NHMUK014092670 Anthrenus S on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Natural History Museum in
 The foundation of the collection was that of the Ulster doctor Sir
The foundation of the collection was that of the Ulster doctor Sir
 Owen saw that the natural history departments needed more space, and that implied a separate building as the British Museum site was limited. Land in South Kensington was purchased, and in 1864 a competition was held to design the new museum. The winning entry was submitted by the civil engineer Captain
Owen saw that the natural history departments needed more space, and that implied a separate building as the British Museum site was limited. Land in South Kensington was purchased, and in 1864 a competition was held to design the new museum. The winning entry was submitted by the civil engineer Captain  Work began in 1873 and was completed in 1880. The new museum opened in 1881, although the move from the old museum was not fully completed until 1883.
Both the interiors and exteriors of the Waterhouse building make extensive use of
Work began in 1873 and was completed in 1880. The new museum opened in 1881, although the move from the old museum was not fully completed until 1883.
Both the interiors and exteriors of the Waterhouse building make extensive use of
 Even after the opening, the Natural History Museum legally remained a department of the British Museum with the formal name British Museum (Natural History), usually abbreviated in the
Even after the opening, the Natural History Museum legally remained a department of the British Museum with the formal name British Museum (Natural History), usually abbreviated in the
 The Darwin Centre (named after
The Darwin Centre (named after
Nature Live
talks on Fridays, Saturdays and Sundays.
 One of the most famous and certainly most prominent of the exhibits—nicknamed "
One of the most famous and certainly most prominent of the exhibits—nicknamed " The blue whale skeleton, Hope, that has replaced Dippy, is another prominent display in the museum. The display of the skeleton, some long and weighing 4.5 tonnes, was only made possible in 1934 with the building of the New Whale Hall (now the Mammals (blue whale model) gallery). The whale had been in storage for 42 years since its stranding on sandbanks at the mouth of
The blue whale skeleton, Hope, that has replaced Dippy, is another prominent display in the museum. The display of the skeleton, some long and weighing 4.5 tonnes, was only made possible in 1934 with the building of the New Whale Hall (now the Mammals (blue whale model) gallery). The whale had been in storage for 42 years since its stranding on sandbanks at the mouth of
 This is the zone that can be entered from Exhibition Road, on the East side of the building. It is a gallery themed around the changing history of the Earth.
''Earth's Treasury'' shows specimens of rocks, minerals and gemstones behind glass in a dimly lit gallery. ''Lasting Impressions'' is a small gallery containing specimens of rocks, plants and minerals, of which most can be touched.
* Earth Hall (''
This is the zone that can be entered from Exhibition Road, on the East side of the building. It is a gallery themed around the changing history of the Earth.
''Earth's Treasury'' shows specimens of rocks, minerals and gemstones behind glass in a dimly lit gallery. ''Lasting Impressions'' is a small gallery containing specimens of rocks, plants and minerals, of which most can be touched.
* Earth Hall (''
 This zone is accessed from the Cromwell Road entrance via the Hintze Hall and follows the theme of the evolution of the planet.
* Birds
* Creepy Crawlies
* Fossil Marine Reptiles
* Hintze Hall (formerly the Central Hall, with
This zone is accessed from the Cromwell Road entrance via the Hintze Hall and follows the theme of the evolution of the planet.
* Birds
* Creepy Crawlies
* Fossil Marine Reptiles
* Hintze Hall (formerly the Central Hall, with
 To the left of the Hintze Hall, this zone explores the diversity of life on the planet.
*
To the left of the Hintze Hall, this zone explores the diversity of life on the planet.
*
 Enables the public to see science at work and also provides spaces for relaxation and contemplation. Accessible from Queens Gate.
* Wildlife Garden
* Darwin Centre
* Zoology Spirit Building
Enables the public to see science at work and also provides spaces for relaxation and contemplation. Accessible from Queens Gate.
* Wildlife Garden
* Darwin Centre
* Zoology Spirit Building
 The museum runs a series of
The museum runs a series of
Picture Library of the Natural History Museum
The Natural History Museum on Google Cultural Institute
Architectural history and description
from the ''Survey of London''
Architecture and history of the NHM
from the Royal Institute of British Architects * Maps of
Nature News article on proposed cuts, June 2010
{{Authority control Natural History Museum, London, British Museum Natural history museums in London Museums sponsored by the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport Grade I listed buildings in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea Grade I listed museum buildings Cultural infrastructure completed in 1880 Alfred Waterhouse buildings Non-departmental public bodies of the United Kingdom government Exempt charities Charities based in London Museums in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea Romanesque Revival architecture in England Terracotta Museums established in 1881 1881 establishments in England National museums of England Dinosaur museums Brompton, London, Natural History Museum, London South Kensington
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
is a museum that exhibits a vast range of specimens from various segments of natural history. It is one of three major museums on Exhibition Road
Exhibition Road is a street in South Kensington, London which is home to several major museums and academic establishments, including the Victoria and Albert Museum, the Science Museum and the Natural History Museum.
Overview
The road gets i ...
in South Kensington
South Kensington, nicknamed Little Paris, is a district just west of Central London in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea. Historically it settled on part of the scattered Middlesex village of Brompton. Its name was supplanted with ...
, the others being the Science Museum
A science museum is a museum devoted primarily to science. Older science museums tended to concentrate on static displays of objects related to natural history, paleontology, geology, industry and industrial machinery, etc. Modern trends in mu ...
and the Victoria and Albert Museum
The Victoria and Albert Museum (often abbreviated as the V&A) in London is the world's largest museum of applied arts, decorative arts and design, housing a permanent collection of over 2.27 million objects. It was founded in 1852 and nam ...
. The Natural History Museum's main frontage, however, is on Cromwell Road
Cromwell Road is a major London road in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea, designated as part of the A4. It was created in the 19th century and is said to be named after Richard Cromwell, son of Oliver Cromwell, who once owned a hou ...
.
The museum is home to life and earth science specimens comprising some 80 million items within five main collections: botany
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek w ...
, entomology
Entomology () is the science, scientific study of insects, a branch of zoology. In the past the term "insect" was less specific, and historically the definition of entomology would also include the study of animals in other arthropod groups, such ...
, mineralogy
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifacts. Specific studies within mineralogy include the proces ...
, palaeontology
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
and zoology
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the Animal, animal kingdom, including the anatomy, structure, embryology, evolution, Biological clas ...
. The museum is a centre of research specialising in taxonomy
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification.
A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. ...
, identification and conservation. Given the age of the institution, many of the collections have great historical as well as scientific value, such as specimens collected by Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended fr ...
