McDonnell F3H Demon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The McDonnell F3H Demon is a subsonic swept-wing
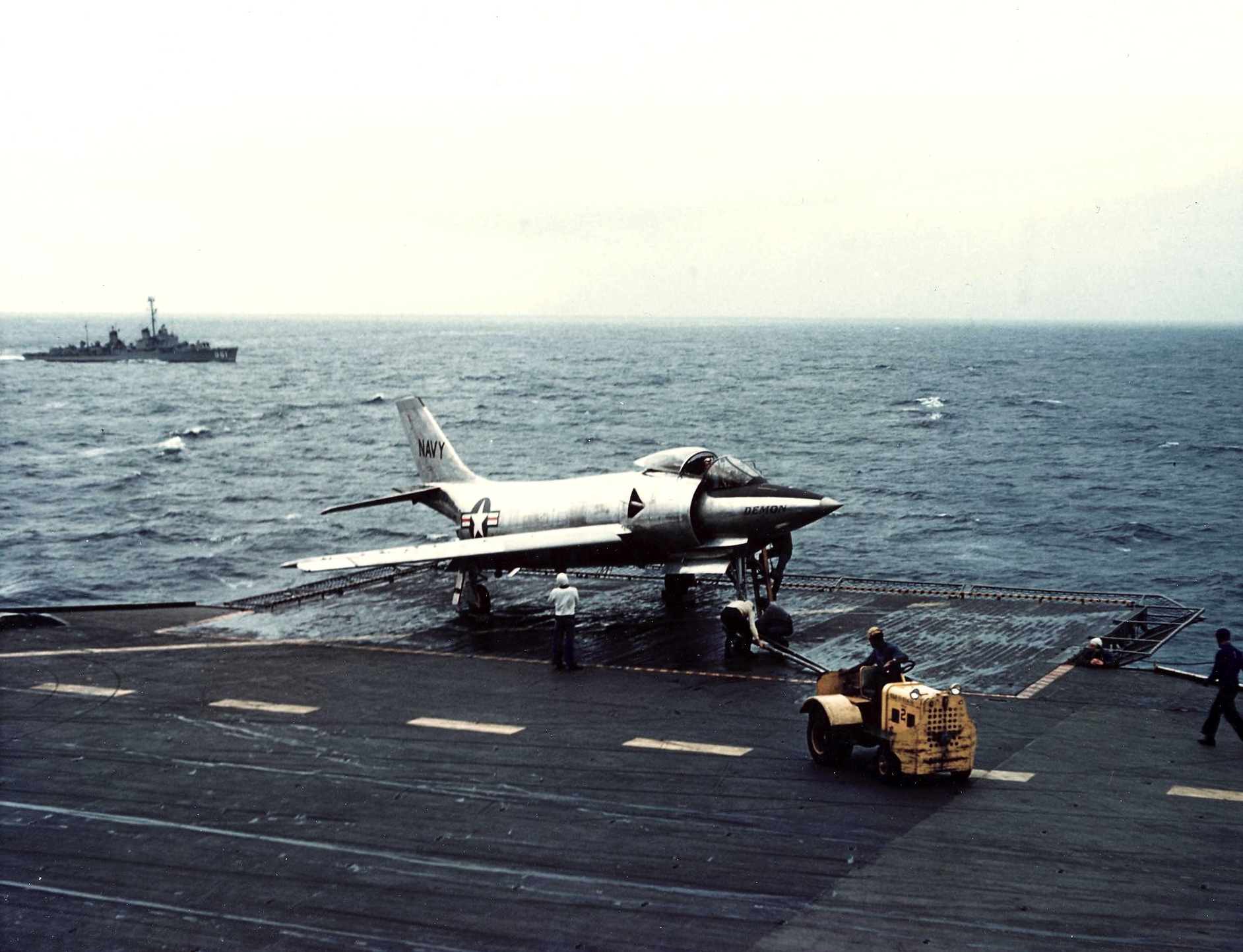

 Development work began in 1949, using a swept wing from the start rather than adapting a straight-winged design as was done with the
Development work began in 1949, using a swept wing from the start rather than adapting a straight-winged design as was done with the
''Time'' magazine called the Navy's grounding of all Westinghouse-powered F3H-1 Demons a "fiasco", with 21 unflyable planes that could be used only for Navy ground training at a loss of $200 million. One high point of the J40 was the 1955 setting of an unofficial time-to-climb record, in a Demon, of in 71 seconds. The proposed F3H-1P reconnaissance version was never built. The J40 program was terminated sometime in 1955. All the aircraft it was to power were either canceled or redesigned to use other engines, notably the J57 and the J71. The F4D Skyray had been designed to accept larger engines in case the J40 did not work out, and was eventually powered by the
 ;XF3H-1
: Prototype single-seat clear-weather interceptor fighter. Powered by ( with afterburner) Westinghouse XJ40-WE-6 engine. Two built.Angelucci and Bowers 1987, p. 305.
