NIRSpec on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The NIRSpec (Near-Infrared Spectrograph) is one of the four scientific instruments flown on the
 The
The 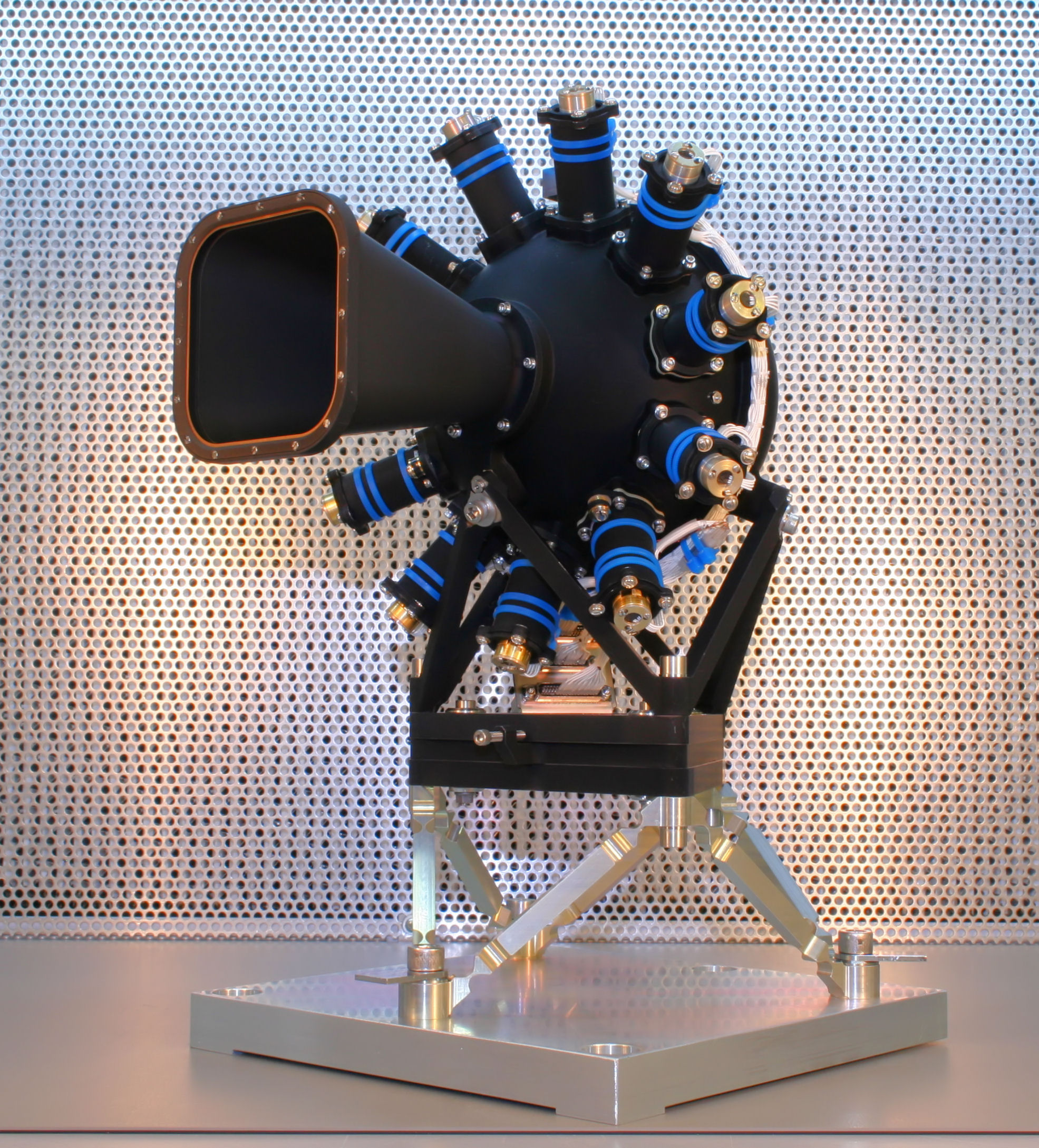 NIRSpec includes 4 mechanisms which are:
* the Filter Wheel Assembly (FWA) – 8 positions, carrying 4 long pass filters for science, 2 broadband filters for target acquisition, one closed and one open position
* the Refocus Mechanism Assembly (RMA) – carrying 2 mirrors for instrument refocusing
* the Micro Shutter Assembly (MSA) – for multi-object spectroscopy but also carrying the fixed slits and IFU aperture
* the Grating Wheel Assembly (GWA) – 8 positions, carrying 6 gratings and one prism for science and one mirror for target acquisition
Further NIRSpec includes two electro-optical assemblies which are:
* Calibration Assembly (CAA) – carrying 11 illumination sources and an integrating sphere; for instrument internal spectral and flat-field calibration
* Focal Plane Assembly (FPA) – includes the focal plane which consists of 2 sensor chip assemblies
And finally the Integral Field Unit (IFU) image slicer, used in the instrument IFU mode.
