Nao de China on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
fil, Galyon ng Maynila
, english_name = Manila Galleon
, duration = From 1565 to 1815 (250 years)
, venue = Between Manila and
(Current Mexico) , motive = Trading maritime route from East Indies to the

 In order to settle and trade with these islands from the Americas, an eastward maritime return path was necessary. The Trinidad, which tried this a few years later, failed. In 1529, Álvaro de Saavedra Cerón also tried sailing east from the Philippines, but could not find the eastward-blowing winds (" westerlies") across the Pacific. In 1543,
In order to settle and trade with these islands from the Americas, an eastward maritime return path was necessary. The Trinidad, which tried this a few years later, failed. In 1529, Álvaro de Saavedra Cerón also tried sailing east from the Philippines, but could not find the eastward-blowing winds (" westerlies") across the Pacific. In 1543,
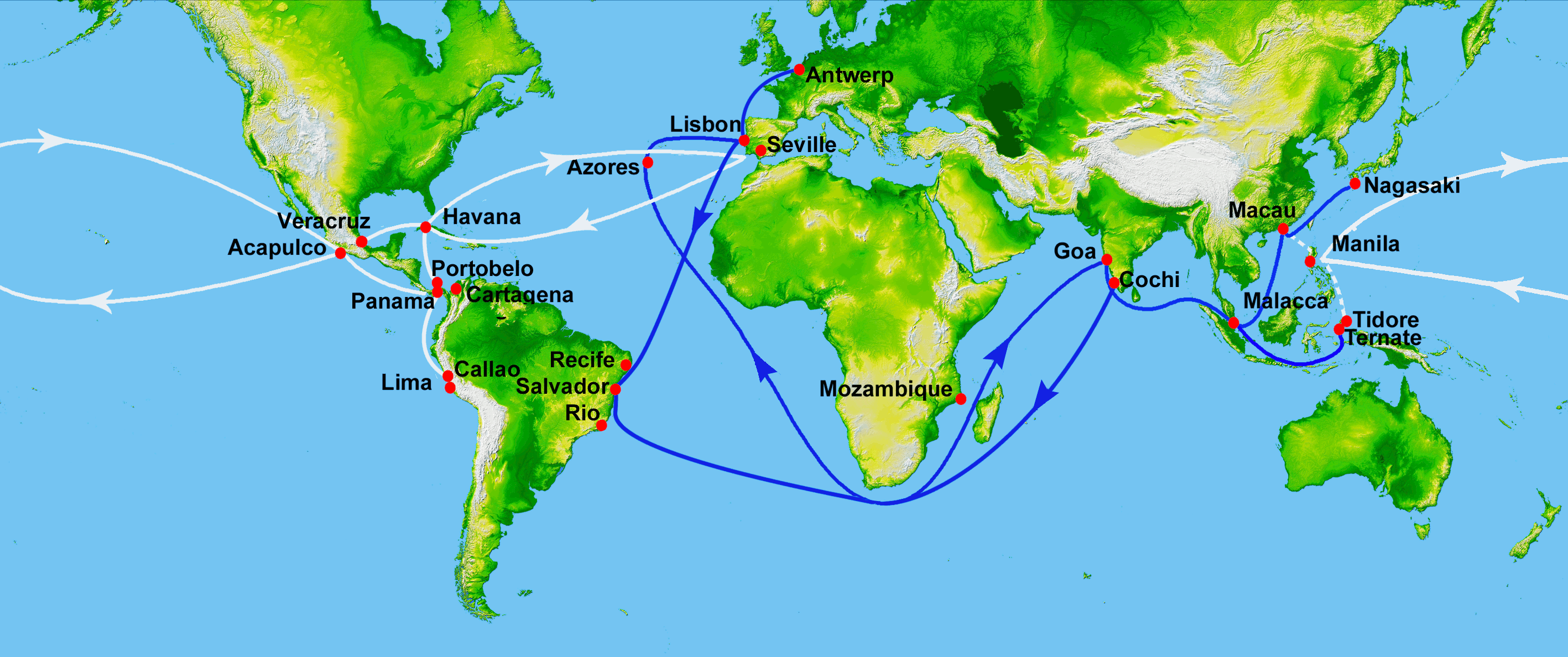 Trade with
Trade with  The galleon trade was supplied by merchants largely from port areas of Fujian, such as
The galleon trade was supplied by merchants largely from port areas of Fujian, such as  Around 80% of the goods shipped back from Acapulco to Manila were from the Americas - silver, cochineal, seeds, sweet potato, corn, tomato, tobacco, chickpeas, chocolate and cocoa, watermelon seeds, vines, and fig trees. The remaining 20% were goods transshipped from Europe and North Africa such as wine and olive oil, and metal goods such as weapons, knobs and spurs.