. The museum is particularly famous for its exhibition of dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
skeletons and ornate architecture—sometimes dubbed a ''cathedral of nature''—both exemplified by the large ''Diplodocus
''Diplodocus'' (, , or ) was a genus of diplodocid sauropod dinosaurs, whose fossils were first discovered in 1877 by S. W. Williston. The generic name, coined by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1878, is a neo-Latin term derived from Greek διπ� ...
'' cast that dominated the vaulted central hall before it was replaced in 2017 with the skeleton of a blue whale hanging from the ceiling. The Natural History Museum Library contains an extensive collection of books, journals, manuscripts, and artwork linked to the work and research of the scientific departments; access to the library is by appointment only. The museum is recognised as the pre-eminent centre of natural history and research of related fields in the world.
Although commonly referred to as the Natural History Museum, it was officially known as British Museum (Natural History) until 1992, despite legal separation from the British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docum ...
itself in 1963. Originating from collections within the British Museum, the landmark Alfred Waterhouse
Alfred Waterhouse (19 July 1830 – 22 August 1905) was an English architect, particularly associated with the Victorian Gothic Revival architecture, although he designed using other architectural styles as well. He is perhaps best known f ...
building was built and opened by 1881 and later incorporated the Geological Museum
The Geological Museum (originally the Museum of Economic Geology then the Museum of Practical Geology), started in 1835 as one of the oldest single science museums in the world and now part of the Natural History Museum in London. It transfe ...
. The Darwin Centre is a more recent addition, partly designed as a modern facility for storing the valuable collections.
Like other publicly funded national museums in the United Kingdom, the Natural History Museum does not charge an admission fee.
The museum is an exempt charity An exempt charity is an institution established in England and Wales for charitable purposes which is exempt from registration with, and oversight by, the Charity Commission for England and Wales.
Exempt charities are largely institutions of furth ...
and a non-departmental public body
In the United Kingdom, non-departmental public body (NDPB) is a classification applied by the Cabinet Office, Treasury, the Scottish Government and the Northern Ireland Executive to public sector organisations that have a role in the process of n ...
sponsored by the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport
, type = Department
, logo = Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport logo.svg
, logo_width =
, logo_caption =
, seal =
, seal_width =
, seal_caption =
, picture = Gove ...
. The Princess of Wales, is a patron of the museum. There are approximately 850 staff at the museum. The two largest strategic groups are the Public Engagement Group and Science Group.
History
Early history
Hans Sloane
Sir Hans Sloane, 1st Baronet (16 April 1660 – 11 January 1753), was an Irish physician, naturalist, and collector, with a collection of 71,000 items which he bequeathed to the British nation, thus providing the foundation of the British Mu ...
(1660–1753), who allowed his significant collections to be purchased by the British Government at a price well below their market value at the time. This purchase was funded by a lottery. Sloane's collection, which included dried plants, and animal and human skeletons, was initially housed in Montagu House, Bloomsbury
Montagu House (sometimes spelled "Montague") was a late 17th-century mansion in Great Russell Street in the Bloomsbury district of London, which became the first home of the British Museum. The first house on the site was destroyed by fire in 1 ...
, in 1756, which was the home of the British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docum ...
.
Most of the Sloane collection had disappeared by the early decades of the nineteenth century. Dr George Shaw George Shaw may refer to:
* George Shaw (biologist) (1751–1813), English botanist and zoologist
* George B. Shaw (1854–1894), U.S. Representative from Wisconsin
* George Bernard Shaw (1856–1950), Irish playwright
* George C. Shaw (1866–196 ...
(Keeper of Natural History 1806–1813) sold many specimens to the Royal College of Surgeons
The Royal College of Surgeons is an ancient college (a form of corporation) established in England to regulate the activity of surgeons. Derivative organisations survive in many present and former members of the Commonwealth. These organisations a ...
and had periodic ''cremations'' of material in the grounds of the museum. His successors also applied to the trustees for permission to destroy decayed specimens. In 1833, the Annual Report states that, of the 5,500 insects listed in the Sloane catalogue, none remained. The inability of the natural history departments to conserve its specimens became notorious: the Treasury refused to entrust it with specimens collected at the government's expense. Appointments of staff were bedevilled by gentlemanly favouritism; in 1862 a nephew of the mistress of a Trustee was appointed Entomological Assistant despite not knowing the difference between a butterfly and a moth.
J. E. Gray
John Edward Gray, Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS (12 February 1800 – 7 March 1875) was a British zoology, zoologist. He was the elder brother of zoologist George Robert Gray and son of the pharmacologist and botanist Samuel Frederick Gray ...
(Keeper of Zoology 1840–1874) complained of the incidence of mental illness amongst staff: George Shaw threatened to put his foot on any shell not in the 12th edition
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. I ...
of Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the ...
' ''Systema Naturae
' (originally in Latin written ' with the ligature æ) is one of the major works of the Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and introduced the Linnaean taxonomy. Although the system, now known as binomial nomen ...
''; another had removed all the labels and registration numbers from entomological
Entomology () is the scientific study of insects, a branch of zoology. In the past the term "insect" was less specific, and historically the definition of entomology would also include the study of animals in other arthropod groups, such as arach ...
cases arranged by a rival. The huge collection of the conchologist
Conchology () is the study of mollusc shells. Conchology is one aspect of malacology, the study of molluscs; however, malacology is the study of molluscs as whole organisms, whereas conchology is confined to the study of their shells. It includ ...
Hugh Cuming
Hugh Cuming (14 February 1791 – 10 August 1865) was an England, English collecting, collector who was interested in natural history, particularly in conchology and botany. He has been described as the "Prince of Collectors".
Born in England, he ...
was acquired by the museum, and Gray's own wife had carried the open trays across the courtyard in a gale: all the labels blew away. That collection is said never to have recovered.
The Principal Librarian at the time was Antonio Panizzi
Sir Antonio Genesio Maria Panizzi (16 September 1797 – 8 April 1879), better known as Anthony Panizzi, was a naturalised British citizen of Italian birth, and an Italian patriot. He was a librarian, becoming the Principal Librarian (i.e. head ...
; his contempt for the natural history departments and for science in general was total. The general public was not encouraged to visit the museum's natural history exhibits. In 1835 to a Select Committee of Parliament, Sir Henry Ellis Henry Ellis may refer to:
* Henry Augustus Ellis (1861–1939), Irish Australian physician and federalist
* Henry Ellis (diplomat) (1788–1855), British diplomat
* Henry Ellis (governor) (1721–1806), explorer, author, and second colonial Gover ...
said this policy was fully approved by the Principal Librarian and his senior colleagues.
