Multnomah people on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Multnomah are a tribe of Chinookan people who live in the area of
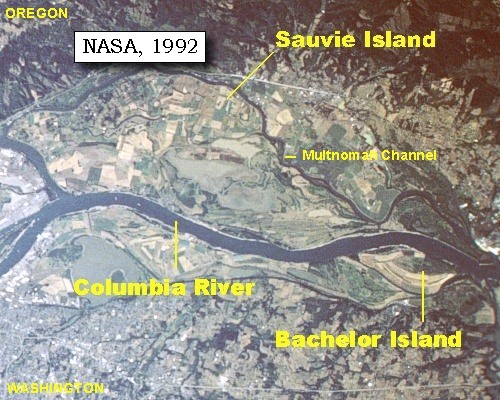 One of the larger villages, Cathlapotle, was located in present-day
One of the larger villages, Cathlapotle, was located in present-day
 What is now called the
What is now called the
 According to Wasco legend, the daughter of Chief Multnomah sacrificed herself to the Great Spirit from the top of
According to Wasco legend, the daughter of Chief Multnomah sacrificed herself to the Great Spirit from the top of
Portland, Oregon
Portland (, ) is a port city in the Pacific Northwest and the largest city in the U.S. state of Oregon. Situated at the confluence of the Willamette and Columbia rivers, Portland is the county seat of Multnomah County, the most populous ...
, in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
. Multnomah villages were located throughout the Portland basin and on both sides of the Columbia River
The Columbia River ( Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia ...
. The Multnomah speak a dialect of the Upper Chinookan language in the Oregon Penutian family.
History
The Multnomah people are a band of theChinookan peoples
Chinookan peoples include several groups of Indigenous people of the Pacific Northwest in the United States who speak the Chinookan languages. Since at least 4000 BCE Chinookan peoples have resided along the Lower and Middle Columbia River (W ...
who originally resided on and near Sauvie Island
Sauvie Island, in the U.S. state of Oregon, originally Wapato Island or Wappatoo Island, is the largest island along the Columbia River, at , and one of the largest river islands in the United States. It lies approximately ten miles northwest o ...
in Oregon. The Multnomah and the related Clackamas tribes lived in a series of villages along the river near the mouth of the Willamette River
The Willamette River ( ) is a major tributary of the Columbia River, accounting for 12 to 15 percent of the Columbia's flow. The Willamette's main stem is long, lying entirely in northwestern Oregon in the United States. Flowing northward b ...
on the Columbia River
The Columbia River ( Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia ...
(the Willamette was also called the "Multnomah" in the early 19th century). According to archaeologists
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes ...
, the villages in the area were home to approximately 3,400 people year-round, and as many as 8,000 during fishing and wappato-harvesting seasons (wappato is a marsh-grown plant like a potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Uni ...
or onion
An onion (''Allium cepa'' L., from Latin ''cepa'' meaning "onion"), also known as the bulb onion or common onion, is a vegetable that is the most widely cultivated species of the genus '' Allium''. The shallot is a botanical variety of the on ...
and a staple food
A staple food, food staple, or simply a staple, is a food that is eaten often and in such quantities that it constitutes a dominant portion of a standard Diet (nutrition), diet for a given person or group of people, supplying a large fraction of ...
).
In 1830, a disease generally thought to have been malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. ...
devastated the Multnomah villages. Within five years, the village of Cathlapotle was abandoned and was briefly inhabited by the Cowlitz Cowlitz may refer to:
People
* Cowlitz people, an indigenous people of the Pacific Northwest
** Cowlitz language, member of the Tsamosan branch of the Coast Salish family of Salishan languages
* Cowlitz Indian Tribe, a federally recognized tribe o ...
tribe. The Multnomah people had nearly been wiped out by the year 1834 due to malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. ...
and smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
outbreaks. With only a few Multnomah left by the year 1910, the remaining people were transferred to the Grand Ronde Community
The Grand Ronde Community is an Indian reservation located on several non-contiguous sections of land in southwestern Yamhill County and northwestern Polk County, Oregon, United States, about east of Lincoln City, near the community of Grand R ...
which is also located in the Northwest of Oregon.
Location
In 1854Multnomah County
Multnomah County is one of the 36 counties in the U.S. state of Oregon. As of the 2020 census, the county's population was 815,428. Multnomah County is part of the Portland–Vancouver– Hillsboro, OR–WA Metropolitan Statistical Area. Th ...
became an official part of Oregon. The Multnomah people were located in today's Multnomah County, but more specifically, they inhabited Sauvie Island
Sauvie Island, in the U.S. state of Oregon, originally Wapato Island or Wappatoo Island, is the largest island along the Columbia River, at , and one of the largest river islands in the United States. It lies approximately ten miles northwest o ...
on the Columbia River
The Columbia River ( Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia ...
