Maryland Terrapins men's basketball players on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Maryland ( ) is a

 The royal charter granted Maryland the land north of the
The royal charter granted Maryland the land north of the
Retrieved February 15, 2008. As the flow of indentured laborers to the colony decreased with improving economic conditions in England, planters in Maryland imported thousands more slaves and racial caste lines hardened. The economy's growth and prosperity were based on slave labor, devoted first to the production of
 Influenced by a changing economy, revolutionary ideals, and preaching by ministers, numerous planters in Maryland freed their slaves in the 20 years after the Revolutionary War. Across the Upper South the free black population increased from less than 1% before the war to 14% by 1810. Abolitionists
Influenced by a changing economy, revolutionary ideals, and preaching by ministers, numerous planters in Maryland freed their slaves in the 20 years after the Revolutionary War. Across the Upper South the free black population increased from less than 1% before the war to 14% by 1810. Abolitionists
 The state remained with the Union during the Civil War, due in significant part to demographics and Federal intervention. The 1860 census, held shortly before the outbreak of the civil war, showed that 49% of Maryland's African Americans were free blacks.Peter Kolchin, ''American Slavery: 1619–1877'', New York: Hill and Wang, 1993, pp. 81–82
Governor
The state remained with the Union during the Civil War, due in significant part to demographics and Federal intervention. The 1860 census, held shortly before the outbreak of the civil war, showed that 49% of Maryland's African Americans were free blacks.Peter Kolchin, ''American Slavery: 1619–1877'', New York: Hill and Wang, 1993, pp. 81–82
Governor
 The
The


 Maryland possesses a variety of
Maryland possesses a variety of

 As is typical of states on the East Coast, Maryland's plant life is abundant and healthy. A modest volume of annual precipitation helps to support many types of plants, including
As is typical of states on the East Coast, Maryland's plant life is abundant and healthy. A modest volume of annual precipitation helps to support many types of plants, including
 The state harbors a considerable number of
The state harbors a considerable number of
 Maryland has a wide array of climates, due to local variances in elevation, proximity to water, and protection from colder weather due to downslope winds.
The eastern half of Maryland — which includes the cities of Ocean City, Salisbury,
Maryland has a wide array of climates, due to local variances in elevation, proximity to water, and protection from colder weather due to downslope winds.
The eastern half of Maryland — which includes the cities of Ocean City, Salisbury,
 Most of the population of Maryland lives in the central region of the state, in the
Most of the population of Maryland lives in the central region of the state, in the
 In the
In the
 In 1970, the U.S. Census Bureau reported Maryland's population as 17.8 percent African-American and 80.4 percent non-Hispanic White.
In 1970, the U.S. Census Bureau reported Maryland's population as 17.8 percent African-American and 80.4 percent non-Hispanic White.
Washington: "Nation's Largest Ethiopian Community Carves Niche"
(). ''
"Washington: Nation's Largest Ethiopian Community Carves Niche"
''
 Maryland has been historically prominent to American Catholic tradition because the English
Maryland has been historically prominent to American Catholic tradition because the English
 The
The
 Maryland has large areas of fertile agricultural land in its coastal and
Maryland has large areas of fertile agricultural land in its coastal and
 Tourism is popular in Maryland. Many tourists visit Baltimore, the beaches of the Eastern Shore, and the nature of western Maryland. Attractions in Baltimore include the
Tourism is popular in Maryland. Many tourists visit Baltimore, the beaches of the Eastern Shore, and the nature of western Maryland. Attractions in Baltimore include the
 Maryland's
Maryland's

"CSX and Maryland."
followed by
 The
The
 Prior to the American Civil War, Maryland's elections were largely controlled by the Democrats, which account for 54.9% of all registered voters as of May 2017.
State elections are dominated by
Prior to the American Civil War, Maryland's elections were largely controlled by the Democrats, which account for 54.9% of all registered voters as of May 2017.
State elections are dominated by
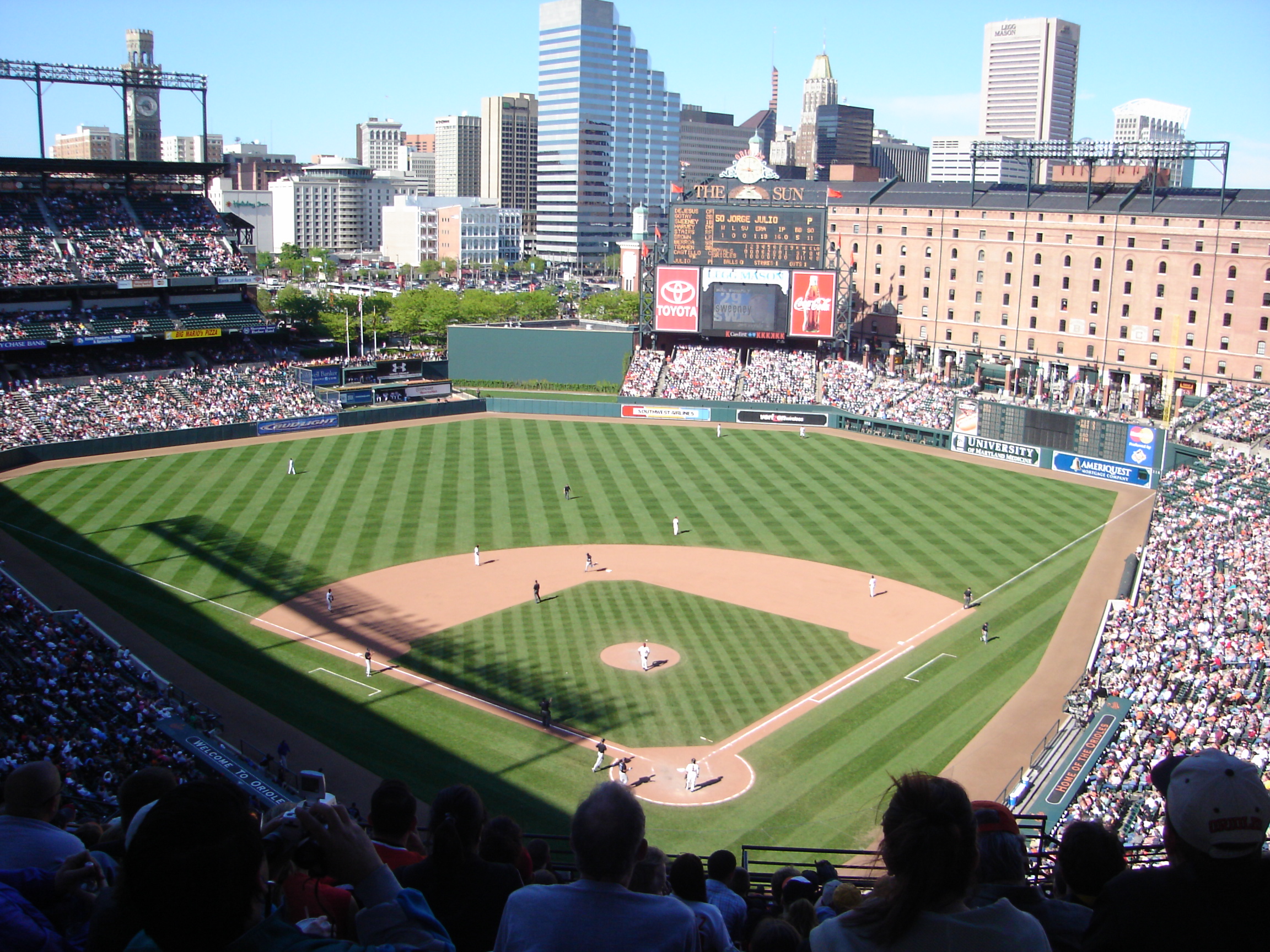

 With two major metropolitan areas, Maryland has a number of major and minor professional sports franchises. Two National Football League teams play in Maryland, the Baltimore Ravens in
With two major metropolitan areas, Maryland has a number of major and minor professional sports franchises. Two National Football League teams play in Maryland, the Baltimore Ravens in
Maryland Office of Tourism
Energy Data & Statistics for Maryland
USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Maryland
Maryland State Facts from USDA
* *
* [http://www.mdhs.org/library/research-resources/county-maps Maryland Historical Society: County Maps]
The Huntingfield Map Collection
{{coord, 39, -77, dim:300000_region:US-MD_type:adm1st, name=State of Maryland, display=title Maryland, 1788 establishments in the United States Contiguous United States Mid-Atlantic states Northeastern United States Southern United States States and territories established in 1788 States of the East Coast of the United States States of the United States
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* '' Our ...
in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
, West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the ...
, and the District of Columbia
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, Na ...
to its south and west; Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; (Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, Mary ...
to its north; and Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
and the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Afr ...
to its east. Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was ...
is the largest city in the state, and the capital is Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Maryland and the county seat of, and only incorporated city in, Anne Arundel County. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east ...
. Among its occasional nicknames are '' Old Line State'', the ''Free State'', and the ''Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / E ...
State''. It is named after Henrietta Maria
Henrietta Maria (french: link=no, Henriette Marie; 25 November 1609 – 10 September 1669) was Queen of England, Scotland, and Ireland from her marriage to King Charles I on 13 June 1625 until Charles was executed on 30 January 1649. She wa ...
, the French-born queen of England, Scotland, and Ireland, who was known then in England as Mary.
Before its coastline was explored by Europeans in the 16th century, Maryland was inhabited by several groups of Native Americans – mostly by Algonquian peoples
The Algonquian are one of the most populous and widespread North American native language groups. Historically, the peoples were prominent along the Atlantic Coast and into the interior along the Saint Lawrence River and around the Great Lakes. T ...
and, to a lesser degree, Iroquoian
The Iroquoian languages are a language family of indigenous peoples of North America. They are known for their general lack of labial consonants. The Iroquoian languages are polysynthetic and head-marking.
As of 2020, all surviving Iroquoian la ...
and Siouan
Siouan or Siouan–Catawban is a language family of North America that is located primarily in the Great Plains, Ohio and Mississippi valleys and southeastern North America with a few other languages in the east.
Name
Authors who call the entire ...
. As one of the original Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Founded in the 17th and 18th centuri ...
of England, Maryland was founded by George Calvert
George Calvert, 1st Baron Baltimore (; 1580 – 15 April 1632), was an English politician and colonial administrator. He achieved domestic political success as a member of parliament and later Secretary of State under King James I. He lost m ...
, 1st Baron Baltimore, a Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
convert"George Calvert and Cecilius Calvert, Barons Baltimore" William Hand Browne, Nabu Press (August 1, 2010), who sought to provide a religious haven for Catholics persecuted in England. In 1632, Charles I of England granted Lord Baltimore a colonial charter A charter is a document that gives colonies the legal rights to exist. Charters can bestow certain rights on a town, city, university, or other institution.
Colonial charters were approved when the king gave a grant of exclusive powers for the go ...
, naming the colony after his wife, Henrietta Maria. Unlike the Pilgrims and Puritans
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to purify the Church of England of Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become more Protestant. ...
, who rejected Catholicism in their settlements, Lord Baltimore envisioned a colony where people of different religious sects would coexist under the principle of toleration
Toleration is the allowing, permitting, or acceptance of an action, idea, object, or person which one dislikes or disagrees with. Political scientist Andrew R. Murphy explains that "We can improve our understanding by defining "toleration" as ...
. Accordingly, in 1649 the Maryland General Assembly passed an Act Concerning Religion, which enshrined this principle by penalizing anyone who "reproached" a fellow Marylander based on religious affiliation. Nevertheless, religious strife was common in the early years, and Catholics remained a minority, albeit in greater numbers than in any other English colony.
Maryland's early settlements and population centers clustered around rivers and other waterways that empty into the Chesapeake Bay. Its economy was heavily plantation-based and centered mostly on the cultivation of tobacco. Demand for cheap labor from Maryland colonists led to the importation of numerous indentured servants
Indentured servitude is a form of Work (human activity), labor in which a person is contracted to work without salary for a specific number of years. The contract, called an "indenture", may be entered "voluntarily" for purported eventual compensa ...
and enslaved Africans
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the triangular trade route and i ...
. In 1760, Maryland's current boundaries took form following the settlement of a long-running border dispute with Pennsylvania. Maryland was an active participant in the events leading up to the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revoluti ...
, and by 1776, its delegates signed the Declaration of Independence
A declaration of independence or declaration of statehood or proclamation of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of the ...
. Many of its citizens subsequently played key political and military roles in the war. In 1790, the state ceded land for the establishment of the U.S. capital of Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, Na ...
Although then a slave state
In the United States before 1865, a slave state was a state in which slavery and the internal or domestic slave trade were legal, while a free state was one in which they were not. Between 1812 and 1850, it was considered by the slave states ...
, Maryland remained in the Union during the American Civil War, its strategic location giving it a significant role in the conflict. After the Civil War, Maryland took part in the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, driven by its seaports, railroad networks, and mass immigration from Europe. Since the 1940s, the state's population has grown rapidly, to approximately six million residents, and it is among the most densely populated U.S. states. , Maryland had the highest median household income of any state, owing in large part to its proximity to Washington, D.C., and a highly diversified economy spanning manufacturing, retail services, public administration, real estate, higher education, information technology, defense contracting, health care, and biotechnology. The state's central role in U.S. history is reflected by its hosting of some of the highest numbers of historic landmarks per capita.
Sixteen of Maryland's twenty-three counties, as well as the city of Baltimore, border the tidal waters of the Chesapeake Bay estuary and its many tributaries, which combined total more than 4,000 miles of shoreline. Although one of the smallest states in the U.S., it features a variety of climates and topographical features that have earned it the moniker of ''America in Miniature''. In a similar vein, Maryland's geography, culture, and history combine elements of the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, and Southern regions of the country.
History
17th century
Maryland's first colonial settlement

George Calvert, 1st Baron Baltimore
George Calvert, 1st Baron Baltimore (; 1580 – 15 April 1632), was an English politician and colonial administrator. He achieved domestic political success as a member of parliament and later Secretary of State under King James I. He lost mu ...
(1579–1632), sought a charter from King Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
for the territory between Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
to the north and Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
to the immediate south.
After Baltimore died in April 1632, the charter was granted to his son, Cecilius Calvert, 2nd Baron Baltimore
Cecil Calvert, 2nd Baron Baltimore (8 August 1605 – 30 November 1675), also often known as Cecilius Calvert, was an English nobleman, who was the first Proprietor of the Province of Maryland, ninth Proprietary Governor of the Colony of Newfou ...
(1605–1675), on June 20, 1632. Officially, the new "Maryland Colony" was named in honor of Henrietta Maria of France
Henrietta Maria (french: link=no, Henriette Marie; 25 November 1609 – 10 September 1669) was Queen of England, Scotland, and Ireland from her marriage to King Charles I on 13 June 1625 until Charles was executed on 30 January 1649. She wa ...
, wife of Charles I of England. Lord Baltimore initially proposed the name "Crescentia", the land of growth or increase, but "the King proposed Terra Mariae ary Land ARY may stand for:
* Abdul Razzak Yaqoob, a Pakistani expatriate businessman
* Andre Romelle Young, real name of Dr. Dre
* Ary and the Secret of Seasons, an action adventure video game
* ARY Digital, a Pakistani television network
* ARY Digital Ne ...
which was concluded on and Inserted in the bill."
The original capital of Maryland was St. Mary's City
St. Mary's City (also known as Historic St. Mary's City) is a former colonial town that was Maryland's first European settlement and capital. It is now a large, state-run historic area, which includes a reconstruction of the original colonial se ...
, on the north shore of the Potomac River
The Potomac River () drains the Mid-Atlantic United States, flowing from the Potomac Highlands into Chesapeake Bay. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map. Retrieved Augu ...
, and the county surrounding it, the first erected/created in the province, was first called Augusta Carolina, after the King, and later named St. Mary's County.
Lord Baltimore's first settlers arrived in the new colony in March 1634, with his younger brother the Honorable Leonard Calvert
The Hon. Leonard Calvert (1606 – June 9, 1647) was the first proprietary governor of the Province of Maryland. He was the second son of The 1st Baron Baltimore (1579–1632), the first proprietor of Maryland. His elder brother Cecil (1605� ...
(1606–1647), as first provincial Governor of Maryland
The Governor of the State of Maryland is the head of government of Maryland, and is the commander-in-chief of the state's National Guard units. The Governor is the highest-ranking official in the state and has a broad range of appointive powe ...
. They made their first permanent settlement at St. Mary's City
St. Mary's City (also known as Historic St. Mary's City) is a former colonial town that was Maryland's first European settlement and capital. It is now a large, state-run historic area, which includes a reconstruction of the original colonial se ...
in what is now St. Mary's County. They purchased the site from the paramount chief
A paramount chief is the English-language designation for the highest-level political leader in a regional or local polity or country administered politically with a chief-based system. This term is used occasionally in anthropological and arch ...
of the region, who was eager to establish trade. St. Mary's became the first capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used fo ...
of Maryland, and remained so for 60 years until 1695. More settlers soon followed. Their tobacco crops were successful and quickly made the new colony profitable. However, given the incidence of malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, fatigue (medical), tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In se ...
, yellow fever
Yellow fever is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains – particularly in the back – and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. I ...
, and typhoid
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by ''Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several d ...
, life expectancy in Maryland was about 10 years less than in New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
.
Persecution of Catholics
Maryland was founded to provide a haven for England's Roman Catholic minority. Although Maryland was the most heavily Catholic of the English mainland colonies, the religion was still in the minority, consisting of less than 10% of the total population. In 1642, a number ofPuritan
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to purify the Church of England of Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become more Protestant. ...
s left Virginia for Maryland and founded Providence (now called Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Maryland and the county seat of, and only incorporated city in, Anne Arundel County. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east ...
) on the western shore of the upper Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / E ...
. A dispute with traders from Virginia over Kent Island
Kent Island is the largest island in the Chesapeake Bay and a historic place in Maryland. To the east, a narrow channel known as the Kent Narrows barely separates the island from the Delmarva Peninsula, and on the other side, the island is se ...
in the Chesapeake led to armed conflict. In 1644, William Claiborne
William Claiborne also, spelled Cleyburne (c. 1600 – c. 1677) was an English pioneer, surveyor, and an early settler in the colonies/provinces of Virginia and Maryland and around the Chesapeake Bay. Claiborne became a wealthy merchant ...
, a Puritan, seized Kent Island while his associate, the pro-Parliament Puritan Richard Ingle, took over St. Mary's. Both used religion as a tool to gain popular support. The two years from 1644 to 1646 when Claiborne and his Puritan associates held sway were known as "The Plundering Time". They captured Jesuit priests, imprisoned them, then sent them back to England.
In 1646, Leonard Calvert
The Hon. Leonard Calvert (1606 – June 9, 1647) was the first proprietary governor of the Province of Maryland. He was the second son of The 1st Baron Baltimore (1579–1632), the first proprietor of Maryland. His elder brother Cecil (1605� ...
returned with troops, recaptured St. Mary's City, and restored order. The House of Delegates passed the "Act concerning Religion" in 1649 granting religious liberty to all Trinitarian
The Christian doctrine of the Trinity (, from 'threefold') is the central dogma concerning the nature of God in most Christian churches, which defines one God existing in three coequal, coeternal, consubstantial divine persons: God the ...
Christians.
In 1650, the Puritans revolted against the proprietary government. "Protestants swept the Catholics out of the legislature... and religious strife returned." The Puritans set up a new government prohibiting both Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and Anglicanism
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the ...
. The Puritan revolutionary government persecuted Maryland Catholics during its reign, known as the "plundering time". Mobs burned down all the original Catholic churches of southern Maryland. The Puritan rule lasted until 1658 when the Calvert family and Lord Baltimore regained proprietary control and re-enacted the Toleration Act.