This Pacific route was the alternative to the trip west across the Indian Ocean, and around the
Around 80% of the goods shipped back from Acapulco to Manila were from the Americas - silver, cochineal, seeds, sweet potato, corn, tomato, tobacco, chickpeas, chocolate and cocoa, watermelon seeds, vines, and fig trees. The remaining 20% were goods transshipped from Europe and North Africa such as wine and olive oil, and metal goods such as weapons, knobs and spurs.
This Pacific route was the alternative to the trip west across the Indian Ocean, and around the
 Between 1609 and 1616, 9 galleons and 6 galleys were constructed in Philippine shipyards. The average cost was 78,000 pesos per galleon and at least 2,000 trees. The galleons constructed included the ''San Juan Bautista'', ''San Marcos'', ''Nuestra Senora de Guadalupe'', ''Angel de la Guardia'', ''San Felipe'', ''Santiago'', ''Salbador'', ''Espiritu Santo'', and ''San Miguel''. "From 1729 to 1739, the main purpose of the Cavite shipyard was the construction and outfitting of the galleons for the Manila to Acapulco trade run."
Due to the route's high profitability but long voyage time, it was essential to build the largest possible galleons, which were the largest class of European ships known to have been built until then. In the 16th century, they averaged from 1,700 to 2,000 tons, were built of Philippine hardwoods and could carry 300 - 500 passengers. The ''Concepción'', wrecked in 1638, was long and displacing some 2,000 tons. The ''Santísima Trinidad'' was long. Most of the ships were built in the Philippines and only eight in Mexico.
Between 1609 and 1616, 9 galleons and 6 galleys were constructed in Philippine shipyards. The average cost was 78,000 pesos per galleon and at least 2,000 trees. The galleons constructed included the ''San Juan Bautista'', ''San Marcos'', ''Nuestra Senora de Guadalupe'', ''Angel de la Guardia'', ''San Felipe'', ''Santiago'', ''Salbador'', ''Espiritu Santo'', and ''San Miguel''. "From 1729 to 1739, the main purpose of the Cavite shipyard was the construction and outfitting of the galleons for the Manila to Acapulco trade run."
Due to the route's high profitability but long voyage time, it was essential to build the largest possible galleons, which were the largest class of European ships known to have been built until then. In the 16th century, they averaged from 1,700 to 2,000 tons, were built of Philippine hardwoods and could carry 300 - 500 passengers. The ''Concepción'', wrecked in 1638, was long and displacing some 2,000 tons. The ''Santísima Trinidad'' was long. Most of the ships were built in the Philippines and only eight in Mexico.
 This navigational activity poses the question as to whether Spanish explorers did arrive in the Hawaiian Islands two centuries before Captain
This navigational activity poses the question as to whether Spanish explorers did arrive in the Hawaiian Islands two centuries before Captain  The westward route from Mexico passed south of Hawaii, making a short stopover in Guam before heading for Manila. The exact route was kept secret to protect the Spanish trade monopoly against competing powers, and to avoid Dutch and English pirates. Due to this policy of discretion, if the Spanish did find Hawaii during their voyages, they would not have published their findings and the discovery would have remained unknown. From Gaetano's account, the Hawaiian islands were not known to have any valuable resources, so the Spanish would not have made an effort to settle them. This happened in the case of the Marianas and the Carolines, which were not effectively settled until the second half of the 17th century. Spanish archives contain a chart that depicts islands in the latitude of Hawaii but with the longitude ten degrees east of the Islands ( reliable methods of determining longitude were not developed until the mid-eighteenth century). In this manuscript, the Island of
The westward route from Mexico passed south of Hawaii, making a short stopover in Guam before heading for Manila. The exact route was kept secret to protect the Spanish trade monopoly against competing powers, and to avoid Dutch and English pirates. Due to this policy of discretion, if the Spanish did find Hawaii during their voyages, they would not have published their findings and the discovery would have remained unknown. From Gaetano's account, the Hawaiian islands were not known to have any valuable resources, so the Spanish would not have made an effort to settle them. This happened in the case of the Marianas and the Carolines, which were not effectively settled until the second half of the 17th century. Spanish archives contain a chart that depicts islands in the latitude of Hawaii but with the longitude ten degrees east of the Islands ( reliable methods of determining longitude were not developed until the mid-eighteenth century). In this manuscript, the Island of
"The Manila Galleon and California"
''Southwestern Historical Quarterly'', Vol. 21, No. 2, pp. 107–126 *Schurz, William Lytle. ''The Manila Galleon''. New York: E. P. Dutton & Co., Inc., 1939.
Findings from the wreck of ''Nuestra Senora de la Concepcion'' in the Marianas, 1638Asociación Cultural Galeón de Manila
Spanish-Philippine research group based in Madrid (in Spanish) {{DEFAULTSORT:Manila Galleon Galleons Spanish East Indies History of the Philippines (1565–1898) Spanish colonization of the Americas Age of Sail ships of Spain Naval ships of Spain Military history of the Pacific Ocean History of Manila History of New Spain Colonial Mexico Pacific Coast of Mexico Sea lanes Merchant sailing ship types New Spain 1565 establishments in Spain 1565 establishments in New Spain 1810s disestablishments in Spain 19th-century disestablishments in New Spain 16th century in the Spanish East Indies 17th century in the Spanish East Indies 18th century in the Spanish East Indies 19th century in the Spanish East Indies Early Modern economics
Acapulco
Acapulco de Juárez (), commonly called Acapulco ( , also , nah, Acapolco), is a city and major seaport in the state of Guerrero on the Pacific Coast of Mexico, south of Mexico City. Acapulco is located on a deep, semicircular bay and has bee ...