Many of these faults were corrected by the palaeontologist
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
Richard Owen
Sir Richard Owen (20 July 1804 – 18 December 1892) was an English biologist, comparative anatomist and paleontologist. Owen is generally considered to have been an outstanding naturalist with a remarkable gift for interpreting fossils.
Owe ...
, appointed Superintendent of the natural history departments of the British Museum in 1856. His changes led Bill Bryson
William McGuire Bryson (; born 8 December 1951) is an American–British journalist and author. Bryson has written a number of nonfiction books on topics including travel, the English language, and science. Born in the United States, he has b ...
to write that "by making the Natural History Museum an institution for everyone, Owen transformed our expectations of what museums are for".
Planning and architecture of new building
 Owen saw that the natural history departments needed more space, and that implied a separate building as the British Museum site was limited. Land in South Kensington was purchased, and in 1864 a competition was held to design the new museum. The winning entry was submitted by the civil engineer Captain
Owen saw that the natural history departments needed more space, and that implied a separate building as the British Museum site was limited. Land in South Kensington was purchased, and in 1864 a competition was held to design the new museum. The winning entry was submitted by the civil engineer Captain Francis Fowke
Francis Fowke (7 July 1823 – 4 December 1865) was an Irish engineer and architect, and a captain in the Corps of Royal Engineers. Most of his architectural work was executed in the Renaissance style, although he made use of relatively new ...
, who died shortly afterwards. The scheme was taken over by Alfred Waterhouse who substantially revised the agreed plans, and designed the façades in his own idiosyncratic Romanesque style which was inspired by his frequent visits to the Continent. The original plans included wings on either side of the main building, but these plans were soon abandoned for budgetary reasons. The space these would have occupied are now taken by the Earth Galleries and Darwin Centre. Work began in 1873 and was completed in 1880. The new museum opened in 1881, although the move from the old museum was not fully completed until 1883.
Both the interiors and exteriors of the Waterhouse building make extensive use of
Work began in 1873 and was completed in 1880. The new museum opened in 1881, although the move from the old museum was not fully completed until 1883.
Both the interiors and exteriors of the Waterhouse building make extensive use of architectural terracotta
Architectural terracotta refers to a fired mixture of clay and water that can be used in a non-structural, semi-structural, or structural capacity on the exterior or interior of a building. Terracotta pottery, as earthenware is called when not us ...
tiles to resist the sooty atmosphere of Victorian London, manufactured by the Tamworth-based company of Gibbs and Canning Limited
Gibbs and Canning Limited was an English manufacturer of terracotta and, in particular, architectural terracotta, located in Glascote, Tamworth, and founded in 1847.
The company manufactured a wide range of terracotta and faience: statues of l ...
. The tiles and bricks feature many relief sculptures of flora and fauna, with living and extinct species featured within the west and east wings respectively. This explicit separation was at the request of Owen, and has been seen as a statement of his contemporary rebuttal of Darwin's attempt to link present species with past through the theory of natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Charle ...
. Though Waterhouse slipped in a few anomalies, such as bats amongst the extinct animals and a fossil ammonite with the living species. The sculptures were produced from clay models by a French sculptor based in London, M Dujardin, working to drawings prepared by the architect.
The central axis of the museum is aligned with the tower of Imperial College London
Imperial College London (legally Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine) is a public research university in London, United Kingdom. Its history began with Prince Albert, consort of Queen Victoria, who developed his vision for a cu ...
(formerly the Imperial Institute) and the Royal Albert Hall
The Royal Albert Hall is a concert hall on the northern edge of South Kensington, London. One of the UK's most treasured and distinctive buildings, it is held in trust for the nation and managed by a registered charity which receives no govern ...
and Albert Memorial
The Albert Memorial, directly north of the Royal Albert Hall in Kensington Gardens, London, was commissioned by Queen Victoria in memory of her beloved husband Prince Albert, who died in 1861. Designed by Sir George Gilbert Scott in the Gothic ...
further north. These all form part of the complex known colloquially as Albertopolis
Albertopolis is the nickname given to the area centred on Exhibition Road in London, named after Prince Albert, consort of Queen Victoria. It contains many educational and cultural sites. It is in South Kensington, split between the Royal Bor ...
.
Separation from the British Museum
 Even after the opening, the Natural History Museum legally remained a department of the British Museum with the formal name British Museum (Natural History), usually abbreviated in the
Even after the opening, the Natural History Museum legally remained a department of the British Museum with the formal name British Museum (Natural History), usually abbreviated in the scientific literature
: ''For a broader class of literature, see Academic publishing.''
Scientific literature comprises scholarly publications that report original empirical and theoretical work in the natural and social sciences. Within an academic field, scient ...
as ''B.M.(N.H.)''. A petition to the Chancellor of the Exchequer
The chancellor of the Exchequer, often abbreviated to chancellor, is a senior minister of the Crown within the Government of the United Kingdom, and head of His Majesty's Treasury. As one of the four Great Offices of State, the Chancellor is ...
was made in 1866, signed by the heads of the Royal
Royal may refer to:
People
* Royal (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name
* A member of a royal family
Places United States
* Royal, Arkansas, an unincorporated community
* Royal, Illinois, a village
* Royal, Iowa, a cit ...
, Linnean and Zoological
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and dis ...
societies as well as naturalists including Darwin, Wallace
Wallace may refer to:
People
* Clan Wallace in Scotland
* Wallace (given name)
* Wallace (surname)
* Wallace (footballer, born 1986), full name Wallace Fernando Pereira, Brazilian football left-back
* Wallace (footballer, born 1987), full name ...
and Huxley, asking that the museum gain independence from the board of the British Museum, and heated discussions on the matter continued for nearly one hundred years. Finally, with the passing of the British Museum Act 1963
The British Museum Act 1963 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It replaced the British Museum Act 1902. The Act forbids the Museum from disposing of its holdings, except in a small number of special circumstances. In May 2005 a ...
, the British Museum (Natural History) became an independent museum with its own board of trustees, although – despite a proposed amendment to the act in the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the Bicameralism, upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by Life peer, appointment, Hereditary peer, heredity or Lords Spiritual, official function. Like the ...
– the former name was retained. In 1989 the museum publicly re-branded itself as the Natural History Museum and stopped using the title British Museum (Natural History) on its advertising and its books for general readers. Only with the Museums and Galleries Act 1992
The Museums and Galleries Act 1992 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom (1992 c. 44) the long title of which is "An Act to establish Boards of Trustees of the National Gallery, the Tate Gallery, the National Portrait Gallery and th ...
did the museum's formal title finally change to the Natural History Museum.
