Mishkan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 According to the
According to the

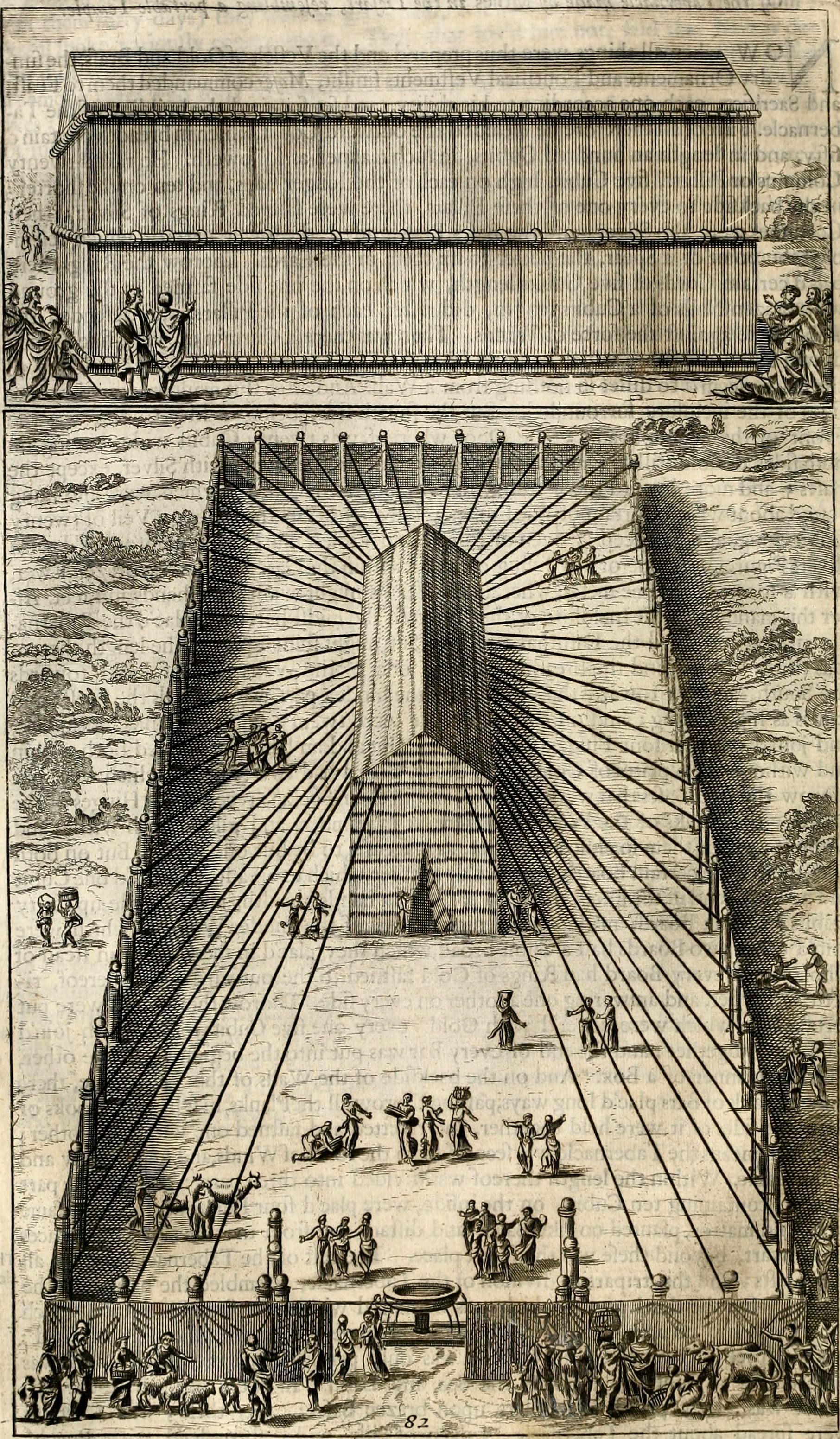
 The more detailed description of a tabernacle, located in Exodus chapters 25–27 and Exodus chapters 35–40, refers to an inner shrine (the most holy place) housing the ark and an outer chamber (holy place), with a six-branch seven-lamp menorah (lampstand), table for
The more detailed description of a tabernacle, located in Exodus chapters 25–27 and Exodus chapters 35–40, refers to an inner shrine (the most holy place) housing the ark and an outer chamber (holy place), with a six-branch seven-lamp menorah (lampstand), table for
Exodus 33:7-11
this tent was for communion with
Numbers 11:24-30
 In Exodus 31, the main builder and maker of the priestly vestments is specified as
In Exodus 31, the main builder and maker of the priestly vestments is specified as
 According to the
According to the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' Yahweh Yahweh *''Yahwe'', was the national god of ancient Israel and Judah. The origins of his worship reach at least to the early Iron Age, and likely to the Late Bronze Age if not somewhat earlier, and in the oldest biblical literature he po ...