. The Native American term for Sauvie Island was Wappatoo Island. The Multnomah people shared Sauvie Island with other Chinook tribes under the collective name The Cathlascans. Furthermore, the Multnomah people were considered “upper Chinook” and spoke the Wasco-wishram language.
 One of the larger villages, Cathlapotle, was located in present-day
One of the larger villages, Cathlapotle, was located in present-day Clark County, Washington
Clark County is the southernmost county in the U.S. state of Washington. As of the 2020 census, the population was 503,311, making it Washington's fifth-most populous county. Its county seat and largest city is Vancouver. It was the first c ...
at the confluence of the Lewis River with the Columbia River and was visited by the Lewis and Clark Expedition
The Lewis and Clark Expedition, also known as the Corps of Discovery Expedition, was the United States expedition to cross the newly acquired western portion of the country after the Louisiana Purchase. The Corps of Discovery was a select gr ...
in 1805. According to their journals, Lewis and Clark found 14 houses in the village, most of them ranging from 14-by-20 ft (4.3 m by 6.0 m) to about 40-by-100 ft (12 m by 30 m). They reported that approximately 900 people lived in the villages. The Cathlacomatup were a group of Multnomah that resided along the Multnomah Channel
The Multnomah Channel is a distributary of the Willamette River. It diverges from the main stem a few miles upstream of the main stem's confluence with the Columbia River in Multnomah County in the U.S. state of Oregon. The channel flows northw ...
at the Wappatoo Inlet. Lewis and Clark
Lewis may refer to:
Names
* Lewis (given name), including a list of people with the given name
* Lewis (surname), including a list of people with the surname
Music
* Lewis (musician), Canadian singer
* "Lewis (Mistreated)", a song by Radiohead ...
came into contact with the Cathalacomatup in 1805.
Chief Multnomah
The Multnomah people received their name from their chief. Yet, the existence of their great chief named Multnomah has been up for debate. Other Native American tribes in the Columbia River Valley area spoke of him in theiroral history
Oral history is the collection and study of historical information about individuals, families, important events, or everyday life using audiotapes, videotapes, or transcriptions of planned interviews. These interviews are conducted with people wh ...
, while Oregon historians dismissed him as just a myth. Therefore, there is conflicting evidence of whether or not he was real. The Oregon Historical Society
The Oregon Historical Society (OHS) is an organization that encourages and promotes the study and understanding of the history of the Oregon Country, within the broader context of U.S. history. Incorporated in 1898, the Society collects, preserv ...
had multiple presidents throughout the 1900s who dismissed him as only an imagined chief. However, on top of the oral descriptions of him there were writings including newspapers and journals, which indicate he was indeed real.
Multnomah was chief of tribes ranging much of the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Thou ...
from Oregon to Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
, and during his 40 years of power he was chief of the Willamettes, as well as war chief of the tribes and communities of Wauna, Oregon
Wauna is an unincorporated community on the Columbia River in Clatsop County, Oregon, United States. According to Oregon Geographic Names, it names a Native American mythological being associated with the Columbia River. There was a post offi ...
, ruling from his station on what is known today as Sauvie Island
Sauvie Island, in the U.S. state of Oregon, originally Wapato Island or Wappatoo Island, is the largest island along the Columbia River, at , and one of the largest river islands in the United States. It lies approximately ten miles northwest o ...
.
Ann Fulton, a history professor at Portland State University
Portland State University (PSU) is a public research university in Portland, Oregon. It was founded in 1946 as a post-secondary educational institution for World War II veterans. It evolved into a four-year college over the following two dec ...
, found and collected much of what is known of Chief Multnomah from many written stories. She documented this in her paper ''The Restoration of an Iłkák'mana: A Chief Called Multnomah''. She hoped to bring more awareness to his existence. Particular accounts came from people such as William Tappan and Dr. Elijah White, both agents of Indian tribes. The many verbal and written accounts of Chief Multnomah were similar. He was regarded highly, and many stated that while he was a warrior chief, he was very respected among his people.
