Narva Baltika on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Narva, russian: Нарва is a municipality and city in Estonia. It is located in
 Captured by the Russians during the Livonian War in 1558, for a short period Narva became an important port and trading city for Russia as a transshipment centre of goods from
Captured by the Russians during the Livonian War in 1558, for a short period Narva became an important port and trading city for Russia as a transshipment centre of goods from  During the Great Northern War of 1700–1721, Narva became the setting for the first great battle between the forces of King
During the Great Northern War of 1700–1721, Narva became the setting for the first great battle between the forces of King 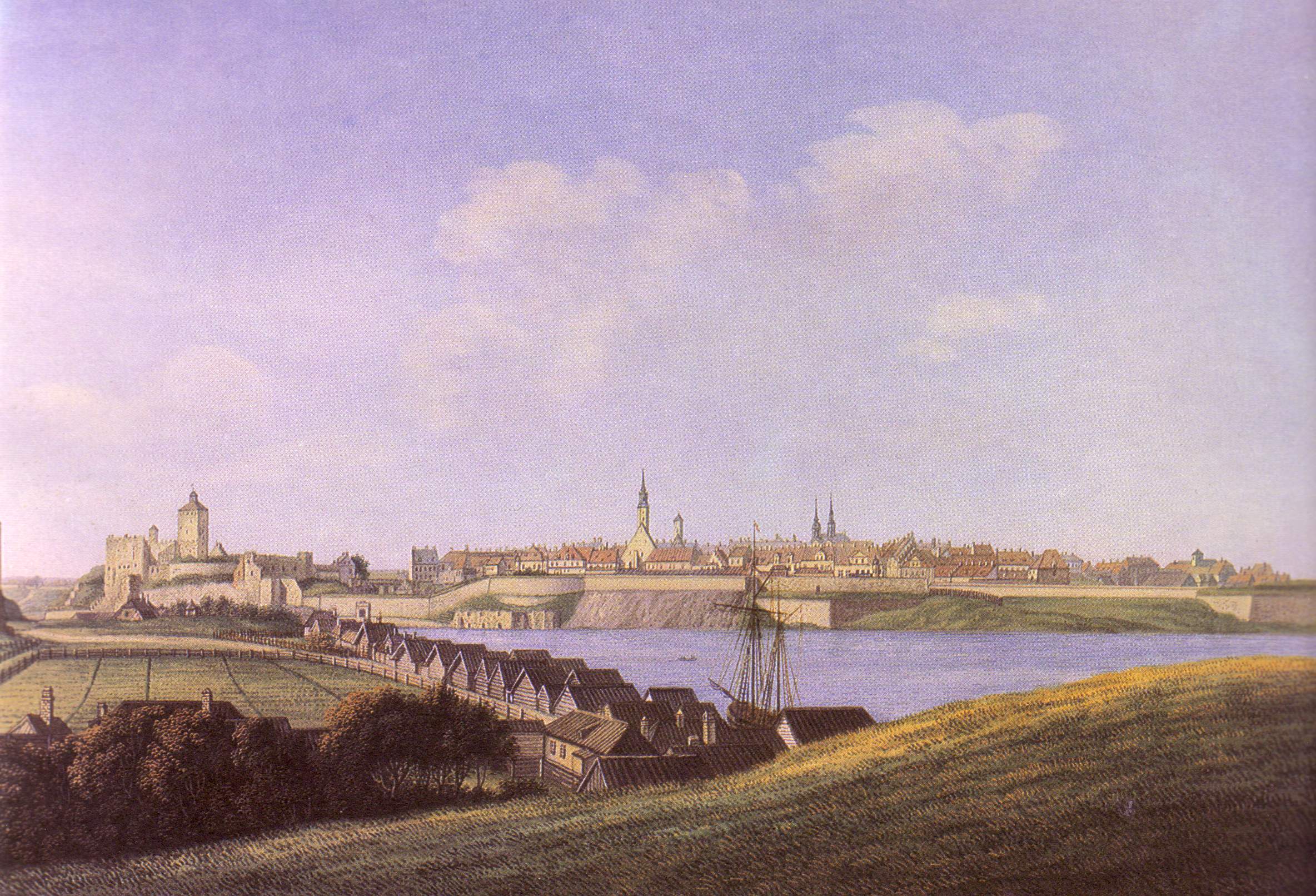 After the war, the bastions were renovated. Narva remained on the list of Russian fortifications until 1863, though there was no real military need for it. During Russian rule Narva formed part of the Saint Petersburg Governorate.
In the middle of the 19th century, Narva started to develop into a major industrial town. Ludwig Knoop established the Krenholm Manufacturing Company in 1857. The factory could use the cheap energy of the powerful Narva waterfalls, and at the end of the century became, with about 10,000 workers, one of the largest cotton mills in Europe and the world. In 1872, Krenholm Manufacturing became the site of the first strike in Estonia. At the end of the 19th century, Narva was the leading industrial town in Estonia – 41% of industrial workers in Estonia worked in Narva, compared to 33% in Tallinn. The first railway in Estonia, completed in 1870, connected Narva to Saint Petersburg and to Tallinn.
After the war, the bastions were renovated. Narva remained on the list of Russian fortifications until 1863, though there was no real military need for it. During Russian rule Narva formed part of the Saint Petersburg Governorate.
