Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (MV; ; nds, Mäkelborg-Vörpommern), also known by its
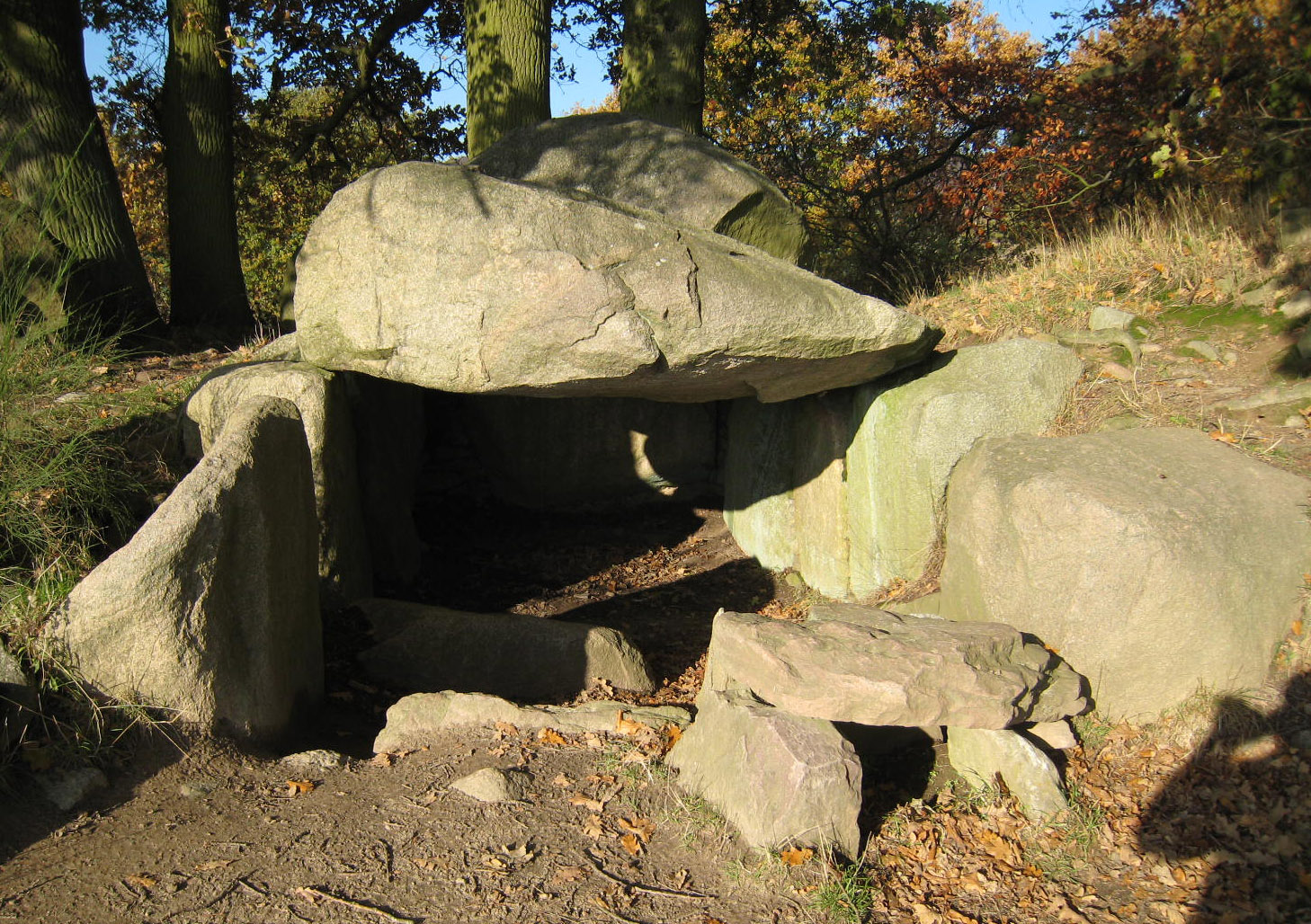 In the aftermath of the
In the aftermath of the
 Human settlement in the area of modern Mecklenburg and Vorpommern began after the
Human settlement in the area of modern Mecklenburg and Vorpommern began after the

 Vorpommern, literally Fore-Pomerania, is the smaller, western part of the former
Vorpommern, literally Fore-Pomerania, is the smaller, western part of the former
 During the war, the make-up of Mecklenburg and Vorpommern's population changed, due to wartime losses and the influx of evacuees (mainly from the Berlin and Hamburg metropolitan areas that were subject to air raids). After the war, people who fled and were expelled from the
During the war, the make-up of Mecklenburg and Vorpommern's population changed, due to wartime losses and the influx of evacuees (mainly from the Berlin and Hamburg metropolitan areas that were subject to air raids). After the war, people who fled and were expelled from the
 On 5 June 1946, a law enacted by the Soviets constituted a provisional German administration (''Beratende Versammlung'', en, "Consulting assembly") under Soviet supervision on 29 June 1946. After elections on 20 October 1946, a ''
On 5 June 1946, a law enacted by the Soviets constituted a provisional German administration (''Beratende Versammlung'', en, "Consulting assembly") under Soviet supervision on 29 June 1946. After elections on 20 October 1946, a ''

 Since 4 September 2011, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern is divided into six ''Kreise'' (districts):
#
Since 4 September 2011, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern is divided into six ''Kreise'' (districts):
#
anglicized
Anglicisation is the process by which a place or person becomes influenced by English culture or British culture, or a process of cultural and/or linguistic change in which something non-English becomes English. It can also refer to the influenc ...
name Mecklenburg–Western Pomerania, is a state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
in the north-east of Germany. Of the country's sixteen states, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern ranks 14th in population; it covers an area of , making it the sixth largest German state in area; and it is 16th in population density. Schwerin
Schwerin (; Mecklenburgian Low German: ''Swerin''; Latin: ''Suerina'', ''Suerinum'') is the capital and second-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern as well as of the region of Mecklenburg, after Rostock. It ...
is the state capital and Rostock
Rostock (), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (german: link=no, Hanse- und Universitätsstadt Rostock), is the largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state, ...
is the largest city. Other major cities
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
include Neubrandenburg
Neubrandenburg (lit. ''New Brandenburg'', ) is a city in the southeast of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is located on the shore of a lake called Tollensesee and forms the urban centre of the Mecklenburg Lakeland.
The city is famous for its ...
, Stralsund, Greifswald
Greifswald (), officially the University and Hanseatic City of Greifswald (german: Universitäts- und Hansestadt Greifswald, Low German: ''Griepswoold'') is the fourth-largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania after Rosto ...
, Wismar
Wismar (; Low German: ''Wismer''), officially the Hanseatic City of Wismar (''Hansestadt Wismar'') is, with around 43,000 inhabitants, the sixth-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, and the fourth-largest city ...
, and Güstrow. It was named after the 2 regions of Mecklenburg and Vorpommern (which means West Pomerania).
The state was established in 1945 after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
through the merger of the historic regions of Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg (; nds, label= Low German, Mękel(n)borg ) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schweri ...
and the Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
n Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Weste ...
by the Soviet military administration in Allied-occupied Germany
Germany was already de facto occupied by the Allies from the real fall of Nazi Germany in World War II on 8 May 1945 to the establishment of the East Germany on 7 October 1949. The Allies (United States, United Kingdom, Soviet Union, and Franc ...
. It became part of the German Democratic Republic
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**G ...
in 1949, but was dissolved in 1952 during administrative reforms and its territory divided into the districts of Rostock
Rostock (), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (german: link=no, Hanse- und Universitätsstadt Rostock), is the largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state, ...
, Schwerin
Schwerin (; Mecklenburgian Low German: ''Swerin''; Latin: ''Suerina'', ''Suerinum'') is the capital and second-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern as well as of the region of Mecklenburg, after Rostock. It ...
, and Neubrandenburg
Neubrandenburg (lit. ''New Brandenburg'', ) is a city in the southeast of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is located on the shore of a lake called Tollensesee and forms the urban centre of the Mecklenburg Lakeland.
The city is famous for its ...
. A state called in German ''Mecklenburg-Vorpommern'' was re-established in 1990 following German reunification and became one of the new states of the Federal Republic of Germany.
On the state's coastline on the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
are many holiday resorts and much unspoilt nature, including the islands of Rügen
Rügen (; la, Rugia, ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
The "gateway" to Rügen island is the Hanseatic city of Stralsund, where ...
, Usedom, and others, as well as the Mecklenburg Lake District
The Mecklenburg Lake Plateau or Mecklenburg Lakeland
- Federal Ministry of Economics ...
, making the state one of Germany's leading tourist destinations. Three of Germany's fourteen national parks, as well as several hundred nature conservation areas, are in the state. The - Federal Ministry of Economics ...
University of Rostock
The University of Rostock (german: link=no, Universität Rostock) is a public university located in Rostock, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. Founded in 1419, it is the third-oldest university in Germany. It is the oldest university in continen ...
