geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Ea ...
, a nappe or thrust sheet is a large sheetlike body of rock that has been moved more than or above a thrust fault
A thrust fault is a break in the Earth's crust, across which older rocks are pushed above younger rocks.
Thrust geometry and nomenclature
Reverse faults
A thrust fault is a type of reverse fault that has a dip of 45 degrees or less.
If ...
from its original position. Nappes form in compressional tectonic settings like continental collision zones or on the overriding plate in active subduction zones. Nappes form when a mass of rock is forced (or "thrust") over another rock mass, typically on a low angle fault plane. The resulting structure may include large-scale recumbent folds
Benjamin Scott Folds (born September 12, 1966) is an American singer-songwriter, musician, and composer, who is the first artistic advisor to the National Symphony Orchestra at the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts, Kennedy Center in ...
, shearing along the fault plane,Twiss, Robert J. and Eldridge M. Moores, ''Structural Geology,'' W. H. Freeman, 1992, p. 236 imbricate thrust stacks, fensters and klippes.
The term stems from the French word for '' tablecloth'' in allusion to a rumpled tablecloth being pushed across a table.
History
Nappes or nappe belts are a major feature of theEurope
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
an Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, ...
, Dinarides, Carpathians
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Ural Mountains, Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The ...
and Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
. Since the 19th century many geologists have uncovered areas with large-scale overthrusts. Some of these were substantiated with paleontological evidence. The concept was developed by Marcel Alexandre Bertrand, who unraveled the complex tectonic history of the Alps and identified the feature as ''nappe de charriage''. He reinterpreted earlier studies by Arnold Escher von der Linth and Albert Heim in the Glarus Alps. His work in Switzerland influenced Escher and Maurice Lugeon. Several years later, nappe structure was investigated in northwestern Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to th ...
by Charles Lapworth. Lugeon later transferred the ideas of nappes to the Carpathians
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Ural Mountains, Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The ...
.
Structure
''Nappe'' can be qualified in a number of ways to indicate various features of a formation. The frontal part in the direction of movement, is called ''the leading edge'' of a nappe; numerousfolds
Benjamin Scott Folds (born September 12, 1966) is an American singer-songwriter, musician, and composer, who is the first artistic advisor to the National Symphony Orchestra at the John F. Kennedy Center for the Performing Arts, Kennedy Center in ...
and secondary thrusts and duplexes are common features here and are sometimes called ''digitations''. The surface of a thrust fault
A thrust fault is a break in the Earth's crust, across which older rocks are pushed above younger rocks.
Thrust geometry and nomenclature
Reverse faults
A thrust fault is a type of reverse fault that has a dip of 45 degrees or less.
If ...
which caused movement of a nappe is called a '' decollement'', ''detachment plane'' or sole of thrust. The ''root area'' is an area where the nappe is completely separated from its substratum. It is often compressed and reduced, even underthrust below the surrounding tectonic units, resulting in a specific structure called a '' suture''. A nappe whose root area is unknown, is called a ''rootless nappe''.
Areas with a nappe structure often contain two types of geological features:
* A ''nappe outlier'' or '' klippe'' is a small area isolated from the main body of the nappe by erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is di ...
that lies on the autochthonous base; the summit of Veľký Rozsutec
Veľký Rozsutec (1,609.7 m; 5,281.17 ft AMSL) is a mountain situated in the Malá Fatra mountain range in the Žilina Region, Slovakia. The peak is situated in the north part of Malá Fatra called Krivánska Malá Fatra and is part of the Ma ...
in the Western Carpathians is a typical example.
* A ''fault inlier'', ''fenster'', or window
A window is an opening in a wall, door, roof, or vehicle that allows the exchange of light and may also allow the passage of sound and sometimes air. Modern windows are usually glazed or covered in some other transparent or translucent mate ...
is an area of the autochthonous basement uncovered by erosion, but entirely surrounded by the body of the nappe; the Hohe Tauern window in the Alps is a typical example.
