Multiple Sclerosis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Multiple (cerebral) sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata or disseminated sclerosis, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of
*
 A person with MS can have almost any neurological symptom or sign, with autonomic, visual, motor, and sensory problems being the most common. The specific symptoms are determined by the locations of the lesions within the nervous system, and may include loss of sensitivity or changes in sensation such as tingling, pins and needles or numbness, muscle weakness, blurred vision, pronounced reflexes, muscle spasms, or difficulty in moving; difficulties with coordination and balance (
A person with MS can have almost any neurological symptom or sign, with autonomic, visual, motor, and sensory problems being the most common. The specific symptoms are determined by the locations of the lesions within the nervous system, and may include loss of sensitivity or changes in sensation such as tingling, pins and needles or numbness, muscle weakness, blurred vision, pronounced reflexes, muscle spasms, or difficulty in moving; difficulties with coordination and balance (
BBC lay summary
of 13 April 2022. A study of individuals in the United States military between 1993 and 2013 (total population greater than 10 million) compared 801 people who developed MS on or after military service to 1,566 matched controls who did not develop MS during this observation period. The study found a 32-fold increased risk of developing MS after infection with EBV. It did not find an increased risk after infection with other viruses, including the similarly transmitted cytomegalovirus. The finding strongly suggests that EBV plays a role in the onset of MS, although EBV alone may be insufficent to cause MS. Although some consider that this goes against the hygiene hypothesis, since the non-infected have probably experienced a more hygienic upbringing, others believe that there is no contradiction, since it is a first encounter with the causative virus relatively late in life that is the trigger for the disease. Other diseases that may be related include
 MS is not considered a hereditary disease; however, a number of genetic variations have been shown to increase the risk. Some of these genes appear to have higher levels of expression in microglial cells than expected by chance. The probability of developing the disease is higher in relatives of an affected person, with a greater risk among those more closely related. An
MS is not considered a hereditary disease; however, a number of genetic variations have been shown to increase the risk. Some of these genes appear to have higher levels of expression in microglial cells than expected by chance. The probability of developing the disease is higher in relatives of an affected person, with a greater risk among those more closely related. An
 The three main characteristics of MS are the formation of lesions in the
The three main characteristics of MS are the formation of lesions in the
 The name ''multiple sclerosis'' refers to the scars (sclerae – better known as plaques or lesions) that form in the nervous system. These lesions most commonly affect the
The name ''multiple sclerosis'' refers to the scars (sclerae – better known as plaques or lesions) that form in the nervous system. These lesions most commonly affect the

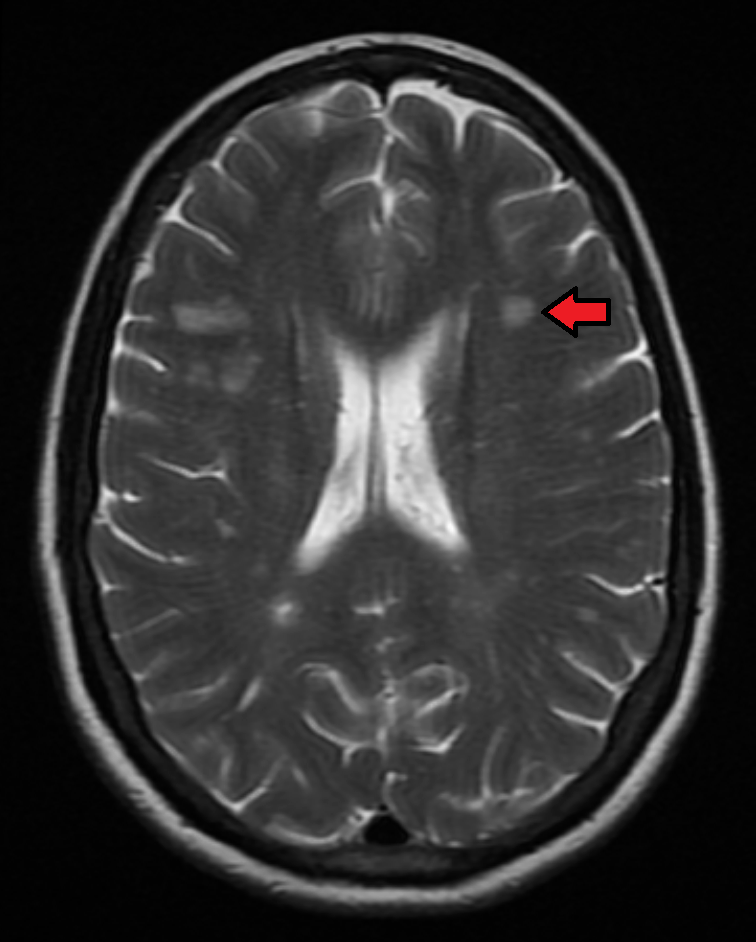 Multiple sclerosis is typically diagnosed based on the presenting signs and symptoms, in combination with supporting
Multiple sclerosis is typically diagnosed based on the presenting signs and symptoms, in combination with supporting
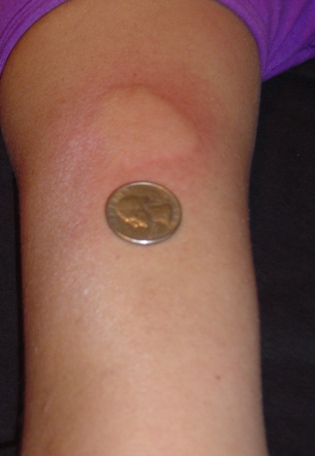 The disease-modifying treatments have several adverse effects. One of the most common is irritation at the injection site for glatiramer acetate and the interferons (up to 90% with subcutaneous injections and 33% with intramuscular injections). Over time, a visible dent at the injection site, due to the local destruction of fat tissue, known as lipoatrophy, may develop. Interferons may produce flu-like symptoms; some people taking glatiramer experience a post-injection reaction with flushing, chest tightness, heart palpitations, and anxiety, which usually lasts less than thirty minutes. More dangerous but much less common are liver damage from interferons,
The disease-modifying treatments have several adverse effects. One of the most common is irritation at the injection site for glatiramer acetate and the interferons (up to 90% with subcutaneous injections and 33% with intramuscular injections). Over time, a visible dent at the injection site, due to the local destruction of fat tissue, known as lipoatrophy, may develop. Interferons may produce flu-like symptoms; some people taking glatiramer experience a post-injection reaction with flushing, chest tightness, heart palpitations, and anxiety, which usually lasts less than thirty minutes. More dangerous but much less common are liver damage from interferons,
 MS is the most common autoimmune disorder of the
MS is the most common autoimmune disorder of the
 Robert Carswell (1793–1857), a British professor of
Robert Carswell (1793–1857), a British professor of
 There are several historical accounts of people who probably had MS and lived before or shortly after the disease was described by Charcot.