, location = New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Am ...
( Spanish Empire) (Current Mexico) , motive = Trading maritime route from East Indies to the
Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
, organisers = Spanish Crown
, coatofarms = File:Coat_of_Arms_of_Spanish_Monarch.svg
, coatofarms_article = Coat of arms of the King of Spain
, image = Felipe_VI_in_2020_(cropped).jpg
, incumbent = Felipe VI
, incumbentsince = 19 Ju ...
The Manila galleons ( es, Galeón de Manila; fil, Galyon ng Maynila) were Spanish trading ships which for two and a half centuries linked the Spanish Crown’s Viceroyalty of New Spain, based in Mexico City, with her Asian territories, collectively known as the Spanish East Indies, across the Pacific Ocean. The ships made one or two round-trip voyages per year between the ports of Acapulco
Acapulco de Juárez (), commonly called Acapulco ( , also , nah, Acapolco), is a city and major seaport in the state of Guerrero on the Pacific Coast of Mexico, south of Mexico City. Acapulco is located on a deep, semicircular bay and has bee ...
and Manila. The name of the galleon changed to reflect the city that the ship sailed from. The term ''Manila galleon'' can also refer to the trade route itself between Acapulco and Manila, which lasted from 1565 to 1815.
The Manila galleons sailed the Pacific for 250 years, bringing to the Americas cargoes of luxury goods
In economics, a luxury good (or upmarket good) is a good for which demand increases more than what is proportional as income rises, so that expenditures on the good become a greater proportion of overall spending. Luxury goods are in contrast to n ...
such as spices and porcelain in exchange for New World silver. The route also fostered cultural exchanges that shaped the identities and culture of the countries involved.
The Manila galleons were also (somewhat confusingly) known in New Spain as ''La Nao de la China'' ("The China Ship") on their voyages from the Philippines because they carried mostly Chinese goods, shipped from Manila.
The Spanish inaugurated the Manila galleon trade route in 1565 after the Augustinian Augustinian may refer to:
*Augustinians, members of religious orders following the Rule of St Augustine
*Augustinianism, the teachings of Augustine of Hippo and his intellectual heirs
*Someone who follows Augustine of Hippo
* Canons Regular of Sain ...
friar and navigator Andrés de Urdaneta pioneered the ''tornaviaje'' or return route from the Philippines to Mexico. Urdaneta and Alonso de Arellano made the first successful round trips that year. The trade using "Urdaneta's route" lasted until 1815, when the Mexican War of Independence broke out.
In 2015 the Philippines and Mexico began preparations for the nomination of the Manila-Acapulco Galleon Trade Route in the UNESCO World Heritage List, with backing from Spain. Spain has also suggested the tri-national nomination of the Archives on the Manila-Acapulco Galleons in the UNESCO Memory of the World Register.
History
Discovery of the route
In 1521, a Spanish expedition led by Ferdinand Magellan sailed west across the Pacific using the westward trade winds. The expedition discovered theMariana Islands
The Mariana Islands (; also the Marianas; in Chamorro: ''Manislan Mariånas'') are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, betw ...
and the Philippines and claimed them for Spain. Although Magellan was killed by natives commanded by Lapulapu during the battle of Mactan, one of his ships, the ''Victoria'', made it back to Spain by continuing westward.

 In order to settle and trade with these islands from the Americas, an eastward maritime return path was necessary. The Trinidad, which tried this a few years later, failed. In 1529, Álvaro de Saavedra Cerón also tried sailing east from the Philippines, but could not find the eastward-blowing winds (" westerlies") across the Pacific. In 1543,
In order to settle and trade with these islands from the Americas, an eastward maritime return path was necessary. The Trinidad, which tried this a few years later, failed. In 1529, Álvaro de Saavedra Cerón also tried sailing east from the Philippines, but could not find the eastward-blowing winds (" westerlies") across the Pacific. In 1543, Bernardo de la Torre Bernardo de la Torre was a Spanish sailor, primarily noted for having explored parts of the Western Pacific Ocean south of Japan in the 16th century.