, founded in 1419, and the University of Greifswald
The University of Greifswald (; german: Universität Greifswald), formerly also known as “Ernst-Moritz-Arndt University of Greifswald“, is a public research university located in Greifswald, Germany, in the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pom ...
, established in 1456, are among the oldest universities in Europe. In 2007, the 33rd G8 summit
The 33rd G8 summit was held at Kempinski Grand Hotel, 6–8 June 2007. The summit took place in Heiligendamm in the Northern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern on the Baltic Coast. The locations of previous G8 summits to have been hosted by ...
took place at the Grand Hotel Heiligendamm
The Grand Hotel Heiligendamm is a luxury hotel and gated community in Heiligendamm on the Mecklenburg Baltic Sea, Baltic coast in Germany.
The five-star grand hotel is counted among the best hotels in Germany. The hotel was the first seaside res ...
on the Mecklenburg Baltic coast during the chancellorship of Angela Merkel
Angela Dorothea Merkel (; ; born 17 July 1954) is a German former politician and scientist who served as Chancellor of Germany from 2005 to 2021. A member of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU), she previously served as Leader of the Opp ...
, a native of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern.
Name
Due to its lengthy name, the state is often abbreviated as ''MV'' or (colloquially) shortened to ''MeckPomm''. In English, it is usually named as "Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania". Inhabitants are called either ''Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg (; nds, label= Low German, Mękel(n)borg ) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schweri ...
er'' or '' Pomeranians'', the combined form is never used.
The full name in German is pronounced . Sometimes, ''Mecklenburg'' is pronounced , because the digraph marks a preceding short vowel in High German
The High German dialects (german: hochdeutsche Mundarten), or simply High German (); not to be confused with Standard High German which is commonly also called ''High German'', comprise the varieties of German spoken south of the Benrath and ...
. However, Mecklenburg is within the historical Low German language area, and the appeared in its name during the period of transition to Standard Standard may refer to:
Symbols
* Colours, standards and guidons, kinds of military signs
* Standard (emblem), a type of a large symbol or emblem used for identification
Norms, conventions or requirements
* Standard (metrology), an object th ...
, High German usage (Low German authors wrote the name ''Meklenborg'' or ''Męklenborg'', depicting proper Low German pronunciation, which itself was a syncope of Middle Low German
Middle Low German or Middle Saxon (autonym: ''Sassisch'', i.e. " Saxon", Standard High German: ', Modern Dutch: ') is a developmental stage of Low German. It developed from the Old Saxon language in the Middle Ages and has been documented i ...
''Mekelenborg''). The introduction of the is explained as follows: Either the signals the stretched pronunciation of the preceding (''Dehnungs-c''), or it signals the pronunciation of the subsequent as an occlusive
In phonetics, an occlusive, sometimes known as a stop, is a consonant sound produced by occluding (i.e. blocking) airflow in the vocal tract, but not necessarily in the nasal tract. The duration of the block is the ''occlusion'' of the consonan ...
to prevent it from falsely being rendered as a fricative
A fricative is a consonant produced by forcing air through a narrow channel made by placing two articulators close together. These may be the lower lip against the upper teeth, in the case of ; the back of the tongue against the soft palate in t ...
following a Low German trend. Another explanation is that the comes from a mannerism in High German officialese
Officialese, bureaucratese, or governmentese is language that sounds official. It is the "language of officialdom". Officialese is characterized by a preference for wordy, long sentences; a preference for complex words, Code word (figure of speech ...
of writing unnecessary letters, a so-called ''Letternhäufelung'' (, as was done sometimes in English with words such as "doubt"). The place name ''Vorpommern'', at its base derives from West Slavic languages
The West Slavic languages are a subdivision of the Slavic language group. They include Polish, Czech, Slovak, Kashubian, Upper Sorbian and Lower Sorbian. The languages have traditionally been spoken across a mostly continuous region encom ...
, with the prefix "po-" meaning ''along'' or ''at'', and the base word "more" meaning ''sea'' — together "po more" means ''Land at the Sea'' — while the German prefix "vor-" denoted a closer location, and is the equivalent of the word "hither" in English.
History
 In the aftermath of the
In the aftermath of the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
and German reunification in 1990, the state was constituted from the historic region of Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg (; nds, label= Low German, Mękel(n)borg ) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schweri ...
and Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Weste ...
, both of which had long and rich independent histories.
Prehistory
Ice Age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gre ...
, about 10,000 BC. About two thousand years ago, Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and e ...
were recorded in the area. Most of them left during the Migration Period, heading towards Spain, Italy, and France, leaving the area relatively deserted. In the sixth century Polabian Slavs
Polabian Slavs ( dsb, Połobske słowjany, pl, Słowianie połabscy, cz, Polabští slované) is a collective term applied to a number of Lechitic ( West Slavic) tribes who lived scattered along the Elbe river in what is today eastern Germ ...
populated the area. While Mecklenburg was settled by the Obotrites
The Obotrites ( la, Obotriti, Abodritorum, Abodritos…) or Obodrites, also spelled Abodrites (german: Abodriten), were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany ...
, Pomerania was settled by the Veleti
The Veleti, also known as Wilzi, Wielzians, and Wiltzes, were a group of medieval Lechitic tribes within the territory of Hither Pomerania, related to Polabian Slavs. They had formed together the Confederation of the Veleti, a loose monarchic c ...
(later ''Liuticians'') and the Rani.Michael North, ''The Baltic: A History'' (2015), pp. 187–189
Along the coast, Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
s and Slavs established trade posts like Reric, Ralswiek and Menzlin. In the 12th century, Mecklenburg and Vorpommern were conquered by Henry the Lion
Henry the Lion (german: Heinrich der Löwe; 1129/1131 – 6 August 1195) was a member of the Welf dynasty who ruled as the duke of Saxony and Bavaria from 1142 and 1156, respectively, until 1180.
Henry was one of the most powerful German p ...
and incorporated into the Duchy of Saxony
The Duchy of Saxony ( nds, Hartogdom Sassen, german: Herzogtum Sachsen) was originally the area settled by the Saxons in the late Early Middle Ages, when they were subdued by Charlemagne during the Saxon Wars from 772 and incorporated into the C ...
, joining the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
in the 1180s. Parts of Mecklenburg and Pomerania were settled with Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
in the '' Ostsiedlung'' process, starting in the 12th century.
Mecklenburg
In the late 12th century,Henry the Lion
Henry the Lion (german: Heinrich der Löwe; 1129/1131 – 6 August 1195) was a member of the Welf dynasty who ruled as the duke of Saxony and Bavaria from 1142 and 1156, respectively, until 1180.
Henry was one of the most powerful German p ...
, Duke of the Saxons, conquered the Obotrites
The Obotrites ( la, Obotriti, Abodritorum, Abodritos…) or Obodrites, also spelled Abodrites (german: Abodriten), were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany ...
, subjugated its Nikloting dynasty, and Christianized its people. In the course of time, German monks, nobility, peasants and traders arrived to settle here. After the 12th century, the territory remained stable and relatively independent of its neighbours; one of the few German territories for which this is true. Mecklenburg first became a duchy of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
in 1348. Though later partitioned and re-partitioned within the same dynasty, Mecklenburg always shared a common history and identity. The states of Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Strelitz became Grand Duchies in 1815, and in 1870 they voluntarily joined the new German Empire, while retaining their own internal autonomy. After the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and the abdication
Abdication is the act of formally relinquishing monarchical authority. Abdications have played various roles in the succession procedures of monarchies. While some cultures have viewed abdication as an extreme abandonment of duty, in other societ ...
of the German Kaiser, the monarchies of the duchies were abolished and republican governments of both Mecklenburg states were established, until the Nazi government merged the two states into a unified , a virtually meaningless administrative decision under the centralised regime.
Western Pomerania

Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
n Province of Pomerania; the eastern part became part of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
after the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
.
In the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, the area was ruled by the Pomeranian dukes as part of the Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (german: Herzogtum Pommern; pl, Księstwo Pomorskie; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country ha ...
. Pomerania was under Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
rule after the Peace of Westphalia from 1648 until 1815 as Swedish Pomerania
Swedish Pomerania ( sv, Svenska Pommern; german: Schwedisch-Pommern) was a dominion under the Swedish Crown from 1630 to 1815 on what is now the Baltic coast of Germany and Poland. Following the Polish War and the Thirty Years' War, Sweden held ...
. Pomerania became a province of Prussia in 1815 and remained so until 1945.
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Wartime
In May 1945, the armies of theSoviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
and the Western allies met east of Schwerin
Schwerin (; Mecklenburgian Low German: ''Swerin''; Latin: ''Suerina'', ''Suerinum'') is the capital and second-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern as well as of the region of Mecklenburg, after Rostock. It ...
. Following the Potsdam Agreement, the Western allies handed over Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg (; nds, label= Low German, Mękel(n)borg ) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schweri ...
to the Soviets. Mecklenburg-West Pomerania was established on 9 July 1945, by order No. 5 of Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army ( Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, afte ...
Marshal Georgy Zhukov
Georgy Konstantinovich Zhukov ( rus, Георгий Константинович Жуков, p=ɡʲɪˈorɡʲɪj kənstɐnʲˈtʲinəvʲɪtɕ ˈʐukəf, a=Ru-Георгий_Константинович_Жуков.ogg; 1 December 1896 – ...
