Mason University College on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mason Science College was a
 The college was established by an English industrialist and philanthropist Sir
The college was established by an English industrialist and philanthropist Sir




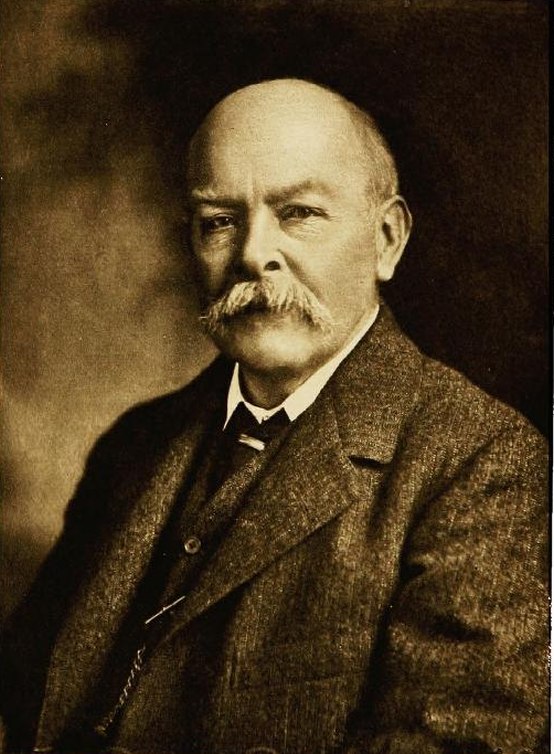
 Notable academics and alumni of the college include:
* Edward Arber, academic and writer
* Francis William Aston, chemist and physicist, 1922
Notable academics and alumni of the college include:
* Edward Arber, academic and writer
* Francis William Aston, chemist and physicist, 1922
Ulrls.lon.ac.uk
Ulrls.lon.ac.uk
Ulrls.lon.ac.uk
Ulrls.lon.ac.uk
Ulrls.lon.ac.uk
Ulrls.lon.ac.uk
Archive.org
Ulrls.lon.ac.uk
Lists of students at Mason Science College
1960s photograph
{{University of Birmingham University of Birmingham Demolished buildings and structures in the West Midlands (county) Science and technology in the West Midlands (county) Educational institutions established in 1875 1875 establishments in England Buildings and structures demolished in 1964
university college
In a number of countries, a university college is a college institution that provides tertiary education but does not have full or independent university status. A university college is often part of a larger university. The precise usage varies ...
in Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the We ...
, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
, and a predecessor college of Birmingham University
, mottoeng = Through efforts to heights
, established = 1825 – Birmingham School of Medicine and Surgery1836 – Birmingham Royal School of Medicine and Surgery1843 – Queen's College1875 – Mason Science College1898 – Mason Univers ...
. Founded in 1875 by industrialist and philanthropist Sir Josiah Mason
Sir Josiah Mason (23 February 1795 – 16 June 1881) was an English industrialist, engaged in pen manufacture and other trades, and a philanthropist. He founded Mason Science College in 1875, which later became the University of Birmingham.
Bi ...
, the college was incorporated into the University of Birmingham
, mottoeng = Through efforts to heights
, established = 1825 – Birmingham School of Medicine and Surgery1836 – Birmingham Royal School of Medicine and Surgery1843 – Queen's College1875 – Mason Science College1898 – Mason Univers ...
in 1900. Two students of the college, Neville Chamberlain
Arthur Neville Chamberlain (; 18 March 18699 November 1940) was a British politician of the Conservative Party who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from May 1937 to May 1940. He is best known for his foreign policy of appeaseme ...
and Stanley Baldwin
Stanley Baldwin, 1st Earl Baldwin of Bewdley, (3 August 186714 December 1947) was a British Conservative Party politician who dominated the government of the United Kingdom between the world wars, serving as prime minister on three occasions, ...
, later went on to become Prime Ministers of the UK.
