Mainz Cathedral on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
, native_name_lang =
, image = Mainzer Dom nw.jpg
, imagesize =
, imagelink =
, imagealt =
, caption =
, pushpin map =
, pushpin label position =
, pushpin map alt =
, pushpin mapsize =
, relief =
, map caption =
, iso region =
, osgraw =
, osgridref =
, location =
 During the time of Mainz Archbishop
During the time of Mainz Archbishop  The cathedral suffered extensive damage from a fire on the day of its inauguration in 1009. Archbishop
The cathedral suffered extensive damage from a fire on the day of its inauguration in 1009. Archbishop
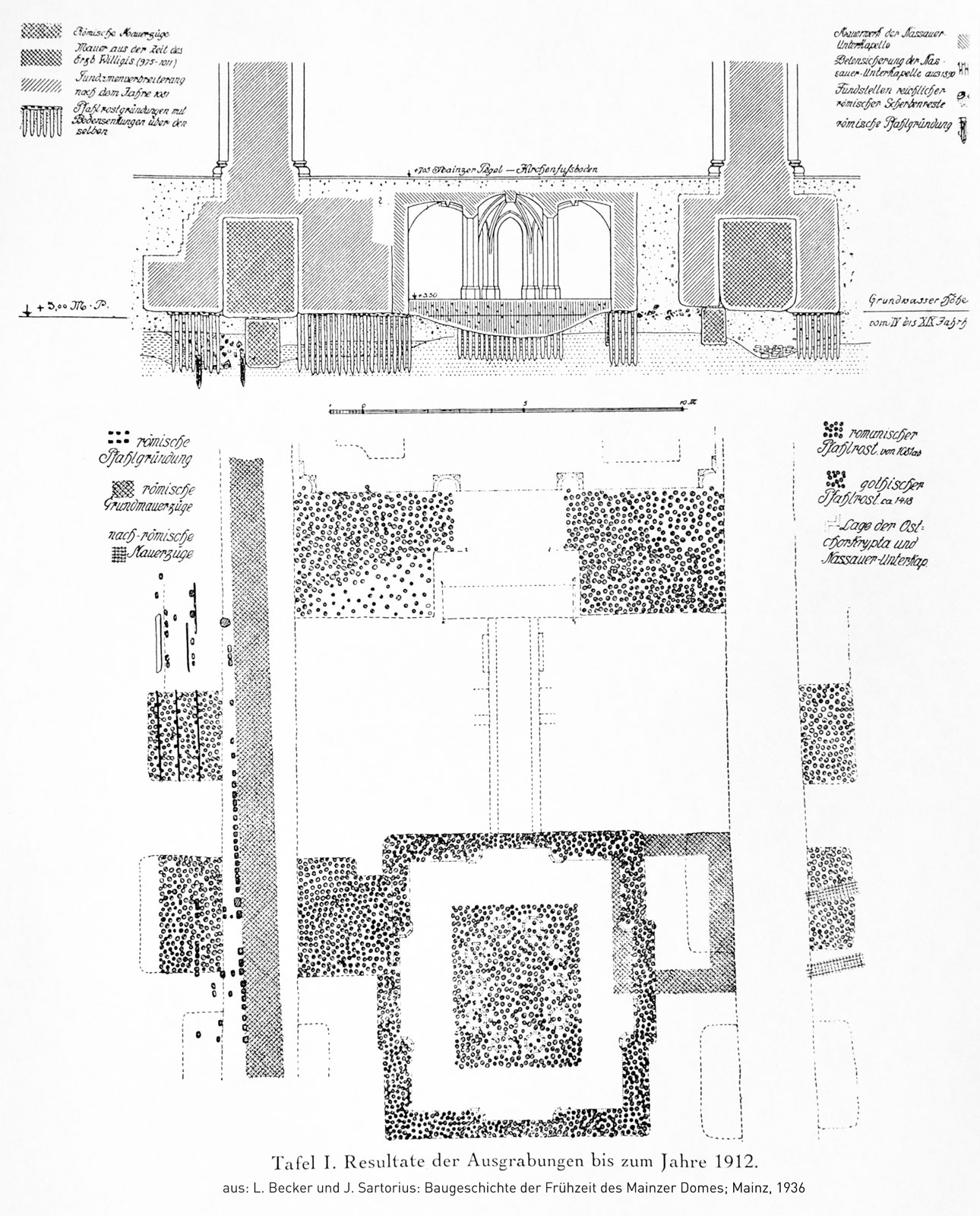 Conservation efforts began in the 1900s to save the cathedral from further damage. After a lowering of the groundwater, the wooden substructures became rotten and the foundations started to fail and needed to be replaced. Beginning in 1909 the old foundations were underpinned. Works stopped in 1916 due to
Conservation efforts began in the 1900s to save the cathedral from further damage. After a lowering of the groundwater, the wooden substructures became rotten and the foundations started to fail and needed to be replaced. Beginning in 1909 the old foundations were underpinned. Works stopped in 1916 due to
The emperors and the pillars of their power
From Charlemagne to Frederick Barbarossa, flyer
Mainz Online: Cathedral
(extended history of the cathedral)
(another history of the cathedral; in German)
Cathedral Museum Mainz
(documentation of artefacts in the cathedral; in German)
Terce (= Mid-Morning Prayer) and Pontifical High Mass in Mainz Cathedral
- Pentecost 2015 with
Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Ma ...