In the middle of the 19th century, Narva started to develop into a major industrial town. Ludwig Knoop established the Krenholm Manufacturing Company in 1857. The factory could use the cheap energy of the powerful Narva waterfalls, and at the end of the century became, with about 10,000 workers, one of the largest cotton mills in Europe and the world. In 1872, Krenholm Manufacturing became the site of the first strike in Estonia. At the end of the 19th century, Narva was the leading industrial town in Estonia – 41% of industrial workers in Estonia worked in Narva, compared to 33% in Tallinn. The first railway in Estonia, completed in 1870, connected Narva to Saint Petersburg and to Tallinn.
 In August 1890, Narva was the site of a key meeting between German Kaiser Wilhelm II and Russian Tsar Alexander III.
In August 1890, Narva was the site of a key meeting between German Kaiser Wilhelm II and Russian Tsar Alexander III.
 Heavy battles occurred both in and around Narva during World War II. The city was damaged in the German invasion of 1941 and by smaller air raids throughout the war, but remained relatively intact until February 1944. However, as the focus of the Battle of Narva, the city was destroyed by Soviet bombardment and fires and explosions set by retreating German troops. The most devastating action was the bombing raids of 6 and 7 March 1944 by the Soviet Air Force, which destroyed the
Heavy battles occurred both in and around Narva during World War II. The city was damaged in the German invasion of 1941 and by smaller air raids throughout the war, but remained relatively intact until February 1944. However, as the focus of the Battle of Narva, the city was destroyed by Soviet bombardment and fires and explosions set by retreating German troops. The most devastating action was the bombing raids of 6 and 7 March 1944 by the Soviet Air Force, which destroyed the

 After 1991, disputes regarding the Estonian-Russian border in the Narva sector remained, as the new constitution of Estonia (adopted in 1992) recognizes the 1920 Treaty of Tartu border to be currently legal.
The Russian Federation, however, considers Estonia to be a successor of the
After 1991, disputes regarding the Estonian-Russian border in the Narva sector remained, as the new constitution of Estonia (adopted in 1992) recognizes the 1920 Treaty of Tartu border to be currently legal.
The Russian Federation, however, considers Estonia to be a successor of the  Those on the Estonian side mainly crossed to buy cheaper petrol, groats, cleaning products, pasta and sugar. Those crossing from the Russian side wanted to make use of the availability of non-sanctioned goods, entertainment facilities and overall better infrastructure.
The invasion and subsequent conflict seriously reduced cooperation between the two neighbours, especially as visas became difficult to obtain and the residents of Narva increased the take up in
Those on the Estonian side mainly crossed to buy cheaper petrol, groats, cleaning products, pasta and sugar. Those crossing from the Russian side wanted to make use of the availability of non-sanctioned goods, entertainment facilities and overall better infrastructure.
The invasion and subsequent conflict seriously reduced cooperation between the two neighbours, especially as visas became difficult to obtain and the residents of Narva increased the take up in
 Narva is officially divided into 15 neighbourhoods:
Narva is officially divided into 15 neighbourhoods:
 Narva's skyline is dominated by the 15th-century castle, with the
Narva's skyline is dominated by the 15th-century castle, with the
Narva – Official site
Visit Narva official city guide
{{Authority control Cities and towns in Estonia Yamburgsky Uyezd Estonia–Russia border crossings Populated places in Ida-Viru County Russian communities Port cities and towns in Estonia
Ida-Viru county
Ida-Viru County ( et, Ida-Viru maakond or ''Ida-Virumaa'') is one of 15 counties of Estonia. It is the most north-eastern part of the country. The county contains large deposits of oil shale - the main mineral mined in Estonia. Oil shale is used ...
, at the eastern extreme point of Estonia, on the west bank of the Narva river which forms the Estonia–Russia international border. With 54,409 inhabitants (as of 2020) Narva is Estonia's third largest city after capital Tallinn and Tartu
Tartu is the second largest city in Estonia after the Northern European country's political and financial capital, Tallinn. Tartu has a population of 91,407 (as of 2021). It is southeast of Tallinn and 245 kilometres (152 miles) northeast of ...
.
In 1944, Narva was nearly completely destroyed during the battles of World War II. During the period of Soviet occupation (1944–1991), the city’s original native inhabitants were not permitted to return after the war, and immigrant workers from Russia and other parts of the former USSR were brought in to populate the city. The city whose population had been, as of 1934 census, 65% ethnic Estonian, became overwhelmingly non-Estonian in the second half of the 20th century. According to more recent data, 46.7% of the city's inhabitants are citizens
Citizenship is a "relationship between an individual and a state to which the individual owes allegiance and in turn is entitled to its protection".
Each state determines the conditions under which it will recognize persons as its citizens, and ...
of Estonia, 36.3% are citizens of the Russian Federation, while 15.3% of the population has undefined citizenship.
History
Early settlement
People settled in the area from the 5th to 4th millennium BC, as witnessed by the archeological traces of the Narva culture, named after the Narva river. The fortified settlement at Narva Joaoru is the oldest known in Estonia, dated to around 1000 BC. The earliest written reference of Narva is in theFirst Novgorod Chronicle
The Novgorod First Chronicle (russian: Новгородская первая летопись) or The Chronicle of Novgorod, 1016–1471 is the most ancient extant Old Russian chronicle of the Novgorodian Rus'. It reflects a tradition different ...
, which in the year 1172 describes a district in Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( rus, links=no, Великий Новгород, t=Great Newtown, p=vʲɪˈlʲikʲɪj ˈnovɡərət), also known as just Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the ol ...
called ''Nerevsky'' or ''Narovsky konets'' (yard). According to historians, this name derives from the name of Narva or Narva river and indicates that a frequently used trade route went through Narva, although there is no evidence of the existence of a trading settlement at the time.