;F3H-1N
: Initial production version. Single-seat all-weather fighter version, powered by ( with afterburner) J40-WE-22 engine. 58 built.
;F3H-1P
: Proposed reconnaissance version of F3H-1. Never built.
;F3H-2N
: All-weather fighter powered by ( Allison J71-A-2 engine and equipped to carry
;XF3H-1
: Prototype single-seat clear-weather interceptor fighter. Powered by ( with afterburner) Westinghouse XJ40-WE-6 engine. Two built.Angelucci and Bowers 1987, p. 305.
;F3H-1N
: Initial production version. Single-seat all-weather fighter version, powered by ( with afterburner) J40-WE-22 engine. 58 built.
;F3H-1P
: Proposed reconnaissance version of F3H-1. Never built.
;F3H-2N
: All-weather fighter powered by ( Allison J71-A-2 engine and equipped to carry
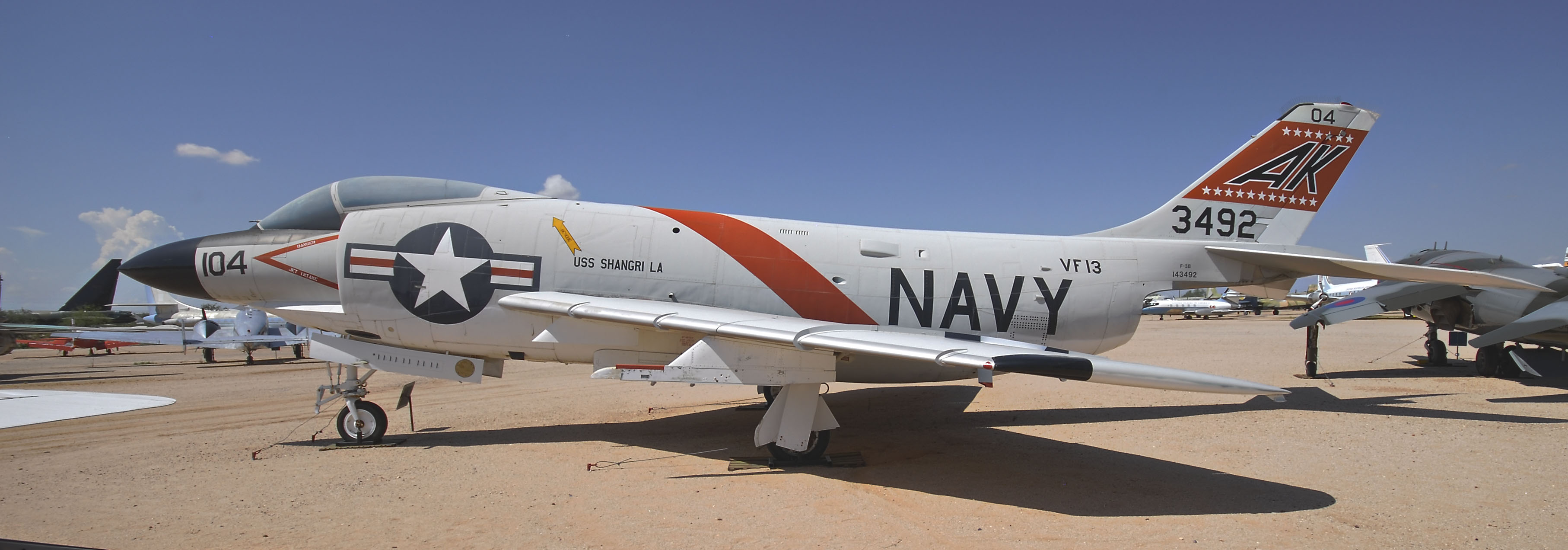 ;F3H-2M
*BuNo 137078 - National Museum Naval Aviation at
;F3H-2M
*BuNo 137078 - National Museum Naval Aviation at "F3H Demon/145221."
