertrophy by reducing turbinate volume. Turbinate hypertrophy is commonly characterised by enlarged nasal turbinates arising from
nasal polyps
Nasal polyps (NP) are noncancerous growths within the nose or sinuses. Symptoms include trouble breathing through the nose, loss of smell, decreased taste, post nasal drip, and a runny nose. The growths are sac-like, movable, and nontender, t ...
, inferior turbinate hypertrophy, and chronic rhinosinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain. Other signs and symptoms may include fever, headac ...
. It encompasses several types of techniques, including rhinoplasty, septoplasty, sinus surgery, and turbinoplasty, each with its respective postoperative treatments. Furthermore, nasal surgery is also conducted for cosmetic purposes. While there are potential risks and complications associated, the advancement of medical instruments and enhanced surgical skills have helped mitigate them.
History
The history of nasal surgery can be separated into three periods. The first was when nasal operations only consisted of the repair of minimal external nose injuries. The second period was characterised by the need for restoring amputated noses in several countries. The third period marks the current era of nasal surgery development. The first period of nasal surgery was dated back to 1500 B.C. There were no attempts to treat nasal damage, leading to complete loss of the nose. Nose amputation served as penalisation for war criminals and women deemed indecent, resulting in the demand for nasal reconstruction. In view of the situation,Sushruta
Sushruta, or ''Suśruta'' (Sanskrit: सुश्रुत, IAST: , ) was an ancient Indian physician. The ''Sushruta Samhita'' (''Sushruta's Compendium''), a treatise ascribed to him, is one of the most important surviving ancient treatises on ...
, regarded as the "Father of Plastic SurgeryAyurveda
Ayurveda () is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. The theory and practice of Ayurveda is pseudoscientific. Ayurveda is heavily practiced in India and Nepal, where around 80% of the population repo ...
in 600 B.C., he used leaves as a template for the damaged nose, together with a cheek skin flap to reconstruct wounded noses. This laid a solid foundation for the evolution of nasal surgery. The emerging idea of nasal surgery has then spread to the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
and other parts of the world.
The third period of nasal surgery continues to this day with the subcategories of rhinoplasty, septoplasty, sinus surgery, and turbinoplasty coupled with the culmination of advanced plastic technology and the ongoing surgical development.
Types of nasal surgery
Nasal surgery is a specialty including the removal of nasal obstruction that cannot be achieved by medication and nasal reconstruction. Currently, it comprises four approaches, namely rhinoplasty, septoplasty, sinus surgery, and turbinoplasty, targeted at different sections of the nasal cavity in the order of their external to internal positions.Rhinoplasty
Rhinoplasty is one of the most common cosmetic approaches despite its intricacy. Rhinoplasty can be categorised into surgical rhinoplasty and non-surgical rhinoplasty. Surgical rhinoplasty emphasises the application of grafting techniques while non-surgical rhinoplasty provides non-invasive options.
Surgical rhinoplasty
Surgical rhinoplasty is an intervention aimed at modifying the nasal appearance in patients. This procedure targets the upper nasal bone and the lowercartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck an ...
. First, an incision is carried out at the nasal floor under local or general anaesthesia. During the process, the nasal bones and cartilage are carefully readjusted, with the duration depending on the amount of bone and cartilage that needs to be removed or added with flaps or tissue grafts. Surgeons can retrieve smaller tissue grafts from the interior of the nose, while larger ones may be taken from ribs, implants, or other long bones of the patient. Additionally, another factor under consideration is the patient’s ethnicity.
There are two main strategies involved for surgical rhinoplasty – open rhinoplasty and closed rhinoplasty. Open rhinoplasty offers a more accessible passage for the surgeon to incise the outer nasal skin, but it may introduce external scarring on the nose. Contrarily, closed rhinoplasty utilises the endoscopic
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are insert ...
approach through the nostril and does not require an incision observable to the eye. The decision between the two depends on the extent of growth abnormalities and the patient's preference.
Non-surgical rhinoplasty
Non-surgical rhinoplasty (liquid rhinoplasty) is a method that incorporateshyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid (; abbreviated HA; conjugate base hyaluronate), also called hyaluronan, is an anionic, nonsulfated glycosaminoglycan distributed widely throughout connective, epithelial, and neural tissues. It is unique among glycosaminoglycans ...
dermal fillers and other non-surgical devices, which act as alternatives for minor nasal reconstructions. They are proven to treat minor external nasal injuries more cost-effectively in comparison to surgical rhinoplasty. With respect to the reduced intraoperative loss of tissue and blood, non-surgical rhinoplasty is capable of preventing the occurrence of ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems wi ...
or even sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
. 