After England's "Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, Rèabhlaid Ghlòrmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and ...
" of 1688, Maryland outlawed Catholicism. In 1704, the Maryland General Assembly prohibited Catholics from operating schools, limited the corporate ownership of property to hamper religious orders from expanding or supporting themselves, and encouraged the conversion of Catholic children. The celebration of the Catholic sacraments was also officially restricted. This state of affairs lasted until after the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
(1775–1783). Wealthy Catholic planters built chapels on their land to practice their religion in relative secrecy.
Into the 18th century, individual priests and lay leaders claimed Maryland farms belonging to the Jesuits as personal property and bequeathed
A bequest is property given by will. Historically, the term ''bequest'' was used for personal property given by will and ''deviser'' for real property. Today, the two words are used interchangeably.
The word ''bequeath'' is a verb form for the act ...
them in order to evade the legal restrictions on religious organizations' owning property.
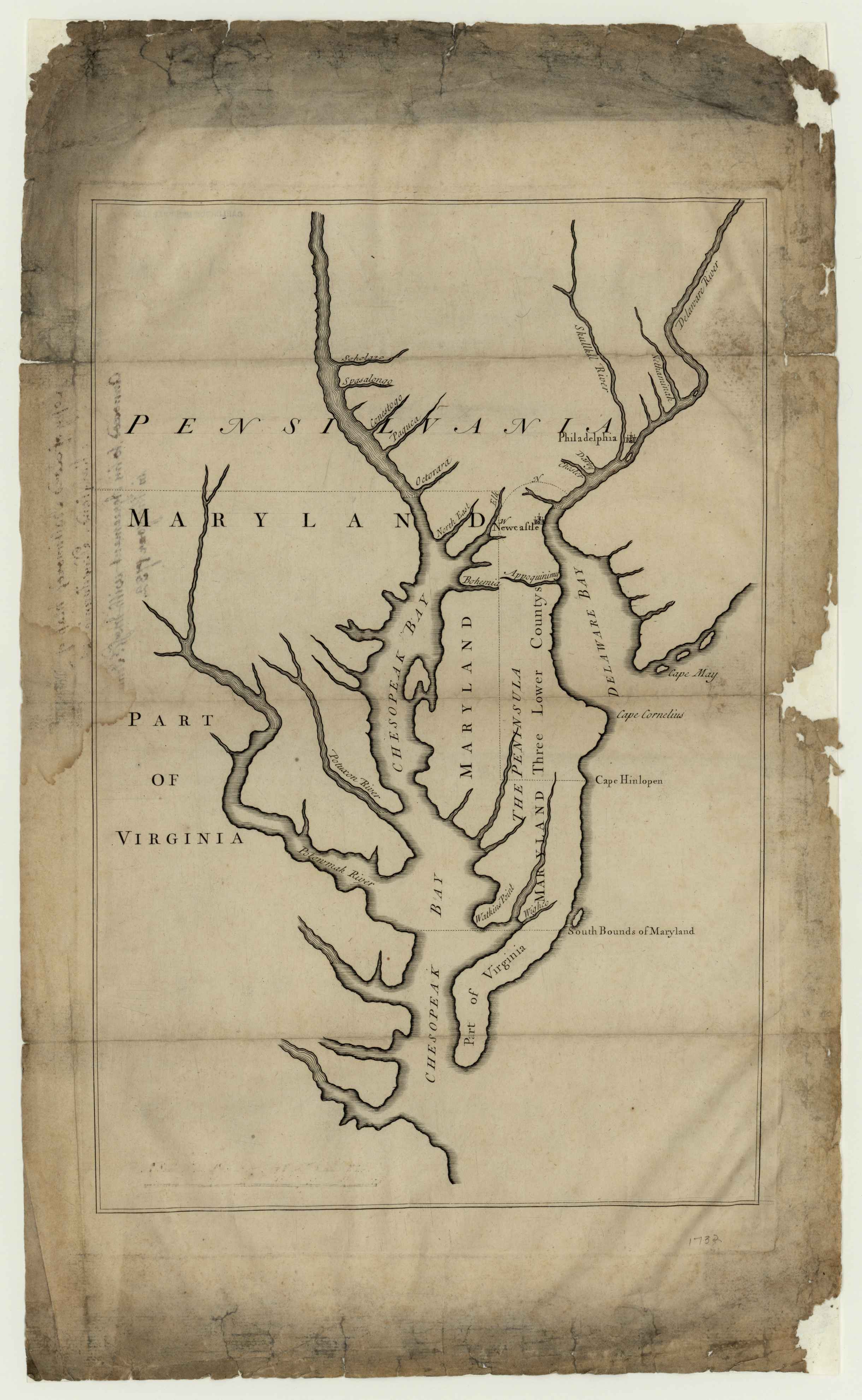
Border disputes (1681–1760)
 The royal charter granted Maryland the land north of the
The royal charter granted Maryland the land north of the Potomac River
The Potomac River () drains the Mid-Atlantic United States, flowing from the Potomac Highlands into Chesapeake Bay. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map. Retrieved Augu ...
up to the 40th parallel. A problem arose when Charles II granted a charter for Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; (Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, Mary ...
. The grant defined Pennsylvania's southern border as identical to Maryland's northern border, the 40th parallel. But the grant indicated that Charles II and William Penn
William Penn ( – ) was an English writer and religious thinker belonging to the Religious Society of Friends (Quakers), and founder of the Province of Pennsylvania, a North American colony of England. He was an early advocate of democracy a ...
assumed the 40th parallel would pass close to New Castle, Delaware
New Castle is a city in New Castle County, Delaware, United States. The city is located six miles (10 km) south of Wilmington and is situated on the Delaware River. As of the 2010 census, the city's population was 5,285.
History
New Castl ...
when it falls north of Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since ...
, the site of which Penn had already selected for his colony's capital city. Negotiations ensued after the problem was discovered in 1681.
A compromise proposed by Charles II in 1682 was undermined by Penn's receiving the additional grant of what is now Delaware. Penn successfully argued that the Maryland charter entitled Lord Baltimore only to unsettled lands, and Dutch settlement in Delaware predated his charter. The dispute remained unresolved for nearly a century, carried on by the descendants of William Penn and Lord Baltimore—the Calvert family
Baron Baltimore, of Baltimore, County Longford, was a title in the Peerage of Ireland. It was created in 1625 and ended in 1771, upon the death of its sixth-generation male heir, aged 40. Holders of the title were usually known as Lord Baltimo ...
, which controlled Maryland, and the Penn family, which controlled Pennsylvania.
The border dispute with Pennsylvania led to Cresap's War in the 1730s. Hostilities erupted in 1730 and escalated through the first half of the decade, culminating in the deployment of military forces by Maryland in 1736 and by Pennsylvania in 1737. The armed phase of the conflict ended in May 1738 with the intervention of King George II, who compelled the negotiation of a cease-fire. A provisional agreement had been established in 1732.
Negotiations continued until a final agreement was signed in 1760. The agreement defined the border between Maryland and Pennsylvania as the line of latitude now known as the Mason–Dixon line. Maryland's border with Delaware was based on a Transpeninsular Line
The Transpeninsular Line (at approximately 38°27′ N) is a surveyed line, the eastern half of which forms the north–south border between Delaware and Maryland. The border turns roughly north from the midpoint of the line towards the Twelve-M ...
and the Twelve-Mile Circle
The Twelve-Mile Circle is an approximately circular arc which forms most of the boundary between Pennsylvania and Delaware. It is not actually a circle, but rather a combination of different circular arcs that have been feathered together.
It is ...
around New Castle.
18th century
Most of the English colonists arrived in Maryland asindentured servant
Indentured servitude is a form of labor in which a person is contracted to work without salary for a specific number of years. The contract, called an "indenture", may be entered "voluntarily" for purported eventual compensation or debt repayment, ...
s, and had to serve a several years' term as laborers to pay for their passage. In the early years, the line between indentured servants and African slaves or laborers was fluid, and white and black laborers commonly lived and worked together, and formed unions. Mixed-race
Mixed race people are people of more than one race or ethnicity. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mixed race people in a variety of contexts, including ''multiethnic'', ''polyethnic'', occasionally ''bi-ethn ...
children born to white mothers were considered free by the principle of ''partus sequitur ventrem
''Partus sequitur ventrem'' (L. "That which is born follows the womb"; also ''partus'') was a legal doctrine passed in colonial Virginia in 1662 and other English crown colonies in the Americas which defined the legal status of children born the ...
'', by which children took the social status of their mothers, a principle of slave law that was adopted throughout the colonies, following Virginia in 1662. During the colonial era, families of free people of color
In the context of the history of slavery in the Americas, free people of color (French: ''gens de couleur libres''; Spanish: ''gente de color libre'') were primarily people of mixed African, European, and Native American descent who were not ...
were formed most often by unions of white women and African men.
Many of the free black families migrated to Delaware, where land was cheaper.Paul Heinegg. ''Free African Americans in Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Maryland and Delaware''Retrieved February 15, 2008. As the flow of indentured laborers to the colony decreased with improving economic conditions in England, planters in Maryland imported thousands more slaves and racial caste lines hardened. The economy's growth and prosperity were based on slave labor, devoted first to the production of
tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus ''Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the chie ...
as the commodity crop.
Maryland was one of the thirteen colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Founded in the 17th and 18th centuri ...
that revolted against British rule in the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revoluti ...
. Near the end of the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
(1775–1783), on February 2, 1781, Maryland became the last and 13th state to approve the ratification of the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union
The Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union was an agreement among the 13 Colonies of the United States of America that served as its first frame of government. It was approved after much debate (between July 1776 and November 1777) by t ...
, first proposed in 1776 and adopted by the Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress was a late-18th-century meeting of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that united in support of the American Revolutionary War. The Congress was creating a new country it first named "United Colonies" and in 1 ...
in 1778, which brought into being the United States as a united, sovereign
''Sovereign'' is a title which can be applied to the highest leader in various categories. The word is borrowed from Old French , which is ultimately derived from the Latin , meaning 'above'.
The roles of a sovereign vary from monarch, ruler or ...
and national state
A nation state is a political unit where the state and nation are congruent. It is a more precise concept than "country", since a country does not need to have a predominant ethnic group.
A nation, in the sense of a common ethnicity, may inc ...
. It also became the seventh state admitted to the Union after ratifying the new federal Constitution in 1788. In December 1790, Maryland donated land selected by first President George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of th ...
to the federal government for the creation of the new national capital of Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, Na ...
The land was provided along the north shore of the Potomac River
The Potomac River () drains the Mid-Atlantic United States, flowing from the Potomac Highlands into Chesapeake Bay. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map. Retrieved Augu ...
from Montgomery and Prince George's counties, as well as from Fairfax County
Fairfax County, officially the County of Fairfax, is a county in the Commonwealth of Virginia. It is part of Northern Virginia and borders both the city of Alexandria and Arlington County and forms part of the suburban ring of Washington, D.C. ...
and Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
on the south shore of the Potomac in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
; however, the land donated by the Commonwealth of Virginia was later returned to that state by the District of Columbia retrocession
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions o ...
in 1846.
19th century
 Influenced by a changing economy, revolutionary ideals, and preaching by ministers, numerous planters in Maryland freed their slaves in the 20 years after the Revolutionary War. Across the Upper South the free black population increased from less than 1% before the war to 14% by 1810. Abolitionists
Influenced by a changing economy, revolutionary ideals, and preaching by ministers, numerous planters in Maryland freed their slaves in the 20 years after the Revolutionary War. Across the Upper South the free black population increased from less than 1% before the war to 14% by 1810. Abolitionists Harriet Tubman
Harriet Tubman (born Araminta Ross, March 10, 1913) was an American abolitionist and social activist. Born into slavery, Tubman escaped and subsequently made some 13 missions to rescue approximately 70 slaves, including family and friends, u ...
and Frederick Douglass
Frederick Douglass (born Frederick Augustus Washington Bailey, February 1817 or 1818 – February 20, 1895) was an American social reformer, abolitionist, orator, writer, and statesman. After escaping from slavery in Maryland, he became ...
were born slaves during this time in Dorchester County and Talbot County, respectively.
During the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States, United States of America and its Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom ...
, the British military attempted to capture Baltimore, which was protected by Fort McHenry
Fort McHenry is a historical American coastal pentagonal bastion fort on Locust Point, now a neighborhood of Baltimore, Maryland. It is best known for its role in the War of 1812, when it successfully defended Baltimore Harbor from an attack ...
. During this bombardment the song "Star-Spangled Banner
"The Star-Spangled Banner" is the national anthem of the United States. The lyrics come from the "Defence of Fort M'Henry", a poem written on September 14, 1814, by 35-year-old lawyer and amateur poet Francis Scott Key after witnessing the ...
" was written by Francis Scott Key
Francis Scott Key (August 1, 1779January 11, 1843) was an American lawyer, author, and amateur poet from Frederick, Maryland, who wrote the lyrics for the American national anthem "The Star-Spangled Banner". Key observed the British bombardment ...
; it was later adopted as the national anthem.
The National Road (U.S. Hwy 40 today) was authorized in 1817 and ran from Baltimore to St. Louis—the first federal highway. The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was the first common carrier railroad and the oldest railroad in the United States, with its first section opening in 1830. Merchants from Baltimore, which had benefited to some extent from the construction of ...
(B&O) was the first chartered railroad in the United States. It opened its first section of track for regular operation in 1830 between Baltimore and Ellicott City, and in 1852 it became the first rail line to reach the Ohio River
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illi ...
from the eastern seaboard.
Civil War
 The state remained with the Union during the Civil War, due in significant part to demographics and Federal intervention. The 1860 census, held shortly before the outbreak of the civil war, showed that 49% of Maryland's African Americans were free blacks.Peter Kolchin, ''American Slavery: 1619–1877'', New York: Hill and Wang, 1993, pp. 81–82
Governor
The state remained with the Union during the Civil War, due in significant part to demographics and Federal intervention. The 1860 census, held shortly before the outbreak of the civil war, showed that 49% of Maryland's African Americans were free blacks.Peter Kolchin, ''American Slavery: 1619–1877'', New York: Hill and Wang, 1993, pp. 81–82
Governor Thomas Holliday Hicks
Thomas Holliday Hicks (September 2, 1798February 14, 1865) was a politician in the divided border-state of Maryland during the American Civil War. As governor, opposing the Democrats, his views accurately reflected the conflicting local loyal ...
suspended the state legislature, and to help ensure the election of a new pro-union governor and legislature, President Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation throu ...
had a number of its pro-slavery politicians arrested, including the Mayor of Baltimore, George William Brown
George William Brown (October 13, 1812 – September 8, 1890) was an American politician, judge and academic. He was mayor of Baltimore from 1860 to 1861, professor in University of Maryland School of Law, and 2nd Chief Judge and Supreme Bench of ...
; suspended several civil liberties, including ''habeas corpus''; and ordered artillery placed on Federal Hill overlooking Baltimore. Historians debate the constitutionality of these wartime actions, and the suspension of civil liberties was later deemed illegal by the U.S. Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
.
In April 1861, Federal units and state regiments were attacked as they marched through Baltimore, sparking the Baltimore riot of 1861
The Baltimore riot of 1861 (also called the "Pratt Street Riots" and the "Pratt Street Massacre") was a civil conflict on Friday, April 19, 1861, on Pratt Street, in Baltimore, Maryland. It occurred between antiwar "Copperhead" Democrats (the ...
, the first bloodshed in the Civil War. Of the 115,000 men from Maryland who joined the military during the Civil War, around 85,000, or 77%, joined the Union army
During the American Civil War, the Union Army, also known as the Federal Army and the Northern Army, referring to the United States Army, was the land force that fought to preserve the Union of the collective states. It proved essential to the ...
, while the remainder joined the Confederate Army
The Confederate States Army, also called the Confederate Army or the Southern Army, was the military land force of the Confederate States of America (commonly referred to as the Confederacy) during the American Civil War (1861–1865), fighting ...
. The largest and most significant battle in the state was the Battle of Antietam
The Battle of Antietam (), or Battle of Sharpsburg particularly in the Southern United States, was a battle of the American Civil War fought on September 17, 1862, between Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia and Union ...
on September 17, 1862, near Sharpsburg. Although a tactical draw, the battle was considered a strategic Union victory and a turning point of the war.
After the war
A new state constitution in 1864 abolished slavery and Maryland was first recognized as a "Free State" in that context. Following passage of constitutional amendments that granted voting rights tofreedmen
A freedman or freedwoman is a formerly enslaved person who has been released from slavery, usually by legal means. Historically, enslaved people were freed by manumission (granted freedom by their captor-owners), emancipation (granted freedom a ...
, in 1867 the state extended suffrage to non-white males.
The Democratic Party Democratic Party most often refers to:
*Democratic Party (United States)
Democratic Party and similar terms may also refer to:
Active parties Africa
* Botswana Democratic Party
* Democratic Party of Equatorial Guinea
*Gabonese Democratic Party
*De ...
rapidly regained power in the state from Republicans. Democrats replaced the Constitution of 1864 with the Constitution of 1867. Following the end of Reconstruction in 1877, Democrats devised means of disenfranchising blacks, initially by physical intimidation and voter fraud, later by constitutional amendments and laws. Blacks and immigrants, however, resisted Democratic Party disfranchisement efforts in the state. Maryland blacks were part of a biracial Republican coalition elected to state government in 1896–1904 and comprised 20% of the electorate.
Compared to some other states, blacks were better established both before and after the civil war. Nearly half the black population was free before the war, and some had accumulated property. Half the population lived in cities. Literacy was high among blacks and, as Democrats crafted means to exclude them, suffrage campaigns helped reach blacks and teach them how to resist. Whites did impose racial segregation
Racial segregation is the systematic separation of people into racial or other ethnic groups in daily life. Racial segregation can amount to the international crime of apartheid and a crime against humanity under the Statute of the Internat ...
in public facilities and Jim Crow
The Jim Crow laws were state and local laws enforcing racial segregation in the Southern United States. Other areas of the United States were affected by formal and informal policies of segregation as well, but many states outside the Sout ...
laws, which effectively lasted until the passage of federal civil rights legislation in the mid-1960s.
Baltimore grew significantly during the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, due in large part to its seaport and good railroad connections, attracting European immigrant labor. Many manufacturing businesses were established in the Baltimore area after the Civil War. Baltimore businessmen, including Johns Hopkins
Johns Hopkins (May 19, 1795 – December 24, 1873) was an American merchant, investor, and philanthropist. Born on a plantation, he left his home to start a career at the age of 17, and settled in Baltimore, Maryland where he remained for most ...
, Enoch Pratt
Enoch Pratt (September 10, 1808 – September 17, 1896) was an American businessman in Baltimore, Maryland. Pratt was also a committed active Unitarian, and a philanthropist. He is best known for his donations to establish the Enoch Pratt Free ...
, George Peabody
George Peabody ( ; February 18, 1795 – November 4, 1869) was an American financier and philanthropist. He is widely regarded as the father of modern philanthropy.
Born into a poor family in Massachusetts, Peabody went into business in dry g ...
, and Henry Walters
Henry Walters (September 26, 1848 – November 30, 1931) was noted as an art collector and philanthropist, a founder of the Walters Art Gallery (now the Walters Art Museum) in Baltimore, Maryland, which he donated to the city in his 1931 will f ...
, founded notable city institutions that bear their names, including respectively a university
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, th ...
, library system
A library consortium is any cooperative association of libraries that coordinates resources and/or activities on behalf of its members, whether they are school, public, academic, special libraries and/or information centers. Consortia exist on a v ...
