Medieval Bulgarian army on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The medieval Bulgarian army was the primary military body of the
КЪМ ВЪПРОСА ЗА БЪЛГАРСКАТА ВОЕННА МОЩ ПРЕЗ ПОСЛЕДНАТА ЧЕТВЪРТ НА X И НАЧАЛОТО НА XI ВЕК. ЗАЩО БЪЛГАРИЯ ЗАГУБИ ДВУБОЯ С ВИЗАНТИЯ?
' During the end of the 9th and the beginning of the 10th centuries, Emperor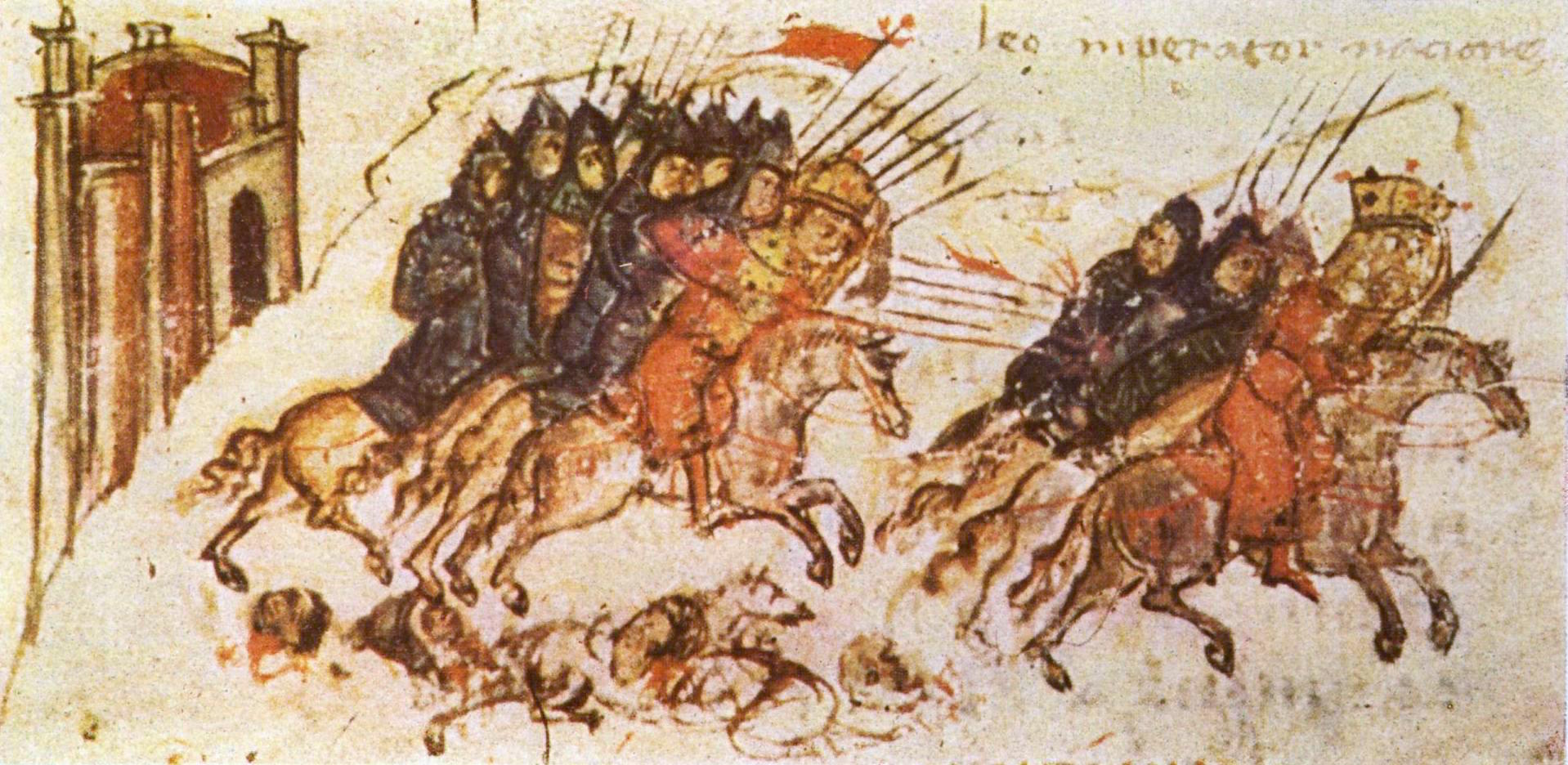
 Traditionally, the army's commander-in-chief was the ruler. The second in the chain of command was the '' kavkhan'' who led the army during the Emperor's absence. The third most important title in the hierarchy was the ''
Traditionally, the army's commander-in-chief was the ruler. The second in the chain of command was the '' kavkhan'' who led the army during the Emperor's absence. The third most important title in the hierarchy was the ''
 However, a major defeat at the
However, a major defeat at the
 In 1185 the
In 1185 the
 Initially, the Ottoman invasion was not considered as a significant threat by both Bulgarians and Byzantines. For only one decade between 1354 and 1364 the Ottomans conquered virtually the whole of
Initially, the Ottoman invasion was not considered as a significant threat by both Bulgarians and Byzantines. For only one decade between 1354 and 1364 the Ottomans conquered virtually the whole of
 The Bulgarian army employed various military
The Bulgarian army employed various military
 The early Bulgarian army was not supplied with strong siege equipment . The Bulgarians used siege machines on a large scale for the first time during the reign of Khan Krum (803–814), when they employed
The early Bulgarian army was not supplied with strong siege equipment . The Bulgarians used siege machines on a large scale for the first time during the reign of Khan Krum (803–814), when they employed







Bulgaria
retrieved on 16 September 2009 *
{{Bulgarian Empire
First
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and reco ...
and the Second Bulgarian Empires, and some Puppet state
A puppet state, puppet régime, puppet government or dummy government, is a state that is ''de jure'' independent but ''de facto'' completely dependent upon an outside power and subject to its orders.Compare: Puppet states have nominal sovere ...
s of the former, like the Despotate of Dobruja
The Despotate of Dobruja or Principality of Karvuna ( bg, Добруджанско деспотство or ; ro, Despotatul Dobrogei or ) was a 14th-century quasi-independent polity in the region of modern Dobruja, that split off from the Secon ...
. During the first decades after the foundation of the country, the army consisted of a Bulgar cavalry and a Slavic infantry. The core of the Bulgarian army was the heavy cavalry
Heavy cavalry was a class of cavalry intended to deliver a battlefield charge and also to act as a tactical reserve; they are also often termed ''shock cavalry''. Although their equipment differed greatly depending on the region and histori ...
, which consisted of ca. 12,000 heavily armed riders. At its height in the 9th and 10th centuries, it was one of the most formidable military forces in Europe and was feared by its enemies. There are several documented cases of Byzantine commanders abandoning an invasion because of a reluctance to confront the Bulgarian army on its home territory.
The army was intrinsically linked to the very existence of the Bulgarian state. Its success under Tsar Simeon I the Great marked the creation of a wide-ranging empire, and its defeat in a prolonged war of attrition in the early 11th century meant the end of Bulgarian independence. When the Bulgarian state was reestablished in 1185, a series of capable emperors achieved a remarkable string of victories over the Byzantines and the Western Crusaders, but as the state and its army fragmented in the 13th and 14th centuries, it proved unable to halt the Ottoman advance, which resulted in the conquest of all of Bulgaria by 1396/1422. It would not be until 1878, with the Liberation of Bulgaria
The Liberation of Bulgaria is the historical process as a result of the Bulgarian Revival. In Bulgarian historiography, the liberation of Bulgaria refers to those events of the Tenth Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878) that led to the re-establishmen ...
, that a Bulgarian military would be restored.
History
7th–8th century
The earlyBulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as nomad ...
were a warlike people and war was part of their everyday life, with every adult Bulgar obliged to fight. The early Bulgars were exclusively horsemen: in their culture, the horse was considered a sacred animal and received special care.