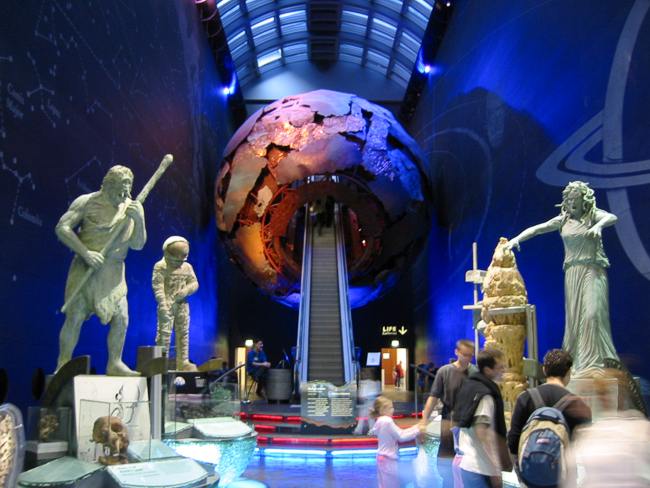
Geological Museum
In 1985, the museum merged with the adjacentGeological Museum
The Geological Museum (originally the Museum of Economic Geology then the Museum of Practical Geology), started in 1835 as one of the oldest single science museums in the world and now part of the Natural History Museum in London. It transfe ...
of the British Geological Survey
The British Geological Survey (BGS) is a partly publicly funded body which aims to advance geoscientific knowledge of the United Kingdom landmass and its continental shelf by means of systematic surveying, monitoring and research.
The BGS h ...
, which had long competed for the limited space available in the area. The Geological Museum became world-famous for exhibitions including an active volcano model and an earthquake machine (designed by James Gardner), and housed the world's first computer-enhanced exhibition (''Treasures of the Earth''). The museum's galleries were completely rebuilt and relaunched in 1996 as ''The Earth Galleries'', with the other exhibitions in the Waterhouse building retitled ''The Life Galleries''. The Natural History Museum's own mineralogy displays remain largely unchanged as an example of the 19th-century display techniques of the Waterhouse building.
The central atrium design by Neal Potter overcame visitors' reluctance to visit the upper galleries by "pulling" them through a model of the Earth made up of random plates on an escalator. The new design covered the walls in recycled slate and sandblasted the major stars and planets onto the wall. The museum's 'star' geological exhibits are displayed within the walls. Six iconic figures were the backdrop to discussing how previous generations have viewed Earth. These were later removed to make place for a ''Stegosaurus
''Stegosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of herbivorous, four-legged, armored dinosaur from the Late Jurassic, characterized by the distinctive kite-shaped upright plates along their backs and spikes on their tails. Fossils of the genus have been foun ...
'' skeleton that was put on display in late 2015.
The Darwin Centre
 The Darwin Centre (named after
The Darwin Centre (named after Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended fr ...
) was designed as a new home for the museum's collection of tens of millions of preserved specimens, as well as new work spaces for the museum's scientific staff and new educational visitor experiences. Built in two distinct phases, with two new buildings adjacent to the main Waterhouse building, it is the most significant new development project in the museum's history.
Phase one of the Darwin Centre opened to the public in 2002, and it houses the zoological
Zoology ()The pronunciation of zoology as is usually regarded as nonstandard, though it is not uncommon. is the branch of biology that studies the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and dis ...
department's 'spirit collections'—organisms preserved in alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
. Phase Two was unveiled in September 2008 and opened to the general public in September 2009. It was designed by the Danish architecture practice C. F. Møller Architects
Arkitektfirmaet C. F. Møller, internationally also known as C. F. Møller Architects, is an architectural firm based in Århus, Denmark. Founded in 1924 by C. F. Møller, it is today the largest architectural firm in Denmark based on number of em ...
in the shape of a giant, eight-story cocoon and houses the entomology
Entomology () is the science, scientific study of insects, a branch of zoology. In the past the term "insect" was less specific, and historically the definition of entomology would also include the study of animals in other arthropod groups, such ...
and botanical
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek wo ...
collections—the 'dry collections'. It is possible for members of the public to visit and view non-exhibited items for a fee by booking onto one of the several Spirit Collection Tours offered daily.
Arguably the most famous creature in the centre is the 8.62-metre-long giant squid
The giant squid (''Architeuthis dux'') is a species of deep-ocean dwelling squid in the family Architeuthidae. It can grow to a tremendous size, offering an example of abyssal gigantism: recent estimates put the maximum size at around Trace ...
, affectionately named Archie.
The Attenborough Studio
As part of the museum's remit to communicate science education and conservation work, a new multimedia studio forms an important part of Darwin Centre Phase 2. In collaboration with the BBC's Natural History Unit (holder of the largest archive of natural history footage) the Attenborough Studio—named after the broadcaster SirDavid Attenborough
Sir David Frederick Attenborough (; born 8 May 1926) is an English broadcaster, biologist, natural historian and author. He is best known for writing and presenting, in conjunction with the BBC Natural History Unit, the nine natural histor ...
—provides a multimedia environment for educational events. The studio holds regular lectures and demonstrations, including freNature Live
talks on Fridays, Saturdays and Sundays.
Major specimens and exhibits
Dippy
Dippy is a composite ''Diplodocus'' skeleton in Pittsburgh's Carnegie Museum of Natural History, and the holotype of the species ''Diplodocus carnegii''. It is considered the most famous single dinosaur skeleton in the world, due to the numerous ...
"—is a -long replica of a ''Diplodocus carnegii
''Diplodocus'' (, , or ) was a genus of diplodocid sauropod dinosaurs, whose fossils were first discovered in 1877 by S. W. Williston. The generic name, coined by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1878, is a neo-Latin term derived from Greek διπλ ...
'' skeleton which was on display for many years within the central hall. The cast was given as a gift by the Scottish-American industrialist Andrew Carnegie
Andrew Carnegie (, ; November 25, 1835August 11, 1919) was a Scottish-American industrialist and philanthropist. Carnegie led the expansion of the American steel industry in the late 19th century and became one of the richest Americans i ...
, after a discussion with King Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until his death in 1910.
The second child and eldest son of Queen Victoria an ...
, then a keen trustee of the British Museum. Carnegie paid £2,000 () for the casting, copying the original held at the Carnegie Museum of Natural History
The Carnegie Museum of Natural History (abbreviated as CMNH) is a natural history museum in the Oakland neighborhood of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was founded by Pittsburgh-based industrialist Andrew Carnegie in 1896.