, music and dance conservatory, and art museum
An art museum or art gallery is a building or space for the display of art, usually from the museum's own collection. It might be in public or private ownership and may be accessible to all or have restrictions in place. Although primarily con ...
.
Cumberland was Maryland's second-largest city in the 19th century. Nearby supplies of natural resources along with railroads fostered its growth into a major manufacturing center.
20th and 21st centuries
Early 20th century
 The
The Progressive Era
The Progressive Era (late 1890s – late 1910s) was a period of widespread social activism and political reform across the United States focused on defeating corruption, monopoly, waste and inefficiency. The main themes ended during Am ...
of the late 19th and early 20th centuries brought political reforms. In a series of laws passed between 1892 and 1908, reformers worked for standard state-issued ballots (rather than those distributed and marked by the parties); obtained closed voting booths to prevent party workers from "assisting" voters; initiated primary election
Primary elections, or direct primary are a voting process by which voters can indicate their preference for their party's candidate, or a candidate in general, in an upcoming general election, local election, or by-election. Depending on the ...
s to keep party bosses from selecting candidates; and had candidates listed without party symbols, which discouraged the illiterate
Literacy in its broadest sense describes "particular ways of thinking about and doing reading and writing" with the purpose of understanding or expressing thoughts or ideas in written form in some specific context of use. In other words, huma ...
from participating. These measures worked against ill-educated whites and blacks. Blacks resisted such efforts, with suffrage groups conducting voter education.
Blacks defeated three efforts to disenfranchise them, making alliances with immigrants to resist various Democratic campaigns. Disenfranchisement bills in 1905, 1907, and 1911 were rebuffed, in large part because of black opposition. Blacks comprised 20% of the electorate and immigrants comprised 15%, and the legislature had difficulty devising requirements against blacks that did not also disadvantage immigrants.
The Progressive Era also brought reforms in working conditions for Maryland's labor force. In 1902, the state regulated conditions in mines; outlawed child labor
Child labour refers to the exploitation of children through any form of work that deprives children of their childhood, interferes with their ability to attend regular school, and is mentally, physically, socially and morally harmful. Such ...
ers under the age of 12; mandated compulsory school attendance; and enacted the nation's first workers' compensation
Workers' compensation or workers' comp is a form of insurance providing wage replacement and medical benefits to employees injured in the course of employment in exchange for mandatory relinquishment of the employee's right to sue his or her emp ...
law. The workers' compensation law was overturned in the courts, but was redrafted and finally enacted in 1910.
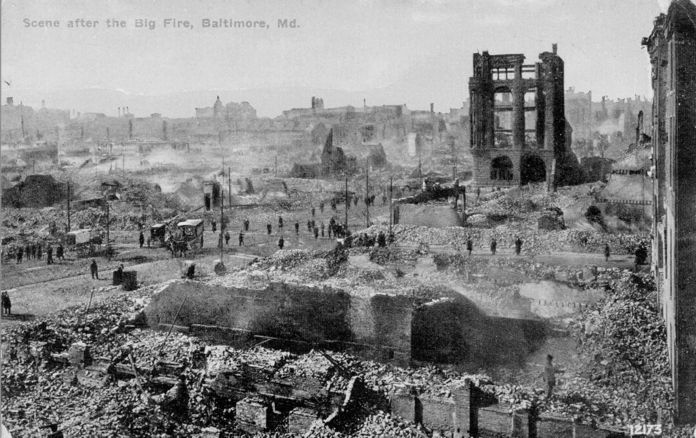
The Great Baltimore Fire
The Great Baltimore Fire raged in Baltimore, Maryland from Sunday, February 7, to Monday, February 8, 1904. More than 1,500 buildings were completely leveled, and some 1,000 severely damaged, bringing property loss from the disaster to an estimate ...
of 1904 burned for more than 30 hours, destroying 1,526 buildings and spanning 70 city blocks. More than 1,231 firefighter
A firefighter is a first responder and rescuer extensively trained in firefighting, primarily to extinguish hazardous fires that threaten life, property, and the environment as well as to rescue people and in some cases or jurisdictions also ...
s worked to bring the blaze under control.
With the nation's entry into World War I in 1917, new military bases such as Camp Meade
Camp George G. Meade near Middletown, Pennsylvania, was a camp established and subsequently abandoned by the U.S. Volunteers during the Spanish–American War.
History
Camp Meade was established August 24, 1898, and soon thereafter was occupi ...
, the Aberdeen Proving Ground
Aberdeen Proving Ground (APG) (sometimes erroneously called Aberdeen Proving ''Grounds'') is a U.S. Army facility located adjacent to Aberdeen, Harford County, Maryland, United States. More than 7,500 civilians and 5,000 military personnel work a ...
, and the Edgewood Arsenal
Aberdeen Proving Ground (APG) (sometimes erroneously called Aberdeen Proving ''Grounds'') is a U.S. Army facility located adjacent to Aberdeen, Harford County, Maryland, United States. More than 7,500 civilians and 5,000 military personnel work ...
were established. Existing facilities, including Fort McHenry
Fort McHenry is a historical American coastal pentagonal bastion fort on Locust Point, now a neighborhood of Baltimore, Maryland. It is best known for its role in the War of 1812, when it successfully defended Baltimore Harbor from an attack ...
, were greatly expanded.
After Georgia congressman William D. Upshaw criticized Maryland openly in 1923 for not passing Prohibition laws, ''Baltimore Sun'' editor Hamilton Owens coined the "Free State" nickname for Maryland in that context, which was popularized by H. L. Mencken
Henry Louis Mencken (September 12, 1880 – January 29, 1956) was an American journalist, essayist, satirist, cultural critic, and scholar of American English. He commented widely on the social scene, literature, music, prominent politicians, ...
in a series of newspaper editorials.
Maryland's urban and rural communities had different experiences during the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagion ...
. The "Bonus Army
The Bonus Army was a group of 43,000 demonstrators – 17,000 veterans of U.S. involvement in World War I, their families, and affiliated groups – who gathered in Washington, D.C., in mid-1932 to demand early cash redemption of their servic ...
" marched through the state in 1932 on its way to Washington, D.C. Maryland instituted its first income tax
An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities (taxpayers) in respect of the income or profits earned by them (commonly called taxable income). Income tax generally is computed as the product of a tax rate times the taxable income. Tax ...
in 1937 to generate revenue for schools and welfare.
Passenger and freight steamboat service, once important throughout Chesapeake Bay and its many tributary rivers, ended in 1962.
Baltimore was a major war production center during World War II. The biggest operations were Bethlehem Steel
The Bethlehem Steel Corporation was an American steelmaking company headquartered in Bethlehem, Pennsylvania. For most of the 20th century, it was one of the world's largest steel producing and shipbuilding companies. At the height of its succe ...
's Fairfield Yard, which built Liberty ship
Liberty ships were a class of cargo ship built in the United States during World War II under the Emergency Shipbuilding Program. Though British in concept, the design was adopted by the United States for its simple, low-cost construction. M ...
s; and Glenn Martin, an aircraft manufacturer.
1950–present
Maryland experienced population growth following World War II. Beginning in the 1960s, as suburban growth took hold around Washington, D.C. and Baltimore, the state began to take on a more mid-Atlantic culture as opposed to the traditionally Southern and Tidewater culture that previously dominated most of the state. Agricultural tracts gave way to residential communities, some of them carefully planned such as Columbia, St. Charles, andMontgomery Village
Montgomery Village is a census-designated place (CDP) in Montgomery County, Maryland, Montgomery County, Maryland, United States, and a northern suburb of Washington, D.C. It is a large, planned suburban community, developed in the late 1960s and ...
. Concurrently the Interstate Highway System
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States. Th ...
was built throughout the state, most notably I-95
Interstate 95 (I-95) is the main north–south Interstate Highway on the East Coast of the United States, running from US Route 1 (US 1) in Miami, Florida, to the Houlton–Woodstock Border Crossing between Maine and the Canad ...
, I-695, and the Capital Beltway
The Capital Beltway is a Interstate Highway in the Washington metropolitan area that surrounds Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States, and its inner suburbs in adjacent Maryland and Virginia. It is the basis of the phrase "inside t ...
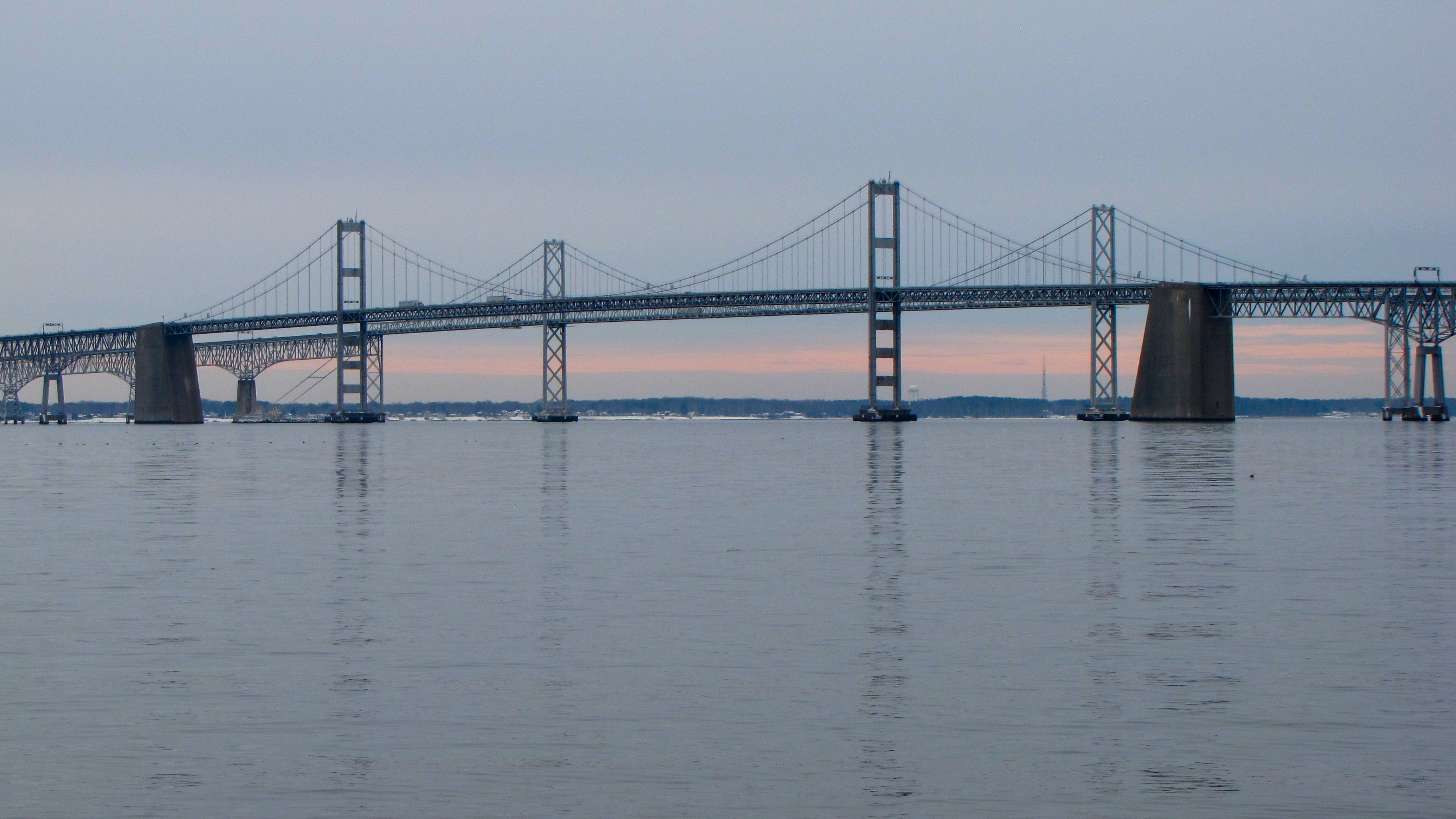
, altering travel patterns. In 1952, the eastern and western halves of Maryland were linked for the first time by the Chesapeake Bay Bridge
The Chesapeake Bay Bridge (also known locally as the Bay Bridge) is a major dual-span bridge in the U.S. state of Maryland. Spanning the Chesapeake Bay, it connects the state's rural Eastern Shore region with the urban Western Shore, between ...
, which replaced a nearby ferry
A ferry is a ship, watercraft or amphibious vehicle used to carry passengers, and sometimes vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A passenger ferry with many stops, such as in Venice, Italy, is sometimes called a water bus or water ta ...
service.
Maryland's regions experienced economic changes following WWII. Heavy manufacturing declined in Baltimore. In Maryland's four westernmost counties, industrial, railroad, and coal mining jobs declined. On the lower Eastern Shore, family farms were bought up by major concerns and large-scale poultry farms and vegetable farming became prevalent. In Southern Maryland, tobacco farming nearly vanished due to suburban development and a state tobacco buy-out program in the 1990s.
In an effort to reverse depopulation due to the loss of working-class industries, Baltimore initiated urban renewal
Urban renewal (also called urban regeneration in the United Kingdom and urban redevelopment in the United States) is a program of land redevelopment often used to address urban decay in cities. Urban renewal involves the clearing out of bligh ...
projects in the 1960s with Charles Center
Charles Center is a large-scale urban redevelopment project in central Baltimore's downtown business district of the late 1950s and early 1960s. Beginning in 1954, a group called the "Committee for Downtown" promoted a master plan for arresting th ...
and the Baltimore World Trade Center
Located on the Inner Harbor of Baltimore, Maryland, the Baltimore World Trade Center is the world's tallest regular pentagonal-based skyscraper (the pentagonal-based JPMorgan Chase Tower in Houston is taller, but is not regular). It was designed ...
. Some resulted in the break-up of intact residential neighborhoods, producing social volatility, and some older residential areas around the harbor have had units renovated and have become popular with new populations.
Geography
Maryland has an area of and is comparable in overall area with Belgium []. It is the 42nd largest and 9th smallest state and is closest in size to the state of Hawaii [], the next smallest state. The next largest state, its neighborWest Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the ...
, is almost twice the size of Maryland [].
Description


 Maryland possesses a variety of
Maryland possesses a variety of topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary scien ...
within its borders, contributing to its nickname ''America in Miniature''. It ranges from sandy dunes
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, fl ...
dotted with seagrass in the east, to low marshlands teeming with wildlife and large bald cypress
''Taxodium distichum'' (bald cypress, swamp cypress; french: cyprès chauve;
''cipre'' in Louisiana) is a deciduous conifer in the family Cupressaceae. It is native to the southeastern United States. Hardy and tough, this tree adapts to a wide ...
near the Chesapeake Bay, to gently rolling hills of oak forests in the Piedmont Region, and pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garden accepts ...
groves in the Maryland mountains to the west.
Maryland is bounded on its north by Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; (Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, Mary ...
, on its north and east by Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
, on its east by the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Afr ...
, and on its south and west, across the Potomac River
The Potomac River () drains the Mid-Atlantic United States, flowing from the Potomac Highlands into Chesapeake Bay. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map. Retrieved Augu ...
, by West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the ...
and Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
. The mid-portion of this latter border is interrupted by the District of Columbia
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, Na ...
, which sits on land that was originally part of Montgomery and Prince George's counties and including the town of Georgetown, Maryland
Georgetown is an unincorporated community in northeastern Kent County, Maryland, United States. The community was laid out in 1736. Georgetown was named for Prince George who later became King of the United Kingdom. Georgetown is located on the ...
. This land was ceded to the United States Federal Government in 1790 to form the District of Columbia
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, Na ...
. (The Commonwealth of Virginia gave land south of the Potomac, including the town of Alexandria, Virginia
Alexandria is an independent city in the northern region of the Commonwealth of Virginia, United States. It lies on the western bank of the Potomac River approximately south of downtown Washington, D.C.
In 2020, the population was 159,467. Th ...
; however, Virginia retroceded its portion in 1846). The Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / E ...
nearly bisects the state and the counties east of the bay are known collectively as the Eastern Shore.
Most of the state's waterways are part of the Chesapeake Bay watershed, with the exceptions of a tiny portion of extreme western Garrett County (drained by the Youghiogheny River
The Youghiogheny River , or the Yough (pronounced Yok ) for short, is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed August 15, 2011 tributary of the Monongahela River in the U.S. s ...
as part of the watershed of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
), the eastern half of Worcester County (which drains into Maryland's Atlantic coastal bays), and a small portion of the state's northeast corner (which drains into the Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock, New York, the river flows for along the borders of New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Delaware, before em ...
watershed). So prominent is the Chesapeake in Maryland's geography and economic life that there has been periodic agitation to change the state's official nickname to the "Bay State", a nickname that has been used by Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
for decades.
The highest point in Maryland, with an elevation of , is Hoye Crest on Backbone Mountain, in the southwest corner of Garrett County, near the border with West Virginia, and near the headwaters of the North Branch of the Potomac River. Close to the small town of Hancock Hancock may refer to:
Places in the United States
* Hancock, Iowa
* Hancock, Maine
* Hancock, Maryland
* Hancock, Massachusetts
* Hancock, Michigan
* Hancock, Minnesota
* Hancock, Missouri
* Hancock, New Hampshire
** Hancock (CDP), New Hampsh ...
, in western Maryland, about two-thirds of the way across the state, less than separates its borders, the Mason–Dixon line
The Mason–Dixon line, also called the Mason and Dixon line or Mason's and Dixon's line, is a demarcation line separating four U.S. states, forming part of the borders of Pennsylvania, Maryland, Delaware, and West Virginia (part of Virginia ...
to the north, and the northwards-arching Potomac River
The Potomac River () drains the Mid-Atlantic United States, flowing from the Potomac Highlands into Chesapeake Bay. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map. Retrieved Augu ...
to the south.
Portions of Maryland are included in various official and unofficial geographic regions. For example, the Delmarva Peninsula
The Delmarva Peninsula, or simply Delmarva, is a large peninsula and proposed state on the East Coast of the United States, occupied by the vast majority of the state of Delaware and parts of the Eastern Shore regions of Maryland and Virginia. ...
is composed of the Eastern Shore counties of Maryland, the entire state of Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
, and the two counties that make up the Eastern Shore of Virginia
The Eastern Shore of Virginia consists of two counties ( Accomack and Northampton) on the Atlantic coast detached from the mainland of the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. The region is part of the Delmarva Peninsula and is s ...
, whereas the westernmost counties of Maryland are considered part of Appalachia
Appalachia () is a cultural region in the Eastern United States that stretches from the Southern Tier of New York State to northern Alabama and Georgia. While the Appalachian Mountains stretch from Belle Isle in Newfoundland and Labrador, C ...
. Much of the Baltimore–Washington corridor lies just south of the Piedmont in the Coastal Plain, though it straddles the border between the two regions.
Geology
Earthquakes in Maryland are infrequent and small due to the state's distance from seismic/earthquake zones. The M5.8 Virginia earthquake in 2011 was felt moderately throughout Maryland. Buildings in the state are not well-designed for earthquakes and can suffer damage easily. Maryland has no natural lakes, mostly due to the lack of glacial history in the area. All lakes in the state today were constructed, mostly via dams.Buckel's Bog
Buckel's Bog was a 160-acre, shallow periglacial lake or a glade that occupied the headwater region of the North Branch of the Casselman River in Garrett County, Maryland during the late Pleistocene epoch. It is the remnant of the only known natu ...
is believed by geologists to have been a remnant of a former natural lake.
Maryland has shale formations containing natural gas, where fracking is theoretically possible.