A young woman called Halldora who lived in
There are several historical accounts of people who probably had MS and lived before or shortly after the disease was described by Charcot.
A young woman called Halldora who lived in
 Since disease progression is the result of degeneration of neurons, the roles of proteins showing loss of nerve tissue such as neurofilaments, tau, and N-acetylaspartate are under investigation.
Improvement in neuroimaging techniques such as positron emission tomography (PET) or
Since disease progression is the result of degeneration of neurons, the roles of proteins showing loss of nerve tissue such as neurofilaments, tau, and N-acetylaspartate are under investigation.
Improvement in neuroimaging techniques such as positron emission tomography (PET) or
Database for analysis and comparison of global data on the epidemiology of MS
{{Authority control Ailments of unknown cause Epstein–Barr virus–associated diseases Myelin disorders Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate (full)
nerve cells
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. ...
in the brain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
and spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
are damaged. This damage disrupts the ability of parts of the nervous system to transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Specific symptoms can include double vision, blindness
Visual impairment, also known as vision impairment, is a medical definition primarily measured based on an individual's better eye visual acuity; in the absence of treatment such as correctable eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment� ...
in one eye, muscle weakness, and trouble with sensation
Sensation (psychology) refers to the processing of the senses by the sensory system.
Sensation or sensations may also refer to:
In arts and entertainment In literature
* Sensation (fiction), a fiction writing mode
* Sensation novel, a Briti ...
or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks (relapsing forms) or building up over time (progressive forms). In the relapsing forms of MS, between attacks, symptoms may disappear completely, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances.
While the cause is unclear, the underlying mechanism is thought to be either destruction by the immune system or failure of the myelin
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can ...
-producing cells. Proposed causes for this include genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar work ...
and environmental factors, such as viral infections. MS is usually diagnosed based on the presenting signs and symptoms and the results of supporting medical tests.
There is no known cure for multiple sclerosis. Treatments attempt to improve function after an attack and prevent new attacks. Physical therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, pat ...
and occupational therapy
Occupational therapy (OT) is a global healthcare profession. It involves the use of assessment and intervention to develop, recover, or maintain the meaningful activities, or ''occupations'', of individuals, groups, or communities. The field of ...
can help with people's ability to function. Many people pursue alternative treatments
Alternative medicine is any practice that aims to achieve the healing effects of medicine despite lacking biological plausibility, testability, repeatability, or evidence from clinical trials. Complementary medicine (CM), complementary and al ...
, despite a lack of evidence of benefit. The long-term outcome is difficult to predict; better outcomes are more often seen in women, those who develop the disease early in life, those with a relapsing course, and those who initially experienced few attacks.
Multiple sclerosis is the most common immune-mediated disorder affecting the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
. There are nearly one million people with MS in the United States in 2022, and in 2020, about 2.8 million people were affected globally, with rates varying widely in different regions and among different populations. The disease usually begins between the ages of twenty and fifty and is twice as common in women as in men. MS was first described in 1868 by French neurologist Jean-Martin Charcot
Jean-Martin Charcot (; 29 November 1825 – 16 August 1893) was a French neurologist and professor of anatomical pathology. He worked on hypnosis and hysteria, in particular with his hysteria patient Louise Augustine Gleizes. Charcot is know ...
. The name ''multiple sclerosis'' refers to the numerous glial scars
Glial scar formation (gliosis) is a reactive cellular process involving astrogliosis that occurs after injury to the central nervous system. As with scarring in other organs and tissues, the glial scar is the body's mechanism to protect and begin ...
(or sclerae – essentially plaques or lesions) that develop on the white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribu ...
of the brain and spinal cord.*
Signs and symptoms
ataxia
Ataxia is a neurological sign consisting of lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements that can include gait abnormality, speech changes, and abnormalities in eye movements. Ataxia is a clinical manifestation indicating dysfunction of ...
); problems with speech or swallowing
Swallowing, sometimes called deglutition in scientific contexts, is the process in the human or animal body that allows for a substance to pass from the mouth, to the pharynx, and into the esophagus, while shutting the epiglottis. Swallowing i ...
, visual problems ( nystagmus, optic neuritis or double vision), feeling tired, acute
Acute may refer to:
Science and technology
* Acute angle
** Acute triangle
** Acute, a leaf shape in the glossary of leaf morphology
* Acute (medicine), a disease that it is of short duration and of recent onset.
** Acute toxicity, the adverse ef ...
or chronic pain, and bladder and bowel difficulties (such as neurogenic bladder), among others. When multiple sclerosis is more advanced, walking difficulties can occur and the risk of falling increases.
Difficulties thinking and emotional problems such as depression or unstable mood are also common. The primary deficit in cognitive function that people with MS experience is slowed information processing speed, with memory also commonly affected, and executive function
In cognitive science and neuropsychology, executive functions (collectively referred to as executive function and cognitive control) are a set of cognitive processes that are necessary for the cognitive control of behavior: selecting and succe ...
less commonly. Intelligence, language, and semantic memory
Semantic memory refers to general world knowledge that humans have accumulated throughout their lives. This general knowledge (word meanings, concepts, facts, and ideas) is intertwined in experience and dependent on culture. We can learn abou ...
are usually preserved, and the level of cognitive impairment varies significantly between people with MS.
Uhthoff's phenomenon, a worsening of symptoms due to exposure to higher than usual temperatures, and Lhermitte's sign, an electrical sensation that runs down the back when bending the neck, are particularly characteristic of MS. The main measure of disability and severity is the expanded disability status scale (EDSS), with other measures such as the multiple sclerosis functional composite being increasingly used in research. EDSS is also correlated with falls in people with MS. While it is a popular measure, EDSS has been criticized for some of its limitations, such as relying too much on walking.
The condition begins in 85% of cases as a clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) over a number of days with 45% having motor or sensory problems, 20% having optic neuritis, and 10% having symptoms related to brainstem dysfunction, while the remaining 25% have more than one of the previous difficulties. The course of symptoms occurs in two main patterns initially: either as episodes of sudden worsening that last a few days to months (called relapses, exacerbations, bouts, attacks, or flare-ups) followed by improvement (85% of cases) or as a gradual worsening over time without periods of recovery (10–15% of cases). A combination of these two patterns may also occur or people may start in a relapsing and remitting course that then becomes progressive later on.
Relapses are usually not predictable, occurring without warning. Exacerbations rarely occur more frequently than twice per year. Some relapses, however, are preceded by common triggers and they occur more frequently during spring and summer. Similarly, viral infections such as the common cold
The common cold or the cold is a viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract that primarily affects the respiratory mucosa of the nose, throat, sinuses, and larynx. Signs and symptoms may appear fewer than two days after expos ...
, influenza, or gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea and gastro, is an inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of energy, and dehydr ...
increase their risk. Stress may also trigger an attack. Women with MS who become pregnant experience fewer relapses; however, during the first months after delivery the risk increases. Overall, pregnancy does not seem to influence long-term disability. Many events have been found not to affect relapse rates including vaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulat ...