Bernardo de la Torre sailed under the instructions of Ruy López de Villalobos, who sent him in Au ...
also failed. In 1542, however, Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo
Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo ( pt, João Rodrigues Cabrilho; c. 1499 – January 3, 1543) was an Iberian maritime explorer best known for investigations of the West Coast of North America, undertaken on behalf of the Spanish Empire. He was the firs ...
helped pave the way by sailing north from Mexico to explore the Pacific coast, reaching as far north as the Russian River, just north of the 38th parallel. The frustration of these failures is shown in a letter sent in 1552 from Portuguese Goa by the Spanish missionary Francis Xavier to Simão Rodrigues
Simão Rodrigues de Azevedo (1510, Vouzela, Portugal - 15 June 1579, Lisbon), also known in English as Simon Rodericks, was a Portuguese Jesuit priest and one of the co-founders of the Society of Jesus.
A Portuguese nobleman, Rodrigues was one o ...
asking that no more fleets attempt the New Spain–East Asia route, lest they be lost.
The letter is referenced as
The Manila–Acapulco galleon trade finally began when Spanish navigators Alonso de Arellano and Andrés de Urdaneta discovered the eastward return route in 1565. Sailing as part of the expedition commanded by Miguel López de Legazpi
Miguel López de Legazpi (12 June 1502 – 20 August 1572), also known as '' El Adelantado'' and ''El Viejo'' (The Elder), was a Spaniard who, from the age of 26, lived and built a career in Mexico (then the Viceroyalty of New Spain) and, i ...
to conquer the Philippines in 1564, Urdaneta was given the task of finding a return route. Reasoning that the trade winds of the Pacific might move in a gyre as the Atlantic winds did, they sailed north, going all the way to the 38th parallel north
The 38th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 38 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, the Mediterranean Sea, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean. The 38th parallel north formed ...
, off the east coast of Japan, before catching the westerlies that would take them back across the Pacific. He commanded a vessel which completed the eastward voyage in 129 days; this marked the opening of the Manila galleon trade.
Reaching the west coast of North America
The human history of the west coast of North America is believed to stretch back to the arrival of the earliest people over the Bering Strait, or alternately along a now-submerged coastal plain, through the development of significant pre-Columbi ...
, Urdaneta's ship, the ''San Pedro'', hit the coast near Santa Catalina Island, California, then followed the shoreline south to San Blas and later to Acapulco
Acapulco de Juárez (), commonly called Acapulco ( , also , nah, Acapolco), is a city and major seaport in the state of Guerrero on the Pacific Coast of Mexico, south of Mexico City. Acapulco is located on a deep, semicircular bay and has bee ...
, arriving on October 8, 1565. Most of his crew died on the long initial voyage, for which they had not sufficiently provisioned. Arellano, who had taken a more southerly route, had already arrived.
The English privateer Francis Drake
Sir Francis Drake ( – 28 January 1596) was an English explorer, sea captain, privateer, slave trader, naval officer, and politician. Drake is best known for his circumnavigation of the world in a single expedition, from 1577 to 1580 (t ...
also reached the California coast, in 1579. After capturing a Spanish ship heading for Manila, Drake turned north, hoping to meet another Spanish treasure ship coming south on its return from Manila to Acapulco. He failed in that regard, but staked an English claim somewhere on the northern California coast. Although the ship's log and other records were lost, the officially accepted location is now called Drakes Bay, on Point Reyes south of Cape Mendocino.
By the 18th century, it was understood that a less northerly track was sufficient when nearing the North American coast, and galleon navigators steered well clear of the rocky and often fogbound northern and central California coast. According to historian William Lytle Schurz, "They generally made their landfall well down the coast, somewhere between Point Conception and Cape San Lucas ... After all, these were preeminently merchant ships, and the business of exploration lay outside their field, though chance discoveries were welcomed".Schurz 1917, p.107-108
The first motivation for land exploration of present-day California was to scout out possible way stations for the seaworn Manila galleons on the last leg of their journey. Early proposals came to little, but in 1769, the Portola expedition established ports at San Diego and Monterey (which became the administrative center of Alta California
Alta California ('Upper California'), also known as ('New California') among other names, was a province of New Spain, formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but ...
), providing safe harbors for returning Manila galleons.
The Manila galleon and California
Monterey, California was about two months and three weeks out from Manila in the 18th century, and the galleon tended to stop there 40 days before arriving in Acapulco. Galleons stopped in Monterey prior to California's settlement by the Spanish in 1769; however visits became regular between 1777 and 1794 because the Crown ordered the galleon to stop in Monterey.Trade
 Trade with
Trade with Ming China
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peop ...
via Manila served a major source of revenue for the Spanish Empire and as a fundamental source of income for Spanish colonists in the Philippine Islands. Galleons used for the trade between East and West were crafted by Filipino artisans. Until 1593, two or more ships would set sail annually from each port. The Manila trade became so lucrative that Seville merchants petitioned king Philip II of Spain
Philip II) in Spain, while in Portugal and his Italian kingdoms he ruled as Philip I ( pt, Filipe I). (21 May 152713 September 1598), also known as Philip the Prudent ( es, Felipe el Prudente), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from ...
to protect the monopoly of the Casa de Contratación based in Seville. This led to the passing of a decree in 1593 that set a limit of two ships sailing each year from either port, with one kept in reserve in Acapulco and one in Manila. An "armada", or armed escort of galleons, was also approved. Due to official attempts at controlling the galleon trade, contraband and understating of ships' cargoes became widespread.