Middle Ages
Narva's favourable location at the intersection of both trade routes and the Narva river was behind the founding ofNarva castle
Hermann Castle ( et, Hermanni linnus, russian: Замок Герман; also known as Hermannsfeste, Herman Castle, Narva Castle (russian: На́рвский за́мок), and Narva fortress) is a castle in Narva, eastern Estonia. It was foun ...
and the subsequent development of the castle's surrounding urban settlement. The castle was founded during the Danish rule of northern Estonia in the second half of the 13th century; the earliest written record of the castle is from 1277. ''Narvia'' village is mentioned in the Danish Census Book already in 1241. A town developed around the stronghold and in 1345 obtained Lübeck City Rights
Lübeck (; Low German also ), officially the Hanseatic City of Lübeck (german: Hansestadt Lübeck), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 217,000 inhabitants, Lübeck is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and in the sta ...
from Danish king Valdemar IV
Valdemar IV Atterdag (the epithet meaning "Return of the Day"), or Waldemar (132024 October 1375) was King of Denmark from 1340 to 1375. He is mostly known for his reunion of Denmark after the bankruptcy and mortgaging of the country to finance ...
. The castle and surrounding town of Narva (''Narwa'', in German) became a possession of the Livonian Order
The Livonian Order was an autonomous branch of the Teutonic Order,
formed in 1237. From 1435 to 1561 it was a member of the Livonian Confederation.
History
The order was formed from the remnants of the Livonian Brothers of the Sword after the ...
in 1346, after the Danish king sold its lands in Northern Estonia. In 1492 Ivangorod fortress across the Narva river was established by Ivan III of Moscow.
Trade, particularly Hanseatic long-distance trade remained Narva's ''raison d'être'' throughout the Middle Ages. However, due to opposition from Tallinn, Narva itself never became part of the Hanseatic League and also remained a small town – its population in 1530 is estimated at 600–750 people.
Swedish and Russian rule
 Captured by the Russians during the Livonian War in 1558, for a short period Narva became an important port and trading city for Russia as a transshipment centre of goods from
Captured by the Russians during the Livonian War in 1558, for a short period Narva became an important port and trading city for Russia as a transshipment centre of goods from Pskov
Pskov ( rus, Псков, a=pskov-ru.ogg, p=pskof; see also names in other languages) is a city in northwestern Russia and the administrative center of Pskov Oblast, located about east of the Estonian border, on the Velikaya River. Population ...
and Novgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( rus, links=no, Великий Новгород, t=Great Newtown, p=vʲɪˈlʲikʲɪj ˈnovɡərət), also known as just Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the ol ...
. Russian rule ended in 1581 when the Swedes under the command of Pontus De la Gardie conquered the city and it became part of Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
. During the Russo-Swedish War (1590–1595), when Arvid Stålarm
Arvid, Arved, Arnvid or Arvydas is a male given name, most common in Scandinavia but also in Iran and Lithuania. In Scandinavia it is derived from Old Norse and means "forest of eagles" or 'eagle wood'. Arvid is a royal male name that is composed ...
was governor, Russian forces attempted to regain the city without success ( Treaty of Teusina, May 1595).
During the Swedish rule, the Old Town of Narva was built. Following a big fire in 1659 that almost completely destroyed the town, only stone buildings were allowed to be built in the central part of the town. Incomes from flourishing trade allowed rebuilding of the town center in two decades. Until World War II, the baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
Old Town underwent practically no changes, and thus became renowned all over Europe. Towards the end of Swedish rule, the defence structures of Narva were greatly improved. Beginning in 1680s, an outstanding system of bastion
A bastion or bulwark is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fi ...
s, planned by the renowned Swedish military engineer Erik Dahlbergh, was built around the town. The new defences were among the most powerful in Northern Europe.
 During the Great Northern War of 1700–1721, Narva became the setting for the first great battle between the forces of King
During the Great Northern War of 1700–1721, Narva became the setting for the first great battle between the forces of King Charles XII of Sweden
Charles XII, sometimes Carl XII ( sv, Karl XII) or Carolus Rex (17 June 1682 – 30 November 1718 O.S.), was King of Sweden (including current Finland) from 1697 to 1718. He belonged to the House of Palatinate-Zweibrücken, a branch line of t ...
and Tsar Peter I of Russia
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
(November 1700). Although outnumbered four to one, the Swedish forces routed their 40,000-strong opponent. Russia subsequently conquered
Conquest is the act of military subjugation of an enemy by force of arms.
Military history provides many examples of conquest: the Roman conquest of Britain, the Mauryan conquest of Afghanistan and of vast areas of the Indian subcontinent, t ...
the city in 1704.