History
 The college was established by an English industrialist and philanthropist Sir
The college was established by an English industrialist and philanthropist Sir Josiah Mason
Sir Josiah Mason (23 February 1795 – 16 June 1881) was an English industrialist, engaged in pen manufacture and other trades, and a philanthropist. He founded Mason Science College in 1875, which later became the University of Birmingham.
Bi ...
in 1875. The building of the college in Edmund Street, Birmingham was designed by Jethro Cossins
Jethro Anstice Cossins (7 July 1830 – 1917) was a British architect, who practised mainly in Birmingham during the 19th century.
Background
He was born on 7 July 1830 in Kingsdon, Somerset, the son of John Cossins.
He died on 5 December 1 ...
and opened on 1 October 1880 and was marked by a speech by Thomas Henry Huxley
Thomas Henry Huxley (4 May 1825 – 29 June 1895) was an English biologist and anthropologist specialising in comparative anatomy. He has become known as "Darwin's Bulldog" for his advocacy of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution.
The stori ...
. In the speech, Huxley considered the opening of the college as a victory for scientific cause and supported Mason's antagonistic views on the classics and theology. The college developed various liberal and vocational subjects, but forced out the artisans. The medical and scientific departments of Queen's College, Birmingham
Queen's College was a medical school in central Birmingham, England, and a predecessor college of the University of Birmingham. It was founded by surgeon William Sands Cox in 1825 as The Birmingham Medical School, a residential college for me ...
moved to the nearby Mason Science College.
In 1898, it became Mason University College, with Joseph Chamberlain
Joseph Chamberlain (8 July 1836 – 2 July 1914) was a British statesman who was first a radical Liberal, then a Liberal Unionist after opposing home rule for Ireland, and eventually served as a leading imperialist in coalition with the C ...
becoming the President of Court of Governors of the college. In 1900 it was incorporated into the University of Birmingham
, mottoeng = Through efforts to heights
, established = 1825 – Birmingham School of Medicine and Surgery1836 – Birmingham Royal School of Medicine and Surgery1843 – Queen's College1875 – Mason Science College1898 – Mason Univers ...
. Students at the College were awarded their degrees by the University of London
The University of London (UoL; abbreviated as Lond or more rarely Londin in post-nominals) is a federal public research university located in London, England, United Kingdom. The university was established by royal charter in 1836 as a degr ...
until the University of Birmingham was established and received degree awarding powers in its own right.
William A. Tilden
Sir William Augustus Tilden (15 August 1842 – 11 December 1926) was a British chemist. He discovered that isoprene could be made from turpentine. He was unable to turn this discovery into a way to make commercially viable synthetic rubber.
L ...
was professor of chemistry from 1880 to 1894. In September 1893, Francis William Aston began his university studies at the college, where he was taught physics by John Henry Poynting and chemistry by Frankland and Tilden.
In 1881, Charles Lapworth became the first professor of geology at the college. In 1891, physics professor John Henry Poynting successfully calculated the mean density of the Earth.
The Mason College building housed Birmingham University
, mottoeng = Through efforts to heights
, established = 1825 – Birmingham School of Medicine and Surgery1836 – Birmingham Royal School of Medicine and Surgery1843 – Queen's College1875 – Mason Science College1898 – Mason Univers ...
's Faculties of Arts and Law for over half a century after the founding of the University in 1900. The Faculty of Arts building on the Edgbaston campus was not constructed until 1959–61. The Faculties of Arts and Law then moved to the Edgbaston Campus.
After the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, the style of architecture was not as appreciated as it is now. Paul Cadbury referred to it in 1952 as a ''neo-gothic monstrosity'' and expected it to be demolished within 50 years. In the event, it was demolished in 1964, along with the original Central Public Library and the Birmingham and Midland Institute
The Birmingham and Midland Institute (popularly known as the Midland Institute) (), is an institution concerned with the promotion of education and learning in Birmingham, England. It is now based on Margaret Street in Birmingham city centre. It ...
, as part of the redevelopment within the inner ring road. The former Central Library stood on the site of the old college, the library having moved to a new site in 2013; the building was demolished in 2016.