(the God of Israel) used by the '' Yahweh Yahweh *''Yahwe'', was the national god of ancient Israel and Judah. The origins of his worship reach at least to the early Iron Age, and likely to the Late Bronze Age if not somewhat earlier, and in the oldest biblical literature he po ...
Israelites
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
from the Exodus
The Exodus (Hebrew: יציאת מצרים, ''Yeẓi’at Miẓrayim'': ) is the founding myth of the Israelites whose narrative is spread over four books of the Torah (or Pentateuch, corresponding to the first five books of the Bible), namely E ...
until the conquest of Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
. Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu ( Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pr ...
was instructed at Mount Sinai
Mount Sinai ( he , הר סיני ''Har Sinai''; Aramaic: ܛܘܪܐ ܕܣܝܢܝ ''Ṭūrāʾ Dsyny''), traditionally known as Jabal Musa ( ar, جَبَل مُوسَىٰ, translation: Mount Moses), is a mountain on the Sinai Peninsula of Egypt. It ...
to construct and transport the tabernacle with the Israelites on their journey through the wilderness and their subsequent conquest of the Promised Land
The Promised Land ( he, הארץ המובטחת, translit.: ''ha'aretz hamuvtakhat''; ar, أرض الميعاد, translit.: ''ard al-mi'ad; also known as "The Land of Milk and Honey"'') is the land which, according to the Tanakh (the Hebrew ...
. After 440 years, Solomon's Temple
Solomon's Temple, also known as the First Temple (, , ), was the Temple in Jerusalem between the 10th century BC and . According to the Hebrew Bible, it was commissioned by Solomon in the United Kingdom of Israel before being inherited by t ...
in Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
superseded it as the dwelling-place of God.
The main source describing the tabernacle is the biblical Book of Exodus
The Book of Exodus (from grc, Ἔξοδος, translit=Éxodos; he, שְׁמוֹת ''Šəmōṯ'', "Names") is the second book of the Bible. It narrates the story of the Exodus, in which the Israelites leave slavery in Biblical Egypt through ...
, specifically Exodus 25–31 and 35–40. Those passages describe an inner sanctuary, the Holy of Holies
The Holy of Holies (Hebrew: ''Qōḏeš haqQŏḏāšīm'' or ''Kodesh HaKodashim''; also הַדְּבִיר ''haDəḇīr'', 'the Sanctuary') is a term in the Hebrew Bible that refers to the inner sanctuary of the Tabernacle, where God's pres ...
, created by the veil suspended by four pillars. This sanctuary contained the Ark of the Covenant
The Ark of the Covenant,; Ge'ez: also known as the Ark of the Testimony or the Ark of God, is an alleged artifact believed to be the most sacred relic of the Israelites, which is described as a wooden chest, covered in pure gold, with an ...
, with its cherub
A cherub (; plural cherubim; he, כְּרוּב ''kərūḇ'', pl. ''kərūḇīm'', likely borrowed from a derived form of akk, 𒅗𒊏𒁍 ''karabu'' "to bless" such as ''karibu'', "one who blesses", a name for the lamassu) is one of the ...
im-covered mercy seat. An outer sanctuary (the "Holy Place") contained a gold lamp-stand or candlestick. On the north side stood a table, on which lay the showbread
Showbread ( he, לחם הפנים ''Leḥem haPānīm'', literally: "Bread of the Faces"), in the King James Version: shewbread, in a biblical or Jewish context, refers to the cakes or loaves of bread which were always present, on a specially-d ...
. On the south side was the Menorah, holding seven oil lamps to give light. On the west side, just before the veil, was the golden altar of incense
Altars ( he, מִזְבֵּחַ, ''mizbeaḥ'', "a place of slaughter or sacrifice") in the Hebrew Bible were typically made of earth () or unwrought stone (). Altars were generally erected in conspicuous places (; ; ; ; ). The first altar recorded ...
. It was constructed of 4 woven layers of curtains and 48 15-foot tall standing wood boards overlaid in gold and held in place by its bars and silver sockets and was richly furnished with valuable materials taken from Egypt at God's command.
This description is generally identified as part of the Priestly source
The Priestly source (or simply P) is perhaps the most widely recognized of the sources underlying the Torah. It is both stylistically and theologically distinct from other material in the Torah, and includes a set of claims that are contradicted b ...
("P"), written in the sixth or fifth century BCE. However, while the first Priestly source takes the form of instructions, the second is largely a repetition of the first in the past tense, i.e., it describes the execution of the instructions. Many scholars contend that it is of a far later date than the time of Moses, and that the description reflects the structure of Solomon's Temple, while some hold that the description derives from memories of a real pre-monarchic shrine, perhaps the sanctuary at Shiloh. Traditional scholars contend that it describes an actual tabernacle used in the time of Moses and thereafter. According to historical criticism
Historical criticism, also known as the historical-critical method or higher criticism, is a branch of criticism that investigates the origins of ancient texts in order to understand "the world behind the text". While often discussed in terms of ...