, breast feeding, physical trauma, and Uhthoff's phenomenon.
Prodromal phase
MS may have a prodromal phase in the years leading up to MS manifestation, characterized by psychiatric issues, cognitive impairment, and increased utilization of healthcare.Causes
The cause of MS is unknown; however, it is believed to occur as a result of some combination of genetic and environmental factors such as infectious agents.Infectious agents
Many microbes have been proposed as triggers of MS. One hypothesis is that infection by a widespread microbe contributes to disease development, and the geographic distribution of this organism significantly influences the epidemiology of MS. Two opposing versions of this hypothesis include thehygiene hypothesis
In medicine, the hygiene hypothesis states that early childhood exposure to particular microorganisms (such as the gut flora and helminth parasites) protects against allergic diseases by contributing to the development of the immune system. In pa ...
and the prevalence hypothesis, the former being more favored. The hygiene hypothesis proposes that exposure to certain infectious agents early in life is protective; the disease is a response to a late encounter with such agents. The prevalence hypothesis proposes that an early, persistent, and silent infection increases risk of disease, and thus the disease is more common where the infectious agent is more common. Only in a few cases and after many years does it cause demyelination.
Human herpes viruses are a candidate group of viruses. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), a herpes virus that can cause infectious mononucleosis and infects approximately 95% of adults, has been increasingly suspected to be an initiating cause of MS, in combination with other genetic and environmental factors, even though only a small proportion of those infected with EBV will later develop MS. SeBBC lay summary
of 13 April 2022. A study of individuals in the United States military between 1993 and 2013 (total population greater than 10 million) compared 801 people who developed MS on or after military service to 1,566 matched controls who did not develop MS during this observation period. The study found a 32-fold increased risk of developing MS after infection with EBV. It did not find an increased risk after infection with other viruses, including the similarly transmitted cytomegalovirus. The finding strongly suggests that EBV plays a role in the onset of MS, although EBV alone may be insufficent to cause MS. Although some consider that this goes against the hygiene hypothesis, since the non-infected have probably experienced a more hygienic upbringing, others believe that there is no contradiction, since it is a first encounter with the causative virus relatively late in life that is the trigger for the disease. Other diseases that may be related include
measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
, mumps and rubella. Evidence for a virus as a cause include the presence of oligoclonal bands
Oligoclonal bands (OCBs) are bands of immunoglobulins that are seen when a patient's blood serum, or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is analyzed. They are used in the diagnosis of various neurological and blood diseases, especially in multiple sclerosis. ...
in the brain and cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates.
CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the ...
of most people with MS, the association of several viruses with human demyelinating encephalomyelitis, and the occurrence of demyelination in animals caused by some viral infections.
Genetics
identical twin
Twins are two offspring produced by the same pregnancy.MedicineNet > Definition of TwinLast Editorial Review: 19 June 2000 Twins can be either ''monozygotic'' ('identical'), meaning that they develop from one zygote, which splits and forms two ...
of an affected individual has a 30% chance of developing MS, 5% for a non-identical twin, 2.5% for a sibling, and an even lower chance for a half-sibling. If both parents are affected the risk in their children is 10 times that of the general population. MS is also more common in some ethnic groups than others.
Specific gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s that have been linked with MS include differences in the human leukocyte antigen
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system or complex is a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans which encode cell-surface proteins responsible for the regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of th ...
(HLA) system—a group of genes on chromosome 6
Chromosome 6 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 6 spans more than 170 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 5.5 and 6% of the total ...
that serves as the major histocompatibility complex (MHC). That differences in the HLA region are related to susceptibility has been known since the 1980s, and this same region has also been implicated in the development of other autoimmune diseases such as diabetes type I and systemic lupus erythematosus. The most consistent finding is the association between multiple sclerosis and allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chrom ...
s of the MHC defined as DR15 and DQ6. Other loci have shown a protective effect, such as HLA-C554 and HLA-DRB1
HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DRB1 beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HLA-DRB1'' gene. DRB1 encodes the most prevalent beta subunit of HLA-DR. DRB1 alleles, especially those encoding amino acid sequence changes a ...
*11. Overall, it has been estimated that HLA differences account for between 20% and 60% of the genetic predisposition
A genetic predisposition is a genetic characteristic which influences the possible phenotypic development of an individual organism within a species or population under the influence of environmental conditions. In medicine, genetic susceptibili ...
. Modern genetic methods ( genome-wide association studies) have revealed at least 200 variants outside the HLA locus that modestly increase the probability of MS.
Geography
MS is more common in people who live farther from theequator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can also ...
, although exceptions exist. These exceptions include ethnic groups that are at low risk and that live far from the equator such as the Sami, Amerindians, Canadian Hutterite
Hutterites (german: link=no, Hutterer), also called Hutterian Brethren (German: ), are a communal ethnoreligious branch of Anabaptists, who, like the Amish and Mennonites, trace their roots to the Radical Reformation of the early 16th centu ...
s, New Zealand Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Co ...
, and Canada's Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territorie ...
, as well as groups that have a relatively high risk and that live closer to the equator such as Sardinians, inland Sicilians, Palestinians
Palestinians ( ar, الفلسطينيون, ; he, פָלַסְטִינִים, ) or Palestinian people ( ar, الشعب الفلسطيني, label=none, ), also referred to as Palestinian Arabs ( ar, الفلسطينيين العرب, label=non ...
, and Parsi. The cause of this geographical pattern is not clear. While the north–south gradient of incidence is decreasing, as of 2010 it is still present.
MS is more common in regions with northern European populations and the geographic variation may simply reflect the global distribution of these high-risk populations.
A relationship between season of birth and MS lends support to this idea, with fewer people born in the northern hemisphere in November compared to May being affected later in life.
Environmental factors may play a role during childhood, with several studies finding that people who move to a different region of the world before the age of 15 acquire the new region's risk of MS. If migration takes place after age 15, however, the person retains the risk of their home country. There is some evidence that the effect of moving may still apply to people older than 15.
Other
Smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is burned and the resulting smoke is typically breathed in to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, which have b ...
may be an independent risk factor for MS. Stress may be a risk factor, although the evidence to support this is weak. Association with occupational exposures and toxin
A toxin is a naturally occurring organic poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. Toxins occur especially as a protein or conjugated protein. The term toxin was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849 ...
s—mainly organic solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for ...
s—has been evaluated, but no clear conclusions have been reached. Vaccinations were studied as causal factors; however, most studies show no association. Several other possible risk factors, such as diet and hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required ...
intake, have been looked at; however, evidence on their relation with the disease is "sparse and unpersuasive". Gout
Gout ( ) is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by recurrent attacks of a red, tender, hot and swollen joint, caused by deposition of monosodium urate monohydrate crystals. Pain typically comes on rapidly, reaching maximal intens ...
occurs less than would be expected and lower levels of uric acid have been found in people with MS. This has led to the theory that uric acid is protective, although its exact importance remains unknown. Obesity during adolescence and young adulthood is a risk factor for MS.