Housing some 22 millio ...
. The pieces were sent to London in 36 crates, and on 12 May 1905, the exhibit was unveiled to great public and media interest. The real fossil had yet to be mounted, as the Carnegie Museum in Pittsburgh was still being constructed to house it. As word of Dippy spread, Mr Carnegie paid to have additional copies made for display in most major European capitals and in Central and South America, making Dippy the most-viewed dinosaur skeleton in the world. The dinosaur quickly became an iconic representation of the museum, and has featured in many cartoons and other media, including the 1975 Disney comedy ''One of Our Dinosaurs Is Missing
''One of Our Dinosaurs is Missing'' is a 1975 comedy film set in the early 1920s, about the theft of a dinosaur skeleton from the Natural History Museum. The film was produced by Walt Disney Productions and released by Buena Vista Distribution C ...
''. After 112 years on display at the museum, the dinosaur replica was removed in early 2017 to be replaced by the actual skeleton of a young blue whale
The blue whale (''Balaenoptera musculus'') is a marine mammal and a baleen whale. Reaching a maximum confirmed length of and weighing up to , it is the largest animal known to have ever existed. The blue whale's long and slender body can ...
, a 128-year-old skeleton nicknamed "Hope". Dippy went on a tour of various British museums starting in 2018 and concluding in 2020 at Norwich Cathedral
Norwich Cathedral is an Anglican cathedral in Norwich, Norfolk, dedicated to the Holy and Undivided Trinity. It is the cathedral church for the Church of England Diocese of Norwich and is one of the Norwich 12 heritage sites.
The cathedral ...
.
 The blue whale skeleton, Hope, that has replaced Dippy, is another prominent display in the museum. The display of the skeleton, some long and weighing 4.5 tonnes, was only made possible in 1934 with the building of the New Whale Hall (now the Mammals (blue whale model) gallery). The whale had been in storage for 42 years since its stranding on sandbanks at the mouth of
The blue whale skeleton, Hope, that has replaced Dippy, is another prominent display in the museum. The display of the skeleton, some long and weighing 4.5 tonnes, was only made possible in 1934 with the building of the New Whale Hall (now the Mammals (blue whale model) gallery). The whale had been in storage for 42 years since its stranding on sandbanks at the mouth of Wexford Harbour
Wexford Harbour ( gle, Loch Garman) in County Wexford, Ireland is the natural harbour at the mouth of the River Slaney. In earlier times, the area occupied by the harbour was considerably larger than it is today, up to ten miles (16 km) wi ...
, Ireland in March 1891 after being injured by whalers. At this time, it was first displayed in the Mammals (blue whale model) gallery, but now takes pride of place in the museum's Hintze Hall. Discussion of the idea of a life-sized model also began around 1934, and work was undertaken within the Whale Hall itself. Since taking a cast of such a large animal was deemed prohibitively expensive, scale models were used to meticulously piece the structure together. During construction, workmen left a trapdoor within the whale's stomach, which they would use for surreptitious cigarette breaks. Before the door was closed and sealed forever, some coins and a telephone directory were placed inside—this soon growing to an urban myth
An urban legend (sometimes contemporary legend, modern legend, urban myth, or urban tale) is a genre of folklore comprising stories or fallacious claims circulated as true, especially as having happened to a "friend of a friend" or a family m ...
that a time capsule
A time capsule is a historic cache of goods or information, usually intended as a deliberate method of communication with future people, and to help future archaeologists, anthropologists, or historians. The preservation of holy relics dates ba ...
was left inside. The work was completed—entirely within the hall and in view of the public—in 1938. At the time it was the largest such model in the world, at in length. The construction details were later borrowed by several American museums, who scaled the plans further. The work involved in removing Dippy and replacing it with Hope was documented in a BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board ex ...
Television special, ''Horizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates the surface of a celestial body from its sky when viewed from the perspective of an observer on or near the surface of the relevant body. This line divides all viewing directions based on whether i ...
: Dippy and the Whale'', narrated by David Attenborough
Sir David Frederick Attenborough (; born 8 May 1926) is an English broadcaster, biologist, natural historian and author. He is best known for writing and presenting, in conjunction with the BBC Natural History Unit, the nine natural histor ...
, which was first broadcast on BBC Two
BBC Two is a British free-to-air public broadcast television network owned and operated by the BBC. It covers a wide range of subject matter, with a remit "to broadcast programmes of depth and substance" in contrast to the more mainstream an ...
on 13 July 2017, the day before Hope was unveiled for public display.
The Darwin Centre is host to Archie
Archie is a masculine given name, a diminutive of Archibald. It may refer to:
People Given name or nickname
*Archie Alexander (1888–1958), African-American mathematician, engineer and governor of the US Virgin Islands
* Archie Blake (mathematici ...
, an 8.62-metre-long giant squid
The giant squid (''Architeuthis dux'') is a species of deep-ocean dwelling squid in the family Architeuthidae. It can grow to a tremendous size, offering an example of abyssal gigantism: recent estimates put the maximum size at around Trace ...
taken alive in a fishing net near the Falkland Islands
The Falkland Islands (; es, Islas Malvinas, link=no ) is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and about from Cape Dubouzet ...
in 2004. The squid is not on general display, but stored in the large tank room in the basement of the Phase 1 building. It is possible for members of the public to visit and view non-exhibited items behind the scenes for a fee by booking onto one of the several Spirit Collection Tours offered daily. On arrival at the museum, the specimen was immediately frozen while preparations commenced for its permanent storage. Since few complete and reasonably fresh examples of the species exist, "wet storage" was chosen, leaving the squid undissected. A 9.45-metre acrylic tank was constructed (by the same team that provide tanks to Damien Hirst
Damien Steven Hirst (; né
Brennan; born 7 June 1965) is an English artist, entrepreneur, and art collector. He is one of the Young British Artists (YBAs) who dominated the art scene in the UK during the 1990s. He is reportedly the United Kingd ...
), and the body preserved using a mixture of formalin
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula and structure . The pure compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde (refer to section Fo ...
and saline solution
Saline (also known as saline solution) is a mixture of sodium chloride (salt) and water. It has a number of uses in medicine including cleaning wounds, removal and storage of contact lenses, and help with dry eyes. By injection into a vein it ...
.
The museum holds the remains and bones of the "River Thames whale
The River Thames whale, affectionately nicknamed Willy by Londoners, was a juvenile female northern bottlenose whale which was discovered swimming in the River Thames in central London on Friday 20 January 2006. According to the BBC, she was fi ...