Septoplasty
Septoplasty is a surgical procedure involving the correction of the nasal septum, which refers to the bone and cartilage dividing the space between the nostrils. When a nasal septum is bent or crooked, it indicates the narrowing or blockage of the airway, leading to breathing difficulties and worsened sinusinfections
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmiss ...
due to poor drainage.
During septoplasty, the surgeon first lifts the mucous membrane enclosing the septum to visualise and assess the cartilage and bone. The surgeon then trims, reshapes or even replaces deviated parts to straighten the nasal septum. A septoplasty typically takes one to three hours and is coupled with other nasal surgeries to ameliorate the defect. The nasal septum is hence repositioned along the midline of one’s nose.
Most septoplasties are typically done with a closed procedure that utilises a thin, flexible endoscope with a tiny camera and a light. In certain cases, septorhinoplasty, which is the combination of rhinoplasty and septoplasty, requires an open procedure with a headlight and nasal speculum to fix the nasal septum.
Sinus surgery
The techniques of sinus surgery vary fromethmoidectomy
Ethmoidectomy is the medical name for a procedure that involves removing the partitions between the ethmoid sinuses in order to create larger sinus cavities. This procedure treats sinus infections and sinus obstructions that have been the cause of ...
to balloon sinuplasty
Balloon sinuplasty is a procedure that ear, nose and throat surgeons may use for the treatment of blocked sinuses. Patients diagnosed with sinusitis but not responding to medications may be candidates for sinus surgery. Balloon technology was ini ...
. They treat chronic sinusitis and nasal polyps by reopening the sinus passageways.
Ethmoidectomy
 Ethmoidectomy treats ethmoid sinusitis through removing the
Ethmoidectomy treats ethmoid sinusitis through removing the inflamed
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecu ...
mucosal lining on the ethmoid sinus
The ethmoid sinuses or ethmoid air cells of the ethmoid bone are one of the four paired paranasal sinuses. The cells are variable in both size and number in the lateral mass of each of the ethmoid bones and cannot be palpated during an extraoral e ...
. The method of conducting ethmoidectomy is classified based on the location of the incision, namely external, intranasal, and transantral approaches. = External ethmoidectomy
= The surgeon carries out an incision on the skin between the medial canthus and the medial palpebral ligament, in which the ligament may be repositioned afterwards. The surgeon then dissects the periosteum and a portion of the anterior ethmoid. By perforating the lamina papycracea, the floor of the ethmoidal bulla can be subsequently resected. With the opening of the posterior ethmoid, the surgeon proceeds with the elimination of the inflamed mucus.= Intranasal ethmoidectomy
= Intranasal ethmoidectomy (Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
Functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS), or functional endoscopic sinus surgery, is a procedure that is used to treat sinusitis and other conditions that affect the sinuses. Sinusitis is an inflammation of the sinuses that can cause symptoms su ...
) is the most predominant type of ethmoidectomy with a success rate of 79%. First, the patient is injected with local anaesthetic and adrenaline to decongest the nasal cavity. Next, the middle turbinate is cautiously medialised to render the cribriform plate intact. The dissection of the infundibulum allows the removal of the uncinate process. With a more accessible view of the ethmoid bulla, the remaining fragments are eliminated along the lamina papyrcea. The use of an endoscope facilitates the dissection from the anterior to posterior ethmoid.
= Transantral ethmoidectomy ( Caldwell-Luc approach)
= Transantral ethmoidectomy is a surgical treatment for recurrent chronic rhinosinusitis and malignant tumours of the maxillary sinus. The operation begins with a puncture through thecanine fossa
In the musculoskeletal anatomy of the human head, lateral to the incisive fossa of the maxilla is a depression called the canine fossa. It is larger and deeper than the comparable incisive fossa, and is separated from it by a vertical ridge, the ...
, allowing the surgeon to view the bulging of the ethmoid bulla in the maxillary sinus. Then, an aperture on the inferior nasal meatus is created for intranasal counter drainage. The surgeon eventually dissects the inflamed anterior and posterior ethmoid cells.

