Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of
Campania
Campania (, also , , , ) is an administrative Regions of Italy, region of Italy; most of it is in the south-western portion of the Italian peninsula (with the Tyrrhenian Sea to its west), but it also includes the small Phlegraean Islands and the i ...
and the third-largest city of
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
, after
Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
and
Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
, with a population of 909,048 within the city's administrative limits as of 2022.
Its province-level municipality is the third-most populous
metropolitan city in Italy with a population of 3,115,320 residents, and
its metropolitan area stretches beyond the boundaries of the city wall for approximately 20 miles.
Founded by Greeks in the
first millennium
File:1st millennium montage.png, From top left, clockwise: Depiction of Jesus, the central figure in Christianity; The Colosseum, a landmark of the once-mighty Roman Empire; Kaaba, the Great Mosque of Mecca, the holiest site of Islam; Chess, a n ...
BC, Naples is one of the oldest continuously inhabited urban areas in the world. In the eighth century BC, a colony known as Parthenope ( grc, Παρθενόπη) was established on the Pizzofalcone hill. In the sixth century BC, it was refounded as Neápolis. The city was an important part of
Magna Graecia
Magna Graecia (, ; , , grc, Μεγάλη Ἑλλάς, ', it, Magna Grecia) was the name given by the Romans to the coastal areas of Southern Italy in the present-day Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania and Sicily; these re ...
, played a major role in the merging of Greek and Roman society, and was a significant cultural centre under the Romans.
Naples served as the capital of the
Duchy of Naples
The Duchy of Naples ( la, Ducatus Neapolitanus, it, Ducato di Napoli) began as a Byzantine province that was constituted in the seventh century, in the reduced coastal lands that the Lombards had not conquered during their invasion of Italy in ...
(661–1139), subsequently as the capital of the
Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was ...
(1282–1816), and finally as the capital of the
Kingdom of the Two Sicilies
The Kingdom of the Two Sicilies ( it, Regno delle Due Sicilie) was a kingdom in Southern Italy from 1816 to 1860. The kingdom was the largest sovereign state by population and size in Italy before Italian unification, comprising Sicily and a ...
— until the
unification of Italy
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century Political movement, political and social movement that resulted in the Merger (politics), consolidation of List of historic stat ...
in 1861. Naples is also considered a capital of the
Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
, beginning with the artist
Caravaggio
Michelangelo Merisi (Michele Angelo Merigi or Amerighi) da Caravaggio, known as simply Caravaggio (, , ; 29 September 1571 – 18 July 1610), was an Italian painter active in Rome for most of his artistic life. During the final four years of hi ...
's career in the 17th century and the artistic revolution he inspired. It was also an important centre of
humanism
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and agency of human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The meaning of the term "humani ...
and
Enlightenment
Enlightenment or enlighten may refer to:
Age of Enlightenment
* Age of Enlightenment, period in Western intellectual history from the late 17th to late 18th century, centered in France but also encompassing (alphabetically by country or culture): ...
. The city has long been a global point of reference for classical music and opera through the
Neapolitan School
In music history, the Neapolitan School is a group, associated with opera, of 17th and 18th-century composers who studied or worked in Naples, Italy,Don Michael Randel (2003). ''The Harvard Dictionary of Music'', p. 549. . the best known of whom is ...
. Between 1925 and 1936, Naples was expanded and upgraded by
Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in 194 ...
's government. During the later years of
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, it sustained
severe damage from Allied bombing as they invaded the peninsula. The city received extensive post-1945 reconstruction work.
Since the late 20th century, Naples has had significant economic growth, helped by the construction of the
Centro Direzionale business district and an advanced transportation network, which includes the
Alta Velocità high-speed rail link to Rome and
Salerno
Salerno (, , ; nap, label= Salernitano, Saliernë, ) is an ancient city and ''comune'' in Campania (southwestern Italy) and is the capital of the namesake province, being the second largest city in the region by number of inhabitants, after ...
and an expanded
subway network. Naples is the third-largest urban economy in Italy by
GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is often ...
, after
Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
and
Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
. The
Port of Naples
The Port of Naples, a port located on the Western coast of Italy, is the 11th largest seaport in Italy having an annual traffic capacity of around 25 million tons of cargo and 500,000 TEU's. It is also serves as a tourist hub, servicing an estima ...
is one of the most important in Europe. In addition to commercial activities, it is home to the
Allied Joint Force Command Naples
Allied Joint Force Command Naples (JFC Naples) is a NATO military command based in Lago Patria, in the Metropolitan City of Naples, Italy. It was activated on 15 March 2004, after effectively redesigning its predecessor command, Allied Forces Sou ...
, the NATO body that oversees
North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, the
Sahel
The Sahel (; ar, ساحل ' , "coast, shore") is a region in North Africa. It is defined as the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a hot semi-arid c ...
, and the Middle East.
Naples' historic city centre is the largest in Europe and has been designated as a UNESCO
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
. A wide range of culturally and historically significant sites are nearby, including the
Palace of Caserta
The Royal Palace of Caserta ( it, Reggia di Caserta ) is a former royal residence in Caserta, southern Italy, constructed by the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies as their main residence as kings of Naples. It is the largest palace erected in Europe ...
and the Roman ruins of
Pompeii
Pompeii (, ) was an ancient city located in what is now the ''comune'' of Pompei near Naples in the Campania region of Italy. Pompeii, along with Herculaneum and many villas in the surrounding area (e.g. at Boscoreale, Stabiae), was buried ...
and
Herculaneum
Herculaneum (; Neapolitan and it, Ercolano) was an ancient town, located in the modern-day ''comune'' of Ercolano, Campania, Italy. Herculaneum was buried under volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in AD 79.
Like the nea ...
. Naples is also known for its natural beauties, such as
Posillipo
Posillipo (; nap, Pusilleco ) is an affluent residential quarter of Naples, southern Italy, located along the northern coast of the Gulf of Naples.
From the 1st century BC the Bay of Naples witnessed the rise of villas constructed by elite Roma ...
,
Phlegraean Fields
The Phlegraean Fields ( it, Campi Flegrei ; nap, Campe Flegree, from Ancient Greek 'to burn') is a large region of supervolcanic calderas situated to the west of Naples, Italy. It was declared a regional park in 2003. The area of the calde ...
,
Nisida
Nisida is a volcanic islet of the Flegrean Islands archipelago, in southern Italy. It lies at a very short distance from Cape Posillipo, just north of Naples; it is now connected to the mainland by a stone bridge. The islet is almost circular, wit ...
and
Vesuvius
Mount Vesuvius ( ; it, Vesuvio ; nap, 'O Vesuvio , also or ; la, Vesuvius , also , or ) is a somma-stratovolcano located on the Gulf of Naples
The Gulf of Naples (), also called the Bay of Naples, is a roughly 15-kilometer-wide (9 ...
.
Neapolitan cuisine
Neapolitan cuisine has ancient historical roots that date back to the Greco-Roman period, which was enriched over the centuries by the influence of the different cultures that controlled Naples and its kingdoms, such as that of Aragon and France ...
is noted for its association with
pizza
Pizza (, ) is a dish of Italian origin consisting of a usually round, flat base of leavened wheat-based dough topped with tomatoes, cheese, and often various other ingredients (such as various types of sausage, anchovies, mushrooms, onions ...
, which originated in the city, as well as numerous other local dishes. Restaurants in the Naples' area have earned the most stars from the
Michelin Guide
The Michelin Guides ( ) are a series of guide books that have been published by the French tyre company Michelin since 1900. The Guide awards up to three Michelin star (classification), stars for excellence to a select few establishments. The ac ...
of any Italian province. Naples'
Centro Direzionale was built in 1994 as the first grouping of skyscrapers in Italy, remaining the only such grouping in Italy until 2009. The most widely-known sports team in Naples is the
Serie A
The Serie A (), also called Serie A TIM for national sponsorship with TIM, is a professional league competition for football clubs located at the top of the Italian football league system and the winner is awarded the Scudetto and the Coppa ...
football club
S.S.C. Napoli
Società Sportiva Calcio Napoli, commonly referred to as Napoli (), is an Italian professional football club based in the city of Naples ( it, Napoli, nap, Napule), Campania that plays in Serie A, the top flight of Italian football. Napoli ha ...
, two-time Italian champions who play at the
Stadio Diego Armando Maradona
Stadio Diego Armando Maradona (formerly known as Stadio San Paolo) is a stadium in the western Fuorigrotta suburb of Naples, Italy. It is the third largest football stadium in Italy, after Milan's San Siro and Rome's Stadio Olimpico, as well as ...
in the southwest of the city, in the
Fuorigrotta
Fuorigrotta ( nap, Forerotta; ) is a western suburb of Naples, southern Italy.
Covering an area of 6,2 km2, it is the most populated suburb of the city (population: 76.521).
Geography
It lies beyond the Posillipo hill and has been joined ...
quarter.
History
Greek birth and Roman acquisition




Naples has been inhabited since the
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
period. In the second millennium BC, a first Mycenaean settlement arose not far from the geographical position of the future city of Parthenope.
Sailors from the Greek island of
Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the So ...
established probably a small commercial port called
Parthenope (, meaning "Pure Eyes", a Siren in
Greek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical co ...
) on the
island of Megaride in the ninth century BC. By the eighth century BC, the settlement was expanded by Cumans, as evidenced by the archaeological findings, to include Monte Echia. In the sixth century BC the city was refounded as Neápolis (), eventually becoming one of the foremost cities of Magna Graecia.
The city grew rapidly due to the influence of the powerful Greek
city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
of
Syracuse
Syracuse may refer to:
Places Italy
*Syracuse, Sicily, or spelled as ''Siracusa''
*Province of Syracuse
United States
*Syracuse, New York
**East Syracuse, New York
**North Syracuse, New York
*Syracuse, Indiana
* Syracuse, Kansas
*Syracuse, Miss ...
,
and became an ally of the
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kin ...
against
Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classi ...
. During the
Samnite Wars
The First, Second, and Third Samnite Wars (343–341 BC, 326–304 BC, and 298–290 BC) were fought between the Roman Republic and the Samnites, who lived on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains south of Rome and north of the Lucanian tribe.
...
, the city, now a bustling centre of trade, was
captured by the
Samnites
The Samnites () were an ancient Italic people who lived in Samnium, which is located in modern inland Abruzzo, Molise, and Campania in south-central Italy.
An Oscan-speaking people, who may have originated as an offshoot of the Sabines, they for ...
; however, the Romans soon captured the city from them and made it a
Roman colony
A Roman (plural ) was originally a Roman outpost established in conquered territory to secure it. Eventually, however, the term came to denote the highest status of a Roman city. It is also the origin of the modern term ''colony''.
Characteri ...
.
During the
Punic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars between 264 and 146BC fought between Roman Republic, Rome and Ancient Carthage, Carthage. Three conflicts between these states took place on both land and sea across the western Mediterranean region and i ...
, the strong walls surrounding Neápolis repelled the invading forces of the Carthaginian general
Hannibal
Hannibal (; xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋, ''Ḥannibaʿl''; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Puni ...
.
The Romans greatly respected Naples as a paragon of
Hellenistic culture
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
. During the Roman era, the people of Naples maintained their
Greek language
Greek ( el, label=Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Al ...
and customs. At the same time, the city was expanded with elegant Roman
villa
A villa is a type of house that was originally an ancient Roman upper class country house. Since its origins in the Roman villa, the idea and function of a villa have evolved considerably. After the fall of the Roman Republic, villas became s ...
s,
aqueducts
Aqueduct may refer to:
Structures
*Aqueduct (bridge), a bridge to convey water over an obstacle, such as a ravine or valley
*Navigable aqueduct, or water bridge, a structure to carry navigable waterway canals over other rivers, valleys, railw ...
, and
public baths
Public baths originated when most people in population centers did not have access to private bathing facilities. Though termed "public", they have often been restricted according to gender, religious affiliation, personal membership, and other cr ...
. Landmarks such as the
Temple of Dioscures were built, and many emperors chose to holiday in the city, including
Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusu ...
and
Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
.
Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; traditional dates 15 October 7021 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: t ...
, the author of Rome's
national epic
A national epic is an epic poem or a literary work of epic scope which seeks or is believed to capture and express the essence or spirit of a particular nation—not necessarily a nation state, but at least an ethnic or linguistic group with as ...
, the ''
Aeneid
The ''Aeneid'' ( ; la, Aenē̆is or ) is a Latin Epic poetry, epic poem, written by Virgil between 29 and 19 BC, that tells the legendary story of Aeneas, a Troy, Trojan who fled the Trojan_War#Sack_of_Troy, fall of Troy and travelled to ...
'', received part of his education in the city, and later resided in its environs.
It was during this period that Christianity first arrived in Naples; the
apostles
An apostle (), in its literal sense, is an emissary, from Ancient Greek ἀπόστολος (''apóstolos''), literally "one who is sent off", from the verb ἀποστέλλειν (''apostéllein''), "to send off". The purpose of such sending ...
Peter
Peter may refer to:
People
* List of people named Peter, a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Peter (given name)
** Saint Peter (died 60s), apostle of Jesus, leader of the early Christian Church
* Peter (surname), a sur ...
and
Paul
Paul may refer to:
*Paul (given name), a given name (includes a list of people with that name)
*Paul (surname), a list of people
People
Christianity
*Paul the Apostle (AD c.5–c.64/65), also known as Saul of Tarsus or Saint Paul, early Chris ...
are said to have preached in the city.
Januarius
Januarius ( ; la, Ianuarius; Neapolitan and it, Gennaro), also known as , was Bishop of Benevento and is a martyr and saint of the Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church. While no contemporary sources on his life are preserved, later ...
, who would become Naples'
patron saint
A patron saint, patroness saint, patron hallow or heavenly protector is a saint who in Catholicism, Anglicanism, or Eastern Orthodoxy is regarded as the heavenly advocate of a nation, place, craft, activity, class, clan, family, or perso ...
, was martyred there in the fourth century AD.
The last emperor of the
Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
,
Romulus Augustulus
Romulus Augustus ( 465 – after 511), nicknamed Augustulus, was Roman emperor of the West from 31 October 475 until 4 September 476. Romulus was placed on the imperial throne by his father, the ''magister militum'' Orestes, and, at that time, ...
, was
exile
Exile is primarily penal expulsion from one's native country, and secondarily expatriation or prolonged absence from one's homeland under either the compulsion of circumstance or the rigors of some high purpose. Usually persons and peoples suf ...
d to Naples by the Germanic king
Odoacer
Odoacer ( ; – 15 March 493 AD), also spelled Odovacer or Odovacar, was a soldier and statesman of barbarian background, who deposed the child emperor Romulus Augustulus and became Rex/Dux (476–493). Odoacer's overthrow of Romulus Augustul ...
in the fifth century AD.
Duchy of Naples