", a northern bottlenose whale
The northern bottlenose whale (''Hyperoodon ampullatus'') is a species of beaked whale in the ziphiid family, being one of two members of the genus ''Hyperoodon''. The northern bottlenose whale was hunted heavily by Norway and Britain in the 19t ...
that lost its way on 20 January 2006 and swam into the Thames. Although primarily used for research purposes, and held at the museum's storage site at Wandsworth
Wandsworth Town () is a district of south London, within the London Borough of Wandsworth southwest of Charing Cross. The area is identified in the London Plan
The London Plan is the statutory spatial development strategy for the Gre ...
.
Dinocochlea, one of the longer-standing mysteries of paleontology (originally thought to be a giant gastropod shell
The gastropod shell is part of the body of a Gastropoda, gastropod or snail, a kind of mollusc. The shell is an exoskeleton, which protects from predators, mechanical damage, and dehydration, but also serves for muscle attachment and calcium s ...
, then a coprolite
A coprolite (also known as a coprolith) is fossilized feces. Coprolites are classified as trace fossils as opposed to body fossils, as they give evidence for the animal's behaviour (in this case, diet) rather than morphology. The name is de ...
, and now a concretion
A concretion is a hard, compact mass of matter formed by the precipitation of mineral cement within the spaces between particles, and is found in sedimentary rock or soil. Concretions are often ovoid or spherical in shape, although irregular ...
of a worm's tunnel), has been part of the collection since its discovery in 1921.
The museum keeps a wildlife garden on its west lawn, on which a potentially new species of insect resembling Arocatus roeselii was discovered in 2007.
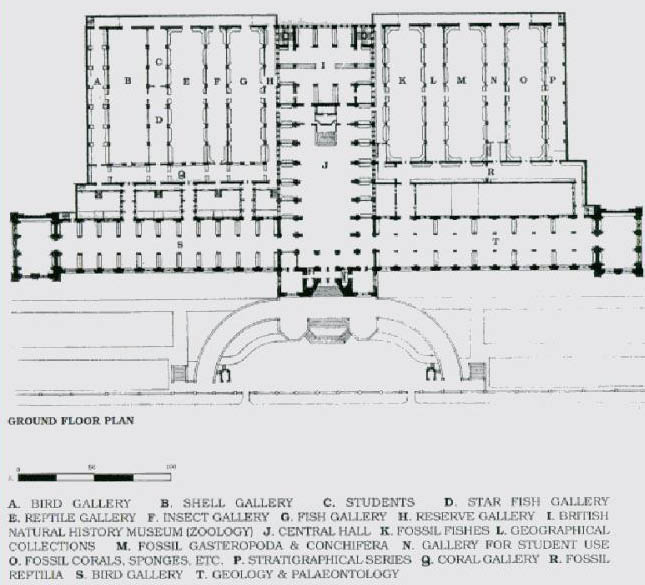
Galleries
The museum is divided into four sets of galleries, or zones, each colour coded to follow a broad theme.Red Zone
 This is the zone that can be entered from Exhibition Road, on the East side of the building. It is a gallery themed around the changing history of the Earth.
''Earth's Treasury'' shows specimens of rocks, minerals and gemstones behind glass in a dimly lit gallery. ''Lasting Impressions'' is a small gallery containing specimens of rocks, plants and minerals, of which most can be touched.
* Earth Hall (''
This is the zone that can be entered from Exhibition Road, on the East side of the building. It is a gallery themed around the changing history of the Earth.
''Earth's Treasury'' shows specimens of rocks, minerals and gemstones behind glass in a dimly lit gallery. ''Lasting Impressions'' is a small gallery containing specimens of rocks, plants and minerals, of which most can be touched.
* Earth Hall (''Stegosaurus
''Stegosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of herbivorous, four-legged, armored dinosaur from the Late Jurassic, characterized by the distinctive kite-shaped upright plates along their backs and spikes on their tails. Fossils of the genus have been foun ...
'' skeleton)
* Human Evolution
* Earth's Treasury
* Lasting Impressions
* Restless Surface
* From the Beginning
* Volcanoes and Earthquakes
* The Waterhouse Gallery (temporary exhibition space)
Green zone
blue whale
The blue whale (''Balaenoptera musculus'') is a marine mammal and a baleen whale. Reaching a maximum confirmed length of and weighing up to , it is the largest animal known to have ever existed. The blue whale's long and slender body can ...
skeleton and giant sequoia
''Sequoiadendron giganteum'' (giant sequoia; also known as giant redwood, Sierra redwood, Sierran redwood, California big tree, Wellingtonia or simply big treea nickname also used by John Muir) is the sole living species in the genus ''Sequoiade ...
)
* Minerals
* The Vault
* Fossils from Britain
* Anning Rooms (exclusive space for members and patrons of the museum)
* Investigate
* East Pavilion (space for changing Wildlife Photographer of the Year exhibition)
Blue zone
 To the left of the Hintze Hall, this zone explores the diversity of life on the planet.
*
To the left of the Hintze Hall, this zone explores the diversity of life on the planet.
* Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s
* Fish, Amphibians and Reptiles
* Human Biology
* Images of Nature
* The Jerwood Gallery (temporary exhibition space)
* Marine Invertebrates
* Mammals
* Mammals Hall (blue whale
The blue whale (''Balaenoptera musculus'') is a marine mammal and a baleen whale. Reaching a maximum confirmed length of and weighing up to , it is the largest animal known to have ever existed. The blue whale's long and slender body can ...
model)
* Treasures in the Cadogan Gallery
Orange zone
 Enables the public to see science at work and also provides spaces for relaxation and contemplation. Accessible from Queens Gate.
* Wildlife Garden
* Darwin Centre
* Zoology Spirit Building
Enables the public to see science at work and also provides spaces for relaxation and contemplation. Accessible from Queens Gate.
* Wildlife Garden
* Darwin Centre
* Zoology Spirit Building
Highlights of the collection
* Otumpairon meteorite
Iron meteorites, also known as siderites, or ferrous meteorites, are a type of meteorite that consist overwhelmingly of an iron–nickel alloy known as meteoric iron that usually consists of two mineral phases: kamacite and taenite. Most iron met ...
weighing , found in 1783 in Campo del Cielo
Campo del Cielo refers to a group of iron meteorites and the area in Argentina where they were found. The site straddles the provinces of Chaco and Santiago del Estero, located north-northwest of Buenos Aires, Argentina and approximately southwe ...
, Argentina
* Latrobe nugget, one of the largest known clusters of cubic gold crystals
* Apollo 16
Apollo 16 (April 1627, 1972) was the tenth crewed mission in the United States Apollo space program, administered by NASA, and the fifth and penultimate to land on the Moon. It was the second of Apollo's " J missions", with an extended sta ...