, an earlier, pre-exilic source, the Elohist
According to the documentary hypothesis, the Elohist (or simply E) is one of four source documents underlying the Torah,McDermott, John J., ''Reading the Pentateuch: A Historical Introduction'' (Pauline Press, 2002) p. 21. Via Books.google.com.au ...
("E"), describes the tabernacle as a simple tent-sanctuary.
Meaning
The English word ''tabernacle'' is derived from theLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
'' tabernāculum'' meaning "tent" or "hut", which in ancient Roman religion
Religion in ancient Rome consisted of varying imperial and provincial religious practices, which were followed both by the people of Rome as well as those who were brought under its rule.
The Romans thought of themselves as highly religious, ...
was a ritual structure. The Hebrew word ''mishkan'' implies "dwell", "rest", or "to live in". In Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, including the Septuagint
The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond t ...
, it is translated σκηνή ('' skēnē''), itself a Semitic loanword meaning "tent."
Description

Historical criticism
Historical criticism, also known as the historical-critical method or higher criticism, is a branch of criticism that investigates the origins of ancient texts in order to understand "the world behind the text". While often discussed in terms of ...
has identified two accounts of the tabernacle in Exodus, a briefer Elohist account and a longer Priestly one. Traditional scholars believe the briefer account describes a different structure, perhaps Moses' personal tent. The Hebrew nouns in the two accounts differ, one is most commonly translated as "tent of meeting," while the other is usually translated as "tabernacle."
Elohist account
refers to "the tabernacle of the congregation" (in some translations, such as theKing James Version
The King James Version (KJV), also the King James Bible (KJB) and the Authorized Version, is an English translation of the Christian Bible for the Church of England, which was commissioned in 1604 and published in 1611, by sponsorship of K ...
) or "the tent of meeting" (in most modern translations), which was set up outside of camp with the "cloudy pillar" visible at its door. The people directed their worship toward this center. Historical criticism attributes this description to the Elohist source (E), which is believed to have been written about 850 BCE or later.
Priestly account
 The more detailed description of a tabernacle, located in Exodus chapters 25–27 and Exodus chapters 35–40, refers to an inner shrine (the most holy place) housing the ark and an outer chamber (holy place), with a six-branch seven-lamp menorah (lampstand), table for
The more detailed description of a tabernacle, located in Exodus chapters 25–27 and Exodus chapters 35–40, refers to an inner shrine (the most holy place) housing the ark and an outer chamber (holy place), with a six-branch seven-lamp menorah (lampstand), table for showbread
Showbread ( he, לחם הפנים ''Leḥem haPānīm'', literally: "Bread of the Faces"), in the King James Version: shewbread, in a biblical or Jewish context, refers to the cakes or loaves of bread which were always present, on a specially-d ...
, and altar of incense
Altars ( he, מִזְבֵּחַ, ''mizbeaḥ'', "a place of slaughter or sacrifice") in the Hebrew Bible were typically made of earth () or unwrought stone (). Altars were generally erected in conspicuous places (; ; ; ; ). The first altar recorded ...
. An enclosure containing the sacrificial altar and bronze laver
The instructions given to Moses in the Book of Exodus included the creation of a bronze laver ( ''kîyōr nəḥōšeṯ''), to be sited outside the Tabernacle of Meeting, between the Tabernacle door and the Altar of Burnt Offering, for Aaron, ...
for the priests to wash surrounded these chambers. This description is identified by historical criticism as part of the Priestly source
The Priestly source (or simply P) is perhaps the most widely recognized of the sources underlying the Torah. It is both stylistically and theologically distinct from other material in the Torah, and includes a set of claims that are contradicted b ...
(P), written in the 6th or 5th century BCE.
Some scholars believe the description is of a far later date than Moses' time, and that it reflects the structure of the Temple of Solomon; others hold that the passage describes a real pre-monarchic shrine, perhaps the sanctuary at Shiloh, while traditional scholars contend that it describes an actual tabernacle used in the time of Moses and thereafter. This view is based on Exodus 36, 37, 38 and 39 that describe in full detail how the actual construction of the tabernacle took place during the time of Moses.
The detailed outlines for the tabernacle and its priests are enumerated in the Book of Exodus:
* : Materials needed: the Ark, the table for 12 showbread, the menorah.
* : The tabernacle, the bars, partitions.
* : The copper altar, the enclosure, oil.
* : Vestments for the priests, ''ephod
An ephod ( he, אֵפוֹד ''ʾēfōḏ''; or ) was a type of apron, which according to the Hebrew Bible, was worn by the Jewish high priest the kohen gadol, an artifact and an object to be revered in ancient Israelite culture, and was closel ...
'' garment, ring settings, the breastplate
A breastplate or chestplate is a device worn over the torso to protect it from injury, as an item of religious significance, or as an item of status. A breastplate is sometimes worn by mythological beings as a distinctive item of clothing. It is ...
, robe, head-plate, tunic, turban, sashes, pants.
* : Consecration of priests and altar.
* : Incense altar, washstand, anointing oil, incense.