, head of the Soviet Military Administration in Germany (SMAD), as the ''Province of Mecklenburg and West Pomerania (zapadnoi Pomeranii)''.
 During the war, the make-up of Mecklenburg and Vorpommern's population changed, due to wartime losses and the influx of evacuees (mainly from the Berlin and Hamburg metropolitan areas that were subject to air raids). After the war, people who fled and were expelled from the
During the war, the make-up of Mecklenburg and Vorpommern's population changed, due to wartime losses and the influx of evacuees (mainly from the Berlin and Hamburg metropolitan areas that were subject to air raids). After the war, people who fled and were expelled from the former eastern territories of Germany
The former eastern territories of Germany (german: Ehemalige deutsche Ostgebiete) refer in present-day Germany to those territories east of the current eastern border of Germany i.e. Oder–Neisse line which historically had been considered Ger ...
east of the Oder-Neisse line settled in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (and elsewhere in Germany), increasing the population by 40%. Before the war, Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg (; nds, label= Low German, Mękel(n)borg ) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schweri ...
and Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Weste ...
had a population of 1,278,700, of whom many perished during the war and others moved west in the course of the Red Army's advance. In 1947, some 1,426,000 refugees from the former eastern parts of Germany were counted. Most of them settled in rural communities, but the urban population also increased, most notably in Schwerin
Schwerin (; Mecklenburgian Low German: ''Swerin''; Latin: ''Suerina'', ''Suerinum'') is the capital and second-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern as well as of the region of Mecklenburg, after Rostock. It ...
from 65,000 (1939) to 99,518 (January 1947), in Wismar
Wismar (; Low German: ''Wismer''), officially the Hanseatic City of Wismar (''Hansestadt Wismar'') is, with around 43,000 inhabitants, the sixth-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, and the fourth-largest city ...
from 29,463 to 44,173, and in Greifswald
Greifswald (), officially the University and Hanseatic City of Greifswald (german: Universitäts- und Hansestadt Greifswald, Low German: ''Griepswoold'') is the fourth-largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania after Rosto ...
from 29,488 to 43,897. Western Pomerania was additionally stripped of the area around the Pomeranian regional capital Stettin/Szczecin as well as the city itself, despite its location to the west of the river Oder.
German Democratic Republic
 On 5 June 1946, a law enacted by the Soviets constituted a provisional German administration (''Beratende Versammlung'', en, "Consulting assembly") under Soviet supervision on 29 June 1946. After elections on 20 October 1946, a ''
On 5 June 1946, a law enacted by the Soviets constituted a provisional German administration (''Beratende Versammlung'', en, "Consulting assembly") under Soviet supervision on 29 June 1946. After elections on 20 October 1946, a ''Landtag
A Landtag (State Diet) is generally the legislative assembly or parliament of a federated state or other subnational self-governing entity in German-speaking nations. It is usually a unicameral assembly exercising legislative competence in non ...
'' replaced the ''Beratende Versammlung'' and created the constitution of 16 January 1947, for the ''Land
Land, also known as dry land, ground, or earth, is the solid terrestrial surface of the planet Earth that is not submerged by the ocean or other bodies of water. It makes up 29% of Earth's surface and includes the continents and various isla ...
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern''. On 18 April 1947, the state's name was shortened to ''Land Mecklenburg''. Mecklenburg became a constituent state ("''Land''") of the German Democratic Republic
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**G ...
(GDR) upon its formation in 1949. In 1952, the East German government abandoned the term ''Land'' in this context and redesignated its administrative territorial divisions as "districts" (German: '' Bezirke''). The territory of Mecklenburg and Vorpommern was divided into three districts that covered roughly the same area: '' Bezirk Rostock'', '' Bezirk Schwerin'' and '' Bezirk Neubrandenburg''. These were commonly known as the ''Nordbezirke'' (northern districts) under the highly centralised GDR government. The East German government developed the shipyards in the old Hanseatic
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label=German language, Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Norther ...
ports (the largest being in Rostock
Rostock (), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (german: link=no, Hanse- und Universitätsstadt Rostock), is the largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state, ...
and Stralsund), and also established the Greifswald Nuclear Power Plant
Greifswald nuclear power station ( German: ''Kernkraftwerk Greifswald'', KKW Greifswald), also known as Lubmin nuclear power station, was the largest nuclear power station in East Germany before closure shortly after the German reunification. ...
in Lubmin
Lubmin () is a coastal resort in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Lubmin is situated near Greifswald and on the Bay of Greifswald.
Apart from tourism, Lubmin is a major transport and industry hub and investment location in the German e ...
near Greifswald
Greifswald (), officially the University and Hanseatic City of Greifswald (german: Universitäts- und Hansestadt Greifswald, Low German: ''Griepswoold'') is the fourth-largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania after Rosto ...
.
Reunification
At the time of German reunification in 1990, the eastern states were reconstituted along their postwar boundaries (with minor adjustments) as they had existed until 1952, and the historic name Mecklenburg-Vorpommern was restored. Since 1990, the state has undergone dramatic changes. What had been largely an industrial and agricultural economy is increasingly driven by the service,tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism mor ...
, and high-tech sectors. The old towns, hundreds of castles and manors, resort buildings, windmills
A windmill is a structure that converts wind power into rotational energy using vanes called sails or blades, specifically to mill grain (gristmills), but the term is also extended to windpumps, wind turbines, and other applications, in some par ...
, churches, and various other cultural monuments of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern have been renovated in recent years. Since 2013, net migration into the state has been positive again.
Geography
Location and urban areas
Sixth-largest in area and fourteenth in overall population among Germany's sixteen Bundesländer (federal states), Mecklenburg-Vorpommern is bounded to the north by theBaltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
, to the west by Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sc ...
, to the southwest by Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
, to the south by Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 sq ...
, and to the east by the West Pomeranian Voivodeship
The West Pomeranian Voivodeship, also known as the West Pomerania Province, is a voivodeship (province) in northwestern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Szczecin. Its area equals 22 892.48 km² (8,838.84 sq mi), and in 2021, it was ...
in Poland.
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern's state capital is Schwerin
Schwerin (; Mecklenburgian Low German: ''Swerin''; Latin: ''Suerina'', ''Suerinum'') is the capital and second-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern as well as of the region of Mecklenburg, after Rostock. It ...
. The largest city is Rostock
Rostock (), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (german: link=no, Hanse- und Universitätsstadt Rostock), is the largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state, ...
with approximately 205,000 people, followed by Schwerin
Schwerin (; Mecklenburgian Low German: ''Swerin''; Latin: ''Suerina'', ''Suerinum'') is the capital and second-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern as well as of the region of Mecklenburg, after Rostock. It ...
. Other major cities include Neubrandenburg
Neubrandenburg (lit. ''New Brandenburg'', ) is a city in the southeast of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is located on the shore of a lake called Tollensesee and forms the urban centre of the Mecklenburg Lakeland.
The city is famous for its ...
, Stralsund, Greifswald
Greifswald (), officially the University and Hanseatic City of Greifswald (german: Universitäts- und Hansestadt Greifswald, Low German: ''Griepswoold'') is the fourth-largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania after Rosto ...
, Wismar
Wismar (; Low German: ''Wismer''), officially the Hanseatic City of Wismar (''Hansestadt Wismar'') is, with around 43,000 inhabitants, the sixth-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, and the fourth-largest city ...
and Güstrow.
Districts
 Since 4 September 2011, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern is divided into six ''Kreise'' (districts):
#
Since 4 September 2011, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern is divided into six ''Kreise'' (districts):
# Landkreis Rostock
Rostock (german: Landkreis Rostock) is a district in the north of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is bounded by (from the west and clockwise) the district Nordwestmecklenburg, the Baltic Sea, the district-free city Rostock and the districts Vo ...
# Ludwigslust-Parchim
Ludwigslust-Parchim is a district in the west of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is bordered by (clockwise starting from the west) the state Schleswig-Holstein, the district Nordwestmecklenburg, the district-free city Schwerin, the districts R ...
# Mecklenburgische Seenplatte
The Mecklenburg Lake Plateau or Mecklenburg Lakeland
- Federal Ministry of Economics ...
# - Federal Ministry of Economics ...
Nordwestmecklenburg
Nordwestmecklenburg (''Northwestern Mecklenburg'') is a ''Kreis'' (district) in the north-western part of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is situated on the coast of the Baltic Sea and borders on Schleswig-Holstein to the west. Neighboring d ...
# Vorpommern-Greifswald
Vorpommern-Greifswald is a district in the east of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is bounded by (from the west and clockwise) the districts of Mecklenburgische Seenplatte and Vorpommern-Rügen, the Baltic Sea, Poland ( West Pomeranian Voivo ...
# Vorpommern-Rügen
Vorpommern-Rügen is a district in the north of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is bounded by (from the west and clockwise) the Baltic Sea and the districts Vorpommern-Greifswald, Mecklenburgische Seenplatte and Rostock. The district seat is ...
