NIST-F2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
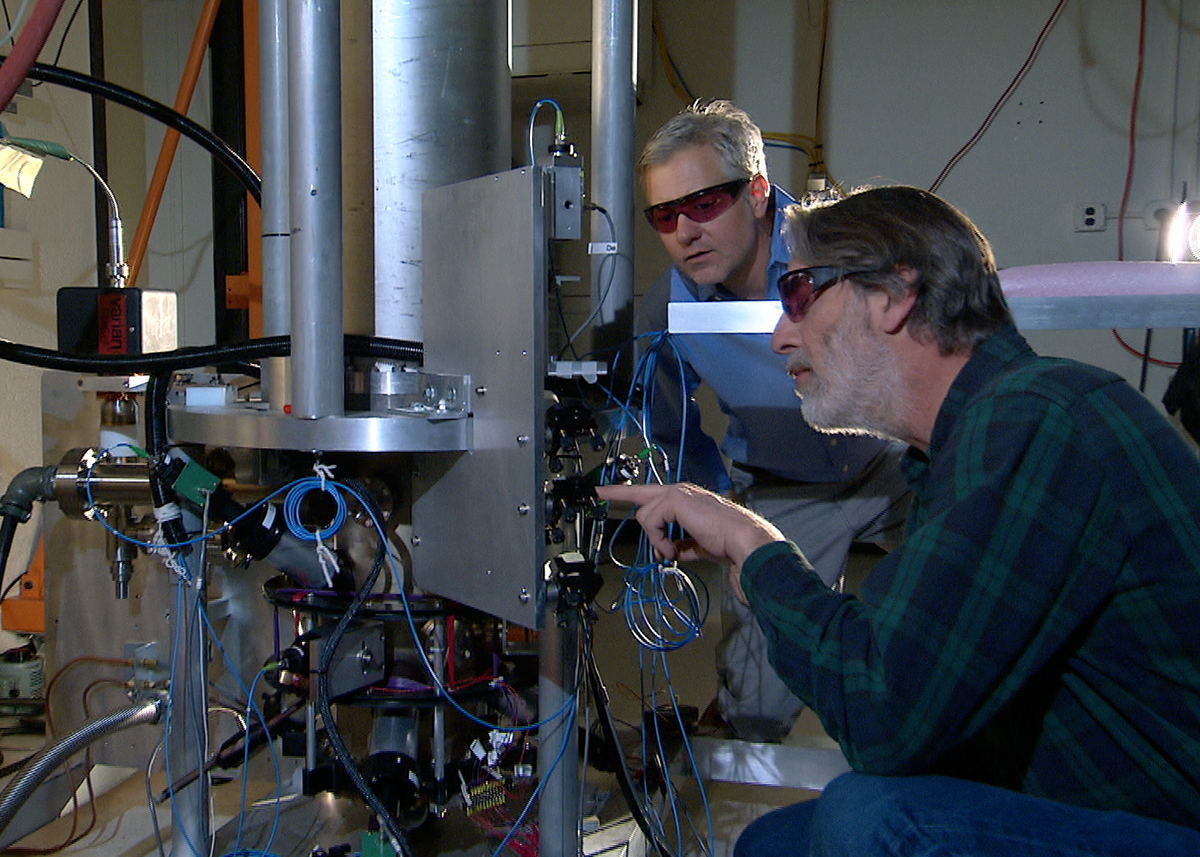 NIST-F2 is a cesium fountain
NIST-F2 is a cesium fountain
/ref> NIST-F2 was brought online on 3 April 2014.First Accuracy Evaluation of NIST-F2, T. P. Heavner, S. R. Jefferts, J. H. Shirley, T. E. Parker, E. A. Donley, N. Ashby, S. Barlow, F. Levi, and G. Costanzo, May 2014
/ref>
available from NIST directly
At this planned performance level the NIST-F2 clock will not lose a second in at least 300 million years.