Tent of the Presence
Some interpreters assert the Tent of the Presence was a special meeting place outside the camp, unlike the Tabernacle which was placed in the center of the camp. According tExodus 33:7-11
this tent was for communion with
Yahweh
Yahweh *''Yahwe'', was the national god of ancient Israel and Judah. The origins of his worship reach at least to the early Iron Age, and likely to the Late Bronze Age if not somewhat earlier, and in the oldest biblical literature he po ...
, to receive oracles and to understand the divine will. The
people's elders were the subject of a remarkable prophetic event at the site of this tent iNumbers 11:24-30
Builders
 In Exodus 31, the main builder and maker of the priestly vestments is specified as
In Exodus 31, the main builder and maker of the priestly vestments is specified as Bezalel
In Exodus 31:1-6 and chapters 36 to 39, Bezalel, Bezaleel, or Betzalel ( he, בְּצַלְאֵל, ''Bəṣalʼēl''), was the chief artisan of the Tabernacle and was in charge of building the Ark of the Covenant, assisted by Oholiab. The secti ...
, son of Uri son of Hur
Hur or HUR may refer to:
People
* Hur (Korean name), also spelled Heo
* Hur (Bible), a number of biblical figures
* Hur-ul-Nisa Begum, first of the fourteen children of Mumtaz Mahal
Places
* Hur, Iran (disambiguation), a number of places
* H ...
of the tribe of Judah
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tribe of Judah (, ''Shevet Yehudah'') was one of the twelve Tribes of Israel, named after Judah, the son of Jacob. Judah was the first tribe to take its place in the Land of Israel, occupying the southern ...
, who was assisted by Oholiab
In the Hebrew Bible, Oholiab ( ''ʾĀholīʾāḇ'', "father's tent"), son of Ahisamakh, of the tribe of Dan, worked under Bezalel as the deputy architect of the Tabernacle and the implements which it housed, including the Ark of the Covenant. He ...
and a number of skilled artisans.
Plan
During theExodus
Exodus or the Exodus may refer to:
Religion
* Book of Exodus, second book of the Hebrew Torah and the Christian Bible
* The Exodus, the biblical story of the migration of the ancient Israelites from Egypt into Canaan
Historical events
* E ...
, the wandering in the desert and the conquest of Canaan
The Book of Joshua ( he, סֵפֶר יְהוֹשֻׁעַ ', Tiberian: ''Sēp̄er Yŏhōšūaʿ'') is the sixth book in the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament, and is the first book of the Deuteronomistic history, the story of Israe ...
the Tabernacle was in part a portable tent, and in part a wooden enclosure draped with ten curtains, of indigo (''tekhelet
''Tekhelet'' ( he, תְּכֵלֶת ''təḵēleṯ''; alternate spellings include ''tekheleth'', ''t'chelet'', ''techelet'' and ''techeiles'') is a "blue-violet", "blue", or "turquoise" dye highly prized by ancient Mediterranean civilizations. I ...
'' תְּכֵלֶת), purple (''’argāmān'' אַרְגָּמָן), and scarlet (''šānî'' שָׁנִי) fabric. It had a rectangular, perimeter fence of fabric, poles and staked cords. This rectangle was always erected when the Israelite tribes would camp, oriented to the east as the east side had no frames. In the center of this enclosure was a rectangular sanctuary draped with goat-hair curtains, with the roof coverings made from rams' skins.
Holy of Holies
Beyond this curtain was the cube-shaped inner room, the ''Qṓḏeš HaQŏḏāšîm'' (Holy of Holies
The Holy of Holies (Hebrew: ''Qōḏeš haqQŏḏāšīm'' or ''Kodesh HaKodashim''; also הַדְּבִיר ''haDəḇīr'', 'the Sanctuary') is a term in the Hebrew Bible that refers to the inner sanctuary of the Tabernacle, where God's pres ...
). This area housed the Ark of the Covenant
The Ark of the Covenant,; Ge'ez: also known as the Ark of the Testimony or the Ark of God, is an alleged artifact believed to be the most sacred relic of the Israelites, which is described as a wooden chest, covered in pure gold, with an ...
, inside which were the two stone tablets brought down from Mount Sinai by Moses on which were written the Ten Commandments
The Ten Commandments (Biblical Hebrew עשרת הדברים \ עֲשֶׂרֶת הַדְּבָרִים, ''aséret ha-dvarím'', lit. The Decalogue, The Ten Words, cf. Mishnaic Hebrew עשרת הדיברות \ עֲשֶׂרֶת הַדִּבְ ...
, a golden urn holding the '' manna'', and Aaron
According to Abrahamic religions, Aaron ''′aharon'', ar, هارون, Hārūn, Greek (Septuagint): Ἀαρών; often called Aaron the priest ()., group="note" ( or ; ''’Ahărōn'') was a prophet, a high priest, and the elder brother of ...