''Pima Air & Space Museum.'' Retrieved: 15 January 2015.
''US Navy F-4 Phantom II MiG Killers 1965–70, Part 1'' (Osprey Combat Aircraft).
London: Osprey Publishing, 2001. . *Gunston, Bill. ''Fighters of the Fifties''. Cambridge, UK: Patrick Stephens Limited, 1981. .
"Naval Aircraft: Demon".
''Naval Aviation News'', March 1974, pp. 22–23. *Spick, Mike. "A Demon Possessed". ''
''F3H Demon Index''Demon Drivers
* {{Authority control Carrier-based aircraft
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
carrier-based jet fighter aircraft. The successor to the F2H Banshee
The McDonnell F2H Banshee (company designation McDonnell Model 24) is an American single-seat carrier-based jet fighter aircraft deployed by the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps from 1948 to 1961. A development of the FH Phanto ...
, the Demon was originally designed to use the Westinghouse J40 engine, but had to be redesigned to accept the Allison J71 after the J40 suffered severe problems and was ultimately abandoned.Angelucci and Bowers 1987, p. 304. Though it lacked sufficient power for supersonic performance, it complemented day fighters such as the Vought F8U Crusader
The Vought F-8 Crusader (originally F8U) is a single-engine, supersonic, carrier-based air superiority jet aircraft built by Vought for the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps (replacing the Vought F7U Cutlass), and for the French ...
and Grumman F11F Tiger as an all-weather, missile-armed interceptor until 1964.
It was withdrawn before it could serve in Vietnam when both it and the Crusader were replaced on ''Forrestal''-class and similar supercarriers by the McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II
The McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II is an American tandem two-seat, twin-engine, all-weather, long-range supersonic jet interceptor and fighter-bomber originally developed by McDonnell Aircraft for the United States Navy.Swanborough and B ...
. McDonnell's Phantom, which was equally capable against ground, fighter, and bomber targets, bears a strong family resemblance, as it was conceived as an advanced development of the Demon. The supersonic United States Air Force F-101 Voodoo
The McDonnell F-101 Voodoo is a supersonic jet fighter which served the United States Air Force (USAF) and the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF).
Initially designed by McDonnell Aircraft Corporation as a long-range bomber escort (known as a ...
was similar in layout, but was derived from the earlier XF-88 Voodoo, which also influenced the Demon's layout.
Development

 Development work began in 1949, using a swept wing from the start rather than adapting a straight-winged design as was done with the
Development work began in 1949, using a swept wing from the start rather than adapting a straight-winged design as was done with the Grumman F9F Panther
The Grumman F9F Panther is one of the United States Navy's first successful carrier-based jet fighters, as well as Grumman’s first jet fighter. A single-engined, straight-winged day fighter, it was armed with four cannons and could carry a wi ...
. A competing contract was also awarded for the delta wing Douglas F4D Skyray
The Douglas F4D Skyray (later redesignated F-6 Skyray) is an American carrier-based fighter/ interceptor built by the Douglas Aircraft Company. Although it was in service for a relatively short time (1956–1964) and never entered combat, it w ...
. The Skyray, with a top speed of , would become the Navy's first fighter to fly supersonic in level flight, while the Demon would never reach that level of performance. The original design work was based at its predecessor, the F2H Banshee
The McDonnell F2H Banshee (company designation McDonnell Model 24) is an American single-seat carrier-based jet fighter aircraft deployed by the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps from 1948 to 1961. A development of the FH Phanto ...
. However, departing from its tradition of using two engines, the Demon would result in McDonnell's only single-engined carrier-based fighter, adopting under some Navy pressure, the Westinghouse J40 engine. That engine was being promoted by the Navy for its next generation of aircraft, and was to have thrust of over 11,000 lbf (49 kN)—three times that of the engines in the F2H Banshee. It was the first swept-wing design produced by McDonnell and among the first U.S. aircraft to have missile armament.
