Namaqualand 0-4-2ST Pioneer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Namaqua Copper Company ''Pioneer'' of 1901 was a South African steam locomotive from the pre-
 The Namaqua Copper Company acquired its first steam locomotive from Dick, Kerr & Company in 1901. It was named ''Pioneer'' and was constructed as a wood-burning locomotive with a balloon chimney which contained a spark arrester. The locomotive had a fuel rack mounted on top of the tank, ahead of the cab.
In service, photographs show the locomotive as a oil-burning engine with the spark arrester removed from the chimney, with oil tanks mounted underneath the running boards below the cab and with a trailing axle added below the cab to carry the additional weight of the tanks at the rear end. Whether these modifications were carried out pre-delivery by Dick, Kerr or post-delivery by the mining company is not known.
In all, the Namaqua Copper Company had five locomotives by 1907, the engine ''Pioneer'' being the first and the smallest. A 9-ton locomotive named ''Volunteer'' (or ''Engineer'') followed in 1902. Three 12-ton locomotives named ''Muleteer'', ''Buccaneer'' (''Nuccaneer'' according to one source) and ''Reindeer'' were delivered in 1903, May 1905 and February 1907 respectively. These locomotives replaced the mules on the Namaqua Copper Company mainline to Braakpits Junction.
The Namaqua Copper Company acquired its first steam locomotive from Dick, Kerr & Company in 1901. It was named ''Pioneer'' and was constructed as a wood-burning locomotive with a balloon chimney which contained a spark arrester. The locomotive had a fuel rack mounted on top of the tank, ahead of the cab.
In service, photographs show the locomotive as a oil-burning engine with the spark arrester removed from the chimney, with oil tanks mounted underneath the running boards below the cab and with a trailing axle added below the cab to carry the additional weight of the tanks at the rear end. Whether these modifications were carried out pre-delivery by Dick, Kerr or post-delivery by the mining company is not known.
In all, the Namaqua Copper Company had five locomotives by 1907, the engine ''Pioneer'' being the first and the smallest. A 9-ton locomotive named ''Volunteer'' (or ''Engineer'') followed in 1902. Three 12-ton locomotives named ''Muleteer'', ''Buccaneer'' (''Nuccaneer'' according to one source) and ''Reindeer'' were delivered in 1903, May 1905 and February 1907 respectively. These locomotives replaced the mules on the Namaqua Copper Company mainline to Braakpits Junction.
 The garrison of O'okiep consisted of some 900 men, mostly employees of the Cape Copper Company, three-quarters of whom were coloured. A chain of blockhouses and other defensive positions had been prepared and early in the siege, the garrison succeeded in repulsing several determined attacks by the commando. However, when the departure of Smuts with a British safe-conduct to the deliberations at Vereeniging heralded the end of the war, the siege became little more than a good-humoured blockade.
On 1 May 1902, the commandos launched an attack on O'okiep, using the commandeered locomotive ''Pioneer'' to propel a mobile bomb in the form of a truck-load of dynamite into the besieged town. The protective defences at O'okiep consisted of a barbed wire fence which was erected across the railway line at Braakpits Junction, just north of the town. The points at the junction were rigged to the fence, with the result that, when the dynamite-laden truck breached the fence, it derailed at the points and spilled its load of dynamite on the ground, where it burned out harmlessly without exploding.
The garrison of O'okiep consisted of some 900 men, mostly employees of the Cape Copper Company, three-quarters of whom were coloured. A chain of blockhouses and other defensive positions had been prepared and early in the siege, the garrison succeeded in repulsing several determined attacks by the commando. However, when the departure of Smuts with a British safe-conduct to the deliberations at Vereeniging heralded the end of the war, the siege became little more than a good-humoured blockade.
On 1 May 1902, the commandos launched an attack on O'okiep, using the commandeered locomotive ''Pioneer'' to propel a mobile bomb in the form of a truck-load of dynamite into the besieged town. The protective defences at O'okiep consisted of a barbed wire fence which was erected across the railway line at Braakpits Junction, just north of the town. The points at the junction were rigged to the fence, with the result that, when the dynamite-laden truck breached the fence, it derailed at the points and spilled its load of dynamite on the ground, where it burned out harmlessly without exploding.
 According to Smuts, the railway between the two towns was still intact, but since there were women and children in O'okiep town, all the commando was allowed to do was to give O'okiep a tremendous fright with a harmless explosion. Boer General Ben Bouwer had inspected the trainload before it was sent hurtling into the besieged town, to make sure that there were no caps in the dynamite.
The Second Boer War ended with the signing of the
According to Smuts, the railway between the two towns was still intact, but since there were women and children in O'okiep town, all the commando was allowed to do was to give O'okiep a tremendous fright with a harmless explosion. Boer General Ben Bouwer had inspected the trainload before it was sent hurtling into the besieged town, to make sure that there were no caps in the dynamite.