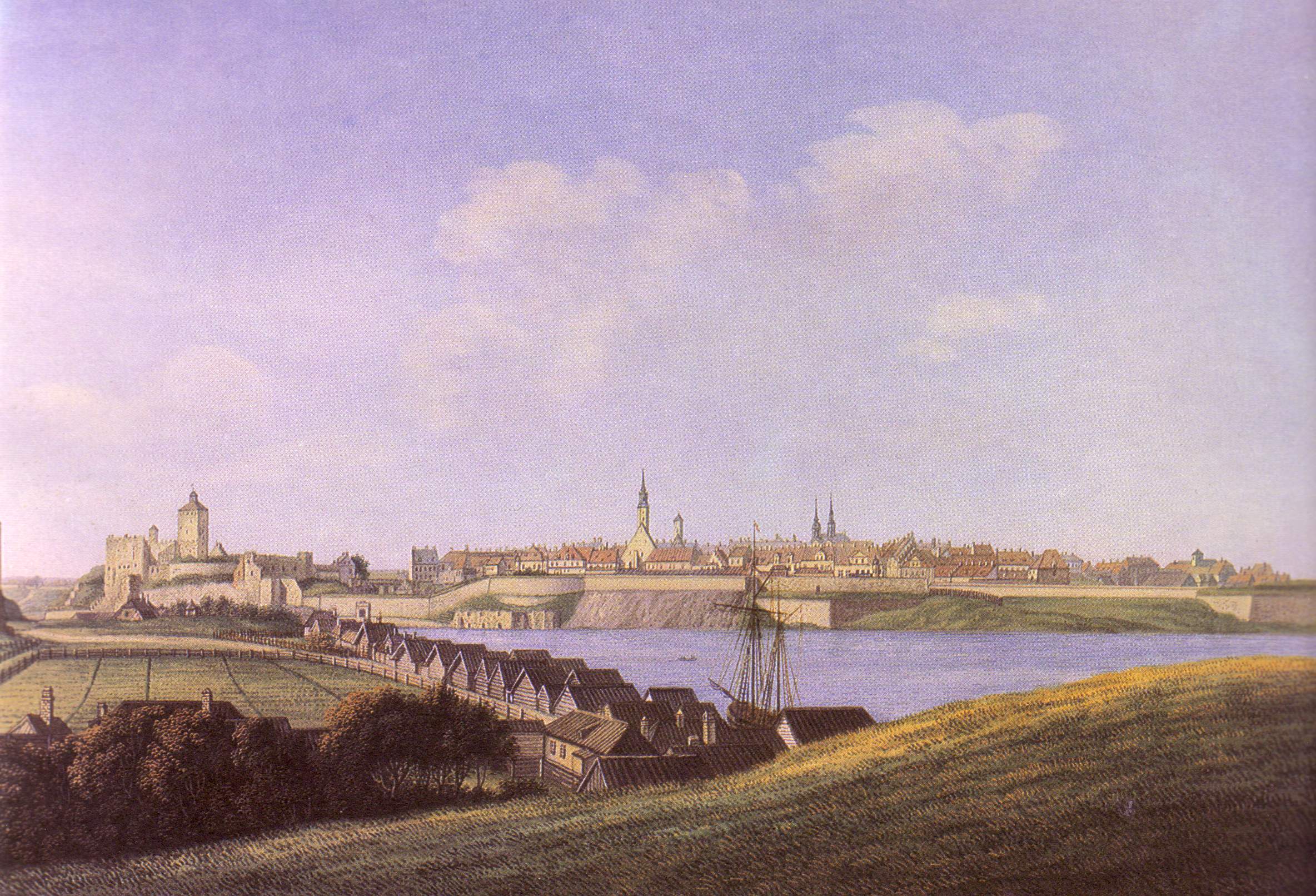 After the war, the bastions were renovated. Narva remained on the list of Russian fortifications until 1863, though there was no real military need for it. During Russian rule Narva formed part of the Saint Petersburg Governorate.
In the middle of the 19th century, Narva started to develop into a major industrial town. Ludwig Knoop established the Krenholm Manufacturing Company in 1857. The factory could use the cheap energy of the powerful Narva waterfalls, and at the end of the century became, with about 10,000 workers, one of the largest cotton mills in Europe and the world. In 1872, Krenholm Manufacturing became the site of the first strike in Estonia. At the end of the 19th century, Narva was the leading industrial town in Estonia – 41% of industrial workers in Estonia worked in Narva, compared to 33% in Tallinn. The first railway in Estonia, completed in 1870, connected Narva to Saint Petersburg and to Tallinn.
After the war, the bastions were renovated. Narva remained on the list of Russian fortifications until 1863, though there was no real military need for it. During Russian rule Narva formed part of the Saint Petersburg Governorate.
In the middle of the 19th century, Narva started to develop into a major industrial town. Ludwig Knoop established the Krenholm Manufacturing Company in 1857. The factory could use the cheap energy of the powerful Narva waterfalls, and at the end of the century became, with about 10,000 workers, one of the largest cotton mills in Europe and the world. In 1872, Krenholm Manufacturing became the site of the first strike in Estonia. At the end of the 19th century, Narva was the leading industrial town in Estonia – 41% of industrial workers in Estonia worked in Narva, compared to 33% in Tallinn. The first railway in Estonia, completed in 1870, connected Narva to Saint Petersburg and to Tallinn.
 In August 1890, Narva was the site of a key meeting between German Kaiser Wilhelm II and Russian Tsar Alexander III.
In August 1890, Narva was the site of a key meeting between German Kaiser Wilhelm II and Russian Tsar Alexander III.