Flora
 As is typical of states on the East Coast, Maryland's plant life is abundant and healthy. A modest volume of annual precipitation helps to support many types of plants, including
As is typical of states on the East Coast, Maryland's plant life is abundant and healthy. A modest volume of annual precipitation helps to support many types of plants, including seagrass
Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four families ( Posidoniaceae, Zosteraceae, Hydrocharitaceae and Cymodoceaceae), all in the ...
and various reeds at the smaller end of the spectrum to the gigantic Wye Oak, a huge example of white oak
The genus ''Quercus'' contains about 500 species, some of which are listed here. The genus, as is the case with many large genera, is divided into subgenera and sections. Traditionally, the genus ''Quercus'' was divided into the two subgenera '' ...
, the state tree, which can grow over tall.
Middle Atlantic coastal forests
The Middle Atlantic coastal forests are a temperate coniferous forest mixed with patches of evergreen broadleaved forests (closer to the Atlantic coast) along the coast of the southeastern United States.
Setting
The Middle Atlantic coastal fore ...
, typical of the southeastern Atlantic coastal plain
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
, grow around Chesapeake Bay and on the Delmarva Peninsula
The Delmarva Peninsula, or simply Delmarva, is a large peninsula and proposed state on the East Coast of the United States, occupied by the vast majority of the state of Delaware and parts of the Eastern Shore regions of Maryland and Virginia. ...
. Moving west, a mixture of Northeastern coastal forests
The Northeastern coastal forests are a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion of the northeast and middle Atlantic region of the United States. The ecoregion covers an area of 34,630 sq miles (89,691 km2) encompassing the Piedmont ...
and Southeastern mixed forests
The Southeastern mixed forests are an ecoregion of the temperate broadleaf and mixed forest biome, in the lower portion of the Eastern United States.
Setting
This ecoregion covers the Piedmont region of the eastern United States, stretching in a ...
cover the central part of the state. The Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
of western Maryland are home to Appalachian-Blue Ridge forests. These give way to Appalachian mixed mesophytic forests
The Appalachian mixed mesophytic forests is an ecoregion of the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome, as defined by the World Wildlife Fund. It consists of mesophytic plants west of the Appalachian Mountains in the Southeastern United Sta ...
near the West Virginia border.
Many foreign species are cultivated in the state, some as ornamentals, others as novelty species. Included among these are the crape myrtle
''Lagerstroemia'' (), commonly known as crape myrtle (also spelled crepe myrtle or crêpe myrtle), is a genus of around 50 species of deciduous and evergreen trees and shrubs native to the Indian subcontinent, southeast Asia, northern Australia ...
, Italian cypress
''Cupressus sempervirens'', the Mediterranean cypress (also known as Italian cypress, Tuscan cypress, Persian cypress, or pencil pine), is a species of cypress native to the eastern Mediterranean region, in northeast Libya, southern Albania, sou ...
, southern magnolia
''Magnolia grandiflora'', commonly known as the southern magnolia or bull bay, is a tree of the family Magnoliaceae native to the Southeastern United States, from Virginia to central Florida, and west to East Texas. Reaching in height, it is a ...
, live oak
Live oak or evergreen oak is any of a number of oaks in several different sections of the genus ''Quercus'' that share the characteristic of evergreen foliage. These oaks are not more closely related to each other than they are to other oaks. ...
in the warmer parts of the state, and even hardy palm trees in the warmer central and eastern parts of the state. USDA plant hardiness zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most wide ...
s in the state range from Zones 5and6 in the extreme western part of the state to Zone7 in the central part, and Zone8 around the southern part of the coast, the bay area, and parts of metropolitan Baltimore. Invasive plant species, such as kudzu
Kudzu (; also called Japanese arrowroot or Chinese arrowroot) is a group of climbing, coiling, and trailing deciduous perennial vines native to much of East Asia, Southeast Asia, and some Pacific islands, but invasive species, invasive in many ...
, tree of heaven
''Ailanthus altissima'' , commonly known as tree of heaven, ailanthus, varnish tree, or in Chinese as ''chouchun'' (), is a deciduous tree in the family Simaroubaceae. It is native to northeast and central China, and Taiwan. Unlike other memb ...
, multiflora rose
''Rosa multiflora'' — (syn. ''Rosa polyantha'') is a species of rose known commonly as multiflora rose, baby rose, Japanese rose, many-flowered rose, seven-sisters rose, Eijitsu rose and rambler rose. It is native to eastern Asia, in China, J ...
, and Japanese stiltgrass, stifle growth of endemic plant life. Maryland's state flower, the black-eyed susan
''Black-Eyed Susan; or, All in the Downs'' is a comic play in three acts by Douglas Jerrold. The story concerns a heroic sailor, William, who has been away from England for three years fighting in the Napoleonic Wars. Meanwhile, his wife, Susa ...
, grows in abundance in wild flower groups throughout the state.
Fauna
 The state harbors a considerable number of
The state harbors a considerable number of white-tailed deer
The white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), also known as the whitetail or Virginia deer, is a medium-sized deer native to North America, Central America, and South America as far south as Peru and Bolivia. It has also been introduced t ...
, especially in the woody and mountainous west of the state, and overpopulation can become a problem. Mammals can be found ranging from the mountains in the west to the central areas and include black bears, bobcat
The bobcat (''Lynx rufus''), also known as the red lynx, is a medium-sized cat native to North America. It ranges from southern Canada through most of the contiguous United States to Oaxaca in Mexico. It is listed as Least Concern on the I ...
s, foxes, coyote
The coyote (''Canis latrans'') is a species of canine native to North America. It is smaller than its close relative, the wolf, and slightly smaller than the closely related eastern wolf and red wolf. It fills much of the same ecological n ...
s, raccoons, and otters.
There is a population of rare wild (feral) horses found on Assateague Island
Assateague Island is a long barrier island located off the eastern coast of the Delmarva Peninsula facing the Atlantic Ocean. The northern two-thirds of the island is in Maryland while the southern third is in Virginia. The Maryland sectio ...
. They are believed to be descended from horses who escaped from Spanish galleon shipwrecks. Every year during the last week of July, they are captured and swim across a shallow bay for sale at Chincoteague, Virginia
Chincoteague ( or ) is a town in Accomack County, Virginia, U.S. The town includes the whole of Chincoteague Island and an area of adjacent water. The population was 2,941 at the 2010 census. The town is known for the Chincoteague Ponies, althou ...
, a conservation technique which ensures the tiny island is not overrun by the horses. The ponies and their sale were popularized by the children's book, ''Misty of Chincoteague
''Misty of Chincoteague'' is a children's novel written by Marguerite Henry, illustrated by Wesley Dennis, and published by Rand McNally in 1947. Set in the island town of Chincoteague, Virginia, the book was inspired by the real-life story of t ...
.''
The purebred Chesapeake Bay Retriever
The Chesapeake Bay Retriever is a large breed of dog belonging to the retriever, gundog, and sporting breed groups. The breed was developed in the United States Chesapeake Bay area during the 19th century. Historically used by local market hu ...
dog was bred specifically for water sports, hunting and search and rescue in the Chesapeake area. In 1878, the Chesapeake Bay Retriever was the first individual retriever breed recognized by the American Kennel Club
The American Kennel Club (AKC) is a registry of purebred dog pedigrees in the United States. In addition to maintaining its pedigree registry, this kennel club also promotes and sanctions events for purebred dogs, including the Westminster Ke ...
. and was later adopted by the University of Maryland, Baltimore County
The University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC) is a public research university in Baltimore County, Maryland. It has a fall 2022 enrollment of 13,991 students, 61 undergraduate majors, over 92 graduate programs (38 master, 25 doctoral, ...
as their mascot.
Maryland's reptile and amphibian population includes the diamondback terrapin
The diamondback terrapin or simply terrapin (''Malaclemys terrapin'') is a species of turtle native to the brackish coastal tidal marshes of the Northeastern and southern United States, and in Bermuda. It belongs to the monotypic genus ''Malaclem ...
turtle, which was adopted as the mascot of University of Maryland, College Park
The University of Maryland, College Park (University of Maryland, UMD, or simply Maryland) is a public land-grant research university in College Park, Maryland. Founded in 1856, UMD is the flagship institution of the University System of Mar ...
, as well as the threatened Eastern box turtle
The eastern box turtle (''Terrapene carolina carolina'') is a subspecies within a group of hinge-shelled turtles normally called box turtles. ''T. c. carolina'' is native to the eastern part of the United States.
The eastern box turtle ...
. The state is part of the territory of the Baltimore oriole
The Baltimore oriole (''Icterus galbula'') is a small icterid blackbird common in eastern North America as a migratory breeding bird. It received its name from the resemblance of the male's colors to those on the coat-of-arms of 17th century L ...
, which is the official state bird and mascot of the MLB team the Baltimore Orioles
The Baltimore Orioles are an American professional baseball team based in Baltimore. The Orioles compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) East division. As one of the American League's eight char ...
. Aside from the oriole, 435 other species of birds have been reported from Maryland.
The state insect is the Baltimore checkerspot butterfly, although it is not as common in Maryland as it is in the southern edge of its range.
Environment
Maryland joined with neighboring states during the end of the 20th century to improve the health of theChesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / E ...
. The bay's aquatic life and seafood industry have been threatened by development and by fertilizer and livestock waste entering the bay.
In 2007, Forbes.com rated Maryland as the fifth "Greenest" state in the country, behind three of the Pacific States
The West Coast of the United States, also known as the Pacific Coast, Pacific states, and the western seaboard, is the coastline along which the Western United States meets the North Pacific Ocean. The term typically refers to the contiguous U.S ...
and Vermont. Maryland ranks 40th in total energy consumption nationwide, and it managed less toxic waste per capita than all but six states in 2005. In April 2007, Maryland joined the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative
The Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI, pronounced "Reggie") is the first mandatory market-based program to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by the United States. RGGI is a cooperative effort among the states of Connecticut, Delaware, Maine, ...
(RGGI) — a regional initiative, formed by all the Northeastern states, Washington, D.C., and three Canadian provinces, to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. In March 2017, Maryland became the first state with proven gas reserves to ban fracking by passing a law against it. Vermont has such a law, but no shale gas, and New York has such a ban, though it was made by executive order.
Climate

 Maryland has a wide array of climates, due to local variances in elevation, proximity to water, and protection from colder weather due to downslope winds.
The eastern half of Maryland — which includes the cities of Ocean City, Salisbury,
Maryland has a wide array of climates, due to local variances in elevation, proximity to water, and protection from colder weather due to downslope winds.
The eastern half of Maryland — which includes the cities of Ocean City, Salisbury, Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Maryland and the county seat of, and only incorporated city in, Anne Arundel County. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east ...
, and the southern and eastern suburbs of Washington, D.C., and Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was ...
— lies on the Atlantic Coastal Plain
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
, with flat topography and sandy or muddy soil. This region has a humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
(Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
''Cfa''), with hot, humid summers and a cool to cold winter; it falls under USDA Hardiness zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most wide ...
8a.
The Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
region, which includes northern and western greater Baltimore, Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster.
The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, Bucki ...
, Gaithersburg
Gaithersburg ( ), officially the City of Gaithersburg, is a city in Montgomery County, Maryland, United States. At the time of the 2020 U.S. Census, Gaithersburg had a population of 69,657, making it the ninth-largest location in the state. Ga ...
, Frederick, and Hagerstown, has average seasonal snowfall totals generally exceeding , and, as part of USDA Hardiness zones 7b and 7a, temperatures below are less rare. From the Cumberland Valley
The Cumberland Valley is a northern constituent valley of the Great Appalachian Valley, within the Atlantic Seaboard watershed in Pennsylvania and Maryland. The Appalachian Trail crosses through the valley.
Geography
The valley is bound to t ...
on westward, the climate begins to transition to a humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezin ...
(Köppen ''Dfa'').
In western Maryland, the higher elevations of Allegany and Garrett counties, including the cities of Cumberland
Cumberland ( ) is a historic county in the far North West England. It covers part of the Lake District as well as the north Pennines and Solway Firth coast. Cumberland had an administrative function from the 12th century until 1974. From 1974 ...
, Frostburg, and Oakland
Oakland is the largest city and the county seat of Alameda County, California, United States. A major West Coast port, Oakland is the largest city in the East Bay region of the San Francisco Bay Area, the third largest city overall in the Bay ...
, display more characteristics of the humid continental zone, due in part to elevation. They fall under USDA Hardiness zones 6b and below.
Precipitation in the state is characteristic of the East Coast. Annual rainfall ranges from with more in higher elevations. Nearly every part of Maryland receives per month of rain. Average annual snowfall varies from in the coastal areas to over in the western mountains of the state.
Because of its location near the Atlantic Coast, Maryland is somewhat vulnerable to tropical cyclones
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
, although the Delmarva Peninsula
The Delmarva Peninsula, or simply Delmarva, is a large peninsula and proposed state on the East Coast of the United States, occupied by the vast majority of the state of Delaware and parts of the Eastern Shore regions of Maryland and Virginia. ...
and the outer banks of North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and S ...
provide a large buffer, such that strikes from major hurricanes (category3 or above) occur infrequently. More often, Maryland gets the remnants of a tropical system that has already come ashore and released most of its energy. Maryland averages around 30–40 days of thunderstorms a year, and averages around six tornado strikes annually.
Cities and metro areas
 Most of the population of Maryland lives in the central region of the state, in the
Most of the population of Maryland lives in the central region of the state, in the Baltimore metropolitan area
The Baltimore–Columbia–Towson Metropolitan Statistical Area, also known as Central Maryland, is a Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA) in Maryland as defined by the United States Office of Management and Budget (OMB). As of the 2010 Census, t ...
and Washington metropolitan area
The Washington metropolitan area, also commonly referred to as the National Capital Region, is the metropolitan area centered on Washington, D.C. The metropolitan area includes all of Washington, D.C. and parts of the states of Maryland, Virgi ...
, both of which are part of the Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area. The majority of Maryland's population is concentrated in the cities and suburbs surrounding Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, Na ...
, as well as in and around Maryland's most populous city, Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was ...
. Historically, these and many other Maryland cities developed along the Fall Line
A fall line (or fall zone) is the area where an upland region and a coastal plain meet and is typically prominent where rivers cross it, with resulting rapids or waterfalls. The uplands are relatively hard crystalline basement rock, and the coas ...
, the line along which rivers, brooks, and streams are interrupted by rapids and waterfalls. Maryland's capital city, Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Maryland and the county seat of, and only incorporated city in, Anne Arundel County. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east ...
, is one exception to this pattern since it lies along the banks of the Severn River, close to where it empties into the Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / E ...
.
The Eastern Shore is less populous and more rural, as are the counties of western Maryland. The two westernmost counties of Maryland, Allegany and Garrett, are mountainous and sparsely populated, resembling West Virginia and Appalachia
Appalachia () is a cultural region in the Eastern United States that stretches from the Southern Tier of New York State to northern Alabama and Georgia. While the Appalachian Mountains stretch from Belle Isle in Newfoundland and Labrador, C ...
more than they do the rest of the state. Both eastern and western Maryland are, however, dotted with cities of regional importance, such as Ocean City, Princess Anne
Anne, Princess Royal (Anne Elizabeth Alice Louise; born 15 August 1950), is a member of the British royal family. She is the second child and only daughter of Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh, and the only sister of Ki ...
, and Salisbury on the Eastern Shore and Cumberland
Cumberland ( ) is a historic county in the far North West England. It covers part of the Lake District as well as the north Pennines and Solway Firth coast. Cumberland had an administrative function from the 12th century until 1974. From 1974 ...
, Frostburg, and Hancock Hancock may refer to:
Places in the United States
* Hancock, Iowa
* Hancock, Maine
* Hancock, Maryland
* Hancock, Massachusetts
* Hancock, Michigan
* Hancock, Minnesota
* Hancock, Missouri
* Hancock, New Hampshire
** Hancock (CDP), New Hampsh ...
in Western Maryland
upright=1.2, An enlargeable map of Maryland's 23 counties and one independent city
Western Maryland, also known as the Maryland Panhandle, is the portion of the U.S. state of Maryland that typically consists of Washington, Allegany, and Garr ...
. Southern Maryland is still somewhat rural, but suburbanization from Washington, D.C., has encroached significantly since the 1960s; important local population centers include Lexington Park, Prince Frederick, California, and Waldorf.
Demographics
 In the
In the 2020 United States census
The United States census of 2020 was the twenty-fourth decennial United States census. Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2020. Other than a pilot study during the 2000 census, this was the first U.S. census to off ...
, the United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the ...
found that population of Maryland was 6,185,278 people, a 7.1% increase from the 2010 United States census
The United States census of 2010 was the twenty-third United States national census. National Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2010. The census was taken via mail-in citizen self-reporting, with enumerators servin ...
. The United States Census Bureau estimated that the population of Maryland was 6,045,680 on July 1, 2019, a 4.71% increase from the 2010 United States census and an increase of 2,962, from the prior year. This includes a natural increase since the last census of 269,166 (464,251 births minus 275,093 deaths) and an increase due to net migration of 116,713 people into the state. Immigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, an ...
from outside the United States resulted in a net increase of 129,730 people, and migration within the country produced a net loss of 13,017 people. The center of population
In demographics, the center of population (or population center) of a region is a geographical point that describes a centerpoint of the region's population. There are several ways of defining such a "center point", leading to different geogr ...
of Maryland is located on the county line between Anne Arundel County
Anne Arundel County (; ), also notated as AA or A.A. County, is located in the U.S. state of Maryland. As of the 2020 United States census, its population was 588,261, an increase of just under 10% since 2010. Its county seat is Annapolis, whi ...
and Howard County, in the unincorporated community
An unincorporated area is a region that is not governed by a local municipal corporation. Widespread unincorporated communities and areas are a distinguishing feature of the United States and Canada. Most other countries of the world either have ...
of Jessup.
Maryland's history as a border state has led it to exhibit characteristics of both the Northern and the Southern regions of the United States. Generally, rural Western Maryland
upright=1.2, An enlargeable map of Maryland's 23 counties and one independent city
Western Maryland, also known as the Maryland Panhandle, is the portion of the U.S. state of Maryland that typically consists of Washington, Allegany, and Garr ...
between the West Virginian Panhandle and Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; (Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, Mary ...
has an Appalachia
Appalachia () is a cultural region in the Eastern United States that stretches from the Southern Tier of New York State to northern Alabama and Georgia. While the Appalachian Mountains stretch from Belle Isle in Newfoundland and Labrador, C ...
n culture; the Southern and Eastern Shore regions of Maryland embody a Southern culture
The culture of the Southern United States, Southern culture, or Southern heritage, is a subculture of the United States. The combination of its unique history and the fact that many Southerners maintain—and even nurture—an identity separate f ...
,
while densely populated Central Maryland – radiating outward from Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was ...
and Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, Na ...
– has more in common with that of the Northeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each ...
. The U.S. Census Bureau designates Maryland as one of the South Atlantic States
The South Atlantic United States form one of the nine Census Bureau Divisions within the United States that are recognized by the United States Census Bureau. This region, U.S. Census Bureau Region 3, Division 5, corresponds to the South (state ...
, but it is commonly associated with the Mid-Atlantic States and Northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States, also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast, is a geographic region of the United States. It is located on the Atlantic coast of North America, with Canada to its north, the Sout ...
by other federal agencies, the media, and some residents.
Birth data
As of 2011, 58.0 percent of Maryland's population younger than age1 were minority background. ''Note: Births in the table do not add up because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race, giving a higher overall number.'' Since 2016, data for births ofWhite Hispanic
White Latin Americans, or European Latin Americans, are Latin Americans who are considered white, typically due to European descent. Latin American countries have often tolerated intermarriage between different ethnic groups since the beginning ...
origin are not collected, but included in one ''Hispanic'' group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race.