, country = Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, denomination = Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
, previous denomination =
, churchmanship =
, membership =
, attendance =
, website =
, former name =
, bull date =
, founded date = 975 or 976
, founder =
, dedication = Martin of Tours
Martin of Tours ( la, Sanctus Martinus Turonensis; 316/336 – 8 November 397), also known as Martin the Merciful, was the third bishop of Tours. He has become one of the most familiar and recognizable Christian saints in France, heralded as the ...
, dedicated date = 29 August 1009 (1st time)
, consecrated date =
, cult =
, relics = Chasuble of Willigis
Willigis ( la, Willigisus; german: Willigis, Willegis; 940 – 23 February 1011 AD) was Archbishop of Mainz from 975 until his death as well as archchancellor of the Holy Roman Empire.
Life
Willigus was born in the Duchy of Saxony, possibly at ...
, events =
, past bishop = Willigis
Willigis ( la, Willigisus; german: Willigis, Willegis; 940 – 23 February 1011 AD) was Archbishop of Mainz from 975 until his death as well as archchancellor of the Holy Roman Empire.
Life
Willigus was born in the Duchy of Saxony, possibly at ...
, people =
, status = Cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the ''cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominations ...
, functional status = Active
, heritage designation =
, designated date =
, architect =
, architectural type =
, style = Romanesque (original)Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
(chapels and bell towers)Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including ...
(roof)
, years built = 975 - 1009
, groundbreaking =
, completed date =
, construction cost =
, closed date =
, demolished date =
, capacity =
, length =
, width =
, width nave =
, height =
, diameter =
, other dimensions =
, floor count =
, floor area =
, dome quantity =
, dome height outer =
, dome height inner =
, dome dia outer =
, dome dia inner =
, spire quantity =
, spire height =
, materials =
, bells =
, bells hung =
, bell weight =
, parish =
, deanery =
, archdeaconry =
, episcopalarea =
, archdiocese =
, metropolis =
, diocese = Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Ma ...
, province = Freiburg im Breisgau
Freiburg im Breisgau (; abbreviated as Freiburg i. Br. or Freiburg i. B.; Low Alemannic: ''Friburg im Brisgau''), commonly referred to as Freiburg, is an independent city in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. With a population of about 230,000 (as o ...
, presbytery =
, synod =
, circuit =
, district =
, division =
, subdivision =
, archbishop =
, bishop = Peter Kohlgraf
, abbot =
, prior =
, subprior =
, vicar =
, exarch =
, provost-rector =
, provost =
, viceprovost =
, rector =
, dean =
, subdean =
, archpriest =
, precentor =
, succentor =
, chancellor =
, canonchancellor =
, canon =
, canonpastor =
, canonmissioner =
, canontreasurer =
, prebendary =
, priestincharge =
, priest =
, asstpriest =
, honpriest =
, curate =
, asstcurate =
, minister =
, assistant =
, seniorpastor =
, pastor =
, assocpastor =
, asstpastor =
, chaplain =
, archdeacon =
, deacon =
, deaconness =
, reader =
, student intern =
, organistdom =
, director =
, elder =
, organist = Daniel Beckmann
Daniel Beckmann (born 1980) is a German organist at Mainz Cathedral.
Beckmann studied catholic church music and organ at the Hochschule für Musik Detmold, where he acquired all degrees (church music A, artistic degree and concert degree) with ...
, organscholar =
, chapterclerk =
, laychapter =
, warden =
, verger =
, businessmgr =
, liturgycoord =
, reledu =
, rcia =
, youthmin =
, flowerguild =
, musicgroup =
, parishadmin =
, serversguild =
, logo =
, logosize =
, logolink =
, logoalt =
, embedded =
Mainz Cathedral or St. Martin's Cathedral (german: Mainzer Dom, Martinsdom or, officially, ') is located near the historical center and pedestrianized market square of the city of Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Ma ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
. This 1000-year-old Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
cathedral is the site of the episcopal see
An episcopal see is, in a practical use of the phrase, the area of a bishop's ecclesiastical jurisdiction.
Phrases concerning actions occurring within or outside an episcopal see are indicative of the geographical significance of the term, mak ...
of the Bishop of Mainz
The Diocese of Mainz, historically known in English as ''Mentz'' as well as by its French name ''Mayence'', is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church in Germany. It was founded in 304, promoted in 780 to Metr ...
.