The Navy desperately needed a high performance fighter to meet the challenge of the swept-wing MiG-15
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-15 (russian: Микоя́н и Гуре́вич МиГ-15; USAF/DoD designation: Type 14; NATO reporting name: Fagot) is a jet fighter aircraft developed by Mikoyan-Gurevich for the Soviet Union. The MiG-15 was one of ...
encountered over Korea. Production of the F3H-1N was hastily ordered even before the first flight of the XF3H-1 prototype on 7 August 1951 by test pilot Robert Edholm. The first test flights of the operational design did not occur until January 1953, by which time the Korean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks a ...
was winding down.
The F3H Demon was originally designed around Navy's ambitious new Westinghouse J40 which was to offer enough power to use just one engine in a number of new aircraft designs. But the engine would ultimately fail to produce the promised thrust or run reliably. The engine was a major disappointment, producing only half of the expected power. Worse, it was temperamental and unreliable. Of 35 F3H-1N aircraft flown with the J40 engine, eight were involved in major accidents. The first production Demons were grounded after the loss of six aircraft and four pilots.Boeing.com: F3H/F-3 Demon Fighter''Time'' magazine called the Navy's grounding of all Westinghouse-powered F3H-1 Demons a "fiasco", with 21 unflyable planes that could be used only for Navy ground training at a loss of $200 million. One high point of the J40 was the 1955 setting of an unofficial time-to-climb record, in a Demon, of in 71 seconds. The proposed F3H-1P reconnaissance version was never built. The J40 program was terminated sometime in 1955. All the aircraft it was to power were either canceled or redesigned to use other engines, notably the J57 and the J71. The F4D Skyray had been designed to accept larger engines in case the J40 did not work out, and was eventually powered by the
Pratt & Whitney J57
The Pratt & Whitney J57 (company designation: JT3C) is an axial-flow turbojet engine developed by Pratt & Whitney in the early 1950s. The J57 (first run January 1950) was the first 10,000 lbf (45 kN) thrust class engine in the United State ...
. But no other engine could simply be fitted into the old Demons, as both the wings and fuselage would have to be redesigned and enlarged. The best alternative turned out to be the Allison J71 engine which was also used in the Douglas B-66 Destroyer
The Douglas B-66 Destroyer is a light bomber that was designed and produced by the American aviation manufacturer Douglas Aircraft Company.
The B-66 was developed for the United States Air Force (USAF) and is heavily based upon the United Stat ...
. Subsequent F3Hs with this powerplant were designated the F3H-2N. In service, the J71 proved problematic, providing insufficient power for an aircraft of the Demon's size. The engine also suffered from frequent flameout
In aviation, a flameout (or flame-out) is the run-down of a jet engine or other turbine engine due to the extinction of the flame in its combustor. The loss of flame can have a variety of causes, such as fuel starvation, excessive altitude, com ...
s and compressor stalls. The first J71-powered Demon flew in October 1954. Another significant problem was the reliability of the ejection seat
In aircraft, an ejection seat or ejector seat is a system designed to rescue the pilot or other crew of an aircraft (usually military) in an emergency. In most designs, the seat is propelled out of the aircraft by an explosive charge or rock ...
s: initial versions were found to be unreliable and were eventually replaced with Martin-Baker
Martin-Baker Aircraft Company Limited is a British manufacturer of ejection seats and safety-related equipment for aviation. The company's origins were originally as an aircraft manufacturer before becoming a pioneer in the field of ejection s ...
ejection seats that were becoming the standard Navy seat of choice due to their higher performance at low altitude and better reliability.
Despite the problems, the Navy ordered 239 F3H-2s, and the first were deployed in March 1956. 519 Demons were built up to the end of production in November 1959. It was not the Navy's first all-weather interceptor with radar (the AN/APG-51 air interception set was used first on the F2H-4 Banshee). The F3H-2 Demon had the AN/APG-51A, later upgraded to the 51-B version with a tunable magnetron then on to 51-C with better counter-measures in the receiver.