Moon rock sample collected in 1972
* Ostro
Ostro ( ca, Migjorn, hr, Oštro, el, Όστρια), or Austro, is a southerly wind in the Mediterranean Sea, especially the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic. Its name is Italian, derived from the Latin name ''Anemoi#Auster, Auster'', which also meant a s ...
Stone, flawless blue topaz
Topaz is a silicate mineral of aluminium and fluorine with the chemical formula Al Si O( F, OH). It is used as a gemstone in jewelry and other adornments. Common topaz in its natural state is colorless, though trace element impurities can mak ...
gemstone weighing 9,381 carats, about , the largest of its kind in the world
* Aurora Pyramid of Hope
The Aurora Pyramid of Hope is a collection of 296 cut natural diamonds in a wide variety of colors, billed as "the most comprehensive natural color diamond collection in the world". It is owned by Aurora Gems, Inc., a diamond merchant specialisin ...
, a collection of 296 natural diamonds in a wide variety of colours
* First Iguanodon
''Iguanodon'' ( ; meaning 'iguana-tooth'), named in 1825, is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur. While many species have been classified in the genus ''Iguanodon'', dating from the late Jurassic Period to the early Cretaceous Period of Asia, Eu ...
teeth ever discovered
* Dippy
Dippy is a composite ''Diplodocus'' skeleton in Pittsburgh's Carnegie Museum of Natural History, and the holotype of the species ''Diplodocus carnegii''. It is considered the most famous single dinosaur skeleton in the world, due to the numerous ...
, plaster cast replica of the fossilised bones of a Diplodocus carnegii
''Diplodocus'' (, , or ) was a genus of diplodocid sauropod dinosaurs, whose fossils were first discovered in 1877 by S. W. Williston. The generic name, coined by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1878, is a neo-Latin term derived from Greek διπλ ...
skeleton
* Mantellisaurus
''Mantellisaurus'' is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur that lived in the Barremian and early Aptian ages of the Early Cretaceous Period of Europe. Its remains are known from Belgium (Bernissart), England, Spain and Germany. The type and only sp ...
and American mastodon
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
skeletons
* Full-sized animatronic model of a Tyrannosaurus rex
''Tyrannosaurus'' is a genus of large theropod dinosaur. The species ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' (''rex'' meaning "king" in Latin), often called ''T. rex'' or colloquially ''T-Rex'', is one of the best represented theropods. ''Tyrannosaurus'' live ...
* The most intact Stegosaurus
''Stegosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of herbivorous, four-legged, armored dinosaur from the Late Jurassic, characterized by the distinctive kite-shaped upright plates along their backs and spikes on their tails. Fossils of the genus have been foun ...
fossil skeleton ever discovered (nicknamed Sophie)
* Large skull of a Triceratops
''Triceratops'' ( ; ) is a genus of herbivore, herbivorous Chasmosaurinae, chasmosaurine Ceratopsidae, ceratopsid dinosaur that first appeared during the late Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous Period (geology), period, about 68 m ...
* First specimen of Archaeopteryx
''Archaeopteryx'' (; ), sometimes referred to by its German name, "" ( ''Primeval Bird''), is a genus of bird-like dinosaurs. The name derives from the ancient Greek (''archaīos''), meaning "ancient", and (''ptéryx''), meaning "feather" ...
ever discovered, one of only 12 found and generally accepted by palaeontologists to be the oldest known bird
* Rare dodo
The dodo (''Raphus cucullatus'') is an extinct flightless bird that was endemic to the island of Mauritius, which is east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. The dodo's closest genetic relative was the also-extinct Rodrigues solitaire. The ...
skeleton, reconstructed from bones over 1,000 years old
* Only surviving specimen of the Great Auk
The great auk (''Pinguinus impennis'') is a species of flightless alcid that became extinct in the mid-19th century. It was the only modern species in the genus ''Pinguinus''. It is not closely related to the birds now known as penguins, wh ...
from the British Isles, collected in 1813 from Papa Westray
Papa Westray () ( sco, Papa Westree), also known as Papay, is one of the Orkney Islands in Scotland, United Kingdom. The fertile soilKeay, J. & Keay, J. (1994) ''Collins Encyclopaedia of Scotland''. London. HarperCollins. has long been a draw ...
in the Orkney Islands
* Broken Hill skull, Middle Paleolithic
The Middle Paleolithic (or Middle Palaeolithic) is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle Paleoli ...
cranium
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
now considered part of a Homo heidelbergensis
''Homo heidelbergensis'' (also ''H. sapiens heidelbergensis''), sometimes called Heidelbergs, is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human which existed during the Middle Pleistocene. It was subsumed as a subspecies of ''H. erectus'' in ...
, discovered in the mine of Broken Hill or Kabwe
Kabwe is the capital of the Zambian Central Province and the Kabwe District, with a population estimated at 202,914 at the 2010 census. Named Broken Hill until 1966, it was founded when lead and zinc deposits were discovered in 1902. Kabwe also ...
in Zambia
Zambia (), officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern and East Africa, although it is typically referred to as being in Southern Africa at its most cent ...
* Gibraltar 1
Gibraltar 1 is the specimen name of a Neanderthal skull, also known as the Gibraltar Skull found at Forbes' Quarry in Gibraltar and presented to the Gibraltar Scientific Society by its secretary, Lieutenant Edmund Henry Réné Flint on 3 March 18 ...
and Gibraltar 2
Gibraltar 2, also known as Devil's Tower Child, represented five skull fragments of a male Neanderthal child discovered in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. The discovery of the fossils at the Devil's Tower (Gibraltar), Devil's Tower Mo ...
, two Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While th ...
skulls found at Forbes' Quarry
Forbes' Quarry is located on the northern face of the Rock of Gibraltar within the Upper Rock Nature Reserve in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. The area was quarried during the 19th century to supply stone for reinforcing the for ...
in Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
* Cross-section of 1,300-year-old giant sequoia
''Sequoiadendron giganteum'' (giant sequoia; also known as giant redwood, Sierra redwood, Sierran redwood, California big tree, Wellingtonia or simply big treea nickname also used by John Muir) is the sole living species in the genus ''Sequoiade ...
, at the museum since 1893
* Rare copy of ''The Birds of America
''The Birds of America'' is a book by naturalist and painter John James Audubon, containing illustrations of a wide variety of birds of the United States. It was first published as a series in sections between 1827 and 1838, in Edinburgh and ...