The supreme commander was the khan
Khan may refer to:
*Khan (inn), from Persian, a caravanserai or resting-place for a travelling caravan
*Khan (surname), including a list of people with the name
*Khan (title), a royal title for a ruler in Mongol and Turkic languages and used by ...
, who mustered the army with the help of the aristocracy. The military ranks from lowest to highest were ''bagain'', ''bagatur'', ''boil'', ''tarkhan''. The permanent army consisted of the khan's guard of select warriors, while the campaign army consisted practically of the entire nation, assembled by clans. In the field, the army was divided into right and left wings.
The Bulgars were well versed in the use of stratagems. They often held a strong cavalry unit in reserve, which would attack the enemy at an opportune moment. They also sometimes concentrated their free horses behind their battle formation to avoid surprise attacks from the rear. They used ambushes and feigned retreats, during which they rode with their backs to the horse, firing clouds of arrows on the enemy. If the enemy pursued disorganized, they would turn back and fiercely attack them. According to contemporary historians, the Bulgars "could see in the dark like bats"Cited in Халенбаков, О. ''Детска енциклопедия България: Държавата – 681 г.'', с. 13 and often fought at night.
The Bulgarian army was well armed according to the Avar model: the soldiers had a sabre
A sabre ( French: �sabʁ or saber in American English) is a type of backsword with a curved blade associated with the light cavalry of the early modern and Napoleonic periods. Originally associated with Central European cavalry such as the ...
or a sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed tip ...
, a long spear
A spear is a pole weapon consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fastene ...
and a bow with an arrow-quiver on the back. On the saddle they hung a round shield, a mace and a lasso
A lasso ( or ), also called lariat, riata, or reata (all from Castilian, la reata 're-tied rope'), is a loop of rope designed as a restraint to be thrown around a target and tightened when pulled. It is a well-known tool of the Spanish an ...
, which the Bulgarians called ''arkani''. On their decorated belts the soldiers carried the most necessary objects such as flints and steel, a knife, a cup and a needle case. The heavy cavalry was supplied with metal armour and helmets. The horses were also armoured. Armour was of two types — chain-mail and plate armour. The commanders had belts with golden or silver buckles which corresponded to their rank and title.
The army had iron discipline, with the officers vigorously checking if everything was ready before a battle. For a horse that was undernourished or not properly taken care of, the punishment was death. The soldiers were under threat of a death penalty when having a loose bow-string or an unmaintained sword; or even if riding a war horse in peacetime.
The infantry of the newly formed state was composed mainly of Slavs, who were generally lightly armed soldiers, although their chieftains usually had small cavalry retinues. The Slavic footmen were equipped with swords, spears, bows and wooden or leather shields. However, they were less disciplined and less effective than the Bulgar cavalry.
In 680, the Byzantines under Constantine IV
Constantine IV ( la, Constantinus; grc-gre, Κωνσταντῖνος, Kōnstantînos; 650–685), called the Younger ( la, iunior; grc-gre, ὁ νέος, ho néos) and sometimes incorrectly the Bearded ( la, Pogonatus; grc-gre, Πωγων ...
were crushed in the battle of Ongal
The Battle of Ongal took place in the summer of 680 in the Ongal area, an unspecified location in and around the Danube delta near the Peuce Island, present-day Tulcea County, Romania. It was fought between the Bulgars, who had recently invaded ...
and were forced to conclude a humiliating peace treaty by which they ''de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legally ...
'' acknowledged the formation of a Bulgarian state on their former territory. In 718, a Bulgarian intervention was crucial in the repulsion of the Second Arab Siege of Constantinople
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds each ...
. According to contemporaries, the Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, No ...
feared the Bulgarian army and built trenches to protect themselves from a cavalry charge. In the decisive battle in the summer that year the Bulgarians slaughtered between 20,000 and 32,000 Arabs. Apart from engaging in battle to the south, the Bulgarians had to fight the Avars to the north-west and the Khazars
The Khazars ; he, כּוּזָרִים, Kūzārīm; la, Gazari, or ; zh, 突厥曷薩 ; 突厥可薩 ''Tūjué Kěsà'', () were a semi-nomadic Turkic people that in the late 6th-century CE established a major commercial empire coverin ...
to the north-east. After bloody fights between the Dnester and the Dneper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and ...
rivers, the Khazar threat was eliminated but the founder of the Bulgarian state Khan Asparukh
Asparuh (also ''Ispor''; bg, Аспарух, Asparuh or (rarely) bg, Исперих, Isperih) was а ruler of Bulgars in the second half of the 7th century and is credited with the establishment of the First Bulgarian Empire in 681.
Early life
...
perished in one of the battles in 700.
Krum's dynasty
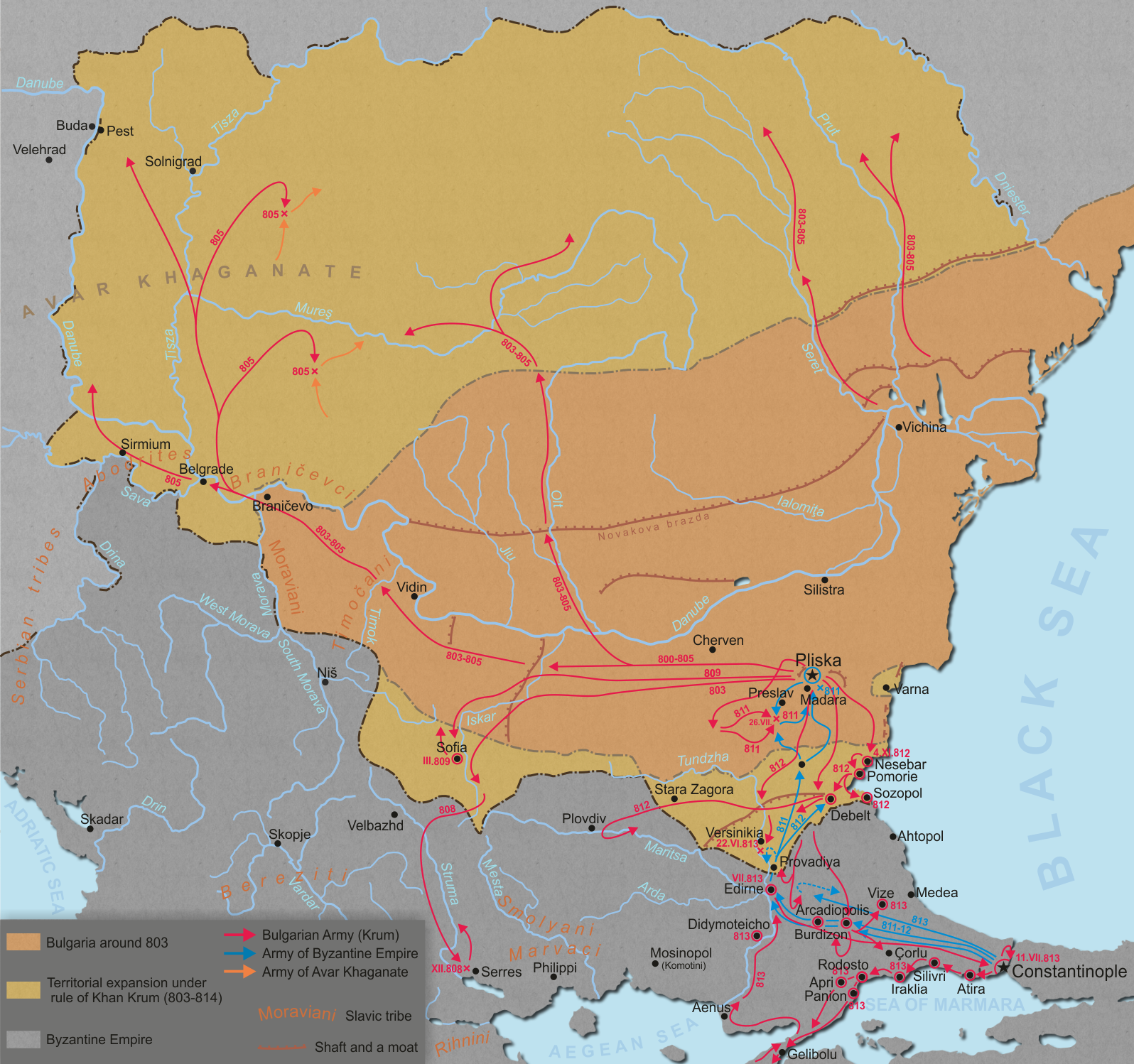
On the turn of the 9th century, the Bulgarian Empire was on the rise. Following the victory over the Byzantines at Marcelae in 792, the country overcame a 50-year crisis and entered the new century stronger and consolidated. During the first years of his reign, KhanKrum
Krum ( bg, Крум, el, Κροῦμος/Kroumos), often referred to as Krum the Fearsome ( bg, Крум Страшни) was the Khan of Bulgaria from sometime between 796 and 803 until his death in 814. During his reign the Bulgarian territo ...