Mainz Cathedral is predominantly Romanesque in style, but later exterior additions over many centuries have resulted in the appearance of various architectural influences seen today. It comprises three aisle
An aisle is, in general, a space for walking with rows of non-walking spaces on both sides. Aisles with seating on both sides can be seen in airplanes, certain types of buildings, such as churches, cathedrals, synagogues, meeting halls, pa ...
s and stands under the patronage of Saint Martin of Tours
Martin of Tours ( la, Sanctus Martinus Turonensis; 316/336 – 8 November 397), also known as Martin the Merciful, was the third bishop of Tours. He has become one of the most familiar and recognizable Christian saints in France, heralded as the ...
. The eastern quire is dedicated to Saint Stephen
Stephen ( grc-gre, Στέφανος ''Stéphanos'', meaning "wreath, crown" and by extension "reward, honor, renown, fame", often given as a title rather than as a name; c. 5 – c. 34 AD) is traditionally venerated as the protomartyr or first ...
.
The interior of the cathedral houses tombs and funerary monuments of former powerful Electoral
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has oper ...
- prince-archbishops, or , of the diocese and contains religious works of art spanning a millennium. The cathedral also has a central courtyard and statues of Saint Boniface
Boniface, OSB ( la, Bonifatius; 675 – 5 June 754) was an English Benedictine monk and leading figure in the Anglo-Saxon mission to the Germanic parts of the Frankish Empire during the eighth century. He organised significant foundations o ...
and The Madonna
In art, a Madonna () is a representation of Mary, either alone or with her child Jesus. These images are central icons for both the Catholic and Orthodox churches. The word is (archaic). The Madonna and Child type is very prevalent in ...
on its grounds.
 During the time of Mainz Archbishop
During the time of Mainz Archbishop Willigis
Willigis ( la, Willigisus; german: Willigis, Willegis; 940 – 23 February 1011 AD) was Archbishop of Mainz from 975 until his death as well as archchancellor of the Holy Roman Empire.
Life
Willigus was born in the Duchy of Saxony, possibly at ...
(975-1011), the city of Mainz flourished economically, and Willigis became one of the most influential politicians of that time, ascending to regent of the empire between 991 and 994. In 975-976 shortly after his installation he ordered the construction of a new cathedral in the pre-Romanesque Ottonian architecture style. This new and impressive building was part of his vision of Mainz as the "second Rome". page 138
This new cathedral was to take over the functions of two churches: the old cathedral and St. Alban's, which was the largest church in the area, belonging to a Benedictine abbey and serving as the burial ground for the bishops and other nobles, including Fastrada, a spouse of Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ...
. Most of the synod
A synod () is a council of a Christian denomination, usually convened to decide an issue of doctrine, administration or application. The word '' synod'' comes from the meaning "assembly" or "meeting" and is analogous with the Latin word mean ...
s and other important meetings were held at St. Alban's Abbey.
The new cathedral consisted of a double chancel
In church architecture, the chancel is the space around the altar, including the choir and the sanctuary (sometimes called the presbytery), at the liturgical east end of a traditional Christian church building. It may terminate in an apse.
...
with two transept
A transept (with two semitransepts) is a transverse part of any building, which lies across the main body of the building. In cruciform churches, a transept is an area set crosswise to the nave in a cruciform ("cross-shaped") building with ...
s. The main hall was built in the typical triple-nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-typ ...
"cross" pattern. As was usual at that time no vault
Vault may refer to:
* Jumping, the act of propelling oneself upwards
Architecture
* Vault (architecture), an arched form above an enclosed space
* Bank vault, a reinforced room or compartment where valuables are stored
* Burial vault (enclosure ...
was included because of structural difficulties relating to the size of the building. Six towers rose from the church. A cloister was enclosed in the structure and a small freestanding church, St. Mary's Church, connected by a colonnade
In classical architecture, a colonnade is a long sequence of columns joined by their entablature, often free-standing, or part of a building. Paired or multiple pairs of columns are normally employed in a colonnade which can be straight or cur ...
. This small church developed later into the collegiate church In Christianity, a collegiate church is a church where the daily office of worship is maintained by a college of canons: a non-monastic or "secular" community of clergy, organised as a self-governing corporate body, which may be presided over by ...
of St. Maria ad Gradus.
Sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicat ...
was used as the primary building material for the cathedral. The inside was plastered white under the Archbishop Bardo, probably in the middle of the 10th century. During renovations ordered by Henry IV in the late 11th century, much of the outside was also plastered, but the cornice
In architecture, a cornice (from the Italian ''cornice'' meaning "ledge") is generally any horizontal decorative moulding that crowns a building or furniture element—for example, the cornice over a door or window, around the top edge of a ...
s were left exposed in their original red and yellow. It is believed that the coloring of the cathedral was changed on a number of occasions, but no further documentation of the coloring is available until records of the Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including ...
works.
Bardo
In some schools of Buddhism, ''bardo'' ( xct, བར་དོ་ Wylie: ''bar do'') or ''antarābhava'' (Sanskrit, Chinese and Japanese: 中有, romanized in Chinese as ''zhōng yǒu'' and in Japanese as ''chū'u'') is an intermediate, transitio ...