Post-WWI period
The status of Narva was resolved in a July 1917 referendum, when the district population, at that time roughly equally divided between ethnic Russians and Estonians, voted to attach itself to the newly autonomous and soon to be independent republic of Estonia. Narva became part of an independent Estonia in 1918, at the end of World War I. The town saw fighting during the Estonian War of Independence. The war started when Russian Bolshevik troops attacked Narva on 28 November 1918, capturing the city on the next day. The Russian Red Army retained control of the city until 19 January 1919. Heavy battles occurred both in and around Narva during World War II. The city was damaged in the German invasion of 1941 and by smaller air raids throughout the war, but remained relatively intact until February 1944. However, as the focus of the Battle of Narva, the city was destroyed by Soviet bombardment and fires and explosions set by retreating German troops. The most devastating action was the bombing raids of 6 and 7 March 1944 by the Soviet Air Force, which destroyed the
Heavy battles occurred both in and around Narva during World War II. The city was damaged in the German invasion of 1941 and by smaller air raids throughout the war, but remained relatively intact until February 1944. However, as the focus of the Battle of Narva, the city was destroyed by Soviet bombardment and fires and explosions set by retreating German troops. The most devastating action was the bombing raids of 6 and 7 March 1944 by the Soviet Air Force, which destroyed the Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
old town.
Soviet occupation 1944–1991
By the end of July 1944, 98% of Narva had been destroyed. After the war, most of the buildings could have been restored as the walls of the houses still existed, but in early 1950s, the Soviet authorities decided to demolish the ruins to make room for apartment buildings. Only three buildings remain of the old town, including theBaroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
-style Town Hall
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or a municipal building (in the Philippines), is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses ...
. The civilian casualties of the bombing were low as the German forces had evacuated the city in January 1944.
Narva was effectively ethnically cleansed
Ethnic cleansing is the systematic forced removal of ethnic, racial, and religious groups from a given area, with the intent of making a region ethnically homogeneous. Along with direct removal, extermination, deportation or population transfer ...
, as the original native inhabitants were not allowed to return after the war, and immigrant Russian-speaking workers from other parts of the USSR were brought in to populate the city. The city which population had been 65% Estonian according to the last census in 1934, became overwhelmingly non-Estonian. The main reason behind this was a plan to build a secret uranium processing plant in the city, which would turn Narva into a closed town. In 1947 nearby Sillamäe was selected as the location of the factory instead of Narva, but the existence of such a plan was decisive for the development of Narva in the postwar years, and thus also shaped its later evolution. The planned uranium factory and other large-scale industrial developments, like the restoring of Kreenholm Manufacture, were the driving force behind the influx of internal migrants from other parts of the Soviet Union, mainly Russia.
In January 1945, Ivangorod, the suburb on the eastern bank of the river was separated from Estonia (and from Narva) by the Soviet authorities, and the settlement around Ivangorod fortress was made administratively part of the neighboring Leningrad Oblast
Leningrad Oblast ( rus, Ленинградская область, Leningradskaya oblast’, lʲɪnʲɪnˈgratskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ, , ) is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia (an oblast). It was established on 1 August 1927, a ...
of the Russian SFSR. Ivangorod became officially a town by itself in 1954.

Restoration of Estonian independence
After Estonia regained its independence in 1991, the city's leaders, holdovers from the Soviet era, wanted autonomy, and contended that the notion of a breakaway "Transnarovan Soviet republic" in northeastern Estonia was becoming increasingly popular, but this was contradicted by polls showing 87% of the region's population opposed secession from Estonia. In 1993, dissatisfaction with newly enacted citizenship and election laws (non-citizens were not allowed to hold office) culminated in the Narva referendum of 16–17 July 1993, which proposed autonomy for both Narva and Sillamäe, a nearby town. Although 97% voted in favor of the referendum, turnout in Narva was a mere 55%, and there were credible charges of vote rigging. After 1991, disputes regarding the Estonian-Russian border in the Narva sector remained, as the new constitution of Estonia (adopted in 1992) recognizes the 1920 Treaty of Tartu border to be currently legal.
The Russian Federation, however, considers Estonia to be a successor of the
After 1991, disputes regarding the Estonian-Russian border in the Narva sector remained, as the new constitution of Estonia (adopted in 1992) recognizes the 1920 Treaty of Tartu border to be currently legal.
The Russian Federation, however, considers Estonia to be a successor of the Estonian SSR
The Estonian SSR,, russian: Эстонская ССР officially the Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic,, russian: Эстонская Советская Социалистическая Республика was an ethnically based adminis ...
and recognizes the 1945 border between the two former national republics. Officially, Estonia has no territorial claims in the area, and which was also reflected in the new Estonian-Russian border treaty signed in Moscow on 18 May 2005. Russia failed to ratify it because, together with the ratification the Estonian parliament, approved a communiqué, which mentioned the Soviet Occupation.
On 18 February 2014 a new border treaty was signed by both countries. However the treaty was not ratified by the parliaments of either Russia or Estonia.
Overall, by 2014, Russian residents were happy with their status as both Estonian and European Union citizens and lived peacefully alongside their compatriots.
Before the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014. The invasion has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths on both sides. It has caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. An ...
, residents mixed relatively freely with the residents across the river in Ivangorod.
 Those on the Estonian side mainly crossed to buy cheaper petrol, groats, cleaning products, pasta and sugar. Those crossing from the Russian side wanted to make use of the availability of non-sanctioned goods, entertainment facilities and overall better infrastructure.
The invasion and subsequent conflict seriously reduced cooperation between the two neighbours, especially as visas became difficult to obtain and the residents of Narva increased the take up in
Those on the Estonian side mainly crossed to buy cheaper petrol, groats, cleaning products, pasta and sugar. Those crossing from the Russian side wanted to make use of the availability of non-sanctioned goods, entertainment facilities and overall better infrastructure.