Language
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
(including Spanish Creole
A Spanish creole, or Spanish-based creole language, is a creole language (contact language with native speakers) for which Spanish serves as its substantial ''lexifier''.
A number of creole languages are influenced to varying degrees by the Sp ...
) is the second most spoken language in Maryland, after English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
. The third and fourth most spoken languages are French (including Patois
''Patois'' (, pl. same or ) is speech or language that is considered nonstandard, although the term is not formally defined in linguistics. As such, ''patois'' can refer to pidgins, creoles, dialects or vernaculars, but not commonly to jargon ...
and Cajun
The Cajuns (; French: ''les Cadjins'' or ''les Cadiens'' ), also known as Louisiana ''Acadians'' (French: ''les Acadiens''), are a Louisiana French ethnicity mainly found in the U.S. state of Louisiana.
While Cajuns are usually described as ...
) and Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of v ...
. Other commonly spoken languages include various African languages
The languages of Africa are divided into several major language families:
* Niger–Congo or perhaps Atlantic–Congo languages (includes Bantu and non-Bantu, and possibly Mande and others) are spoken in West, Central, Southeast and Souther ...
, Korean
Korean may refer to:
People and culture
* Koreans, ethnic group originating in the Korean Peninsula
* Korean cuisine
* Korean culture
* Korean language
**Korean alphabet, known as Hangul or Chosŏn'gŭl
**Korean dialects and the Jeju language
** ...
, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, Tagalog, Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
* Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and p ...
, Vietnamese, Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional It ...
, various Asian languages
A wide variety of languages are spoken throughout Asia, comprising different language families and some unrelated isolates. The major language families include Austroasiatic, Austronesian, Caucasian, Dravidian, Indo-European, Afroasiatic, Tur ...
, Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
, Hindi
Hindi (Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been d ...
, and other Indic languages, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, and Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
.
African Americans
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of enslav ...
form a sizable portion of the state's population, 31.1% as of 2020. Most are descendants of people transported to the area as slaves from West Africa, and many are of mixed race, including European and Native American ancestry. Concentrations of African Americans live in Baltimore City
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore wa ...
, Prince George's County
)
, demonym = Prince Georgian
, ZIP codes = 20607–20774
, area codes = 240, 301
, founded date = April 23
, founded year = 1696
, named for = Prince George of Denmark
, leader_title = Executive
, leader_name = Angela D. Alsobrook ...
, a suburb of Washington, D.C., where many work; Charles County
Charles County is a county in Southern Maryland. As of the 2020 census, the population was 166,617. The county seat is La Plata. The county was named for Charles Calvert (1637–1715), third Baron Baltimore. Charles County is part of the Washi ...
, western parts of Baltimore County
Baltimore County ( , locally: or ) is the third-most populous county in the U.S. state of Maryland and is part of the Baltimore metropolitan area. Baltimore County (which partially surrounds, though does not include, the independent City of ...
, and the southern Eastern Shore. New residents of African descent include 20th-century and later immigrants from Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of G ...
, particularly of the Igbo and Yoruba tribes. Maryland also hosts populations from other African and Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean S ...
nations. Many immigrants from the Horn of Africa have settled in Maryland, with large communities existing in the suburbs of Washington, D.C. (particularly Montgomery County and Prince George's County), and the city of Baltimore. The Greater Washington area has the largest population of Ethiopians
Ethiopians are the native inhabitants of Ethiopia, as well as the global diaspora of Ethiopia. Ethiopians constitute several component ethnic groups, many of which are closely related to ethnic groups in neighboring Eritrea and other parts of ...
outside of Africa.
*Westley, BrianWashington: "Nation's Largest Ethiopian Community Carves Niche"
(). ''
USA Today
''USA Today'' (stylized in all uppercase) is an American daily middle-market newspaper and news broadcasting company. Founded by Al Neuharth on September 15, 1982, the newspaper operates from Gannett's corporate headquarters in Tysons, Virgini ...
''. Associated Press. October 17, 2005."Washington: Nation's Largest Ethiopian Community Carves Niche"
''
The Southeast Missourian
''The Southeast Missourian'' is a 3 day per week newspaper published in Cape Girardeau, Missouri, and serves (as the name implies) the southeastern portion of Missouri.
History
The paper began publication on October 3, 1904 as ''The Daily Rep ...
''. ''Associated Press''. October 23, 2005. p. 7C. Retrieved August 25, 2018. The Ethiopian community of Greater D.C. was historically based in Washington, D.C.'s Adams Morgan
Adams Morgan is a neighborhood in Northwest Washington, D.C., centered at the intersection of 18th Street NW and Columbia Road, about 1.5 miles (2.54 km) north of the White House. Notable establishments in the neighborhood include t ...
and Shaw
Shaw may refer to:
Places Australia
*Shaw, Queensland
Canada
* Shaw Street, a street in Toronto
England
* Shaw, Berkshire, a village
* Shaw, Greater Manchester, a location in the parish of Shaw and Crompton
* Shaw, Swindon, a suburb of Swindon ...
neighborhoods, but as the community has grown, many Ethiopians have settled in Silver Spring. The Washington, D.C., metropolitan area is also home to large Eritrean and Somali communities.
The top reported ancestries by Maryland residents are: German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
(15%), Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
(11%), English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
(8%), American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
(7%), Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional It ...
(6%), and Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin scree ...
(3%).
Irish American
, image = Irish ancestry in the USA 2018; Where Irish eyes are Smiling.png
, image_caption = Irish Americans, % of population by state
, caption = Notable Irish Americans
, population =
36,115,472 (10.9%) alone ...
populations can be found throughout the Baltimore area, and the Northern and Eastern suburbs of Washington, D.C., in Maryland (descendants of those who moved out to the suburbs of Washington's once predominantly Irish neighborhoods), as well as Western Maryland, where Irish immigrant laborers helped to build the B&O Railroad. Smaller but much older Irish populations can be found in Southern Maryland, with some roots dating as far back as the early Maryland colony. This population, however, still remains culturally very active and yearly festivals are held.
A large percentage of the population of the Eastern Shore and Southern Maryland
Southern Maryland is a geographical, cultural and historic region in Maryland composed of the state's southernmost counties on the Western Shore of the Chesapeake Bay. According to the state of Maryland, the region includes all of Calvert, Ch ...
are descendants of British American
British American usually refers to Americans whose ancestral origin originates wholly or partly in the United Kingdom ( England, Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland, Cornwall, Orkney, and the Isle of Man). It is primarily a demographic or histo ...
ancestry. The Eastern Shore was settled by Protestants, chiefly Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's ...
and the southern counties were initially settled by English Catholics. Western and northern Maryland have large German-American
German Americans (german: Deutschamerikaner, ) are Americans who have full or partial German ancestry. With an estimated size of approximately 43 million in 2019, German Americans are the largest of the self-reported ancestry groups by the Unit ...
populations. More recent European immigrants of the late 19th and early 20th century settled first in Baltimore, attracted to its industrial jobs. Many of their ethnic Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional It ...
, Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin scree ...
, Czech
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus'
Places
* Czech ...
, Lithuanian
Lithuanian may refer to:
* Lithuanians
* Lithuanian language
* The country of Lithuania
* Grand Duchy of Lithuania
* Culture of Lithuania
* Lithuanian cuisine
* Lithuanian Jews as often called "Lithuanians" (''Lita'im'' or ''Litvaks'') by other Jew ...
, and Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
descendants still live in the area.
Large ethnic minorities
The term 'minority group' has different usages depending on the context. According to its common usage, a minority group can simply be understood in terms of demographic sizes within a population: i.e. a group in society with the least number o ...
include Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
ans such as Croatians, Belarusians
, native_name_lang = be
, pop = 9.5–10 million
, image =
, caption =
, popplace = 7.99 million
, region1 =
, pop1 = 600,000–768,000
, region2 =
, pop2 ...
, Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
and Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Or ...
. The shares of European immigrants born in Eastern Europe increased significantly between 1990 and 2010. Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Yugoslavia, and Czechoslovakia, many immigrants from Eastern Europe came to the United States—12 percent of whom currently reside in Maryland.
Hispanic immigrants of the later 20th century have settled in Aspen Hill, Hyattsville/ Langley Park, Glenmont/ Wheaton, Bladensburg, Riverdale Park, Gaithersburg
Gaithersburg ( ), officially the City of Gaithersburg, is a city in Montgomery County, Maryland, United States. At the time of the 2020 U.S. Census, Gaithersburg had a population of 69,657, making it the ninth-largest location in the state. Ga ...
, as well as Highlandtown and Greektown in East Baltimore. Salvadorans
Salvadorans ( Spanish: ''Salvadoreños''), also known as Salvadorians (alternate spelling: Salvadoreans), are citizens of El Salvador, a country in Central America. Most Salvadorans live in El Salvador, although there is also a significant Salvad ...
are the largest Hispanic group in Maryland. Other Hispanic groups with significant populations in the state include Mexicans and Puerto Ricans
Puerto Ricans ( es, Puertorriqueños; or boricuas) are the people of Puerto Rico, the inhabitants, and citizens of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico and their descendants.
Overview
The culture held in common by most Puerto Ricans is referred t ...
and Hondurans
Hondurans ( Spanish: ''Hondureñas'' or ''Hondureños'') are the citizens of Honduras. Most Hondurans live in Honduras, although there is also a significant Honduran diaspora, particularly in the United States, Spain, and many smaller communitie ...
. Though the Salvadoran population is more concentrated in the area around Washington, D.C., and the Puerto Rican population is more concentrated in the Baltimore area, all other major Hispanic groups in the state are evenly dispersed between these two areas. Maryland has one of the most diverse Hispanic populations in the country, with significant populations from various Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean S ...
and Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. C ...
n nations.
Asian Americans are concentrated in the suburban counties surrounding Washington, D.C., and in Howard County, with Korean American
Korean Americans are Americans of Korean ancestry (mostly from South Korea). In 2015, the Korean-American community constituted about 0.56% of the United States population, or about 1.82 million people, and was the fifth-largest Asian Americans ...
and Taiwanese American
Taiwanese Americans () are Americans who carry full or partial ancestry from Taiwan. This includes American-born citizens who descend from migrants from Taiwan.
As of the 2010 U.S. Census, 49% of Taiwanese Americans lived in the state of Califo ...
communities in Rockville, Gaithersburg
Gaithersburg ( ), officially the City of Gaithersburg, is a city in Montgomery County, Maryland, United States. At the time of the 2020 U.S. Census, Gaithersburg had a population of 69,657, making it the ninth-largest location in the state. Ga ...
, and Germantown Germantown or German Town may refer to:
Places
Australia
* Germantown, Queensland, a locality in the Cassowary Coast Region
United States
* Germantown, California, the former name of Artois, a census-designated place in Glenn County
* G ...
, and a Filipino American
Filipino Americans ( fil, Mga Pilipinong Amerikano) are Americans of Filipino ancestry. Filipinos and other Asian ethnicities in North America were first documented in the 16th century as slaves and prisoners on ships sailing to and from New ...
community in Fort Washington. Numerous Indian Americans
Indian Americans or Indo-Americans are citizens of the United States with ancestry from India. The United States Census Bureau uses the term Asian Indian to avoid confusion with Native Americans, who have also historically been referred to ...
live across the state, especially in central Maryland.
Attracting educated Asians and Africans to the professional jobs in the region, Maryland has the fifth-largest proportions of racial minorities in the country.
In 2006, 645,744 were counted as foreign born, which represents mainly people from Latin America and Asia. About four percent are undocumented immigrants
Illegal immigration is the migration of people into a country in violation of the immigration laws of that country or the continued residence without the legal right to live in that country. Illegal immigration tends to be financially upwar ...
. Maryland also has a large Korean American population. In fact, 1.7 percent are Korean, while as a whole, 6.7 percent are Asian.
According to The Williams Institute's analysis of the 2010 U.S. census, 12,538 same-sex couples are living in Maryland, representing 5.8 same-sex couples per 1,000 households.
In 2019, non-Hispanic white Americans were 49.8% of Maryland's population (White Americans
White Americans are Americans who identify as and are perceived to be white people. This group constitutes the majority of the people in the United States. As of the 2020 Census, 61.6%, or 204,277,273 people, were white alone. This represented ...
, including White Hispanics, were 57.3%), which made Maryland a majority minority
A majority-minority or minority-majority area is a term used to refer to a subdivision in which one or more racial, ethnic, and/or religious minorities (relative to the whole country's population) make up a majority of the local population.
Term ...
state. 50.2% of Maryland's population is non-white, or is Hispanic or Latino, the highest percentage of any state on the East Coast, and the highest percentage after the majority-minority states of Hawaii, New Mexico, Texas, California, and Nevada. By 2031, minorities are projected to become the majority of voting eligible residents of Maryland.
Religion
 Maryland has been historically prominent to American Catholic tradition because the English
Maryland has been historically prominent to American Catholic tradition because the English colony of Maryland
The Province of Maryland was an English and later British colony in North America that existed from 1632 until 1776, when it joined the other twelve of the Thirteen Colonies in rebellion against Great Britain and became the U.S. state of Maryla ...
was intended by George Calvert
George Calvert, 1st Baron Baltimore (; 1580 – 15 April 1632), was an English politician and colonial administrator. He achieved domestic political success as a member of parliament and later Secretary of State under King James I. He lost m ...
as a haven for English Catholics. Baltimore was the seat of the first Catholic bishop in the U.S. (1789), and Emmitsburg was the home and burial place of the first American-born citizen to be canonized
Canonization is the declaration of a deceased person as an officially recognized saint, specifically, the official act of a Christian communion declaring a person worthy of public veneration and entering their name in the canon catalogue of ...
, St. Elizabeth Ann Seton. Georgetown University, the first Catholic University, was founded in 1789 in what was then part of Maryland (it became a part of the District of Columbia when it was created in the 1790s). The Basilica of the National Shrine of the Assumption of the Virgin Mary
The Basilica of the National Shrine of the Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary, also called the Baltimore Basilica, was the first Roman Catholic cathedral built in the United States, and was among the first major religious buildings constru ...
in Baltimore was the first Roman Catholic cathedral built in the United States, and the Archbishop of Baltimore
The Metropolitan Archdiocese of Baltimore ( la, link=no, Archidiœcesis Baltimorensis) is the premier (or first) see of the Latin Church of the Catholic Church in the United States. The archdiocese comprises the City of Baltimore and nine of Ma ...
is, albeit without formal primacy, the United States' quasi-primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians (monkeys and apes, the latter including hum ...
, and often a cardinal. Among the immigrants of the 19th and 20th centuries from eastern and southern Europe were many Catholics.
Despite its historic relevance to the Catholic Church in the United States, the percentage of Catholics in the state of Maryland is below the national average of 20%. Demographically, both Protestants and those identifying with no religion are more numerous than Catholics.
According to the Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan American think tank (referring to itself as a "fact tank") based in Washington, D.C.
It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the wo ...
in 2014, 69 percent of Maryland's population identifies themselves as Christian. Nearly 52% of the adult population are Protestants
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
. Following Protestantism, Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
is the second largest religious affiliation, comprising 15% percent of the population. Amish
The Amish (; pdc, Amisch; german: link=no, Amische), formally the Old Order Amish, are a group of traditionalist Anabaptist Christian church fellowships with Swiss German and Alsatian origins. They are closely related to Mennonite churche ...
/Mennonite
Mennonites are groups of Anabaptist Christian church communities of denominations. The name is derived from the founder of the movement, Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland. Through his writings about Reformed Christianity during the Radic ...
communities are found in St. Mary's, Garrett, and Cecil counties. Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
is the largest non-Christian religion in Maryland, with 241,000 adherents, or four percent of the total population. Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
are numerous throughout Montgomery County and in Pikesville
Pikesville is a census-designated place (CDP) in Baltimore County, Maryland, United States. Pikesville is just northwest of the Baltimore city limits. It is the northwestern suburb closest to Baltimore.
The population was 30,764 at the 2010 cens ...
and Owings Mills northwest of Baltimore. An estimated 81,500 Jewish Americans live in Montgomery County, constituting approximately 10% of the total population. The Seventh-day Adventist Church
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is an Adventist Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the seventh day of the week in the Christian (Gregorian) and the Hebrew calendar, as the Sabbath, and i ...
's world headquarters and Ahmadiyya
Ahmadiyya (, ), officially the Ahmadiyya Muslim Community or the Ahmadiyya Muslim Jama'at (AMJ, ar, الجماعة الإسلامية الأحمدية, al-Jamāʿah al-Islāmīyah al-Aḥmadīyah; ur, , translit=Jamā'at Aḥmadiyyah Musl ...
Muslims' national headquarters are located in Silver Spring, just outside the District of Columbia.
Per the Public Religion Research Institute
The Public Religion Research Institute (PRRI) is an American nonprofit, nonpartisan research and education organization that conducts public opinion polls on a variety of topics, specializing in the quantitative and qualitative study of politica ...
in 2020, 61 percent of Maryland's population identified with Christianity. Protestantism and Roman Catholicism continued to dominate the Christian landscape, and the Jewish community remained at 3% of the total religious population. Of the unaffiliated, the PRRI study determined their increase to 28% of the population.
Economy
 The
The Bureau of Economic Analysis
The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) of the United States Department of Commerce is a U.S. government agency that provides official macroeconomic and industry statistics, most notably reports about the gross domestic product (GDP) of the United ...
estimates that Maryland's gross state product in 2016 was $382.4billion. However, Maryland has been using Genuine Progress Indicator, an indicator of well-being, to guide the state's development, rather than relying only on growth indicators like GDP. According to the U.S. Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the ...
, Maryland households are currently the wealthiest in the country, with a 2013 median household income of $72,483, which puts it ahead of New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
and Connecticut, which are second and third respectively. Two of Maryland's counties, Howard and Montgomery, are the second and eleventh wealthiest counties in the nation respectively. Maryland has the most millionaires per capita in 2013, with a ratio of 7.7 percent. Also, the state's poverty rate of 7.8 percent is the lowest in the country. Per capita personal income in 2006 was $43,500, fifth in the nation. As of March 2022, the state's unemployment rate was 4.6 percent.
Maryland's economy benefits from the state's proximity to the federal government in Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, Na ...
, with an emphasis on technical and administrative tasks for the defense/aerospace industry and bio-research laboratories, as well as staffing of satellite government headquarters in the suburban or exurban Baltimore/Washington area. Ft. Meade serves as the headquarters of the Defense Information Systems Agency
The Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA), known as the Defense Communications Agency (DCA) until 1991, is a United States Department of Defense (DoD) combat support agency composed of military, federal civilians, and contractors. DISA pro ...
, United States Cyber Command
United States Cyber Command (USCYBERCOM) is one of the eleven unified combatant commands of the United States Department of Defense (DoD). It unifies the direction of cyberspace operations, strengthens DoD cyberspace capabilities, and integr ...
, and the National Security Agency
The National Security Agency (NSA) is a national-level intelligence agency of the United States Department of Defense, under the authority of the Director of National Intelligence (DNI). The NSA is responsible for global monitoring, collectio ...
/Central Security Service
The Central Security Service (CSS) is a combat support agency of the United States Department of Defense which was established in 1972 to integrate the National Security Agency (NSA) and the Service Cryptologic Components (SCC) of the United St ...
. In addition, a number of educational and medical research institutions are located in the state. In fact, the various components of The Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University (Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private research university in Baltimore, Maryland. Founded in 1876, Johns Hopkins is the oldest research university in the United States and in the western hemisphere. It consiste ...
and its medical research facilities are now the largest single employer in the Baltimore area. Altogether, white collar White collar may refer to:
* White-collar worker, a salaried professional or an educated worker who performs semi-professional office, administrative, and sales-coordination tasks, as opposed to a blue-collar worker, whose job requires manual labor ...
technical and administrative workers comprise 25 percent of Maryland's labor force
The workforce or labour force is a concept referring to the pool of human beings either in employment or in unemployment. It is generally used to describe those working for a single company or industry, but can also apply to a geographic regi ...