 The galleon trade was supplied by merchants largely from port areas of Fujian, such as
The galleon trade was supplied by merchants largely from port areas of Fujian, such as Quanzhou
Quanzhou, postal map romanization, alternatively known as Chinchew, is a prefecture-level city, prefecture-level port city on the north bank of the Jin River, beside the Taiwan Strait in southern Fujian, China. It is Fujian's largest metrop ...
, as depicted in the Selden Map
The Selden Map of China (Bodleian Library, MS Selden Supra 105) is an early 17th century map of East Asia formerly owned by the legal scholar and maritime theorist John Selden. It shows a system of navigational routes emanating from a point near ...
, and Yuegang (the old port of Haicheng in Zhangzhou, Fujian), who traveled to Manila to sell the Spaniards spices, porcelain, ivory, lacquerware, processed silk cloth and other valuable commodities. Cargoes varied from one voyage to another but often included goods from all over Asia: jade, wax, gunpowder and silk from China; amber, cotton and rugs from India; spices from Indonesia and Malaysia; and a variety of goods from Japan, the Spanish part of the so-called Namban trade
or the , was a period in the history of Japan from the arrival of Europeans in 1543 to the first ''Sakoku'' Seclusion Edicts of isolationism in 1614. Nanban (南蛮 Lit. "Southern barbarian") is a Japanese word which had been used to designate ...
, including fans, chests, screens
Screen or Screens may refer to:
Arts
* Screen printing (also called ''silkscreening''), a method of printing
* Big screen, a nickname associated with the motion picture industry
* Split screen (filmmaking), a film composition paradigm in which mul ...
, porcelain and lacquerware.
Galleons transported the goods to be sold in the Americas, namely in New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Am ...
and Peru, as well as in European markets. East Asia trading primarily functioned on a silver standard due to Ming China's use of silver ingots as a medium of exchange. As such, goods were mostly bought by silver mined from New Spain and Potosí
Potosí, known as Villa Imperial de Potosí in the colonial period, is the capital city and a municipality of the Department of Potosí in Bolivia. It is one of the highest cities in the world at a nominal . For centuries, it was the location o ...
. In addition, slaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
from various origins were transported from Manila.
The cargoes arrived in Acapulco and were transported by land across Mexico. Mule trains would carry the goods along the China Road from Acapulco first to the administrative center of Mexico City, then on to the port of Veracruz on the Gulf of Mexico, where they were loaded onto the Spanish treasure fleet bound for Spain. The transport of goods overland by porters, the housing of travelers and sailors at inns by innkeepers, and the stocking of long voyages with food and supplies provided by haciendas before departing Acapulco helped to stimulate the economy of New Spain.
The trade of goods and exchanges of people were not limited to Mexico and the Philippines since Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by H ...
, Panama, Ecuador, and Peru also served as supplementary streams to the main one between Mexico and Philippines.
Cape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( af, Kaap die Goeie Hoop ) ;''Kaap'' in isolation: pt, Cabo da Boa Esperança is a rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
A common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is t ...
, which was reserved to Portugal according to the Treaty of Tordesillas
The Treaty of Tordesillas, ; pt, Tratado de Tordesilhas . signed in Tordesillas, Spain on 7 June 1494, and authenticated in Setúbal, Portugal, divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between the Portuguese Empire and the Spanish Emp ...
. It also avoided stopping over at ports controlled by competing powers, such as Portugal and the Netherlands. From the early days of exploration, the Spanish knew that the American continent was much narrower across the Panamanian isthmus
The Isthmus of Panama ( es, Istmo de Panamá), also historically known as the Isthmus of Darien (), is the narrow strip of land that lies between the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, linking North and South America. It contains the country ...
than across Mexico. They tried to establish a regular land crossing there, but the thick jungle and tropical diseases such as yellow fever and malaria made it impractical.
It took at least four months to sail across the Pacific Ocean from Manila to Acapulco, and the galleons were the main link between the Philippines and the viceregal capital at Mexico City and thence to Spain itself. Many of the so-called "Kastilas" or Spaniards in the Philippines were actually of Mexican descent, and the Hispanic culture of the Philippines is influenced by Spanish and Mexican culture in particular. Soldiers and settlers recruited from Mexico and Peru were also gathered in Acapulco before they were sent to settle at the presidios of the Philippines. Even after the galleon era, and at the time when Mexico finally gained its independence, the two nations still continued to trade, except for a brief lull during the Spanish–American War.
In Manila, the safety of ocean crossings was commended to the virgin Nuestra Señora de la Soledad de Porta Vaga
Our Lady of the Porta Vaga (, ) is a Roman Catholic Marian title of the Blessed Virgin Mary associated with a venerated Marian painting.