Balloon sinuplasty
Balloon sinuplasty is an optimal treatment for chronic rhinosinusitis. A flexibleballoon catheter
A balloon catheter is a type of "soft" catheter with an inflatable "balloon" at its tip which is used during a catheterization procedure to enlarge a narrow opening or passage within the Human body, body. The deflated balloon catheter is positione ...
is initially inserted into the inflamed sinus. Next, the inflation of the balloon widens the sinus while preserving the lining. Consequently, the expanded opening aids mucosal drainage. After the removal of the balloon, the irrigation catheter sprays saline
Saline may refer to:
* Saline (medicine), a liquid with salt content to match the human body
* Saline water, non-medicinal salt water
* Saline, a historical term (especially US) for a salt works or saltern
Places
* Saline, Calvados, a commune in ...
on the inflamed sinus to expel the pus
Pus is an exudate, typically white-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammation during bacterial or fungal infection. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collection ...
. Given the simplicity of the process, around 87% of balloon sinuplasty was conducted as an outpatient
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by healthcare professionals. The patient is most often ill or injured and in need of treatment by a physician, nurse, optometrist, dentist, veterinarian, or other health care ...
procedure, with a duration of approximately thirty minutes and a recovery of one to two days.
Turbinoplasty
 Turbinoplasty is an intervention aiming to treat turbinate hypertrophy by reducing turbinate volume. Turbinate hypertrophy is commonly characterised by enlarged nasal turbinates arising from
Turbinoplasty is an intervention aiming to treat turbinate hypertrophy by reducing turbinate volume. Turbinate hypertrophy is commonly characterised by enlarged nasal turbinates arising from allergic rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis, of which the seasonal type is called hay fever, is a type of inflammation in the nose that occurs when the immune system overreacts to allergens in the air. Signs and symptoms include a runny or stuffy nose, sneezing, red, i ...
. This procedure has a success rate of 82% and can be carried out in a clinic as a same-day procedure.
Turbinoplasty is classified as intraturbinoplasty and extraturbinoplasty. Intraturbinoplasty only involves the resection of soft tissue, while extraturbinoplasty also removes a portion of the inferior turbinate bone. Intraturbinoplasty can be conducted through an improved mucosal-sparing approach with microdebrider or radiofrequency, thus alleviating postoperative complications.
Turbinoplasty is performed with different equipment shown as follows:
Coblation turbinoplasty
Coblation turbinoplasty incorporates radiofrequency to vapourise and disintegrate the soft erectile tissue of the turbinate, lowering the turbinate size and causing tissue fibrosis. The reduction in turbinate volume alleviates the conditions of inferior turbinate hypertrophy. Since fibrosis stiffens the attachment of the mucosa to the periosteum, it remedies the shortcomings of possiblesequela
A sequela (, ; usually used in the plural, sequelae ) is a pathological condition resulting from a disease, injury, therapy, or other trauma. Derived from the Latin word, meaning “sequel”, it is used in the medical field to mean a complication ...
. According to the review, this technique outcompetes its conventional counterpart in terms of safety and effectiveness.
Radiofrequency turbinoplasty
First, an incision is carried out on the inferior turbinate bone to allow the insertion of the Piezo. Using an electric current, the Piezo reduces the turbinate volume and prevents direct damage. It is followed by lateralisation of the turbinate by theMayo scissors
Mayo scissors are a type of surgical scissor, often used in the cutting of fascia.
Etymology
Mayo scissors were developed by Mayo Clinic surgeons.
Description
Mayo scissors may be made from stainless steel or titanium, with stainless steel ones ...
. To ameliorate intraoperative bleeding, bipolar cautery is used along with the insertion of a Merocell sponge between the turbinate and nasal septum. It is notably distinctive from coblation turbinoplasty in the absence of saline.
Microdebrider turbinoplasty
The use of the microdebrider maintains continuous blood drainage, creating a more precisevisual field
The visual field is the "spatial array of visual sensations available to observation in introspectionist psychological experiments". Or simply, visual field can be defined as the entire area that can be seen when an eye is fixed straight at a point ...