Following the decline of the
Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period fr ...
, Naples was captured by the
Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the larg ...
, a
Germanic people
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
, and incorporated into the
Ostrogothic Kingdom
The Ostrogothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of Italy (), existed under the control of the Germanic peoples, Germanic Ostrogoths in Italian peninsula, Italy and neighbouring areas from 493 to 553.
In Italy, the Ostrogoths led by Theodoric the ...
.
However,
Belisarius
Belisarius (; el, Βελισάριος; The exact date of his birth is unknown. – 565) was a military commander of the Byzantine Empire under the emperor Justinian I. He was instrumental in the reconquest of much of the Mediterranean terri ...
of the
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
recaptured Naples in 536, after entering the city via an aqueduct.
In 543, during the
Gothic Wars
The Gothic Wars were a long series of conflicts between the Goths and the Roman Empire between the years 249 and 554. The main wars are detailed below.
Gothic War (249–253)
(Goths under Cniva against the Roman Empire)
The War was probably in ...
,
Totila
Totila, original name Baduila (died 1 July 552), was the penultimate King of the Ostrogoths, reigning from 541 to 552 AD. A skilled military and political leader, Totila reversed the tide of the Gothic War, recovering by 543 almost all the t ...
briefly took the city for the Ostrogoths, but the Byzantines seized control of the area following the
Battle of Mons Lactarius
The Battle of Mons Lactarius (also known as Battle of the Vesuvius) took place in 552 or 553 AD during the Gothic War (535–552), Gothic War waged on behalf of Justinian I against the Ostrogoths in Italy.
After the Battle of Taginae, in which t ...
on the slopes of
Vesuvius
Mount Vesuvius ( ; it, Vesuvio ; nap, 'O Vesuvio , also or ; la, Vesuvius , also , or ) is a somma-stratovolcano located on the Gulf of Naples
The Gulf of Naples (), also called the Bay of Naples, is a roughly 15-kilometer-wide (9 ...
.
Naples was expected to keep in contact with the
Exarchate of Ravenna
The Exarchate of Ravenna ( la, Exarchatus Ravennatis; el, Εξαρχάτο της Ραβέννας) or of Italy was a lordship of the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire) in Italy, from 584 to 751, when the last exarch was put to death by the ...
, which was the centre of Byzantine power on the
Italian Peninsula.
After the
exarch
An exarch (;
from Ancient Greek ἔξαρχος ''exarchos'', meaning “leader”) was the holder of any of various historical offices, some of them being political or military and others being ecclesiastical.
In the late Roman Empire and ea ...
ate fell, a
Duchy of Naples
The Duchy of Naples ( la, Ducatus Neapolitanus, it, Ducato di Napoli) began as a Byzantine province that was constituted in the seventh century, in the reduced coastal lands that the Lombards had not conquered during their invasion of Italy in ...
was created. Although Naples'
Greco-Roman
The Greco-Roman civilization (; also Greco-Roman culture; spelled Graeco-Roman in the Commonwealth), as understood by modern scholars and writers, includes the geographical regions and countries that culturally—and so historically—were di ...
culture endured, it eventually switched allegiance from
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
to Rome under Duke
Stephen II, putting it under
papal
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
suzerainty
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is cal ...
by 763.
The years between 818 and 832 saw tumultuous relations with the
Byzantine Emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as le ...
, with numerous local pretenders feuding for possession of the ducal throne.
was appointed without imperial approval; his appointment was later revoked and
Theodore II took his place. However, the disgruntled general populace chased him from the city and elected
Stephen III instead, a man who minted coins with his initials rather than those of the Byzantine Emperor. Naples gained complete independence by the early ninth century.
Naples allied with the Muslim
Saracens
file:Erhard Reuwich Sarazenen 1486.png, upright 1.5, Late 15th-century Germany in the Middle Ages, German woodcut depicting Saracens
Saracen ( ) was a term used in the early centuries, both in Greek language, Greek and Latin writings, to refer ...
in 836 and asked for their support to repel the siege of
Lombard troops coming from the neighbouring
Duchy of Benevento
The Duchy of Benevento (after 774, Principality of Benevento) was the southernmost Lombard duchy in the Italian Peninsula that was centred on Benevento, a city in Southern Italy. Lombard dukes ruled Benevento from 571 to 1077, when it was conq ...
. However, during the 850s,
Muhammad I Abu 'l-Abbas
Abu'l-Abbas Muhammad I ibn al-Aghlab () (died 856) was the fifth emir of the Aghlabids, Aghlabid dynasty, who ruled over Ifriqiya, Islam in Malta, Malta, and most of Sicily from 841 until his death. He also led the Arab raid against Rome, raid o ...
led the Arab-
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
to sack the city.
The duchy was under the direct control of the
Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 and ...
for a brief period after the capture by
Pandulf IV of the
Principality of Capua
The Principality of Capua ( la, italic=yes, Principatus Capuae or ''Capue'', it, italic=yes, Principato di Capua) was a Lombard state centred on Capua in Southern Italy, usually ''de facto'' independent, but under the varying suzerainty of Ho ...
, a long-term rival of Naples; however, this regime lasted only three years before the Greco-Roman-influenced dukes were reinstated.
By the 11th century, Naples had begun to employ
Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
mercenaries to battle their rivals; Duke
Sergius IV
Pope Sergius IV (died 12 May 1012) was the bishop of Rome and nominal ruler of the Papal States from 31 July 1009 to his death. His temporal power was eclipsed by the patrician John Crescentius. Sergius IV may have called for the expulsion of Mu ...
hired
Rainulf Drengot Rainulf Drengot (also Ranulph, Ranulf, or Rannulf; died June 1045) was a Norman adventurer and mercenary in southern Italy. In 1030 he became the first count of Aversa. He was a member of the Drengot family.
Early life and arrival in Italy
When Ra ...
to wage war on Capua for him.
By 1137, the Normans had attained great influence in Italy, controlling previously independent principalities and duchies such as
Capua
Capua ( , ) is a city and ''comune'' in the province of Caserta, in the region of Campania, southern Italy, situated north of Naples, on the northeastern edge of the Campanian plain.
History
Ancient era
The name of Capua comes from the Etrusc ...
,
Benevento
Benevento (, , ; la, Beneventum) is a city and ''comune'' of Campania, Italy, capital of the province of Benevento, northeast of Naples. It is situated on a hill above sea level at the confluence of the Calore Irpino (or Beneventano) and the ...
,
Salerno
Salerno (, , ; nap, label= Salernitano, Saliernë, ) is an ancient city and ''comune'' in Campania (southwestern Italy) and is the capital of the namesake province, being the second largest city in the region by number of inhabitants, after ...
,
Amalfi
Amalfi (, , ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Salerno, in the region of Campania, Italy, on the Gulf of Salerno. It lies at the mouth of a deep ravine, at the foot of Monte Cerreto (1,315 metres, 4,314 feet), surrounded by dramatic c ...
,
Sorrento
Sorrento (, ; nap, Surriento ; la, Surrentum) is a town overlooking the Bay of Naples in Southern Italy. A popular tourist destination, Sorrento is located on the Sorrentine Peninsula at the south-eastern terminus of the Circumvesuviana rail ...
and
Gaeta
Gaeta (; lat, Cāiēta; Southern Laziale: ''Gaieta'') is a city in the province of Latina, in Lazio, Southern Italy. Set on a promontory stretching towards the Gulf of Gaeta, it is from Rome and from Naples.
The town has played a consp ...
; it was in this year that Naples, the last independent duchy in the southern part of the peninsula, came under Norman control. The last ruling duke of the duchy,
Sergius VII
Sergius VII (died 30 October 1137) was the thirty-ninth and last duke
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, ...
, was forced to surrender to
Roger II
Roger II ( it, Ruggero II; 22 December 1095 – 26 February 1154) was King of Sicily and Africa, son of Roger I of Sicily and successor to his brother Simon. He began his rule as Count of Sicily in 1105, became Duke of Apulia and Calabria in ...
, who had been proclaimed
King of Sicily
The monarchs of Sicily ruled from the establishment of the County of Sicily in 1071 until the "perfect fusion" in the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies in 1816.
The origins of the Sicilian monarchy lie in the Norman conquest of southern Italy which occ ...
by
Antipope Anacletus II
Anacletus II (died January 25, 1138), born Pietro Pierleoni, was an antipope who ruled in opposition to Pope Innocent II from 1130 until his death in 1138. After the death of Pope Honorius II, the college of cardinals was divided over his succ ...
seven years earlier. Naples thus joined the
Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily ( la, Regnum Siciliae; it, Regno di Sicilia; scn, Regnu di Sicilia) was a state that existed in the south of the Italian Peninsula and for a time the region of Ifriqiya from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 un ...
, with
Palermo
Palermo ( , ; scn, Palermu , locally also or ) is a city in southern Italy, the capital (political), capital of both the autonomous area, autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan ...
as the capital.
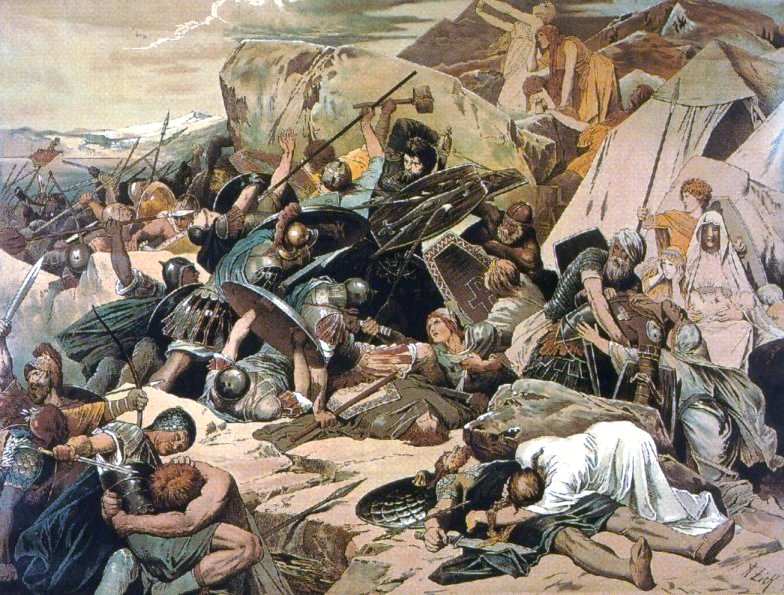
As part of the Kingdom of Sicily

After a period of Norman rule, in 1189 the
Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily ( la, Regnum Siciliae; it, Regno di Sicilia; scn, Regnu di Sicilia) was a state that existed in the south of the Italian Peninsula and for a time the region of Ifriqiya from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 un ...
was in a succession dispute between
Tancred, King of Sicily
Tancred ( it, Tancredi; 113820 February 1194) was King of Sicily from 1189 to 1194. He was born in Lecce an illegitimate son of Roger III, Duke of Apulia (the eldest son of King Roger II) by his mistress Emma, a daughter of Achard II, Count of ...
of an illegitimate birth and the
Hohenstaufens
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynasty ...
, a Germanic
royal house
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family,''Oxford English Dictionary'', "dynasty, ''n''." Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1897. usually in the context of a monarchy, monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in repu ...
, as its Prince Henry had married
Princess Constance the last legitimate heir to the Sicilian throne. In 1191 Henry invaded Sicily after being crowned as
Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor
Henry VI (German: ''Heinrich VI.''; November 1165 – 28 September 1197), a member of the Hohenstaufen dynasty, was King of Germany ( King of the Romans) from 1169 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1191 until his death. From 1194 he was also King of S ...
, and many cities surrendered. Still, Naples resisted him from May to August under the leadership of
Richard, Count of Acerra
Richard, count of Acerra (died 30 November 1196) was an Italo-Norman nobleman, grandson of Robert of Medania, a Frenchman of Anjou. Brother of Sibylla, queen of Tancred of Sicily, Richard was the chief peninsular supporter of his brother-in-law du ...
,
Nicholas of Ajello Nicholas of AjelloHe was not a native of Ajello ( Calabria), but Salerno. His elder brother, Richard, received the county of Ajello from King Tancred and the name has been applied to the entire family. ( it, Nicolò d'Aiello; died 10 February 122 ...
,
Aligerno Cottone and
Margaritus of Brindisi
Margaritus of Brindisi (also Margarito; Italian ''Margaritone'' or Greek ''Megareites'' or ''Margaritoni'' �αργαριτώνη c. 1149 – 1197), called "the new Neptune", was the last great '' ammiratus ammiratorum'' (Grand Admiral) of Sic ...
before the Germans suffered from disease and were forced to retreat.
Conrad II, Duke of Bohemia
Conrad II Otto (; /1140 – 9 September 1191), a member of Přemyslid dynasty, was the first margrave of Moravia from 1182 to 1189 and duke of Bohemia from 1189 until his death.
Family history
Conrad was the son of count Conrad II of Znojmo ...
and
Philip I, Archbishop of Cologne
Philip I () (c. 1130 – 13 August 1191) was the Archbishop of Cologne and Archchancellor of Italy from 1167 to 1191.
He was the son of Count Goswin II of Heinsberg and Adelaide of Sommerschenburg. He received his ecclesiastic training in Cologne ...
died of disease during
the siege
''The Siege'' is a 1998 American action thriller film directed by Edward Zwick. The film is about a fictional situation in which terrorist cells have made several attacks in New York City. The film stars Denzel Washington, Annette Bening, Tony ...
. During his counterattack, Tancred captured Constance, now empress. He had the empress imprisoned at
Castel dell'Ovo
Castel dell'Ovo ("Egg Castle") is a seafront castle in Naples, located on the former island of Megaride, now a peninsula, on the Gulf of Naples in Italy. The castle's name comes from a legend about the Roman poet Virgil, who had a reputation in ...
at Naples before her release on May 1192 under the pressure of
Pope Celestine III
Pope Celestine III ( la, Caelestinus III; c. 1106 – 8 January 1198), was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 30 March or 10 April 1191 to his death in 1198. He had a tense relationship with several monarchs, ...
. In 1194 Henry started his second campaign upon the death of Tancred, but this time Aligerno surrendered without resistance, and finally, Henry conquered Sicily, putting it under the rule of Hohenstaufens.
The
University of Naples
The University of Naples Federico II ( it, Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II) is a public university in Naples, Italy. Founded in 1224, it is the oldest public non-sectarian university in the world, and is now organized into 26 depar ...
, the first university in Europe dedicated to training secular administrators, was founded by
Frederick II, making Naples the intellectual centre of the kingdom. Conflict between the Hohenstaufens and the
Papacy
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
led in 1266 to
Pope Innocent IV
Pope Innocent IV ( la, Innocentius IV; – 7 December 1254), born Sinibaldo Fieschi, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 25 June 1243 to his death in 1254.
Fieschi was born in Genoa and studied at the universitie ...
crowning the
Angevin
Angevin or House of Anjou may refer to:
*County of Anjou or Duchy of Anjou, a historical county, and later Duchy, in France
** Angevin (language), the traditional langue d'oïl spoken in Anjou
**Counts and Dukes of Anjou
*House of Ingelger, a Frank ...
duke
Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
King of Sicily:
Charles officially moved the capital from Palermo to Naples, where he resided at the
Castel Nuovo
Castel Nuovo (; "New Castle"), often called Maschio Angioino (; "Angevin Keep"), is a medieval castle located in front of Piazza Municipio and the city hall ( Palazzo San Giacomo) in central Naples, Campania, Italy. Its scenic location and impo ...
. Having a great interest in architecture, Charles I imported French architects and workmen and was personally involved in several building projects in the city. Many examples of
Gothic architecture
Gothic architecture (or pointed architecture) is an architectural style that was prevalent in Europe from the late 12th to the 16th century, during the High and Late Middle Ages, surviving into the 17th and 18th centuries in some areas. It e ...
sprang up around Naples, including the
Naples Cathedral
The Naples Cathedral ( it, Duomo di Napoli; nap, Viscuvato 'e Napule), or Cathedral of the Assumption of Mary ( it, Cattedrale di Santa Maria Assunta, links=no), is a Roman Catholic cathedral, the main church of Naples, southern Italy, and the s ...
, which remains the city's main church.
Kingdom of Naples

In 1282, after the
Sicilian Vespers
The Sicilian Vespers ( it, Vespri siciliani; scn, Vespiri siciliani) was a successful rebellion on the island of Sicily that broke out at Easter 1282 against the rule of the French-born king Charles I of Anjou, who had ruled the Kingdom of S ...
, the Kingdom of Sicily was divided into two. The Angevin
Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was ...
included the southern part of the Italian peninsula, while the island of
Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
became the
Aragonese Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily ( la, Regnum Siciliae; it, Regno di Sicilia; scn, Regnu di Sicilia) was a state that existed in the south of the Italian Peninsula and for a time the region of Ifriqiya from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 un ...
.
Wars between the competing dynasties continued until the
Peace of Caltabellotta
The Peace of Caltabellotta, signed on 31 August 1302, was the last of a series of treaties, including those of Tarascon and Anagni, designed to end the conflict between the Houses of Anjou and Barcelona for ascendancy in the Mediterranean and espec ...
in 1302, which saw
Frederick III recognised as king of Sicily, while
Charles II was recognised as king of Naples by
Pope Boniface VIII
Pope Boniface VIII ( la, Bonifatius PP. VIII; born Benedetto Caetani, c. 1230 – 11 October 1303) was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 24 December 1294 to his death in 1303. The Caetani, Caetani family was of b ...
.
Despite the split, Naples grew in importance, attracting
Pisan
Pisa ( , or ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, central Italy, straddling the Arno just before it empties into the Ligurian Sea. It is the capital city of the Province of Pisa. Although Pisa is known worldwide for its leaning tower, the cit ...
and
Genoese merchants,
Tuscan bankers, and some of the most prominent
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
artists of the time, such as
Boccaccio
Giovanni Boccaccio (, , ; 16 June 1313 – 21 December 1375) was an Italian people, Italian writer, poet, correspondent of Petrarch, and an important Renaissance humanism, Renaissance humanist. Born in the town of Certaldo, he became so we ...
,
Petrarch
Francesco Petrarca (; 20 July 1304 – 18/19 July 1374), commonly anglicized as Petrarch (), was a scholar and poet of early Renaissance Italy, and one of the earliest humanists.
Petrarch's rediscovery of Cicero's letters is often credited w ...
and
Giotto
Giotto di Bondone (; – January 8, 1337), known mononymously as Giotto ( , ) and Latinised as Giottus, was an Italian painter and architect from Florence during the Late Middle Ages. He worked during the Gothic/Proto-Renaissance period. Giot ...
. During the 14th century, the
Hungarian Angevin king
Louis the Great
Louis I, also Louis the Great ( hu, Nagy Lajos; hr, Ludovik Veliki; sk, Ľudovít Veľký) or Louis the Hungarian ( pl, Ludwik Węgierski; 5 March 132610 September 1382), was King of Hungary and Croatia from 1342 and King of Poland from 1370. ...
captured the city several times. In 1442,
Alfonso I conquered Naples after his victory against the last
Angevin
Angevin or House of Anjou may refer to:
*County of Anjou or Duchy of Anjou, a historical county, and later Duchy, in France
** Angevin (language), the traditional langue d'oïl spoken in Anjou
**Counts and Dukes of Anjou
*House of Ingelger, a Frank ...
king,
René
René (''born again'' or ''reborn'' in French) is a common first name in French-speaking, Spanish-speaking, and German-speaking countries. It derives from the Latin name Renatus.
René is the masculine form of the name (Renée being the feminine ...
, and Naples was unified with Sicily again for a brief period.
Aragonese and Spanish
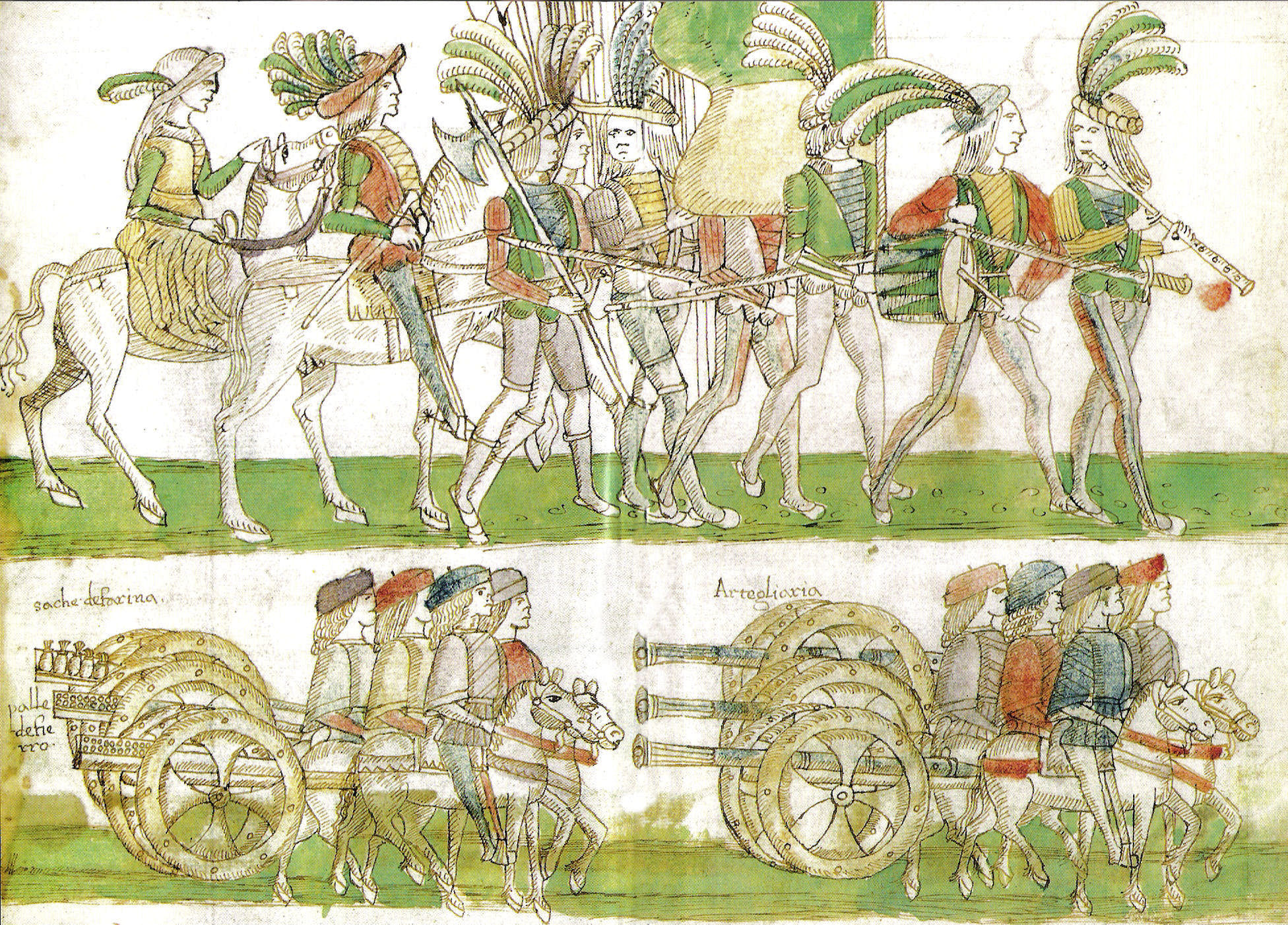

Sicily and Naples were separated since 1282, but remained dependencies of
Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to sou ...
under
Ferdinand I. The new dynasty enhanced Naples' commercial standing by establishing relations with the
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
. Naples also became a centre of the Renaissance, with artists such as
Laurana,
da Messina,
Sannazzaro
Jacopo Sannazaro (; 28 July 1458 – 6 August 1530) was an Italian poet, humanist and epigrammist from Naples.
He wrote easily in Latin, in Italian and in Neapolitan, but is best remembered for his humanist classic '' Arcadia'', a masterwork ...
and
Poliziano
Agnolo (Angelo) Ambrogini (14 July 1454 – 24 September 1494), commonly known by his nickname Poliziano (; anglicized as Politian; Latin: '' Politianus''), was an Italian classical scholar and poet of the Florentine Renaissance. His scho ...
arriving in the city. In 1501, Naples came under direct rule from
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
under
Louis XII
Louis XII (27 June 14621 January 1515), was King of France from 1498 to 1515 and King of Naples from 1501 to 1504. The son of Charles, Duke of Orléans, and Maria of Cleves, he succeeded his 2nd cousin once removed and brother in law at the tim ...
, with the Neapolitan king
Frederick Frederick may refer to:
People
* Frederick (given name), the name
Nobility
Anhalt-Harzgerode
*Frederick, Prince of Anhalt-Harzgerode (1613–1670)
Austria
* Frederick I, Duke of Austria (Babenberg), Duke of Austria from 1195 to 1198
* Frederi ...
being taken as a prisoner to France; however, this state of affairs did not last long, as Spain won Naples from the French at the
Battle of Garigliano
The Battle of Garigliano was fought in 915 between Christian forces and the Saracens. Pope John X personally led the Christian forces into battle. The aim was to destroy the Arab fortress on the Garigliano River, which had threatened central Ital ...
in 1503.

