Morphology (archaeology) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
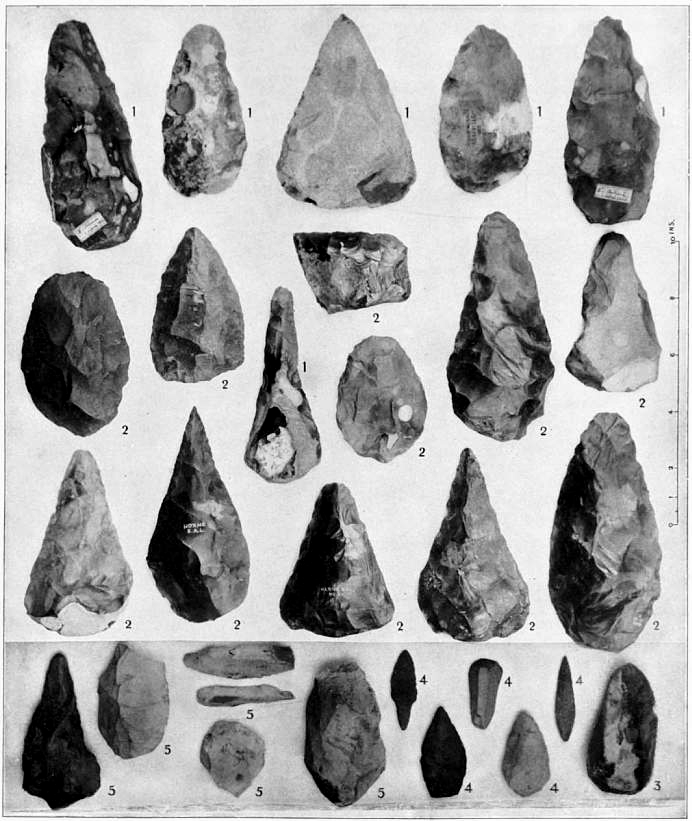 In
In
JSTOR
/ref>
 In
In archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landsc ...
, morphology is the study of the shape of artefacts and ecofacts
In archaeology, a biofact (more commonly known as an ecofact) is any organic material including flora or fauna material found at an archaeological site that has not been technologically altered by humans yet still has cultural relevance. Biofact ...
.
Morphology is a major consideration in grouping artefacts into period styles and, despite modern techniques like radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was de ...
, remains a crucial tool in the identification and dating not only of works of art but all classes of archaeological artefact
An artifact, or artefact (see American and British English spelling differences), is a general term for an item made or given shape by humans, such as a tool or a work of art, especially an object of archaeological interest. In archaeology, the ...
, including purely functional ones (ignoring the question of whether purely functional artefacts exist). The term morphology ("study of shapes", from the Greek) is more often used for this. Morphological analyses of many individual artefacts are used to construct typologies for different types of artefact, and by the technique of seriation a relative dating
Relative dating is the science of determining the relative order of past events (i.e., the age of an object in comparison to another), without necessarily determining their absolute age (i.e., estimated age). In geology, rock or superficial dep ...
based on shape and style for a site or group of sites is achieved where scientific absolute dating
Absolute dating is the process of determining an age on a specified chronology in archaeology and geology. Some scientists prefer the terms chronometric or calendar dating, as use of the word "absolute" implies an unwarranted certainty of accurac ...
techniques cannot be used, in particular where only stone, ceramic or metal artefacts or remains are available, which is often the case. That artefacts such as pottery very often survive only in fragments makes precise knowledge of morphology even more necessary, as it is often necessary to identify and date a piece of pottery from only a few sherd
In archaeology, a sherd, or more precisely, potsherd, is commonly a historic or prehistoric fragment of pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are ...
s.
In contrast to recent trends in academic art history, the succession of schools of archaeological theory in the last century, from culture-historical archaeology to processual archaeology and finally the rise of post-processual archaeology
Post-processual archaeology, which is sometimes alternately referred to as the interpretative archaeologies by its adherents, is a movement in archaeological theory that emphasizes the subjectivity of archaeological interpretations. Despite having ...
in recent decades has if anything increased the importance of the study of style in archaeology.Review by Mary Ann Levine of ''The Uses of Style in Archaeology'', edited by Margaret Conkey
Margaret W. Conkey (born 1943) is an American archaeologist and academic,Haviland, William; Walrath, Dana & Prins, Harald (2007) ''Evolution and Prehistory: The Human Challenge'', Wadsworth, , p. 210 who specializes in the Magdalenian period of the ...
and Christine Hastorf (see further reading), pp. 779-780, ''American Antiquity'', Vol. 58, No. 4 (Oct., 1993), Society for American ArchaeologyJSTOR
/ref>
References
{{reflist Archaeological theory Dating methodologies in archaeology Methods in archaeology Morphology