destroyed the Avar Khaganate and doubled Bulgaria's territory, taking over the fertile Pannonian Plain
The Pannonian Basin, or Carpathian Basin, is a large basin situated in south-east Central Europe. The geomorphological term Pannonian Plain is more widely used for roughly the same region though with a somewhat different sense, with only th ...
and the salt and gold mines of Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
. Krum achieved major victories over the Byzantine Empire, annihilating the Byzantine armies in the battle of Pliska
The Battle of Pliska or Battle of Vărbitsa Pass was a series of battles between troops, gathered from all parts of the Byzantine Empire, led by the Emperor Nicephorus I, and the First Bulgarian Empire, governed by Khan Krum. The Byzantines plu ...
(811) and at Versinikia
The Battle of Versinikia ( bg, Битката при Версиникия; el, Μάχη της Βερσινικίας) was fought in 813 between the Byzantine Empire and the Bulgarian Empire, near the city of Adrianople (Edirne).
While the Bul ...
(813), while capturing the important city of Sofia in 809.
The Byzantine historian Pseudo-Simeon stated that Krum sent a 30,000 strong cavalry, "the whole armoured with iron", which devastated Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to th ...
. According to inscriptions found in the region of Pliska
Pliska ( , cu, Пльсковъ, translit=Plĭskovŭ) was the first capital of the First Bulgarian Empire during the Middle Ages and is now a small town in Shumen Province, on the Ludogorie plateau of the Danubian Plain, 20 km northeast of ...
, Preslav
The modern Veliki Preslav or Great Preslav ( bg, Велики Преслав, ), former Preslav ( bg, link=no, Преслав; until 1993), is a city and the seat of government of the Veliki Preslav Municipality (Great Preslav Municipality, new B ...
, Madara and Shabla in north-eastern Bulgaria, armaments for 1,713 heavy riders were available. Assuming that the surviving inscriptions are around 1/10 of the total number, that makes 17,130 men only in the so-called "inner region" of Bulgaria. After comparison with the data of Pseudo-Simeon, it can be assumed that the heavy cavalry component of the Bulgarian army numbered between 17–20,000 and 30,000 men, depending on the level of mobilization
Mobilization is the act of assembling and readying military troops and supplies for war. The word ''mobilization'' was first used in a military context in the 1850s to describe the preparation of the Prussian Army. Mobilization theories and t ...
.Иванов, И. КЪМ ВЪПРОСА ЗА БЪЛГАРСКАТА ВОЕННА МОЩ ПРЕЗ ПОСЛЕДНАТА ЧЕТВЪРТ НА X И НАЧАЛОТО НА XI ВЕК. ЗАЩО БЪЛГАРИЯ ЗАГУБИ ДВУБОЯ С ВИЗАНТИЯ?
' During the end of the 9th and the beginning of the 10th centuries, Emperor
Simeon the Great
Tsar Simeon (also Symeon) I the Great ( cu, цѣсар҄ь Сѷмеѡ́нъ А҃ Вели́къ, cěsarĭ Sỳmeonŭ prĭvŭ Velikŭ bg, цар Симеон I Велики, Simeon I Veliki el, Συμεών Αʹ ὁ Μέγας, Sumeṓn prôto ...
was able to lead in battle more than 60,000 soldiers.

 Traditionally, the army's commander-in-chief was the ruler. The second in the chain of command was the '' kavkhan'' who led the army during the Emperor's absence. The third most important title in the hierarchy was the ''
Traditionally, the army's commander-in-chief was the ruler. The second in the chain of command was the '' kavkhan'' who led the army during the Emperor's absence. The third most important title in the hierarchy was the ''ichirgu-boil The Ichirgu- boila or Chargobilya ( el, ητζιργου βοιλα; Old Bulgarian: , bg, Ичиргу боила) was a high-ranking official in the First Bulgarian Empire. He was the commander of the garrison of the capital and was the third most ...
'' who commanded the garrison of the capital. In the field, the army was divided into three parts: center, right flank and left flank. The center was commanded by the ruler, the left flank by the ''kavkhan'' and the right flank by the ''ichirgu-boil''. Other higher military ranks included the ''tarkhan
Tarkhan ( otk, 𐱃𐰺𐰴𐰣, Tarqan, mn, or ; fa, ترخان; ; ar , طرخان; alternative spellings ''Tarkan'', ''Tarkhaan'', ''Tarqan'', ''Tarchan'', ''Turxan'', ''Tarcan'', ''Turgan, Tárkány, Tarján'') is an ancient Central Asia ...
'' which was equal to the Byzantine ''strategos
''Strategos'', plural ''strategoi'', Latinized ''strategus'', ( el, στρατηγός, pl. στρατηγοί; Doric Greek: στραταγός, ''stratagos''; meaning "army leader") is used in Greek to mean military general. In the Hellenisti ...
'' according to Steven Runciman
Sir James Cochran Stevenson Runciman ( – ), known as Steven Runciman, was an English historian best known for his three-volume ''A History of the Crusades'' (1951–54).
He was a strong admirer of the Byzantine Empire. His history's negative ...
, and the higher officers were called ''bagain''. All higher military ranks were part of the Bulgarian nobility called bolyar
A boyar or bolyar was a member of the highest rank of the feudal nobility in many Eastern European states, including Kievan Rus', Bulgaria, Russia, Wallachia and Moldavia, and later Romania, Lithuania and among Baltic Germans. Boyars were se ...
s or boils.
Decline under Peter I
During the long years of warfare underTsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East Slavs, East and South Slavs, South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''Caesar (title), caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" i ...
Simeon I the Great (893–927), the country was exhausted. The constant wars were unpopular enough so that 20,000 people sought refuge in Byzantium because of Simeon's "warlike rush and relentless intentions". His successor Peter I Peter I may refer to:
Religious hierarchs
* Saint Peter (c. 1 AD – c. 64–88 AD), a.k.a. Simon Peter, Simeon, or Simon, apostle of Jesus
* Pope Peter I of Alexandria (died 311), revered as a saint
* Peter I of Armenia (died 1058), Catholico ...
concluded a favourable peace treaty with the Byzantines, but the situation inside the country saw no improvement. There were many reasons for the decline — some historians dismiss Peter I as a weak ruler, incapable of handling his own family (two of his brothers rose up against him). Furthermore, in the mid-10th century the new Bogomil
Bogomilism ( Bulgarian and Macedonian: ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", bogumilstvo, богумилство) was a Christian neo-Gnostic or dualist sect founded in the First Bulgarian Empire by the priest Bogomil during the reign of Tsar P ...
heresy
Heresy is any belief or theory that is strongly at variance with established beliefs or customs, in particular the accepted beliefs of a church or religious organization. The term is usually used in reference to violations of important religi ...
spread itself widely over the country. The Bogomils preached that people must not follow secular authorities, pay taxes or enroll in the army. As a result, the Bulgarians were unable to stop the Magyars
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Urali ...