, attributable in part to nearby Maryland being a part of the Washington Metro Area where the federal government office employment is relatively high.
Manufacturing, while large in dollar value, is highly diversified with no sub-sector contributing over 20 percent of the total. Typical forms of manufacturing include electronics, computer equipment, and chemicals. The once-mighty primary metals sub-sector, which once included what was then the largest steel factory in the world at Sparrows Point
Sparrow's Point is an unincorporated community in Baltimore County, Maryland, United States, adjacent to Dundalk. Named after Thomas Sparrow, landowner, it was the site of a very large industrial complex owned by Bethlehem Steel, known for steelm ...
, still exists, but is pressed with foreign competition, bankruptcies
Bankruptcy is a legal process through which people or other entities who cannot repay debts to creditors may seek relief from some or all of their debts. In most jurisdictions, bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the debto ...
, and merger
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are business transactions in which the ownership of companies, other business organizations, or their operating units are transferred to or consolidated with another company or business organization. As an aspect ...
s. During World War II the Glenn Martin Company (now part of Lockheed Martin
The Lockheed Martin Corporation is an American aerospace, arms, defense, information security, and technology corporation with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta in March 1995. It is ...
) airplane factory employed some 40,000 people.
Mining other than construction materials is virtually limited to coal, which is located in the mountainous western part of the state. The brownstone quarries in the east, which gave Baltimore and Washington much of their characteristic architecture in the mid-19th century, were once a predominant natural resource. Historically, there used to be small gold-mining operations in Maryland, some near Washington, but these no longer exist.
Port of Baltimore
One major service activity is transportation, centered on thePort of Baltimore
Helen Delich Bentley Port of Baltimore is a shipping port along the tidal basins of the three branches of the Patapsco River in Baltimore, Maryland on the upper northwest shore of the Chesapeake Bay. It is the nation's largest port facilities fo ...
and its related rail
Rail or rails may refer to:
Rail transport
*Rail transport and related matters
* Rail (rail transport) or railway lines, the running surface of a railway
Arts and media Film
* ''Rails'' (film), a 1929 Italian film by Mario Camerini
* ''Rail'' ...
and trucking access. The port ranked 17th in the U.S. by tonnage in 2008. Although the port handles a wide variety of products, the most typical imports are raw materials and bulk commodities, such as iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the for ...
, petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude ...
, sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double s ...
, and fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
s, often distributed to the relatively close manufacturing centers of the inland Midwest
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. I ...
via good overland transportation. The port also receives several brands of imported motor vehicles and is the number one auto port in the U.S.
Baltimore City is among the top 15 largest ports in the nation, and was one of six major U.S. ports that were part of the February 2006 controversy over the Dubai Ports World
DP World is an Emirati multinational logistics company based in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. It specialises in cargo logistics, port terminal operations, maritime services and free trade zones. Formed in 2005 by the merger of Dubai Ports Auth ...
deal. The state as a whole is heavily industrialized, with a booming economy and influential technology centers. Its computer industries are some of the most sophisticated in the United States, and the federal government has invested heavily in the area. Maryland is home to several large military bases and scores of high-level government jobs.
The Chesapeake and Delaware Canal
The Chesapeake & Delaware Canal (C&D Canal) is a -long, -wide and -deep ship canal that connects the Delaware River with the Chesapeake Bay in the states of Delaware and Maryland in the United States.
In the mid‑17th century, mapmaker Aug ...
is a canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface fl ...
on the Eastern Shore that connects the waters of the Delaware River with those of the Chesapeake Bay, and in particular with the Port of Baltimore, carrying 40 percent of the port's ship traffic.
Fishing
Maryland has a large food-production sector. A large component of this is commercialfishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from fish stocking, stocked bodies of water such as fish pond, ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. ...
, centered in the Chesapeake Bay, but also including activity off the short Atlantic seacoast. The largest catches by species are the blue crab Blue crab may refer to:
* Blue Crab 11, an American sailboat design
* ''Callinectes sapidus
''Callinectes sapidus'' (from the Ancient Greek ,"beautiful" + , "swimmer", and Latin , "savory"), the blue crab, Atlantic blue crab, or regionally as t ...
, oysters
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but not al ...
, striped bass
The striped bass (''Morone saxatilis''), also called the Atlantic striped bass, striper, linesider, rock, or rockfish, is an anadromous perciform fish of the family Moronidae found primarily along the Atlantic coast of North America. It has als ...
, and menhaden
Menhaden, also known as mossbunker and bunker and "the most important fish in the sea", are forage fish of the genera ''Brevoortia'' and ''Ethmidium'', two genera of marine fish in the family Clupeidae. ''Menhaden'' is a blend of ''poghaden' ...
. The Bay also has overwintering waterfowl in its wildlife refuges. The waterfowl support a tourism sector of sportsmen.
Agriculture
 Maryland has large areas of fertile agricultural land in its coastal and
Maryland has large areas of fertile agricultural land in its coastal and Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
zones, though this land use is being encroached upon by urbanization. Agriculture is oriented to dairy farming (especially in foothill and piedmont areas) for nearby large city milksheads, plus specialty perishable horticulture crops, such as cucumber
Cucumber (''Cucumis sativus'') is a widely-cultivated creeping vine plant in the Cucurbitaceae family that bears usually cylindrical fruits, which are used as culinary vegetables.watermelon
Watermelon (''Citrullus lanatus'') is a flowering plant species of the Cucurbitaceae family and the name of its edible fruit. A scrambling and trailing vine-like plant, it is a highly cultivated fruit worldwide, with more than 1,000 variet ...
s, sweet corn
Sweet corn (''Zea mays'' convar. ''saccharata'' var. ''rugosa''), also called sugar corn and pole corn, is a variety of maize grown for human consumption with a high sugar content. Sweet corn is the result of a naturally occurring recessive muta ...
, tomato
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to the Spanish word ...
es, muskmelon
''Cucumis melo'', also known as melon, is a species of '' Cucumis'' that has been developed into many cultivated varieties. The fruit is a pepo. The flesh is either sweet or bland, with or without a musky aroma, and the rind can be smooth (such ...
s, squash
Squash may refer to:
Sports
* Squash (sport), the high-speed racquet sport also known as squash racquets
* Squash (professional wrestling), an extremely one-sided match in professional wrestling
* Squash tennis, a game similar to squash but pla ...
, and peas
The pea is most commonly the small spherical seed or the seed-pod of the flowering plant species ''Pisum sativum''. Each pod contains several peas, which can be green or yellow. Botanically, pea pods are fruit, since they contain seeds and d ...
(Source:USDA Crop Profiles). The southern counties of the western shoreline of Chesapeake Bay are warm enough to support a tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus ''Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the chie ...
cash crop
A cash crop or profit crop is an agricultural crop which is grown to sell for profit. It is typically purchased by parties separate from a farm. The term is used to differentiate marketed crops from staple crop (or "subsistence crop") in subsisten ...
zone, which has existed since early Colonial times, but declined greatly after a state government buy-out in the 1990s. There is also a large automated chicken-farming sector in the state's southeastern part; Salisbury is home to Perdue Farms
Perdue Farms is the parent company of Perdue Foods and Perdue AgriBusiness, based in Salisbury, Maryland. Perdue Foods is a major chicken, turkey, and pork processing company in the United States. Perdue AgriBusiness ranks among the top United S ...
. Maryland's food-processing plants are the most significant type of manufacturing by value in the state. Farming suffers from weeds as anywhere else, including an unusual multiply resistant ragweed (''Ambrosia artemisiifolia
''Ambrosia artemisiifolia'', with the common names common ragweed, annual ragweed, and low ragweed, is a species of the genus ''Ambrosia'' native to regions of the Americas.
Taxonomy
The species name, ''artemisiifolia'', is given because the lea ...
'') found by Rousonelos ''et al.'', 2012 with both ALS- and PPO-resistances and which by 2016 had developed a third, EPSP resistance. This ragweed population is a drag on soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses.
Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu an ...
cultivation and, , is the worst multiresistant weed problem in the state.
Biotechnology
Maryland is a major center forlife sciences
This list of life sciences comprises the branches of science that involve the scientific study of life – such as microorganisms, plants, and animals including human beings. This science is one of the two major branches of natural science, th ...
research and development. With more than 400 biotechnology companies located there, Maryland is the fourth largest nexus in this field in the United States.
Institutions and government agencies with an interest in research and development located in Maryland include the Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University (Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private research university in Baltimore, Maryland. Founded in 1876, Johns Hopkins is the oldest research university in the United States and in the western hemisphere. It consiste ...
, the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory
The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (Applied Physics Laboratory, or APL) is a not-for-profit university-affiliated research center (UARC) in Howard County, Maryland. It is affiliated with Johns Hopkins University and emplo ...
, more than one campus of the University System of Maryland
The University System of Maryland (USM) is a public higher education system in the U.S. state of Maryland. The system is composed of the eleven campuses at College Park, Baltimore County, Baltimore, Princess Anne, Towson, Salisbury, Bowie, ...
, Goddard Space Flight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC emp ...
, the United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the ...
, the National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late 1 ...
(NIH), the National Institute of Standards and Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical sci ...
(NIST), the National Institute of Mental Health
The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) is one of 27 institutes and centers that make up the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The NIH, in turn, is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services and is the prima ...
(NIMH), the Walter Reed National Military Medical Center
The Walter Reed National Military Medical Center (WRNMMC), formerly known as the National Naval Medical Center and colloquially referred to as the Bethesda Naval Hospital, Walter Reed, or Navy Med, is a United States' tri-service military medi ...
, the federal Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food s ...
(FDA), the Howard Hughes Medical Institute
The Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) is an American non-profit medical research organization based in Chevy Chase, Maryland. It was founded in 1953 by Howard Hughes, an American business magnate, investor, record-setting pilot, engineer, fi ...
, the Celera Genomics
Celera is a subsidiary of Quest Diagnostics which focuses on genetic sequencing and related technologies. It was founded in 1998 as a business unit of Applera, spun off into an independent company in 2008, and finally acquired by Quest Diagnosti ...
company, the J. Craig Venter Institute
The J. Craig Venter Institute (JCVI) is a non-profit genomics research institute founded by J. Craig Venter, Ph.D. in October 2006. The institute was the result of consolidating four organizations: the Center for the Advancement of G ...
(JCVI), and AstraZeneca
AstraZeneca plc () is a British-Swedish multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company with its headquarters at the Cambridge Biomedical Campus in Cambridge, England. It has a portfolio of products for major diseases in areas includi ...
(formerly MedImmune
MedImmune, LLC was a wholly owned subsidiary of AstraZeneca before February 14, 2019, when it was announced that the MedImmune name and branding would be discontinued in favor of AstraZeneca.
MedImmune was founded in 1988 as Molecular Vaccines, ...
).
Maryland is home to defense contractor Emergent BioSolutions
Emergent BioSolutions Inc. is an American multinational specialty biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Gaithersburg, Maryland. It develops vaccines and antibody therapeutics for infectious diseases and opioid overdoses, and it provides me ...
, which manufactures and provides an anthrax vaccine
Anthrax vaccines are vaccines to prevent the livestock and human disease anthrax, caused by the bacterium ''Bacillus anthracis''.
They have had a prominent place in the history of medicine, from Pasteur's pioneering 19th-century work with cattle ...
to U.S. government military personnel.
Tourism
 Tourism is popular in Maryland. Many tourists visit Baltimore, the beaches of the Eastern Shore, and the nature of western Maryland. Attractions in Baltimore include the
Tourism is popular in Maryland. Many tourists visit Baltimore, the beaches of the Eastern Shore, and the nature of western Maryland. Attractions in Baltimore include the Harborplace
Harborplace is a shopping complex on the Inner Harbor in Baltimore, Maryland.
Description
The property is composed of 2 two-story pavilions: the Pratt Street Pavilion and the Light Street Pavilion. Each of these buildings contains many stores an ...
, the Baltimore Aquarium, Fort McHenry
Fort McHenry is a historical American coastal pentagonal bastion fort on Locust Point, now a neighborhood of Baltimore, Maryland. It is best known for its role in the War of 1812, when it successfully defended Baltimore Harbor from an attack ...
, as well as the Camden Yards
The Oriole Park at Camden Yards is a baseball stadium located in Baltimore, Maryland. It is the home field of Major League Baseball's Baltimore Orioles, and the first of the "retro" major league ballparks constructed during the 1990s and early ...
baseball stadium. Ocean City on the Atlantic Coast has been a popular beach destination in summer, particularly since the Chesapeake Bay Bridge
The Chesapeake Bay Bridge (also known locally as the Bay Bridge) is a major dual-span bridge in the U.S. state of Maryland. Spanning the Chesapeake Bay, it connects the state's rural Eastern Shore region with the urban Western Shore, between ...
was built in 1952 connecting the Eastern Shore to the more populated Maryland cities. The state capital of Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Maryland and the county seat of, and only incorporated city in, Anne Arundel County. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east ...
offers sites such as the state capitol building, the historic district
A historic district or heritage district is a section of a city which contains older buildings considered valuable for historical or architectural reasons. In some countries or jurisdictions, historic districts receive legal protection from ce ...
, and the waterfront. Maryland also has several sites of interest to military history, given Maryland's role in the American Civil War and in the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States, United States of America and its Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom ...
. Other attractions include the historic and picturesque towns along the Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / E ...
, such as Saint Mary's, Maryland's first colonial settlement and original capital.
Healthcare
As of 2017, the top two health insurers including all types of insurance wereCareFirst BlueCross BlueShield
CareFirst BlueCross BlueShield is a health insurance provider serving 3.5 million individuals and groups in Maryland and the Washington metropolitan area. It has dual headquarters in Baltimore, Maryland and Washington, D.C. It is a nonprofit organ ...
with 47% market share followed by UnitedHealth Group
UnitedHealth Group Incorporated is an American multinational managed healthcare and insurance company based in Minnetonka, Minnesota. It offers health care products and insurance services. UnitedHealth Group is the world's seventh largest c ...
at 15%.
Maryland has experimented with healthcare payment reforms, notably beginning in the 1970s with an all-payer rate setting program regulated by the Health Services Cost Review Commission. In 2014, it switched to a global budget revenue system, whereby hospitals receive a capitated payment to care for their population.
Transportation
TheMaryland Department of Transportation
The Maryland Department of Transportation (MDOT) is an organization comprising five business units and one Authority:
* Maryland Transportation Authority (Transportation Secretary serves as chairman of the Maryland Transportation Authority)
* ...
oversees most transportation in the state through its various administration-level agencies. The independent Maryland Transportation Authority
The Maryland Transportation Authority (MDTA) is an independent state agency responsible for financing, constructing, operating, and maintaining eight transportation facilities, currently consisting of two toll roads, two tunnels, and four brid ...
maintains and operates the state's eight toll facilities.
Roads
 Maryland's
Maryland's Interstate highways
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States. Th ...
include of Interstate95 (I-95), which enters the northeast portion of the state, travels through Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was ...
, and becomes part of the eastern section of the Capital Beltway
The Capital Beltway is a Interstate Highway in the Washington metropolitan area that surrounds Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States, and its inner suburbs in adjacent Maryland and Virginia. It is the basis of the phrase "inside t ...
to the Woodrow Wilson Bridge
The Woodrow Wilson Memorial Bridge (also known as the Woodrow Wilson Bridge or the Wilson Bridge) is a bascule bridge that spans the Potomac River between the independent city of Alexandria, Virginia, and Oxon Hill in Prince George's County, ...
. I-68 travels , connecting the western portions of the state to I-70
Interstate 70 (I-70) is a major east–west Interstate Highway in the United States that runs from I-15 near Cove Fort, Utah, to a park and ride lot just east of I-695 in Baltimore, Maryland, and is the fifth-longest Interstate in the c ...
at the small town of Hancock. I-70 enters from Pennsylvania north of Hancock and continues east for to Baltimore, connecting Hagerstown and Frederick along the way.
I-83
Interstate 83 (I-83) is an Interstate Highway in the Eastern United States. Its southern terminus is at a signalized intersection with Fayette Street in Baltimore, Maryland; its northern terminus is at I-81 near Harrisburg, Pennsylvania.
Mos ...
has in Maryland and connects Baltimore to southern central Pennsylvania (Harrisburg
Harrisburg is the capital city of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Dauphin County. With a population of 50,135 as of the 2021 census, Harrisburg is the 9th largest city and 15th largest municipality in P ...
and York, Pennsylvania
York (Pennsylvania Dutch: ''Yarrick''), known as the White Rose City (after the symbol of the House of York), is the county seat of York County, Pennsylvania, United States. It is located in the south-central region of the state. The populatio ...
). Maryland also has an portion of I-81
Interstate 81 (I-81) is a north–south (physically northeast–southwest) Interstate Highway in the eastern part of the United States. Its southern terminus is at I-40 in Dandridge, Tennessee; its northern terminus is on Wellesley Islan ...
that travels through the state near Hagerstown. I-97, fully contained within Anne Arundel County and the shortest () one- or two-digit interstate highway in the contiguous US, connects the Baltimore area to the Annapolis area.
There are also several auxiliary Interstate highways
Auxiliary may refer to:
* A backup site or system
In language
* Auxiliary language (disambiguation)
* Auxiliary verb
In military and law enforcement
* Auxiliary police
* Auxiliaries, civilians or quasi-military personnel who provide support o ...
in Maryland. Among them are two beltways encircling the major cities of the region: I-695, the McKeldin (Baltimore) Beltway, which encircles Baltimore; and a portion of I-495 Interstate 495 (I-495) is the designation for several Interstate Highways in the United States, all of which are related to Interstate 95, listed from south to north:
* The Capital Beltway, a beltway around Washington, D.C., running through Virgini ...
, the Capital Beltway, which encircles Washington, D.C. I-270, which connects the Frederick area with Northern Virginia and the District of Columbia through major suburbs to the northwest of Washington, is a major commuter route and is as wide as fourteen lanes at points. I-895, also known as the Harbor Tunnel Thruway, provides an alternate route to I-95 across the Baltimore Harbor.
Both I-270 and the Capital Beltway were extremely congested; however, the Intercounty Connector
Maryland Route 200 (MD 200), also known as the Intercounty Connector or ICC, is an , six-lane toll road in the U.S. state of Maryland. A controlled-access highway, it connects Gaithersburg in Montgomery County and Laurel in Prince George's Cou ...
(ICC; MD200) has alleviated some congestion over time. Construction of the ICC was a major part of the campaign platform of former Governor Robert Ehrlich
Robert Leroy Ehrlich Jr. (born November 25, 1957) is an American lawyer and politician who served as the 60th Governor of Maryland from 2003 to 2007. A Republican, Ehrlich represented Maryland's 2nd Congressional district in the U.S. House o ...
, who was in office from 2003 until 2007, and of Governor Martin O'Malley
Martin Joseph O'Malley (born January 18, 1963) is an American lawyer and former politician who served as the 61st Governor of Maryland from 2007 to 2015. A member of the Democratic Party, he was Mayor of Baltimore from 1999 to 2007.
O'Malley ...