Classification
According to petrographical composition, two basic types of nappes are known: * Basement nappes are composed generally of crystalline basement rocks (but may contain basement sedimentary cover), forming so-called thick-skinned style. Nappes of this type usually reach a large thickness and form independent superunits such as Penninic nappes. * Cover nappes or so called ''superficial nappes'' are composed generally ofsedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particle ...
s that form the upper part of crust, forming so-called thin-skinned style. Therefore, nappes of this type form smaller units, such as the Hallstatt nappe in the Austroalpine nappes of the Alps.
Mechanisms of emplacement
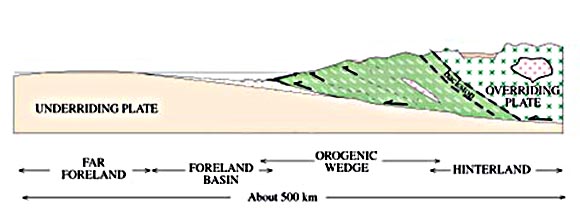 Nappes are generally considered as compressional structures, however some exceptions could be found especially among the gravitational slides along low angle faults. Gravitational forces could even be important in certain cases during emplacement of compressional thrusts. The movement of huge masses of rock may be influenced by several forces, forces that may act together or sequentially. These forces frequently result in high temperature and pressure metamorphism and strong deformation of nappe rocks.
At shallower depths, low
Nappes are generally considered as compressional structures, however some exceptions could be found especially among the gravitational slides along low angle faults. Gravitational forces could even be important in certain cases during emplacement of compressional thrusts. The movement of huge masses of rock may be influenced by several forces, forces that may act together or sequentially. These forces frequently result in high temperature and pressure metamorphism and strong deformation of nappe rocks.
At shallower depths, low pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country a ...
s and temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on ...
s can't cause the plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptab ...
and viscous behavior of solid rock necessary to move along low angle faults. It is considered that such characteristics may be achieved at significantly less extreme conditions in the clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay part ...
ey rocks or evaporites, which can then act as tectonic lubricants. The process, which significantly reduces the friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding (motion), sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:
*Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative la ...
al resistance, is the fluid overpressure, which acts against the normal pressure, thereby reducing high lithostatic pressures and allowing fracturation, cataclasis A cataclastic rock is a type of fault rock that has been wholly or partly formed by the progressive fracturing and comminution of existing rocks, a process known as ''cataclasis''. Cataclasis involves the granulation, crushing, or milling of the ori ...
and formation of tectonic breccia or fault gouge that could act as a decollement plane. Evaporites are also often related the decollement and thrust planes. Evaporites are strongly prone to shear deformation
image:boudin_vein.jpg, Boudinaged quartz vein (with strain fringe) showing ''Fault (geology), sinistral shear sense'', Starlight Pit, Fortnum Gold Mine, Western Australia
In geology, shear is the response of a rock to Deformation (engineering), ...
and therefore preferred planes of detachment.
Behavior of thrust
Thrust is a reaction force
In physics, a force is an influence that can change the motion of an object. A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (e.g. moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate. Force can al ...
sheets is currently explained on the model of the orogenic wedge, which is dependent on the internal wedge taper θ. Gravitational sliding is movement generated by the movement down an inclined plane under the action of gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the str ...
. Gravitational spreading, possibly accompanied by an initial phase of diapirism, is generated by large heat flow that causes detachment in a hinterland.Price, N.J., McClay, K.R., 1981''Introduction.''
p. 1-5 in Price, N.J., McClay, K.R. (Eds.), ''Thrust and Nappe Tectonics.'' Geological Society, Special Publications vol. 9, London, 528 p. Other mechanisms, such as push from behind, action of tangential compressive forces, and shortening of the basement, are essentially variations of the previous mechanisms.
References
{{Authority control Plate tectonics Structural geology