The F3H-2N's standard armament was four 20 mm (.79 in) Colt Mk 12 cannon
{{Infobox weapon
, name= Colt Mk 12
, image= 20 mm Mk 12 cannon of RNZAF A-4K Skyhawk 1984.jpg
, image_size =
, caption= Mk 12 cannon of a RNZAF Douglas A-4K Skyhawk.
, origin= United States
, type= Autocannon
, is_ranged= yes
, service= 1950 ...
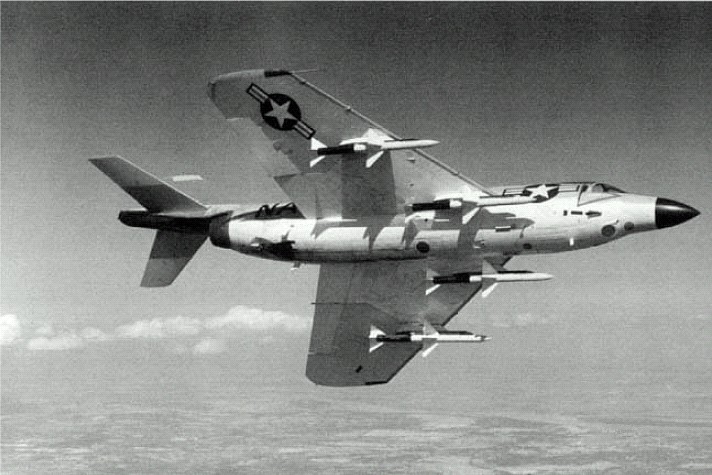
s. In later years, the upper two cannons were often omitted to save weight. Later models, redesignated F3H-2M, were equipped to fire the Raytheon AAM-N-2 Sparrow and later the Sidewinder air-to-air missiles. Deployed aircraft carried both types of missiles, the Sparrow on the inboard rails and the Sidewinder outboard. Cannons were not used in carrier air defense applications, but they were installed and armed when situations (such as the Cuban Missile Crisis) dictated, and where the aircraft might be deployed against surface targets.
A reconnaissance
In military operations, reconnaissance or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, terrain, and other activities.
Examples of reconnaissance include patrolling by troops (skirmisher ...
version, the F3H-2P, was proposed, but never built. It remained the Navy's front-line fighter until 1962, when it was succeeded by the F-4 Phantom II (which was a development of a proposed "Super Demon", a larger and much heavier version of the F3H). Developed during the Korean War to counter the MiG-15, it did not claim any aerial victories with missiles or dogfights, although it flew over Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
and Quemoy
Kinmen, alternatively known as Quemoy, is a group of islands governed as a county by the Republic of China (Taiwan), off the southeastern coast of mainland China. It lies roughly east of the city of Xiamen in Fujian, from which it is separate ...
in 1958.
In 1962, the F3H was redesignated F-3. The F3H-2N became the F-3C, the F3H-2M became MF-3B, and the F3H-2 changed to F-3B.
The last Demon-equipped squadron, VF-161 'Chargers', traded their F-3s for F-4 Phantom IIs in September 1964.
Due to excellent visibility from the cockpit, the Demon earned the nickname "The Chair". Demon pilots were known colloquially as "Demon Drivers" and those who worked on the aircraft were known as "Demon Doctors". The unfavorable power-to-weight ratio gave rise to the less flattering nickname "lead sled", sometimes shortened to "sled".
Variants

 ;XF3H-1
: Prototype single-seat clear-weather interceptor fighter. Powered by ( with afterburner) Westinghouse XJ40-WE-6 engine. Two built.Angelucci and Bowers 1987, p. 305.
;F3H-1N
: Initial production version. Single-seat all-weather fighter version, powered by ( with afterburner) J40-WE-22 engine. 58 built.
;F3H-1P
: Proposed reconnaissance version of F3H-1. Never built.
;F3H-2N
: All-weather fighter powered by ( Allison J71-A-2 engine and equipped to carry
;XF3H-1
: Prototype single-seat clear-weather interceptor fighter. Powered by ( with afterburner) Westinghouse XJ40-WE-6 engine. Two built.Angelucci and Bowers 1987, p. 305.