Also counting two independent urban districts:
# Rostock
Rostock (), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (german: link=no, Hanse- und Universitätsstadt Rostock), is the largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state, ...
(HRO)
# Schwerin
Schwerin (; Mecklenburgian Low German: ''Swerin''; Latin: ''Suerina'', ''Suerinum'') is the capital and second-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern as well as of the region of Mecklenburg, after Rostock. It ...
(SN)
Landscape
The state'sBaltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
coast is about long and features several islands, most notably Germany's two biggest islands Rügen
Rügen (; la, Rugia, ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
The "gateway" to Rügen island is the Hanseatic city of Stralsund, where ...
and Usedom, but also a number of smaller islands such as Hiddensee
Hiddensee () is a car-free island in the Baltic Sea, located west of Germany's largest island, Rügen, on the German coast.
The island has about 1,000 inhabitants. It was a holiday destination for East German tourists during German Democratic ...
and Poel. Mecklenburg-Vorpommern's varied coastline also has many peninsulas such as Fischland-Darß-Zingst
Fischland-Darß-Zingst or Fischland-Darss-Zingst''Fischland-Darss-Zi ...
and various lagoons
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into ''coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons'') an ...
(also known as ''Bodden'' or ''Haff'').
A total of 283 nature reserves, 110 landscape reserves and three of Germany's fourteen national parks
A national park is a natural park in use for conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state declares or owns. Although individua ...
are scattered all over the state.
Lakes
The southern part of the state is characterized by a multitude of lakes within the Mecklenburg Lakeland, the largest of which is Lake Müritz (also the largest German lake), followed byLake Schwerin
Lake SchwerinPlauer See and Lake Kummerow. The "land of a thousand lakes" (German: ''Land der tausend Seen'') is hallmarked by its unspoilt nature. Due to its clean air and idyllic setting,

 The largest publicly funded theatres in the state are the Mecklenburg State Theatre, the
The largest publicly funded theatres in the state are the Mecklenburg State Theatre, the
 Today the vast majority of people speak Standard German; a few centuries ago most people spoke Low German (German: ''Plattdeutsch'' or ''Niederdeutsch''), a language that is still kept alive within various communities and cultural events.
Today the vast majority of people speak Standard German; a few centuries ago most people spoke Low German (German: ''Plattdeutsch'' or ''Niederdeutsch''), a language that is still kept alive within various communities and cultural events.
 Mecklenburg-Vorpommern has the two oldest
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern has the two oldest
 The executive is led by a cabinet, in turn led by a Minister-President, who is the official head of state and government. The election to determine the Minister-President is held no later than four weeks after the newly elected Landtag is convened.
The executive is led by a cabinet, in turn led by a Minister-President, who is the official head of state and government. The election to determine the Minister-President is held no later than four weeks after the newly elected Landtag is convened.
 The last election of the
The last election of the
File:Röbel Müritz Hafen 2.JPG, Mecklenburg Lakeland, Röbel
File:The Pier, Sellin.jpg, Sellin on the island of
 Notable from Mecklenburg-Vorpommern include:
* Arts:
Notable from Mecklenburg-Vorpommern include:
* Arts:
Image:Stralsund, Altstadt (2011-05-21) 4.JPG, Stralsund − aerial view of an old town, protected by
Official Mecklenburg-Vorpommern portal
* ;Tourism
Off to MV - Official tourism website of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
{{Authority control 1946 establishments in Germany NUTS 1 statistical regions of the European Union States and territories established in 1946 States of Germany
medical tourism
Medical tourism refers to people traveling abroad to obtain medical treatment. In the past, this usually referred to those who traveled from less-developed countries to major medical centers in highly developed countries for treatment unavailable a ...
has become a notable tourism sector in the region.
National parks
Culture
Over the centuries, Mecklenburg and Vorpommern have developed and maintained strong regional cultures. It can generally be described as North German and has similar linguistic and historic characteristics to other north German states, such asSchleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sc ...
. People in Vorpommern, as a result of that territory being a former province of Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
, tend to look slightly more towards Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within ci ...
and Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 sq ...
than people in Mecklenburg would.
Architecture
The cities are characterised by a certain "Hanseatic
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label=German language, Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Norther ...
" style also found in other parts of northern Germany (e.g. Lübeck
Lübeck (; Low German also ), officially the Hanseatic City of Lübeck (german: Hansestadt Lübeck), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 217,000 inhabitants, Lübeck is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and in the state ...
) as well as in countries bordering the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
like Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
(e.g. Tallinn
Tallinn () is the most populous and capital city of Estonia. Situated on a bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, Tallinn has a population of 437,811 (as of 2022) and administratively lies in the Harju '' ...
) or Latvia (e.g. Riga). A common feature of many towns in Mecklenburg and Vorpommern are red Brick Gothic churches and houses dating back to the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
. Also stepped and tailed gables are a typical feature of the Hanseatic
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label=German language, Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Norther ...
old towns, such as Stralsund, Wismar
Wismar (; Low German: ''Wismer''), officially the Hanseatic City of Wismar (''Hansestadt Wismar'') is, with around 43,000 inhabitants, the sixth-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, and the fourth-largest city ...
and Greifswald
Greifswald (), officially the University and Hanseatic City of Greifswald (german: Universitäts- und Hansestadt Greifswald, Low German: ''Griepswoold'') is the fourth-largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania after Rosto ...
.
The old towns are usually built around one or several market places with a church or the town hall. Often towns were founded at the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
, one of the many lakes or a river for logistical and trade motives.
Rural areas of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern are often characterized by Brick Gothic village churches and agricultural heritage, like brick homestead
Homestead may refer to:
*Homestead (buildings), a farmhouse and its adjacent outbuildings; by extension, it can mean any small cluster of houses
* Homestead (unit), a unit of measurement equal to 160 acres
*Homestead principle, a legal concept t ...
s, thatched roof houses, windmills
A windmill is a structure that converts wind power into rotational energy using vanes called sails or blades, specifically to mill grain (gristmills), but the term is also extended to windpumps, wind turbines, and other applications, in some par ...
, manor houses and castles.

Museums, art and theatres
 The largest publicly funded theatres in the state are the Mecklenburg State Theatre, the
The largest publicly funded theatres in the state are the Mecklenburg State Theatre, the Rostock People's Theatre
The Volkstheater Rostock ( en, Rostock People's Theatre, link=no) is the municipal theatre of the Hanseatic city of Rostock. It has three venues: the ''Großes Haus'', the ''Theater im Stadthafen'' and the ''Kleine Komödie'' and puts on plays, ...
, the Theatre of West Pomerania
The Theatre of West Pomerania (german: Theater Vorpommern) is a theatre in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern that is operated legally as a '' GmbH'', a form of public limited company. Its shareholders are the Hanseatic towns of Stralsu ...
, with venues in Stralsund, Putbus
Putbus () is a town on the southeastern coast of the island of Rügen, in the county of Vorpommern-Rügen in the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, close to the Baltic Sea. The town has 4,741 inhabitants and is a significant tourist destina ...
and Greifswald
Greifswald (), officially the University and Hanseatic City of Greifswald (german: Universitäts- und Hansestadt Greifswald, Low German: ''Griepswoold'') is the fourth-largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania after Rosto ...
, and the Mecklenburg State Theatre of Neustrelitz with venues in Neubrandenburg
Neubrandenburg (lit. ''New Brandenburg'', ) is a city in the southeast of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is located on the shore of a lake called Tollensesee and forms the urban centre of the Mecklenburg Lakeland.
The city is famous for its ...
and Neustrelitz
Neustrelitz (; East Low German: ''Niegenstrelitz'') is a town in the Mecklenburgische Seenplatte district in the state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is situated on the shore of the Zierker See in the Mecklenburg Lake District. From 17 ...
. All four theatres offer both drama and musical theatre as well as orchestral music.
Other important theatres are the Ernst Barlach Theatre of Güstrow, the Theatre of Parchim
Parchim (; Mecklenburgisch: ''Parchen'') is a town in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is the capital of the Ludwigslust-Parchim district. It was the birthplace of Helmuth von Moltke the Elder, to whom a monument was erected in 1876.
Foun ...
, the Anklam Theatre and the Wismar Theatre.
There are also many small theatres on the Baltic coast and in individual artist's villages and resorts (e.g. the popular concert pavilions at the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
). Since its growing importance for summer tourism, open-air theatres and festivals become more common again as well, such as the Störtebeker Festival on the island of Rügen
Rügen (; la, Rugia, ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
The "gateway" to Rügen island is the Hanseatic city of Stralsund, where ...
, and the ''Vineta Festival'' on Usedom.
Since 1993, the Störtebeker Festival has taken place in Ralswiek on the island of Rügen. It is Germany's most successful open-air theatre.