Departments
During the first academic session of the college in 1880 courses in physics, chemistry, biology and mathematics were offered to students. By 1881 courses in geology and mineralogy, botany and vegetable physiology, engineering, English language and literature, Greek and Latin, and French and German language and literature were also available. From 1882 Medical students atQueen's College, Birmingham
Queen's College was a medical school in central Birmingham, England, and a predecessor college of the University of Birmingham. It was founded by surgeon William Sands Cox in 1825 as The Birmingham Medical School, a residential college for me ...
were able to attend classes in botany, physiology and chemistry, and in 1892 the medical faculty of Queen's College was transferred to Mason College. There was also a short-lived department of ‘Mental and Moral Science’, which was not successful despite funds being gifted specifically to support the endeavor in 1882.
Academics and alumni




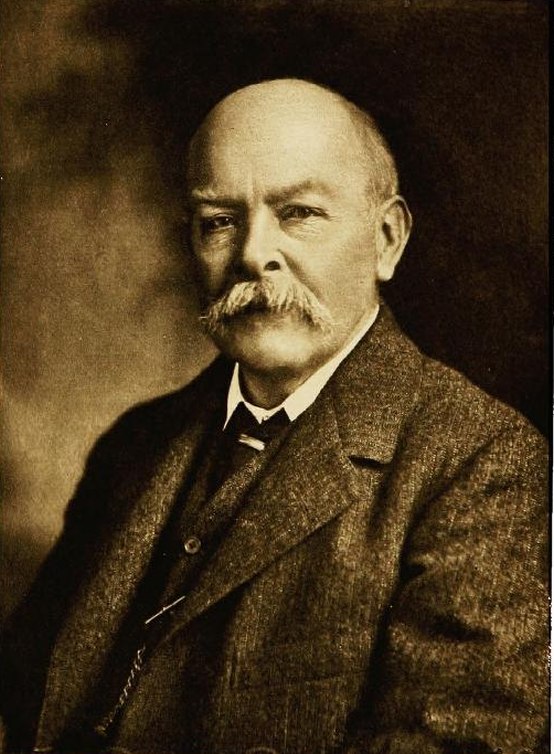
Nobel Prize in Chemistry
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "M ...
* Stanley Baldwin
Stanley Baldwin, 1st Earl Baldwin of Bewdley, (3 August 186714 December 1947) was a British Conservative Party politician who dominated the government of the United Kingdom between the world wars, serving as prime minister on three occasions, ...
, British Prime Minister
The prime minister of the United Kingdom is the head of government of the United Kingdom. The prime minister advises the sovereign on the exercise of much of the royal prerogative, chairs the Cabinet and selects its ministers. As moder ...
* Sir Gilbert Barling
Sir Harry Gilbert Barling, 1st Baronet (30 April 1855 – 27 April 1940) was an English surgeon.
Barling was born at Newnham on Severn, Gloucestershire and educated at a boarding school at
Weston, near Bath. He went to Birmingham in 1875 a ...
, 1st Baronet, physician
* John Belling
John Belling (7 October 1866–28 February 1933) was a cytogeneticist who developed the iron-acetocarmine staining technique which is used in the study of chromosomes.
Born in Aldershot in England in 1866, the son of John Belling (1827– ...
, cytogeneticist who developed the iron-acetocarmine staining technique which is used in the study of chromosomes
* Sir Nathan Bodington
Sir Nathan Bodington (29 May 1848 – 12 May 1911) was the first Vice Chancellor of the University of Leeds having been Principal and Professor of Greek at the Yorkshire College since 1883.''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' accessed 25 J ...
, Professor of classics
* Adrian John Brown, FRS, pioneer in the study of enzyme kinetics
* Arthur Henry Reginald Buller
Arthur Henry Reginald Buller, (19 August 1874 – 3 July 1944) was a British-Canadian mycologist. He is mainly known as a researcher of fungi and wheat rust.
Academic career
Born in Moseley, Birmingham, England, he was educated at Queen's C ...
, British-Canadian mycologist mainly known as a researcher of fungi and wheat rust
* Neville Chamberlain
Arthur Neville Chamberlain (; 18 March 18699 November 1940) was a British politician of the Conservative Party who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from May 1937 to May 1940. He is best known for his foreign policy of appeaseme ...