, who looted and plundered the countryside, further contributing to the grim situation of the state. When the Byzantines paid the Rus'
Rus or RUS may refer to:
People and places
* Rus (surname), a Romanian-language surname
* East Slavic historical territories and peoples (). See Names of Rus', Russia and Ruthenia
** Rus' people, the people of Rus'
** Rus' territories
*** Kievan ...
''knyaz
, or (Old Church Slavonic: Кнѧзь) is a historical Slavic title, used both as a royal and noble title in different times of history and different ancient Slavic lands. It is usually translated into English as prince or duke, dependin ...
'' Svyatoslav I
; (943 – 26 March 972), also spelled Svyatoslav, was Grand Prince of Kiev famous for his persistent campaigns in the east and south, which precipitated the collapse of two great powers of Eastern Europe, Khazaria and the First Bulgarian Empire. He ...
to invade Bulgaria in 968, Peter I could send only 30,000 men against the 60,000 strong invading force.Cedrenus: II, p. 383 During the Rus' invasion between 968 and 971 the Bulgarians ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by la ...
'' lost control of the north-eastern parts of their country, including the capital Preslav
The modern Veliki Preslav or Great Preslav ( bg, Велики Преслав, ), former Preslav ( bg, link=no, Преслав; until 1993), is a city and the seat of government of the Veliki Preslav Municipality (Great Preslav Municipality, new B ...
, and in 970, Svyatoslav massacre
A massacre is the killing of a large number of people or animals, especially those who are not involved in any fighting or have no way of defending themselves. A massacre is generally considered to be morally unacceptable, especially when per ...
d 300 Bulgarian nobles, the elite of the Bulgarian nation and army, in Silistra
Silistra ( bg, Силистра ; tr, Silistre; ro, Silistra) is a town in Northeastern Bulgaria. The town lies on the southern bank of the lower Danube river, and is also the part of the Romanian border where it stops following the Danube. Si ...
.
Cometopuli dynasty
The fall of the north-eastern parts of the Bulgarian Empire under Byzantine rule and the decimation of its military elite had a severe impact on the Bulgarian army, especially since most of the heavy cavalry which was instrumental in the earlier successes over the Byzantines was recruited exactly in that region. Contemporary sources continue to mention the existence of a Bulgarian cavalry, but it was much reduced in size and was mostlylight cavalry
Light cavalry comprised lightly armed and armored cavalry troops mounted on fast horses, as opposed to heavy cavalry, where the mounted riders (and sometimes the warhorses) were heavily armored. The purpose of light cavalry was primarily ra ...
.
Consequently, the infantry's importance grew and the tactics changed to reflect the new conditions: the ambush
An ambush is a long-established military tactic in which a combatant uses an advantage of concealment or the element of surprise to attack unsuspecting enemy combatants from concealed positions, such as among dense underbrush or behind mo ...
, although employed in the past, now became the cornerstone of Bulgarian tactics — most Bulgarian victories in that period were a result of ambush and careful exploitation of the terrain. During this period, the Bulgarians acquired a reputation for their skillful archers.
Despite those difficulties, Emperor Samuil
Samuel (also Samuil; bg, Самуил, ; mk, Самоил/Самуил, ; Old Church Slavonic: Самоилъ; died October 6, 1014) was the Tsar (''Emperor'') of the First Bulgarian Empire from 997 to 6 October 1014. From 977 to 997, he was ...
resisted the Byzantine army, which reached its zenith under Basil II
Basil II Porphyrogenitus ( gr, Βασίλειος Πορφυρογέννητος ;) and, most often, the Purple-born ( gr, ὁ πορφυρογέννητος, translit=ho porphyrogennetos).. 958 – 15 December 1025), nicknamed the Bulgar ...
, for nearly half a century. In 976 the Bulgarians led by the Cometopuli
The Kometopuli dynasty ( Bulgarian: ,
Bulgarian; ; Byzantine Greek: , ) was the last royal dynasty in the First Bulgarian Empire, ruling from ca. 976 until the fall of Bulgaria under Byzantine rule in 1018. The most notable member of the dynas ...
brothers reconquered the north-eastern parts of the realm. The first Byzantine attempts for counter-attack were repulsed after the annihilation of a 60,000 force in the battle of the Gates of Trajan
The Battle of the Gates of Trajan ( bg, Битка край Траянови врати, grc-x-byzant, Μάχη στις Πύλες του Τραϊανού) was a battle between Byzantine and Bulgarian forces in the year 986.
It took place in ...
in 986 in which Basil II himself barely escaped. In the following decade the Bulgarians took Thessaly
Thessaly ( el, Θεσσαλία, translit=Thessalía, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thess ...
, destroyed the Principality of Duklja
Duklja ( sh-Cyrl, Дукља; el, Διόκλεια, Diokleia; la, Dioclea) was a medieval South Slavic state which roughly encompassed the territories of modern-day southeastern Montenegro, from the Bay of Kotor in the west to the Bojana Riv ...
, advanced deep to the south as far as Corinth on the Peloponnese
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge which ...
peninsula and campaigned in Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see names in other languages) is one of the four historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of the Adriatic Sea, str ...
and Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and H ...
.
 However, a major defeat at the
However, a major defeat at the battle of Spercheios
The Battle of Spercheios ( bg, Битка при Сперхей, el, Μάχη του Σπερχειού) took place in 997 AD, on the shores of the Spercheios river near the city of Lamia in central Greece. It was fought between a Bulgarian army ...
in 996 signaled that the tide of the war had begun to change in the Byzantines' favour. From 1001 onwards, Basil II launched yearly campaigns into Bulgarian territory, methodically taking important cities such as Preslav
The modern Veliki Preslav or Great Preslav ( bg, Велики Преслав, ), former Preslav ( bg, link=no, Преслав; until 1993), is a city and the seat of government of the Veliki Preslav Municipality (Great Preslav Municipality, new B ...
, Pliska
Pliska ( , cu, Пльсковъ, translit=Plĭskovŭ) was the first capital of the First Bulgarian Empire during the Middle Ages and is now a small town in Shumen Province, on the Ludogorie plateau of the Danubian Plain, 20 km northeast of ...
and Vidin
Vidin ( bg, Видин, ; Old Romanian: Diiu) is a port city on the southern bank of the Danube in north-western Bulgaria. It is close to the borders with Romania and Serbia, and is also the administrative centre of Vidin Province, as well as ...
, and inflicting several defeats on Samuil. In addition, in 1003 Samuil was involved in a war with the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
. After years of campaigning, in 1014, in the decisive battle of Kleidion
The Battle of Kleidion ( grc-gre, Κλειδίον; or Clidium, after the medieval name of the village of Klyuch, "(the) key"; also known as the Battle of Belasitsa) took place on July 29, 1014, between the Byzantine Empire and the Bulgarian Em ...
the Bulgarian army was crushed and 14,000 captured Bulgarian soldiers were blinded and sent to Samuil, who died at the sight of his army on 6 October.
