Multiplexed Point-of-care Testing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Multiplexed
Multiplexed
 Multiplexed
Multiplexed point-of-care testing
Point-of-care testing (POCT or bedside testing) is defined as medical diagnostic testing at or near the point of care—that is, at the time and place of patient care. This contrasts with the historical pattern in which testing was wholly or most ...
(xPOCT) is a more complex form of point-of-care testing
Point-of-care testing (POCT or bedside testing) is defined as medical diagnostic testing at or near the point of care—that is, at the time and place of patient care. This contrasts with the historical pattern in which testing was wholly or most ...
(POCT), or bedside testing. Point-of-care testing is designed to provide diagnostic tests at or near the time and place that the patient is admitted. POCT uses the concentrations of analytes
An analyte, component (in clinical chemistry), or chemical species is a substance or chemical constituent that is of interest in an analytical procedure. The purest substances are referred to as analytes, such as 24 karat gold, NaCl, water, etc. ...
to provide the user with information on the physiological state of the patient. An analyte is a substance, chemical or biological, that is being analyzed using a certain instrument. While point-of-care testing is the quantification of one analyte from one in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology an ...
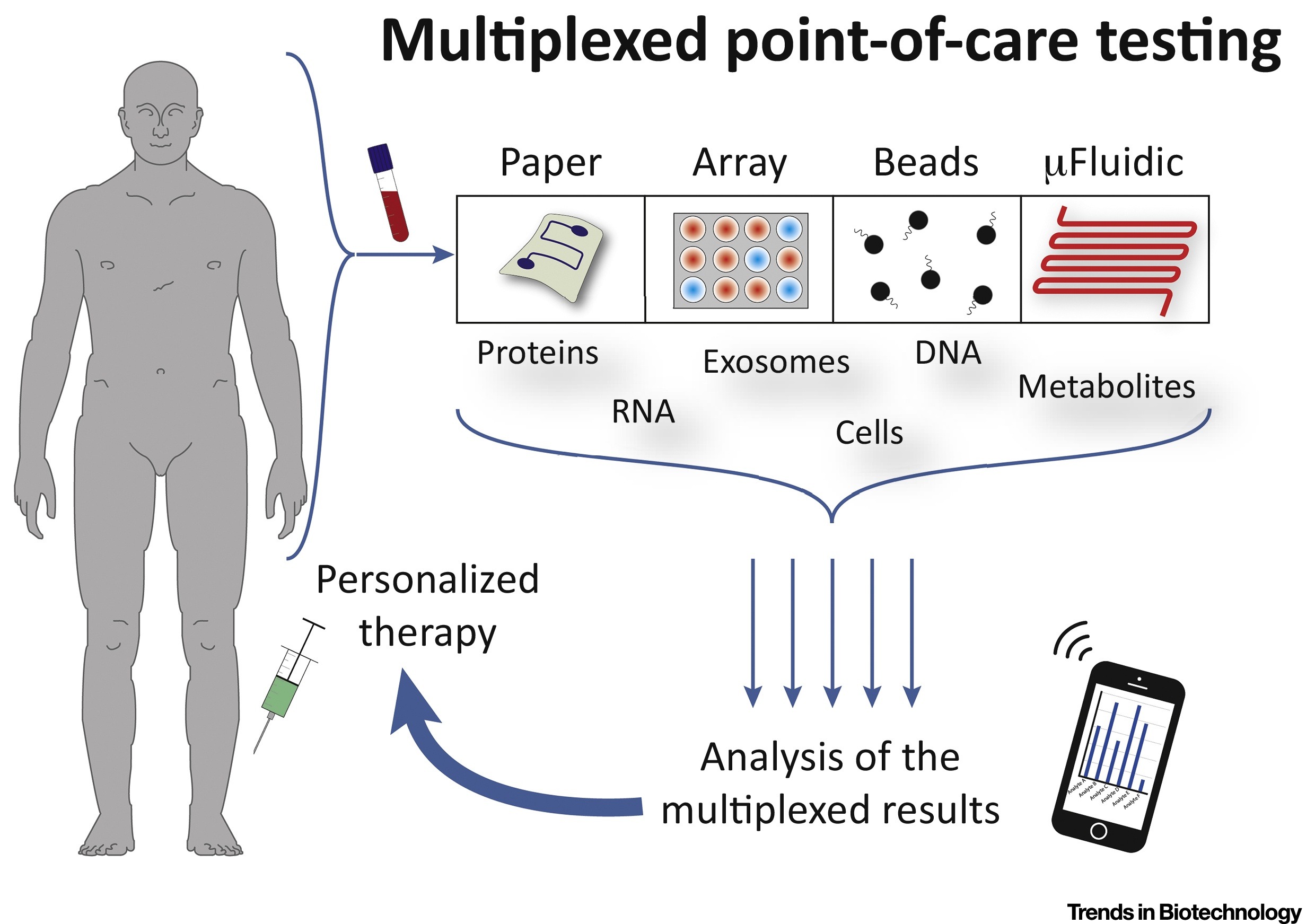
(e.g. blood, plasma or urine) sample, multiplexed point-of-care testing is the simultaneous on-site quantification of various analytes from a single sample.