, British Prime Minister
The prime minister of the United Kingdom is the head of government of the United Kingdom. The prime minister advises the sovereign on the exercise of much of the royal prerogative, chairs the Cabinet and selects its ministers. As moder ...
* Lawrence Crawford (mathematician) FRSE
Fellowship of the Royal Society of Edinburgh (FRSE) is an award granted to individuals that the Royal Society of Edinburgh, Scotland's national academy of science and letters, judged to be "eminently distinguished in their subject". This soci ...
(1867–1951), taught in the college
* Sir Guy Dain
Sir Harry Guy Dain FRCS (5 November 1870 – 26 February 1966) was a British physician.
Between 1887 and 1894 Dain studied science and medicine at Mason College (a predecessor college of the University of Birmingham). He graduated with a Un ...
, Chairman of the British Medical Association
The British Medical Association (BMA) is a registered trade union for doctors in the United Kingdom. The association does not regulate or certify doctors, a responsibility which lies with the General Medical Council. The association's headqua ...
1943–49 (M.B. medicine)
* Hermann Georg Fiedler, German scholar
* Sir Henry Fowler, locomotive engineer
* Percy F. Frankland, chemist
* Ernest Gold, set up the first operational (military) meteorological service, Deputy Director of the Meteorological Office
* John Berry Haycraft
John Berry Haycraft FRSE (bapt. 15 March 1857 – 30 December 1922) was a British physician and professor in physiology who carried out important medical research.
Biography
Haycraft was born in Lewes, East Sussex, England, in 1857, the son o ...
, discovered an anticoagulant
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where t ...
created by the leech
Leeches are segmented parasitism, parasitic or Predation, predatory worms that comprise the Class (biology), subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the Oligochaeta, oligochaetes, which include the earthwor ...
, which he named hirudin
Hirudin is a naturally occurring peptide in the salivary glands of blood-sucking leeches (such as '' Hirudo medicinalis'') that has a blood anticoagulant property. This is fundamental for the leeches’ habit of feeding on blood, since it keeps ...
* John Rippiner Heath John Rippiner Heath (4 January 1887 - 23 December 1950) was a British composer, violinist and physician who lived and worked for most of his life in Wales.
Life
Heath was born in Birmingham the son of Professor Robert Heath, principal of Birmingham ...
, physician and composer
* Micaiah John Muller Hill
Micaiah John Muller Hill FRS (1856–1929) was an English mathematician, known for Hill's spherical vortex and Hill's tetrahedra.
He was born on 22 February 1856 in Bengal, India, the son of Revd. Samuel John Hill (1825–1881) and Leonora Jo ...
, FRS, English mathematician, known for Hill's spherical vortex and Hill's tetrahedra
* Charles William Hobley, pioneering colonial administrator in Kenya
* Frank Horton, Professor of Physics at Royal Holloway College
Royal Holloway, University of London (RHUL), formally incorporated as Royal Holloway and Bedford New College, is a public research university and a constituent college of the federal University of London. It has six schools, 21 academic departm ...
and Vice-Chancellor
A chancellor is a leader of a college or university, usually either the executive or ceremonial head of the university or of a university campus within a university system.
In most Commonwealth and former Commonwealth nations, the chancellor ...
of the University of London
The University of London (UoL; abbreviated as Lond or more rarely Londin in post-nominals) is a federal public research university located in London, England, United Kingdom. The university was established by royal charter in 1836 as a degr ...
1939–45
* Henry Eliot Howard, ornithologist
* Arthur Lapworth, FRS, chemist
* Charles Lapworth, FRS, FGS, geologist who pioneered faunal analysis using index fossils and identified the Ordovician period
* Robert Thomson Leiper, parasitologist and helminthologist
* Lionel Simeon Marks, engineer and one of the pioneers of aeronautics
* Gerald Rusgrove Mills, publisher who established the publishing company Mills & Boon
* John Henry Muirhead
John Henry Muirhead (28 April 1855 – 24 May 1940) was a British philosopher best known for having initiated the Muirhead Library of Philosophy in 1890. He became the first person named to the Chair of Philosophy at the University of Birmingham ...