Notable museums include, for example, the Schwerin State Museum and the Pomeranian State Museum at Greifswald. The German Oceanographic Museum
The German Oceanographic Museum (german: Deutsche Meeresmuseum), also called the Museum for Oceanography and Fisheries, Aquarium (german: Museum für Meereskunde und Fischerei, Aquarium, links=no), in the Stralsund, Hanseatic town of Stralsund, ...
with its Ozeaneum in Stralsund is the most popular museum in northern Germany. Furthermore, the German Amber Museum in Ribnitz-Damgarten
Ribnitz-Damgarten () is a town in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany, situated on Lake Ribnitz (''Ribnitzer See''). Ribnitz-Damgarten is in the west of the district Vorpommern-Rügen.
The border between the historical regions of Mecklenburg and ...
, Rostock's Abbey of the Holy Cross and Rostock Art Gallery are of national importance. The oldest museum in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania is Stralsund's Cultural History Museum, the smallest is the Professor Wandschneider Sculpture Museum in Plau am See.
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern is home to many cultural events throughout the year. During summer, many open-air concerts and operas are open to visitors. The Mecklenburg-Vorpommern Festival (''Festspiele Mecklenburg-Vorpommern'') attracts a sizeable audience by performing classical concerts in parks, churches and castles.
Caspar David Friedrich, a famous romanticist
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate ...
painter born in Greifswald
Greifswald (), officially the University and Hanseatic City of Greifswald (german: Universitäts- und Hansestadt Greifswald, Low German: ''Griepswoold'') is the fourth-largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania after Rosto ...
, immortalised parts of the state in several of his paintings.
Language
Food and drinks
Like most German regions, Mecklenburg and Vorpommern have their own traditional dishes, often including fish, beef and pork. Rostock has its own type ofbratwurst
Bratwurst () is a type of German sausage made from pork or, less commonly, beef or veal. The name is derived from the Old High German ''Brätwurst'', from ''brät-'', finely chopped meat, and ''Wurst'', sausage, although in modern German it is o ...
called ''Rostocker Bratwurst''. A famous dish from Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Weste ...
is Bismarck Herring
Bismarck most often refers to:
* Otto von Bismarck (1815–1898), Prussian statesman and first Chancellor of Germany
* Bismarck, North Dakota, the capital of North Dakota, U.S.
* German battleship ''Bismarck'', a 1939 German World War II battlesh ...
. Rote Grütze
Rote can refer to:
People
*Jason Butler Rote, American TV writer
*Kyle Rote (1928–2002), American football player and father of:
*Kyle Rote, Jr. (born 1950), American soccer player
*Ryan Rote (born 1982), baseball pitcher
*Tobin Rote (1928–200 ...
is a popular dessert. The largest beer
Beer is one of the oldest and the most widely consumed type of alcoholic drink in the world, and the third most popular drink overall after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches, mainly derived from ce ...
breweries are '' Mecklenburgische Brauerei Lübz'' ( Lübzer Pils), ''Hanseatische Brauerei Rostock
Rostock (), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (german: link=no, Hanse- und Universitätsstadt Rostock), is the largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state, ...
'', ''Dargun
Dargun is a town in the Mecklenburgische Seenplatte district, in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Germany. It is situated km west of Demmin. It is famous for Dargun Palace, a former Cistercian abbey.
History
From 1815 to 1918 Dargun was part of ...
er Brauerei'' and ''Störtebeker Braumanufaktur'' ( Stralsund, multiple winner of the World Beer Cup
The World Beer Cup is an international beer competition organized by the Brewers Association, a trade group
A trade association, also known as an industry trade group, business association, sector association or industry body, is an organizat ...
). Besides, there are many smaller breweries and craft beer variations, such as the '' Mellenthin Castle Beer'' from Usedom Island.
Religion
As of 2020, the majority (82.4%) of the citizens of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania are not religious or adhere to other religions. 14.2% are members of theEvangelical Church in Germany
The Evangelical Church in Germany (german: Evangelische Kirche in Deutschland, abbreviated EKD) is a federation of twenty Lutheran, Reformed (Calvinist) and United (e.g. Prussian Union) Protestant regional churches and denominations in German ...
and 3.4% of the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
.
Following the Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
, led in Germany by Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Protestant Reformation and the namesake of Lutherani ...
, as well as a period of Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
rule, the traditional faith in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern is Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
, specifically Lutheranism
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
. There are also a number of Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
s and people of other faiths.
In May 2012 the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Mecklenburg merged with North Elbian Evangelical Lutheran Church and Pomeranian Evangelical Church
The Pomeranian Evangelical Church (german: link=no, Pommersche Evangelische Kirche; PEK) was a Protestant regional church in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, serving the citizens living in Hither Pomerania. The Pomeranian Evangelical C ...
into the new Evangelical Lutheran Church in Northern Germany.
Some parishes of the state belong to Evangelical Church of Berlin and Brandenburg.
There are also Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
communities, in the state capital of Schwerin
Schwerin (; Mecklenburgian Low German: ''Swerin''; Latin: ''Suerina'', ''Suerinum'') is the capital and second-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern as well as of the region of Mecklenburg, after Rostock. It ...
(including Wismar
Wismar (; Low German: ''Wismer''), officially the Hanseatic City of Wismar (''Hansestadt Wismar'') is, with around 43,000 inhabitants, the sixth-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, and the fourth-largest city ...
) and in the city of Rostock
Rostock (), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (german: link=no, Hanse- und Universitätsstadt Rostock), is the largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state, ...
. Historically, there were also synagogues in smaller towns, of which some are still preserved (like Röbel, Krakow am See
Krakow am See is a municipality in the Rostock district, in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Germany.
It is situated southeast of Güstrow at lake Krakower See
File:Krakow_Rathaus.jpg, Town hall in Krakow am See
File:Aussichtsturm_Krakow ...
and Boizenburg
Boizenburg () is a municipality in the Ludwigslust-Parchim district in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Germany. It is situated on the right bank of the Elbe, 53 km west of Ludwigslust, 25 km northeast of Lüneburg and 50 km east of ...
). The state's Jewish organisation is part of the Central Council of Jews in Germany
The Central Council of Jews in Germany (German name: Zentralrat der Juden in Deutschland) is a federation of German Jews. It was founded on 19 July 1950, as a response to the increasing isolation of German Jews by the international Jewish communi ...
.
Immigration
Largest immigrant communities:Vital statistics
*Births from January to September 2016 = 10,224 *Births from January to September 2017 = 9,836 *Deaths from January to September 2016 = 15,251 *Deaths from January to September 2017 = 15,532 *Natural growth from January to September 2016 = 5,027 *Natural growth from January to September 2017 = 5,696Education
Universities and colleges

 Mecklenburg-Vorpommern has the two oldest
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern has the two oldest universities
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, ...
of the Baltic Sea region, also among the oldest of Germany and all of Europe:
*University of Greifswald
The University of Greifswald (; german: Universität Greifswald), formerly also known as “Ernst-Moritz-Arndt University of Greifswald“, is a public research university located in Greifswald, Germany, in the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pom ...
(established 1456)
*University of Rostock
The University of Rostock (german: link=no, Universität Rostock) is a public university located in Rostock, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. Founded in 1419, it is the third-oldest university in Germany. It is the oldest university in continen ...
(established 1419)
Also, there are further colleges / technological universities:
* Fachhochschule des Mittelstands (FHM) in Rostock
Rostock (), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (german: link=no, Hanse- und Universitätsstadt Rostock), is the largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state, ...
and Schwerin
Schwerin (; Mecklenburgian Low German: ''Swerin''; Latin: ''Suerina'', ''Suerinum'') is the capital and second-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern as well as of the region of Mecklenburg, after Rostock. It ...
(private)
* Rostock University of Music and Theatre
* Hochschule Wismar (''University of Applied Sciences: Technology, Business and Design'')
* Fachhochschule Stralsund (''University of Applied Sciences'')
* Hochschule Neubrandenburg (''University of Applied Sciences'')
* Fachhochschule für öffentliche Verwaltung, Rechtspflege und Polizei Güstrow (''University of Administration, Judicature and Police in Güstrow'')
* Hochschule der Bundesagentur für Arbeit with its Schwerin
Schwerin (; Mecklenburgian Low German: ''Swerin''; Latin: ''Suerina'', ''Suerinum'') is the capital and second-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern as well as of the region of Mecklenburg, after Rostock. It ...
campus
* DesignSchule Schwerin with options to study design (private; game/fashion/media/web design)
Schools
The state's school system is centralised. There are two main types of schools, ''Regionalschule'' (for the majority of pupils) and ''Gymnasium'' (for the top 30% of each year's students, leading to the university entrance qualification " Abitur"). Besides, there are also independent schools, comprehensive schools and trade schools.Politics
Article 20 of the State Constitution states that theLandtag
A Landtag (State Diet) is generally the legislative assembly or parliament of a federated state or other subnational self-governing entity in German-speaking nations. It is usually a unicameral assembly exercising legislative competence in non ...
is the "site of political decision-making". The Mecklenburg-Vorpommern Landtag is elected democratically by the citizens of the state and sits for a 5-year legislative period. The seat of the Landtag is located at Schwerin Palace in Schwerin
Schwerin (; Mecklenburgian Low German: ''Swerin''; Latin: ''Suerina'', ''Suerinum'') is the capital and second-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern as well as of the region of Mecklenburg, after Rostock. It ...