's rod which had budded and borne ripe almonds. (, , ; )
Tachash
''Tachash'' is referred to fifteen times in theHebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' Leviticus 10:8-15
* Individuals with the
Leviticus 17
There is a strict set of rules to be followed for transporting the tabernacle laid out in the
Leviticus 6:8–30
*
Leviticus 7
* Ceremony of Ordination
Leviticus 8
* Octave of Ordination
*
Leviticus 16
*
Numbers 5:11-29
* Dedication of
Numbers 6:1-21
* Preparation of the ashes of a red heifer for the
Numbers 19
An Israelite healed of ''
 During the conquest of
During the conquest of
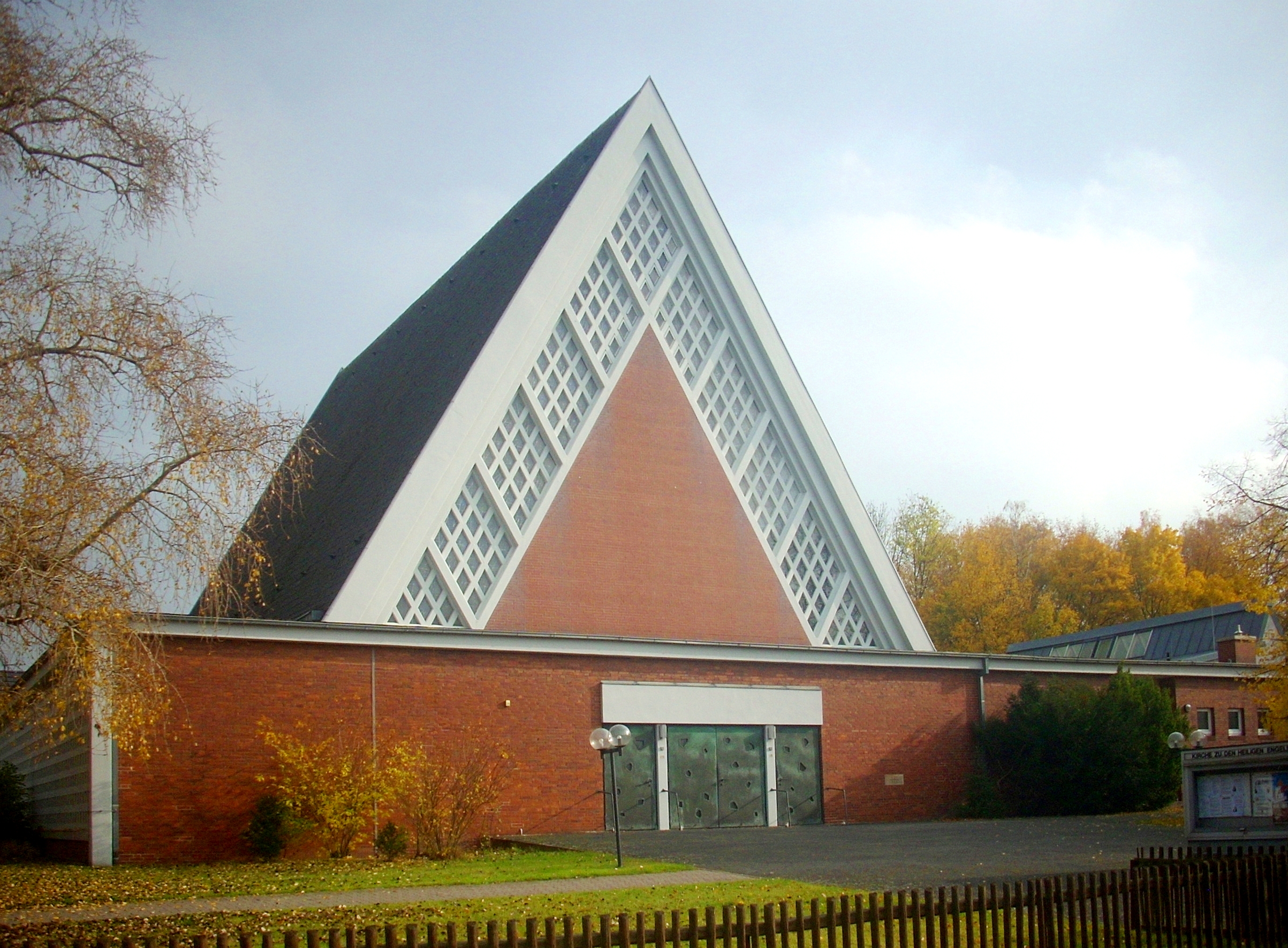 Some Christian churches are built like a tent, to symbolize the tent of God with men, including St. Matthew Cathedral, São Mateus, Brazil, Zu den heiligen Engeln (To the Holy Angels),
Some Christian churches are built like a tent, to symbolize the tent of God with men, including St. Matthew Cathedral, São Mateus, Brazil, Zu den heiligen Engeln (To the Holy Angels),
 A ''Mashkhanna'' (hebrew cognate );Secunda, Shai, and Steven Fine. Brill, 2012.p345 ''Beth Manda''; ''Beit Manda''; ''Mandi'' ('house of knowledge'), is a cultic hut and place of worship for followers of
A ''Mashkhanna'' (hebrew cognate );Secunda, Shai, and Steven Fine. Brill, 2012.p345 ''Beth Manda''; ''Beit Manda''; ''Mandi'' ('house of knowledge'), is a cultic hut and place of worship for followers of
Precise reconstruction of the Tabernacle
Full color, 3d, printable model of the tabernacle
A study of the Tabernacle
The offerings of the Tabernacle
Jewish Encyclopedia article
Textual descriptions of the Tabernacle and all internal components.