Pathophysiology
 The three main characteristics of MS are the formation of lesions in the
The three main characteristics of MS are the formation of lesions in the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
(also called plaques), inflammation and the destruction of myelin sheaths of neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa ...
s. These features interact in a complex and not yet fully understood manner to produce the breakdown of nerve tissue and in turn the signs and symptoms of the disease.
Cholesterol crystal A cholesterol crystal is a solid, crystalline form of cholesterol found in gallstones and atherosclerosis. Gallstones occurring in industrialized societies typically contain more than 70-90% cholesterol by weight, much of which is crystalline. Chol ...
s are believed both to impair myelin repair and to aggravate inflammation. MS is believed to be an immune-mediated disorder that develops from an interaction of the individual's genetics and as yet unidentified environmental causes. Damage is believed to be caused, at least in part, by attack on the nervous system by a person's own immune system.
Lesions
 The name ''multiple sclerosis'' refers to the scars (sclerae – better known as plaques or lesions) that form in the nervous system. These lesions most commonly affect the
The name ''multiple sclerosis'' refers to the scars (sclerae – better known as plaques or lesions) that form in the nervous system. These lesions most commonly affect the white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribu ...
in the optic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve is derived fro ...
, brain stem, basal ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG), or basal nuclei, are a group of subcortical nuclei, of varied origin, in the brains of vertebrates. In humans, and some primates, there are some differences, mainly in the division of the globus pallidus into an ext ...
, and spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
, or white matter tracts close to the lateral ventricles. The function of white matter cells is to carry signals between grey matter
Grey matter is a major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal cell bodies, neuropil ( dendrites and unmyelinated axons), glial cells ( astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), synapses, and capillaries. Grey matter is ...
areas, where the processing is done, and the rest of the body. The peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brai ...
is rarely involved.
To be specific, MS involves the loss of oligodendrocytes, the cells responsible for creating and maintaining a fatty layer—known as the myelin
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can ...
sheath—which helps the neurons carry electrical signals (action potentials). This results in a thinning or complete loss of myelin and, as the disease advances, the breakdown of the axons of neurons. When the myelin is lost, a neuron can no longer effectively conduct electrical signals. A repair process, called remyelination, takes place in early phases of the disease, but the oligodendrocytes are unable to completely rebuild the cell's myelin sheath. Repeated attacks lead to successively less effective remyelinations, until a scar-like plaque is built up around the damaged axons. These scars are the origin of the symptoms and during an attack magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
(MRI) often shows more than ten new plaques. This could indicate that there are a number of lesions below which the brain is capable of repairing itself without producing noticeable consequences. Another process involved in the creation of lesions is an abnormal increase in the number of astrocytes due to the destruction of nearby neurons. A number of lesion patterns have been described.
Inflammation
Apart from demyelination, the other sign of the disease isinflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
. Fitting with an immunological
Immunology is a branch of medicineImmunology for Medical Students, Roderick Nairn, Matthew Helbert, Mosby, 2007 and biology that covers the medical study of immune systems in humans, animals, plants and sapient species. In such we can see the ...
explanation, the inflammatory process is caused by T cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
s, a kind of lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic a ...
that plays an important role in the body's defenses. T cells gain entry into the brain as a result of disruptions in the blood–brain barrier. The T cells recognize myelin as foreign and attack it, explaining why these cells are also called "autoreactive lymphocytes."
The attack on myelin starts inflammatory processes, which trigger other immune cells and the release of soluble factors like cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in au ...
s and antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of ...
. A further breakdown of the blood-brain barrier, in turn, causes a number of other damaging effects such as swelling, activation of macrophages
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
, and more activation of cytokines and other destructive proteins. Inflammation can potentially reduce transmission of information between neurons in at least three ways. The soluble factors released might stop neurotransmission by intact neurons. These factors could lead to or enhance the loss of myelin, or they may cause the axon to break down completely.
Blood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a part of thecapillary
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the bod ...
system that prevents the entry of T cells into the central nervous system. It may become permeable to these types of cells secondary to an infection by a virus or bacteria. After it repairs itself, typically once the infection has cleared, T cells may remain trapped inside the brain. Gadolinium cannot cross a normal BBB and, therefore, gadolinium-enhanced MRI is used to show BBB breakdowns.
Diagnosis

 Multiple sclerosis is typically diagnosed based on the presenting signs and symptoms, in combination with supporting
Multiple sclerosis is typically diagnosed based on the presenting signs and symptoms, in combination with supporting medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to re ...
and laboratory testing. It can be difficult to confirm, especially early on, since the signs and symptoms may be similar to those of other medical problems.
The McDonald criteria
The McDonald criteria are diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis (MS). These criteria are named after neurologist W. Ian McDonald who directed an international panel in association with the National Multiple Sclerosis Society (NMSS) of America ...
, which focus on clinical, laboratory, and radiologic evidence of lesions at different times and in different areas, is the most commonly used method of diagnosis with the Schumacher
Schumacher or Schuhmacher is an occupational surname (German language, German, "shoemaker", pronounced , both variants can be used as surnames, with Schumacher being the more popular one, however, only the variant with three "h"s can also be used ...
and Poser criteria
Poser criteria are diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis (MS). They replaced the older Schumacher criteria, and now they are considered obsolete as McDonald criteria have superseded them. Nevertheless, some of the concepts introduced have r ...
being of mostly historical significance.
, there is no single test (including biopsy) that can provide a definitive diagnosis.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain and spine may show areas of demyelination (lesions or plaques). Gadolinium can be administered intravenously as a contrast agent to highlight active plaques and, by elimination, demonstrate the existence of historical lesions not associated with symptoms at the moment of the evaluation.
Central vein signs (CVS) have been proposed as a good indicator of MS in comparison with other conditions causing white lesions. One small study found fewer CVS in older and hypertensive people. Further research on CVS as a biomarker for MS is ongoing.
Brain atrophy is seen as an indicator of MS.
Testing of cerebrospinal fluid obtained from a lumbar puncture can provide evidence of chronic inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
in the central nervous system. The cerebrospinal fluid is tested for oligoclonal bands of IgG on electrophoresis, which are inflammation markers found in 75–85% of people with MS.
Differential diagnosis
There are several diseases that present similarly to multiple sclerosis. Intractable vomiting, severe optic neuritis, or bilateral optic neuritis raises suspicion for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD). Involvement of multiple cranial nerves raises suspicion for neurosarcoidosis. Longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis (LETM), in which spinal cord damage spans three or more vertebral segments, raises suspicion for NMOSD, neurosarcoidosis, anti-MOG–associated myelitis, systemic rheumatologic disease, or a paraneoplastic disorder.Types and variants
Severalphenotypes
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological prop ...