. The essential functions of the Landtag are to elect the Minister-President
A minister-president or minister president is the head of government in a number of European countries or subnational governments with a parliamentary or semi-presidential system of government where they preside over the council of ministers. I ...
of the state; to discuss and decide on laws which have been proposed by the government, by any four members of the Landtag, or a people's initiative or petition for a referendum initiated directly by the people; and to control the state government.
Minister-President
 The executive is led by a cabinet, in turn led by a Minister-President, who is the official head of state and government. The election to determine the Minister-President is held no later than four weeks after the newly elected Landtag is convened.
The executive is led by a cabinet, in turn led by a Minister-President, who is the official head of state and government. The election to determine the Minister-President is held no later than four weeks after the newly elected Landtag is convened.
Landtag
 The last election of the
The last election of the Landtag of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
The Landtag of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern is the people's representative body or the state parliament of the German federal state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Thus it is also a constitutional body of the state.
The Landtag convenes in Schwerin and curre ...
took place on 26 September 2021. The SPD won a landslide plurality of almost 40% of votes, a nine percentage point increase from 2016. The opposition Alternative for Germany (AfD) remained the second largest party but declined to under 17%. The CDU recorded its worst ever result in the state with 13.3%, while The Left also declined to 10%. Alliance 90/The Greens and the Free Democratic Party (FDP) both won around 6% of votes and re-entered the Landtag after previously falling out in 2016 and 2011, respectively.
The Landtag has been led by Minister President Manuela Schwesig
Manuela Schwesig (' Frenzel, born 23 May 1974) is a German politician of the Social Democratic Party serving as Minister President of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern since 4 July 2017. She is the first woman to serve as head of government of this state. P ...
since 2017.
On 13 October 2021, Schwesig announced the SPD would enter coalition talks with The Left. She stated her motivations for reorienting the coalition as a desire for "a new departure", and described The Left as a "social, pragmatic party" with decisive policy overlap with the SPD. She said that The Left had been a reliable partner to the government even while in opposition, and had assumed "state-political responsibility" during the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
.
On 5 November 2021, the SPD and The Left agreed to a coalition government and plan to form a cabinet, which is to be approved by each party-congress by mid-November.
Economy
Thegross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is oft ...
(GDP) of the state was 44.5 billion euros in 2018, accounting for 1.3% of German economic output. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was 25,400 euros or 84% of the EU27 average in the same year. The GDP per employee was 83% of the EU average. The GDP per capita was the lowest of all German states.
Labour market
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern is the least densely populated and least industrial German state, being the sixth largest in area, but only the 14th in population. Formerly, unemployment has been negatively affected by the breakdown of non-competitive former GDR industries after the German reunification in the 1990s. As of 2018 unemployment is the lowest in more than 15 years while the economy is growing and the number of jobs is increasing continually. Growing sectors arebiotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used ...
, information technology
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange all kinds of Data (computing), data . and information. IT forms part of information and communications technology (ICT). An information te ...
, life sciences, maritime industry
Maritime transport (or ocean transport) and hydraulic effluvial transport, or more generally waterborne transport, is the transport of people (passengers) or goods (cargo) via waterways. Freight transport by sea has been widely used throu ...
and tourist
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
services.
In Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, approximately 732,200 people were gainfully employed in 2008 with 657,100 of them were white and blue collar workers. About 4,200 new jobs were created in 2007. Employees worked an average of 1,455 hours a year. The number of self-employed did not change in 2008. Three out of every four of all workers are employed in the service sector. In October 2018 the unemployment rate stood at 7.1% and was the third highest rate in Germany.
Tourism
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern is the top destination for intra-German tourism and is gaining importance forinternational tourism
International tourism is tourism that crosses national borders. Globalisation has made tourism a popular global leisure activity. The World Tourism Organization defines tourists as people "traveling to and staying in places outside their usual en ...
.
The main tourist regions are:
* Islands: Rugia and Usedom (Germany's two largest islands), Poel and Hiddensee
Hiddensee () is a car-free island in the Baltic Sea, located west of Germany's largest island, Rügen, on the German coast.
The island has about 1,000 inhabitants. It was a holiday destination for East German tourists during German Democratic ...
;
* Peninsula: Fischland-Darß-Zingst
Fischland-Darß-Zingst or Fischland-Darss-Zingst''Fischland-Darss-Zi ...
(with Ahrenshoop
Ahrenshoop is a municipality in the Vorpommern-Rügen district, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany on the Fischland-Darß-Zingst peninsula of the Baltic Sea. It used to be a small fishing village, but is today known for its tourism and as a holi ...
and Zingst
Zingst ( Polabian ''Sgoni'') is the easternmost portion of the three-part Fischland-Darß-Zingst Peninsula, located in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany, between the cities of Rostock and Stralsund on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea.
T ...
);
* Seaside resorts: Binz
Binz is the largest seaside resort on the German island of Rügen.
It is situated between the bay of Prorer Wiek and the ''Schmachter See'' (a lake) in the southeast of the island. To the north of Binz stretches the Schmale Heide (the "narrow he ...
, Boltenhagen, Graal-Müritz, Heringsdorf
Heringsdorf is a semi-urban municipality and a popular seaside resort on Usedom Island in Western Pomerania, Germany. It is also known by the name Kaiserbad ('' en, Imperial Spa'').
The municipality was formed in January 2005 out of the former ...
(including Bansin and Ahlbeck
Ahlbeck is a village (''Ortsteil'') of the Heringsdorf municipality on the island of Usedom on the Baltic coast. It is the easternmost of the so-called ''Kaiserbäder'' ("Imperial Spas") seaside resorts on the German part of the island, situa ...
), Heiligendamm
Heiligendamm () is a German seaside resort founded in 1793.
It is the oldest seaside spa in continental Europe. Heiligendamm is part of the town Bad Doberan in the States of Germany, state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and historically belongs to Mec ...
, Kühlungsborn, Warnemünde
(, literally ''Mouth of the Warnow'') is a seaside resort and a district of the city of Rostock in Mecklenburg, Germany. It is located on the Baltic Sea and, as the name implies, at the estuary of the river Warnow. is one of the world's busi ...
and Zinnowitz;
* Stettin Lagoon
Szczecin Lagoon ( pl, Zalew Szczeciński, german: Stettiner Haff, since 1945 sometimes also ''Oderhaff'' (Oder lagoon) or ''Pommersches Haff'' (Pomeranian lagoon)) is a lagoon in the Oder estuary, shared by Germany and Poland. It is separated f ...
: Ueckermünde;
* Hinterland: particularly the Mecklenburg Lakeland; and
* Cities: Stralsund and Wismar
Wismar (; Low German: ''Wismer''), officially the Hanseatic City of Wismar (''Hansestadt Wismar'') is, with around 43,000 inhabitants, the sixth-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, and the fourth-largest city ...
(both listed as UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
s), Schwerin
Schwerin (; Mecklenburgian Low German: ''Swerin''; Latin: ''Suerina'', ''Suerinum'') is the capital and second-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern as well as of the region of Mecklenburg, after Rostock. It ...
, Güstrow, Rostock
Rostock (), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (german: link=no, Hanse- und Universitätsstadt Rostock), is the largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state, ...
and Greifswald
Greifswald (), officially the University and Hanseatic City of Greifswald (german: Universitäts- und Hansestadt Greifswald, Low German: ''Griepswoold'') is the fourth-largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania after Rosto ...
, which have a diverse cultural heritage.
* Night sky: Mecklenburg-Vorpommern is home to some of the most pristine night skies in Germany, especially in the area near Nationalpark Müritz. It is a potential site for a Dark Sky Park.
As a reminder of its rich history, nearly 2,000 castles, palaces and manor house
A manor house was historically the main residence of the lord of the manor. The house formed the administrative centre of a manor in the European feudal system; within its great hall were held the lord's manorial courts, communal meals w ...
s exist in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, many of which are used as venues for public events like concerts and festivals, such as Festpiele MV (a classical music festival).
Medical tourism
Medical tourism refers to people traveling abroad to obtain medical treatment. In the past, this usually referred to those who traveled from less-developed countries to major medical centers in highly developed countries for treatment unavailable a ...
based on the clean air and idyllic settings by the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
has a growing importance to the regional tourism industry.
Rügen
Rügen (; la, Rugia, ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
The "gateway" to Rügen island is the Hanseatic city of Stralsund, where ...
File:Moonrise over Nationalpark Müritz.jpg, Moonrise over Nationalpark Müritz
File:48 Peenemuende A4 300915.jpg, V2 rocket
The V-2 (german: Vergeltungswaffe 2, lit=Retaliation Weapon 2), with the technical name ''Aggregat 4'' (A-4), was the world’s first long-range guided ballistic missile. The missile, powered by a liquid-propellant rocket engine, was developed ...
replica in Peenemünde. These rockets were the first man-made objects to reach space.