;F3H-1N
: Initial production version. Single-seat all-weather fighter version, powered by ( with afterburner) J40-WE-22 engine. 58 built.
;F3H-1P
: Proposed reconnaissance version of F3H-1. Never built.
;F3H-2N
: All-weather fighter powered by ( Allison J71-A-2 engine and equipped to carry AIM-9 Sidewinder
The AIM-9 Sidewinder (where "AIM" stands for "Air Intercept Missile") is a short-range air-to-air missile which entered service with the US Navy in 1956 and subsequently was adopted by the US Air Force in 1964. Since then the Sidewinder has prove ...
air-to-air missiles. 239 built. Redesignated F-3C in 1962.Angelucci and Bowers 1957, pp. 304–306.
;F3H-2M
: Derivative of F3H-2N armed with four AIM-7 Sparrow air-to-air missiles. 80 built. Redesignated ''MF-3B'' in 1962.
;F3H-2
: Single-seat strike fighter version, retaining Sidewinder and Sparrow capability of the −2M/N and adding payload of 6,000 lb (2,730 kg) bombs or rockets. 239 built. Redesignated ''F-3B'' in 1962.
;F3H-2P
: Proposed photo-reconnaissance version of −2. Unbuilt.
;F3H-3
: Proposed version with the General Electric J73
The General Electric J73 turbojet was developed by General Electric from the earlier J47 engine. Its original USAF designation was J47-21, but with innovative features including variable inlet guide vanes, double-shell (inner and outer) combusto ...
engine. Unbuilt.
Operators
; *United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
Aircraft on display
 ;F3H-2M
*BuNo 137078 - National Museum Naval Aviation at
;F3H-2M
*BuNo 137078 - National Museum Naval Aviation at Naval Air Station Pensacola
Naval Air Station Pensacola or NAS Pensacola (formerly NAS/KNAS until changed circa 1970 to allow Nassau International Airport, now Lynden Pindling International Airport, to have IATA code NAS), "The Cradle of Naval Aviation", is a United State ...
, Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
.
;F3H-2N
*BuNo 133566 - USS Intrepid Museum in New York City, New York
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
.