(commonly termed ''types''), or patterns of progression, have been described. Phenotypes use the past course of the disease in an attempt to predict the future course. They are important not only for prognosis but also for treatment decisions.
The International Advisory Committee on Clinical Trials of MS describes four types of MS (revised in 2013) in what is known as the Lublin classification:
# Clinically isolated syndrome (CIS)
# Relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS)
# Primary progressive MS (PPMS)
# Secondary progressive MS (SPMS)
Relapsing-remitting MS is characterized by unpredictable relapses followed by periods of months to years of relative quiet (remission
Remission often refers to:
*Forgiveness
Remission may also refer to:
Healthcare and science
*Remission (medicine), the state of absence of disease activity in patients with a chronic illness, with the possibility of return of disease activity
*R ...
) with no new signs of disease activity. Deficits that occur during attacks may either resolve or leave problems, the latter in about 40% of attacks and being more common the longer a person has had the disease. This describes the initial course of 80% of individuals with MS.
The relapsing-remitting subtype usually begins with a clinically isolated syndrome (CIS). In CIS, a person has an attack suggestive of demyelination, but does not fulfill the criteria for multiple sclerosis. 30 to 70% of persons who experience CIS, later develop MS.
Primary progressive MS occurs in approximately 10–20% of individuals with the disease, with no remission after the initial symptoms. It is characterized by progression of disability from onset, with no, or only occasional and minor, remissions and improvements. The usual age of onset for the primary progressive subtype is later than of the relapsing-remitting subtype. It is similar to the age that secondary progressive usually begins in relapsing-remitting MS, around 40 years of age.
Secondary progressive MS occurs in around 65% of those with initial relapsing-remitting MS, who eventually have progressive neurologic decline between acute attacks without any definite periods of remission. Occasional relapses and minor remissions may appear. The most common length of time between disease onset and conversion from relapsing-remitting to secondary progressive MS is 19 years.
Special courses
Independently of the types published by the MS associations, regulatory agencies like the FDA often consider special courses, trying to reflect some clinical trials results on their approval documents. Some examples could be "Highly Active MS" (HAMS), "Active Secondary MS" (similar to the old Progressive-Relapsing) and "Rapidly progressing PPMS". Also, when deficits always resolve between attacks, this is sometimes referred to as ''benign MS'', although people will still build up some degree of disability in the long term. On the other hand, the term '' malignant multiple sclerosis'' is used to describe people with MS having reached significant level of disability in a short period. An international panel has published a standardized definition for the course HAMS.Variants
Atypical variants of MS have been described; these includetumefactive multiple sclerosis
Tumefactive multiple sclerosis is a condition in which the central nervous system of a person has multiple demyelinating lesions with atypical characteristics for those of standard multiple sclerosis (MS). It is called tumefactive as the lesions ...
, Balo concentric sclerosis, Schilder's diffuse sclerosis, and Marburg multiple sclerosis. There is debate on whether they are MS variants or different diseases. Some diseases previously considered MS variants like Devic's disease
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD), including neuromyelitis optica (NMO), are autoimmune diseases characterized by acute inflammation of the optic nerve (optic neuritis, ON) and the spinal cord (myelitis). Episodes of ON and myelitis ...
are now considered outside the MS spectrum.
Management
Although there is no known cure for multiple sclerosis, several therapies have proven helpful. Several effective treatments can significantly decrease the number of attacks and the rate of progression. The primary aims of therapy are returning function after an attack, preventing new attacks, and preventing disability. Starting medications is generally recommended in people after the first attack when more than two lesions are seen on MRI. Older medications used to treat MS were modestly effective, could have side effects, and were poorly tolerated. However, several treatment options with better safety and tolerability profiles have been introduced, changing the prognosis of MS. In the treatment era, 16% of people with relapsing MS went on to need a cane to walk after 20 years. As with any medical treatment, medications used in the management of MS have several adverse effects.Alternative treatments
Alternative medicine is any practice that aims to achieve the healing effects of medicine despite lacking biological plausibility, testability, repeatability, or evidence from clinical trials. Complementary medicine (CM), complementary and al ...
are pursued by some people, despite the shortage of supporting evidence of efficacy.
Acute attacks
During symptomatic attacks, administration of high doses of intravenouscorticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are inv ...
s, such as methylprednisolone, is the usual therapy, with oral corticosteroids seeming to have a similar efficacy and safety profile. Although effective in the short term for relieving symptoms, corticosteroid treatments do not appear to have a significant impact on long-term recovery. The long-term benefit is unclear in optic neuritis as of 2020. The consequences of severe attacks that do not respond to corticosteroids might be treatable by plasmapheresis.
Disease-modifying treatments
Relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis
As of 2021, multiple disease-modifying medications were approved by regulatory agencies for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). In RRMS they are modestly effective at decreasing the number of attacks. The interferons and glatiramer acetate are first-line treatments and are roughly equivalent, reducing relapses by approximately 30%. Early-initiated long-term therapy is safe and improves outcomes. Treatment of clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) withinterferon
Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten th ...
s decreases the chance of progressing to clinical MS. Efficacy of interferons and glatiramer acetate in children has been estimated to be roughly equivalent to that of adults. The role of some newer agents such as fingolimod, teriflunomide, and dimethyl fumarate, is not yet entirely clear. It is difficult to make firm conclusions about the best treatment, especially regarding the long‐term benefit and safety of early treatment, given the lack of studies directly comparing disease modifying therapies or long-term monitoring of patient outcomes.
The relative effectiveness of different treatments is unclear, as most have only been compared to placebo or a small number of other therapies. Direct comparisons of interferon
Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten th ...
s and glatiramer acetate
Glatiramer acetate (also known as Copolymer 1, Cop-1), sold under the brand name Copaxone among others, is an immunomodulator medication used to treat multiple sclerosis. Glatiramer acetate is approved in the United States to reduce the frequency ...
indicate similar effects or only small differences in effects on relapse rate, disease progression and magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
measures. Alemtuzumab, natalizumab, and fingolimod may be more effective than other drugs in reducing relapses over the short term in people with RRMS. Natalizumab and interferon beta-1a ( Rebif) may reduce relapses compared to both placebo and interferon beta-1a (Avonex
Interferon beta-1a (also interferon beta 1-alpha) is a cytokine in the interferon family used to treat multiple sclerosis (MS). It is produced by mammalian cells, while interferon beta-1b is produced in modified ''E. coli''. Some research indic ...
) while Interferon beta-1b
Interferon beta-1b is a cytokine in the interferon family used to treat the relapsing-remitting and secondary-progressive forms of multiple sclerosis (MS). It is approved for use after the first MS event. Closely related is interferon beta 1a, als ...
(Betaseron
Interferon beta-1b is a cytokine in the interferon family used to treat the relapsing-remitting and secondary-progressive forms of multiple sclerosis (MS). It is approved for use after the first MS event. Closely related is interferon beta 1a, al ...