Following the Spanish victory, Naples became part of the
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
, and remained so throughout the
Spanish Habsburg
Habsburg Spain is a contemporary historiographical term referring to the huge extent of territories (including modern-day Spain, a piece of south-east France, eventually Portugal, and many other lands outside of the Iberian Peninsula) ruled be ...
period.
The Spanish sent
viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the French word ''roy'', meaning "k ...
s
to Naples to directly deal with local issues: the most important of these viceroys was
Pedro Álvarez de Toledo
Pedro is a masculine given name. Pedro is the Spanish, Portuguese, and Galician name for ''Peter''. Its French equivalent is Pierre while its English and Germanic form is Peter.
The counterpart patronymic surname of the name Pedro, meaning " ...
, who was responsible for considerable social, economic and urban reforms in the city; he also tried to introduce the
Inquisition
The Inquisition was a group of institutions within the Catholic Church whose aim was to combat heresy, conducting trials of suspected heretics. Studies of the records have found that the overwhelming majority of sentences consisted of penances, ...
. In 1544, around 7,000 people were taken as
slaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
by
Barbary pirates
The Barbary pirates, or Barbary corsairs or Ottoman corsairs, were Muslim pirates and privateers who operated from North Africa, based primarily in the ports of Salé, Rabat, Algiers, Tunis and Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli. This area was known i ...
and brought to the
Barbary Coast of North Africa (see
Sack of Naples
The sack of Naples occurred in 1544 when Algerians captured the Bay of Naples and enslaved 7,000 Italians.
In 1544 Algerian corsairs sailed into the Bay of Naples and captured it. They then took an astounding amount of 7,000 Italian slaves.
Th ...
).
By the 17th century, Naples had become Europe's second-largest city – second only to Paris – and the largest European Mediterranean city, with around 250,000 inhabitants. The city was a major cultural centre during the
Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
era, being home to artists such as
Caravaggio
Michelangelo Merisi (Michele Angelo Merigi or Amerighi) da Caravaggio, known as simply Caravaggio (, , ; 29 September 1571 – 18 July 1610), was an Italian painter active in Rome for most of his artistic life. During the final four years of hi ...
,
Salvator Rosa
Salvator Rosa (1615 –1673) is best known today as an Italian Baroque painter, whose romanticized landscapes and history paintings, often set in dark and untamed nature, exerted considerable influence from the 17th century into the early 19th ...
and
Bernini
Gian Lorenzo (or Gianlorenzo) Bernini (, , ; Italian Giovanni Lorenzo; 7 December 159828 November 1680) was an Italian sculptor and architect. While a major figure in the world of architecture, he was more prominently the leading sculptor of his ...
, philosophers such as
Bernardino Telesio
Bernardino Telesio (; 7 November 1509 – 2 October 1588) was an Italian philosopher and natural scientist. While his natural theories were later disproven, his emphasis on observation made him the "first of the moderns" who eventually devel ...
,
Giordano Bruno
Giordano Bruno (; ; la, Iordanus Brunus Nolanus; born Filippo Bruno, January or February 1548 – 17 February 1600) was an Italian philosopher, mathematician, poet, cosmological theorist, and Hermetic occultist. He is known for his cosmologic ...
,
Tommaso Campanella
Tommaso Campanella (; 5 September 1568 – 21 May 1639), baptized Giovanni Domenico Campanella, was an Italian Dominican friar, philosopher, theologian, astrologer, and poet.
He was prosecuted by the Roman Inquisition for heresy in 1594 and w ...
and
Giambattista Vico
Giambattista Vico (born Giovan Battista Vico ; ; 23 June 1668 – 23 January 1744) was an Italian philosopher, rhetorician, historian, and jurist during the Italian Enlightenment. He criticized the expansion and development of modern rationali ...
, and writers such as
Giambattista Marino
Giovanni Battista was a common Italian given name (see Battista for those with the surname) in the 16th-18th centuries. It refers to "John the Baptist" in English, the French equivalent is "Jean-Baptiste". Common nicknames include Giambattista, Gia ...
. A revolution led by the local fisherman
Masaniello
Masaniello (, ; an abbreviation of Tommaso Aniello; 29 June 1620 – 16 July 1647) was an Italian fisherman who became leader of the 1647 revolt against the rule of Habsburg Spain in the Kingdom of Naples.
Name and place of birth
Until recent ...
saw the creation of a brief independent
Neapolitan Republic in 1647. However, this lasted only a few months before Spanish rule was reasserted.
In 1656, an outbreak of
bubonic plague
Bubonic plague is one of three types of plague caused by the plague bacterium (''Yersinia pestis''). One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and vomiting, as well a ...
killed about half of Naples' 300,000 inhabitants.

In 1714, Spanish rule over Naples came to an end as a result of the
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phil ...
; the Austrian
Charles VI ruled the city from
Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
through viceroys of his own. However, the
War of the Polish Succession
The War of the Polish Succession ( pl, Wojna o sukcesję polską; 1733–35) was a major European conflict sparked by a Polish civil war over the succession to Augustus II of Poland, which the other regional power, European powers widened in p ...
saw the Spanish regain Sicily and Naples as part of a personal union, with the 1738 Treaty of Vienna (1738), Treaty of Vienna recognising the two polities as independent under a cadet branch of the Spanish House of Bourbon, Bourbons.
In 1755, the Duke of Noja commissioned an accurate topographic map of Naples, later known as the Map of the Duke of Nojo, employing rigorous surveying accuracy and becoming an essential urban planning tool for Naples.
During the time of Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies, Ferdinand IV, the effects of the French Revolution were felt in Naples: Horatio Nelson, 1st Viscount Nelson, Horatio Nelson, an ally of the Bourbons, arrived in the city in 1798 to warn against the French republicans. Ferdinand was forced to retreat and fled to
Palermo
Palermo ( , ; scn, Palermu , locally also or ) is a city in southern Italy, the capital (political), capital of both the autonomous area, autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan ...
, where he was protected by a Royal Navy, British fleet.
However, Naples' Social class, lower class ''Naples Lazzaroni, lazzaroni'' were strongly Piety, pious and Monarchism, royalist, favouring the Bourbons; in the mêlée that followed, they fought the Neapolitan pro-Italy, Republican aristocracy, causing a civil war.
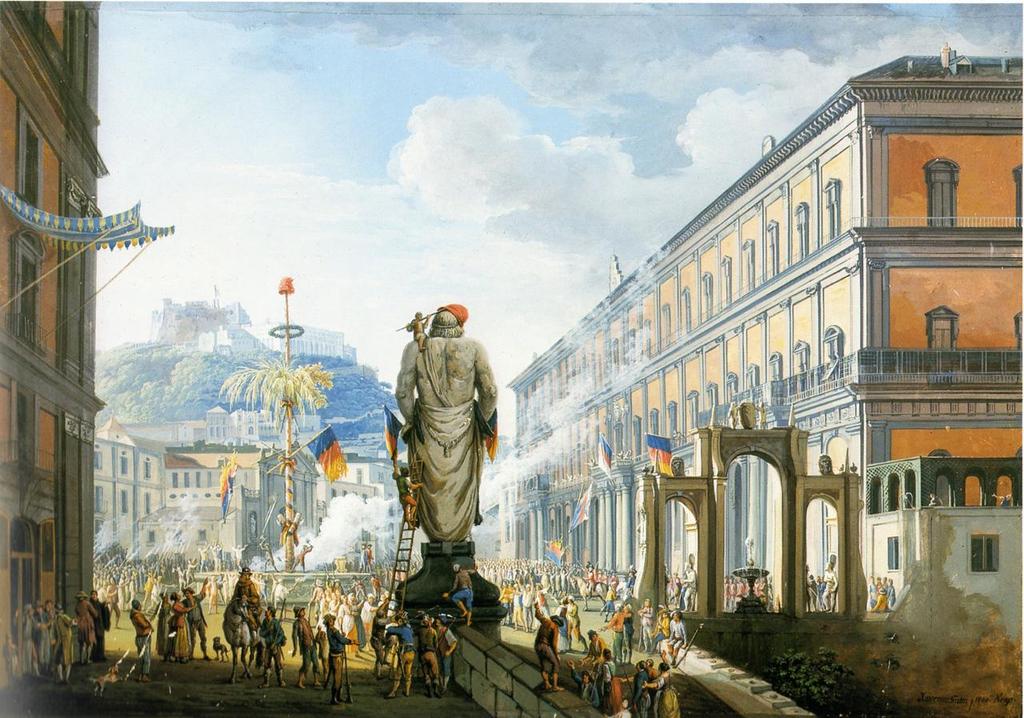

Eventually, the Republicans conquered Castel Sant'Elmo and proclaimed a Parthenopaean Republic, secured by the French Army.
A counter-revolutionary religious army of ''lazzaroni'' known as the ''sanfedismo, sanfedisti'' under Cardinal Fabrizio Ruffo was raised; they met with great success, and the French were forced to surrender the Neapolitan castles, with their fleet sailing back to Toulon.
Ferdinand IV was restored as king; however, after only seven years, Napoleon I of France, Napoleon conquered the kingdom and installed House of Bonaparte, Bonapartist kings, including his brother Joseph Bonaparte (King of Spain).
With the help of the Austrian Empire and its allies, the Bonapartists were defeated in the Neapolitan War. Ferdinand IV once again regained the throne and the kingdom.
Independent Two Sicilies
The Congress of Vienna in 1815 saw the kingdoms of Naples and Sicily combine to form the
Kingdom of the Two Sicilies
The Kingdom of the Two Sicilies ( it, Regno delle Due Sicilie) was a kingdom in Southern Italy from 1816 to 1860. The kingdom was the largest sovereign state by population and size in Italy before Italian unification, comprising Sicily and a ...
,
with Naples as the capital city. In 1839, Naples became the first city on the Italian peninsula to have a railway, with the construction of the Naples–Portici railway line, Naples–Portici railway.
Italian unification to the present day
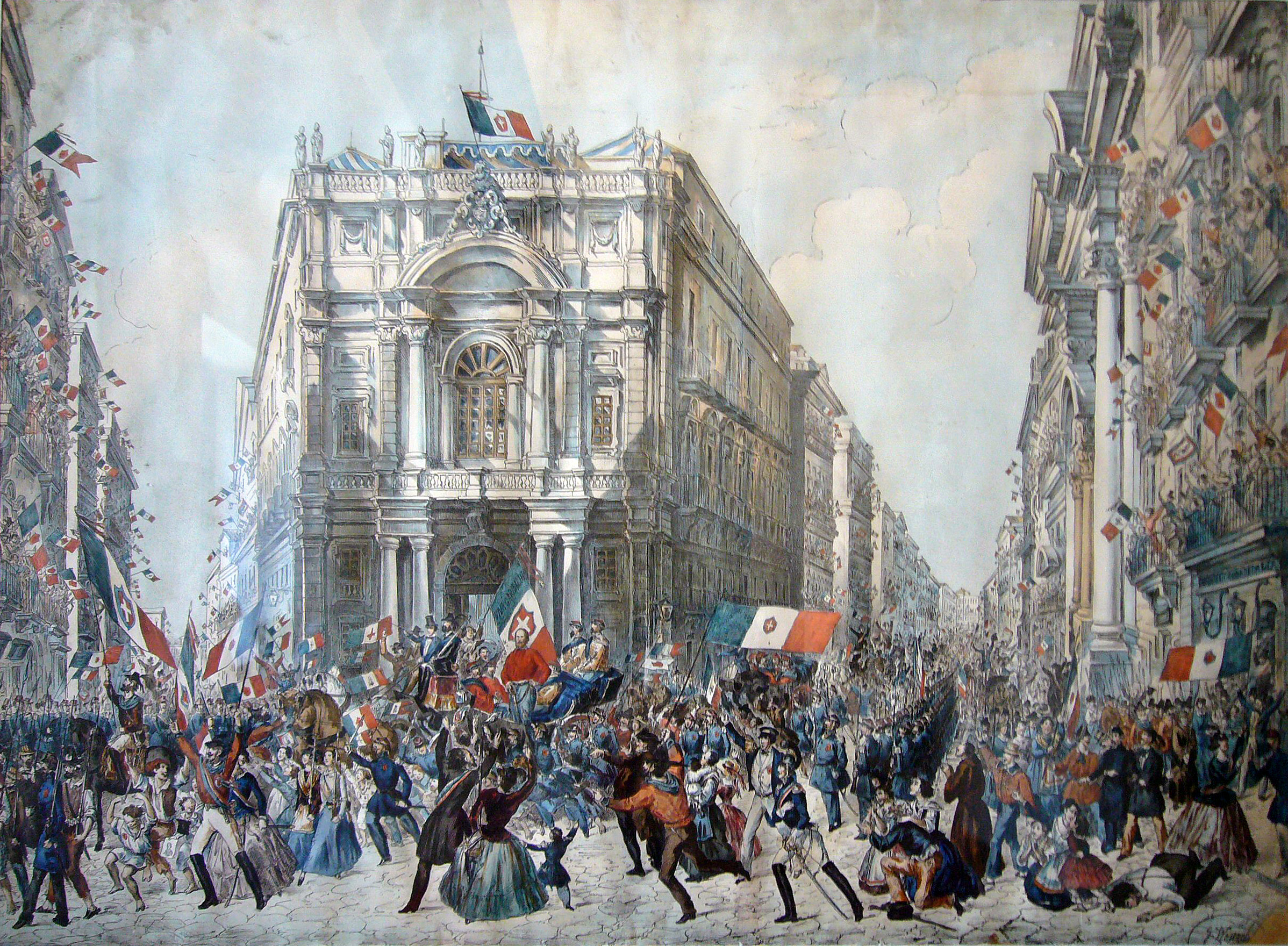

After the Expedition of the Thousand led by Giuseppe Garibaldi, which culminated in the controversial Siege of Gaeta (1860), Siege of Gaeta, Naples became part of the Kingdom of Italy in 1861 as part of the Italian unification, ending the era of Bourbon rule. The economy of the area formerly known as the Two Sicilies declined, leading to an unprecedented Italian diaspora, wave of emigration,
with an estimated 4 million people emigrating from the Naples area between 1876 and 1913. In the forty years following unification, the population of Naples grew by only 26%, vs. 63% for Turin and 103% for Milan; however, by 1884, Naples was still the largest city in Italy with 496,499 inhabitants, or roughly 64,000 per square kilometre (more than twice the population density of Paris).
Public health conditions in certain areas of the city were poor, with twelve epidemics of cholera and typhoid fever claiming some 48,000 people between 1834 and 1884. A death rate 31.84 per thousand, high even for the time, insisted in the absence of epidemics between 1878 and 1883. Then in 1884, Naples fell victim to a major cholera epidemic, caused largely by the city's poor sewerage infrastructure. In response to these problems, in 1852, the government prompted a radical transformation of the city called ''risanamento'' to improve the sewerage infrastructure and replace the most clustered areas, considered the main cause of insalubrity, with large and airy avenues. The project proved difficult to accomplish politically and economically due to corruption, as shown in the Saredo Inquiry, land speculation and extremely long bureaucracy. This led to the project to massive delays with contrasting results. The most notable transformations made were the construction of Via Caracciolo in place of the beach along the promenade, the creation of Galleria Umberto I and c:Galleria Principe di Napoli (Naples), Galleria Principe and the construction of Corso Umberto.
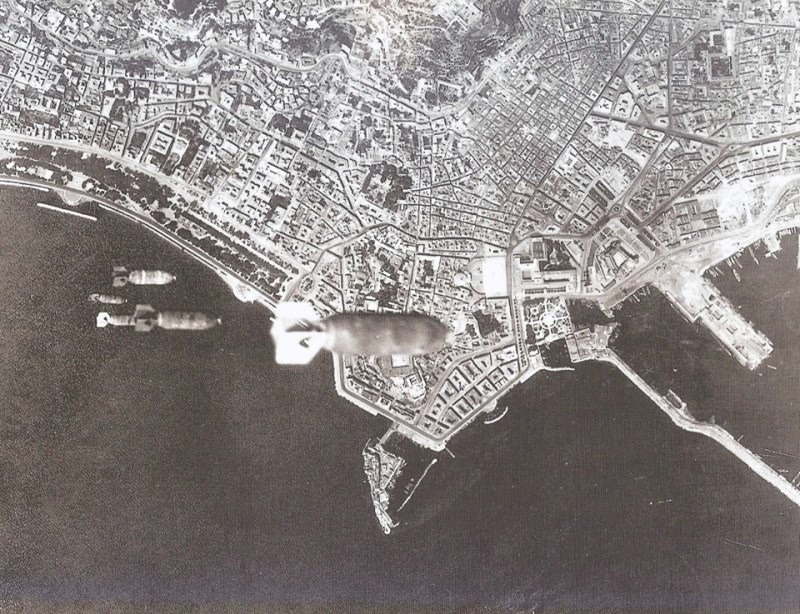