'' by John James Audubon
John James Audubon (born Jean-Jacques Rabin; April 26, 1785 – January 27, 1851) was an American self-trained artist, naturalist, and ornithologist. His combined interests in art and ornithology turned into a plan to make a complete pictoria ...
, containing illustrations of a wide variety of birds from the United States
* Rare first edition of Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended fr ...
's ''On the Origin of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life''),The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by Me ...
''
Education and research
 The museum runs a series of
The museum runs a series of educational
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Vari ...
and public engagement programmes. These include for example a highly praised "How Science Works" hands on workshop for school students demonstrating the use of microfossils in geological research. The museum also played a major role in securing designation of the Jurassic Coast
The Jurassic Coast is a World Heritage Site on the English Channel coast of southern England. It stretches from Exmouth in East Devon to Studland Bay in Dorset, a distance of about , and was inscribed on the World Heritage List in mid-December ...
of Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devon is ...
and Dorset
Dorset ( ; archaically: Dorsetshire , ) is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The ceremonial county comprises the unitary authority areas of Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole and Dorset (unitary authority), Dors ...
as a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
and has subsequently been a lead partner in the Lyme Regis
Lyme Regis is a town in west Dorset, England, west of Dorchester and east of Exeter. Sometimes dubbed the "Pearl of Dorset", it lies by the English Channel at the Dorset–Devon border. It has noted fossils in cliffs and beaches on the Herita ...
Fossil Festivals.
In 2005, the museum launched a project to develop notable gallery characters to patrol display cases, including 'facsimiles' of Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the ...
, Mary Anning
Mary Anning (21 May 1799 – 9 March 1847) was an English fossil collector, dealer, and palaeontologist who became known around the world for the discoveries she made in Jurassic marine fossil beds in the cliffs along the English Channel ...
, Dorothea Bate
Dorothea Minola Alice Bate FGS (8 November 1878 – 13 January 1951), also known as Dorothy Bate, was a Welsh palaeontologist and pioneer of archaeozoology. Her life's work was to find fossils of recently extinct mammals with a view to underst ...
and William Smith. They tell stories and anecdotes of their lives and discoveries and aim to surprise visitors.
In 2010, a six-part BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board ex ...
documentary series was filmed at the museum entitled ''Museum of Life
The Museum of Life is located at the Oswaldo Cruz Foundation, in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
Location
The museum is located on the campus of Oswaldo Cruz Foundation
The Oswaldo Cruz Foundation (Portuguese ''Fundação Oswaldo Cruz'', also known a ...
'' exploring the history and behind the scenes aspects of the museum.
Since May 2001, the Natural History Museum admission has been free for some events and permanent exhibitions. However, there are certain temporary exhibits and shows that require a fee.
The Natural History museum combines the museum's life and earth science collections with specialist expertise in "taxonomy, systematics, biodiversity, natural resources, planetary science, evolution and informatics" to tackle scientific questions.
In 2011, the museum led the setting up of an International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natu ...
Bumblebee Specialist Group, chaired by Dr. Paul H. Williams, to assess the threat status of bumblebee species worldwide using Red List criteria.
Access
The closest London Underground station is South Kensington tube station, South Kensington — there is a tunnel from the station that emerges close to the entrances of all three museums. Admission is free, though there are donation boxes in the foyer. Museum Lane immediately to the north provides disabled access to the museum. A connecting bridge between the Natural History and Science museums closed to the public in the late 1990s.In popular culture
The museum plays an important role in the 1975 London-based Disney live-action feature ''One of Our Dinosaurs Is Missing
''One of Our Dinosaurs is Missing'' is a 1975 comedy film set in the early 1920s, about the theft of a dinosaur skeleton from the Natural History Museum. The film was produced by Walt Disney Productions and released by Buena Vista Distribution C ...
''; the eponymous skeleton is stolen from the museum, and a group of intrepid nanny, nannies hide inside the mouth of the museum's blue whale model (in fact a specially created prop – the nannies peer out from behind the whale's teeth, but a blue whale is a baleen whale and has no teeth). Additionally, the film is set in the 1920s, before the blue whale model was built.
The museum features as a base for Prodigium, a secret society which studies and fights monsters, first appearing on '.
In the 2014 film ''Paddington (film), Paddington'', Millicent Clyde is a devious and trecherous taxidermist at the museum. She kidnaps Paddington, intending to kill and stuff him, but is thwarted by the Brown family after scenes involving chases inside and on the roof of the building.
The museum features prominently in the level Lud's Gate from Tomb Raider III, with Core Design launching the game with Jonathan Ross at the museum on 15 October 1998.
Andy Day's CBeebies shows, ''Andy's Dinosaur Adventures'' and ''Andy's Prehistoric Adventures'' are filmed in the Natural History Museum.
The museum was site of the first The Amazing Race#Pit Stop, Pit Stop on ''The Amazing Race 33''.
Natural History Museum at Tring
The NHM also has an outpost in Tring, Hertfordshire, built by local eccentric Lionel Walter Rothschild. The NHM took ownership in 1938. In 2007, the museum announced that the name would be changed to the Natural History Museum at Tring, though the older name, the Walter Rothschild Zoological Museum, is still in widespread use.See also
* James John Joicey * Keeper of Entomology, Natural History Museum * Stegosaurus, Sophie the Stegosaurus * :Employees of the Natural History Museum, LondonReferences
Bibliography
* ''Dr Martin Lister: A bibliography'' by Geoffrey Keynes. St Paul's Bibliographies (UK). . (Includes illustrations by Lister's wife and daughter). * ''The Travelling Naturalists'' (1985) by Clare Lloyd. (Study of 18th Century Natural History — includes Charles Waterton, John Hanning Speke, Henry Seebohm and Mary Kingsley). Contains colour and black and white reproductions. Croom Helm (UK). . * ''Dry storeroom no 1: The Secret Life of the Natural History Museum'' (2009) by Richard Fortey. HarperPress (UK). .External links
*Picture Library of the Natural History Museum
The Natural History Museum on Google Cultural Institute
Architectural history and description
from the ''Survey of London''
Architecture and history of the NHM
from the Royal Institute of British Architects * Maps of
Nature News article on proposed cuts, June 2010
{{Authority control Natural History Museum, London, British Museum Natural history museums in London Museums sponsored by the Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport Grade I listed buildings in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea Grade I listed museum buildings Cultural infrastructure completed in 1880 Alfred Waterhouse buildings Non-departmental public bodies of the United Kingdom government Exempt charities Charities based in London Museums in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea Romanesque Revival architecture in England Terracotta Museums established in 1881 1881 establishments in England National museums of England Dinosaur museums Brompton, London, Natural History Museum, London South Kensington