The oldest dated Marian painting in the Philippines and the Patroness of Cavite is permanently enshrined at ...
in masses held by the Archbishop of Manila. If the expedition was successful the voyagers would go to La Ermita (the church) to pay homage, and offer gold and other precious gems or jewelries from Hispanic countries to the image of the virgin. So it came to be that the virgin was named the "Queen of the Galleons".
Economic shocks due to the arrival of Spanish-American silver in China were among the factors that led to the end of the Ming dynasty.
End of the Galleons
In 1740, as part of the administrative changes of the Bourbon Reforms, the Spanish crown began allowing the use of registered ships or ''navíos de registro'' in the Pacific. These ships traveled solo, outside the convoy system of the galleons. While these solo voyages would not immediately replace the galleon system, they were more efficient and better able to avoid being captured by the Royal Navy of Great Britain. The Manila-Acapulco galleon trade ended in 1815, a few years before Mexico gained independence from Spain in 1821. After this, the Spanish Crown took direct control of the Philippines, and governed directly from Madrid. Sea transport became easier in the mid-19th century after the invention of steam powered ships and the opening of theSuez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular ...
, which reduced the travel time from Spain to the Philippines to 40 days.
Galleons
Construction
 Between 1609 and 1616, 9 galleons and 6 galleys were constructed in Philippine shipyards. The average cost was 78,000 pesos per galleon and at least 2,000 trees. The galleons constructed included the ''San Juan Bautista'', ''San Marcos'', ''Nuestra Senora de Guadalupe'', ''Angel de la Guardia'', ''San Felipe'', ''Santiago'', ''Salbador'', ''Espiritu Santo'', and ''San Miguel''. "From 1729 to 1739, the main purpose of the Cavite shipyard was the construction and outfitting of the galleons for the Manila to Acapulco trade run."
Due to the route's high profitability but long voyage time, it was essential to build the largest possible galleons, which were the largest class of European ships known to have been built until then. In the 16th century, they averaged from 1,700 to 2,000 tons, were built of Philippine hardwoods and could carry 300 - 500 passengers. The ''Concepción'', wrecked in 1638, was long and displacing some 2,000 tons. The ''Santísima Trinidad'' was long. Most of the ships were built in the Philippines and only eight in Mexico.
Between 1609 and 1616, 9 galleons and 6 galleys were constructed in Philippine shipyards. The average cost was 78,000 pesos per galleon and at least 2,000 trees. The galleons constructed included the ''San Juan Bautista'', ''San Marcos'', ''Nuestra Senora de Guadalupe'', ''Angel de la Guardia'', ''San Felipe'', ''Santiago'', ''Salbador'', ''Espiritu Santo'', and ''San Miguel''. "From 1729 to 1739, the main purpose of the Cavite shipyard was the construction and outfitting of the galleons for the Manila to Acapulco trade run."
Due to the route's high profitability but long voyage time, it was essential to build the largest possible galleons, which were the largest class of European ships known to have been built until then. In the 16th century, they averaged from 1,700 to 2,000 tons, were built of Philippine hardwoods and could carry 300 - 500 passengers. The ''Concepción'', wrecked in 1638, was long and displacing some 2,000 tons. The ''Santísima Trinidad'' was long. Most of the ships were built in the Philippines and only eight in Mexico.
Crews
Sailors averaged age 28 or 29 while the oldest were between 40 and 50. Ships pages were children who entered service mostly at age 8, many orphans or poor taken from the streets of Seville, Mexico and Manila. Apprentices were older than the pages and if successful would be certified a sailor at age 20. Because mortality rates were high with ships arriving in Manila with a majority of their crew often dead from starvation, disease and scurvy, especially in the early years, Spanish officials in Manila found it difficult to find men to crew their ships to return to Acapulco. Many ''indios'' of Filipino and Southeast Asian origin made up the majority of the crew. Other crew were made up of deportees and criminals from Spain and the colonies. Many criminals were sentenced to serve as crew on royal ships. Less than a third of the crew was Spanish and they usually held key positions aboard the galleon. At port, goods were unloaded by dockworkers, and food was often supplied locally. In Acapulco, the arrival of the galleons provided seasonal work, as for dockworkers who were typically free black men highly paid for their back breaking labor, and for farmers andhacienda
An ''hacienda'' ( or ; or ) is an estate (or ''finca''), similar to a Roman ''latifundium'', in Spain and the former Spanish Empire. With origins in Andalusia, ''haciendas'' were variously plantations (perhaps including animals or orchards), ...
s across Mexico who helped stock the ships with food before voyages. On land, travelers were often housed at inns or ''mesones'', and had goods transported by muleteers, which provided opportunities for Indigenous people in Mexico. By providing for the galleons, Spanish colonial America was tied into the broader global economy.