Naples was the Bombing of Naples in World War II, most-bombed Italian city during
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
.
Though Neapolitans did not rebel under Italian Fascism, Naples was the first Italian city to Four days of Naples, rise up against Nazi Germany, German military occupation; the city was completely freed by 1 October 1943, when British and American forces entered the city. Departing Germans Book burning, burned the library of University of Naples Federico II, the university, as well as the Italian Royal Society. They also destroyed the city archives. Time bombs planted throughout the city continued to explode into November. The symbol of the rebirth of Naples was the rebuilding of the church of Santa Chiara (Naples), Santa Chiara, which had been destroyed in a United States Air Force, United States Army Air Corps bombing raid.
Special funding from the Italian government's Cassa per il Mezzogiorno, Fund for the South was provided from 1950 to 1984, helping the Neapolitan economy to improve somewhat, with city landmarks such as the Piazza del Plebiscito being renovated. However, high unemployment continues to affect Naples.
Italian media attributed the past city's Naples waste management issue, waste disposal issues to the activity of the Camorra organised crime network. Due to this event, environmental contamination and increased health risks are also prevalent.
In 2007, Silvio Berlusconi's government held senior meetings in Naples to demonstrate their intention to solve these problems. However, the late-2000s recession had a severe impact on the city, intensifying its waste-management and unemployment problems. By August 2011, the number of unemployed in the Naples area had risen to 250,000, sparking public protests against the economic situation. In June 2012, allegations of blackmail, extortion, and illicit contract tendering emerged concerning the city's waste management issues.
["Cricca veneta sui rifiuti di Napoli: arrestati i fratelli Gavioli" (in Italian)]
. ''Il Mattino''. 20 June 2012. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
. ''Il Mattino di Padova''. 21 June 2012. Retrieved 14 July 2012.
Naples hosted the sixth World Urban Forum in September 2012 and the 63rd International Astronautical Congress in October 2012. In 2013, it was the host of the Universal Forum of Cultures and the host for the 2019 Summer Universiade.
Architecture
UNESCO World Heritage Site

Naples' 2,800-year history has left it with a wealth of historical buildings and monuments, from medieval castles to classical ruins, and a wide range of culturally and historically significant sites nearby, including the
Palace of Caserta
The Royal Palace of Caserta ( it, Reggia di Caserta ) is a former royal residence in Caserta, southern Italy, constructed by the House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies as their main residence as kings of Naples. It is the largest palace erected in Europe ...
and the Roman ruins of
Pompeii
Pompeii (, ) was an ancient city located in what is now the ''comune'' of Pompei near Naples in the Campania region of Italy. Pompeii, along with Herculaneum and many villas in the surrounding area (e.g. at Boscoreale, Stabiae), was buried ...
and
Herculaneum
Herculaneum (; Neapolitan and it, Ercolano) was an ancient town, located in the modern-day ''comune'' of Ercolano, Campania, Italy. Herculaneum was buried under volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in AD 79.
Like the nea ...
. In 2017 the BBC defined Naples as «the Italian city with too much history to handle».
The most prominent forms of architecture visible in present-day Naples are the Medieval architecture, Medieval, Renaissance architecture, Renaissance and Baroque architecture, Baroque styles. Naples has a total of 448 historical churches (1000 in total), making it one of the most Catholic cities in the world in terms of the number of places of worship.
In 1995, the historic centre of Naples was listed by UNESCO as a
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
, a United Nations programme which aims to catalogue and conserve sites of outstanding cultural or natural importance to the common heritage of mankind.
Piazzas, palaces and castles

The main city square or ''piazza'' of the city is the Piazza del Plebiscito. Its construction was begun by the Bonapartist king Joachim Murat and finished by the Bourbon king Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies, Ferdinand IV. The piazza is bounded on the east by the Royal Palace (Naples), Royal Palace and on the west by the church of San Francesco di Paola (Naples), San Francesco di Paola, with the colonnades extending on both sides. Nearby is the Teatro di San Carlo, which is the oldest opera house in Italy. Directly across San Carlo is Galleria Umberto I, Galleria Umberto.
Naples is well known for its castles: The most ancient is
Castel dell'Ovo
Castel dell'Ovo ("Egg Castle") is a seafront castle in Naples, located on the former island of Megaride, now a peninsula, on the Gulf of Naples in Italy. The castle's name comes from a legend about the Roman poet Virgil, who had a reputation in ...
("Egg Castle"), which was built on the tiny islet of Megarides, where the original Cumaean colonists had founded the city. In Roman times the islet became part of Lucullus's villa, later hosting
Romulus Augustulus
Romulus Augustus ( 465 – after 511), nicknamed Augustulus, was Roman emperor of the West from 31 October 475 until 4 September 476. Romulus was placed on the imperial throne by his father, the ''magister militum'' Orestes, and, at that time, ...
, the exiled last western Roman emperor. It had also been the prison for Constance, Queen of Sicily, Empress Constance between 1191 and 1192 after her being captured by Sicilians, and Conradin and Giovanna I of Naples before their executions.
Castel Nuovo
Castel Nuovo (; "New Castle"), often called Maschio Angioino (; "Angevin Keep"), is a medieval castle located in front of Piazza Municipio and the city hall ( Palazzo San Giacomo) in central Naples, Campania, Italy. Its scenic location and impo ...
, also known as ''Maschio Capetian House of Anjou, Angioino'', is one of the city's top landmarks; it was built during the time of
Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
, the first List of monarchs of Naples, king of Naples. Castel Nuovo has seen many notable historical events: for example, in 1294, Pope Celestine V resigned as pope in a hall of the castle, and following this
Pope Boniface VIII
Pope Boniface VIII ( la, Bonifatius PP. VIII; born Benedetto Caetani, c. 1230 – 11 October 1303) was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 24 December 1294 to his death in 1303. The Caetani, Caetani family was of b ...
was elected pope by the cardinal Collegium (ancient Rome), collegium, before moving to Rome.
Castel Capuano was built in the 12th century by William I of Sicily, William I, the son of Roger II of Sicily, the first monarch of the
Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was ...
. It was expanded by
Frederick II and became one of his royal palaces. The castle was the residence of many kings and queens throughout its history. In the 16th century, it became the Hall of Justice.
Another Neapolitan castle is Castel Sant'Elmo, which was completed in 1329 and is built in the shape of a star. Its strategic position overlooking the entire city made it a target of various invaders. During the uprising of
Masaniello
Masaniello (, ; an abbreviation of Tommaso Aniello; 29 June 1620 – 16 July 1647) was an Italian fisherman who became leader of the 1647 revolt against the rule of Habsburg Spain in the Kingdom of Naples.
Name and place of birth
Until recent ...
in 1647, the Spanish took refuge in Sant'Elmo to escape the revolutionaries.
The Carmine Castle, built in 1392 and highly modified in the 16th century by the Spanish, was demolished in 1906 to make room for the Via Marina, although two of the castle's towers remain as a monument. The Vigliena Fort, built in 1702, was destroyed in 1799 during the royalist war against the Parthenopean Republic and is now abandoned and in ruin.
Museums


Naples is widely known for its wealth of historical museums. The Naples National Archaeological Museum is one of the city's main museums, with one of the most extensive collections of artifact (archaeology), artefacts of the Roman Empire in the world.
It also houses many of the antiques unearthed at
Pompeii
Pompeii (, ) was an ancient city located in what is now the ''comune'' of Pompei near Naples in the Campania region of Italy. Pompeii, along with Herculaneum and many villas in the surrounding area (e.g. at Boscoreale, Stabiae), was buried ...
and
Herculaneum
Herculaneum (; Neapolitan and it, Ercolano) was an ancient town, located in the modern-day ''comune'' of Ercolano, Campania, Italy. Herculaneum was buried under volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in AD 79.
Like the nea ...
, as well as some artefacts from the Magna Graecia, Greek and
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
periods.
Previously a Bourbon palace, now a museum and art gallery, the Museo di Capodimonte is another museum of note. The List of works in the Galleria Nazionale di Capodimonte, gallery features paintings from the 13th to the 18th centuries, including major works by Simone Martini, Raphael, Titian,
Caravaggio
Michelangelo Merisi (Michele Angelo Merigi or Amerighi) da Caravaggio, known as simply Caravaggio (, , ; 29 September 1571 – 18 July 1610), was an Italian painter active in Rome for most of his artistic life. During the final four years of hi ...
, El Greco, Jusepe de Ribera and Luca Giordano. The royal apartments are furnished with antique 18th-century furniture and a collection of porcelain and Victorian majolica, majolica from the various royal residences: the famous Capodimonte porcelain, Capodimonte Porcelain Factory once stood just adjacent to the palace.
In front of the Royal Palace of Naples stands the Galleria Umberto I, which contains the Coral Jewellery Museum. Occupying a 19th-century palazzo renovated by the Portuguese architect Álvaro Siza, the Museo d'Arte Contemporanea Donnaregina (MADRE) features an enfilade procession of permanent installations by artists such as Francesco Clemente, Richard Serra, and Rebecca Horn. The 16th-century palace of Roccella hosts the Palazzo delle Arti Napoli, which contains the civic collections of art belonging to the City of Naples, and features temporary exhibits of art and culture. Palazzo Como, which dates from the 15th century, hosts the Museo Filangieri of plastic arts, created in 1883 by Gaetano Filangieri.
Churches and other religious structures




Naples is the seat of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Naples, Archdiocese of Naples; there are hundreds of churches in the city.
The Naples Cathedral, Cathedral of Naples is the city's premier place of worship; each year on 19 September, it hosts the longstanding Miracle of Januarius, Saint Januarius, the city's
patron saint
A patron saint, patroness saint, patron hallow or heavenly protector is a saint who in Catholicism, Anglicanism, or Eastern Orthodoxy is regarded as the heavenly advocate of a nation, place, craft, activity, class, clan, family, or perso ...
.
During the miracle, which thousands of Neapolitans flock to witness, the dried blood of Januarius is said to turn to liquid when brought close to holy relics said to be of his body.
Below is a selective list of Naples' major churches, chapels, and monastery complexes:
* Certosa di San Martino
*
Naples Cathedral
The Naples Cathedral ( it, Duomo di Napoli; nap, Viscuvato 'e Napule), or Cathedral of the Assumption of Mary ( it, Cattedrale di Santa Maria Assunta, links=no), is a Roman Catholic cathedral, the main church of Naples, southern Italy, and the s ...
* San Francesco di Paola (Naples), San Francesco di Paola
* Gesù Nuovo
* Girolamini, Naples, Girolamini
* San Domenico Maggiore
* Santa Chiara (Naples), Santa Chiara
* San Paolo Maggiore
* Santa Maria della Sanità, Naples
* Santa Maria del Carmine (Naples), Santa Maria del Carmine
* Sant'Agostino alla Zecca
* Madre del Buon Consiglio
* Santa Donna Regina Nuova, Santa Maria Donna Regina Nuova
* San Lorenzo Maggiore, Naples, San Lorenzo Maggiore
* Santa Maria Donna Regina Vecchia
* Santa Caterina a Formiello
* Santissima Annunziata Maggiore, Naples, Santissima Annunziata Maggiore
* San Gregorio Armeno
* San Giovanni a Carbonara
* Santa Maria La Nova
* Sant'Anna dei Lombardi
* Sant'Eligio Maggiore
* Santa Restituta
* Cappella Sansevero, Sansevero Chapel
* San Pietro a Maiella
* San Gennaro extra Moenia
* San Ferdinando (Naples), San Ferdinando
* Pio Monte della Misericordia
* Santa Maria di Montesanto, Naples, Santa Maria di Montesanto
* Chiesa di Sant'Antonio Abate, Sant'Antonio Abate
* Santa Caterina a Chiaia
* San Pietro Martire (Naples), San Pietro Martire
* Hermitage of Camaldoli (Naples), Hermitage of Camaldoli
* Archbishop's Palace (Naples), Archbishop's Palace
Other features
Aside from the Piazza del Plebiscito, Naples has two other major public squares: the Piazza Dante (Naples), Piazza Dante and the Piazza dei Martiri. The latter originally had only a memorial to religious martyrs, but in 1866, after the Italian unification, four lions were added, representing the four rebellions against the Bourbons.
The San Gennaro dei Poveri is a Renaissance-era hospital for the poor, erected by the Spanish in 1667. It was the forerunner of a much more ambitious project, the Ospedale L'Albergo Reale dei Poveri, Naples, Bourbon Hospice for the Poor started by Charles III of Spain, Charles III. This was for the destitute and ill of the city; it also provided a self-sufficient community where the poor would live and work. Though a notable landmark, it is no longer a functioning hospital.
Subterranean Naples
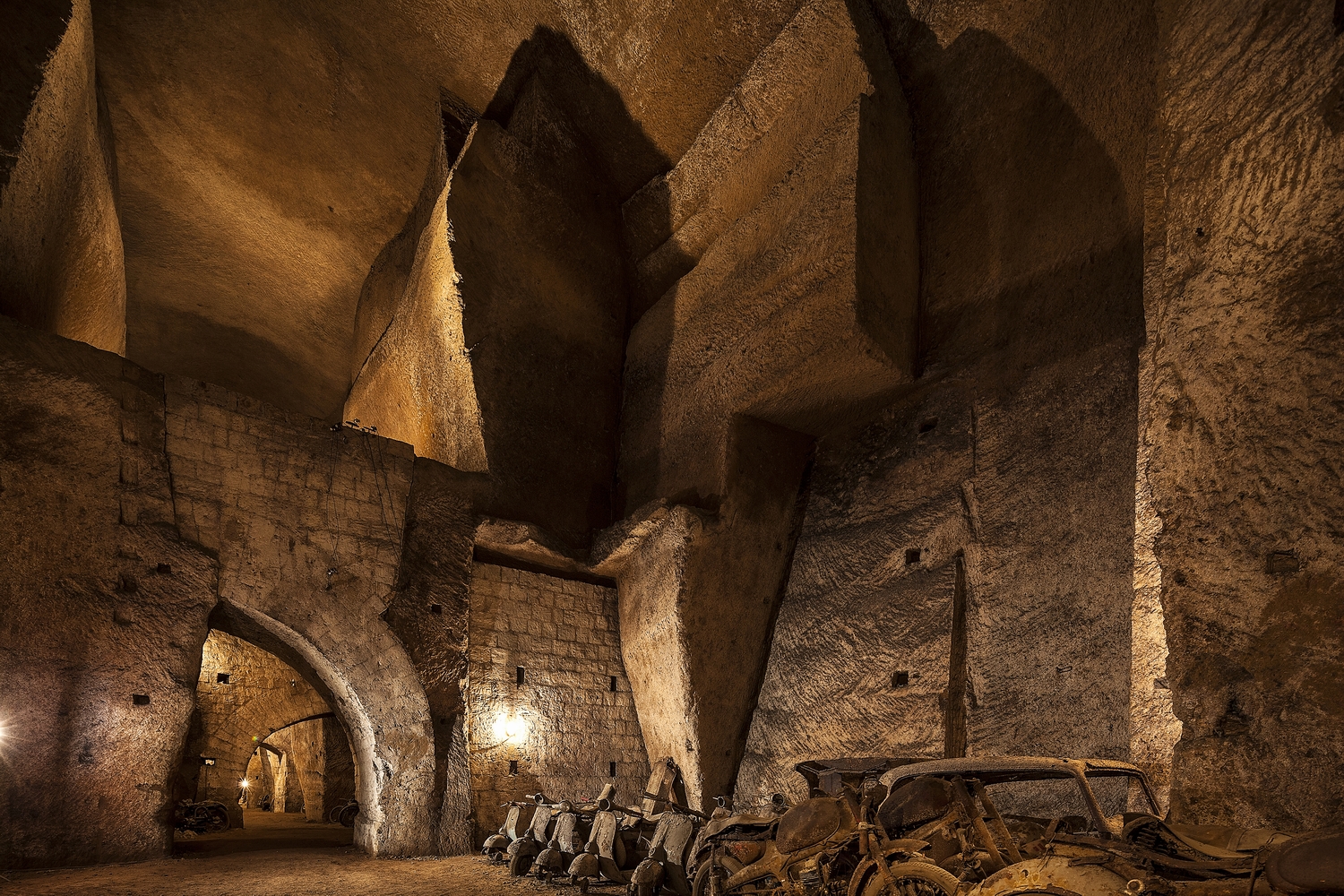

Naples underground geothermal zone, Underneath Naples lies a series of caves and structures created by centuries of mining, and the city rests atop a major geothermal (geology), geothermal zone. There are also several ancient Greco-Roman reservoirs dug out from the soft tuff, tufo stone on which, and from which, much of the city is built. Approximately of the many kilometres of tunnels under the city can be visited from the Naples underground geothermal zone, Napoli Sotteranea, situated in the historic centre of the city in Via dei Tribunali (Naples), Via dei Tribunali. This system of tunnels and cisterns underlies most of the city and lies approximately below ground level. During
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, these tunnels were used as air-raid shelters, and there are inscriptions on the walls depicting the suffering endured by the refugees of that era.
There are large Catacombs of San Gennaro, catacombs in and around the city, and other landmarks such as the Piscina Mirabilis, the main cistern serving the Bay of Naples during Roman times.
Several archeological excavations are also present; they revealed in San Lorenzo Maggiore, Naples, San Lorenzo Maggiore the macellum of Naples, and in Santa Chiara, Naples, Santa Chiara, the biggest thermal complex of the city in Roman times.
Parks, gardens, villas, fountains and stairways

Of the various park, public parks in Naples, the most prominent are the Villa Comunale, which was built by the Bourbon king Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies, Ferdinand IV in the 1780s; the park was originally a "Royal Garden", reserved for members of the royal family, but open to the public on special holidays. The Bosco di Capodimonte, the city's largest green space, served as a royal hunting reserve. The Park has 16 additional historical buildings, including residences, lodges, churches, fountains, statues, orchards and woods.
Another important park is the Parco Virgiliano, which looks towards the tiny volcanic islet of
Nisida
Nisida is a volcanic islet of the Flegrean Islands archipelago, in southern Italy. It lies at a very short distance from Cape Posillipo, just north of Naples; it is now connected to the mainland by a stone bridge. The islet is almost circular, wit ...
; beyond Nisida lie Procida and Ischia.
Parco Virgiliano (Mergellina), Parco Virgiliano was named after
Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; traditional dates 15 October 7021 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: t ...
, the classical Roman poet and Latin writer who is thought to be Virgil's tomb, entombed nearby.
Naples is noted for its numerous stately
villa
A villa is a type of house that was originally an ancient Roman upper class country house. Since its origins in the Roman villa, the idea and function of a villa have evolved considerably. After the fall of the Roman Republic, villas became s ...
s, fountains and stairways, such as the Neoclassical architecture, Neoclassical Villa Floridiana, the Fountain of Neptune, Naples, Fountain of Neptune and the Pedamentina stairways.
Neo-Gothic, ''Liberty Napoletano'' and modern architecture