(Bardo of Oppershofen) presided over the completion of the cathedral begun under Willigis. By 1037 the main portions of the body of Mainz Cathedral were complete. Willigis was buried in the second church he had initiated, St. Stephan's, in 1011.
The two chancels
From the ninth to 12th century, several important churches in theHoly Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
were built with choirs on both ends. One of the first was Cologne Cathedral
Cologne Cathedral (german: Kölner Dom, officially ', English: Cathedral Church of Saint Peter) is a Catholic cathedral in Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia. It is the seat of the Archbishop of Cologne and of the administration of the Archdiocese ...
of 855 ("Hildebld's Cathedral"). One of the oldest preserved examples is St. Michael's Church, Hildesheim, erected since 1010. Gernrode Abbey church was added a second choir, in the 12th century. This type of footplans also was acquired in Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
(Tum Collegiate Church
, image=SM Tum kolegiata ID 612614.jpg
, image_size=250px
, caption=The church in 2012
, pushpin map=Poland
, coordinates=
, location=Tum, Łęczyca, Łódź Voivodeship
, country=Poland
, denomination= Roman Catholic
, consecrated date=21 May 1161 ...
) and Hungary (Pécs Cathedral
The Sts. Peter and Paul's Cathedral Basilica ( hu, Szent Péter és Szent Pál székesegyház), also called Pécs Cathedral, is a religious building of the Catholic church that serves as the cathedral of the Diocese of Pécs, and is located in the ...
). The reason for building two chancels is not entirely clear. Many scholars suggest that there is some symbolic significance, such as empire
An empire is a "political unit" made up of several territories and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the empire (sometimes referred to as the metropole) ex ...
and church
Church may refer to:
Religion
* Church (building), a building for Christian religious activities
* Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination
* Church service, a formalized period of Christian communal worship
* Chri ...
, or body and spirit, but no irrefutable evidence for these theories exists. Others claim that the construction has a functional purpose for ceremonial procession
A procession is an organized body of people walking in a formal or ceremonial manner.
History
Processions have in all peoples and at all times been a natural form of public celebration, as forming an orderly and impressive ceremony. Religious ...
s. Whatever the original intent of the double chancel, the eastern chancel came to serve as the location for the mass and the western chancel was reserved for the bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is ...
and pontiff
A pontiff (from Latin ''pontifex'') was, in Roman antiquity, a member of the most illustrious of the colleges of priests of the Roman religion, the College of Pontiffs."Pontifex". "Oxford English Dictionary", March 2007 The term "pontiff" was l ...
s.
Bardo's western chancel
In most cathedrals at the time, the main chancel lay on the east side. Willigis, however, designed his cathedral with the main chancel on the west, presumably modeled after the great basilicas in Rome, which were constructed this way. (Willigis's design bore a striking resemblance toOld St. Peter's Basilica
Old St. Peter's Basilica was the building that stood, from the 4th to 16th centuries, where the new St. Peter's Basilica stands today in Vatican City. Construction of the basilica, built over the historical site of the Circus of Nero, began dur ...
.)
The chancel was badly damaged in the fire of 1009, and remained that way under Archbishops Erkanbald
Erkanbald (died 17 August 1021) was the Abbot of Fulda from 997 and afterwards Archbishop of Mainz from 1011 until his death.
Erkanbald was a member of the family of the counts of Ölsburg and was thus related to Bernard III of Sommerescheburg ...
and Aribo. The chancel was finally reconstructed under Bardo. He then buried his predecessor Aribo there, before the rest of the cathedral was even finished. (Willigis's remains are not, as sometimes believed, in Mainz Cathedral; he was buried in his second construction project, St. Stephen's.)
Henry IV's eastern chancel
In 1081, fire once again struck the cathedral, and the appearance of the Salian western end is not known. In 1100, Henry IV ordered reconstruction in the old Lombardic style. The old flat chancel end on the east side was replaced with a largeapse
In architecture, an apse (plural apses; from Latin 'arch, vault' from Ancient Greek 'arch'; sometimes written apsis, plural apsides) is a semicircular recess covered with a hemispherical vault or semi-dome, also known as an '' exedra''. ...
, which external gallery with a narrow arcade
Arcade most often refers to:
* Arcade game, a coin-operated game machine
** Arcade cabinet, housing which holds an arcade game's hardware
** Arcade system board, a standardized printed circuit board
* Amusement arcade, a place with arcade games
* ...
supported by short columns crowned the semicircular wall with a wide pseudo arcade and tall pilasters
In classical architecture, a pilaster is an architectural element used to give the appearance of a supporting column and to articulate an extent of wall, with only an ornamental function. It consists of a flat surface raised from the main wal ...
on both sides. The new chancel had a triple-nave crypt
A crypt (from Latin '' crypta'' " vault") is a stone chamber beneath the floor of a church or other building. It typically contains coffins, sarcophagi, or religious relics.