It is believed that the end of Chief Multnomah's reign occurred with the eruption of Mount Hood
Mount Hood is a potentially active stratovolcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc. It was formed by a subduction zone on the Pacific coast and rests in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is located about east-southeast of Portl ...
during the 1780s. In 1792, Captain George Vancouver
Captain George Vancouver (22 June 1757 – 10 May 1798) was a British Royal Navy officer best known for his 1791–1795 expedition, which explored and charted North America's northwestern Pacific Coast regions, including the coasts of what are ...
and his crew did not encounter Chief Multnomah along their expedition, according to their records, however, later in 1805 when Lewis and Clark
Lewis may refer to:
Names
* Lewis (given name), including a list of people with the given name
* Lewis (surname), including a list of people with the surname
Music
* Lewis (musician), Canadian singer
* "Lewis (Mistreated)", a song by Radiohead ...
reached Sauvie Island they wrote of the “mulknomah” people. This referenced Chief Multnomah, as well as the group of tribes that made up his people.
Culture
The houses of the Multnomah, like the otherChinookan peoples
Chinookan peoples include several groups of Indigenous people of the Pacific Northwest in the United States who speak the Chinookan languages. Since at least 4000 BCE Chinookan peoples have resided along the Lower and Middle Columbia River (W ...
, were largely longhouse
A longhouse or long house is a type of long, proportionately narrow, single-room building for communal dwelling. It has been built in various parts of the world including Asia, Europe, and North America.
Many were built from timber and often re ...
s made of Western Redcedar
''Thuja plicata'' is an evergreen coniferous tree in the cypress family Cupressaceae, native to western North America. Its common name is western redcedar (western red cedar in the UK), and it is also called Pacific redcedar, giant arborvitae, w ...
planks. The size of a home depended on the wealth of the owner, with the larger houses furnishing living quarters for up to 100 people. Within each house, a particular family had a separate cubicle separated by woven mats. Each family had its own fire, with the families also sharing a communal central fire in the household.
The Multnomah diet included salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family Salmonidae, which are native to tributaries of the North Atlantic (genus '' Salmo'') and North Pacific (genus '' Onco ...
, eels, sturgeon
Sturgeon is the common name for the 27 species of fish belonging to the family Acipenseridae. The earliest sturgeon fossils date to the Late Cretaceous, and are descended from other, earlier acipenseriform fish, which date back to the Early ...
, elk, water birds
A water bird, alternatively waterbird or aquatic bird, is a bird that lives on or around water. In some definitions, the term ''water bird'' is especially applied to birds in freshwater ecosystems, although others make no distinction from seabi ...
and especially wapato.
Legends
Land and name claim
In one legend described in Jeanne Eder's, ''The Bridge of Gods'', the name for the Multnomah people came from a dispute between two brothers. The Great Spirit, who maintained no physical form, took care of the world's people. Although everyone was content, the two brothers were not satisfied. The Great Spirit brought the siblings to the top of a mountain that overlooked their land. He told the brothers to shoot an arrow in opposite directions, and the Great Spirit allowed each brother to claim their land and chief hood based on where their arrows landed. What is now called the
What is now called the Columbia River
The Columbia River ( Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia ...
became the dividing border between the two brothers’ land claims. The first brother's arrow landed in the Willamette Valley
The Willamette Valley ( ) is a long valley in Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. The Willamette River flows the entire length of the valley and is surrounded by mountains on three sides: the Cascade Range to the eas ...
where he became Chief Multnomah of the Multnomah people. The second arrow landed north of the river in what is now modern day Klickitat County
Klickitat County is a county located in the U.S. state of Washington. As of the 2020 census, the population was 22,735. The county seat and largest city is Goldendale. The county is named after the Klickitat tribe.
History
Klickitat Count ...
where he became chief of the Klickitat people.
Legend of Multnomah Falls
 According to Wasco legend, the daughter of Chief Multnomah sacrificed herself to the Great Spirit from the top of
According to Wasco legend, the daughter of Chief Multnomah sacrificed herself to the Great Spirit from the top of Multnomah Falls
Multnomah Falls is a waterfall located on Multnomah Creek in the Columbia River Gorge, east of Troutdale, between Corbett and Dodson, Oregon, United States. The waterfall is accessible from the Historic Columbia River Highway and Interstate 84. ...
. Tribes along the Columbia River celebrated the marriage of the Chief's daughter to a neighboring tribe. The happiness didn't last long, however, before the area experienced an illness that affected all of the tribes along the river. The medicine man claimed the Great Spirit told him all of the tribe would die unless the Spirit received a sacrifice; the Chief's daughter's life. The Chief wouldn't allow it, but when the daughter saw the sickness affect her loved ones, she willingly left in the middle of the night to go to the top of the cliff overlooking the Columbia River. She threw herself off the cliff. When the Chief found his daughter's body, he prayed to the Great Spirit for a sign that her spirit was well. Water began pouring from the cliff and became known as Multnomah Falls.