, who succeeded him. I-595, which is an unsigned highway
Road sign along Aurora_to_exit_the_freeway._The_road_at_this_exit_is_officially_designated_ Sigurd_and_Aurora,_Utah">Aurora_to_exit_the_freeway._The_road_at_this_exit_is_officially_designated_Utah_State_Route_259">SR 259,_a_short_connector;_ ...
concurrent with US50/ US301, is the longest unsigned interstate in the country and connects Prince George's County
)
, demonym = Prince Georgian
, ZIP codes = 20607–20774
, area codes = 240, 301
, founded date = April 23
, founded year = 1696
, named for = Prince George of Denmark
, leader_title = Executive
, leader_name = Angela D. Alsobrook ...
and Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, Na ...
with Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Maryland and the county seat of, and only incorporated city in, Anne Arundel County. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east ...
and the Eastern Shore via the Chesapeake Bay Bridge
The Chesapeake Bay Bridge (also known locally as the Bay Bridge) is a major dual-span bridge in the U.S. state of Maryland. Spanning the Chesapeake Bay, it connects the state's rural Eastern Shore region with the urban Western Shore, between ...
.
Maryland also has a state highway
A state highway, state road, or state route (and the equivalent provincial highway, provincial road, or provincial route) is usually a road that is either ''numbered'' or ''maintained'' by a sub-national state or province. A road numbered by a ...
system that contains routes numbered from 2through 999, however most of the higher-numbered routes are either unsigned or are relatively short. Major state highways include Routes 2 (Governor Ritchie Highway/Solomons Island Road/Southern Maryland Blvd.), 4 (Pennsylvania Avenue
Pennsylvania Avenue is a diagonal street in Washington, D.C., and Prince George's County, Maryland, that connects the White House and the United States Capitol and then crosses the city to Maryland. In Maryland it is also Maryland Route 4 (MD 4 ...
/Southern Maryland Blvd./Patuxent Beach Road/St. Andrew's Church Road), 5 (Branch Avenue/Leonardtown Road/Point Lookout Road), 32, 45 (York Road), 97 (Georgia Avenue), 100
100 or one hundred (Roman numeral: C) is the natural number following 99 and preceding 101.
In medieval contexts, it may be described as the short hundred or five score in order to differentiate the English and Germanic use of "hundred" to des ...
(Paul T. Pitcher Memorial Highway), 210 (Indian Head Highway), 235
__NOTOC__
Year 235 ( CCXXXV) was a common year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Severus and Quintianus (or, less frequently, year 988 '' ...
(Three Notch Road), 295 (Baltimore-Washington Parkway), 355
__NOTOC__
Year 355 ( CCCLV) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Arbitio and Maesius (or, less frequently, year 1108 ''Ab ...
(Wisconsin Avenue/Rockville Pike/Frederick Road), 404 (Queen Anne Highway/ Shore Highway), and 650
__NOTOC__
Year 650 (DCL) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 650 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era beca ...
(New Hampshire Avenue).
Airports
Maryland's largest airport isBaltimore-Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport
Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport , commonly referred to as BWI or BWI Marshall, is an international airport in the Eastern United States serving mainly Baltimore, Maryland and Washington, D.C. With Dulles Internatio ...
, more commonly referred to as BWI. The airport is named for the Baltimore-born Thurgood Marshall
Thurgood Marshall (July 2, 1908 – January 24, 1993) was an American civil rights lawyer and jurist who served as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1967 until 1991. He was the Supreme Court's first African- ...
, the first African-American Supreme Court justice
The Supreme Court of the United States is the highest-ranking judicial body in the United States. Its membership, as set by the Judiciary Act of 1869, consists of the chief justice of the United States and eight associate justices, any six of ...
. The only other airports with commercial service are at Hagerstown and Salisbury.
The Maryland suburbs of Washington, D.C. are also served by the other two airports in the region, Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport
Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport , sometimes referred to colloquially as National Airport, Washington National, Reagan National Airport, DCA, Reagan, or simply National, is an international airport in Arlington County, Virginia, across ...
and Dulles International Airport
Washington Dulles International Airport , typically referred to as Dulles International Airport, Dulles Airport, Washington Dulles, or simply Dulles ( ), is an international airport in the Eastern United States, located in Loudoun County and Fa ...
, both in Northern Virginia
Northern Virginia, locally referred to as NOVA or NoVA, comprises several County (United States), counties and independent city (United States), independent cities in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. I ...
. The College Park Airport
College Park Airport is a public airport located in the City of College Park, in Prince George's County, Maryland, United States. It is the world's oldest continuously operated airport. The airport is located south of Paint Branch and Lake Ar ...
is the nation's oldest, founded in 1909, and is still used. Wilbur Wright trained military aviators at this location.
Rail

Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, doing business as Amtrak () , is the national passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates inter-city rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous U.S. States and nine cities in Canada. ...
trains, including the high-speed Acela Express
The ''Acela'' ( ; originally the ''Acela Express'' until September 2019) is Amtrak's flagship service along the Northeast Corridor (NEC) in the Northeastern United States between Washington, D.C. and Boston via 13 intermediate stops, includi ...
serve Baltimore's Penn Station, BWI Airport
Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport , commonly referred to as BWI or BWI Marshall, is an international airport in the Eastern United States serving mainly Baltimore, Maryland and Washington, D.C. With Dulles Interna ...
, New Carrollton, and Aberdeen
Aberdeen (; sco, Aiberdeen ; gd, Obar Dheathain ; la, Aberdonia) is a city in North East Scotland, and is the third most populous city in the country. Aberdeen is one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas (as Aberdeen City), and ...
along the Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, Na ...
to Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- most p ...
Northeast Corridor
The Northeast Corridor (NEC) is an electrified railroad line in the Northeast megalopolis of the United States. Owned primarily by Amtrak, it runs from Boston through Providence, New Haven, Stamford, New York City, Philadelphia, Wilmington, ...
. In addition, train service is provided to Rockville and Cumberland
Cumberland ( ) is a historic county in the far North West England. It covers part of the Lake District as well as the north Pennines and Solway Firth coast. Cumberland had an administrative function from the 12th century until 1974. From 1974 ...
by Amtrak's Washington, D.C., to Chicago Capitol Limited
The ''Capitol Limited'' is a daily Amtrak train between Washington, D.C., and Chicago, running via Pittsburgh and Cleveland. Service began in 1981 and was named after the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad's ''Capitol Limited'' which ended in 1971 u ...
.
The WMATA
The Washington Metropolitan Area Transit Authority (WMATA ), commonly referred to as Metro, is a tri-jurisdictional government agency that operates transit service in the Washington metropolitan area. WMATA was created by the United States Con ...
's Metrorail
METRORail is the light rail system in Houston, Texas (United States). In , the system had a ridership of , or about per weekday as of . METRORail ranks as the second most-traveled light rail system in the Southern United States and the 12th ...
rapid transit
Rapid transit or mass rapid transit (MRT), also known as heavy rail or metro, is a type of high-capacity public transport generally found in urban areas. A rapid transit system that primarily or traditionally runs below the surface may be c ...
and Metrobus local bus systems (the 2nd
A second is the base unit of time in the International System of Units (SI).
Second, Seconds or 2nd may also refer to:
Mathematics
* 2 (number), as an ordinal (also written as ''2nd'' or ''2d'')
* Second of arc, an angular measurement unit, ...
and 6th busiest in the nation of their respective modes) provide service in Montgomery and Prince George's counties and connect them to Washington, D.C., with the express Metrobus ''Route B30'' serving BWI Airport
Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport , commonly referred to as BWI or BWI Marshall, is an international airport in the Eastern United States serving mainly Baltimore, Maryland and Washington, D.C. With Dulles Interna ...
. The Maryland Transit Administration
The Maryland Transit Administration (MTA) is a state-operated mass transit administration in Maryland, and is part of the Maryland Department of Transportation. The MTA operates a comprehensive transit system throughout the Baltimore-Washingto ...
(often abbreviated as "MTA Maryland"), a state agency part of the Maryland Department of Transportation
The Maryland Department of Transportation (MDOT) is an organization comprising five business units and one Authority:
* Maryland Transportation Authority (Transportation Secretary serves as chairman of the Maryland Transportation Authority)
* ...
also provides transit services within the state. Headquartered in Baltimore, MTA's transit services are largely focused on central Maryland, as well as some portions of the Eastern Shore and Southern MD. Baltimore's Light RailLink
Baltimore Light RailLink (formerly Baltimore Light Rail, and also known simply as the "Light Rail") is a light rail system serving Baltimore, Maryland, United States, as well as its surrounding suburbs. It is operated by the Maryland Transit A ...
and Metro SubwayLink
The Metro SubwayLink is a rapid transit line serving the greater area of Baltimore, Maryland, in the United States, and is operated by the Maryland Transit Administration. The segment in Downtown Baltimore is underground, and most of the line ou ...
systems serve its densely populated inner-city and the surrounding suburbs. The MTA also serves the city and its suburbs with its local bus
In computer architecture, a local bus is a computer bus that connects directly, or almost directly, from the central processing unit (CPU) to one or more slots on the expansion bus. The significance of direct connection to the CPU is avoiding ...
service (the 9th largest system in the nation). The MTA's Commuter Bus system provides express coach service on longer routes connecting Washington, D.C. and Baltimore to parts of Central and Southern MD as well as the Eastern Shore. The commuter rail service, known as MARC Marc or MARC may refer to:
People
* Marc (given name), people with the first name
* Marc (surname), people with the family name
Acronyms
* MARC standards, a data format used for library cataloging,
* MARC Train, a regional commuter rail system o ...
, operates three lines which all terminate at Washington Union Station
Washington Union Station is a major train station, transportation hub, and leisure destination in Washington, D.C. Designed by Daniel Burnham and opened in 1907, it is Amtrak's headquarters, the railroad's second-busiest station, and North Ameri ...
and provide service to Baltimore's Penn and Camden stations, Perryville, Frederick, and Martinsburg, WV. In addition, many suburban counties operate local bus systems which connect to and complement the larger MTA and WMATA/Metro services.
The MTA will also administer the Purple Line, an under-construction light rail line that will connect the Maryland branches of the Red
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondary ...
, Green
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by a combin ...
/Yellow
Yellow is the color between green and orange on the spectrum of light. It is evoked by light with a dominant wavelength of roughly 575585 nm. It is a primary color in subtractive color systems, used in painting or color printing. In the RG ...
, and Orange
Orange most often refers to:
*Orange (fruit), the fruit of the tree species '' Citrus'' × ''sinensis''
** Orange blossom, its fragrant flower
*Orange (colour), from the color of an orange, occurs between red and yellow in the visible spectrum
* ...
lines of the Washington Metro, as well as offer transfers to all three lines of the MARC commuter rail system.
Freight rail transport
Rail freight transport is the use of railroads and trains to transport cargo as opposed to human passengers.
A freight train, cargo train, or goods train is a group of freight cars (US) or goods wagons (International Union of Railways) hauled ...
is handled principally by two Class I railroad
In the United States, railroad carriers are designated as Class I, II, or III, according to annual revenue criteria originally set by the Surface Transportation Board in 1992. With annual adjustments for inflation, the 2019 thresholds were US$5 ...
s, as well as several smaller regional and local carriers. CSX Transportation
CSX Transportation , known colloquially as simply CSX, is a Class I freight railroad operating in the Eastern United States and the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. The railroad operates approximately 21,000 route miles () of track. ...
has more extensive trackage throughout the state, with ,CSX Transportation. Jacksonville, FL (2010)"CSX and Maryland."
followed by
Norfolk Southern Railway
The Norfolk Southern Railway is a Class I freight railroad in the United States formed in 1982 with the merger of Norfolk and Western Railway and Southern Railway. With headquarters in Atlanta, the company operates 19,420 route miles (31, ...
. Major rail yard
A rail yard, railway yard, railroad yard (US) or simply yard, is a series of tracks in a rail network for storing, sorting, or loading and unloading rail vehicles and locomotives. Yards have many tracks in parallel for keeping rolling stock or u ...
s are located in Baltimore and Cumberland, with an intermodal terminal (rail, truck and marine) in Baltimore.
Law and government
 The
The government of Maryland
The government of Maryland is conducted according to the Maryland Constitution. The United States is a federation; consequently, the government of Maryland, like the other 49 state governments, has exclusive authority over matters that lie entir ...
is conducted according to the state constitution. The government of Maryland, like the other 49 state governments
A state government is the government that controls a subdivision of a country in a federal form of government, which shares political power with the federal or national government. A state government may have some level of political autonomy, o ...
, has exclusive authority over matters that lie entirely within the state's borders, except as limited by the Constitution of the United States
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven articles, it delineates the nation ...
.
Power in Maryland is divided among three branches of government: executive
Executive ( exe., exec., execu.) may refer to:
Role or title
* Executive, a senior management role in an organization
** Chief executive officer (CEO), one of the highest-ranking corporate officers (executives) or administrators
** Executive d ...
, legislative
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers of government.
Laws enacted by legislatures are usually known a ...
, and judicial
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law ...
. The Maryland General Assembly
The Maryland General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Maryland that convenes within the State House in Annapolis. It is a bicameral body: the upper chamber, the Maryland Senate, has 47 representatives and the lower chamb ...
is composed of the Maryland House of Delegates
The Maryland House of Delegates is the lower house of the legislature of the State of Maryland. It consists of 141 delegates elected from 47 districts. The House of Delegates Chamber is in the Maryland State House on State Circle in Annapolis, ...
and the Maryland Senate
The Maryland Senate, sometimes referred to as the Maryland State Senate, is the upper house of the General Assembly, the state legislature of the U.S. state of Maryland. Composed of 47 senators elected from an equal number of constituent single- ...
. Maryland's governor is unique in the United States as the office is vested with significant authority in budgeting. The legislature may not increase the governor's proposed budget expenditures. Unlike many other states, significant autonomy is granted to many of Maryland's counties.
Most of the business of government is conducted in Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Maryland and the county seat of, and only incorporated city in, Anne Arundel County. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east ...
, the state capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used fo ...
however some cabinet departments and state officials have their offices in Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was ...
. Elections for governor and most statewide offices, as well as most county elections, are held in midterm-election years (even-numbered years not divisible by four).
The judicial branch of state government consists of one united District Court of Maryland that sits in every county and Baltimore City, as well as 24 Circuit Courts sitting in each County and Baltimore City, the latter being courts of general jurisdiction for all civil disputes over $30,000, all equitable jurisdiction and major criminal proceedings. The intermediate appellate court is known as the Appellate Court of Maryland
The Appellate Court of Maryland is the intermediate appellate court for the U.S. state of Maryland. The Appellate Court of Maryland was created in 1966 in response to the rapidly growing caseload in the Supreme Court of Maryland. Like the state ...
and the state supreme court
In the United States, a state supreme court (known by other names in some states) is the highest court in the state judiciary of a U.S. state. On matters of state law, the judgment of a state supreme court is considered final and binding in b ...
is the Supreme Court of Maryland
The Supreme Court of Maryland is the highest court of the U.S. state of Maryland. Its name was changed on December 14, 2022, from the Maryland Court of Appeals, after a voter-approved change to the state constitution. The court, which is compose ...
. The appearance of the justices of the Supreme Court of Maryland is unique; Maryland is the only state whose justices wear red robes.
Taxation
Maryland imposes fiveincome tax
An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities (taxpayers) in respect of the income or profits earned by them (commonly called taxable income). Income tax generally is computed as the product of a tax rate times the taxable income. Tax ...
brackets, ranging from 2to 6.25 percent of personal income. The city of Baltimore and Maryland's 23 counties levy local "piggyback" income taxes at rates between 1.25 and 3.2 percent of Maryland taxable income. Local officials set the rates and the revenue is returned to the local governments quarterly. The top income tax bracket of 9.45 percent is the fifth highest combined state and local income tax rates in the country, behind New York City's 11.35 percent, California's 10.3 percent, Rhode Island's 9.9 percent, and Vermont's 9.5 percent.
Maryland's state sales tax
A sales tax is a tax paid to a governing body for the sales of certain goods and services. Usually laws allow the seller to collect funds for the tax from the consumer at the point of purchase. When a tax on goods or services is paid to a govern ...
is six percent. All real property in Maryland is subject to the property tax
A property tax or millage rate is an ad valorem tax on the value of a property.In the OECD classification scheme, tax on property includes "taxes on immovable property or net wealth, taxes on the change of ownership of property through inheri ...
. Generally, properties that are owned and used by religious, charitable, or educational organizations or property owned by the federal, state or local governments are exempt. Property tax rates vary widely. No restrictions or limitations on property taxes are imposed by the state, meaning cities and counties can set tax rates at the level they deem necessary to fund governmental services.
Elections
 Prior to the American Civil War, Maryland's elections were largely controlled by the Democrats, which account for 54.9% of all registered voters as of May 2017.
State elections are dominated by
Prior to the American Civil War, Maryland's elections were largely controlled by the Democrats, which account for 54.9% of all registered voters as of May 2017.
State elections are dominated by Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was ...
and the populous suburban counties bordering Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, Na ...
, and Baltimore: Montgomery, Prince George's, Anne Arundel, and Baltimore counties. As of July 2017, 66 percent of the state's population resides in these six jurisdictions, most of which contain large, traditionally Democratic voting bloc A voting bloc is a group of voters that are strongly motivated by a specific common concern or group of concerns to the point that such specific concerns tend to dominate their voting patterns, causing them to vote together in elections. For example ...
s: African Americans
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of enslav ...
in Baltimore City and Prince George's; federal employees in Prince George's, Anne Arundel, and Montgomery; and post-graduates in Montgomery. The remainder of the state, particularly Western Maryland
upright=1.2, An enlargeable map of Maryland's 23 counties and one independent city
Western Maryland, also known as the Maryland Panhandle, is the portion of the U.S. state of Maryland that typically consists of Washington, Allegany, and Garr ...
and the Eastern Shore, is more supportive of Republicans. One of Maryland's best known political figures is a Republican – former governor Spiro Agnew
Spiro Theodore Agnew (November 9, 1918 – September 17, 1996) was the 39th vice president of the United States, serving from 1969 until his resignation in 1973. He is the second vice president to resign the position, the other being John ...
, who pled no contest
' is a legal term that comes from the Latin phrase for "I do not wish to contend". It is also referred to as a plea of no contest or no defense.
In criminal trials in certain United States jurisdictions, it is a plea where the defendant neithe ...
to tax evasion and resigned in 1973.
In 1980
Events January
* January 4 – U.S. President Jimmy Carter proclaims a grain embargo against the USSR with the support of the European Commission.
* January 6 – Global Positioning System time epoch begins at 00:00 UTC.
* January 9 – In ...
, Maryland was one of six states to vote for Jimmy Carter
James Earl Carter Jr. (born October 1, 1924) is an American politician who served as the 39th president of the United States from 1977 to 1981. A member of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the 76th governor of Georgia from 19 ...
. In 1992
File:1992 Events Collage V1.png, From left, clockwise: 1992 Los Angeles riots, Riots break out across Los Angeles, California after the Police brutality, police beating of Rodney King; El Al Flight 1862 crashes into a residential apartment buildi ...
, Bill Clinton fared better in Maryland than any other state, except his home state of Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the Osage la ...
. In 1996
File:1996 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: A Centennial Olympic Park bombing, bomb explodes at Centennial Olympic Park in Atlanta, set off by a radical Anti-abortion violence, anti-abortionist; The center fuel tank explodes on TWA Flight 8 ...
, Maryland was Clinton's sixth best; in 2000
File:2000 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: Protests against Bush v. Gore after the 2000 United States presidential election; Heads of state meet for the Millennium Summit; The International Space Station in its infant form as seen from S ...
, Maryland ranked fourth for Gore; and in 2004
2004 was designated as an International Year of Rice by the United Nations, and the International Year to Commemorate the Struggle Against Slavery and its Abolition (by UNESCO).