by the
/ref> In March 2014 and March 2015 the NIST-F2 cesium fountain clock reported a ''u''''B'' of in the BIPM reports of evaluation of primary frequency standards. The last submission of NIST-F1 to BIPM TAI was February 2016. At the request of the Italian standards organization, NIST manufactured many duplicate components for a second version of NIST-F2, known as IT-CsF2 to be operated by the Istituto Nazionale di Ricerca Metrologica (INRiM), NIST's counterpart in
NIST Time and Frequency Div. — 2004: Strategic Focus 1
(National Institute of Standards and Technology) * * {{cite web, title=Time gets an upgrade, url=https://www.newscientist.com/article/mg22229642-700-60-seconds/, website=newscientist.com, publisher=
 NIST-F2 is a cesium fountain
NIST-F2 is a cesium fountain atomic clock
An atomic clock is a clock that measures time by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms. It is based on atoms having different energy levels. Electron states in an atom are associated with different energy levels, and in transitions betw ...
that, along with NIST-F1, serves as the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
' primary time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, t ...
and frequency standard.NIST Launches a New U.S. Time Standard: NIST-F2 Atomic Clock/ref> NIST-F2 was brought online on 3 April 2014.First Accuracy Evaluation of NIST-F2, T. P. Heavner, S. R. Jefferts, J. H. Shirley, T. E. Parker, E. A. Donley, N. Ashby, S. Barlow, F. Levi, and G. Costanzo, May 2014
/ref>
Accuracy
NIST-F1, a cesium fountain atomic clock used since 1999, has a fractional inaccuracy (δ''f / f'') of less than . The planned performance of NIST-F2 is δ''f / f'' < . Alsavailable from NIST directly
At this planned performance level the NIST-F2 clock will not lose a second in at least 300 million years.
Evaluated accuracy
The evaluated accuracy (''u''''B'') reports of various primary frequency and time standards arby the
International Bureau of Weights and Measures
The International Bureau of Weights and Measures (french: Bureau international des poids et mesures, BIPM) is an intergovernmental organisation, through which its 59 member-states act together on measurement standards in four areas: chemistry ...
(BIPM).
The first in-house accuracy evaluation of NIST-F2 reported a ''u''''B'' of .Heavner T P, Donley E A , Levi F, Costanzo G, Parker TE, Shirley J H, Ashby N, Barlow S and Jefferts SR, “First accuracy evaluation of NIST-F2,” 2014 Metrologia 51, 174–182, May 2014/ref> In March 2014 and March 2015 the NIST-F2 cesium fountain clock reported a ''u''''B'' of in the BIPM reports of evaluation of primary frequency standards. The last submission of NIST-F1 to BIPM TAI was February 2016. At the request of the Italian standards organization, NIST manufactured many duplicate components for a second version of NIST-F2, known as IT-CsF2 to be operated by the Istituto Nazionale di Ricerca Metrologica (INRiM), NIST's counterpart in
Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital from 1861 to 1865. Th ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
. As of February 2016 the IT-CsF2 cesium fountain clock started reporting a ''u''''B'' of in the BIPM reports of evaluation of primary frequency standards. tp://ftp2.bipm.org/pub/tai/data/PSFS_reports/it-csf2_57414-57444.pdf February 2016 IT-CsF2 TAI evaluation/ref> tp://ftp2.bipm.org/pub/tai/data/PSFS_reports/it-csf2_58284-58299.pdf June 2018 IT-CsF2 TAI evaluation/ref>
References
External links
NIST Time and Frequency Div. — 2004: Strategic Focus 1
(National Institute of Standards and Technology) * * {{cite web, title=Time gets an upgrade, url=https://www.newscientist.com/article/mg22229642-700-60-seconds/, website=newscientist.com, publisher=
New Scientist
''New Scientist'' is a magazine covering all aspects of science and technology. Based in London, it publishes weekly English-language editions in the United Kingdom, the United States and Australia. An editorially separate organisation publish ...
, accessdate=27 February 2018, language=English
National Institute of Standards and Technology
Atomic clocks