The Multnomah today
Most of the Multnomah people who are still alive today reside in the Grand Ronde Federation andWarm Springs Indian Reservation
The Warm Springs Indian Reservation consists of in north-central Oregon, in the United States, and is governed by the Confederated Tribes of Warm Springs.
Tribes
Three tribes form the confederation: the Wasco, Tenino (Warm Springs) and P ...
, but the Multnomah no longer exist as a distinct tribe or people.
The name "Multnomah"
Many locations in the Pacific Northwest can accredit their names to the Multnomah people.Multnomah County
Multnomah County is one of the 36 counties in the U.S. state of Oregon. As of the 2020 census, the county's population was 815,428. Multnomah County is part of the Portland–Vancouver– Hillsboro, OR–WA Metropolitan Statistical Area. Th ...
takes its designation from this Native American word. It can also be found in the titles of the Multnomah Athletic Club, Multnomah Falls, Multnomah Village, and the statue of Chief Multnomah in a Portland park.
Artwork
Located inPortland, Oregon
Portland (, ) is a port city in the Pacific Northwest and the largest city in the U.S. state of Oregon. Situated at the confluence of the Willamette and Columbia rivers, Portland is the county seat of Multnomah County, the most populous ...
, Washington Park features a statue of Chief Multnomah called '' Coming of the White Man''. The bronze statue was erected in 1904 by the sculptor Hermon Atkins MacNeil
Hermon Atkins MacNeil (February 27, 1866 – October 2, 1947) was an American sculptor born in Everett, Massachusetts. He is known for designing the ''Standing Liberty'' quarter, struck by the Mint from 1916-1930; and for sculpting ''Justi ...
. He drew inspiration from the popularity of Frederic Balch's book ''Bridge of the Gods: A Romance of Indian Oregon'', which took the stories Balch had heard from Native Americans while growing up and embellished them. The statue features two Native Americans looking eastward along the Oregon Trail
The Oregon Trail was a east–west, large-wheeled wagon route and emigrant trail in the United States that connected the Missouri River to valleys in Oregon. The eastern part of the Oregon Trail spanned part of what is now the state of Kans ...
. The two men look down upon the route that ox teams trudged bringing settlers to the western United States. The older of the two men is said to be Chief Multnomah of the Multnomah people. The statue was donated to the city of Portland from the descendants of David P. Thompson. MacNeil went on the make other statuettes
A figurine (a diminutive form of the word ''figure'') or statuette is a small, three-dimensional sculpture that represents a human, deity or animal, or, in practice, a pair or small group of them. Figurines have been made in many media, with clay ...
of Chief Multnomah.
The inspiration and the name of this sculpture comes from Meriwether Lewis
Meriwether Lewis (August 18, 1774 – October 11, 1809) was an American explorer, soldier, politician, and public administrator, best known for his role as the leader of the Lewis and Clark Expedition, also known as the Corps of Discovery, wit ...
and William Clark
William Clark (August 1, 1770 – September 1, 1838) was an American explorer, soldier, Indian agent, and territorial governor. A native of Virginia, he grew up in pre-statehood Kentucky before later settling in what became the state of Miss ...
’s expedition across the United States. In 1805, upon arriving in Oregon, Lewis and Clark
Lewis may refer to:
Names
* Lewis (given name), including a list of people with the given name
* Lewis (surname), including a list of people with the surname
Music
* Lewis (musician), Canadian singer
* "Lewis (Mistreated)", a song by Radiohead ...
encountered a village. The men described the village of Native Americans who were known as “mulknomahs” encamped on Sauvie Island
Sauvie Island, in the U.S. state of Oregon, originally Wapato Island or Wappatoo Island, is the largest island along the Columbia River, at , and one of the largest river islands in the United States. It lies approximately ten miles northwest o ...
, and they originally referred to the now Willamette River as the Mulknoma.
Chief Multnomah was also depicted on linen postcards during the 1900s around 1930 and 1945. He is shown in colorful, traditional clothing. A print is currently part of The Tichnor Brothers Collection from the Boston Public Library
The Boston Public Library is a municipal public library system in Boston, Massachusetts, United States, founded in 1848. The Boston Public Library is also the Library for the Commonwealth (formerly ''library of last recourse'') of the Commonwea ...
. It is part of a series of Oregon related postcards and published by Angelus Commercial Studio of Portland, Oregon.
Notes
Further reading
* {{authority control Chinookan tribes Native American tribes in Oregon Lewis and Clark Expedition Multnomah County, Oregon Indigenous peoples of the Northwest Plateau