The optical path is represented by the following
NIRSpec includes 4 mechanisms which are:
* the Filter Wheel Assembly (FWA) – 8 positions, carrying 4 long pass filters for science, 2 broadband filters for target acquisition, one closed and one open position
* the Refocus Mechanism Assembly (RMA) – carrying 2 mirrors for instrument refocusing
* the Micro Shutter Assembly (MSA) – for multi-object spectroscopy but also carrying the fixed slits and IFU aperture
* the Grating Wheel Assembly (GWA) – 8 positions, carrying 6 gratings and one prism for science and one mirror for target acquisition
Further NIRSpec includes two electro-optical assemblies which are:
* Calibration Assembly (CAA) – carrying 11 illumination sources and an integrating sphere; for instrument internal spectral and flat-field calibration
* Focal Plane Assembly (FPA) – includes the focal plane which consists of 2 sensor chip assemblies
And finally the Integral Field Unit (IFU) image slicer, used in the instrument IFU mode.
The optical path is represented by the following
 In order to achieve the scientific objectives NIRSpec has four operational modes:
Multi-Object Spectroscopy (MOS)
In MOS the total instrument field of view of 3 × 3
In order to achieve the scientific objectives NIRSpec has four operational modes:
Multi-Object Spectroscopy (MOS)
In MOS the total instrument field of view of 3 × 3
 The individual subcontractors and their corresponding contributions were:
* APCO Technologies SA – Mechanical Ground Support Equipment and Kinematic Mounts
*
The individual subcontractors and their corresponding contributions were:
* APCO Technologies SA – Mechanical Ground Support Equipment and Kinematic Mounts
*
File:NRSMOS-COMBO-41.jpg, NIRSpec in Multi-Object Mode. The image shows the spectra of a Spectral Line Calibration Lamp (Fabry–Perot type) imaged onto the 2 detector Sensor Chip Assemblies (SCA)
File:Micro4.jpg, Microshutter closeup
File:Micro7.jpg, NIRSpec Microshutter arrays
;Integral Field Unit
File:NRSMON-COMBO-IFU-42.jpg, NIRSpec in IFU Mode. The image shows the spectra of a Spectral Line Calibration Lamp (Fabry–Perot type) imaged onto the 2 detector SCA's.
File:Basic principle of Integral Field Spectroscopy.png, Basic principle of Integral Field Spectroscopy
File:NIRSpec CAD view with main Assemblies.PNG, NIRSpec CAD view with main assemblies
File:NIRSpec-3.jpg, NIRSpec and the optical path
James Webb Space Telescope on NASA
James Webb Space Telescope on ESA
NIRSpec on YouTube
{{Space observatories James Webb Space Telescope instruments Infrared telescopes Spectrographs
James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope which conducts infrared astronomy. As the largest optical telescope in space, its high resolution and sensitivity allow it to view objects too old, distant, or faint for the Hubble Spa ...
(JWST). The JWST is the follow-on mission to the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versa ...
(HST) and is developed to receive more information about the origins of the universe by observing infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
light from the first stars and galaxies. In comparison to HST, its instruments will allow looking further back in time and will study the so-called Dark Ages during which the universe was opaque, about 150 to 800 million years after the Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the ...
.