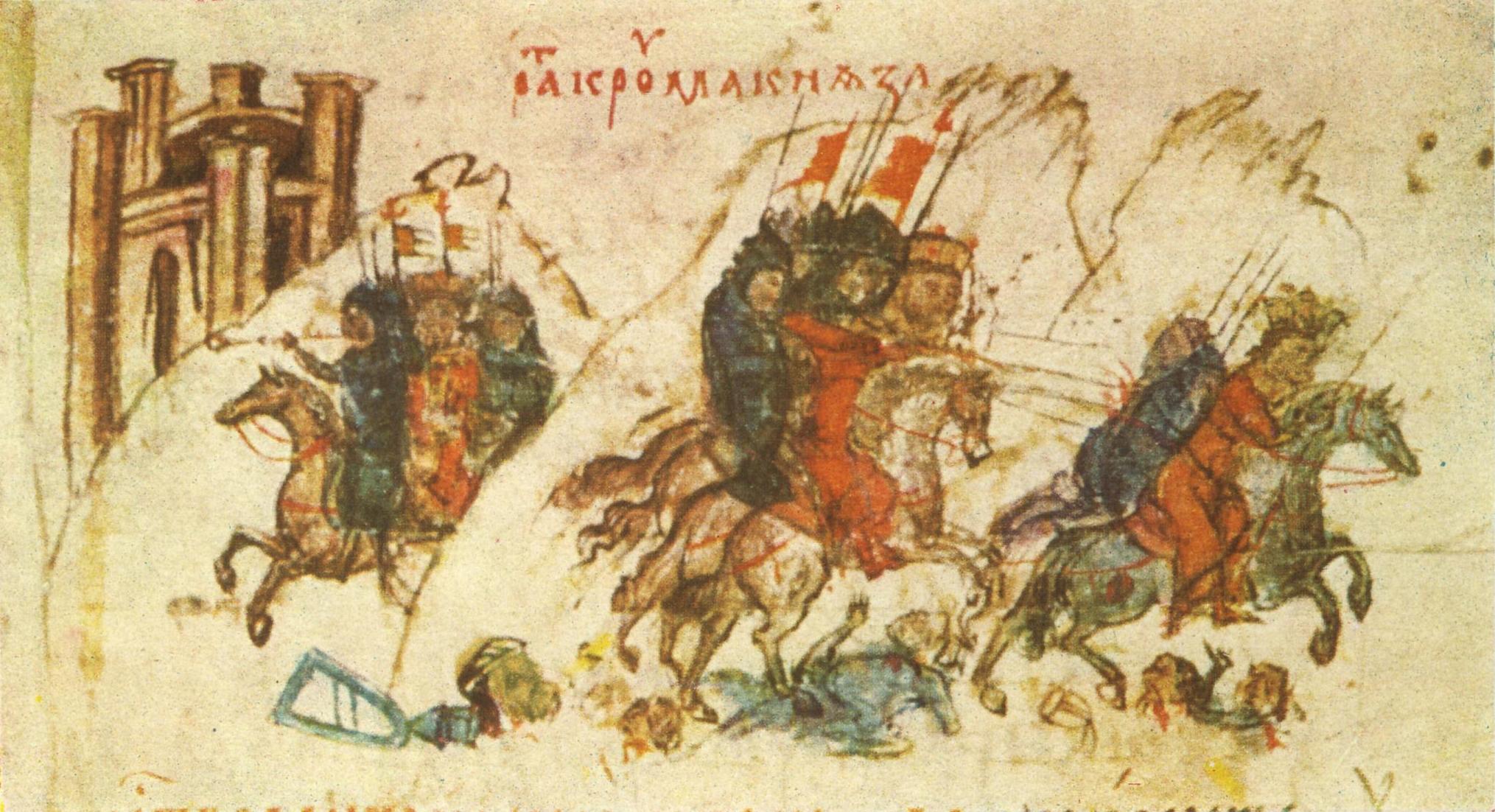
In the battle of Kleidion the Bulgarian army numbered around 20,000 soldiers. According some estimates the total number of the army including the squads of local militia reached a maximum level of 45,000. The Byzantine historian Georgius Monachus Continuatus wrote that the Bulgarian army had 360,000 men, a greatly exaggerated number, the actual being 10 times smaller.
Asen dynasty
 In 1185 the
In 1185 the Bulgarian Empire
In the medieval history of Europe, Bulgaria's status as the Bulgarian Empire ( bg, Българско царство, ''Balgarsko tsarstvo'' ) occurred in two distinct periods: between the seventh and the eleventh centuries and again between th ...
was restored as a result of the successful Rebellion of Asen and Peter, who founded the new Asen dynasty
The Asen dynasty ( bg, Асеневци, ''Asenevtsi'') founded and ruled a medieval Bulgarian state, called in modern historiography the Second Bulgarian Empire, between 1185 and 1280.
The Asen dynasty rose as the leaders of Bulgaria after a r ...
. The long period of Byzantine rule had left its mark on the Bulgarian army — the titles during the Second Empire were mostly borrowed from Byzantium. In the absence of the Emperor the commander-in-chief was called ''velik (great) voivoda''; the commander of smaller squads was a ''voivoda
Voivode (, also spelled ''voievod'', ''voevod'', ''voivoda'', ''vojvoda'' or ''wojewoda'') is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe since the Early Middle Ages. It primarily referred to the m ...
'' and a ''strator'' was the person responsible for the defense of certain regions and the recruitment of soldiers.
In the late 12th century the army numbered 40,000 men-at-arms. The country was able to mobilize around 100,000 men in the first decade of the 13th century (Kaloyan
Kaloyan or Kalojan, also known as Ioannitsa or Johannitsa ( bg, Калоян, Йоаница; 1170 – October 1207), was emperor or tsar of Bulgaria from 1196 to 1207. He was the younger brother of Theodor and Asen, who led the anti-Byzant ...
reportedly offered the leader of the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
Baldwin I 100,000 soldiers to help him take Constantinople). In that period the Bulgarian army used large numbers of Cuman
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian exonym ), were a Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the Mongol invasion (1237), many sou ...
cavalry which numbered between 10,000 and 30,000 riders, depending on the campaign. These were drawn from among the Cumans who inhabited Wallachia and Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and former principality in Cent ...
, and were at least nominally under the suzerainty of the Bulgarian Emperors. The army was well supplied with siege equipment
A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick city walls and other fortifications in siege warfare. Some are immobile, constructed in place to attack enemy fortifications from a distance, while othe ...
, including battering ram
A battering ram is a siege engine that originated in ancient times and was designed to break open the masonry walls of fortifications or splinter their wooden gates. In its simplest form, a battering ram is just a large, heavy log carried by ...
s, siege tower
A Roman siege tower or breaching tower (or in the Middle Ages, a belfry''Castle: Stephen Biesty's Cross-Sections''. Dorling Kindersley Pub (T); 1st American edition (September 1994). Siege towers were invented in 300 BC. ) is a specialized siege ...
s and catapult
A catapult is a ballistic device used to launch a projectile a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants – particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden release of stored ...
s.
In the first fifty years after the reestablishment of the Empire, the Bulgarians, led by skillful commanders such as Peter IV, Ivan Asen I
Ivan Asen I, also known as Asen I or John Asen I ( bg, Иван Асен I; died in 1196), was emperor or tsar of Bulgaria from 1187/1188 to 1196 as co-ruler with his elder brother, Peter II. Hailing from the Byzantine theme of Paristrion, hi ...
, Kaloyan and Ivan Asen II
Ivan Asen II, also known as John Asen II ( bg, Иван Асен II, ; 1190s – May/June 1241), was Emperor (Tsar) of Bulgaria from 1218 to 1241. He was still a child when his father Ivan Asen I one of the founders of the Second Bulgarian Empi ...
, achieved massive military successes. After a number of successful battles between 1185 and 1204, the Byzantine Empire was effectively driven from the lands it held in the northern Balkans, and the Imperial crown and cross. The army of the Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
, who established the new Latin Empire
The Latin Empire, also referred to as the Latin Empire of Constantinople, was a feudal Crusader state founded by the leaders of the Fourth Crusade on lands captured from the Byzantine Empire. The Latin Empire was intended to replace the Byzanti ...
, were in turn annihilated in the battle of Adrianople (1205)
The Battle of Adrianople occurred around Adrianople on April 14, 1205 between Bulgarians, Vlachs and Cumans under Tsar Kaloyan of Bulgaria, and Crusaders under Baldwin I, who only months before had been crowned Emperor of Constantinople, ...