), glatiramer acetate
Glatiramer acetate (also known as Copolymer 1, Cop-1), sold under the brand name Copaxone among others, is an immunomodulator medication used to treat multiple sclerosis. Glatiramer acetate is approved in the United States to reduce the frequency ...
, and mitoxantrone may also prevent relapses. Evidence on relative effectiveness in reducing disability progression is unclear. All medications are associated with adverse effects that may influence their risk to benefit profiles.
Progressive multiple sclerosis
, only one medication, mitoxantrone, had been approved for secondary progressive MS. In this population tentative evidence supports mitoxantrone moderately slowing the progression of the disease and decreasing rates of relapses over two years. As of 2013, review of 9 immunomodulators andimmunosuppressant
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified in ...
s found no evidence of any being effective in preventing disability progression in people with progressive MS.
In March 2017 the FDA approved ocrelizumab as a treatment for primary progressive MS in adults, the first drug to gain that approval, with requirements for several Phase IV clinical trials. It is also used for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis, to include clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease in adults.
In 2019, siponimod
Siponimod, sold under the brand name Mayzent, is a selective sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator for oral use that is used for multiple sclerosis (MS). It is intended for once-daily oral administration.
In March 2019, it was approved in ...
and cladribine were approved in the United States for the treatment of secondary progressive multiple sclerosis.
Adverse effects
systolic dysfunction
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, an ...
(12%), infertility, and acute myeloid leukemia (0.8%) from mitoxantrone, and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy occurring with natalizumab (occurring in 1 in 600 people treated).
Fingolimod may give rise to hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high b ...
and slowed heart rate, macular edema, elevated liver enzymes, or a reduction in lymphocyte levels. Tentative evidence supports the short-term safety of teriflunomide, with common side effects including: headaches, fatigue, nausea, hair loss, and limb pain. There have also been reports of liver failure and PML with its use and it is dangerous for fetal development. Most common side effects of dimethyl fumarate are flushing and gastrointestinal problems. While dimethyl fumarate may lead to a reduction in the white blood cell count there were no reported cases of opportunistic infections during trials.Associated symptoms
Both medications and neurorehabilitation have been shown to improve some symptoms, though neither changes the course of the disease. Some symptoms have a good response to medication, such as bladder spasticity, while others are little changed. Equipment such as catheters for neurogenic bladder or mobility aids can be helpful in improving functional status. A multidisciplinary approach is important for improving quality of life; however, it is difficult to specify a 'core team' as many health services may be needed at different points in time. Multidisciplinary rehabilitation programs increase activity and participation of people with MS but do not influence impairment level. Studies investigating information provision in support of patient understanding and participation suggest that while interventions (written information, decision aids, coaching, educational programmes) may increase knowledge, the evidence of an effect on decision making and quality of life is mixed and low certainty. There is limited evidence for the overall efficacy of individual therapeutic disciplines, though there is good evidence that specific approaches, such as exercise, and psychological therapies are effective. Cognitive training, alone or combined with other neuropsychological interventions, may show positive effects for memory and attention though firm conclusions are not possible given small sample numbers, variable methodology, interventions and outcome measures. The effectiveness of palliative approaches in addition to standard care is uncertain, due to lack of evidence. The effectiveness of interventions, including exercise, specifically for the prevention of falls in people with MS is uncertain, while there is some evidence of an effect on balance function and mobility. Cognitive behavioral therapy has shown to be moderately effective for reducing MS fatigue. The evidence for the effectiveness of non-pharmacological interventions for chronic pain is insufficient to recommend such interventions alone, however their use in combination with medications may be reasonable.Non-pharmaceutical
There is some evidence thataquatic therapy
Aquatic therapy refers to treatments and exercises performed in water for relaxation, fitness, physical rehabilitation, and other therapeutic benefit. Typically a qualified aquatic therapist gives constant attendance to a person receiving treat ...
is a beneficial intervention.
The spasticity associated with MS can be difficult to manage because of the progressive and fluctuating course of the disease. Although there is no firm conclusion on the efficacy in reducing spasticity, PT interventions can be a safe and beneficial option for patients with multiple sclerosis. Physical therapy including vibration interventions, electrical stimulation, exercise therapy, standing therapy, and radial shock wave therapy (RSWT), were beneficial for limiting spasticity, helping limit excitability, or increasing range of motion.
Alternative treatments
Over 50% of people with MS may usecomplementary and alternative medicine
Alternative medicine is any practice that aims to achieve the healing effects of medicine despite lacking biological plausibility, testability, repeatability, or evidence from clinical trials. Complementary medicine (CM), complementary and al ...
, although percentages vary depending on how alternative medicine is defined. Regarding the characteristics of users, they are more frequently women, have had MS for a longer time, tend to be more disabled and have lower levels of satisfaction with conventional healthcare. The evidence for the effectiveness for such treatments in most cases is weak or absent. Treatments of unproven benefit used by people with MS include dietary supplementation and regimens, vitamin D, relaxation technique
A relaxation technique (also known as relaxation training) is any method, process, procedure, or activity that helps a person to relax; to attain a state of increased calmness; or otherwise reduce levels of pain, anxiety, stress or anger. Rela ...
s such as yoga
Yoga (; sa, योग, lit=yoke' or 'union ) is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines which originated in ancient India and aim to control (yoke) and still the mind, recognizing a detached witness-consciou ...
, herbal medicine
Herbal medicine (also herbalism) is the study of pharmacognosy and the use of medicinal plants, which are a basis of traditional medicine. With worldwide research into pharmacology, some herbal medicines have been translated into modern remedie ...
(including medical cannabis), hyperbaric oxygen therapy, self-infection with hookworms, reflexology, acupuncture, and mindfulness. Evidence suggests vitamin D supplementation, irrespective of the form and dose, provides no benefit for people with MS; this includes for measures such as relapse recurrence, disability, and MRI lesions while effects on health‐related quality of life and fatigue are unclear. There is insufficient evidence supporting high-dose biotin
Biotin (or vitamin B7) is one of the B vitamins. It is involved in a wide range of metabolic processes, both in humans and in other organisms, primarily related to the utilization of fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids. The name ''biotin'', bo ...
and some evidence for increased disease activity and higher risk of relapse with its use.