The Second Boer War ended with the signing of the
Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
era in the Cape of Good Hope.
In 1901, the Namaqua Copper Company acquired its first locomotive, a shunting engine named ''Pioneer'', for use on its tramway line between its main mine at Tweefontein and Flat Mine at Concordia.
Namaqua Copper Company
The Namaqua United Copper Company was formed to take over the Namaqua Copper Company from 1 January 1888 and, on 14 May 1888, it was reconstructed as the Namaqua Copper Company. In 1889, the mine built a branch line from Braakpits Junction, nearO'okiep
Okiep is a small town in the Northern Cape province of South Africa, and was in the 1870s ranked as having the richest copper mine in the world. The town is on the site of a spring that was known in the Khoekhoe language of the Nama people as ''U ...
, to Flat Mine where the Company's ore crusher was located. The line was opened to traffic on 23 April 1889. Braakpits Junction was on the Namaqualand Railway
The Namaqualand Railway was a narrow gauge railway operating between Port Nolloth and O'okiep in the Namaqualand region of the former Cape Colony in South Africa. It was originally a mule-drawn railway built to provide an outlet for the copper ...
of the Cape Copper Company, which ran from Port Nolloth on the West Coast to the copper mines around O'okiep
Okiep is a small town in the Northern Cape province of South Africa, and was in the 1870s ranked as having the richest copper mine in the world. The town is on the site of a spring that was known in the Khoekhoe language of the Nama people as ''U ...
.
A tramway line was also constructed from Flat Mine to the Company's most important mine at Tweefontein, as well as branch lines to the Company stores at Concordia and the copper floor at Flat Mine. At the Port Nolloth end of the Namaqualand Railway, a short line was also built to serve the Company store at Port Nolloth. Trains were mule-hauled from the beginning.
Copper ore from the Namaqua Copper Company's mines and other Company traffic made use of the Cape Copper Company line between Braakpits Junction and Porth Nolloth. Until the Namaqua Copper Company acquired its own 8 ton capacity mainline trucks, goods and ore had to be transshipped at Braakpits Junction. By 1906, the company had a fleet of thirty trucks.
The Company survived the post-First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
depression in spite of a prolonged stoppage of mining from May 1918, but towards the end of the 1920s its copper reserves were running out and the collapse in the copper price led to final closure in July 1931. The assets of the Namaqua Copper Company were sold in 1932 and 1933 and the properties were taken over by the O'okiep Copper Company in 1939.
The locomotive ''Pioneer''
 The Namaqua Copper Company acquired its first steam locomotive from Dick, Kerr & Company in 1901. It was named ''Pioneer'' and was constructed as a wood-burning locomotive with a balloon chimney which contained a spark arrester. The locomotive had a fuel rack mounted on top of the tank, ahead of the cab.
In service, photographs show the locomotive as a oil-burning engine with the spark arrester removed from the chimney, with oil tanks mounted underneath the running boards below the cab and with a trailing axle added below the cab to carry the additional weight of the tanks at the rear end. Whether these modifications were carried out pre-delivery by Dick, Kerr or post-delivery by the mining company is not known.
In all, the Namaqua Copper Company had five locomotives by 1907, the engine ''Pioneer'' being the first and the smallest. A 9-ton locomotive named ''Volunteer'' (or ''Engineer'') followed in 1902. Three 12-ton locomotives named ''Muleteer'', ''Buccaneer'' (''Nuccaneer'' according to one source) and ''Reindeer'' were delivered in 1903, May 1905 and February 1907 respectively. These locomotives replaced the mules on the Namaqua Copper Company mainline to Braakpits Junction.
The Namaqua Copper Company acquired its first steam locomotive from Dick, Kerr & Company in 1901. It was named ''Pioneer'' and was constructed as a wood-burning locomotive with a balloon chimney which contained a spark arrester. The locomotive had a fuel rack mounted on top of the tank, ahead of the cab.
In service, photographs show the locomotive as a oil-burning engine with the spark arrester removed from the chimney, with oil tanks mounted underneath the running boards below the cab and with a trailing axle added below the cab to carry the additional weight of the tanks at the rear end. Whether these modifications were carried out pre-delivery by Dick, Kerr or post-delivery by the mining company is not known.
In all, the Namaqua Copper Company had five locomotives by 1907, the engine ''Pioneer'' being the first and the smallest. A 9-ton locomotive named ''Volunteer'' (or ''Engineer'') followed in 1902. Three 12-ton locomotives named ''Muleteer'', ''Buccaneer'' (''Nuccaneer'' according to one source) and ''Reindeer'' were delivered in 1903, May 1905 and February 1907 respectively. These locomotives replaced the mules on the Namaqua Copper Company mainline to Braakpits Junction.