Sport
Main sporting attractions include theGerman football league
The German Football League (GFL) is an American football league in Germany and was formed in 1979. Playing rules are based on those of the American NCAA. In 1999, the league switched its name from ''American-Football-Bundesliga'' to ''German Foot ...
games of F.C. Hansa Rostock and the international sailing event Hanse Sail. If the bid for the 2012 summer Olympics in Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as ...
had been successful, the sailing competitions would have taken place off the coast of Rostock
Rostock (), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (german: link=no, Hanse- und Universitätsstadt Rostock), is the largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state, ...
.
Notable people
 Notable from Mecklenburg-Vorpommern include:
* Arts:
Notable from Mecklenburg-Vorpommern include:
* Arts: Ernst Barlach
Ernst Heinrich Barlach (2 January 1870 – 24 October 1938) was a German expressionist sculptor, medallist, printmaker and writer. Although he was a supporter of the war in the years leading to World War I, his participation in the war made hi ...
, Friedrich von Flotow
Friedrich Adolf Ferdinand, Freiherr von Flotow /flo:to/ (27 April 1812 – 24 January 1883) was a German composer. He is chiefly remembered for his opera ''Martha'', which was popular in the 19th century and the early part of the 20th.
Life
...
, Caspar David Friedrich, Marianne Hoppe, Till Lindemann
Till Lindemann (; born 4 January 1963) is a German singer, songwriter and poet. He is best known as the lead vocalist and lyricist of Neue Deutsche Härte band Rammstein and solo project Lindemann. Rammstein has sold over 25 million records ...
, Philipp Otto Runge
Philipp Otto Runge (; 1777–1810) was a German artist, a draftsman, painter, and color theorist. Runge and Caspar David Friedrich are often regarded as the leading painters of the German Romantic movement.Koerner, Joseph Leo. 1990. ''Caspar Dav ...
* Business: Ernst Heinkel
Dr. Ernst Heinkel (24 January 1888 – 30 January 1958) was a German aircraft designer, manufacturer, '' Wehrwirtschaftsführer'' in Nazi Germany, and member of the Nazi party. His company Heinkel Flugzeugwerke produced the Heinkel He 178, th ...
, Carl Heinrich von Siemens
Carl Heinrich von Siemens (often just Carl von Siemens) (3 March 1829 – 21 March 1906) was a German entrepreneur.
He was born in Menzendorf, Mecklenburg, one of the fourteen children of a tenant farmer of the Siemens family, an old family of ...
, Leonhard Tietz, Georg Wertheim
Georg Wertheim (11 February 1857 in Stralsund – 31 December 1939 in Berlin) was a German merchant and founder of the popular Wertheim chain of department stores.
Early years
Wertheim grew up in Stralsund. After being an apprentice at ''W ...
* Literature: Ernst Moritz Arndt
Ernst Moritz Arndt (26 December 1769 – 29 January 1860) was a German nationalist historian, writer and poet. Early in his life, he fought for the abolition of serfdom, later against Napoleonic dominance over Germany. Arndt had to flee to Swe ...
, John Brinckman
John Brinckman, originally Johann Friedrich Brinckmann (3 July 1814, Rostock - 20 September 1870, Güstrow) was a German author of humorous works in Plattdeutsch.
Biography
He was the second of nine children born to Caspar Christoph Michael ...
, Hans Fallada, Walter Kempowski, Fritz Reuter, Rudolf Tarnow, Ehm Welk
Emil "Ehm" Welk (August 29, 1884 – December 19, 1966) was a German journalist, writer, professor and founder of ''Volkshochschulen'' (adult education centres). He became known for his work ''Die Heiden von Kummerow'' (''The Heathens of Kummer ...
* Politics: Ernst Moritz Arndt
Ernst Moritz Arndt (26 December 1769 – 29 January 1860) was a German nationalist historian, writer and poet. Early in his life, he fought for the abolition of serfdom, later against Napoleonic dominance over Germany. Arndt had to flee to Swe ...
, Dietmar Bartsch, Joachim Gauck
Joachim Wilhelm Gauck (; born 24 January 1940) is a German politician and civil rights activist who served as President of Germany from 2012 to 2017. A former Lutheran pastor, he came to prominence as an anti-communist civil rights activist in E ...
, Egon Krenz
Egon Rudi Ernst Krenz (; born 19 March 1937) is a German former politician who was the last Communist leader of the German Democratic Republic (East Germany) during the Revolutions of 1989. He succeeded Erich Honecker as the General Secretary ...
, Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher
Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher, Fürst von Wahlstatt (; 21 December 1742 – 12 September 1819), ''Graf'' (count), later elevated to ''Fürst'' (sovereign prince) von Wahlstatt, was a Prussian '' Generalfeldmarschall'' (field marshal). He earne ...
, Angela Merkel
Angela Dorothea Merkel (; ; born 17 July 1954) is a German former politician and scientist who served as Chancellor of Germany from 2005 to 2021. A member of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU), she previously served as Leader of the Opp ...
, Helmuth von Moltke the Elder, Harald Ringstorff
* Science: Theodor Billroth
Christian Albert Theodor Billroth (26 April 18296 February 1894) was a German surgeon and amateur musician.
As a surgeon, he is generally regarded as the founding father of modern abdominal surgery. As a musician, he was a close friend and conf ...
, Friedrich Chrysander
Karl Franz Friedrich Chrysander (8 July 1826 – 3 September 1901) was a German music historian, critic and publisher, whose edition of the works of George Frideric Handel and authoritative writings on many other composers established him as a ...
, Walther Flemming
Walther Flemming (21 April 1843 – 4 August 1905) was a German biologist and a founder of cytogenetics.
He was born in Sachsenberg (now part of Schwerin) as the fifth child and only son of the psychiatrist Carl Friedrich Flemming (1799–18 ...
, Gottlob Frege
Friedrich Ludwig Gottlob Frege (; ; 8 November 1848 – 26 July 1925) was a German philosopher, logician, and mathematician. He was a mathematics professor at the University of Jena, and is understood by many to be the father of analytic ph ...
, Otto Lilienthal
Karl Wilhelm Otto Lilienthal (23 May 1848 – 10 August 1896) was a German pioneer of aviation who became known as the "flying man". He was the first person to make well-documented, repeated, successful flights with gliders, therefore making ...
, Gustav Mie
Gustav Adolf Feodor Wilhelm Ludwig Mie (; 29 September 1868 – 13 February 1957) was a German physicist.
Life
Mie was born in Rostock, Mecklenburg-Schwerin, Germany in 1868. From 1886 he studied mathematics and physics at the University of ...
, Ferdinand von Mueller, Paul Pogge, Carl Wilhelm Scheele
Carl Wilhelm Scheele (, ; 9 December 1742 – 21 May 1786) was a Swedish German pharmaceutical chemist.
Scheele discovered oxygen (although Joseph Priestley published his findings first), and identified molybdenum, tungsten, barium, hyd ...
, Heinrich Schliemann, Johannes Stark
Johannes Stark (, 15 April 1874 – 21 June 1957) was a German physicist who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1919 "for his discovery of the Doppler effect in canal rays and the splitting of spectral lines in electric fields". This phe ...
* Sports: Tim Borowski, Andreas Dittmer, Thomas Doll, Carsten Jancker, Marita Koch, Toni Kroos
Toni Kroos (born 4 January 1990) is a German professional footballer who plays as a midfielder for La Liga club Real Madrid. Kroos plays mainly as a central midfielder, but has also been deployed as a deep-lying playmaker in his career. He is kn ...
, Sebastian Sylvester
Sebastian Sylvester (born 9 July 1980) is a German former professional boxer who competed from 2002 to 2011 and held the International Boxing Federation, IBF middleweight title from 2009 to 2011.
Professional career
In March 2007 Sylvester ret ...
, Jan Ullrich
Jan Ullrich (; born 2 December 1973) is a German former professional road bicycle racer. Ullrich won gold and silver medals in the 2000 Summer Olympics in Sydney, Australia, Sydney. He won the 1999 Vuelta a España and the HEW Cyclassics in fro ...
, Jens Voigt
Jens Voigt (; born 17 September 1971) is a German former professional road bicycle racer and, upon retirement, became a cycling sports broadcast commentator. During his cycling career, Voigt raced for several teams, the last one being UCI ProTe ...
Miscellaneous
* Mecklenburg-Vorpommern is Germany's number-one tourist location, the main destinations being theBaltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
coastline with islands such as Rügen
Rügen (; la, Rugia, ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
The "gateway" to Rügen island is the Hanseatic city of Stralsund, where ...
or Usedom, spa towns like Heiligendamm
Heiligendamm () is a German seaside resort founded in 1793.
It is the oldest seaside spa in continental Europe. Heiligendamm is part of the town Bad Doberan in the States of Germany, state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and historically belongs to Mec ...
, Kühlungsborn, Boltenhagen or Warnemünde
(, literally ''Mouth of the Warnow'') is a seaside resort and a district of the city of Rostock in Mecklenburg, Germany. It is located on the Baltic Sea and, as the name implies, at the estuary of the river Warnow. is one of the world's busi ...
and the Mecklenburg Lake District
The Mecklenburg Lake Plateau or Mecklenburg Lakeland
- Federal Ministry of Economics ...