The invasion and subsequent conflict seriously reduced cooperation between the two neighbours, especially as visas became difficult to obtain and the residents of Narva increased the take up in Estonian citizenship
Estonian citizenship law details the conditions by which a person is a citizen of Estonia. The primary law currently governing these requirements is the Citizenship Act, which came into force on 1 April 1995.
Estonia is a member state of the ...
. Narva took many Ukrainian refugees fleeing the war and previously popular among older russophone residents Russian TV stations were banned by the Estonian government.
On June 10, 2022, the Estonian foreign ministry summoned the Russian ambassador to protest about remarks by President Vladimir Putin praising Peter the Great
Peter I ( – ), most commonly known as Peter the Great,) or Pyotr Alekséyevich ( rus, Пётр Алексе́евич, p=ˈpʲɵtr ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪtɕ, , group=pron was a Russian monarch who ruled the Tsardom of Russia from t ...
for having captured Narva in the early 18th century.
In August 2022, a Soviet T-34 tank memorial was removed from a stretch of road between the city centre and Narva-Jõesuu
Narva-Jõesuu (; russian: Усть-Нарва, ''Ust'-Narva'', Нарва-Йыэсуу, Усть-Нарова) is a town in Ida-Viru County, in northeastern Estonia.
Geography
It is located on the country's northern Baltic coast of the Gul ...
, to mixed responses. It was moved to the Estonian War Museum in Viimsi near Tallinn. In response to the tank's removal, the following month Russian authorities erected a similar T-34 tank monument in Ivangorod near the border crossing point with Narva.
Demographics
On 1 January 2013 Narva's population was 59,888, down from 60,454 inhabitants a year earlier. The population was 83,000 in 1992. 95.7% of the population of Narva are native Russian speakers, and 87.7% are ethnic Russians. Most non-Estonians are ethnically Russian, Belarusian, or Ukrainian immigrants or the children of immigrants, though 69% of Narva residents in the early 1990s had been born in Narva or had lived there for more than 30 years. Ethnic Estonians account for 5.2% of total population. Much of the city was destroyed during World War II and for several years during the following reconstruction the Soviet authorities largely prohibited return of Narva's pre-war residents (among whom ethnic Estonians had been the majority, forming 64.8% of the town's population of 23,512 according to the 1934 census), thus radically altering the city's ethnic composition. Nevertheless, ethnic Russians had already formed a significant minority: 29.7% of the city's population were Russian in the census of 1934. 46.7% of the city's inhabitants are Estonian citizens, 36.3% are citizens of the Russian Federation, while 15.3% of the population has undefined citizenship. Since the2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014. The invasion has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths on both sides. It has caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. An ...
there has been increased the take up in Estonian citizenship
Estonian citizenship law details the conditions by which a person is a citizen of Estonia. The primary law currently governing these requirements is the Citizenship Act, which came into force on 1 April 1995.
Estonia is a member state of the ...
in the city.
A concern in Narva is the spread of HIV, which infected 1.2% of Estonia's population in 2012. Between 2001 and 2008, more than 1,600 cases of HIV were registered in Narva, making it one of the worst areas in Estonia, alongside Tallinn and the rest of Ida-Viru County
Ida-Viru County ( et, Ida-Viru maakond or ''Ida-Virumaa'') is one of 15 counties of Estonia. It is the most north-eastern part of the country. The county contains large deposits of oil shale - the main mineral mined in Estonia. Oil shale is used ...
. The HIV infection rate in Estonia declined in 2014, with 59 new cases in Narva.
Geography
Narva is situated in the eastern extreme point of Estonia, to the east from the Estonian capital Tallinn and southwest from Saint Petersburg. The capital of Ida-Viru County, Jõhvi, lies to the west. The eastern border of the city along the Narva river (which drains Lake Peipus) coincides with the Estonian-Russian border. The Estonian part of the Narva Reservoir lies mostly within the territory of Narva, to the southwest of city center. The mouth of the Narva river to theGulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland ( fi, Suomenlahti; et, Soome laht; rus, Фи́нский зали́в, r=Finskiy zaliv, p=ˈfʲinskʲɪj zɐˈlʲif; sv, Finska viken) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and E ...
is about downstream from the city.
The municipality of Narva covers , of which the city proper occupies (excluding the reservoir), while two separate districts surrounded by Vaivara Parish
Vaivara Parish is a former municipality of Ida-Viru County in northern Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across fro ...
, Kudruküla and Olgina, cover and , respectively. Kudruküla is the largest of Narva's dacha regions, located to northwest from the main city, near Narva-Jõesuu
Narva-Jõesuu (; russian: Усть-Нарва, ''Ust'-Narva'', Нарва-Йыэсуу, Усть-Нарова) is a town in Ida-Viru County, in northeastern Estonia.
Geography
It is located on the country's northern Baltic coast of the Gul ...
.
Climate
Narva has a warm-summer humid continental climate ( Köppen climate classification ''Dfb'') with mild to warm, rainy summers with cool nights and cold, cloudy and snowy winters. Narva is one of the coldest settlements in Estonia, being located at the very northeast of the country and bordering Russia.Neighbourhoods
 Narva is officially divided into 15 neighbourhoods:
Narva is officially divided into 15 neighbourhoods: Elektrijaama
Narva is officially divided into 15 neighborhood
A neighbourhood (British English, Irish English, Australian English and Canadian English) or neighborhood (American English; see spelling differences) is a geographically localised commun ...
, Joaoru
Narva
Narva, russian: Нарва is a municipality and city in Estonia. It is located in Ida-Viru county, at the eastern extreme point of Estonia, on the west bank of the Narva river which forms the Estonia–Russia international borde ...