, when their Emperor was captured, and again at Rusion in 1206. The Hungarians were defeated after several fights along the valley of the Morava river in 1202. After several setbacks under Boril I (1207–1218), Ivan Asen II decisively defeated the Despotate of Epirus
The Despotate of Epirus ( gkm, Δεσποτᾶτον τῆς Ἠπείρου) was one of the Greek successor states of the Byzantine Empire established in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade in 1204 by a branch of the Angelos dynasty. It clai ...
in the battle of Klokotnitsa
The Battle of Klokotnitsa ( bg, Битката при Клокотница, ''Bitkata pri Klokotnitsa'') occurred on 9 March 1230 near the village of Klokotnitsa (today in Haskovo Province, Bulgaria) between Second Bulgarian Empire and Empire ...
, in which the much smaller Bulgarian army outmaneuvered its enemy. In 1241, the Tsar defeated a Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of ...
army, fighting under Batu Khan
Batu Khan ( – 1255),, ''Bat haan'', tt-Cyrl, Бату хан; ; russian: хан Баты́й was a Mongol ruler and founder of the Golden Horde, a constituent of the Mongol Empire. Batu was a son of Jochi, thus a grandson of Genghis Khan. ...
and Subutai
Subutai ( Classical Mongolian: ''Sübügätäi'' or ''Sübü'ätäi''; Modern Mongolian: Сүбээдэй, ''Sübeedei''. ; ; c. 1175–1248) was a Mongol general and the primary military strategist of Genghis Khan and Ögedei Khan. He directed ...
.
Terter and Shishman dynasties
The country and the army declined after Ivan Asen II's death. His successors could not cope neither with the external nor with the internal problems. Mongol, Byzantine and Hungarian invasions were combined withseparatism
Separatism is the advocacy of cultural, ethnic, tribal, religious, racial, governmental or gender separation from the larger group. As with secession, separatism conventionally refers to full political separation. Groups simply seeking greate ...
among the nobility and several civil wars. In 1277, a peasant named Ivailo rebelled against Emperor Constantine Tikh
Konstantin Tih ( bg, Константин Тих Асен) or Constantine I Tikh (Константин I), was the tsar of Bulgaria from 1257 to 1277, he was offered the throne from Mitso Asen. He led the Bulgarian Empire at a time when the nearb ...
. In the ensuing battle the Emperor was defeated and slain, and Ivailo proclaimed himself Emperor of Bulgaria in Tarnovo
Veliko Tarnovo ( bg, Велико Търново, Veliko Tărnovo, ; "Great Tarnovo") is a town in north central Bulgaria and the administrative centre of Veliko Tarnovo Province.
Often referred as the "''City of the Tsars''", Veliko Tarnovo ...
. Although he managed to defeat both the Mongols and the Byzantines, a plot among the nobility forced him to seek refuge among the Mongol Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragmenta ...
, where he was killed in 1280. The army now numbered less than 10,000 men — it is recorded that Ivailo defeated two Byzantine armies of 5,000 and 10,000 men, and that his troops were outnumbered in both cases.
After the end of the rebellion of Ivailo, the Bulgarians were no match for the Mongols who plundered the country undisturbed for 20 years. With the reign of Theodore Svetoslav
Theodore Svetoslav ( bg, Тодор Светослав, ''Todor Svetoslav'' and also Теодор Светослав, ''Teodor Svetoslav'') ruled as emperor (tsar) of Bulgaria from 1300 to 1322. The date of his birth is unknown. He expanded the ter ...
(1300–1321), the situation of the army improved — in 1304 he defeated the Byzantines at Skafida. Under his successor the garrison of Plovdiv
Plovdiv ( bg, Пловдив, ), is the second-largest city in Bulgaria, standing on the banks of the Maritsa river in the historical region of Thrace. It has a population of 346,893 and 675,000 in the greater metropolitan area. Plovdiv is the c ...
numbered 2,000 heavily armed footmen and 1,000 horsemen. In 1330 Michael III Shishman raised a 15,000-strong army to face the Serbs but was defeated at the battle of Velbazhd
The Battle of Velbazhd ( bg, битка при Велбъжд, ''bitka pri Velbazhd''; sr, Битка код Велбужда, ''Bitka kod Velbužda'') is a battle which took place between Bulgarian and Serbian armies on 28 July 1330, near the t ...
. Two years later the Bulgarian army numbered 11,000 men.Andreev, J. ''The Bulgarian Khans and Tsars'' (''Balgarskite hanove i tsare'', ''Българските ханове и царе'', Veliko Tarnovo, 1996, p. 269
When the Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
invaded Bulgaria and the Balkans in the mid-14th century, the once glorious Bulgarian army was only a shadow of its former self. Feudal disunion and the widespread heretical movements such as Bogomilism
Bogomilism ( Bulgarian and Macedonian: ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", bogumilstvo, богумилство) was a Christian neo-Gnostic or dualist sect founded in the First Bulgarian Empire by the priest Bogomil during the reign of Tsar Pe ...
, the Adamites
The Adamites, or Adamians, were adherents of an Early Christian group in North Africa in the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th centuries. They wore no clothing during their religious services. There were later reports of similar sects in Central Europe during ...
or the Varlaamites did not allow the country to maintain a significant force. The Bulgarians relied on their fortified cities and castles for defense, but due to the lack of a common leadership, coordination amongst them was feeble and they were defeated and occupied in detail.
 Initially, the Ottoman invasion was not considered as a significant threat by both Bulgarians and Byzantines. For only one decade between 1354 and 1364 the Ottomans conquered virtually the whole of
Initially, the Ottoman invasion was not considered as a significant threat by both Bulgarians and Byzantines. For only one decade between 1354 and 1364 the Ottomans conquered virtually the whole of Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to th ...
seizing large cities such as Plovdiv
Plovdiv ( bg, Пловдив, ), is the second-largest city in Bulgaria, standing on the banks of the Maritsa river in the historical region of Thrace. It has a population of 346,893 and 675,000 in the greater metropolitan area. Plovdiv is the c ...
, Beroia, Dianopolis (Yambol
Yambol ( bg, Ямбол ) is a town in Southeastern Bulgaria and administrative centre of Yambol Province. It lies on both banks of the Tundzha river in the historical region of Thrace. It is occasionally spelled ''Jambol''.
Yambol is the adm ...
) and Adrianople
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis (Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, ...
and defeating several small Bulgarian forces. The centuries-old mistrust between Bulgarians and Byzantines spoiled the negotiations between the two empires for an alliance and even led to the last Byzantine-Bulgarian war in 1364. In 1371 a large Bulgarian-Serb army under Vukašin Mrnjavčević
Vukašin (Cyrillic script: Вукашин) is an old Slavic name of Serbian origin. It is composed from two words: Vuk (wolf) and sin (son), so it means sin vuka (son of wolf). In some places in Croatia and Bosnia it can be found as a surname.
...
and Jovan Uglješa Jovan may refer to:
*Jovan (given name), a list of people with this given name
*Jovan, Mawal, a village on the western coastal region of Maharashtra, India
*Jōvan Musk, a cologne
*Deli Jovan, a mountain in eastern Serbia
*Róbert Jován (born 1967 ...
, two feudal lords in Macedonia, was annihilated by the Ottomans under Lala Shahin Pasha
Lala may refer to:
Geography
* Lala language (disambiguation) Places
* Lala (Naples Metro), an underground metro station in Naples, Italy
* Lala, Assam, a town in Assam, India
* Lala, Ilam, a village in Ilam Province, Iran
* Lala, Lanao de ...
at Chernomen and soon the Bulgarian Emperor had to admit the defeat and became a vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain. ...
to the invaders. Numerous Bulgarian fortresses in the Rhodope mountains
The Rhodopes (; bg, Родопи, ; el, Ροδόπη, ''Rodopi''; tr, Rodoplar) are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, and the largest by area in Bulgaria, with over 83% of its area in the southern part of the country and the remainder in ...
, Sofia valley and eastern Bulgaria were captured one by one over the next twenty years. In 1393 the capital Tarnovo
Veliko Tarnovo ( bg, Велико Търново, Veliko Tărnovo, ; "Great Tarnovo") is a town in north central Bulgaria and the administrative centre of Veliko Tarnovo Province.