The NIRSpec instrument is a multi-object spectrograph
An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify mate ...
and is capable of simultaneously measuring the near-infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of Light, visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from ...
spectrum of up to 100 objects like stars or galaxies with low, medium and high spectral resolutions. The observations are performed in a 3 arcmin
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The na ...
× 3 arcmin field of view over the wavelength range from 0.6 µm to 5.0 µm. It also features a set of slits and an aperture for high contrast spectroscopy of individual sources, as well as an integral-field unit (IFU) for 3D spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter wa ...
.
The instrument is a contribution of the European Space Agency
, owners =
, headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France
, coordinates =
, spaceport = Guiana Space Centre
, seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png
, seal_size = 130px
, image = Views in the Main Control Room (1205 ...
(ESA) and is built by Astrium
Astrium was an aerospace manufacturer subsidiary of the European Aeronautic Defence and Space Company (EADS) that provided civil and military space systems and services from 2006 to 2013. In 2012, Astrium had a turnover of €5.8 billion and 18 ...
together with a group of European subcontractors.
Overview
 The
The James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope which conducts infrared astronomy. As the largest optical telescope in space, its high resolution and sensitivity allow it to view objects too old, distant, or faint for the Hubble Spa ...
's main science themes are:
* First light and reionization
In the fields of Big Bang theory and cosmology, reionization is the process that caused matter in the universe to reionize after the lapse of the " dark ages".
Reionization is the second of two major phase transitions of gas in the universe (t ...
* the assembly of galaxies,
* the birth of stars and protoplanetary systems
* the birth of planetary systems and the origins of life
In biology, abiogenesis (from a- 'not' + Greek bios 'life' + genesis 'origin') or the origin of life is the natural process by which life has arisen from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The prevailing scientific hypothes ...
The NIRSpec instrument operates at −235 °C and is passively cooled by cold space radiators
Radiators are heat exchangers used to transfer thermal energy from one medium to another for the purpose of cooling and heating. The majority of radiators are constructed to function in cars, buildings, and electronics.
A radiator is always a s ...
which are mounted on the JWST Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM). The radiators are connected to NIRSpec using thermally conductive heat straps. The mirror mounts and the optical bench base plate all manufactured out of silicon carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder and crystal sin ...
ceramic SiC100. The instrument size is approximately and weighs including 100 kg of silicon carbide. The operation of the instrument is performed with three electronic boxes.
 NIRSpec includes 4 mechanisms which are:
* the Filter Wheel Assembly (FWA) – 8 positions, carrying 4 long pass filters for science, 2 broadband filters for target acquisition, one closed and one open position
* the Refocus Mechanism Assembly (RMA) – carrying 2 mirrors for instrument refocusing
* the Micro Shutter Assembly (MSA) – for multi-object spectroscopy but also carrying the fixed slits and IFU aperture
* the Grating Wheel Assembly (GWA) – 8 positions, carrying 6 gratings and one prism for science and one mirror for target acquisition
Further NIRSpec includes two electro-optical assemblies which are:
* Calibration Assembly (CAA) – carrying 11 illumination sources and an integrating sphere; for instrument internal spectral and flat-field calibration
* Focal Plane Assembly (FPA) – includes the focal plane which consists of 2 sensor chip assemblies
And finally the Integral Field Unit (IFU) image slicer, used in the instrument IFU mode.
The optical path is represented by the following
NIRSpec includes 4 mechanisms which are:
* the Filter Wheel Assembly (FWA) – 8 positions, carrying 4 long pass filters for science, 2 broadband filters for target acquisition, one closed and one open position
* the Refocus Mechanism Assembly (RMA) – carrying 2 mirrors for instrument refocusing
* the Micro Shutter Assembly (MSA) – for multi-object spectroscopy but also carrying the fixed slits and IFU aperture
* the Grating Wheel Assembly (GWA) – 8 positions, carrying 6 gratings and one prism for science and one mirror for target acquisition
Further NIRSpec includes two electro-optical assemblies which are:
* Calibration Assembly (CAA) – carrying 11 illumination sources and an integrating sphere; for instrument internal spectral and flat-field calibration
* Focal Plane Assembly (FPA) – includes the focal plane which consists of 2 sensor chip assemblies
And finally the Integral Field Unit (IFU) image slicer, used in the instrument IFU mode.