Prognosis
The availability of treatments that modify the course of multiple sclerosis beginning in the 1990s, known as disease-modifying therapies (DMTs), has improved prognosis. These treatments can reduce relapses and slow progression, but as of 2022 there is no cure. The prognosis of MS depends on the subtype of the disease, and there is also great individual variation in the progression of the disease. For relapsing MS, which is the most common subtype, approximately one of every five people later transition to secondary progressive MS, a form characterized by more progressive decline. A 2016 cohort study found that after a median of 16.8 years from onset, one in ten of those with relapsing MS needed a walking aid, and almost two in ten transitioned to secondary progressive MS. With treatments available in the 2020s, relapses can be eliminated or substantially reduced. However, "silent progression" of the disease still occurs. In addition to secondary progressive MS (SPMS), a small proportion of people with MS (10-15%) experience progressive decline from the onset, known as primary progressive MS (PPMS). Most treatments have been approved for use in relapsing MS; there are limited effective treatments for progressive forms of MS, and treatments aren't as effective. The prognosis for progressive MS is worse, with faster accumulation of disability, though the rate of decline varies considerably between people. In untreated PPMS, the median time from onset to requiring a walking aid is estimated as seven years. In SPMS, a 2014 cohort study reported that people required a walking aid after an average of five years from onset of SPMS, and were chair or bedbound after average fifteen years. After diagnosis of MS, characteristics that predict a worse course are male sex, older age, and greater disability at the time of diagnosis. Female sex, though, is associated with a higher relapse rate. As of 2018, no biomarker can accurately predict disease progression in every patient. Spinal cord lesions, abnormalities on MRI, and morebrain atrophy
Cerebral atrophy is a common feature of many of the diseases that affect the brain. Atrophy of any tissue means a decrement in the size of the cell, which can be due to progressive loss of cytoplasmic proteins. In brain tissue, atrophy describes ...
are predictive of a worse course, though brain atrophy as a predictor of disease course is experimental and not used in clinical practice as of 2018. Early treatment leads to a better prognosis, but a higher relapse frequency when treated with DMTs is associated with a poorer prognosis.
Epidemiology
central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
. As of 2022, there are nearly one million known cases of multiple sclerosis in the United States. In 2020, the number of people with MS was 2.8 million globally, with rates varying widely in different regions. In Africa rates are less than 0.5 per 100,000, while they are 2.8 per 100,000 in South East Asia, 8.3 per 100,000 in the Americas, and 80 per 100,000 in Europe. Rates surpass 200 per 100,000 in certain populations of Northern European descent. The number of new cases that develop per year is about 2.5 per 100,000.
Increasing rates of MS may be explained simply by better diagnosis. Studies on populational and geographical patterns have been common and have led to a number of theories about the cause.
MS usually appears in adults in their late twenties or early thirties but it can rarely start in childhood and after 50 years of age. The primary progressive subtype is more common in people in their fifties. Similarly to many autoimmune disorders, the disease is more common in women, and the trend may be increasing. As of 2008, globally it is about two times more common in women than in men. In children, it is even more common in females than males, while in people over fifty, it affects males and females almost equally.
History
Medical discovery
 Robert Carswell (1793–1857), a British professor of
Robert Carswell (1793–1857), a British professor of pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in ...
, and Jean Cruveilhier (1791–1873), a French professor of pathologic anatomy, described and illustrated many of the disease's clinical details, but did not identify it as a separate disease. Specifically, Carswell described the injuries he found as "a remarkable lesion of the spinal cord accompanied with atrophy". Under the microscope, Swiss pathologist Georg Eduard Rindfleisch (1836–1908) noted in 1863 that the inflammation-associated lesions were distributed around blood vessels.
The French neurologist Jean-Martin Charcot
Jean-Martin Charcot (; 29 November 1825 – 16 August 1893) was a French neurologist and professor of anatomical pathology. He worked on hypnosis and hysteria, in particular with his hysteria patient Louise Augustine Gleizes. Charcot is know ...
(1825–1893) was the first person to recognize multiple sclerosis as a distinct disease in 1868. Summarizing previous reports and adding his own clinical and pathological observations, Charcot called the disease ''sclerose en plaques''.
Diagnosis history
The first attempt to establish a set of diagnostic criteria was also due to Charcot in 1868. He published what now is known as the "Charcot Triad", consisting in nystagmus, intention tremor, andtelegraphic speech
Telegraphic speech, according to linguistics and psychology, is speech during the two-word stage of language acquisition in children, which is laconic and efficient.
Background
The name derives from the fact that someone sending a telegram wa ...
(scanning speech). Charcot also observed cognition changes, describing his patients as having a "marked enfeeblement of the memory" and "conceptions that formed slowly".
Diagnosis was based on Charcot triad and clinical observation until Schumacher
Schumacher or Schuhmacher is an occupational surname (German language, German, "shoemaker", pronounced , both variants can be used as surnames, with Schumacher being the more popular one, however, only the variant with three "h"s can also be used ...
made the first attempt to standardize criteria in 1965 by introducing some fundamental requirements: Dissemination of the lesions in time (DIT) and space (DIS), and that "signs and symptoms cannot be explained better by another disease process". The DIT and DIS requirement was later inherited by Poser criteria
Poser criteria are diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis (MS). They replaced the older Schumacher criteria, and now they are considered obsolete as McDonald criteria have superseded them. Nevertheless, some of the concepts introduced have r ...
and McDonald criteria
The McDonald criteria are diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis (MS). These criteria are named after neurologist W. Ian McDonald who directed an international panel in association with the National Multiple Sclerosis Society (NMSS) of America ...
, whose 2017 revision is in use.
During the 20th century, theories about the cause and pathogenesis were developed and effective treatments began to appear in the 1990s. Since the beginning of the 21st century, refinements of the concepts have taken place. The 2010 revision of the McDonald criteria allowed for the diagnosis of MS with only one proved lesion (CIS).
In 1996, the US National Multiple Sclerosis Society (NMSS) (Advisory Committee on Clinical Trials) defined the first version of the clinical phenotypes that is in use. In this first version they provided standardized definitions for four MS clinical courses: relapsing-remitting (RR), secondary progressive (SP), primary progressive (PP), and progressive relapsing (PR). In 2010, PR was dropped and CIS was incorporated. Three years later, the 2013 revision of the "phenotypes for the disease course" were forced to consider CIS as one of the phenotypes of MS, making obsolete some expressions like "conversion from CIS to MS". Other organizations have proposed later new clinical phenotypes, like HAMS (Highly Active MS).
Historical cases
 There are several historical accounts of people who probably had MS and lived before or shortly after the disease was described by Charcot.
A young woman called Halldora who lived in
There are several historical accounts of people who probably had MS and lived before or shortly after the disease was described by Charcot.
A young woman called Halldora who lived in Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
around 1200 suddenly lost her vision and mobility but recovered them seven days after. Saint Lidwina of Schiedam (1380–1433), a Dutch nun, may be one of the first clearly identifiable people with MS. From the age of 16 until her death at 53, she had intermittent pain, weakness of the legs and vision loss: symptoms typical of MS. Both cases have led to the proposal of a "Viking gene" hypothesis for the dissemination of the disease.