Service
The locomotive ''Pioneer'' was too light for work on the Company's mainline to Braakpits Junction and was placed in service on the tramway to Tweefontein. It gained its place in history during theSecond Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the South ...
, when it was commandeered by Boer forces.
Towards the end of the Second Boer War, the Cape of Good Hope was invaded by Boer commandos and, on 4 April 1902, the town Concordia surrendered to Boer forces. From 8 April to 3 May, the neighbouring town O'okiep was besieged by the Boer forces under General J.C. Smuts, whose strategy was to capture the rich copper fields and thus force the British to send troops from Cape Town to O'okiep, which would leave Cape Town vulnerable to attack.
 The garrison of O'okiep consisted of some 900 men, mostly employees of the Cape Copper Company, three-quarters of whom were coloured. A chain of blockhouses and other defensive positions had been prepared and early in the siege, the garrison succeeded in repulsing several determined attacks by the commando. However, when the departure of Smuts with a British safe-conduct to the deliberations at Vereeniging heralded the end of the war, the siege became little more than a good-humoured blockade.
On 1 May 1902, the commandos launched an attack on O'okiep, using the commandeered locomotive ''Pioneer'' to propel a mobile bomb in the form of a truck-load of dynamite into the besieged town. The protective defences at O'okiep consisted of a barbed wire fence which was erected across the railway line at Braakpits Junction, just north of the town. The points at the junction were rigged to the fence, with the result that, when the dynamite-laden truck breached the fence, it derailed at the points and spilled its load of dynamite on the ground, where it burned out harmlessly without exploding.
The garrison of O'okiep consisted of some 900 men, mostly employees of the Cape Copper Company, three-quarters of whom were coloured. A chain of blockhouses and other defensive positions had been prepared and early in the siege, the garrison succeeded in repulsing several determined attacks by the commando. However, when the departure of Smuts with a British safe-conduct to the deliberations at Vereeniging heralded the end of the war, the siege became little more than a good-humoured blockade.
On 1 May 1902, the commandos launched an attack on O'okiep, using the commandeered locomotive ''Pioneer'' to propel a mobile bomb in the form of a truck-load of dynamite into the besieged town. The protective defences at O'okiep consisted of a barbed wire fence which was erected across the railway line at Braakpits Junction, just north of the town. The points at the junction were rigged to the fence, with the result that, when the dynamite-laden truck breached the fence, it derailed at the points and spilled its load of dynamite on the ground, where it burned out harmlessly without exploding.
 According to Smuts, the railway between the two towns was still intact, but since there were women and children in O'okiep town, all the commando was allowed to do was to give O'okiep a tremendous fright with a harmless explosion. Boer General Ben Bouwer had inspected the trainload before it was sent hurtling into the besieged town, to make sure that there were no caps in the dynamite.
The Second Boer War ended with the signing of the
According to Smuts, the railway between the two towns was still intact, but since there were women and children in O'okiep town, all the commando was allowed to do was to give O'okiep a tremendous fright with a harmless explosion. Boer General Ben Bouwer had inspected the trainload before it was sent hurtling into the besieged town, to make sure that there were no caps in the dynamite.
The Second Boer War ended with the signing of the Treaty of Vereeniging
The Treaty of Vereeniging was a peace treaty, signed on 31 May 1902, that ended the Second Boer War between the South African Republic and the Orange Free State, on the one side, and the United Kingdom on the other.
This settlement provided f ...
in Pretoria on 31 May 1902. When it later transpired that the coloured members of the O'okiep garrison were excluded from receiving the Queen's South Africa Medal
The Queen's South Africa Medal is a British campaign medal awarded to British and Colonial military personnel, and to civilians employed in an official capacity, who served in the Second Boer War in South Africa. Altogether twenty-six clasps wer ...
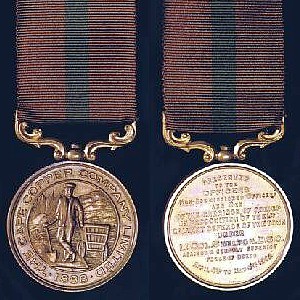
, the Cape Copper Company struck a medal of its own and presented it to all the defenders, regardless of race. The obverse of the Cape Copper Company Medal for the Defence of O'okiep
In the Colonies and Boer Republics which became the Union of South Africa in 1910, several unofficial military decorations and medals were instituted and awarded during the nineteenth and early twentieth century. The Cape Copper Company Medal fo ...
depicts a miner with a spade, standing next to an ore truck.
The locomotive ''Pioneer'' was eventually retrieved from O'okiep on 29 July 1902, repaired and placed back in service. By 1906, the locomotive was described as being "past much work" and was only occasionally used for light work.
References
{{Locomotives of South Africa 0610 0-4-2ST locomotives B1 locomotives Dick, Kerr locomotives Railway locomotives introduced in 1901 1901 in South Africa 2 ft 6 in gauge locomotives Scrapped locomotives