. It also offers important historical cities, such as Stralsund, - Federal Ministry of Economics ...
Wismar
Wismar (; Low German: ''Wismer''), officially the Hanseatic City of Wismar (''Hansestadt Wismar'') is, with around 43,000 inhabitants, the sixth-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, and the fourth-largest city ...
, Greifswald
Greifswald (), officially the University and Hanseatic City of Greifswald (german: Universitäts- und Hansestadt Greifswald, Low German: ''Griepswoold'') is the fourth-largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania after Rosto ...
and Rostock
Rostock (), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (german: link=no, Hanse- und Universitätsstadt Rostock), is the largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state, ...
as former Hanseatic
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label=German language, Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Norther ...
cities − or Schwerin
Schwerin (; Mecklenburgian Low German: ''Swerin''; Latin: ''Suerina'', ''Suerinum'') is the capital and second-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern as well as of the region of Mecklenburg, after Rostock. It ...
, Güstrow, Ludwigslust
Ludwigslust () is a central castle town of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany, 40 km south of Schwerin. Since 2011 it has been part of the Ludwigslust-Parchim district.
Ludwigslust is part of the Hamburg Metropolitan Region. The former royal re ...
and Neustrelitz
Neustrelitz (; East Low German: ''Niegenstrelitz'') is a town in the Mecklenburgische Seenplatte district in the state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is situated on the shore of the Zierker See in the Mecklenburg Lake District. From 17 ...
as former residences.
* The first rocket
A rocket (from it, rocchetto, , bobbin/spool) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely fr ...
s to reach outer space
Outer space, commonly shortened to space, is the expanse that exists beyond Earth and its atmosphere and between celestial bodies. Outer space is not completely empty—it is a near-perfect vacuum containing a low density of particles, pred ...
were launched in 1944 during World War II in Peenemünde
Peenemünde (, en, " Peene iverMouth") is a municipality on the Baltic Sea island of Usedom in the Vorpommern-Greifswald district in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is part of the ''Amt'' (collective municipality) of Usedom-Nord. The commu ...
on the present-day territory of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern.
* During the chancellorship of Angela Merkel
Angela Dorothea Merkel (; ; born 17 July 1954) is a German former politician and scientist who served as Chancellor of Germany from 2005 to 2021. A member of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU), she previously served as Leader of the Opp ...
, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern hosted the first official public meeting with President George W. Bush in 2006 and the 33rd G8 summit
The 33rd G8 summit was held at Kempinski Grand Hotel, 6–8 June 2007. The summit took place in Heiligendamm in the Northern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern on the Baltic Coast. The locations of previous G8 summits to have been hosted by ...
in 2007. Both political events were financed by state and federal budgets.
Gallery
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
Image:Baederarchitektur-Binz 1658.jpg, Binz
Binz is the largest seaside resort on the German island of Rügen.
It is situated between the bay of Prorer Wiek and the ''Schmachter See'' (a lake) in the southeast of the island. To the north of Binz stretches the Schmale Heide (the "narrow he ...
− typical German resort architecture
Resort architecture (german: Bäderarchitektur) is an architectural style that is especially characteristic of spas and seaside resorts on the German Baltic coast. The style evolved since the foundation of Heiligendamm in 1793, and flourished espec ...
(''Bäderarchitektur'') at the Baltic Sea
Image:Rostock-Warnemünde, Seepromenade, 489-595.jpg, Beach Promenade of Warnemünde
(, literally ''Mouth of the Warnow'') is a seaside resort and a district of the city of Rostock in Mecklenburg, Germany. It is located on the Baltic Sea and, as the name implies, at the estuary of the river Warnow. is one of the world's busi ...
, part of Rostock
Rostock (), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (german: link=no, Hanse- und Universitätsstadt Rostock), is the largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state, ...
Image:Rostock.jpg, Rostock
Rostock (), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (german: link=no, Hanse- und Universitätsstadt Rostock), is the largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state, ...
− Shopping street
Image:Kerkhoffhaus.jpg, Rostock
Rostock (), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (german: link=no, Hanse- und Universitätsstadt Rostock), is the largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state, ...
− Brick Gothic gable house
Image:Greifswald - Marktplatz 1.jpg, Greifswald
Greifswald (), officially the University and Hanseatic City of Greifswald (german: Universitäts- und Hansestadt Greifswald, Low German: ''Griepswoold'') is the fourth-largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania after Rosto ...
− Gable
A gable is the generally triangular portion of a wall between the edges of intersecting roof pitches. The shape of the gable and how it is detailed depends on the structural system used, which reflects climate, material availability, and aesth ...
houses at market square
Image:Schwerin 20090410.jpg, Schwerin
Schwerin (; Mecklenburgian Low German: ''Swerin''; Latin: ''Suerina'', ''Suerinum'') is the capital and second-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern as well as of the region of Mecklenburg, after Rostock. It ...
− capital of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Image:Wismar hafen.jpg, Harbour of Wismar
Wismar (; Low German: ''Wismer''), officially the Hanseatic City of Wismar (''Hansestadt Wismar'') is, with around 43,000 inhabitants, the sixth-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, and the fourth-largest city ...
, a historical Hanseatic city sharing its World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
status with Stralsund
Image:Grabow Rathaus.jpg, Grabow
Grabow () is a town in the Ludwigslust-Parchim district, in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Germany. It is situated on the river Elde, 7 km (4.35 mi) southeast of Ludwigslust, and 34 km (21.12 mi) northwest of Wittenberge. It ...
− Half timbered town hall
Image:Marienkirche Neubrandenburg1.jpg, Neubrandenburg
Neubrandenburg (lit. ''New Brandenburg'', ) is a city in the southeast of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is located on the shore of a lake called Tollensesee and forms the urban centre of the Mecklenburg Lakeland.
The city is famous for its ...
− Concert Church St. Marien
Image:Benz Holländer Windmühle Berg Dorf Schmollensee.jpg, Usedom − Benz windmill, one of many windmills in MV
Image:Schloss Ralswiek 2 crop.jpg, Rügen
Rügen (; la, Rugia, ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
The "gateway" to Rügen island is the Hanseatic city of Stralsund, where ...
− Ralswiek castle, one of many castles in MV
Image:Jagdschloss Granitz 4.jpg, Rügen
Rügen (; la, Rugia, ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
The "gateway" to Rügen island is the Hanseatic city of Stralsund, where ...
− Granitz Hunting Castle near Binz
Binz is the largest seaside resort on the German island of Rügen.
It is situated between the bay of Prorer Wiek and the ''Schmachter See'' (a lake) in the southeast of the island. To the north of Binz stretches the Schmale Heide (the "narrow he ...
Image:Ahlbeck hotel ahlbecker hof.jpg, Ahlbeck
Ahlbeck is a village (''Ortsteil'') of the Heringsdorf municipality on the island of Usedom on the Baltic coast. It is the easternmost of the so-called ''Kaiserbäder'' ("Imperial Spas") seaside resorts on the German part of the island, situa ...
− Hotel "Ahlbecker Hof" ( Usedom Island)
Image:Steilküste bei Ahrenshoop.jpg, Ahrenshoop
Ahrenshoop is a municipality in the Vorpommern-Rügen district, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany on the Fischland-Darß-Zingst peninsula of the Baltic Sea. It used to be a small fishing village, but is today known for its tourism and as a holi ...
− steep coast, peninsula of Fischland-Darß-Zingst
Fischland-Darß-Zingst or Fischland-Darss-Zingst''Fischland-Darss-Zi ...
Image:Kreidefelsen Ruegen.jpg, Rügen
Rügen (; la, Rugia, ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
The "gateway" to Rügen island is the Hanseatic city of Stralsund, where ...
Island − Jasmund National Park
The Jasmund National Park (German: ''Nationalpark Jasmund'') is a nature reserve on the Jasmund peninsula, in the northeast of Rügen island in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is famous for containing the largest chalk cliffs in Germany, the ...
Image:Hiddensee Dornbusch.jpg, Hiddensee
Hiddensee () is a car-free island in the Baltic Sea, located west of Germany's largest island, Rügen, on the German coast.
The island has about 1,000 inhabitants. It was a holiday destination for East German tourists during German Democratic ...
Island − Dornbusch Lighthouse
Image:Müritz Röbel 1.jpg, Müritz Lake − near Röbel
See also
* History of Pomerania * List of places in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern *List of towns in Vorpommern
The List of towns in Western Pomerania includes all towns in present-day German Pomerania, and thus excludes towns which lie west of the Oder river, but east of the Oder-Neisse line (''Stettiner Zipfel'' area), and thus historically are associ ...
* Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg (; nds, label= Low German, Mękel(n)borg ) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schweri ...
* Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
References
External links
Official Mecklenburg-Vorpommern portal
* ;Tourism
Off to MV - Official tourism website of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
{{Authority control 1946 establishments in Germany NUTS 1 statistical regions of the European Union States and territories established in 1946 States of Germany