The optical path is represented by the following silicon carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder and crystal sin ...
mirror assemblies:
* the Coupling Optics Assembly – which couples the light from the JWST telescope into NIRSpec
* the Fore Optics TMA (FOR) – which provides the intermediate focal plane for the MSA
* the Collimator Optics TMA (COL) – collimating the light onto the Grating Wheel dispersive element
* the Camera Optics TMA (CAM) – which finally images the spectra on the detector
Science objectives
* The end of the Dark Ages – first light and re-ionization:Near-infrared spectroscopy
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a spectroscopic method that uses the near-infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum (from 780 nm to 2500 nm). Typical applications include medical and physiological diagnostics and research incl ...
(NIRS) at spectral resolutions around 100 and 1000 for studying the first light sources (stars, galaxies and active nuclei) that mark the beginning of the phase of re-ionization of the Universe that is believed to take place between redshifts 15–14 and 6.
* The assembly of galaxies: Near-infrared multi-object spectroscopic observations (redshift range typically from 1 to 7) at spectral resolutions around 1000 observation of a large number of galaxies and spatially-resolved NIRS at spectral resolutions around 1000 and 3000 in order to conduct detailed studies of a smaller number of objects.
* The birth of stars and planetary systems: Near-infrared high-contrast slit spectroscopy at spectral resolution ranging from 100 to several thousands in order to gain a more complete view of the formation and evolution of the stars and their planetary systems.
*Planetary systems and the origin of life: In order to observe various components of the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar S ...
(from planets and satellites to comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena ar ...
s and Kuiper belt
The Kuiper belt () is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System, extending from the orbit of Neptune at 30 astronomical units (AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but is far larger—20 times ...
objects as well as of extra-solar planetary systems, high-contrast and spatially resolved NIRS at medium to high spectral resolution while maintaining high relative spectro-photometric stability is required.
Operational modes
 In order to achieve the scientific objectives NIRSpec has four operational modes:
Multi-Object Spectroscopy (MOS)
In MOS the total instrument field of view of 3 × 3
In order to achieve the scientific objectives NIRSpec has four operational modes:
Multi-Object Spectroscopy (MOS)
In MOS the total instrument field of view of 3 × 3 arcminute
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The na ...
s is covered using 4 arrays of programmable slit masks. These programmable slit masks consist of 250 000 micro shutters where each can individually be programmed to 'open' or 'closed'. The contrast between an 'open' or 'closed' shutter is better than 1:2000.
If an object like e.g. a galaxy is placed into an 'open' shutter, the spectra of the light emitted by the object can be dispersed and imaged onto the detector plane.
In this mode up to 100 objects can simultaneously be observed and the spectra be measured.
Integral Field Unit Mode (IFU)
The integral field spectrometry will primarily be used for large, extended objects like galaxies. In this mode a 3 × 3 arcsecond field of view is sliced into 0.1 arcsecond bands which are thereafter re-arranged into a long slit. This allows to obtain spatially resolved spectra of large scenes and can be used to measure the motion speed and direction within an extended object.
Since measured spectra in the IFU mode would overlap with spectra of the MOS mode it can not be used in parallel.
High-Contrast Slit Spectroscopy (SLIT)
A set of 5 fixed slits are available in order to perform high contrast spectroscopic observations which is e.g. required for spectroscopic observations of transiting extra-solar planets.
Of the five fixed slits, three are 0.2 arcseconds wide, one is 0.4 arcsecond wide and one is a square aperture of 1.6 arcseconds.
The SLIT mode can be used simultaneously with the MOS or IFU modes.
Imaging Mode (IMA)
The imaging mode is used for target acquisition
Target acquisition is the detection and identification of the location of a target in sufficient detail to permit the effective employment of lethal and non-lethal means. The term is used for a broad area of applications.
A "target" here is an e ...
only. In this mode no dispersive element is placed in the optical path and any objects are directly imaged on the detector. Since the microshutter array which is sitting in an instrument intermediate focal plan is imaged in parallel, it is possible to arrange the JWST observatory such that any to be observed objects fall directly into the center of open shutters (MOS-mode), the IFU aperture (IFU-mode) or the slits (SLIT mode).