Various buildings inspired by the Gothic Revival Architecture, Gothic Revival are extant in Naples, due to the influence that this movement had on the Scottish-Indian architect Lamont Young (Naples), Lamont Young, one of the most active Neapolitan architects of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Young left a significant footprint in the cityscape and designed many urban projects, such as the city's first subway.
In the first years of the 20th century, a local version of the Art Nouveau phenomenon, known as "Liberty Napoletano", developed in the city, creating many buildings which still stand today. In 1935, the Rationalist architect Luigi Cosenza designed a new fish market for the city. During the
Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in 194 ...
era, the first structures of the city's "service center" were built, all in a Rationalist-Functionalist style, including the Palazzo delle Poste and the Pretura buildings. The Centro Direzionale (Naples), Centro Direzionale di Napoli is the only adjacent cluster of skyscrapers in southern Europe.
Geography

The city is situated on the Gulf of Naples, on the western coast of southern Italy; it rises from sea level to an elevation of . The small rivers that formerly crossed the city's centre have since been covered by construction. It lies between two notable volcanic regions, Mount Vesuvius and the Campi Flegrei ( en, Phlegraean Fields). The islands of Procida, Capri and Ischia can all be reached from Naples by hydrofoils and ferries. Sorrento, Italy, Sorrento and the Amalfi Coast are situated south of the city. At the same time, the Roman ruins of
Pompeii
Pompeii (, ) was an ancient city located in what is now the ''comune'' of Pompei near Naples in the Campania region of Italy. Pompeii, along with Herculaneum and many villas in the surrounding area (e.g. at Boscoreale, Stabiae), was buried ...
,
Herculaneum
Herculaneum (; Neapolitan and it, Ercolano) was an ancient town, located in the modern-day ''comune'' of Ercolano, Campania, Italy. Herculaneum was buried under volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in AD 79.
Like the nea ...
, Oplontis and Stabiae, which were destroyed in the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 AD, are also visible nearby. The port towns of Pozzuoli and Baiae, Baia, which were part of the Roman naval facility of Portus Julius, lie to the west of the city.
Quarters

The thirty quarters (''quartiere, quartieri'') of Naples are listed below. For administrative purposes, these thirty districts are grouped together into ten governmental community boards.
Climate
Naples has a Mediterranean climate (''Csa'') in the Köppen climate classification. The climate and fertility of the Gulf of Naples made the region famous during Roman times, when emperors such as
Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusu ...
and
Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
holidayed near the city.
The climate is a crossover between maritime and continental features, as typical of peninsular Italy. Maritime features mitigate the winters but occasionally cause heavy rainfall, particularly in the autumn and winter. Summers feature high temperatures and humidity. The continental influence still ensures summer highs averaging near , and Naples falls within the subtropical climate range with summer daily-mean above with hot days, warm nights and occasional summer thunderstorms.
Winters are mild, and snow is rare in the city area but frequent on Mount Vesuvius.
November is the wettest month in Naples, while July is the driest.
Demographics

, the population of the ''comune di Napoli'' totals around 910,000. Naples' wider Naples metropolitan area, metropolitan area, sometimes known as Greater Naples, has a population of approximately 4.4 million.
The demographic profile for the Neapolitan province in general is relatively young: 19% are under the age of 14, while 13% are over 65, compared to the national average of 14% and 19%, respectively.
Naples has a higher percentage of females (52.5%) than males (47.5%).
[‘City’ population (i.e. that of the ''comune'' or municipality)]
City of Naples
. Comuni-italiani.it. 2012. Retrieved 11 April 2012. Naples currently has a higher birth rate than other parts of Italy, with 10.46 births per 1,000 inhabitants, compared to the Italian average of 9.45 births.
Naples's population rose from 621,000 in 1901 to 1,226,000 in 1971, declining to 910,000 in 2022 as city dwellers moved to the suburbs. According to different sources, Naples' Naples metropolitan area, metropolitan area is either the List of cities in Italy by population, second-most-populated metropolitan area in Italy after
Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
(with 4,434,136 inhabitants according to Svimez Data) or the third (with 3.5 million inhabitants according to the OECD).
In addition, Naples is Italy's most densely populated major city, with approximately 8,182 people per square kilometre;
however, it has seen a notable decline in population density since 2003, when the figure was over 9,000 people per square kilometre.
In contrast to many northern Italian cities, there are relatively few foreign immigrants in Naples; 94.3% of the city's inhabitants are Italian people, Italian nationals. In 2017, there were a total of 58,203 foreigners in the city of Naples; the majority of these are mostly from Sri Lanka, China, Ukraine, Pakistan and Romania.
Statistics show that, in the past, the vast majority of immigrants in Naples were female; this happened because male immigrants in Italy tended to head to the wealthier north.
Education
Naples is noted for its numerous higher education institutes and research centres. Naples hosts what is thought to be the oldest state university in the world, in the form of the University of Naples Federico II, which was founded by
Frederick II in 1224. The university is among the most prominent in Italy, with around 100,000 students and over 3,000 professors in 2007. It is host to the Botanical Garden of Naples, which was opened in 1807 by Joseph Bonaparte, using plans drawn up under the Bourbon king Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies, Ferdinand IV. The garden's 15 hectares feature around 25,000 samples of over 10,000 species.
Naples is also served by the "Università degli Studi della Campania Luigi Vanvitelli, Second University" (today named Università degli Studi della Campania Luigi Vanvitelli, University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli), a modern university which opened in 1989, and which has strong links to the nearby province of Caserta. Another notable centre of education is the Naples Eastern University, Istituto Universitario Orientale, which specialises in Eastern world, Eastern culture, and was founded by the Society of Jesus, Jesuit missionary Matteo Ripa in 1732, after he returned from the court of Kangxi Emperor, Kangxi, the Emperor of China, Emperor of the Manchu people, Manchu Qing Dynasty of China.
Other prominent universities in Naples include the Parthenope University of Naples, the private Suor Orsola Benincasa University of Naples, Istituto Universitario Suor Orsola Benincasa, and the Society of Jesus, Jesuit San Luigi Papal Theological Seminary of Southern Italy, Theological Seminary of Southern Italy. The Music conservatories of Naples, San Pietro a Maiella music conservatory is the city's foremost institution of musical education; the earliest Neapolitan music conservatories were founded in the 16th century under the Spanish. The Accademia di Belle Arti di Napoli, Academy of Fine Arts located on the Via Santa Maria di Costantinopoli is the city's foremost art school and one of the oldest in Italy.
Naples hosts also the Astronomical Observatory of Capodimonte, established in 1812 by the king Joachim Murat and the astronomer Federigo Zuccari, the oldest marine zoology, marine zoological study station in the world, Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn, created in 1872 by German scientist Anton Dohrn, and the world's oldest permanent volcano observatory, the Vesuvius Observatory, founded in 1841. The Observatory lies on the slopes of Mount Vesuvius, near the city of Ercolano, and is now a permanent specialised institute of the :it:Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia, Italian National Institute of Geophysics.
Politics


Governance
Each of the 7,904 ''comune'' in Italy is today represented locally by a city council headed by an elected mayor, known as a ''sindaco'' and informally called the first citizen (''primo cittadino''). This system, or one very similar to it, has been in place since the invasion of Italy by Napoleon I of France, Napoleonic forces in 1808. When the
Kingdom of the Two Sicilies
The Kingdom of the Two Sicilies ( it, Regno delle Due Sicilie) was a kingdom in Southern Italy from 1816 to 1860. The kingdom was the largest sovereign state by population and size in Italy before Italian unification, comprising Sicily and a ...
was restored, the system was kept in place with members of the nobility filling mayoral roles. By the end of the 19th century, political party, party politics had begun to emerge; during the Italian Fascism, fascist era, each commune was represented by a ''podestà''. Since
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the political landscape of Naples has been neither strongly right-wing politics, right-wing nor left-wing politics, left-wing – both Christian democracy, Christian democrats and democratic socialism, democratic socialists have governed the city at different times, with roughly equal frequency. Currently, the mayor of Naples is Gaetano Manfredi, an independent politician, former Italian Minister of University and Research, minister of university and research in the Conte II Cabinet, second Conte government, and former rector of the University of Naples Federico II.
Administrative subdivisions
Economy


Naples, within its administrative limits, is Italy's fourth-largest economy after
Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
, Rome and Turin, and is the world's List of cities by GDP, 103rd-largest urban economy by purchasing power, with an estimated 2011 GDP of US$83.6 billion, equivalent to $28,749 per capita.
["Which are the largest city economies in the world and how might this change by 2025?"](_blank)
PricewaterhouseCoopers. November 2009. Retrieved 23 April 2012.
Naples is a major Container terminal, cargo terminal, and the port of Naples is one of the Mediterranean's largest and busiest. The city has experienced significant economic growth since World War II, but joblessness remains a major problem, and the city is characterised by high levels of political corruption and organised crime, as well as in other cities of the country.
Naples is a major national, and international tourist destination, one of Italy's and Europe's top tourist cities. Tourists began visiting Naples in the 18th century during the Grand Tour.
In the last decades, there has been a move away from a traditional agriculture-based economy in the province of Naples to one based on Tertiary sector of the economy, service industries. The service sector employs the majority of Neapolitans, although more than half of these are small enterprises with fewer than 20 workers; about 70 companies are said to be medium-sized with more than 200 workers, and about 15 have more than 500 workers.
Tourism
Naples is, with Florence,
Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, Venice and
Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
, one of the main Italian tourist destinations. With 3,700,000 visitors in 2018, the city has completely emerged from the strong tourist depression of past decades (due primarily to the unilateral destination of an industrial city but also to the damage to image caused by the Italian media, from the 1980 Irpinia earthquake and the Waste crisis in Naples, waste crisis, in favor of the coastal centers of its Naples metropolitan area, metropolitan area). To adequately assess the phenomenon, however, it must be considered that a large slice of tourists visit Naples per year, staying in the numerous localities in its surroundings, connected to the city with both private and public direct lines. Daily visits to Naples are carried out by various Roman tour operators and by all the main tourist resorts of
Campania
Campania (, also , , , ) is an administrative Regions of Italy, region of Italy; most of it is in the south-western portion of the Italian peninsula (with the Tyrrhenian Sea to its west), but it also includes the small Phlegraean Islands and the i ...
: as of 2019, Naples is the tenth most visited Municipalities of Italy, municipality in Italy and the first in the Southern Italy, South.
The sector is constantly growing and the prospect of reaching the art cities of its level is once again expected in a relatively short time; tourism is increasingly assuming a decisive weight for the city's economy, which is why, exactly as happened for example in the case of Venice or Florence, the risk of gentrification of the Historic Centre of Naples, historic center is now high.
Transport



Naples is served by several major motorways (Italian language, it: ''autostrade''). The Autostrada A1 (Italy), Autostrada A1, the longest Autostrade of Italy, motorway in Italy, links Naples to
Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
. The Autostrada A3 (Italy), A3 runs southwards from Naples to
Salerno
Salerno (, , ; nap, label= Salernitano, Saliernë, ) is an ancient city and ''comune'' in Campania (southwestern Italy) and is the capital of the namesake province, being the second largest city in the region by number of inhabitants, after ...
, where the A2 (Italy), motorway to Reggio Calabria begins, while the A16 runs east to Canosa di Puglia, Canosa. The A16 is nicknamed the ''autostrada dei Due Mari'' ("Motorway of the Two Seas") because it connects the Tyrrhenian Sea to the Adriatic Sea.
Regional rail, Suburban rail services are provided by Trenitalia, Circumvesuviana, Ferrovia Cumana and Metronapoli.
The city's main railway station is Napoli Centrale railway station, Napoli Centrale, which is located in Piazza Garibaldi; other significant stations include the Napoli Campi Flegrei railway station, Napoli Campi Flegrei and Napoli Mergellina railway station, Napoli Mergellina. Napoli Afragola railway station, Napoli Afragola serves high-speed trains that do not start or finish at Napoli Centrale. Naples' streets are famously narrow (it was the first city in the world to set up a pedestrian one-way street), so the general public commonly use compact hatchback cars and scooter (motorcycle), scooters for personal transit. Since 2007 trains running at have connected Naples with Rome with a journey time of under an hour, and direct high speed services also operate to Florence, Bologna, Milan, Turin and Salerno. Direct sleeper 'boat train' services operate nightly to cities in Sicily.
The port of Naples runs several ferry, hydrofoil, and Catamaran#SWATH and wave-piercing designs, SWATH catamaran lines to Capri, Ischia and Sorrento,
Salerno
Salerno (, , ; nap, label= Salernitano, Saliernë, ) is an ancient city and ''comune'' in Campania (southwestern Italy) and is the capital of the namesake province, being the second largest city in the region by number of inhabitants, after ...
, Positano and Amalfi.
Services are also available to
Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, Sardinia, Ponza and the Aeolian Islands.
The port serves over 6 million local passengers annually,
plus a further 1 million international cruise ship passengers.
A regional hydrofoil transport service, the "Metropolitana del Mare", runs annually from July to September, maintained by a consortium of shipowners and local administrations.
The Naples International Airport is located in the suburb of San Pietro a Patierno. It is the largest airport in southern Italy, with around 250 national and international flights arriving or departing daily.
The average commute with public transit in Naples on a weekday is 77 minutes. Nineteen per cent of public transit commuters ride for more than 2 hours every day. The average time people wait at a stop or station for public transit is 27 minutes, while 56% of riders wait for over 20 minutes. The average distance people usually ride in a single trip with public transit is , while 11% travel for over in a single direction.
Urban public transport
Naples has an extensive public transport network, including Trams in Naples, trams, buses and trolleybuses,
most of which are operated by the municipally owned company ANM (Naples), Azienda Napoletana Mobilità (ANM).
The city furthermore operates the ''Metropolitana di Napoli'', the Naples Metro, an underground rapid transit rail transport, railway system which integrates both surface railway lines and the city's List of Naples metro stations, metro stations, Art Stations of the Naples Metro, many of which are noted for their decorative architecture and public art. In fact, the station of Via Toledo is often in the top spots of the rankings of the most beautiful metro stations in the world.
There are also four funiculars in the city (operated by ANM): Central Funicular, ''Centrale'', Chiaia Funicular, ''Chiaia'', Montesanto Funicular, ''Montesanto'' and Mergellina Funicular, ''Mergellina''. Four public elevators are in operation in the city: within the bridge of Chiaia, in via Acton, near the Sanità Bridge, and in the Ventaglieri Park, accompanied by two public escalators.
Culture
Art
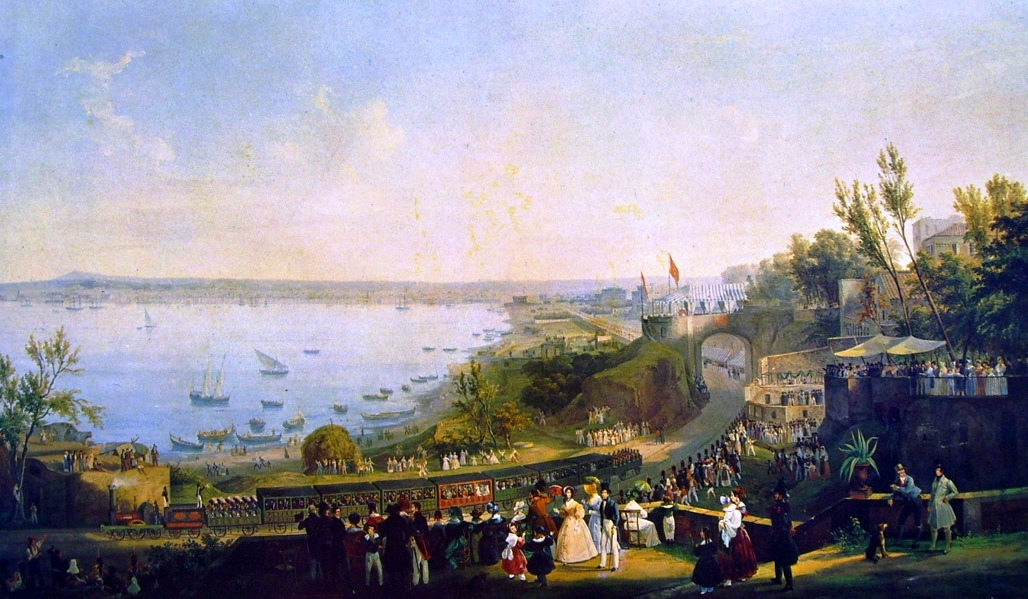
Naples has long been a centre of art and architecture, dotted with Medieval-, Baroque- and Renaissance-era churches, castles and palaces. A critical factor in the development of the Neapolitan school of painting was Caravaggio's arrival in Naples in 1606. In the 18th century, Naples went through a period of neoclassicism, following the discovery of the remarkably intact Roman ruins of
Herculaneum
Herculaneum (; Neapolitan and it, Ercolano) was an ancient town, located in the modern-day ''comune'' of Ercolano, Campania, Italy. Herculaneum was buried under volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in AD 79.
Like the nea ...
and
Pompeii
Pompeii (, ) was an ancient city located in what is now the ''comune'' of Pompei near Naples in the Campania region of Italy. Pompeii, along with Herculaneum and many villas in the surrounding area (e.g. at Boscoreale, Stabiae), was buried ...
.
The Accademia di Belle Arti di Napoli, Neapolitan Academy of Fine Arts, founded by Charles III of Spain, Charles III of Bourbon in 1752 as the Real Accademia di Disegno (English language, en: ''Royal Academy of Design''), was the centre of the artistic School of
Posillipo
Posillipo (; nap, Pusilleco ) is an affluent residential quarter of Naples, southern Italy, located along the northern coast of the Gulf of Naples.
From the 1st century BC the Bay of Naples witnessed the rise of villas constructed by elite Roma ...
in the 19th century. Artists such as Domenico Morelli, Giacomo Di Chirico, Francesco Saverio Altamura and Gioacchino Toma worked in Naples during this period, and many of their works are now exhibited in the academy's art collection. The modern Academy offers courses in painting, Interior design, decorating, sculpture, design, Conservation-restoration, restoration, and urban planning. Naples is also known for its theatres, which are among the oldest in Europe: the Teatro di San Carlo opera house dates back to the 18th century.
Naples is also the home of the artistic tradition of Capodimonte porcelain. In 1743, Charles of Bourbon founded the Royal Factory of Capodimonte, many of whose artworks are now on display in the Museum of Capodimonte. Several of Naples' mid-19th-century porcelain factories remain active today.
Cuisine