, philosopher
* Constance Naden, poet and philosopher
* Charles Talbut Onions
Charles Talbut Onions (C. T. Onions) (10 September 1873 – 8 January 1965) was an English grammarian and lexicographer and the fourth editor of the ''Oxford English Dictionary''.
Life
Onions was born in Edgbaston, Birmingham, the eldest son ...
, English grammarian and lexicographer and the fourth editor of the Oxford English Dictionary
* Kineton Parkes, novelist and art historian
* Sir Leonard Parsons
Sir Leonard Gregory Parsons MRCS FRCP FRCOG FRS (25 November 1879 - 17 December 1950) was a British Paediatrician.
Parsons studied at Mason College and the University of Birmingham from 1896 to 1903. He graduated with a University of Lond ...
, Professor of Paediatrics, dean of Birmingham medical school, in 1932 the first to use synthetic vitamin C to treat scurvy
Scurvy is a deficiency disease, disease resulting from a lack of vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Early symptoms of deficiency include weakness, feeling tired and sore arms and legs. Without treatment, anemia, decreased red blood cells, gum disease, ch ...
in children
* Sir Robert Howson Pickard Sir Robert Howson Pickard FRS (27 September 1874 – 18 October 1949) was a chemist who did pioneering work in stereochemistry and also for the cotton industry in Lancashire. He was also involved in educational administration and was Vice Chancello ...
, chemist who did pioneering work in stereochemistry and was Vice Chancellor of the University of London from 1937–1939
* John Henry Poynting, physicist
* Dame Ethel Shakespear
Dame Ethel Mary Reader Shakespear (née Wood; 17 July 1871 – 17 January 1946) was an English geologist, Justice of the Peace, public servant, and philanthropist.Biography, ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' She is most famously known f ...
, geologist, public servant and philanthropist
* Edward Adolf Sonnenschein, Classical Scholar and writer on Latin grammar and verse
* F. J. M. Stratton, Professor of Astrophysics at the University of Cambridge
* Sir William A. Tilden
Sir William Augustus Tilden (15 August 1842 – 11 December 1926) was a British chemist. He discovered that isoprene could be made from turpentine. He was unable to turn this discovery into a way to make commercially viable synthetic rubber.
L ...
, chemist
* Swale Vincent, physiologist
* William Whitehead Watts
Prof William Whitehead Watts FRS HFRSE FGS FMS LLD (7 June 1860 – 30 July 1947) was a British geologist.
Life
He was born near Broseley in Shropshire, the eldest of two sons of Isaac Watts, but then a music master, and his wife, Maria Whitehea ...
, FRS, geologist
* Wilmer Cave Wright, philologist and historian of science and medicine
* John Howard Whitehouse
John Howard Whitehouse (1873–1955) was the founder and first Warden of Bembridge School on the Isle of Wight, United Kingdom, and a Member of Parliament. His father, George Whitehouse, was a Quaker and an uncompromising Gladstonian Liberal wh ...
, Liberal Member of Parliament
* Sir Bertram Windle
Sir Bertram Coghill Alan Windle, (8 May 1858 – 14 February 1929) was a British anatomist, administrator, archaeologist, scientist, educationalist and writer.
Biography
He was born at Mayfield Vicarage, in Staffordshire, where his father, ...
, physician
References
Sources
*Ordnance Survey 1st Edition Map, 1890Ulrls.lon.ac.uk
Ulrls.lon.ac.uk
Ulrls.lon.ac.uk
Ulrls.lon.ac.uk
Ulrls.lon.ac.uk
Ulrls.lon.ac.uk
Archive.org
Ulrls.lon.ac.uk
External links
Lists of students at Mason Science College
1960s photograph
{{University of Birmingham University of Birmingham Demolished buildings and structures in the West Midlands (county) Science and technology in the West Midlands (county) Educational institutions established in 1875 1875 establishments in England Buildings and structures demolished in 1964