{{Ark of the Covenant Book of Exodus
'' Leviticus 10:8-15
* Individuals with the
Tzaraat
''Tzaraath'' (Hebrew צָרַעַת ''ṣāraʿaṯ''), variously transcribed into English and frequently mistranslated as leprosy, describes various ritually unclean disfigurative conditions of the skin, hair of the beard and head, clothing mad ...
skin affliction were not permitted entry to the tabernacle.
* Sacrifice only at the tabernacleLeviticus 17
There is a strict set of rules to be followed for transporting the tabernacle laid out in the
Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' meal offering A meal offering, grain offering, or gift offering ( hbo, מנחה}, ), is a type of Biblical sacrifice, specifically a sacrifice that did not include sacrificial animals. In older English it is sometimes called an oblation, from Latin. The Hebr ...
'' meal offering A meal offering, grain offering, or gift offering ( hbo, מנחה}, ), is a type of Biblical sacrifice, specifically a sacrifice that did not include sacrificial animals. In older English it is sometimes called an oblation, from Latin. The Hebr ...
Leviticus 6:8–30
*
Guilt offering A guilt offering ( he, אשם, ’āšām, translation=guilt, trespass; plural ), also referred to as a trespass offering (KJV, 1611), was a type of Biblical sacrifice, specifically a sacrifice made as a compensation payment for unintentional and ...
s and peace offering
The peace offering ( he, זֶבַח שְׁלָמִים, zevah shelamim) was one of the sacrifices and offerings in the Hebrew Bible (Leviticus 3; 7.11–34). The term "peace offering" is generally constructed from "slaughter offering" and the p ...
sLeviticus 7
* Ceremony of Ordination
Leviticus 8
* Octave of Ordination
*
Yom Kippur
Yom Kippur (; he, יוֹם כִּפּוּר, , , ) is the holiest day in Judaism and Samaritanism. It occurs annually on the 10th of Tishrei, the first month of the Hebrew calendar. Primarily centered on atonement and repentance, the day' ...
Leviticus 16
*
Ordeal of the bitter water
The ordeal of the bitter water was a trial by ordeal administered to the wife whose husband suspected her of adultery but who had no witnesses to make a formal case. The ordeal is expanded in the Talmud, in the seventh tractate of ''Nashim''.
Ac ...
for suspected adulteressesNumbers 5:11-29
* Dedication of
Nazirite
In the Hebrew Bible, a nazirite or a nazarite ( he, נָזִיר ''Nāzīr'') is one who voluntarily took a vow which is described in . "Nazarite" comes from the Hebrew word ''nazir'' meaning "consecrated" or "separated". Those who put themselves ...
sNumbers 6:1-21
* Preparation of the ashes of a red heifer for the
water of purification
The water of lustration or water of purification was the water created with the ashes of the red heifer, according to the instructions given by God to Moses and Aaron in the Book of Numbers.
Biblical references
The Hebrew Bible taught that any Is ...
Numbers 19
An Israelite healed of ''
tzaraath
''Tzaraath'' (Hebrew צָרַעַת ''ṣāraʿaṯ''), variously transcribed into English and frequently mistranslated as leprosy, describes various ritually unclean disfigurative conditions of the skin, hair of the beard and head, clothing mad ...
'' would be presented by the priest who had confirmed his healing "at the door of the tabernacle of meeting", and a woman healed of prolonged menstruation
Menstruation (also known as a period, among other colloquial terms) is the regular discharge of blood and mucosal tissue from the inner lining of the uterus through the vagina. The menstrual cycle is characterized by the rise and fall of ...
would present her offering (two turtledoves or two young pigeons) to the priest "at the door of the tabernacle of meeting".
It was at the door of the tabernacle that the community wept in sorrow when all the chiefs of the people were impaled and the men who had joined in worship to the Baal of Peor were killed on God's orders.
Subsequent history
Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
, the main Israelite camp was at Gilgal
Gilgal ( he, גִּלְגָּל ''Gilgāl''), also known as Galgala or Galgalatokai of the 12 Stones ( grc-gre, Γαλαγα or , ''Dōdekalithōn''), is the name of one or more places in the Hebrew Bible. Gilgal is mentioned 39 times, in particula ...
(; ) and the tabernacle was probably erected within the camp: "…and returned into the camp" (''see'' "…they shall camp facing the tent of meeting on every side").