Originally, crypts were typically found below the main apse of a c ...
. The damaged square tower had been replaced with an octagonal dome
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a m ...
, above which an octagonal tower was added later. Flanking stair turrets remained from the first cathedral. These changes closely resembled the renovations Henry had overseen on Speyer Cathedral
, native_name_lang = German
, image = Speyer_dom_11.jpg
, imagesize = 280px
, imagelink =
, imagealt =
, landscape =
, caption =
, pushpin ma ...
a few years earlier.
Henry also undertook a few other minor changes, such as raising the transept on the east side and adding openings at the column level. These column-level portals were among the first ever such constructed.
Henry died in 1106, before his intended changes were complete. With his death, the funding for the renovation of the cathedral dried up and so the remaining construction was abandoned. Mainz Cathedral is considered one of the three ''Kaiserdome'' ("Emperor's Cathedrals") of the Holy Roman (German) Empire, along with Worms Cathedral
St Peter's Cathedral (German: ''Wormser Dom'') is a Roman Catholic church and former cathedral in Worms, southern Germany.
The cathedral is located on the highest point of the inner city of Worms and is the most important building of the Ro ...
and Speyer Cathedral
, native_name_lang = German
, image = Speyer_dom_11.jpg
, imagesize = 280px
, imagelink =
, imagealt =
, landscape =
, caption =
, pushpin ma ...
.
Evolution of the main nave
Archbishop Adalbert I of Saarbrücken (1110–1137) had a two-storychapel
A chapel is a Christian place of prayer and worship that is usually relatively small. The term has several meanings. Firstly, smaller spaces inside a church that have their own altar are often called chapels; the Lady chapel is a common type ...
, called the Gotthard Chapel, built as the official palace chapel next to the cathedral. It is believed that he also ordered the renovation of the main body of the cathedral, mainly due to similarities between the main hall and the vault
Vault may refer to:
* Jumping, the act of propelling oneself upwards
Architecture
* Vault (architecture), an arched form above an enclosed space
* Bank vault, a reinforced room or compartment where valuables are stored
* Burial vault (enclosure ...
of the new chapel.
Conception for the renovations was again taken from the Romanesque Speyer Cathedral. This time, however, without money from the emperor, the builders lacked the resources to acquire the high-quality sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicat ...
used in Henry's additions. They instead used limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms w ...
. The other aspects of the renovations were also much cheaper, and the extravagant style of Speyer Cathedral was largely avoided.
The central nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-typ ...
was built to an impressive 28 meters, five meters short of Speyer Cathedral's 33. It seems that the blind arch
A blind arch is an arch found in the wall of a building that has been infilled with solid construction and so cannot serve as a passageway, door or window.''A Dictionary of Architecture''; Fleming, John; Honour, Hugh & Pevsner, Nikolaus (1966) T ...
es were intended to encompass the windows, as in Speyer Cathedral, but the height of the roof did not allow this. The resulting three-level effect, due to the arches ending before the windows, was a technique not before seen in architecture.
The main hall was further renovated throughout the entire 12th century. The entire outer wall structure was eventually replaced. Around the year 1200, the ceiling was replaced with a ribbed vault
A rib vault or ribbed vault is an architectural feature for covering a wide space, such as a church nave, composed of a framework of crossed or diagonal arched ribs. Variations were used in Roman architecture, Byzantine architecture, Islamic a ...
, a rather new technique for the time.
Additional renovations
Around the time that the ribbed vault was installed it was decided to renovate the western half of the cathedral, which had stayed relatively unchanged since Willigis' construction. In contrast to the eastern renovations done earlier, which were in a high-Romanesque style, these new changes were carried out in a late Romanesque style. A new vault was added to span the north and south arms of the transept. Large windows were added to the wall separating the transept from the main hall. The large dome connecting the transept to the main hall was decorated withfrieze
In architecture, the frieze is the wide central section part of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic or Doric order, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Paterae are also usually used to decorate friezes. Even when neither columns nor ...
s and pillars.
Three small apse
In architecture, an apse (plural apses; from Latin 'arch, vault' from Ancient Greek 'arch'; sometimes written apsis, plural apsides) is a semicircular recess covered with a hemispherical vault or semi-dome, also known as an '' exedra''. ...
s and two very large pillar
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member. ...
s were added to support the small flank towers. Pediment
Pediments are gables, usually of a triangular shape.
Pediments are placed above the horizontal structure of the lintel, or entablature, if supported by columns. Pediments can contain an overdoor and are usually topped by hood moulds.
A pedim ...
s were added to the three open sides of the chancel. In general, the western section of the cathedral was extensively decorated to keep up with the newly renovated eastern section.
Post-Romanesque building and renovation
Already at the time of renovations on the western segment of the cathedral, new architectural styles were being ushered in. This includedGothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
additions and, later, Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including ...
pieces as well.