Often referred as the "''City of the Tsars''", Veliko Tarnovo ...
was besieged and seized by the Ottoman Turks and three years later fell Vidin
Vidin ( bg, Видин, ; Old Romanian: Diiu) is a port city on the southern bank of the Danube in north-western Bulgaria. It is close to the borders with Romania and Serbia, and is also the administrative centre of Vidin Province, as well as ...
– the last major Bulgarian city. Resistance to the invaders continued until 1422 when the country was fully conquered. The Ottoman invasion was a disaster for the Bulgarian army — the nobility and the leaders of the nation were killed or emigrated and civilians were not allowed to have weapons until the 19th century.
Tactics
 The Bulgarian army employed various military
The Bulgarian army employed various military tactics
Tactic(s) or Tactical may refer to:
* Tactic (method), a conceptual action implemented as one or more specific tasks
** Military tactics, the disposition and maneuver of units on a particular sea or battlefield
** Chess tactics
In chess, a ta ...
. It relied both on the experience of the soldiers and the peculiarities of the terrain. The Balkan mountains
The Balkan mountain range (, , known locally also as Stara planina) is a mountain range in the eastern part of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeastern Europe. The range is conventionally taken to begin at the peak of Vrashka Chuka on the border be ...
played a significant role in the military history of Bulgaria and facilitated the country's defense against the strong Byzantine army which conveyed the Roman military art in the Middle Ages. Most of the nine campaigns of the ambitious Emperor Constantine V
Constantine V ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντῖνος, Kōnstantīnos; la, Constantinus; July 718 – 14 September 775), was Byzantine emperor from 741 to 775. His reign saw a consolidation of Byzantine security from external threats. As an able ...
to eliminate the young Bulgarian state, which suffered political crisis, failed in the mountain passes of the Balkan. In 811 the whole Byzantine army was destroyed in the Varbitsa Pass
Varbitsa Pass ( bg, Върбишки проход ) is a mountain pass in the Balkan Mountains (Stara Planina) in Bulgaria. It connects Shumen and Petolachka crossroads.
The famous Battle of Pliska was fought in the pass on July 26, 811 between t ...
and in 12th–13th centuries several other Byzantine forces shared that doom. The Bulgarians maintained many outposts and castles which guarded the passes and were able to locate an invading force and quickly inform the high command about any enemy moves.
Another widely used tactic was to make a false retreat and then suddenly attack the enemy — breaking the lines when in pursuit. This trick won many victories, most notably at the battle of Adrianople
The Battle of Adrianople (9 August 378), sometimes known as the Battle of Hadrianopolis, was fought between an Eastern Roman army led by the Eastern Roman Emperor Valens and Gothic rebels (largely Thervings as well as Greutungs, non-Gothic ...
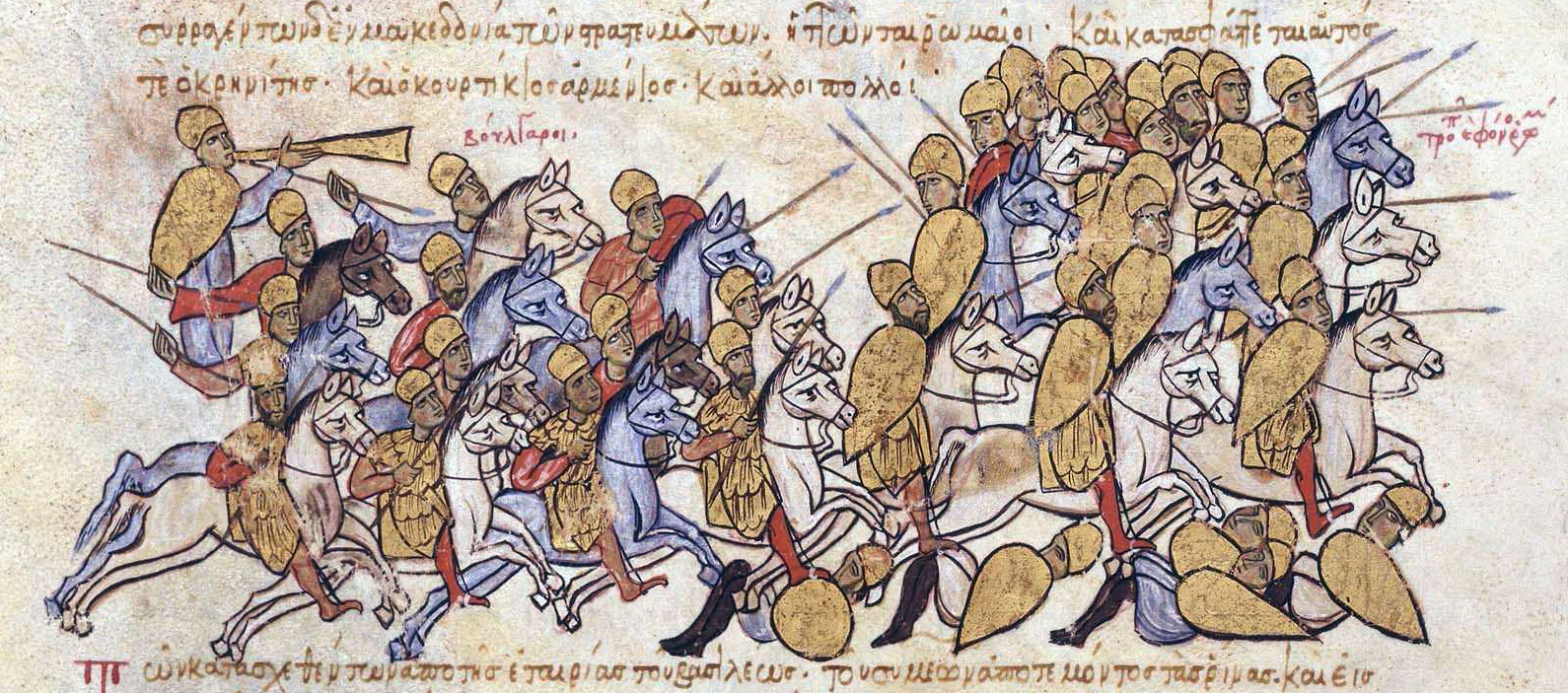
in 1205 against the Crusaders. Sometimes the Bulgarians left a strong cavalry force in reserve which attacked in the sublime moment and tipped the balance in Bulgarians' favour, for instance in the battle of Anchialus in 917. Ambush was another widely used and very successful strategy especially during the Cometopuli dynasty.
The Bulgarians usually avoided frontal assault and waited the enemy to attack first. After the opponent inevitably breaks his battle formation the Bulgarians would counter-attack with their heavy cavalry. In several battles the Bulgarian troops waited the Byzantines for days until the latter attack — for instance at Marcelae (792) or Versinikia
The Battle of Versinikia ( bg, Битката при Версиникия; el, Μάχη της Βερσινικίας) was fought in 813 between the Byzantine Empire and the Bulgarian Empire, near the city of Adrianople (Edirne).
While the Bul ...
(813) – and scored decisive victories. In one of the rare occasions in which the army made a frontal attack on the enemy, the result was a defeat despite the heavy casualties the enemy suffered – battle of Anchialus (763)
The battle of Anchialus ( bg, Битката при Анхиало) occurred in 763, near the town of Pomorie on the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast. The result was a Byzantine victory.
Origins of the conflict
After the success in the battle of the ...
. After a successful battle the Bulgarian would pursue the enemy in depth in order to eliminate as much soldiers as possible and not to allow him to reorganize his forces quickly and effectively. For instance after the victory at Ongal in 680 the Byzantines were chased for 150–200 km. After the success at Anchialus in 917 the Byzantines were not given time to prepare their resistance properly and the result was the annihilation of their last forces in the battle of Katasyrtai }
The battle of Katasyrtai (Kατασυρται) occurred in the fall of 917, shortly after the striking Bulgarian triumph at Achelous near the village of the same name close to the Byzantine capital Constantinople, (now Istanbul). The result was a ...