After the conquest and division of the land among the tribes, the tabernacle was moved to Shiloh in Ephraimite territory (Joshua's tribe) to avoid disputes among the other tribes (; ; ; ). It remained there during the 300-year period of the biblical judges
The biblical judges ''šōp̄êṭ''/''shofet'', pl. ''šōp̄əṭîm''/''shoftim'') are described in the Hebrew Bible, and mostly in the Book of Judges, as people who served roles as military leaders in times of crisis, in the period before an ...
(the rules of the individual judges total about 350 years but most ruled regionally and some terms overlapped). According to , the Ark, and thus possibly the tabernacle, was at Bethel
Bethel ( he, בֵּית אֵל, translit=Bēṯ 'Ēl, "House of El" or "House of God",Bleeker and Widegren, 1988, p. 257. also transliterated ''Beth El'', ''Beth-El'', ''Beit El''; el, Βαιθήλ; la, Bethel) was an ancient Israelite sanc ...
while Phinehas, grandson of Aaron, was still alive.
The subsequent history of the structure is separate from that of the Ark of the Covenant. After the Ark was captured by the Philistines
The Philistines ( he, פְּלִשְׁתִּים, Pəlīštīm; Koine Greek ( LXX): Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''Phulistieím'') were an ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan from the 12th century BC until 604 BC, whe ...
, King Saul
Saul (; he, , ; , ; ) was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the first monarch of the United Kingdom of Israel. His reign, traditionally placed in the late 11th century BCE, supposedly marked the transition of Israel and Judah from a scattered tri ...
moved the tabernacle to Nob, near his home town of Gibeah
Gibeah (; he, גִּבְעָה ''Gīḇəʿā''; he, גִּבְעַת, link=no ''Gīḇəʿaṯ'') is the name of three places mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, in the tribes of Benjamin, Judah, and Ephraim respectively.
Gibeah of Benjamin is th ...
, but after he massacred the priests there (), it was moved to Gibeon, a Yahwist
The Jahwist, or Yahwist, often abbreviated J, is one of the most widely recognized sources of the Pentateuch (Torah), together with the Deuteronomist, the Priestly source and the Elohist. The existence of the Jahwist is somewhat controversial, ...
hill-shrine (; ; , 13). Just prior to David's moving the ark to Jerusalem, the ark was located in Kiriath-Jearim ().
The Ark was eventually brought to Jerusalem, where it was placed "inside the tent David had pitched for it" (; ), not in the tabernacle, which remained at Gibeon. The altar of the tabernacle at Gibeon was used for sacrificial worship (; ; ), until Solomon finally brought the structure and its furnishings to Jerusalem to furnish and dedicate the Temple. ()
There is no mention of the tabernacle in the Tanakh after the destruction of Jerusalem and the Temple by the Babylonians in c. 587 BCE.
Relationship to the golden calf
Some rabbis have commented on the proximity of the narrative of the tabernacle with that of the episode known as the sin of thegolden calf
According to the Bible, the golden calf (עֵגֶל הַזָּהָב '' ‘ēgel hazzāhāv'') was an idol (a cult image) made by the Israelites when Moses went up to Mount Sinai. In Hebrew, the incident is known as ''ḥēṭə’ hā‘ēgel'' ...
recounted in . Maimonides
Musa ibn Maimon (1138–1204), commonly known as Maimonides (); la, Moses Maimonides and also referred to by the acronym Rambam ( he, רמב״ם), was a Sephardic Jewish philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Torah ...
asserts that the tabernacle and its accoutrements, such as the golden Ark of the Covenant and the golden Menorah were meant as "alternates" to the human weakness and needs for physical idols as seen in the golden calf episode. Other scholars, such as Nachmanides
Moses ben Nachman ( he, מֹשֶׁה בֶּן־נָחְמָן ''Mōše ben-Nāḥmān'', "Moses son of Nachman"; 1194–1270), commonly known as Nachmanides (; el, Ναχμανίδης ''Nakhmanídēs''), and also referred to by the acronym Ra ...
disagree and maintain that the tabernacle's meaning is not tied in with the golden calf, but instead symbolizes higher mystical lessons that symbolize God's constant closeness to the Children of Israel.
Blueprint for synagogues
Synagogue
A synagogue, ', 'house of assembly', or ', "house of prayer"; Yiddish: ''shul'', Ladino: or ' (from synagogue); or ', "community". sometimes referred to as shul, and interchangeably used with the word temple, is a Jewish house of wor ...
construction over the last two thousand years has followed the outlines of the original tabernacle. Every synagogue has at its front an ark, ''aron kodesh'', containing the Torah
The Torah (; hbo, ''Tōrā'', "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. In that sense, Torah means the ...
scrolls, comparable to the Ark of the Covenant which contained the tablets with Ten Commandments. This is the holiest spot in a synagogue, equivalent to the Holy of Holies.
There is also usually a constantly lighted lamp, ''Ner tamid
Malta - Mosta - Rotunda in 57 ies.