Shipwrecks
The wrecks of the Manila galleons are legends second only to the wrecks of treasure ships in the Caribbean. In 1568, Miguel López de Legazpi's own ship, the ''San Pablo'' (300 tons), was the first Manila galleon to be wrecked en route to Mexico. Between the years 1576 when the ''Espiritu Santo'' was lost and 1798 when the ''San Cristobal (2)'' was lost there were twenty Manila galleons wrecked within the Philippine archipelago. In 1596 the '' San Felipe'' was wrecked in Japan. The cargo was seized by the Japanese authorities and the behavior of the crew prompted persecution against the Christians. At least one galleon, probably the ''Santo Cristo de Burgos'', is believed to have wrecked on the coast of Oregon in 1693. Known as theBeeswax wreck
The Beeswax Wreck is a shipwreck off the coast of the U.S. state of Oregon, discovered by Craig Andes near Cape Falcon in 2013 in Tillamook County. The ship, thought to be the Spanish Manila galleon ''Santo Cristo de Burgos'' that was wrecked in ...
, the event is described in the oral histories of the Tillamook and Clatsop, which suggest that some of the crew survived.
Between 1565 and 1815, 108 ships operated as Manila galleons, of which 26 were lost at sea for various reasons, including four captured by the enemy (English or British) in wartime: the ''Santa Anna'' captured in 1587 by Thomas Cavendish , the ''Encarnacion'' captured by the British 1709, the ''Nuestra Senora de la Covadonga'' captured in 1743 by George Anson, and the '' Nuestra Senora de la Santisima Trinidad'' captured in 1762 by HMS ''Panther'' and HMS ''Argo''.
Possible contact with Hawaii
Over 250 years, there were hundreds of Manila galleon crossings of the Pacific Ocean between present-day Mexico and the Philippines, with their route taking them just south of theHawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kur ...
on the westward leg of their round trip and yet there are no records of contact with the Hawaiians. British historian Henry Kamen
Henry A. Kamen (born 4 October 1936 in Rangoon) is a British historian, who has published extensively on Europe, Spain, and the Spanish Empire.
Biography
Henry Arthur Kamen was born in Rangoon (then part of British Burma) in 1936, the son ...
maintains that the Spanish did not have the ability to properly explore the Pacific Ocean and were not capable of finding the islands which lay at a latitude 20° north of the westbound galleon route and its currents. However, Spanish exploration in the Pacific was paramount until the late 18th century. Spanish navigators discovered many islands including Guam, the Marianas
The Mariana Islands (; also the Marianas; in Chamorro: ''Manislan Mariånas'') are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, betw ...
, the Carolines and the Philippines in the North Pacific, as well as Tuvalu, the Marquesas, the Solomon Islands, New Guinea, and Easter Island in the South Pacific. Spanish navigators also discovered the Pitcairn and Vanuatu archipelagos during their search for Terra Australis in the 17th century.
James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean an ...
's first visit in 1778. Ruy López de Villalobos commanded a fleet of six ships that left Acapulco in 1542 with a Spanish sailor named Ivan Gaetan or Juan Gaetano aboard as pilot. Depending on the interpretation, Gaetano's reports seem to describe either the discovery of Hawaii or the Marshall Islands in 1555. If it was Hawaii, Gaetano would have been one of the first Europeans to find the islands.
Maui
The island of Maui (; Hawaiian: ) is the second-largest of the islands of the state of Hawaii at 727.2 square miles (1,883 km2) and is the 17th largest island in the United States. Maui is the largest of Maui County's four islands, which ...
is named "La Desgraciada" (the unhappy, or unfortunate), and what appears to be the Island of Hawaii is named "La Mesa" (the table). Islands resembling Kahoolawe, Lanai
Lanai ( haw, Lānai, , , also ,) is the sixth-largest of the Hawaiian Islands and the smallest publicly accessible inhabited island in the chain. It is colloquially known as the Pineapple Island because of its past as an island-wide pineapple pl ...
, and Molokai
Molokai , or Molokai (), is the fifth most populated of the eight major islands that make up the Hawaiian Islands, Hawaiian Islands archipelago in the middle of the Pacific Ocean. It is 38 by 10 miles (61 by 16 km) at its greatest length an ...
are named "Los Monjes" (the monks).
The theory that the first European visitors to Hawaii were Spanish is reinforced by the findings of William Ellis, a writer and missionary who lived in early 19th century Hawaii, and recorded several folk stories about foreigners who had visited Hawaii prior to first contact with Cook. According to Hawaiian writer Herb Kawainui Kane
In general use, herbs are a widely distributed and widespread group of plants, excluding vegetables and other plants consumed for macronutrients, with savory or aromatic properties that are used for flavoring and garnishing food, for medicinal ...