*BuNo 145221 - Pima Air & Space Museum
The Pima Air & Space Museum, located in Tucson, Arizona, is one of the world's largest non-government funded aerospace museums. The museum features a display of nearly 300 aircraft spread out over 80 acres (320,000 m²) on a campus oc ...
, adjacent to Davis-Monthan AFB in Tucson, Arizona
, "(at the) base of the black ill
, nicknames = "The Old Pueblo", "Optics Valley", "America's biggest small town"
, image_map =
, mapsize = 260px
, map_caption = Interactive map ...
.''Pima Air & Space Museum.'' Retrieved: 15 January 2015.
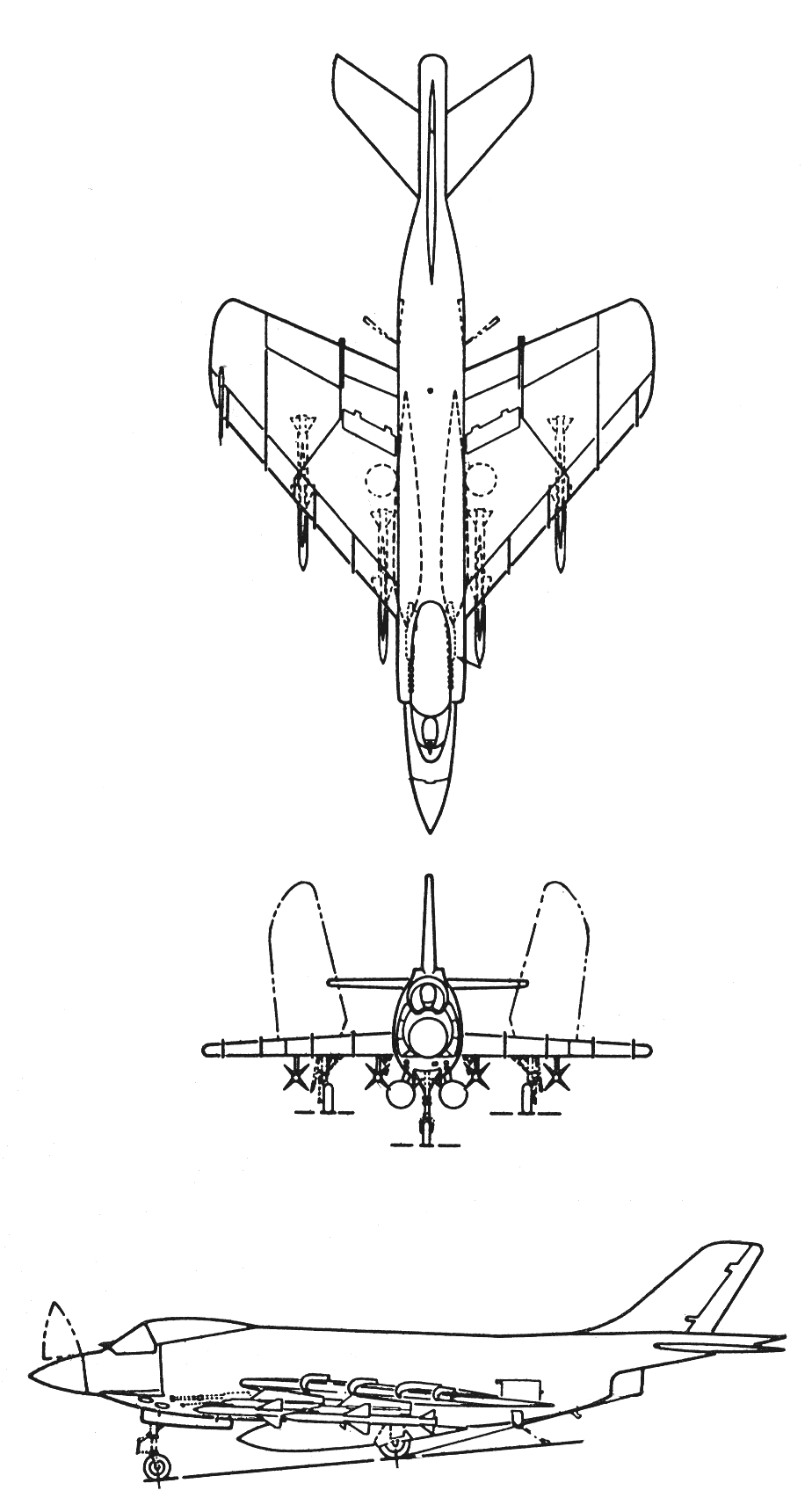
Specifications (F3H-2)

See also
References
Notes
Bibliography
*Angelucci, Enzo and Peter M. Bowers. ''The American Fighter''. Sparkford, Somerset, UK: Haynes Publishing Group, 1987. . *Dorr, Robert F. "McDonnell F3H Demon". '' Aeroplane'', Volume 36, No. 3, March 2008, pp. 58–73. London: IBC. *Elward, Brad A. and Peter Davies''US Navy F-4 Phantom II MiG Killers 1965–70, Part 1'' (Osprey Combat Aircraft).
London: Osprey Publishing, 2001. . *Gunston, Bill. ''Fighters of the Fifties''. Cambridge, UK: Patrick Stephens Limited, 1981. .
"Naval Aircraft: Demon".
''Naval Aviation News'', March 1974, pp. 22–23. *Spick, Mike. "A Demon Possessed". ''
Air Enthusiast
''Air Enthusiast'' was a British, bi-monthly, aviation magazine, published by the Key Publishing group. Initially begun in 1974 as ''Air Enthusiast Quarterly'', the magazine was conceived as a historical adjunct to ''Air International'' maga ...
'', Forty-three, 1991, pp. 40–49. Stamford, UK: Key Publishing. ISSN 0143-5450.
External links
''F3H Demon Index''
* {{Authority control Carrier-based aircraft
F3H Demon
The McDonnell F3H Demon is a subsonic swept-wing United States Navy carrier-based jet fighter aircraft. The successor to the F2H Banshee, the Demon was originally designed to use the Westinghouse J40 engine, but had to be redesigned to acc ...
McDonnell F03H Demon
Low-wing aircraft
Single-engined jet aircraft
Aircraft first flown in 1951
Second-generation jet fighters