A sanctuary lamp, chancel lamp, altar lamp, everlasting light, or eternal flame is a light that shines before the altar of sanctuaries in many Jewish and Christian places of worship. Prescribed in Exodus 27:20- ...
'', or a candelabrum, lighted during services, near a spot similar to the position of the original Menorah. At the center of the synagogue is a large elevated area, known as the ''bimah'', where the Torah is read. This is equivalent to the tabernacle's altars upon which incense and animal sacrifices were offered. On the main holidays the priests
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particu ...
gather at the front of the synagogue to bless the congregation as did their priestly ancestors in the tabernacle from Aaron onwards ().
Inspiration for churches
 Some Christian churches are built like a tent, to symbolize the tent of God with men, including St. Matthew Cathedral, São Mateus, Brazil, Zu den heiligen Engeln (To the Holy Angels),
Some Christian churches are built like a tent, to symbolize the tent of God with men, including St. Matthew Cathedral, São Mateus, Brazil, Zu den heiligen Engeln (To the Holy Angels), Hanover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany ...
, Germany and the Cardboard Cathedral
The Cardboard Cathedral, formally called the Transitional Cathedral, in Christchurch, New Zealand, is the transitional pro-cathedral of the Anglican Diocese of Christchurch, replacing ChristChurch Cathedral, which was significantly damaged in t ...
, Christchurch, New Zealand.
New Testament references
The tabernacle is mentioned several times in theEpistle to the Hebrews
The Epistle to the Hebrews ( grc, Πρὸς Ἑβραίους, Pros Hebraious, to the Hebrews) is one of the books of the New Testament.
The text does not mention the name of its author, but was traditionally attributed to Paul the Apostle. Most ...
in the New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chris ...
. For example, according to and Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
serves as the true climactic high priest
The term "high priest" usually refers either to an individual who holds the office of ruler-priest, or to one who is the head of a religious caste.
Ancient Egypt
In ancient Egypt, a high priest was the chief priest of any of the many gods rev ...
in heaven
Heaven or the heavens, is a common religious cosmological or transcendent supernatural place where beings such as deities, angels, souls, saints, or venerated ancestors are said to originate, be enthroned, or reside. According to the belie ...
, the true tabernacle, to which its counterpart on earth was a symbol and foreshadow of what was to come ().
Mandaeism
 A ''Mashkhanna'' (hebrew cognate );Secunda, Shai, and Steven Fine. Brill, 2012.p345 ''Beth Manda''; ''Beit Manda''; ''Mandi'' ('house of knowledge'), is a cultic hut and place of worship for followers of
A ''Mashkhanna'' (hebrew cognate );Secunda, Shai, and Steven Fine. Brill, 2012.p345 ''Beth Manda''; ''Beit Manda''; ''Mandi'' ('house of knowledge'), is a cultic hut and place of worship for followers of Mandaeism
Mandaeism (Classical Mandaic: ࡌࡀࡍࡃࡀࡉࡉࡀ ; Arabic: المندائيّة ), sometimes also known as Nasoraeanism or Sabianism, is a Gnostic, monotheistic and ethnic religion. Its adherents, the Mandaeans, revere Adam, Abe ...
. A ''Mashkhanna'' must be built beside a river in order to perform maṣbuta (baptism
Baptism (from grc-x-koine, βάπτισμα, váptisma) is a form of ritual purification—a characteristic of many religions throughout time and geography. In Christianity, it is a Christian sacrament of initiation and adoption, almost ...
) and other ceremonies because ''Living Water'' is an essential element in the Mandaean
Mandaeans ( ar, المندائيون ), also known as Mandaean Sabians ( ) or simply as Sabians ( ), are an ethnoreligious group who are followers of Mandaeism. They believe that John the Baptist was the final and most important prophet. ...
faith.
See also
*Church tabernacle
A tabernacle or sacrament house is a fixed, locked box in which the Eucharist in the Catholic Church, Eucharist (consecrated communion hosts) is stored as part of the "reserved sacrament" rite (Christianity), rite. A container for the same pur ...
* Priestly covenant
* Replicas of the Jewish Temple
Replicas of the Jewish Temple are scale models or authentic buildings that attempt to replicate the Temple of Solomon, Second Temple and Herod's Temple in Jerusalem.
Scale models
In the seventeenth century, Rabbi Jacob Judah Leon of Amsterdam ...
* Tabernacle (LDS Church)
In the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, a tabernacle is a multipurpose religious building, used for church services and conferences, and as community centers. Tabernacles were typically built as endeavors of multiple congregations (t ...
* Tabernacle (Methodist)
In Methodism (inclusive of the holiness movement), a tabernacle is the center of a camp meeting, where revival services occur. Tabernacles may be constructed in a cruciform-shaped fashion and are most often made of wood. Like the interior of m ...
References
External links
Precise reconstruction of the Tabernacle
Full color, 3d, printable model of the tabernacle
A study of the Tabernacle
The offerings of the Tabernacle
Jewish Encyclopedia article
Textual descriptions of the Tabernacle and all internal components.
{{Ark of the Covenant Book of Exodus