, Kalevi Kalevi may refer to
* Kalevi (mythology), an ancient Finnish and Estonian ruler, known from the Finnish epic Kalevala and Estonian epic Kalevipoeg.
* Kalevi, Estonia
Kalevi is a village in Rapla Parish, Rapla County in northwestern Estonia
...
, Kerese
Narva
Narva, russian: Нарва is a municipality and city in Estonia. It is located in Ida-Viru county, at the eastern extreme point of Estonia, on the west bank of the Narva river which forms the Estonia–Russia international borde ...
, Kreenholmi, Kudruküla
Kudruküla is a village in Narva-Jõesuu, Ida-Viru County in northeastern Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across ...
, Kulgu, Olgina
Olgina is a small borough (') in Narva-Jõesuu, Ida-Viru County in northeastern Estonia. At the 2011 Census, the settlement's population was 459, of which ethnic Estonians
Estonians or Estonian people ( et, eestlased) are a Finnic eth ...
, Paemurru
Narva is officially divided into 15 neighborhood
A neighbourhood (British English, Irish English, Australian English and Canadian English) or neighborhood (American English; see spelling differences) is a geographically localised communi ...
, Pähklimäe
Narva is officially divided into 15 neighborhood
A neighbourhood (British English, Irish English, Australian English and Canadian English) or neighborhood (American English; see spelling differences) is a geographically localised communi ...
, Siivertsi
Narva is officially divided into 15 neighborhood
A neighbourhood (British English, Irish English, Australian English and Canadian English) or neighborhood (American English; see spelling differences) is a geographically localised communi ...
, Soldina
Soldina is a village in Narva-Jõesuu municipality, Ida-Viru County in northeastern Estonia. (retrieved 28 July 2021) Prior to the 2017 administrative reform of local governments, it was located in Vaivara Parish.
Narva Airfield (ICAO
...
, Sutthoffi
Narva
Narva, russian: Нарва is a municipality and city in Estonia. It is located in Ida-Viru county, at the eastern extreme point of Estonia, on the west bank of the Narva river which forms the Estonia–Russia international borde ...
, Vanalinn
Vanalinn (Estonian for ''"Old Town"'') is a subdistrict ( et, asum) in the district of Kesklinn (Midtown), Tallinn, the capital of Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It ...
and Veekulgu
Narva is officially divided into 15 neighborhood
A neighbourhood (British English, Irish English, Australian English and Canadian English) or neighborhood (American English; see spelling differences) is a geographically localised communi ...
.
Landmarks
 Narva's skyline is dominated by the 15th-century castle, with the
Narva's skyline is dominated by the 15th-century castle, with the Pikk Hermann
Pikk Hermann or Tall Hermann (german: Langer Hermann) is a tower of the Toompea Castle, on Toompea hill in Tallinn, the capital of Estonia. The first part was built 1360–70. It was rebuilt (height brought to ) in the 16th century. A staircase ...
tower as its most prominent landmark. The sprawling complex of the Kreenholm Manufacture
The Kreenholm Manufacturing Company (historical alternate spelling: Krenholm; et, Kreenholmi Manufaktuur; german: Krähnholm Manufaktur; russian: Кренгольмская мануфактура) was a textile manufacturing company located on th ...
, located in the proximity of scenic waterfalls, is one of the largest textile mills of 19th-century Northern Europe. Other notable buildings include Swedish mansions of the 17th century, a Baroque town hall (1668–71), and remains of Erik Dahlberg's fortifications.
Across the Narva river lies the Russian Ivangorod fortress, established during the rule of Grand Prince Ivan III of Muscovy in 1492 and also referred to in some contemporary sources as the "Counter-Narva". From the 17th century until 1945, both the fortress and the adjacent suburb of Ivangorod ( et, Jaanilinn) were an administrative part of Narva.
Narva Kreenholmi Stadium
Narva Kreenholm Stadium (also Kreenholm Stadium; et, Narva Kreenholmi staadion) is a multi-purpose stadium in Narva, Estonia.
It is currently used mostly for football matches and hosts the matches of JK Narva Trans
JK Narva Trans, commonly ...
is home to Meistriliiga football team, FC Narva Trans.
Transportation
TheNarva railway station
Narva railway station ( et, Narva raudteejaam) is the easternmost railway station in Estonia, serving the city of Narva.
The station was opened in 1870, and the first station building was destroyed in 1919 during the Estonian War of Independenc ...
is located on an international railway line between Estonia and Russia ( Tallinn–Narva railway). A daily international passenger train used to link (as of 2019) the two countries: the overnight train between Moscow via St. Petersburg to Tallinn, which stops at Narva.
Four daily domestic trains run between Narva and Tallinn - modern trains were introduced in 2016 and now take less than 3 hours between the two cities.
Adjacent to the central rail station is a central bus station, which has multiple domestic and international connections (including to Russia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Belarus etc.). There is a general aviation grass airfield
An aerodrome ( Commonwealth English) or airdrome (American English) is a location from which aircraft flight operations take place, regardless of whether they involve air cargo, passengers, or neither, and regardless of whether it is for publ ...
near Narva (ICAO: EENA).
Sport
The two main professional sports in the city are ice hockey andfootball
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
.
Narva PSK play at the Narva Ice Hall, which also was the host arena of the 2005 World Junior Ice Hockey Division I Championship Group B.