Processing of one biological sample to yield multiple biomarker
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, ...
results allows for POCT testing to be done for patients who may have conditions that require the confirmation of multiple biomarkers and tests before diagnosis (e.g. many types of cancers). xPOCT has important emerging applications in resource-limited settings, (e.g. in the developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
, in doctor's practices, or at home by non experts) xPOCT has recently become more important for ''in vitro'' diagnostics.
Background
Historically, medical testing has been a tedious, long and expensive process in a clinical setting. It usually involves taking a large sample from the patient (e.g. urine, blood, saliva, tissue swab), and processing it in a separate laboratory, which takes hours or sometimes days to complete. In that time frame, the patient needs to be provided with care, which is not favorable to do without the desired information from the laboratory test. As far back as the 1950s,radioimmunoassay
A radioimmunoassay (RIA) is an immunoassay that uses radiolabeled molecules in a stepwise formation of immune complexes. A RIA is a very sensitive in vitro assay technique used to measure concentrations of substances, usually measuring antigen conc ...
s were first demonstrated for the sensitive detection of insulin and thyroxine levels in human plasma. In the 1990s, research that was being conducted in the microelectronics industry was applied to the design of immunoassays and since then the applications for immunoassays have expanded.
There has been a movement towards quicker, more simplistic and cost effective technologies that require small amounts of biological substances to yield results. This movement has been dubbed as microfluidic
Microfluidics refers to the behavior, precise control, and manipulation of fluids that are geometrically constrained to a small scale (typically sub-millimeter) at which surface forces dominate volumetric forces. It is a multidisciplinary field tha ...
and lab-on-a-chip
A lab-on-a-chip (LOC) is a device that integrates one or several laboratory functions on a single integrated circuit (commonly called a "chip") of only millimeters to a few square centimeters to achieve automation and high-throughput screening. ...
technology and aims to bring the results of a test accurately, quickly, and conveniently back to the patient with low cost and complexity to ensure the best patient care. Multiplexed point-of-care testing aims to do all of these things, but with multiple biomarker
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, ...
s at once. Microfluidics refers to the study and control of very small amounts of liquids and lab-on-a-chip is an electronic chip that is usually about 3 square millimeters that has the ability to perform various laboratory like capillary electrophoresis
Capillary electrophoresis (CE) is a family of electrokinetic separation methods performed in submillimeter diameter capillaries and in micro- and nanofluidic channels. Very often, CE refers to capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE), but other electr ...
and PCR.
xPOCT technology characteristics
An ideal device for multiplexed point-of-care testing should offer high sensitivity and the capability to process one sample using multiple types of tests. It should be capable of testing various kinds of substances, includingprotein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s, drug
A drug is any chemical substance that causes a change in an organism's physiology or psychology when consumed. Drugs are typically distinguished from food and substances that provide nutritional support. Consumption of drugs can be via insuffla ...
s, RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
s and cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
, at the same time. A high sensor performance that requires small samples, short turnaround times, low system complexity for non experts, and low cost are some characteristics of xPOCT technology. Especially for the resource-limited settings (developing countries, doctors offices, directly at home), equipment-free or smartphone-based devices are very advantageous.
xPOCT devices has to fulfill the following:
* Low sample consumption (e.g. blood from a finger prick) or the ability to measure in noninvasive samples (e.g. saliva, urine or exhaled breath condensate)
* Fast sample-to-result times enabling an immediate treatment
* Long shelf life with extended reagent storage
*Ease of storage
* Comparable test results with central laboratory findings ensuring international quality standards (ISO 15189
''ISO 15189 Medical laboratories — Requirements for quality and competence'' is an international standard that specifies the quality management system requirements particular to medical laboratories. The standard was developed by the Internationa ...
)
* Automatic or facile system operation with minimized user intervention
* Cheap and portable readout systems (e.g. handheld readers) along with disposable test strips or cartridges fulfilling the ''in vitro'' diagnostics guideline (EU Directives
A directive is a legal act of the European Union that requires member states to achieve a particular result without dictating the means of achieving that result. Directives first have to be enacted into national law by member states before thei ...
or FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
regulations).
Technologies
Multianalyte detection is mostly achieved through three different approaches but the technology mainly aims to use a single or small set of biological samples to split or separate them to be read by various types of assays: # Regional separation employing distinct sections of a channel network or array of electrodes # Spatial separation of detection sites with the help of various wells or spots # Application of multiple labels such asenzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
s, redox
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate (chemistry), substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of Electron, electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction ...
molecules, beads, and dyes
Other xPOCT devices use mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is use ...
(MS) to directly identify biomarkers for example, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization
In mass spectrometry, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) is an ionization technique that uses a laser energy absorbing matrix to create ions from large molecules with minimal fragmentation. It has been applied to the analysis of ...
(MALDI)-MS to rapidly identify pathogens, but devices that use this technology tend to be bulky and difficult to use. For the signal readout, optical and electrochemical detection methods are mainly employed.
Current types of diagnostic devices that are being used are:
* Paper-based systems - Lateral flow assays like pregnancy tests, which use samples that react with colored particles and require the device to read the color signature
* Array-based systems - Devices with electrodes or fluorescent molecules in them that are sensitive to certain analytes
* Bead-based systems - Systems that use beads as a material for the analytes to bind specifically to and those complexes are subsequently filtered or separates by size or color, for example bead based flow cytometry
Flow cytometry (FC) is a technique used to detect and measure physical and chemical characteristics of a population of cells or particles.
In this process, a sample containing cells or particles is suspended in a fluid and injected into the flo ...
Benefits and challenges
xPOCT has incredible benefits and applications for the healthcare and technology. It allows for a more cost effective, more rapid, portable, less painful, less complex yet accurate technology that can be used to test for indicators of conditions that previously required multiple samples and several hours or days to do. In addition to its implications in the clinical setting, the low complexity and portability of many multiplexed point-of-care test devices allows for its use by non experts at home both for those who require at home health monitoring systems and for other personalized medicinal uses. The incidence of false positives or false negatives seem to be low. Reaching the optimal space of high performance and low complexity, cost, and size has some challenges. Scientists, hospitals, manufacturers, and policy makers must ensure that the data gathered from these devices would be secure, and that the devices and the materials used in conjunction with it remain affordable and safe. In addition to these things, the devices themselves should be functional for long periods of time and should find ways to deal with their sensitivity to patient to patient variations, and the environment (humidity, temperature etc.).Future research
Current research that is being done regarding xPOCT is focusing on making the requirements for something to be considered a xPOCT easier and cheaper to obtain. Scientists are working to make multiplexed point-of-care devices smaller, more portable, and affordable. Research is also being done on the maximum number of analytes that can be tested at once, if smartphones are a good device to use to present the results of a test, and could there be a device that allows a patient to wear a xPOC device that continuously monitors biomarkers of interest.References
{{Reflist Medical terminology Medical tests