, one of these stories:
concerned seven foreigners who landed eight generations earlier at Kealakekua Bay in a painted boat with an awning or canopy over the stern. They were dressed in clothing of white and yellow, and one wore a sword at his side and a feather in his hat. On landing, they kneeled down in prayer. TheSome scholars, particularly American, have dismissed these claims as lacking credibility. Debate continues as to whether the Hawaiian Islands were actually visited by the Spanish in the 16th century with researchers like Richard W. Rogers looking for evidence of SpanishHawaiians Native Hawaiians (also known as Indigenous Hawaiians, Kānaka Maoli, Aboriginal Hawaiians, First Hawaiians, or simply Hawaiians) ( haw, kānaka, , , and ), are the indigenous ethnic group of Polynesian people of the Hawaiian Islands. Hawaii ..., most helpful to those who were most helpless, received them kindly. The strangers ultimately married into the families of chiefs, but their names could not be included in genealogies".
shipwreck
A shipwreck is the wreckage of a ship that is located either beached on land or sunken to the bottom of a body of water. Shipwrecking may be intentional or unintentional. Angela Croome reported in January 1999 that there were approximately ...
s.
Preparations for UNESCO nominations
In 2010, the Philippines foreign affairs secretary organized a diplomatic reception attended by at least 32 countries, for discussions about the historic galleon trade and the possible establishment of a galleon museum. Various Mexican and Filipino institutions and politicians also made discussions about the importance of the galleon trade in their shared history. In 2013, the Philippines released a documentary regarding the Manila galleon trade route. In 2014, the idea to nominate the Manila-Acapulco Galleon Trade Route as a World Heritage Site was initiated by the Mexican and Filipino ambassadors to UNESCO. Spain has also backed the nomination and suggested that the archives related to the route under the possession of the Philippines, Mexico, and Spain be nominated as part of another UNESCO list, the Memory of the World Register. In 2015, the Unesco National Commission of the Philippines (Unacom) and the Department of Foreign Affairs organized an expert's meeting to discuss the trade route's nomination. Some of the topics presented include the Spanish colonial shipyards in Sorsogon, underwater archaeology in the Philippines, the route's influences on Filipino textile, the galleon's eastward trip from the Philippines to Mexico called ''tornaviaje'', and the historical dimension of the galleon trade focusing on important and rare archival documents In 2017, the Philippines established the Manila-Acapulco Galleon Museum in Metro Manila, one of the necessary steps in nominating the trade route to UNESCO. In 2018, Mexico reopened its Manila galleon gallery at the Archaeological Museum of Puerto Vallarta, Cuale. In 2020, Mexico released a documentary regarding the Manila galleon trade route.See also
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Notes
References
Sources
*Further reading
* Bjork, Katharine. "The Link that Kept the Philippines Spanish: Mexican Merchant Interests and the Manila Trade, 1571–1815." ''Journal of World History'' vol. 9, no. 1, (1998) 25–50. * Carrera Stampa, Manuel. "La Nao de la China." ''Historia Mexicana'' 9 no. 33 (1959) 97-118. * Fish, Shirley. ''The Manila-Acapulco Galleons: The Treasure Ships of the Pacific, with an Annotated List of the Transpacific Galleons 1565–1815''. Central Milton Keynes, England: Authorhouse 2011. * Gasch-Tomás, José Luis. ''The Atlantic World and the Manila Galleon: Circulation, Market, and Consumption of Asian Goods in the Spanish Empires, 1565-1650''. Leiden: Brill, 2018. * Giraldez, Arturo. ''The Age of Trade: The Manila Galleons and the Dawn of the Global Economy''. Lanham, MA: Rowman & Littlefield, 2015. * Luengo, Josemaria Salutan. ''A History of the Manila-Acapulco Slave Trade, 1565–1815''. Tubigon, Bohol: Mater Dei Publications 1996. * McCarthy, William J. "Between Policy and Prerogative: Malfeasance in the Inspection of the Manila Galleons at Acapulco, 1637." ''Colonial Latin American Historical Review'' 2, no. 2 (1993) 163–83. * Oropeza Keresey, Deborah. "Los 'indios chinos' en la Nueva España: la inmigración de la Nao de China, 1565–1700." PhD dissertation, El Colegio de México, Centro de Estudios Históricos, 2007. *Rogers, R. (1999). ''Shipwreck of Hawai'i: a maritime history of the Big Island''. Haleiwa, Hawaii: Pilialoha Publishing. *Schurz, William Lytle. (1917"The Manila Galleon and California"
''Southwestern Historical Quarterly'', Vol. 21, No. 2, pp. 107–126 *Schurz, William Lytle. ''The Manila Galleon''. New York: E. P. Dutton & Co., Inc., 1939.
External links
Findings from the wreck of ''Nuestra Senora de la Concepcion'' in the Marianas, 1638
Spanish-Philippine research group based in Madrid (in Spanish) {{DEFAULTSORT:Manila Galleon Galleons Spanish East Indies History of the Philippines (1565–1898) Spanish colonization of the Americas Age of Sail ships of Spain Naval ships of Spain Military history of the Pacific Ocean History of Manila History of New Spain Colonial Mexico Pacific Coast of Mexico Sea lanes Merchant sailing ship types New Spain 1565 establishments in Spain 1565 establishments in New Spain 1810s disestablishments in Spain 19th-century disestablishments in New Spain 16th century in the Spanish East Indies 17th century in the Spanish East Indies 18th century in the Spanish East Indies 19th century in the Spanish East Indies Early Modern economics