.
During war the Bulgarians usually sent light cavalry to devastate the enemy lands on a broad front pillaging villages and small towns, burning the crops and taking people and cattle. During the Second Empire that task was usually assigned to the Cumans. The Bulgarian army was very mobile — for instance prior to the battle of Klokotnitsa for four days it covered a distance three times longer than the Epirote army for a week; in 1332 it covered 230 km for five days.
Siege equipment
 The early Bulgarian army was not supplied with strong siege equipment . The Bulgarians used siege machines on a large scale for the first time during the reign of Khan Krum (803–814), when they employed
The early Bulgarian army was not supplied with strong siege equipment . The Bulgarians used siege machines on a large scale for the first time during the reign of Khan Krum (803–814), when they employed Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, No ...
renegades to gain experience. By 814 they possessed a large number of enormous siege machines – battering ram
A battering ram is a siege engine that originated in ancient times and was designed to break open the masonry walls of fortifications or splinter their wooden gates. In its simplest form, a battering ram is just a large, heavy log carried by ...
s, ballista
The ballista (Latin, from Greek βαλλίστρα ''ballistra'' and that from βάλλω ''ballō'', "throw"), plural ballistae, sometimes called bolt thrower, was an ancient missile weapon that launched either bolts or stones at a distant ta ...
s, mangonel
The mangonel, also called the traction trebuchet, was a type of trebuchet used in Ancient China starting from the Warring States period, and later across Eurasia by the 6th century AD. Unlike the later counterweight trebuchet, the mangonel operat ...
s, catapult
A catapult is a ballistic device used to launch a projectile a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants – particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden release of stored ...
s, siege tower
A Roman siege tower or breaching tower (or in the Middle Ages, a belfry''Castle: Stephen Biesty's Cross-Sections''. Dorling Kindersley Pub (T); 1st American edition (September 1994). Siege towers were invented in 300 BC. ) is a specialized siege ...
s, machines against battlement
A battlement in defensive architecture, such as that of city walls or castles, comprises a parapet (i.e., a defensive low wall between chest-height and head-height), in which gaps or indentations, which are often rectangular, occur at interva ...
s. They were transported by 5,000 iron-covered carts, hauled by 10,000 oxen. In addition, after the siege of Mesembria
Mesembria ( grc, Μεσημβρία; grc-x-doric, Μεσαμβρία, Mesambria) was an important Greek city in ancient Thrace. It was situated on the coast of the Euxine and at the foot of Mount Haemus; consequently upon the confines of Moe ...
, the Bulgarians captured 36 copper siphons which the Byzantines used to throw the famous Greek fire
Greek fire was an incendiary weapon used by the Eastern Roman Empire beginning . Used to set fire to enemy ships, it consisted of a combustible compound emitted by a flame-throwing weapon. Some historians believe it could be ignited on contact w ...
.
A wide range of siege equipment was also used during the Second Empire. During the siege of Adrianople
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis (Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, ...
in 1207, Emperor Kaloyan had 33 catapults and an engineer corps which was tasked with destroying the city walls. In the beginning of the 13th century, during the siege of Varna, the Bulgarians constructed an enormous siege tower which was wider than the moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch, either dry or filled with water, that is dug and surrounds a castle, fortification, building or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. In some places moats evolved into more extensive ...
of the fortress.
Foreign and mercenary soldiers
After the Bulgarians conquered the Avar Khanate in 804–805, Avar soldiers, who were now subjects of the Bulgarian crown, were recruited in the army, especially during the campaign againstNicephorus I
Nikephoros I or Nicephorus I ( gr, Νικηφόρος; 750 – 26 July 811) was Byzantine emperor from 802 to 811. Having served Empress Irene as '' genikos logothetēs'', he subsequently ousted her from power and took the throne himself. In ...
in 811, when the Byzantines burned down the capital, Pliska
Pliska ( , cu, Пльсковъ, translit=Plĭskovŭ) was the first capital of the First Bulgarian Empire during the Middle Ages and is now a small town in Shumen Province, on the Ludogorie plateau of the Danubian Plain, 20 km northeast of ...
. In the 9th–10th centuries the Bulgarians often resorted to the services of the Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peçenek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: Печенег(и), uk, Печеніг(и), hu, Besenyő(k), gr, Πατζινάκοι, Πετσενέγοι, Πατζινακίται, ka, პა� ...
, who were probably Bulgarian federates. When the Byzantines stirred the Kievan Rus' up against the Empire, the Bulgarian diplomacy in turn used the Pechenegs against Rus'.
During the Second Empire, foreign and mercenary soldiers became an important part of the Bulgarian army and its tactics. Since the very beginning of the rebellion of Asen and Peter, the light and mobile Cuman
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian exonym ), were a Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the Mongol invasion (1237), many sou ...
cavalry was effectively used against the Byzantines and later the Crusaders. For instance, fourteen thousand of them were used by Kaloyan in the battle of Adrianople. The Cumans were the empire's most effective military component.David Nicolle, Angus McBride: Hungary and the Fall of Eastern Europe 1000–1568, Osprey Publishing, 1988, p.24 The Cuman leaders entered the ranks of Bulgarian nobility, and some of them received high military or administrative posts in the state. During the 14th century the Bulgarian army increasingly relied on foreign mercenaries
A mercenary, sometimes also known as a soldier of fortune or hired gun, is a private individual, particularly a soldier, that joins a military conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any ...
, which included Western knights, Mongols, Ossetians
The Ossetians or Ossetes (, ; os, ир, ирæттæ / дигорӕ, дигорӕнттӕ, translit= ir, irættæ / digoræ, digorænttæ, label= Ossetic) are an Iranian ethnic group who are indigenous to Ossetia, a region situated across the ...
or came from vassal Wallachia. Both Michael III Shishman and Ivan Alexander had a 3,000-strong Mongol cavalry detachment in their armies.Nic. Gregoras. I, р. 455. 7–9. In the 1350s, Emperor Ivan Alexander even hired Ottoman bands, as did the Byzantine Emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as le ...
. Russians were also hired as mercenaries.
Conflicts
Byzantine–Bulgarian wars
The Byzantine–Bulgarian wars were a series of conflicts fought between the Byzantines and Bulgarians which began when the Bulgars first settled in the Balkan peninsula in the 5th century, and intensified with the expansion of the Bulgarian Em ...





Bulgarian–Hungarian wars
The Bulgarian–Hungarian wars were a series of conflicts that occurred during the 9th–14th centuries between the Bulgarian Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary. The nearly 500-year conflict encompassed the northern and western Balkans, or what ...


Bulgarian–Latin wars
The Bulgarian–Latin wars were a series of conflicts between the Second Bulgarian Empire (1185–1396) and the Latin Empire (1204–61). The wars affected the northern border of the Latin Empire throughout its existence.
The initial expansion ...
Bulgarian–Ottoman wars
The Bulgarian–Ottoman wars were fought between the kingdoms remaining from the disintegrating Second Bulgarian Empire, and the Ottoman Empire, in the second half of the 14th century. The wars resulted with the collapse and subordination of t ...
See also
*Medieval Bulgarian navy
During most of the Middle Ages the Bulgarians did not maintain naval forces. The first records of Bulgarians ships come from the reign of Khan Omurtag: during his war against the Franks (827-829) he came with ships from the Danube and landed tro ...
* Byzantine army
* Medieval warfare
Medieval warfare is the warfare of the Middle Ages. Technological, cultural, and social advancements had forced a severe transformation in the character of warfare from antiquity, changing military tactics and the role of cavalry and artillery ...
Notes
*Note that the works Byzantine authors are usually from their Bulgarian edition ''ГИБИ'' (''Гръцки Извори за Българската История'' – ''Greek Sources for the Bulgarian History'')References
* * * * * * *Bulgaria
retrieved on 16 September 2009 *
{{Bulgarian Empire
Army
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
Military history of Bulgaria
Military units and formations of the Middle Ages
Medieval armies