Mark 15 torpedo on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
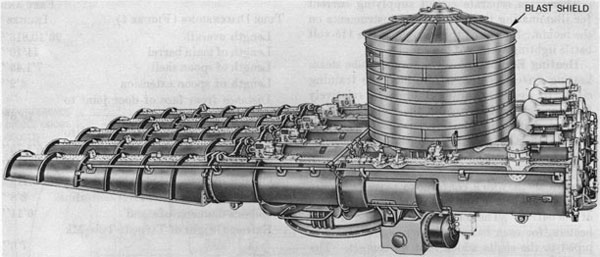
The Mark 15 torpedo, the standard American
 Anticipating the possibility of war with Japan, the United States planned to move their battleships across the Pacific with the fleet train. Cruisers and destroyers would be responsible for defending this large formation at night. Fleet exercises held during the 1930s revealed the confusing nature of close range engagements during hours of darkness. In 1932, during
Anticipating the possibility of war with Japan, the United States planned to move their battleships across the Pacific with the fleet train. Cruisers and destroyers would be responsible for defending this large formation at night. Fleet exercises held during the 1930s revealed the confusing nature of close range engagements during hours of darkness. In 1932, during
destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in ...
-launched torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, su ...
of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, was very similar in design to the Mark 14 torpedo
The Mark 14 torpedo was the United States Navy's standard submarine-launched anti-ship torpedo of World War II. This weapon was plagued with many problems which crippled its performance early in the war. It was supplemented by the Mark 18 elec ...
except that it was longer, heavier, and had greater range and a larger warhead. It was developed by the Naval Torpedo Station
The Naval Undersea Warfare Center (NUWC) is the United States Navy's full-spectrum research, development, test and evaluation, engineering and fleet support center for submarines, autonomous underwater systems, and offensive and defensive weapons ...
Newport concurrently with the Mark 14 and was first deployed in 1938. It replaced the Mark 8 torpedo on surface ships with tubes that could accommodate the longer Mark 15; this primarily included destroyers
In navy, naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a Naval fleet, fleet, convoy or Carrier battle group, battle group and defend them against powerful short range attack ...
built after 1930. Older destroyers, primarily the ''Wickes'' and ''Clemson'' classes, continued to use the Mark 8, as did PT boat
A PT boat (short for patrol torpedo boat) was a motor torpedo boat used by the United States Navy in World War II. It was small, fast, and inexpensive to build, valued for its maneuverability and speed but hampered at the beginning of the wa ...
s early in World War II. During the war 9,700 were produced at Newport and at the Naval Ordnance Station Forest Park
Naval Ordnance Station Forest Park (NOSF) was in Forest Park, Illinois. It was founded during World War II (1942-1945) as ''Naval Ordnance Plant Forest Park (NOPF)''. The Forest Park Station was instrumental in building torpedoes for the Navy, emp ...
, Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolita ...
.
The Mark 15 had the same basic design problems that plagued the Mark 14 for the first 20 months following U.S. entry into the war, though this was not realized nearly as quickly by the destroyer crews as it was by the submariners. One major shared deficiency was the Mark 6 exploder
The Mark 6 exploder was a United States Navy torpedo exploder developed in the 1920s. It was the standard exploder of the Navy's Mark 14 torpedo and Mark 15 torpedo.
Development
Early torpedoes used contact exploders. A typical exploder had a ...
, which usually caused duds. Another was a tendency to run deeper than set, often missing the target. Surface-combatant torpedo attacks very often included confusing splashes from gunnery and aerial bombs, obscuring smoke screens, and quick maneuvering to evade counterattack. Rarely was a destroyer given a chance for a slow, careful surprise attack. Torpedo results were difficult to estimate under these circumstances. The correction of the Mark 15's problems would depend on the submariners solving theirs. Another problem with early war-built Mark 15s was the substitution of zinc for cadmium as interior plating for air flask sections and water compartments, due to a wartime shortage of cadmium. This resulted in zinc oxide clogging water strainers, leading to erratic runs and engine failures. After the failure of corrosion inhibition efforts, the ultimate solution was to re-coat the areas with cadmium or phenolic resin
Phenol formaldehyde resins (PF) or phenolic resins (also infrequently called phenoplasts) are synthetic polymers obtained by the reaction of phenol or substituted phenol with formaldehyde. Used as the basis for Bakelite, PFs were the first commerc ...
(Heresite).
The Battle of Vella Gulf
The was a naval battle of the Pacific campaign of World War II fought on the night of 6–7 August 1943 in Vella Gulf between Vella Lavella Island and Kolombangara Island in the Solomon Islands of the Southwest Pacific.
This engagement was t ...
on the night of August 6–7, 1943, was the first in which a surprise torpedo attack by U.S. gave the Americans an overwhelming advantage in the following gun battle, though one Japanese warship was hit by a dud torpedo and escaped. By September 1943, effective methods of torpedo deployment were beginning to be distributed to all U.S. destroyers.
Tactics

 Anticipating the possibility of war with Japan, the United States planned to move their battleships across the Pacific with the fleet train. Cruisers and destroyers would be responsible for defending this large formation at night. Fleet exercises held during the 1930s revealed the confusing nature of close range engagements during hours of darkness. In 1932, during
Anticipating the possibility of war with Japan, the United States planned to move their battleships across the Pacific with the fleet train. Cruisers and destroyers would be responsible for defending this large formation at night. Fleet exercises held during the 1930s revealed the confusing nature of close range engagements during hours of darkness. In 1932, during Fleet Problem XIII The Fleet Problems are a series of naval exercises of the United States Navy conducted in the interwar period, and later resurrected by Pacific Fleet around 2014.
The first twenty-one Fleet Problems — labeled with roman numerals as Fleet Proble ...
, "attacking" destroyers closed to within of before being detected. Fleet Problem XV in 1934 placed the destroyer screen beyond the battleship formation, but the battleships were unable to differentiate "friend" from "foe" at that distance. Screening destroyers were subsequently stationed at effective searchlight illumination range, . Recognition improved at that distance, but torpedo hit probability increased as evasive maneuvering of the large, compact force was restricted within the closer screen.
United States Navy ''War Instructions'' (FTP 143) published in 1934 remained in effect through the initial 1942 engagements in the Solomon Islands. The instructions emphasized defense to avoid the attrition objective of Japanese planning:
* Cruisers were advised to avoid night action unless conditions were favorable.
* Destroyers were to attack at once with guns, but reserve torpedoes for use against capital ships.
Searchlight illumination range effectively covered launch positions of United States torpedoes, but not the Japanese Type 93 torpedo
The was a -diameter torpedo of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), launched from surface ships. It is commonly referred to as the Long Lance by most modern English-language naval historians, a nickname given to it after the war by Samuel Eliot Mori ...
. Japanese ships could remain outside of illumination range, launching torpedoes at American ships that revealed their positions with gunfire and use of searchlights.
See also
*American 21 inch torpedo
There have been a number of 21-inch torpedoes in service with the United States. These have been used on ships and submarines of the U.S. Navy. American 21-inch torpedoes are in diameter.
Ship classes that carried 21-inch torpedoes include:
* '' ...
References
{{Mark-series torpedoes Torpedoes of the United States World War II naval weapons World War II weapons of the United States Military equipment introduced in the 1930s