Performance parameters
The NIRSpec key performance parameters are: .Industrial partners
NIRSpec has been built by Astrium Germany with subcontractors and partners spread over Europe and with the contribution of NASA from the US which provided the Detector Subsystem and the Micro-shutter Assembly. The individual subcontractors and their corresponding contributions were:
* APCO Technologies SA – Mechanical Ground Support Equipment and Kinematic Mounts
*
The individual subcontractors and their corresponding contributions were:
* APCO Technologies SA – Mechanical Ground Support Equipment and Kinematic Mounts
* Astrium
Astrium was an aerospace manufacturer subsidiary of the European Aeronautic Defence and Space Company (EADS) that provided civil and military space systems and services from 2006 to 2013. In 2012, Astrium had a turnover of €5.8 billion and 18 ...
CASA Espacio – Optical Instrument Harness
* Astrium CRISA – Instrument Control Electronic and Software
* Astrium SAS – Silicon Carbide (SiC) Engineering Support
* (AIP) – Instrument Quick Look, Analysis and Calibration Software Contribution
* Boostec – SiC Mirrors and Structures Manufacturing
* Cassidian Optronics:
**Filter Wheel Assembly
**Grating Wheel Assembly
* (CRAL) – Instrument Performance Simulator
* European Space Agency (ESA) – NIRSpec Customer
* Iberespacio – Optical Assembly Cover
* (IABG) – Instrument Test Facilities
* Mullard Space Science Laboratory
The UCL Mullard Space Science Laboratory (MSSL) is the United Kingdom's largest university space research group. MSSL is part of the Department of Space and Climate Physics at University College London (UCL), one of the first universities in the ...
(MSSL):
**Calibration Assembly
**Optical Ground Support Equipment (Shack-Hartman-Sensor, Calibration Light Source)
* National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) – Customer Furnished Items:
**Detector Subsytem
**Microshutter Subsystem
* Sagem – Mirror Polishing and Mirror Assembly, Integration and Testing
* Selex Galileo
Selex ES was a subsidiary of Finmeccanica S.p.A., active in the electronics and information technology business, based in Italy and the UK, and formed in January 2013, following Finmeccanica's decision to combine its existing SELEX Elsag and ...
– Refocus Mechanism
* Surrey Satellite Technology
Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd, or SSTL, is a company involved in the manufacture and operation of small satellites. A spin-off company of the University of Surrey, it is presently wholly owned by Airbus Defence and Space.
The company began ...
Ltd (SSTL) – Integral Field Unit
* Terma – Electrical Ground Support Equipment (Data Handling System)
Images
;Multi-Object Spectroscopy (MOS)See also
*Fine Guidance Sensor and Near Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph
Fine Guidance Sensor and Near Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph (FGS-NIRISS) is an instrument on the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) that combines a Fine Guidance Sensor and a science instrument, a near-infrared imager and a spectrogra ...
*MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument)
MIRI, or Mid-Infrared Instrument, is an instrument on the James Webb Space Telescope. MIRI is a camera and a spectrograph that observes mid to long infrared radiation from 5 to 28 microns. It also has coronagraphs, especially for observing ex ...
(JWST's 5–28 micron camera/spectrograph)
*NIRCam
NIRCam (Near-InfraRed Camera) is an instrument aboard the James Webb Space Telescope. It has two major tasks, as an imager from 0.6 to 5 micron wavelength, and as a wavefront sensor to keep the 18-section mirrors functioning as one. In other wor ...
(NIR camera for JWST up to 5 micron wavelength light)
*Integrated Science Instrument Module
Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM) is a component of the James Webb Space Telescope, a large international infrared space telescope launched on . ISIM is the heart of the JWST, and holds the main science payload which includes four scienc ...
(ISIM, houses NIRSpec and the other JWST instruments)
References
External links
James Webb Space Telescope on NASA
James Webb Space Telescope on ESA
NIRSpec on YouTube
{{Space observatories James Webb Space Telescope instruments Infrared telescopes Spectrographs