Naples is internationally famous for its Neapolitan cuisine, cuisine and wine; it draws culinary influences from the numerous cultures which have inhabited it throughout its history, including the Ancient Greece, Greeks, Spanish and French. Neapolitan cuisine emerged as a distinct form in the 18th century. The ingredients are typically rich in taste while remaining affordable to the general populace.
Naples is traditionally credited as the home of
pizza
Pizza (, ) is a dish of Italian origin consisting of a usually round, flat base of leavened wheat-based dough topped with tomatoes, cheese, and often various other ingredients (such as various types of sausage, anchovies, mushrooms, onions ...
.
This originated as a meal of the poor, but under Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies, Ferdinand IV it became popular among the upper classes: famously, the Margherita (pizza), Margherita pizza was named after Queen Margherita of Savoy after her visit to the city.
Cooked traditionally in a wood-burning Masonry oven, oven, the ingredients of Neapolitan pizza have been strictly regulated by law since 2004, and must include wheat flour type "00" with the addition of flour type "0" yeast, natural mineral water, peeled tomatoes or fresh cherry tomatoes, mozzarella, sea salt and extra virgin olive oil.
["Proposal of recognition of the Specialita' Traditionale Garantita 'Pizza Napoletana'"]
. Forno Bravo. 24 May 2004. Retrieved 27 November 2011.
Spaghetti is also associated with the city and is commonly eaten with clams ''vongole or lupini di mare'': a popular Neapolitan folklore, folkloric symbol is the comic figure Pulcinella eating a plate of spaghetti. Other dishes popular in Naples include ''Parmigiana di melanzane'', ''spaghetti alle vongole'' and ''casatiello''. As a coastal city, Naples is furthermore known for numerous seafood dishes, including ''impepata di cozze'' (peppered mussels), ''purpetiello affogato'' (octopus poached in broth), ''alici marinate'' (marinated anchovies), ''baccalà alla napoletana'' (salt cod) and ''baccalà fritto'' (fried cod), a dish commonly eaten during the Christmas period.
Naples is well known for its sweet dishes, including colourful gelato, which is similar to ice cream, though more fruit-based. Popular Neapolitan pastry dishes include ''zeppole'' (more commonly called "'a Pasta Cresciuta" and "'e fFritt' 'e Viento") ''Rum baba, babà'', ''sfogliatelle'' and ''pastiera'', the latter of which is prepared specially for Easter celebrations. Another seasonal sweet is ''struffoli'', a sweet-tasting honey dough decorated and eaten around Christmas. Neapolitan coffee is also widely acclaimed. The traditional Neapolitan flip coffee pot, known as the ''cuccuma'' or ''cuccumella'', was the basis for the invention of the espresso machine, and also inspired the Moka pot.
Wineries in the Vesuvius area produce wines such as the ''Lacryma Christi'' ("tears of Christ") and ''Terzigno''. Naples is also the home of ''limoncello'', a popular lemon liqueur.
Festivals
The cultural significance of Naples is often represented through a series of festivals held in the city. The following is a list of several festivals that take place in Naples (note: some festivals are not held on an annual basis).

* ''Festa di Piedigrotta'' ("Piedigrotta Festival") – A musical event typically held in September in memory of the famous Madonna of Piedigrotta. Throughout the month, a series of musical workshops, concerts, religious events and children's events are held to entertain the citizens of Naples and surrounding areas.
* ''Pizzafest'' – As Naples is famous for being home to pizza, the city hosts an eleven-day festival dedicated to this iconic dish. This is a key event for Neapolitans and tourists alike, as various stations are open for tasting a wide range of true Neapolitan pizza. In addition to pizza tasting, a variety of entertainment shows are displayed.
* ''Maggio dei Monumenti'' ("May of Monuments") – A cultural event where the city hosts a variety of special events dedicated to the birth of King Charles of Bourbon. It festival features art and music of the 18th century, and many buildings which may normally be closed throughout the year are opened for visitors to view.
* ''Il Ritorno della festa di San Gennaro'' ("The Return of the Feast of San Gennaro") – An annual celebration and feast of faith held over three days, commemorating Saint Januarius, Gennaro. Throughout the festival, parades, religious processions and musical entertainment are featured. An annual celebration is also held in "Little Italy, Manhattan, Little Italy" in Manhattan.
Language
The Naples language, considered to be a distinct language and mainly spoken in the city, is also found in the region of
Campania
Campania (, also , , , ) is an administrative Regions of Italy, region of Italy; most of it is in the south-western portion of the Italian peninsula (with the Tyrrhenian Sea to its west), but it also includes the small Phlegraean Islands and the i ...
and has been diffused into other areas of Southern Italy by Neapolitan migrants, and in many different places in the world.
On 14 October 2008, a regional law was enacted by Campania which has the effect that the use of the Neapolitan language is protected.
The term "Neapolitan language" is often used to describe the language of all of
Campania
Campania (, also , , , ) is an administrative Regions of Italy, region of Italy; most of it is in the south-western portion of the Italian peninsula (with the Tyrrhenian Sea to its west), but it also includes the small Phlegraean Islands and the i ...
(except Cilento), and is sometimes applied to the entire South Italian language; ''Ethnologue'' refers to the latter as ''Napoletano-Calabrese''.
This linguistic group is spoken throughout most of southern continental Italy, including the Gaeta and Sora, Italy, Sora district of southern Lazio, the southern part of Marche and Abruzzo, Molise, Basilicata, northern Calabria, and northern and central Apulia. In 1976, there were an estimated 7,047,399 first language, native speakers of this group of dialects.
Literature and philosophy

Naples is one of the leading centres of Italian literature. The history of the Neapolitan language was deeply entwined with that of the Tuscan dialect, which then became the current Italian language. The first written testimonies of the Italian language are the Placiti Cassinensi legal documents, dated 960 A.D., preserved in the Monte Cassino Abbey, which are, in fact, evidence of a language spoken in a southern dialect. The Tuscan poet Boccaccio lived for many years at the court of King Robert the Wise and his successor Joanna I of Naples, Joanna of Naples, using Naples as a setting for ''The Decameron'' and a number of his later novels. His works contain some words that are taken from Neapolitan instead of the corresponding Italian, e.g. "testo" (neap.: "testa"), which in Naples indicates a large terracotta jar used to cultivate shrubs and little trees. King Alfonso V of Aragon stated in 1442 that the Neapolitan language was to be used instead of Latin in official documents.

Later Neapolitan was replaced by Italian in the first half of the 16th century, during Spanish domination. In 1458 the ''Accademia Pontaniana'', one of the first academies in Italy, was established in Naples as a free initiative by men of letters, science and literature. In 1480 the writer and poet Jacopo Sannazzaro wrote the first pastoral romance, ''Arcadia'', which influenced Italian literature. In 1634 Giambattista Basile collected ''Pentamerone, Lo Cunto de li Cunti'' five books of ancient tales written in the Neapolitan dialect rather than Italian. Philosopher
Giordano Bruno
Giordano Bruno (; ; la, Iordanus Brunus Nolanus; born Filippo Bruno, January or February 1548 – 17 February 1600) was an Italian philosopher, mathematician, poet, cosmological theorist, and Hermetic occultist. He is known for his cosmologic ...
, who theorised the existence of infinite solar systems and the infinity of the entire universe, completed his studies at the University of Naples. Due to philosophers such as
Giambattista Vico
Giambattista Vico (born Giovan Battista Vico ; ; 23 June 1668 – 23 January 1744) was an Italian philosopher, rhetorician, historian, and jurist during the Italian Enlightenment. He criticized the expansion and development of modern rationali ...
, Naples became one of the centres of the Italian peninsula for historical and philosophy of history studies.
Jurisprudence studies were enhanced in Naples thanks to eminent personalities of jurists like Bernardo Tanucci, Gaetano Filangieri and Antonio Genovesi. In the 18th century Naples, together with
Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
, became one of the most important sites from which the
Enlightenment
Enlightenment or enlighten may refer to:
Age of Enlightenment
* Age of Enlightenment, period in Western intellectual history from the late 17th to late 18th century, centered in France but also encompassing (alphabetically by country or culture): ...
penetrated Italy. Poet and philosopher Giacomo Leopardi visited the city in 1837 and died there. His works influenced Francesco de Sanctis, who studied in Naples and eventually became Minister of Instruction during the Italian kingdom. De Sanctis was one of the first literary critics to discover, study and diffuse the poems and literary works of the great poet from Recanati.
Writer and journalist Matilde Serao co-founded the newspaper Il Mattino with her husband Edoardo Scarfoglio in 1892. Serao was an acclaimed novelist and writer during her day. Poet Salvatore Di Giacomo was one of the most famous writers in the Neapolitan dialect, and many of his poems were adapted to music, becoming famous Neapolitan songs. In the 20th century, philosophers like Benedetto Croce pursued the long tradition of philosophy studies in Naples, and personalities like jurists and lawyer Enrico De Nicola pursued legal and constitutional studies. De Nicola later helped to draft the modern Constitution of the Italian Republic and was eventually elected to the office of President of the Italian Republic. Other noted Neapolitan writers and journalists include Antonio De Curtis, Curzio Malaparte, Giancarlo Siani, Roberto Saviano and Elena Ferrante.
Theatre

Naples was one of the centres of the peninsula from which originated the modern theatre genre as nowadays intended, evolving from 16th century "commedia dell'arte, comedy of art".
The masked character of Pulcinella is a worldwide famous figure either as a theatrical character or puppetry character.
The music Opera genre of opera buffa was created in Naples in the 18th century and then spread to Rome and northern Italy. In the period of Belle Époque, Naples rivalled Paris for its Café-chantants, and many famous Neapolitan songs were originally created to entertain the public in the cafès of Naples. Perhaps the most well-known song is "Ninì Tirabusciò". The history of how this song was born was dramatised in the eponymous comedy movie "Ninì Tirabusciò: la donna che inventò la mossa" starring Monica Vitti.
The Neapolitan popular genre of "Sceneggiata" is an important genre of modern folk theatre worldwide, dramatising common canon themes of thwarted love stories, comedies, tearjerker stories, commonly about honest people becoming camorra outlaws due to unfortunate events. The Sceneggiata became very popular amongst Neapolitans and eventually one of the best-known genres of Italian cinematography thanks to actors and singers like Mario Merola (singer), Mario Merola and Nino D'Angelo. Many writers and playwrights, such as Raffaele Viviani, wrote comedies and dramas for this genre. Actors and comedians like Eduardo Scarpetta and then his sons Eduardo De Filippo, Peppino De Filippo and Titina De Filippo contributed to making the Neapolitan theatre. Its comedies and tragedies, such as "Filumena Marturano" and "Side Street Story, Napoli Milionaria", are well-known.
Music

Naples has played an important role in the history of Classical music, Western European art music for more than four centuries. The first music conservatories of Naples, music conservatories were established in the city under Spanish rule in the 16th century. The San Pietro a Majella music conservatory, founded in 1826 by Francis I of the Two Sicilies, Francesco I of Bourbon, continues to operate today as both a prestigious centre of musical education and a musical museum.
During the late Baroque music, Baroque period, Alessandro Scarlatti, the father of Domenico Scarlatti, established the Neapolitan school of opera; this was in the form of ''opera seria'', which was a new development for its time. Another form of opera originating in Naples is ''opera buffa'', a style of comic opera strongly linked to Giovanni Battista Pergolesi, Battista Pergolesi and Niccolò Piccinni, Piccinni; later contributors to the genre included Gioachino Rossini, Rossini and Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart. The Teatro di San Carlo, built in 1737, is the oldest working theatre in Europe, and remains the operatic centre of Naples.


The earliest six-string guitar was created by the Neapolitan Gaetano Vinaccia in 1779; the instrument is now referred to as the romantic guitar. The Vinaccia family also developed the mandolin. Influenced by the Spanish, Neapolitans became pioneers of classical guitar music, with Ferdinando Carulli and Mauro Giuliani being prominent exponents. Giuliani, who was actually from Apulia but lived and worked in Naples, is widely considered to be one of the greatest guitarist, guitar players and composers of the 19th century, along with his Catalonia, Catalan contemporary Fernando Sor. Another Neapolitan musician of note was opera singer Enrico Caruso, one of the most prominent opera tenors of all time: he was considered a man of the people in Naples, hailing from a working-class background.
A popular traditional dance in Southern Italy and Naples is the Tarantella, which originated in Apulia and spread throughout the
Kingdom of the Two Sicilies
The Kingdom of the Two Sicilies ( it, Regno delle Due Sicilie) was a kingdom in Southern Italy from 1816 to 1860. The kingdom was the largest sovereign state by population and size in Italy before Italian unification, comprising Sicily and a ...
. The Neapolitan tarantella is a courtship dance performed by couples whose "rhythms, melodies, gestures, and accompanying songs are quite distinct", featuring faster, more cheerful music.
A notable element of popular Neapolitan music is the ''Canzone Napoletana'' style, essentially the traditional music of the city, with a repertoire of hundreds of folklore, folk songs, some of which can be traced back to the 13th century.
The genre became a formal institution in 1835, after the introduction of the annual Festival of Piedigrotta songwriting competition.
Some of the best-known recording artists in this field include Roberto Murolo, Sergio Bruni and Renato Carosone. There are furthermore various forms of music popular in Naples but not well known outside it, such as ''cantautore'' ("singer-songwriter") and ''sceneggiata'', which has been described as a musical soap opera; the most well-known exponent of this style is Mario Merola (singer), Mario Merola.
Cinema and television

Naples has had a significant influence on Italian cinema. Because of the city's relevance, many films and television shows are set (entirely or partially) in Naples. In addition to serving as the backdrop for several movies and shows, many talented celebrities (actors, actresses, directors, and producers) are originally from Naples.
Naples was the location for several early Italian cinema masterpieces. ''Assunta Spina (1915 film), Assunta Spina'' (1915) was a silent film adapted from a theatrical drama by Neapolitan writer Salvatore Di Giacomo. The film was directed by Neapolitan Gustavo Serena. Serena also starred in the 1912 film ''Romeo and Juliet''.
A list of some well-known films that take place (fully or partially) in Naples includes:
* ''Shoeshine (film), Shoeshine'' (1946), directed by Neapolitan, Vittorio De Sica
* ''Hands over the City'' (1963), directed by Neapolitan, Francesco Rosi
* ''Journey to Italy'' (1954), directed by Roberto Rossellini
* ''Marriage Italian Style'' (1964), directed by Neapolitan, Vittorio De Sica
* ''It Started in Naples'' (1960), Directed by Melville Shavelson
* ''The Hand of God (film)'' (2021), Directed by Paolo Sorrentino
Naples is home to one of the first Italian colour films, ''Toto in Color'' (1952), starring Totò (Antonio de Curtis), a famous comedic actor born in Naples.
Some notable comedies set in Naples include ''Ieri, Oggi e Domani'' (Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow), by Vittorio De Sica, starring Sophia Loren and Marcello Mastroianni, ''Adelina of Naples'' (Academy Award-winning movie), ''It Started in Naples'', ''L'oro di Napoli'' again by Vittorio De Sica, dramatic movies like Dino Risi's ''Profumo di donna, Scent of a Woman'', war movies like ''The Four Days of Naples (film), The Four Days of Naples'' by Sardinian director Nanni Loy, music and Sceneggiata movies like ''Zappatore'', from the eponymous song by Libero Bovio, starring singer and actor Mario Merola (singer), Mario Merola, crime movies like ''Il Camorrista'' with Ben Gazzara playing the part of infamous camorra boss Raffaele Cutolo, and historical or costume movies like ''That Hamilton Woman'' starring Vivien Leigh and Laurence Olivier.
More modern Neapolitan films include ''Ricomincio da tre'', which depicts the misadventures of a young emigrant in the late 20th century. The 2008 film ''Gomorrah (film), Gomorrah'', based on the book by Roberto Saviano, explores the dark underbelly of the city of Naples through five intertwining stories about the powerful Camorra, Neapolitan crime syndicate, as well as the Gomorrah (TV series), TV series of the same name.
The Japanese series ''JoJo's Bizarre Adventure''s Part 5, Golden Wind (manga), Vento Aureo, takes place in the city.
Several episodes of the animated series ''Tom and Jerry'' also have references/influences from Naples. The song "Santa Lucia (song), Santa Lucia" played by Tom Cat in ''Cat and Dupli-cat'' has its origins in Naples. Neapolitan Mouse takes place in the same city.
Naples has appeared in episodes of TV serials such as ''The Sopranos'' and the 1998 version of ''The Count of Monte Cristo (1998 miniseries), The Count of Monte Cristo'', starring Gérard Depardieu.
Sports