Gothic additions
The first post-Romanesque addition to the cathedral was the westernrood screen
The rood screen (also choir screen, chancel screen, or jubé) is a common feature in late medieval church architecture. It is typically an ornate partition between the chancel and nave, of more or less open tracery constructed of wood, stone, o ...
. This was done in the Gothic style at the time of the western renovations. Following this example, the intersect area was heavily renovated in the next few centuries in the Gothic style.
Starting in 1279, Gothic chapels featuring large decorative windows were built onto the cathedral. In 1418 the Nassauer Chapel, a freestanding burial chapel in the middle nave was built at the request of Archbishop John II of Nassau. The construction of this chapel is attributed to Madern Gerthener
Madern Gerthener (1360/1370 – 1430) was a German stonemason and late Gothic architect.
Biography
Gerthener was born in Frankfurt to Johann Gerthener, a stonemason whose business the younger Gerthener took over by 1391. In 1395 he entered the ...
, who was also responsible for the Memorial Chapel built into the entrance hall to the western wing of the intersect area.
The towers were also renovated during this period. Belfries were added to the two towers at the crossings, on the eastern tower in 1361 and on the western in 1418. These towers were topped with Gothic-style pyramid roofs. (These towers turned out to be so heavy that the eastern tower had to be supported by a pillar erected in 1430.)
The cloister
A cloister (from Latin ''claustrum'', "enclosure") is a covered walk, open gallery, or open arcade running along the walls of buildings and forming a quadrangle or garth. The attachment of a cloister to a cathedral or church, commonly against ...
was heavily renovated and the ''Liebfrauenkirche'' was completely replaced at this time, marking the last of the Gothic renovations to the building. The roof on the eastern tower, however, was replaced in 1579 by a flatter one due to weight concerns. After that, no major alterations were made to the cathedral for almost two centuries.
Baroque additions
In 1767 the western cross-tower was struck by lightning and its roof was destroyed. In 1769 the engineer Franz Ignaz Michael Neumann designed a new multi-story roof for the tower. All the towers in the western wing were roofed with this new Baroque stone design, although care was taken to preserve the previous styles as well. The pinnacles of the pediments on the chapels were replaced with urn-like structures. The famed weathervane, called the ''Domsgickel'', was added at this time as well. The inside of the cathedral was heavily whitewashed. A statue of St. Martin and the Beggar was erected on the roof of the western chancel in 1769.19th-century reconstruction
TheArchbishopric of Mainz
The Electorate of Mainz (german: Kurfürstentum Mainz or ', la, Electoratus Moguntinus), previously known in English as Mentz and by its French name Mayence, was one of the most prestigious and influential states of the Holy Roman Empire. In t ...
suffered heavily in the late 18th century. Following the invasion by French revolutionary troops in 1792, Mainz came under attack from Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
n troops in 1793 in the siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characteriz ...
that led to the end of the Republic of Mainz
The Republic of Mainz was the first democratic state in the current German territoryThe short-lived republic is often ignored in identifying the "first German democracy", in favour of the Weimar Republic; e.g. "the failure of the first German ...
. This attack damaged large portions of the cathedral, particularly the east wing, the cloister, and the ''Liebfrauenkirche'', which was demolished in 1803 (the year after Mainz lost its archbishopric and became a regular diocese
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associ ...
). The cathedral was used as an army camp for several years, and therefore large amounts of the cathedral's artefacts were sold, the wooden interior was burned for heat.
Bishop Joseph Ludwig Colmar
Joseph Ludwig Colmar (born at Strasburg, 22 June 1760; died at Mainz, 15 December 1818) was a German Catholic Bishop of Mainz.
Life
After his ordination (20 December 1783) he was professor of history and Greek at the Royal Seminary, and curate ...
(1802–1818), with support from Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
, set into motion restoration efforts. These efforts were interrupted by quartering needs for the French Army in 1813, and the cathedral was used as a church in 1814 for the first time in eleven years. By 1831, the reparations had been for the most part completed. The major change to the building was an iron cupola
In architecture, a cupola () is a relatively small, most often dome-like, tall structure on top of a building. Often used to provide a lookout or to admit light and air, it usually crowns a larger roof or dome.
The word derives, via Italian, f ...
on the main eastern tower built by architect Georg Moller. But this cupola was removed in 1870 because it was too heavy.
After that, Pierre Cuypers
Petrus Josephus Hubertus "Pierre" Cuypers (16 May 1827 – 3 March 1921) was a Dutch architect. His name is most frequently associated with the Amsterdam Central Station (1881–1889) and the Rijksmuseum (1876–1885), both in Amsterdam. ...
undertook a lengthy restoration work. The support pillar in the eastern cross-tower was removed, as the heavy belfry no longer stood. The crypt in the eastern chancel was rebuilt, but not to the original specifications of the one built by Henry IV. At the conclusion of these reconstructions, a neo-Romanesque
Romanesque Revival (or Neo-Romanesque) is a style of building employed beginning in the mid-19th century inspired by the 11th- and 12th-century Romanesque architecture. Unlike the historic Romanesque style, Romanesque Revival buildings tended to ...
tower was erected in place of the eastern cross-tower in 1875.