Events January
* January 3 – Flash Airlines Flight 60 ...
, John Kerry
John Forbes Kerry (born December 11, 1943) is an American attorney, politician and diplomat who currently serves as the first United States special presidential envoy for climate. A member of the Forbes family and the Democratic Party, he p ...
showed his fifth-best performance in Maryland. In 2008
File:2008 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: Lehman Brothers went bankrupt following the Subprime mortgage crisis; Cyclone Nargis killed more than 138,000 in Myanmar; A scene from the opening ceremony of the 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing; ...
, Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
won the state's 10 electoral votes with 61.9 percent of the vote, to John McCain
John Sidney McCain III (August 29, 1936 – August 25, 2018) was an American politician and United States Navy officer who served as a United States senator from Arizona from 1987 until his death in 2018. He previously served two terms ...
's 36.5 percent.
In 2002, former Governor Robert Ehrlich
Robert Leroy Ehrlich Jr. (born November 25, 1957) is an American lawyer and politician who served as the 60th Governor of Maryland from 2003 to 2007. A Republican, Ehrlich represented Maryland's 2nd Congressional district in the U.S. House o ...
was the first Republican to be elected to that office in four decades, and after one term, he lost his seat to Baltimore Mayor
The mayor of Baltimore is the head of the executive branch of the government of the City of Baltimore, Maryland. The Mayor has the duty to enforce city laws, and the power to either approve or veto bills, ordinances, or resolutions passed by the ...
and Democrat Martin O'Malley
Martin Joseph O'Malley (born January 18, 1963) is an American lawyer and former politician who served as the 61st Governor of Maryland from 2007 to 2015. A member of the Democratic Party, he was Mayor of Baltimore from 1999 to 2007.
O'Malley ...
. Ehrlich ran again for governor in 2010, losing again to O'Malley.
The 2006 election brought no change in the pattern of Democratic dominance. After Democratic Senator Paul Sarbanes
Paul Spyros Sarbanes (; February 3, 1933 – December 6, 2020) was an American politician and attorney. A member of the Democratic Party from Maryland, he served as a member of the United States House of Representatives from 1971 to 1977 a ...
announced that he was retiring, Democratic Congressman Benjamin Cardin
Benjamin Louis Cardin (born October 5, 1943) is an American lawyer and politician serving as the senior United States senator from Maryland, a seat he has held since 2007. A member of the Democratic Party, he previously was the U.S. representat ...
defeated Republican Lieutenant Governor Michael S. Steele
Michael Stephen Steele (born October 19, 1958) is an American political commentator, attorney, and Republican Party politician. Steele served as the seventh lieutenant governor of Maryland from 2003 to 2007; he was the first African-American ...
, with 55 percent of the vote, against Steele's 44 percent.
While Republicans usually win more counties, by piling up large margins in the west and east, they are also usually swamped by the more densely populated and heavily Democratic Baltimore–Washington axis. In 2008, for instance, McCain won 17 counties to Obama's six; Obama also carried Baltimore City. While McCain won most of the western and eastern counties by margins of 2-to-1 or more, he was almost completely shut out in the larger counties surrounding Baltimore and Washington; every large county, except Anne Arundel, went for Obama.
From 2007 to 2011, U.S. Congressman Steny Hoyer
Steny Hamilton Hoyer (born June 14, 1939) is an American politician and attorney serving as the U.S. representative for since 1981 and as House Majority Leader since 2019. A Democrat, Hoyer was first elected in a special election on May 19, 19 ...
( MD-5), a Democrat, was elected as Majority Leader
In U.S. politics (as well as in some other countries utilizing the presidential system), the majority floor leader is a partisan position in a legislative body.
for the 110th Congress
The 110th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, between January 3, 2007, and January 3, 2009, during the last two years of the Presidency of George W. Bush. It was composed of ...
and 111th Congress
The 111th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government from January 3, 2009, until January 3, 2011. It began during the last weeks of the George W. Bush administration, with th ...
of the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entitles. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often c ...
, serving in that post again starting in 2019. In addition, Hoyer served as House Minority Whip from 2003 to 2006 and 2012 to 2018. His district covers parts of Anne Arundel and Prince George's counties, in addition to all of Charles, Calvert, and St. Mary's counties in southern Maryland
Southern Maryland is a geographical, cultural and historic region in Maryland composed of the state's southernmost counties on the Western Shore of the Chesapeake Bay. According to the state of Maryland, the region includes all of Calvert, Ch ...
.
In 2010, Republicans won control of most counties. The Democratic Party remained in control of eight county governments, including that of Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was ...
.
In 2014, Larry Hogan
Lawrence Joseph Hogan Jr. (born May 25, 1956) is an American politician and businessman serving as the 62nd governor of Maryland since 2015. A moderate member of the Republican Party, he was secretary of appointments under Maryland governor Bo ...
, a moderate Republican, was elected Governor of Maryland. Hogan is the second Republican to become the Governor of Maryland since Spiro Agnew, who resigned in 1969 to become vice president. In 2018, Hogan was re-elected to a second term of office. Per the Constitution of Maryland
The current Constitution of the State of Maryland, which was ratified by the people of the state on September 18, 1867, forms the basic law for the U.S. state of Maryland. It replaced the short-lived Maryland Constitution of 1864 and is the fourt ...
, Hogan is term-limited, and may not run for a third consecutive term in the 2022 Maryland gubernatorial election
The 2022 Maryland gubernatorial election was held on November 8, 2022, to elect the next Governor of Maryland. Governor Larry Hogan, the incumbent two-term Republican, was term-limited and could not seek re-election to a third consecutive te ...
.
In a 2020 study, Maryland was ranked by the ''Election Law Journal
''Election Law Journal: Rules, Politics, and Policy'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed law journal published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. covering legal issues related to elections and voting rights. It was established in 2002 with Daniel H. Lowenstein ...
'' as the 5th easiest state for citizens to vote in.
LGBT rights and community
The first person known to describe himself as adrag queen
A drag queen is a person, usually male, who uses drag clothing and makeup to imitate and often exaggerate female gender signifiers and gender roles for entertainment purposes. Historically, drag queens have usually been gay men, and part of ...
was William Dorsey Swann
William Dorsey Swann (March 1860 – c. December 23, 1925) was an American LGBT activist in a time where leadership in the movement was uncommon. An African-American born into slavery, Swann was the first person in the United States to lead ...
, born enslaved in Hancock, Maryland. Swann was the first American on record who pursued legal and political action to defend the LGBTQ community
The LGBT community (also known as the LGBTQ+ community, GLBT community, gay community, or queer community) is a loosely defined grouping of lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and other queer individuals united by a common culture and social ...
's right to assemble
Freedom of peaceful assembly, sometimes used interchangeably with the freedom of association, is the individual right or ability of people to come together and collectively express, promote, pursue, and defend their collective or shared ide ...
.
In February 2010, Attorney General Doug Gansler
Douglas Friend Gansler (born October 30, 1962) is an American lawyer and politician who served as the 45th Attorney General of Maryland. Gansler previously served as the State's Attorney for Montgomery County, Maryland, from 1999 to 2007. He won ...
issued an opinion stating that Maryland law should honor same-sex marriages from out of state. At the time, the state Supreme Court wrote a decision upholding marriage discrimination.
On March 1, 2012, Maryland Governor Martin O'Malley
Martin Joseph O'Malley (born January 18, 1963) is an American lawyer and former politician who served as the 61st Governor of Maryland from 2007 to 2015. A member of the Democratic Party, he was Mayor of Baltimore from 1999 to 2007.
O'Malley ...
signed the freedom to marry bill into law after it passed in the state legislature. Opponents of same-sex marriage began collecting signatures to overturn the law. The law faced a referendum, as Question 6, in the November 2012 election.
A large majority (57%) of Maryland voters said they would vote to uphold the freedom to marry, with 37% saying they would vote against. This is consistent with a January 2011 Gonzales Research & Marketing Strategies poll showing 51% support for marriage in the state.
Voters voted 52% to 48% for Question6 on November 6, 2012. Same-sex couples began marrying in Maryland on January 1, 2013.
In May 2012, Maryland's Court of Appeals ruled that the state will recognize marriages of same-sex couples who married out-of-state, no matter the outcome of the November election.
Media
A well-known newspaper in Maryland is ''The Baltimore Sun
''The Baltimore Sun'' is the largest general-circulation daily newspaper based in the U.S. state of Maryland and provides coverage of local and regional news, events, issues, people, and industries.
Founded in 1837, it is currently owned by Tr ...
''.
Many residents of the Washington metropolitan area
The Washington metropolitan area, also commonly referred to as the National Capital Region, is the metropolitan area centered on Washington, D.C. The metropolitan area includes all of Washington, D.C. and parts of the states of Maryland, Virgi ...
receive ''The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'' (also known as the ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'') is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C. It is the most widely circulated newspaper within the Washington metropolitan area and has a large nat ...
.''
The most populous areas are served by either Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was ...
or Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, Na ...
broadcast stations. The Eastern Shore is served primarily by broadcast media
Broadcasting is the distribution of audio or video content to a dispersed audience via any electronic mass communications medium, but typically one using the electromagnetic spectrum (radio waves), in a one-to-many model. Broadcasting began wi ...
based around the Delmarva Peninsula
The Delmarva Peninsula, or simply Delmarva, is a large peninsula and proposed state on the East Coast of the United States, occupied by the vast majority of the state of Delaware and parts of the Eastern Shore regions of Maryland and Virginia. ...
; the northeastern section receives both Baltimore and Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since ...
stations. Garrett County, which is mountainous, is served by stations from Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Western Pennsylvania, the second-most populous city in Pennsylv ...
, and requires cable or satellite for reception. Maryland is served by statewide PBS
The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is an American public broadcaster and non-commercial, free-to-air television network based in Arlington, Virginia. PBS is a publicly funded nonprofit organization and the most prominent provider of educati ...
member station Maryland Public Television
Maryland Public Television (MPT) is the Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) member state network for the U.S. state of Maryland. It operates under the auspices of the Maryland Public Broadcasting Commission, an agency of the Maryland state govern ...
(MPT).
Education
Primary and secondary education
''Education Week'' ranked Maryland #1 in its nationwide 2009–2013 Quality Counts reports. The College Board's 9th Annual AP Report to the Nation also ranked Maryland first. Primary and secondary education in Maryland is overseen by theMaryland State Department of Education
Maryland State Department of Education (MSDE) is a division of the state government of Maryland in the United States. The agency oversees public school districts, which are 24 local school systems—one for each of Maryland's 23 counties plus one ...
, which is headquartered in Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was ...
. The highest educational official in the state is the State Superintendent of Schools, who is appointed by the State Board of Education to a four-year term of office. The Maryland General Assembly has given the Superintendent and State Board autonomy to make educationally related decisions, limiting its influence on the day-to-day functions of public education. Each county and county-equivalent in Maryland has a local Board of Education charged with running the public schools in that particular jurisdiction.
The budget for education was $5.5billion in 2009, representing about 40 percent of the state's general fund. Data from the 2017 census shows that, among large school districts, four Maryland districts are in the top six for per-pupil annual spending, exceeded only by the Boston and New York City districts.
Maryland has a broad range of private primary and secondary schools. Many of these are affiliated with various religious sects, including parochial schools
A parochial school is a private primary or secondary school affiliated with a religious organization, and whose curriculum includes general religious education in addition to secular subjects, such as science, mathematics and language arts. The wo ...
of the Catholic Church, Quaker
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's abili ...
schools, Seventh-day Adventist
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is an Adventist Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the seventh day of the week in the Christian (Gregorian) and the Hebrew calendar, as the Sabbath, and i ...
schools, and Judaism, Jewish schools. In 2003, Maryland law was changed to allow for the creation of publicly funded charter schools, although the charter schools must be approved by their local Board of Education and are not exempt from state laws on education, including collective bargaining laws.
In 2008, the state led the entire country in the percentage of students passing Advanced Placement examinations. 23.4 percent of students earned passing grades on the AP tests given in May 2008. This marks the first year that Maryland earned this honor. Three Maryland high schools (in Montgomery County) were ranked among the top 100 in the country by US News in 2009, based in large part on AP test scores.
Colleges and universities
Maryland has several historic and renowned private colleges and universities, the most prominent of which isJohns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University (Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private research university in Baltimore, Maryland. Founded in 1876, Johns Hopkins is the oldest research university in the United States and in the western hemisphere. It consiste ...
, founded in 1876 with a grant from Baltimore entrepreneur Johns Hopkins
Johns Hopkins (May 19, 1795 – December 24, 1873) was an American merchant, investor, and philanthropist. Born on a plantation, he left his home to start a career at the age of 17, and settled in Baltimore, Maryland where he remained for most ...
.
The first public university in the state is the University of Maryland, Baltimore, which was founded in 1807 and contains the University of Maryland's only public academic University of Maryland School of Medicine, health, human services, and one of two University of Maryland School of Law, law centers (the other being the University of Baltimore School of Law). Seven professional and graduate schools train the majority of the state's physicians, nurses, dentists, lawyers, social workers, and pharmacists. The flagship university and largest undergraduate institution in Maryland is the University of Maryland, College Park
The University of Maryland, College Park (University of Maryland, UMD, or simply Maryland) is a public land-grant research university in College Park, Maryland. Founded in 1856, UMD is the flagship institution of the University System of Mar ...
which was founded as the Maryland Agricultural College in 1856 and became a public land grant college in 1864. Towson University, founded in 1866, is the state's second largest university.
In 1974, Maryland, along with seven other states, mainly in the South, submitted plans to desegregate its state universities; Maryland's plans were approved by the U.S. Department of Health, Education and Welfare.
Baltimore is home to the University of Maryland, Baltimore County
The University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC) is a public research university in Baltimore County, Maryland. It has a fall 2022 enrollment of 13,991 students, 61 undergraduate majors, over 92 graduate programs (38 master, 25 doctoral, ...
and the Maryland Institute College of Art. The majority of public universities in the state (Bowie State University, Coppin State University, Frostburg State University, Salisbury University and the University of Maryland-Eastern Shore) are affiliated with the University System of Maryland
The University System of Maryland (USM) is a public higher education system in the U.S. state of Maryland. The system is composed of the eleven campuses at College Park, Baltimore County, Baltimore, Princess Anne, Towson, Salisbury, Bowie, ...
. Two state-funded institutions, Morgan State University and St. Mary's College of Maryland, as well as two federally funded institutions, the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences and the United States Naval Academy, are not affiliated with the University System of Maryland. The University of Maryland Global Campus is the largest public university in Maryland and one of the largest distance-learning institutions in the world.
St. John's College (Annapolis/Santa Fe), St. John's College in Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Maryland and the county seat of, and only incorporated city in, Anne Arundel County. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east ...
and Washington College in Chestertown, Maryland, Chestertown, both private institutions, are the oldest colleges in the state and among the oldest in the country. Other private institutions include Mount St. Mary's University, McDaniel College (formerly known as Western Maryland College), Hood College, Stevenson University (formerly known as Villa Julie College), Loyola University Maryland, and Goucher College, among others.
Public libraries
Maryland's 24 public library systems deliver public education for everyone in the state of Maryland through a curriculum that comprises three pillars: Self-Directed Education (books and materials in all formats, e-resources), Research Assistance & Instruction (individualized research assistance, classes for students of all ages), and Instructive & Enlightening Experiences (e.g., Summer Reading Clubs, author events). Maryland's library systems include, in part: * Baltimore County Public Library System * Cecil County Public Library * Enoch Pratt Free Library * Frederick County Public Library * Harford County Public Library * Howard County Public Library * Montgomery County Public Libraries * Prince George's County Memorial Library System * St. Mary's County Public Library Many of the library systems have established formalized partnerships with other educational institutions in their counties and regions.Sports

 With two major metropolitan areas, Maryland has a number of major and minor professional sports franchises. Two National Football League teams play in Maryland, the Baltimore Ravens in
With two major metropolitan areas, Maryland has a number of major and minor professional sports franchises. Two National Football League teams play in Maryland, the Baltimore Ravens in Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was ...
and the Washington Commanders in Landover, Maryland, Landover. The History of the Baltimore Colts, Baltimore Colts represented the NFL in Baltimore from 1953 to 1983 before moving to Indianapolis.
The Baltimore Orioles
The Baltimore Orioles are an American professional baseball team based in Baltimore. The Orioles compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) East division. As one of the American League's eight char ...
are the state's Major League Baseball franchise. The National Hockey League's Washington Capitals and the National Basketball Association's Washington Wizards formerly played in Maryland, until the construction of an arena in Washington, D.C. in 1997 (now known as Capital One Arena). University of Maryland, College Park, University of Maryland's team is the Maryland Terrapins.
Maryland enjoys considerable historical repute for the talented sports players of its past, including Cal Ripken Jr. and Babe Ruth. In 2012, ''The Baltimore Sun
''The Baltimore Sun'' is the largest general-circulation daily newspaper based in the U.S. state of Maryland and provides coverage of local and regional news, events, issues, people, and industries.
Founded in 1837, it is currently owned by Tr ...
'' published a list of Maryland's top ten athletes in the state's history. The list includes Babe Ruth, Cal Ripken Jr, Johnny Unitas, Brooks Robinson, Frank Robinson, Ray Lewis, Michael Phelps, Jimmie Foxx, Jim Parker (American football), Jim Parker, and Wes Unseld.
Other professional sports franchises in the state include three affiliated minor league baseball teams, one independent league baseball team, the Baltimore Blast (current), Baltimore Blast indoor soccer team, two indoor football teams, three low-level outdoor soccer teams, and the Chesapeake Bayhawks of Major League Lacrosse. Maryland is also home to one of the three races in horse racing's annual Triple Crown, the Preakness Stakes, which is run every spring at Pimlico Race Course in Baltimore. Baltimore Stallions, The Baltimore Stallions were a Canadian Football Team in the Canadian Football League, CFL that played the 1994–95 season.
The Congressional Country Club has hosted three golf tournaments for the U.S. Open (golf), U.S. Open and a PGA Championship.
The official state sport of Maryland, since 1962, is jousting; the official team sport since 2004 is lacrosse. The National Lacrosse Hall of Fame is located on the Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University (Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private research university in Baltimore, Maryland. Founded in 1876, Johns Hopkins is the oldest research university in the United States and in the western hemisphere. It consiste ...
campus in Baltimore. In 2008, intending to promote physical fitness for all ages, walking became the official state exercise. Maryland is the first state with an official state exercise.
Friendship partners
Maryland has relationships with many provinces, states, and other entities worldwide. * Bong County, Bong and Maryland County, Maryland Counties, in Liberia * Jalisco, Mexico (1996) * Cross River State, Cross River and Ondo States, Nigeria * Kwazulu-Natal, South Africa * Victoria (Australia), Victoria, AustraliaSee also
* Index of Maryland-related articles * Outline of MarylandNotes
References
Bibliography
* * * Davis, William Wilkins. ''Religion and Politics in Maryland on the Eve of the Civil War: The Letters of W. Wilkins Davis''. Foreword by Charles W. Mitchell. 1988; rev. ed., Eugene, Ore.: Wipf & Stock, 2009. * *External links
*Maryland Office of Tourism
Energy Data & Statistics for Maryland
USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Maryland
Maryland State Facts from USDA
* *
* [http://www.mdhs.org/library/research-resources/county-maps Maryland Historical Society: County Maps]
The Huntingfield Map Collection
{{coord, 39, -77, dim:300000_region:US-MD_type:adm1st, name=State of Maryland, display=title Maryland, 1788 establishments in the United States Contiguous United States Mid-Atlantic states Northeastern United States Southern United States States and territories established in 1788 States of the East Coast of the United States States of the United States