. It also facilitates the specific elimination of the submucosal tissue without damaging the turbinate bone. Besides preserving the mucosa, shorter operative time, lower blood loss, and improved accuracy are significant advancements brought by microdebrider. Also, research found that it is more effective at mitigating nasal blockade than radiofrequency turbinoplasty. Ultrasound turbinoplasty
Emerging as a novel technique in sinus surgery, the principle ofultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequency, frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing range, hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hea ...
turbinoplasty is highly similar to that of coblation and radiofrequency turbinoplasty. First, an ultrasonic nasal probe is placed along the submucosal lining of the inferior turbinate, and is then moved forward and backward repeatedly. Compared to radiofrequency turbinoplasty, the destruction of swelling tissues by ultrasound exhibits increased nasal flow and minimal postoperative complications.
Post-operative treatment
Patients who have undergone rhinoplasty and septoplasty are placed on bed rest with the head raised. To lowermucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It is ...
build-up, physicians may prescribe appropriate dosage of corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involve ...
at regular intervals for several days. This can therefore reduce the likelihood of postoperative ecchymosis. After the surgery, internal bandages, nasal packs, and silicone
A silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer made up of siloxane (−R2Si−O−SiR2−, where R = organic group). They are typically colorless oils or rubber-like substances. Silicones are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cooking ...
splints may be applied to the wound for a week to support the skin grafts and the realigned nasal septum. Doctors can also use a small piece of gauze
Gauze is a thin, translucent fabric with a loose open weave. In technical terms "gauze" is a weave structure in which the weft yarns are arranged in pairs and are crossed before and after each warp yarn keeping the weft firmly in place. ...
(drip pad) to absorb any possible drainage on top of the aforementioned.
Ethmoidectomy and turbinoplasty patients are prescribed nasal saline spray. It is applied four to five times daily to remove blood clots
A thrombus (plural thrombi), colloquially called a blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of cr ...
and moisturise the nasal cavity. Depending on the patient's conditions, doctors may administer medication ranging from nasal steroids that can alleviate mucosal inflammation to antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention o ...
that can negate the risk of recurrence.
After three to five days of ethmoidectomy, the physician will eliminate the middle meatus packing and debride the dried blood clots during a follow-up visit. The patient recovers from ethmoidectomy after a month, while the recovery from turbinoplasty takes six weeks.
Risk and complications
Rhinoplasty and septoplasty may precipitate certain issues such as the collapse and perforation of the nasal septal cartilage. The tip projection of nasal alar cartilages may also deviate without adequate support depending on the individual’s nasal structure. This will lead to asymmetry and concavity of the nasal sidewall. Common complications of sinus surgery and turbinoplasty include haemorrhage. Additionally, sinus surgery may potentially result in visual impairment and the leakage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The loss of vision and haemorrhage can be caused by unintentional injuries of theoptic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual system, visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve i ...
and the internal carotid artery
The internal carotid artery (Latin: arteria carotis interna) is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior circulation of the brain. In human anatomy, the internal and external carotids arise from the common carotid arteries, where these b ...
in the ethmoid sinus respectively. CSF leakage may lead to meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Other symptoms include confusion or ...
, which is resulted from the fracture of the cribriform plate.
Current development
The Rhinoplasty Outcome Evaluation (ROE) questionnaire is distributed among rhinoplasty patients to examine the results collected. ROE also encourages the application of more innovative techniques, for instance the incorporation of Piezoelectric equipment. Septoplasty is still considered to be a relatively risky procedure with a high incidence of postoperative complications compared to other types of nasal surgeries. In response to this, specialists in nasal surgery are working to establish apeer-reviewed
Peer review is the evaluation of work by one or more people with similar competencies as the producers of the work (peers). It functions as a form of self-regulation by qualified members of a profession within the relevant field. Peer review ...
classification database that can define each type of anomaly involved.
See also
* Rhinoplasty * Septoplasty *Ethmoidectomy
Ethmoidectomy is the medical name for a procedure that involves removing the partitions between the ethmoid sinuses in order to create larger sinus cavities. This procedure treats sinus infections and sinus obstructions that have been the cause of ...
* Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
Functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS), or functional endoscopic sinus surgery, is a procedure that is used to treat sinusitis and other conditions that affect the sinuses. Sinusitis is an inflammation of the sinuses that can cause symptoms su ...
* Balloon sinuplasty
Balloon sinuplasty is a procedure that ear, nose and throat surgeons may use for the treatment of blocked sinuses. Patients diagnosed with sinusitis but not responding to medications may be candidates for sinus surgery. Balloon technology was ini ...
* Turbinoplasty
References
{{reflist Nose surgery