At this time the cathedral was once again repainted. Large and colorful Nazarene movement
The epithet Nazarene was adopted by a group of early 19th-century German Romantic painters who aimed to revive spirituality in art. The name Nazarene came from a term of derision used against them for their affectation of a biblical manner of c ...
mural
A mural is any piece of graphic artwork that is painted or applied directly to a wall, ceiling or other permanent substrate. Mural techniques include fresco, mosaic, graffiti and marouflage.
Word mural in art
The word ''mural'' is a Spanis ...
s, including some by Philipp Veit
Philipp Veit (13 February 179318 December 1877) was a German Romantic painter and one of the main exponents of the Nazarene movement. It is to Veit that the credit of having been the first to revive the nearly forgotten technique of fresco ...
, were painted to decorate the inside of the cathedral.
20th century restorations
 Conservation efforts began in the 1900s to save the cathedral from further damage. After a lowering of the groundwater, the wooden substructures became rotten and the foundations started to fail and needed to be replaced. Beginning in 1909 the old foundations were underpinned. Works stopped in 1916 due to
Conservation efforts began in the 1900s to save the cathedral from further damage. After a lowering of the groundwater, the wooden substructures became rotten and the foundations started to fail and needed to be replaced. Beginning in 1909 the old foundations were underpinned. Works stopped in 1916 due to World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
. Between 1924 and 1928 the fundaments were completely reinforced by a new fundament made of concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most wid ...
. Concrete and steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistan ...
were used to anchor the towers and main vault.
A new floor, made of red marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite. Marble is typically not foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorphose ...
, was constructed in this period. Architect Paul Meyer-Speer
Paul may refer to:
* Paul (given name), a given name (includes a list of people with that name)
*Paul (surname), a list of people
People
Christianity
*Paul the Apostle (AD c.5–c.64/65), also known as Saul of Tarsus or Saint Paul, early Chri ...
engineered a system to modify the inner walls with colorful sandstone, removing most of the paintings by Veit and restoring a look similar to the original Willigis-Bardo construction. Unfortunately this system did not withstand continuing restoration efforts, and by 1959 most of the color was gone.
In World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, Mainz was a target of Allied bombing multiple times. The cathedral was hit several times in August 1942. Most of the roofs burned, and the top level of the cloister was destroyed. The vault, however, withstood the attacks and remained intact. The damaged elements were restored as authentically as possible, a process which continued well into the 1970s. In addition, much of the glass in the cathedral was replaced.
The outside of the cathedral was colored red to match the historical buildings of Mainz. In addition, extensive cleaning and restoration efforts were undertaken, ending in 1975. In that year, the thousandth year since the beginning of the cathedral's construction was celebrated.
In 2001, new efforts were begun to restore the cathedral both inside and outside. They were expected to take from ten to fifteen years.
In 2004, two large windows, by the renowned glass artist Johannes Schreiter
Johannes Schreiter (born 8 March 1930) is a German graphic artist, printmaker, designer of stained glass, theoretician and cultural critic. Born in Buchholz in 1930, Schreiter studied in Munster, Mainz, and Berlin, before receiving a scholarship ...
, were installed.
Emperors and the cathedral
When Mainz was an archbishopric, the cathedral was the official seat of the archdiocese. In 1184 Emperor Barbarossa celebrated the accolade of his sons in the cathedral. The feast of 1184 on the Maaraue, the Diet of Pentecost, became legendary in history as the greatest feast of the Middle Ages. It was from this cathedral thatFrederick Barbarossa
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (german: link=no, Friedrich I, it, Federico I), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death 35 years later. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt ...
, the Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
of the time, officially announced his support for the Third Crusade
The Third Crusade (1189–1192) was an attempt by three European monarchs of Western Christianity ( Philip II of France, Richard I of England and Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor) to reconquer the Holy Land following the capture of Jerusalem by ...
during the ''Curia Christi
The ''Curia Christi'' ("Court of Christ") or ''Curia Dei'' ("Court of God") was a diet or court day (''Hoftag'') of the Holy Roman Empire held in Mainz on 27 March 1188. It was so called because it was notionally under the presidency of Jesus Chr ...
'' of 27 March 1188.From Charlemagne to Frederick Barbarossa, flyer
General Directorate for Cultural Heritage Rhineland-Palatinate
The Rhineland-Palatinate General Directorate for Cultural Heritage (german: Generaldirektion Kulturelles Erbe Rheinland-Pfalz or ''Generaldirektion Kulturelles Erbe RLP'') is a state agency responsible for monument protection and preservation in ...
, Landesmuseum Mainz for the Grand State Exhibition 2020
During the Middle Ages, the right to crown German kings (and queens) was given to the Archbishop of Mainz. The crowning in Mainz awarded the monarch the kingdom of Germany, and a subsequent in Rome granted him the Holy Roman Empire (a nominal difference only). Because the cathedral was damaged several times, many crownings were not held there.