JK Narva Trans play at the Narva Kreenholm Stadium
Narva Kreenholm Stadium (also Kreenholm Stadium; et, Narva Kreenholmi staadion) is a multi-purpose stadium in Narva, Estonia.
It is currently used mostly for football matches and hosts the matches of JK Narva Trans
JK Narva Trans, commonly ...
. They are founding members of the Meistriliiga, and are one of two clubs which have never been relegated from the Estonian top division. They have won 2 Estonian Cups and 2 Estonian Supercups.
Notable residents
*Evert Horn
Evert Karlsson Horn af Kanckas (11 June 1585 – 30 July 1615) was a Sweden, Swedish Field Marshal and Governor of Narva.
Biography
He was born at Haapsalu Castle in the Estonia under Swedish rule, Swedish province of Estonia. He was a son of ...
(1585–1615), governor of Narva (1613)
*Ludwig Busbetzky
Ludwig Busbetzky (Lovies Busbetsky ; Busbet) was an Estonian organist and composer during the 17th century. Coming from a family of musicians, Busbetzky studied with Dieterich Buxtehude in Lübeck around 1680.
From 1687 to 1699 Busbetzky was the ...
(1687-1699), composer and organist at the German Church in Narva
*Aleksander Promet
Aleksander Promet (10 November 1879, in Narva – 18 September 1938, in Tallinn) was an Estonian painter and graphic artist.
Biography
His parents were blue-collar workers who were employed at the Krenholm Manufacturing Company.Obituary, 29 ...
(1879–1938), artist
* Raimund Kull (1882–1942), conductor and composer
* Adolf Szyszko-Bohusz (1883–1948), architect
*Albert Üksip
Albert Aleksander Üksip (8 December 1886 – 10 August 1966, in Tallinn) was an Estonian actor, botanist and translator.
He born in Narva. In 1902 he graduated from Narva city school. 1902-1923 he worked at Kreenholm Manufacturing Company
The ...
(1886–1966), botanist
*Emmanuel Steinschneider
Emmanuel Efimovich Steinschneider (russian: Эммануил Ефимович Штайншнайдер; 21 December 1886 – 2 December 1970), was a Russian Empire and USSR physician and medical researcher, best known for his studies on inf ...
(1886–1970), professor.
*Nikolai Stepulov
Nikolai Stepulov (20 March 1913 – 2 January 1968) was an Estonian lightweight boxer, military officer and criminal. As a boxer he won silver medals at the 1936 Olympic Games in Berlin and 1937 European Championships, and fought professionally ...
(1913–1968), Olympic boxer
*Kersti Merilaas
Kersti Merilaas ( in Narva – 8 March 1986 in Tallinn) was an Estonian poet and translator. In addition, she wrote poems and prose for children and plays.
Early life and education
Kersti Merilaas was born Eugenie Moorberg in Narva, Estonia ...
(1913–1986), poet, playwright
* Paul Keres (1916–1975), chess grandmaster
*Paul Felix Schmidt
Paul Felix Schmidt ( – 11 August 1984) was an Estonian and German chess player, writer and chemist.
Biography
In June 1935, Schmidt won, ahead of Paul Keres, at Tallinn. In May 1936, he drew a match against Keres (+3 –3 =1) at Pärnu. ...
(1916–1984), chess player
* Ortvin Sarapu (1924–1999), chess player
* Valeri Karpin (born 1969), Russian football player
* Maksim Gruznov (1974), football player
*Reinar Hallik
Reinar Hallik (born 5 January 1984) is an Estonian retired professional basketball player. Standing at 2.08 m (6 ft 10 in), he played at the power forward position.
Hallik represented the Estonian national basketball team internationally si ...
(1984), basketball player
* Leo Komarov (1987), ice hockey player
In popular culture
In the first-person shooter video game ''Squad
In military terminology, a squad is among the smallest of military organizations and is led by a non-commissioned officer. NATO and US doctrine define a squad as an organization "larger than a team, but smaller than a section." while US Army do ...
'', the map Narva is loosely based on the real city, containing Narva Castle
Hermann Castle ( et, Hermanni linnus, russian: Замок Герман; also known as Hermannsfeste, Herman Castle, Narva Castle (russian: На́рвский за́мок), and Narva fortress) is a castle in Narva, eastern Estonia. It was foun ...
, Ivangorod Fortress and a southern industrial area.
Twin towns – sister cities
Narva istwinned
Twinning (making a twin of) may refer to:
* In biology and agriculture, producing two offspring (i.e., twins) at a time, or having a tendency to do so;
* Twin towns and sister cities, towns and cities involved in town twinning
* Twinning inst ...
with:
* Bălți, Moldova
* Barysaw, Belarus
* Bel Air, United States
* Elbląg
Elbląg (; german: Elbing, Old Prussian: ''Elbings'') is a city in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland, located in the eastern edge of the Żuławy region with 117,390 inhabitants, as of December 2021. It is the capital of Elbląg County.
...
, Poland
* Gorna Oryahovitsa, Bulgaria
* Ivangorod, Russia
* Kanta-Häme, Finland
* Karlskoga, Sweden
* Kingiseppsky District, Russia
* Kirovsky (Saint Petersburg), Russia
* Kobuleti, Georgia
* Lahti, Finland
* Petrozavodsk, Russia
Notes
References
External links
Narva – Official site
Visit Narva official city guide
{{Authority control Cities and towns in Estonia Yamburgsky Uyezd Estonia–Russia border crossings Populated places in Ida-Viru County Russian communities Port cities and towns in Estonia