Augustus Frederick d'Este (1794–1848), son of Prince Augustus Frederick, Duke of Sussex and Lady Augusta Murray and a grandson of George III of the United Kingdom, almost certainly had MS. D'Este left a detailed diary describing his 22 years living with the disease. His diary began in 1822 and ended in 1846, although it remained unknown until 1948. His symptoms began at age 28 with a sudden transient visual loss ( amaurosis fugax) after the funeral of a friend. During his disease, he developed weakness of the legs, clumsiness of the hands, numbness, dizziness, bladder disturbance and erectile dysfunction. In 1844, he began to use a wheelchair. Despite his illness, he kept an optimistic view of life. Another early account of MS was kept by the British diarist W. N. P. Barbellion, pen name
A pen name, also called a ''nom de plume'' or a literary double, is a pseudonym (or, in some cases, a variant form of a real name) adopted by an author and printed on the title page or by-line of their works in place of their real name.
A pen na ...
of Bruce Frederick Cummings (1889–1919), who maintained a detailed log of his diagnosis and struggle. His diary was published in 1919 as '' The Journal of a Disappointed Man''.
Research
Epstein-Barr virus ongoing studies
As of 2022, the pathogenesis of MS as it relates to EBV is actively investigated, as are disease-modifying therapies; understanding of how risk factors combine with EBV to initiate MS is sought. Whether EBV is the only cause of MS might be better understood if an EBV vaccine is developed and shown to prevent MS as well.Medications
Medications that influence voltage-gated sodium ion channels are under investigation as a potential neuroprotective strategy because of hypothesized role of sodium in the pathological process leading to axonal injury and accumulating disability. There is insufficient evidence of an effect of sodium channel blockers for people with MS.Pathogenesis
MS is a clinically defined entity with several atypical presentations. Some auto-antibodies have been found in atypical MS cases, giving birth to separate disease families and restricting the previously wider concept of MS. Anti-AQP4 autoantibodies were found inneuromyelitis optica
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD), including neuromyelitis optica (NMO), are autoimmune diseases characterized by acute inflammation of the optic nerve ( optic neuritis, ON) and the spinal cord ( myelitis). Episodes of ON and myeli ...
(NMO), which was previously considered a MS variant. A spectrum of diseases named NMOSD (NMO spectrum diseases) or anti-AQP4 diseases has been accepted. Some cases of MS were presenting anti-MOG autoantibodies, mainly overlapping with the Marburg variant. Anti-MOG autoantibodies were found to be also present in ADEM, and a second spectrum of separated diseases is being considered. This spectrum is named inconsistently across different authors, but it is normally something similar to anti-MOG demyelinating diseases.
A third kind of auto-antibodies is accepted. They are several anti-neurofascin auto-antibodies which damage the Ranvier nodes of the neurons. These antibodies are more related to the peripheral nervous demyelination, but they were also found in chronic progressive PPMS and combined central and peripheral demyelination
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) is an acquired autoimmune disease of the peripheral nervous system characterized by progressive weakness and impaired sensory function in the legs and arms. The disorder is sometimes called ...
(CCPD, which is considered another atypical MS presentation).
In addition to the significance of auto-antibodies in MS, four different patterns of demyelination have been reported, opening the door to consider MS as a heterogeneous disease.
Disease biomarkers
 Since disease progression is the result of degeneration of neurons, the roles of proteins showing loss of nerve tissue such as neurofilaments, tau, and N-acetylaspartate are under investigation.
Improvement in neuroimaging techniques such as positron emission tomography (PET) or
Since disease progression is the result of degeneration of neurons, the roles of proteins showing loss of nerve tissue such as neurofilaments, tau, and N-acetylaspartate are under investigation.
Improvement in neuroimaging techniques such as positron emission tomography (PET) or magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
(MRI) carry a promise for better diagnosis and prognosis predictions. Regarding MRI, there are several techniques that have already shown some usefulness in research settings and could be introduced into clinical practice, such as double-inversion recovery sequences, magnetization transfer, diffusion tensor, and functional magnetic resonance imaging
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area o ...
. These techniques are more specific for the disease than existing ones, but still lack some standardization of acquisition protocols and the creation of normative values. This is particularly the case for proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy, for which a number of methodological variations observed in the literature may underlie continued inconsistencies in central nervous system metabolic abnormalities, particularly in N-acetyl aspartate, myoinositol
Inositol, or more precisely ''myo''-inositol, is a carbocycle, carbocyclic sugar that is abundant in the brain and other mammalian tissues; it mediates cell signal transduction in response to a variety of hormones, neurotransmitters, and growth f ...
, choline, glutamate, GABA, and GSH, observed for multiple sclerosis and its subtypes. There are other techniques under development that include contrast agents capable of measuring levels of peripheral macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
s, inflammation, or neuronal dysfunction, and techniques that measure iron deposition that could serve to determine the role of this feature in MS, or that of cerebral perfusion.
COVID-19
The hospitalization rate was found to be higher among individuals with MS and COVID-19 infection, at 10%, while the pooled infection rate is estimated at 4%. The pooled prevalence of death in hospitalized individuals with MS is estimated as 4%.Other emerging theories
One emerging hypothesis, referred to as the hygiene hypothesis, suggests that early-life exposure to infectious agents helps to develop the immune system and reduces susceptibility to allergies and autoimmune disorders, including MS. Germ-free mice infected with transplanted fecal matter from MS patients exhibit an increased risk of developing EAE, an animal model of MS. It has also been proposed that certain bacteria found in the gut use molecular mimicry to infiltrate the brain via the gut-brain axis, initiating an inflammatory response and increasing blood-brain barrier permeability.Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of Lipophilicity, fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group ar ...
levels have also been correlated with MS; lower levels of vitamin D correspond to an increased risk of MS, suggesting a reduced prevalence in the tropics - an area with more Vitamin D-rich sunlight - strengthening the impact of geographical location on MS development. MS mechanisms begin when peripheral autoreactive effector CD4+ T cells
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are consider ...
get activated and move into the CNS. Antigen-presenting cells
An antigen-presenting cell (APC) or accessory cell is a cell that displays antigen bound by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins on its surface; this process is known as antigen presentation. T cells may recognize these complexes usin ...
localize the reactivation of autoreactive effector CD4-T cells once they have entered the CNS, attracting more T cells and macrophages
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
to form the inflammatory lesion. In MS patients, macrophages and microglia assemble at locations where demyelination and neurodegeneration are actively occurring, and microglial activation is more apparent in the normal-appearing white matter of MS patients. Astrocytes
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" + , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of ...
generate neurotoxic chemicals like nitric oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its ...
and TNFα
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
, attract neurotoxic inflammatory monocytes to the CNS, and are responsible for astrogliosis, the scarring that prevents the spread of neuroinflammation and kills neurons inside the scarred area.
See also
*List of multiple sclerosis organizations
List of multiple sclerosis organizations in different countries around the world.
International
*Multiple Sclerosis International Federation
Australasia
Australia
* MS Research Australia
Europe United Kingdom
*Multiple Sclerosis So ...
* List of people with multiple sclerosis
References
External links
*Database for analysis and comparison of global data on the epidemiology of MS
{{Authority control Ailments of unknown cause Epstein–Barr virus–associated diseases Myelin disorders Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate (full)