Association football, Football is by far the most popular sport in Naples. Brought to the city by the British during the early 20th century,
the sport is deeply embedded in local culture: it is popular at every level of society, from the ''scugnizzi'' (street children) to wealthy professionals. The city's best known football club (association football), football club is S.S.C. Napoli, SSC Napoli, which plays its home games at the Stadio San Paolo in
Fuorigrotta
Fuorigrotta ( nap, Forerotta; ) is a western suburb of Naples, southern Italy.
Covering an area of 6,2 km2, it is the most populated suburb of the city (population: 76.521).
Geography
It lies beyond the Posillipo hill and has been joined ...
. The club's stadium was renamed Stadio Diego Armando Maradona in honour of the Argentinian attacking midfielder who played for them for seven years. The team plays in the
Serie A
The Serie A (), also called Serie A TIM for national sponsorship with TIM, is a professional league competition for football clubs located at the top of the Italian football league system and the winner is awarded the Scudetto and the Coppa ...
league and has won the ''Scudetto'' twice, the Coppa Italia six times and the Supercoppa Italiana twice. The team has also won the UEFA Europa League, UEFA Cup,
and once named FIFA Player of the Century Diego Maradona among its players. Naples is the birthplace of numerous prominent professional footballers, including Ciro Ferrara and Fabio Cannavaro. Cannavaro was Italy national football team, captain of Italy's national team until 2010 and led the team to victory in the 2006 FIFA World Cup, 2006 World Cup. He was consequently named FIFA World Player of the Year, World Player of the Year.
Some of the city's smaller clubs include F.C. Sporting Neapolis Mugnano, Sporting Neapolis and Internapoli Camaldoli S.S.D., Internapoli, which play at the Stadio Arturo Collana. The city also has teams in a variety of other sports: Basket Napoli, Eldo Napoli represents the city in basketball's Serie A (basketball), Serie A and plays in the city of Bagnoli. The city co-hosted the EuroBasket 1969. Partenope Rugby is the city's best-known rugby union side: the team has won the rugby union Serie A (rugby union), Serie A twice. Other popular local sports include water polo, horse racing, sailing, fencing, boxing and martial arts. The Accademia Nazionale di Scherma (National Academy and Fencing School of Naples) is the only place in Italy where the titles "Master of Sword" and "Master of Kendo" can be obtained.
Tailoring
Neapolitan tailoring was born as an attempt to loosen up the stiffness of English tailoring, which didn't suit the Neapolitan lifestyle.
Characteristics of Neapolitan tailoring:
* The Shoulders: the Neapolitan jacket has no shoulder padding. Neapolitan tailors removed the shoulder padding from their jackets to provide more movement freedom. For this reason, the Neapolitan shoulder on informal jackets is sewn like a shirt sleeve ("spalla a camicia"), and it follows the natural curve of the human body rather than giving it shape. This type of sleeve is cut about 10 cm larger than the armhole, and it can be finished with the "repecchia" – that shirring the tailor creates with the extra fabric. This little flair is known as "manica a mappina" and gives the jacket a "rugged" appearance. For formal occasions, the Neapolitan shoulder features a "rollino" – a little roll of padding that raises the sleeve head to drape more cleanly.
* The Sleeves: the Neapolitan sleeve is shorter than that found on other jackets, as Neapolitans like shirt cuffs to show right above their wrists, especially when adorned with cufflinks. The sleeves are cut closer to the arms to avoid extra fabric hanging when these are raised.
* The Pockets: the pockets of a Neapolitan jackets are curved and applied as patches; the breast pocket is called "a barchetta", which means "little boat",
due to the higher top corner of the pocket, which, along with the rounded bottom, gives it the shape of a stylized boat. The side pockets are equally curved, and their shape recalls that of a pot; hence the name "a pignata". Neither feature has any practical functionality, but they are particular to Neapolitan tailoring and contribute to the look of a jacket made in Naples. Double-hand finished stitching may also run throughout the sides of the patch pockets – a recurring feature in informal Neapolitan tailoring.
* The Lining: lining is considered an unnecessary burden, and the Neapolitan tailors keep it as minimal as possible. Usually, the jacket is unlined or only half lined; even the sleeves are entirely unlined, as they're meant to fit closely. Additionally, the lining is often left open ("volante," literally "flying") so that people can admire the fine details and construction of the jacket.
* The Lapels: Neapolitan jackets are famous for their wide lapels, which are often peaked ("a punta") for double-breasted jackets, formal jackets, and coats. The "risvolto dentellato" (the "classic" style of lapels – not peaked) is wider in Neapolitan jackets: they can be as wide as 4 inches (compared to the 3 inches of a regular lapel width). Just as is the case for the pockets, the Neapolitan lapel features double stitching running along the sides – a peculiar detail of a Neapolitan creation – although reserved for the less formal pieces. The "scollo a martiello" (literally "hammer neck") is the opening of the jacket over the shirt, which in Neapolitan tailoring is parallel to the lapels. The cran is the space that separates the lapel and the neck, and it is usually higher in Neapolitan tailoring to create the illusion of a more slender figure.
* The Body: Neapolitan jackets tend to be shorter in the back; in Neapolitan dialect, they say the jacket "zompa arrèto," which roughly translates as "it jumps in the back". This characteristic allows the jacket to "slide" gracefully along the body. The vents on the sides are pretty deep in Neapolitan jackets – up to 12 inches. The Dart (sewing), darts in the front goes all the way down to help the fabric follow the shape of the body and create elegant quarters.
* Buttons and Buttonholes: the three-roll-two construction features a lapel that hides the third button to provide extra freedom of movement thanks to a longer opening in the front. The buttonhole on the lapel is called "occhiello" in Italian, and it means "little eye" to its elongated almond shape. There isn't a tradition for a specific type of buttonhole in Naples, but there is a tendency of Neapolitan tailors to prefer slightly shorter and thicker buttonholes that resemble those of a shirt, while "regular" buttonholes of English tradition are more elongated and slender. Some tailors add a slight teardrop shape at the end of the buttonhole, an aesthetic choice that does not refer to a particular tradition. The buttons on the sleeves are always working and overlapping buttons.
Neapolitans
Honorary citizens
People awarded honorary citizenship of Naples include:
International relations
Twin towns and sister cities
Naples is town twinning, twinned with:
* Gafsa, Tunisia
* Kragujevac, Serbia
* Palma de Mallorca, Spain
* Athens, Greece
* Santiago de Cuba, Cuba
* Santiago de Cuba Province, Cuba
* Nosy Be, Madagascar
* Nablus, Palestine
* Sassari, Italy
Partnerships
* Sighetu Marmației, Romania
[
* Călărași, Romania][
* Budapest, Hungary][
* Kagoshima, Japan][Fraternity cities on Sarajevo Official Web Site](_blank)
. City of Sarajevo. 2008. Retrieved 9 November 2008.
See also
* Neapolitan Mastiff
Notes
References
Bibliography
* Acton, Harold (1956). ''The Bourbons of Naples (1734–1825)''. London: Methuen Publishing, Methuen.
* Acton, Harold (1961). ''The Last Bourbons of Naples (1825–1861)''. London: Methuen.
*
* Chaney, Edward (2000). "Inigo Jones in Naples" in ''The Evolution of the Grand Tour''. London: Routledge.
* De Grand, Alexander J. (2001).
The hunchback's tailor: Giovanni Giolitti and liberal Italy from the challenge of mass politics to the rise of fascism, 1882–1922
', Wesport/London: Praeger,
*
* Snowden, Frank M. (1995)
Naples in the Time of Cholera, 1884–1911
', Cambridge: Cambridge University Press,
External links
*
{{Authority control
Naples,
Cities and towns in Campania
Coastal towns in Campania
Cumaean colonies
Colonies of Magna Graecia
Capitals of former nations
Mediterranean port cities and towns in Italy
Populated places established in the 7th century BC
World Heritage Sites in Italy
Burial sites of the House of Dampierre


 Naples has been inhabited since the
Naples has been inhabited since the  Following the decline of the
Following the decline of the  After a period of Norman rule, in 1189 the
After a period of Norman rule, in 1189 the  Sicily and Naples were separated since 1282, but remained dependencies of
Sicily and Naples were separated since 1282, but remained dependencies of  Following the Spanish victory, Naples became part of the
Following the Spanish victory, Naples became part of the  In 1714, Spanish rule over Naples came to an end as a result of the
In 1714, Spanish rule over Naples came to an end as a result of the  Eventually, the Republicans conquered Castel Sant'Elmo and proclaimed a Parthenopaean Republic, secured by the French Army. A counter-revolutionary religious army of ''lazzaroni'' known as the ''sanfedismo, sanfedisti'' under Cardinal Fabrizio Ruffo was raised; they met with great success, and the French were forced to surrender the Neapolitan castles, with their fleet sailing back to Toulon.
Ferdinand IV was restored as king; however, after only seven years, Napoleon I of France, Napoleon conquered the kingdom and installed House of Bonaparte, Bonapartist kings, including his brother Joseph Bonaparte (King of Spain). With the help of the Austrian Empire and its allies, the Bonapartists were defeated in the Neapolitan War. Ferdinand IV once again regained the throne and the kingdom.
Eventually, the Republicans conquered Castel Sant'Elmo and proclaimed a Parthenopaean Republic, secured by the French Army. A counter-revolutionary religious army of ''lazzaroni'' known as the ''sanfedismo, sanfedisti'' under Cardinal Fabrizio Ruffo was raised; they met with great success, and the French were forced to surrender the Neapolitan castles, with their fleet sailing back to Toulon.
Ferdinand IV was restored as king; however, after only seven years, Napoleon I of France, Napoleon conquered the kingdom and installed House of Bonaparte, Bonapartist kings, including his brother Joseph Bonaparte (King of Spain). With the help of the Austrian Empire and its allies, the Bonapartists were defeated in the Neapolitan War. Ferdinand IV once again regained the throne and the kingdom.
 After the Expedition of the Thousand led by Giuseppe Garibaldi, which culminated in the controversial Siege of Gaeta (1860), Siege of Gaeta, Naples became part of the Kingdom of Italy in 1861 as part of the Italian unification, ending the era of Bourbon rule. The economy of the area formerly known as the Two Sicilies declined, leading to an unprecedented Italian diaspora, wave of emigration, with an estimated 4 million people emigrating from the Naples area between 1876 and 1913. In the forty years following unification, the population of Naples grew by only 26%, vs. 63% for Turin and 103% for Milan; however, by 1884, Naples was still the largest city in Italy with 496,499 inhabitants, or roughly 64,000 per square kilometre (more than twice the population density of Paris).
Public health conditions in certain areas of the city were poor, with twelve epidemics of cholera and typhoid fever claiming some 48,000 people between 1834 and 1884. A death rate 31.84 per thousand, high even for the time, insisted in the absence of epidemics between 1878 and 1883. Then in 1884, Naples fell victim to a major cholera epidemic, caused largely by the city's poor sewerage infrastructure. In response to these problems, in 1852, the government prompted a radical transformation of the city called ''risanamento'' to improve the sewerage infrastructure and replace the most clustered areas, considered the main cause of insalubrity, with large and airy avenues. The project proved difficult to accomplish politically and economically due to corruption, as shown in the Saredo Inquiry, land speculation and extremely long bureaucracy. This led to the project to massive delays with contrasting results. The most notable transformations made were the construction of Via Caracciolo in place of the beach along the promenade, the creation of Galleria Umberto I and c:Galleria Principe di Napoli (Naples), Galleria Principe and the construction of Corso Umberto.
After the Expedition of the Thousand led by Giuseppe Garibaldi, which culminated in the controversial Siege of Gaeta (1860), Siege of Gaeta, Naples became part of the Kingdom of Italy in 1861 as part of the Italian unification, ending the era of Bourbon rule. The economy of the area formerly known as the Two Sicilies declined, leading to an unprecedented Italian diaspora, wave of emigration, with an estimated 4 million people emigrating from the Naples area between 1876 and 1913. In the forty years following unification, the population of Naples grew by only 26%, vs. 63% for Turin and 103% for Milan; however, by 1884, Naples was still the largest city in Italy with 496,499 inhabitants, or roughly 64,000 per square kilometre (more than twice the population density of Paris).
Public health conditions in certain areas of the city were poor, with twelve epidemics of cholera and typhoid fever claiming some 48,000 people between 1834 and 1884. A death rate 31.84 per thousand, high even for the time, insisted in the absence of epidemics between 1878 and 1883. Then in 1884, Naples fell victim to a major cholera epidemic, caused largely by the city's poor sewerage infrastructure. In response to these problems, in 1852, the government prompted a radical transformation of the city called ''risanamento'' to improve the sewerage infrastructure and replace the most clustered areas, considered the main cause of insalubrity, with large and airy avenues. The project proved difficult to accomplish politically and economically due to corruption, as shown in the Saredo Inquiry, land speculation and extremely long bureaucracy. This led to the project to massive delays with contrasting results. The most notable transformations made were the construction of Via Caracciolo in place of the beach along the promenade, the creation of Galleria Umberto I and c:Galleria Principe di Napoli (Naples), Galleria Principe and the construction of Corso Umberto.
 Naples was the Bombing of Naples in World War II, most-bombed Italian city during
Naples was the Bombing of Naples in World War II, most-bombed Italian city during  Naples' 2,800-year history has left it with a wealth of historical buildings and monuments, from medieval castles to classical ruins, and a wide range of culturally and historically significant sites nearby, including the
Naples' 2,800-year history has left it with a wealth of historical buildings and monuments, from medieval castles to classical ruins, and a wide range of culturally and historically significant sites nearby, including the  The main city square or ''piazza'' of the city is the Piazza del Plebiscito. Its construction was begun by the Bonapartist king Joachim Murat and finished by the Bourbon king Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies, Ferdinand IV. The piazza is bounded on the east by the Royal Palace (Naples), Royal Palace and on the west by the church of San Francesco di Paola (Naples), San Francesco di Paola, with the colonnades extending on both sides. Nearby is the Teatro di San Carlo, which is the oldest opera house in Italy. Directly across San Carlo is Galleria Umberto I, Galleria Umberto.
Naples is well known for its castles: The most ancient is
The main city square or ''piazza'' of the city is the Piazza del Plebiscito. Its construction was begun by the Bonapartist king Joachim Murat and finished by the Bourbon king Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies, Ferdinand IV. The piazza is bounded on the east by the Royal Palace (Naples), Royal Palace and on the west by the church of San Francesco di Paola (Naples), San Francesco di Paola, with the colonnades extending on both sides. Nearby is the Teatro di San Carlo, which is the oldest opera house in Italy. Directly across San Carlo is Galleria Umberto I, Galleria Umberto.
Naples is well known for its castles: The most ancient is 
 Naples is widely known for its wealth of historical museums. The Naples National Archaeological Museum is one of the city's main museums, with one of the most extensive collections of artifact (archaeology), artefacts of the Roman Empire in the world. It also houses many of the antiques unearthed at
Naples is widely known for its wealth of historical museums. The Naples National Archaeological Museum is one of the city's main museums, with one of the most extensive collections of artifact (archaeology), artefacts of the Roman Empire in the world. It also houses many of the antiques unearthed at 


 Naples is the seat of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Naples, Archdiocese of Naples; there are hundreds of churches in the city. The Naples Cathedral, Cathedral of Naples is the city's premier place of worship; each year on 19 September, it hosts the longstanding Miracle of Januarius, Saint Januarius, the city's
Naples is the seat of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Naples, Archdiocese of Naples; there are hundreds of churches in the city. The Naples Cathedral, Cathedral of Naples is the city's premier place of worship; each year on 19 September, it hosts the longstanding Miracle of Januarius, Saint Januarius, the city's  Naples underground geothermal zone, Underneath Naples lies a series of caves and structures created by centuries of mining, and the city rests atop a major geothermal (geology), geothermal zone. There are also several ancient Greco-Roman reservoirs dug out from the soft tuff, tufo stone on which, and from which, much of the city is built. Approximately of the many kilometres of tunnels under the city can be visited from the Naples underground geothermal zone, Napoli Sotteranea, situated in the historic centre of the city in Via dei Tribunali (Naples), Via dei Tribunali. This system of tunnels and cisterns underlies most of the city and lies approximately below ground level. During
Naples underground geothermal zone, Underneath Naples lies a series of caves and structures created by centuries of mining, and the city rests atop a major geothermal (geology), geothermal zone. There are also several ancient Greco-Roman reservoirs dug out from the soft tuff, tufo stone on which, and from which, much of the city is built. Approximately of the many kilometres of tunnels under the city can be visited from the Naples underground geothermal zone, Napoli Sotteranea, situated in the historic centre of the city in Via dei Tribunali (Naples), Via dei Tribunali. This system of tunnels and cisterns underlies most of the city and lies approximately below ground level. During  Of the various park, public parks in Naples, the most prominent are the Villa Comunale, which was built by the Bourbon king Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies, Ferdinand IV in the 1780s; the park was originally a "Royal Garden", reserved for members of the royal family, but open to the public on special holidays. The Bosco di Capodimonte, the city's largest green space, served as a royal hunting reserve. The Park has 16 additional historical buildings, including residences, lodges, churches, fountains, statues, orchards and woods.
Another important park is the Parco Virgiliano, which looks towards the tiny volcanic islet of
Of the various park, public parks in Naples, the most prominent are the Villa Comunale, which was built by the Bourbon king Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies, Ferdinand IV in the 1780s; the park was originally a "Royal Garden", reserved for members of the royal family, but open to the public on special holidays. The Bosco di Capodimonte, the city's largest green space, served as a royal hunting reserve. The Park has 16 additional historical buildings, including residences, lodges, churches, fountains, statues, orchards and woods.
Another important park is the Parco Virgiliano, which looks towards the tiny volcanic islet of 
 Various buildings inspired by the Gothic Revival Architecture, Gothic Revival are extant in Naples, due to the influence that this movement had on the Scottish-Indian architect Lamont Young (Naples), Lamont Young, one of the most active Neapolitan architects of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Young left a significant footprint in the cityscape and designed many urban projects, such as the city's first subway.
In the first years of the 20th century, a local version of the Art Nouveau phenomenon, known as "Liberty Napoletano", developed in the city, creating many buildings which still stand today. In 1935, the Rationalist architect Luigi Cosenza designed a new fish market for the city. During the
Various buildings inspired by the Gothic Revival Architecture, Gothic Revival are extant in Naples, due to the influence that this movement had on the Scottish-Indian architect Lamont Young (Naples), Lamont Young, one of the most active Neapolitan architects of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Young left a significant footprint in the cityscape and designed many urban projects, such as the city's first subway.
In the first years of the 20th century, a local version of the Art Nouveau phenomenon, known as "Liberty Napoletano", developed in the city, creating many buildings which still stand today. In 1935, the Rationalist architect Luigi Cosenza designed a new fish market for the city. During the  The city is situated on the Gulf of Naples, on the western coast of southern Italy; it rises from sea level to an elevation of . The small rivers that formerly crossed the city's centre have since been covered by construction. It lies between two notable volcanic regions, Mount Vesuvius and the Campi Flegrei ( en, Phlegraean Fields). The islands of Procida, Capri and Ischia can all be reached from Naples by hydrofoils and ferries. Sorrento, Italy, Sorrento and the Amalfi Coast are situated south of the city. At the same time, the Roman ruins of
The city is situated on the Gulf of Naples, on the western coast of southern Italy; it rises from sea level to an elevation of . The small rivers that formerly crossed the city's centre have since been covered by construction. It lies between two notable volcanic regions, Mount Vesuvius and the Campi Flegrei ( en, Phlegraean Fields). The islands of Procida, Capri and Ischia can all be reached from Naples by hydrofoils and ferries. Sorrento, Italy, Sorrento and the Amalfi Coast are situated south of the city. At the same time, the Roman ruins of  The thirty quarters (''quartiere, quartieri'') of Naples are listed below. For administrative purposes, these thirty districts are grouped together into ten governmental community boards.
The thirty quarters (''quartiere, quartieri'') of Naples are listed below. For administrative purposes, these thirty districts are grouped together into ten governmental community boards.
 , the population of the ''comune di Napoli'' totals around 910,000. Naples' wider Naples metropolitan area, metropolitan area, sometimes known as Greater Naples, has a population of approximately 4.4 million. The demographic profile for the Neapolitan province in general is relatively young: 19% are under the age of 14, while 13% are over 65, compared to the national average of 14% and 19%, respectively. Naples has a higher percentage of females (52.5%) than males (47.5%).‘City’ population (i.e. that of the ''comune'' or municipality)
, the population of the ''comune di Napoli'' totals around 910,000. Naples' wider Naples metropolitan area, metropolitan area, sometimes known as Greater Naples, has a population of approximately 4.4 million. The demographic profile for the Neapolitan province in general is relatively young: 19% are under the age of 14, while 13% are over 65, compared to the national average of 14% and 19%, respectively. Naples has a higher percentage of females (52.5%) than males (47.5%).‘City’ population (i.e. that of the ''comune'' or municipality)


 Naples, within its administrative limits, is Italy's fourth-largest economy after
Naples, within its administrative limits, is Italy's fourth-largest economy after 

 Naples is served by several major motorways (Italian language, it: ''autostrade''). The Autostrada A1 (Italy), Autostrada A1, the longest Autostrade of Italy, motorway in Italy, links Naples to
Naples is served by several major motorways (Italian language, it: ''autostrade''). The Autostrada A1 (Italy), Autostrada A1, the longest Autostrade of Italy, motorway in Italy, links Naples to 
 Naples is internationally famous for its Neapolitan cuisine, cuisine and wine; it draws culinary influences from the numerous cultures which have inhabited it throughout its history, including the Ancient Greece, Greeks, Spanish and French. Neapolitan cuisine emerged as a distinct form in the 18th century. The ingredients are typically rich in taste while remaining affordable to the general populace.
Naples is traditionally credited as the home of
Naples is internationally famous for its Neapolitan cuisine, cuisine and wine; it draws culinary influences from the numerous cultures which have inhabited it throughout its history, including the Ancient Greece, Greeks, Spanish and French. Neapolitan cuisine emerged as a distinct form in the 18th century. The ingredients are typically rich in taste while remaining affordable to the general populace.
Naples is traditionally credited as the home of  * ''Festa di Piedigrotta'' ("Piedigrotta Festival") – A musical event typically held in September in memory of the famous Madonna of Piedigrotta. Throughout the month, a series of musical workshops, concerts, religious events and children's events are held to entertain the citizens of Naples and surrounding areas.
* ''Pizzafest'' – As Naples is famous for being home to pizza, the city hosts an eleven-day festival dedicated to this iconic dish. This is a key event for Neapolitans and tourists alike, as various stations are open for tasting a wide range of true Neapolitan pizza. In addition to pizza tasting, a variety of entertainment shows are displayed.
* ''Maggio dei Monumenti'' ("May of Monuments") – A cultural event where the city hosts a variety of special events dedicated to the birth of King Charles of Bourbon. It festival features art and music of the 18th century, and many buildings which may normally be closed throughout the year are opened for visitors to view.
* ''Il Ritorno della festa di San Gennaro'' ("The Return of the Feast of San Gennaro") – An annual celebration and feast of faith held over three days, commemorating Saint Januarius, Gennaro. Throughout the festival, parades, religious processions and musical entertainment are featured. An annual celebration is also held in "Little Italy, Manhattan, Little Italy" in Manhattan.
* ''Festa di Piedigrotta'' ("Piedigrotta Festival") – A musical event typically held in September in memory of the famous Madonna of Piedigrotta. Throughout the month, a series of musical workshops, concerts, religious events and children's events are held to entertain the citizens of Naples and surrounding areas.
* ''Pizzafest'' – As Naples is famous for being home to pizza, the city hosts an eleven-day festival dedicated to this iconic dish. This is a key event for Neapolitans and tourists alike, as various stations are open for tasting a wide range of true Neapolitan pizza. In addition to pizza tasting, a variety of entertainment shows are displayed.
* ''Maggio dei Monumenti'' ("May of Monuments") – A cultural event where the city hosts a variety of special events dedicated to the birth of King Charles of Bourbon. It festival features art and music of the 18th century, and many buildings which may normally be closed throughout the year are opened for visitors to view.
* ''Il Ritorno della festa di San Gennaro'' ("The Return of the Feast of San Gennaro") – An annual celebration and feast of faith held over three days, commemorating Saint Januarius, Gennaro. Throughout the festival, parades, religious processions and musical entertainment are featured. An annual celebration is also held in "Little Italy, Manhattan, Little Italy" in Manhattan.
 Naples is one of the leading centres of Italian literature. The history of the Neapolitan language was deeply entwined with that of the Tuscan dialect, which then became the current Italian language. The first written testimonies of the Italian language are the Placiti Cassinensi legal documents, dated 960 A.D., preserved in the Monte Cassino Abbey, which are, in fact, evidence of a language spoken in a southern dialect. The Tuscan poet Boccaccio lived for many years at the court of King Robert the Wise and his successor Joanna I of Naples, Joanna of Naples, using Naples as a setting for ''The Decameron'' and a number of his later novels. His works contain some words that are taken from Neapolitan instead of the corresponding Italian, e.g. "testo" (neap.: "testa"), which in Naples indicates a large terracotta jar used to cultivate shrubs and little trees. King Alfonso V of Aragon stated in 1442 that the Neapolitan language was to be used instead of Latin in official documents.
Naples is one of the leading centres of Italian literature. The history of the Neapolitan language was deeply entwined with that of the Tuscan dialect, which then became the current Italian language. The first written testimonies of the Italian language are the Placiti Cassinensi legal documents, dated 960 A.D., preserved in the Monte Cassino Abbey, which are, in fact, evidence of a language spoken in a southern dialect. The Tuscan poet Boccaccio lived for many years at the court of King Robert the Wise and his successor Joanna I of Naples, Joanna of Naples, using Naples as a setting for ''The Decameron'' and a number of his later novels. His works contain some words that are taken from Neapolitan instead of the corresponding Italian, e.g. "testo" (neap.: "testa"), which in Naples indicates a large terracotta jar used to cultivate shrubs and little trees. King Alfonso V of Aragon stated in 1442 that the Neapolitan language was to be used instead of Latin in official documents.
 Naples was one of the centres of the peninsula from which originated the modern theatre genre as nowadays intended, evolving from 16th century "commedia dell'arte, comedy of art".
The masked character of Pulcinella is a worldwide famous figure either as a theatrical character or puppetry character.
The music Opera genre of opera buffa was created in Naples in the 18th century and then spread to Rome and northern Italy. In the period of Belle Époque, Naples rivalled Paris for its Café-chantants, and many famous Neapolitan songs were originally created to entertain the public in the cafès of Naples. Perhaps the most well-known song is "Ninì Tirabusciò". The history of how this song was born was dramatised in the eponymous comedy movie "Ninì Tirabusciò: la donna che inventò la mossa" starring Monica Vitti.
The Neapolitan popular genre of "Sceneggiata" is an important genre of modern folk theatre worldwide, dramatising common canon themes of thwarted love stories, comedies, tearjerker stories, commonly about honest people becoming camorra outlaws due to unfortunate events. The Sceneggiata became very popular amongst Neapolitans and eventually one of the best-known genres of Italian cinematography thanks to actors and singers like Mario Merola (singer), Mario Merola and Nino D'Angelo. Many writers and playwrights, such as Raffaele Viviani, wrote comedies and dramas for this genre. Actors and comedians like Eduardo Scarpetta and then his sons Eduardo De Filippo, Peppino De Filippo and Titina De Filippo contributed to making the Neapolitan theatre. Its comedies and tragedies, such as "Filumena Marturano" and "Side Street Story, Napoli Milionaria", are well-known.
Naples was one of the centres of the peninsula from which originated the modern theatre genre as nowadays intended, evolving from 16th century "commedia dell'arte, comedy of art".
The masked character of Pulcinella is a worldwide famous figure either as a theatrical character or puppetry character.
The music Opera genre of opera buffa was created in Naples in the 18th century and then spread to Rome and northern Italy. In the period of Belle Époque, Naples rivalled Paris for its Café-chantants, and many famous Neapolitan songs were originally created to entertain the public in the cafès of Naples. Perhaps the most well-known song is "Ninì Tirabusciò". The history of how this song was born was dramatised in the eponymous comedy movie "Ninì Tirabusciò: la donna che inventò la mossa" starring Monica Vitti.
The Neapolitan popular genre of "Sceneggiata" is an important genre of modern folk theatre worldwide, dramatising common canon themes of thwarted love stories, comedies, tearjerker stories, commonly about honest people becoming camorra outlaws due to unfortunate events. The Sceneggiata became very popular amongst Neapolitans and eventually one of the best-known genres of Italian cinematography thanks to actors and singers like Mario Merola (singer), Mario Merola and Nino D'Angelo. Many writers and playwrights, such as Raffaele Viviani, wrote comedies and dramas for this genre. Actors and comedians like Eduardo Scarpetta and then his sons Eduardo De Filippo, Peppino De Filippo and Titina De Filippo contributed to making the Neapolitan theatre. Its comedies and tragedies, such as "Filumena Marturano" and "Side Street Story, Napoli Milionaria", are well-known.
 Naples has played an important role in the history of Classical music, Western European art music for more than four centuries. The first music conservatories of Naples, music conservatories were established in the city under Spanish rule in the 16th century. The San Pietro a Majella music conservatory, founded in 1826 by Francis I of the Two Sicilies, Francesco I of Bourbon, continues to operate today as both a prestigious centre of musical education and a musical museum.
During the late Baroque music, Baroque period, Alessandro Scarlatti, the father of Domenico Scarlatti, established the Neapolitan school of opera; this was in the form of ''opera seria'', which was a new development for its time. Another form of opera originating in Naples is ''opera buffa'', a style of comic opera strongly linked to Giovanni Battista Pergolesi, Battista Pergolesi and Niccolò Piccinni, Piccinni; later contributors to the genre included Gioachino Rossini, Rossini and Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart. The Teatro di San Carlo, built in 1737, is the oldest working theatre in Europe, and remains the operatic centre of Naples.
Naples has played an important role in the history of Classical music, Western European art music for more than four centuries. The first music conservatories of Naples, music conservatories were established in the city under Spanish rule in the 16th century. The San Pietro a Majella music conservatory, founded in 1826 by Francis I of the Two Sicilies, Francesco I of Bourbon, continues to operate today as both a prestigious centre of musical education and a musical museum.
During the late Baroque music, Baroque period, Alessandro Scarlatti, the father of Domenico Scarlatti, established the Neapolitan school of opera; this was in the form of ''opera seria'', which was a new development for its time. Another form of opera originating in Naples is ''opera buffa'', a style of comic opera strongly linked to Giovanni Battista Pergolesi, Battista Pergolesi and Niccolò Piccinni, Piccinni; later contributors to the genre included Gioachino Rossini, Rossini and Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart. The Teatro di San Carlo, built in 1737, is the oldest working theatre in Europe, and remains the operatic centre of Naples.

 The earliest six-string guitar was created by the Neapolitan Gaetano Vinaccia in 1779; the instrument is now referred to as the romantic guitar. The Vinaccia family also developed the mandolin. Influenced by the Spanish, Neapolitans became pioneers of classical guitar music, with Ferdinando Carulli and Mauro Giuliani being prominent exponents. Giuliani, who was actually from Apulia but lived and worked in Naples, is widely considered to be one of the greatest guitarist, guitar players and composers of the 19th century, along with his Catalonia, Catalan contemporary Fernando Sor. Another Neapolitan musician of note was opera singer Enrico Caruso, one of the most prominent opera tenors of all time: he was considered a man of the people in Naples, hailing from a working-class background.
A popular traditional dance in Southern Italy and Naples is the Tarantella, which originated in Apulia and spread throughout the
The earliest six-string guitar was created by the Neapolitan Gaetano Vinaccia in 1779; the instrument is now referred to as the romantic guitar. The Vinaccia family also developed the mandolin. Influenced by the Spanish, Neapolitans became pioneers of classical guitar music, with Ferdinando Carulli and Mauro Giuliani being prominent exponents. Giuliani, who was actually from Apulia but lived and worked in Naples, is widely considered to be one of the greatest guitarist, guitar players and composers of the 19th century, along with his Catalonia, Catalan contemporary Fernando Sor. Another Neapolitan musician of note was opera singer Enrico Caruso, one of the most prominent opera tenors of all time: he was considered a man of the people in Naples, hailing from a working-class background.
A popular traditional dance in Southern Italy and Naples is the Tarantella, which originated in Apulia and spread throughout the  Naples has had a significant influence on Italian cinema. Because of the city's relevance, many films and television shows are set (entirely or partially) in Naples. In addition to serving as the backdrop for several movies and shows, many talented celebrities (actors, actresses, directors, and producers) are originally from Naples.
Naples was the location for several early Italian cinema masterpieces. ''Assunta Spina (1915 film), Assunta Spina'' (1915) was a silent film adapted from a theatrical drama by Neapolitan writer Salvatore Di Giacomo. The film was directed by Neapolitan Gustavo Serena. Serena also starred in the 1912 film ''Romeo and Juliet''.
A list of some well-known films that take place (fully or partially) in Naples includes:
* ''Shoeshine (film), Shoeshine'' (1946), directed by Neapolitan, Vittorio De Sica
* ''Hands over the City'' (1963), directed by Neapolitan, Francesco Rosi
* ''Journey to Italy'' (1954), directed by Roberto Rossellini
* ''Marriage Italian Style'' (1964), directed by Neapolitan, Vittorio De Sica
* ''It Started in Naples'' (1960), Directed by Melville Shavelson
* ''The Hand of God (film)'' (2021), Directed by Paolo Sorrentino
Naples is home to one of the first Italian colour films, ''Toto in Color'' (1952), starring Totò (Antonio de Curtis), a famous comedic actor born in Naples.
Some notable comedies set in Naples include ''Ieri, Oggi e Domani'' (Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow), by Vittorio De Sica, starring Sophia Loren and Marcello Mastroianni, ''Adelina of Naples'' (Academy Award-winning movie), ''It Started in Naples'', ''L'oro di Napoli'' again by Vittorio De Sica, dramatic movies like Dino Risi's ''Profumo di donna, Scent of a Woman'', war movies like ''The Four Days of Naples (film), The Four Days of Naples'' by Sardinian director Nanni Loy, music and Sceneggiata movies like ''Zappatore'', from the eponymous song by Libero Bovio, starring singer and actor Mario Merola (singer), Mario Merola, crime movies like ''Il Camorrista'' with Ben Gazzara playing the part of infamous camorra boss Raffaele Cutolo, and historical or costume movies like ''That Hamilton Woman'' starring Vivien Leigh and Laurence Olivier.
More modern Neapolitan films include ''Ricomincio da tre'', which depicts the misadventures of a young emigrant in the late 20th century. The 2008 film ''Gomorrah (film), Gomorrah'', based on the book by Roberto Saviano, explores the dark underbelly of the city of Naples through five intertwining stories about the powerful Camorra, Neapolitan crime syndicate, as well as the Gomorrah (TV series), TV series of the same name.
The Japanese series ''JoJo's Bizarre Adventure''s Part 5, Golden Wind (manga), Vento Aureo, takes place in the city.
Several episodes of the animated series ''Tom and Jerry'' also have references/influences from Naples. The song "Santa Lucia (song), Santa Lucia" played by Tom Cat in ''Cat and Dupli-cat'' has its origins in Naples. Neapolitan Mouse takes place in the same city.
Naples has appeared in episodes of TV serials such as ''The Sopranos'' and the 1998 version of ''The Count of Monte Cristo (1998 miniseries), The Count of Monte Cristo'', starring Gérard Depardieu.
Naples has had a significant influence on Italian cinema. Because of the city's relevance, many films and television shows are set (entirely or partially) in Naples. In addition to serving as the backdrop for several movies and shows, many talented celebrities (actors, actresses, directors, and producers) are originally from Naples.
Naples was the location for several early Italian cinema masterpieces. ''Assunta Spina (1915 film), Assunta Spina'' (1915) was a silent film adapted from a theatrical drama by Neapolitan writer Salvatore Di Giacomo. The film was directed by Neapolitan Gustavo Serena. Serena also starred in the 1912 film ''Romeo and Juliet''.
A list of some well-known films that take place (fully or partially) in Naples includes:
* ''Shoeshine (film), Shoeshine'' (1946), directed by Neapolitan, Vittorio De Sica
* ''Hands over the City'' (1963), directed by Neapolitan, Francesco Rosi
* ''Journey to Italy'' (1954), directed by Roberto Rossellini
* ''Marriage Italian Style'' (1964), directed by Neapolitan, Vittorio De Sica
* ''It Started in Naples'' (1960), Directed by Melville Shavelson
* ''The Hand of God (film)'' (2021), Directed by Paolo Sorrentino
Naples is home to one of the first Italian colour films, ''Toto in Color'' (1952), starring Totò (Antonio de Curtis), a famous comedic actor born in Naples.
Some notable comedies set in Naples include ''Ieri, Oggi e Domani'' (Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow), by Vittorio De Sica, starring Sophia Loren and Marcello Mastroianni, ''Adelina of Naples'' (Academy Award-winning movie), ''It Started in Naples'', ''L'oro di Napoli'' again by Vittorio De Sica, dramatic movies like Dino Risi's ''Profumo di donna, Scent of a Woman'', war movies like ''The Four Days of Naples (film), The Four Days of Naples'' by Sardinian director Nanni Loy, music and Sceneggiata movies like ''Zappatore'', from the eponymous song by Libero Bovio, starring singer and actor Mario Merola (singer), Mario Merola, crime movies like ''Il Camorrista'' with Ben Gazzara playing the part of infamous camorra boss Raffaele Cutolo, and historical or costume movies like ''That Hamilton Woman'' starring Vivien Leigh and Laurence Olivier.
More modern Neapolitan films include ''Ricomincio da tre'', which depicts the misadventures of a young emigrant in the late 20th century. The 2008 film ''Gomorrah (film), Gomorrah'', based on the book by Roberto Saviano, explores the dark underbelly of the city of Naples through five intertwining stories about the powerful Camorra, Neapolitan crime syndicate, as well as the Gomorrah (TV series), TV series of the same name.
The Japanese series ''JoJo's Bizarre Adventure''s Part 5, Golden Wind (manga), Vento Aureo, takes place in the city.
Several episodes of the animated series ''Tom and Jerry'' also have references/influences from Naples. The song "Santa Lucia (song), Santa Lucia" played by Tom Cat in ''Cat and Dupli-cat'' has its origins in Naples. Neapolitan Mouse takes place in the same city.
Naples has appeared in episodes of TV serials such as ''The Sopranos'' and the 1998 version of ''The Count of Monte Cristo (1998 miniseries), The Count of Monte Cristo'', starring Gérard Depardieu.
 Association football, Football is by far the most popular sport in Naples. Brought to the city by the British during the early 20th century, the sport is deeply embedded in local culture: it is popular at every level of society, from the ''scugnizzi'' (street children) to wealthy professionals. The city's best known football club (association football), football club is S.S.C. Napoli, SSC Napoli, which plays its home games at the Stadio San Paolo in
Association football, Football is by far the most popular sport in Naples. Brought to the city by the British during the early 20th century, the sport is deeply embedded in local culture: it is popular at every level of society, from the ''scugnizzi'' (street children) to wealthy professionals. The city's best known football club (association football), football club is S.S.C. Napoli, SSC Napoli, which plays its home games at the Stadio San Paolo in