The following monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority ...
s were crowned in Mainz Cathedral:
* Agnes de Poitou
Agnes of Poitou ( – 14 December 1077), was the queen of Germany from 1043 and empress of the Holy Roman Empire from 1046 until 1056 as the wife of Emperor Henry III. From 1056 to 1061, she ruled the Holy Roman Empire as regent during the m ...
in 1043 by Archbishop Bardo
* Rudolf of Rheinfelden
Rudolf of Rheinfelden ( – 15 October 1080) was Duke of Swabia from 1057 to 1079. Initially a follower of his brother-in-law, the Salian emperor Henry IV, his election as German anti-king in 1077 marked the outbreak of the Great Saxon Revolt an ...
(anti-king
An anti-king, anti king or antiking (german: Gegenkönig; french: antiroi; cs, protikrál) is a would-be king who, due to succession disputes or simple political opposition, declares himself king in opposition to a reigning monarch. OED "Anti-, ...
) on 26 March or 7 April 1077 by Siegfried I
* Matilda
Matilda or Mathilda may refer to:
Animals
* Matilda (chicken) (1990–2006), World's Oldest Living Chicken record holder
* Matilda (horse) (1824–1846), British Thoroughbred racehorse
* Matilda, a dog of the professional wrestling tag-team The ...
(later wife of Henry V Henry V may refer to:
People
* Henry V, Duke of Bavaria (died 1026)
* Henry V, Holy Roman Emperor (1081/86–1125)
* Henry V, Duke of Carinthia (died 1161)
* Henry V, Count Palatine of the Rhine (c. 1173–1227)
* Henry V, Count of Luxembourg (121 ...
), on 25 July 1110 by Frederick I, Archbishop of Cologne
* Philip of Swabia
Philip of Swabia (February/March 1177 – 21 June 1208) was a member of the House of Hohenstaufen and King of Germany from 1198 until his assassination.
The death of his older brother Emperor Henry VI in 1197 meant that the Hohenstaufen rule (w ...
on 8 September 1198 by Bishop Aimo of Tarantaise
* Frederick II on 9 December 1212 by Siegfried II of Eppstein
* Heinrich Raspe on 22 May 1246 by Siegfried III of Eppstein
Siegfried III von Eppstein (died 9 March 1249) was Archbishop of Mainz from 1230 to 1249. He in 1244 granted freedom to the citizens of Mainz, who subsequently could run their affairs more independently though their own council; in law it remaine ...
Burials
*Bardo (archbishop)
Bardo (c. 980 – 10/11 June 1051) was the Archbishop of Mainz from 1031 until 1051, the Abbot of Werden from 1030 until 1031, and the Abbot of Hersfeld in 1031.
Bardo was born in Oppershofen in the Wetterau. He was educated and trained at th ...
*Wezilo
Wezilo, died 1088, was Archbishop of Mainz from 1084 to 1088. He was a leading supporter of the Holy Roman Emperor Henry IV in the Investiture Controversy, and of antipope Clement III.
A priest in Halberstadt, Wezilo owed his promotion to the s ...
* Marianus Scotus
*Bertold von Henneberg
Bertold von Henneberg-Römhild (1442–1504) was Archbishop of Mainz and Prince-elector of the Holy Roman Empire from 1484, imperial chancellor from 1486, and leader of the reform faction within the Empire.
Biography
The son of George, Count o ...
See also
*History of medieval Arabic and Western European domes
The early domes of the Middle Ages, particularly in those areas recently under Byzantine control, were an extension of earlier Roman architecture. The domed church architecture of Italy from the sixth to the eighth centuries followed that of the ...
References
Sources
*Wilhelm Jung: ''Mainz cathedral'' ; Translation: Margaret Marks, Editor: Schnell und Steiner, Regensburg, 1994 *Ron Baxter: ''The tombs of the archbishops of Mainz'', in Ute Engel and Alexandra Gajewski (eds), Mainz and the Middle Rhine Valley, (British Archaeological Assoc. Conference Transactions, 30, Leeds,British Archaeological Association
The British Archaeological Association (BAA) was founded in 1843 and aims to inspire, support and disseminate high quality research in the fields of Western archaeology, art and architecture, primarily of the mediaeval period, through lectures, co ...
and Maney Publishing
Maney Publishing was an independent academic publishing company that was taken over by Taylor & Francis in 2015. Maney Publishing specialised in peer-reviewed academic journals in materials science and engineering, the humanities, and healt ...
. , 2007, pp. 68–79.
. ''The German article references the following sources:''
* ''Die Bischofskirche St. Martin zu Mainz'', ed.: Friedhelm Jürgensmeier, Knecht Publishers, Frankfurt/Main 1986
* ''Lebendiger Dom - St. Martin zu Mainz in Geschichte und Gegenwart'', ed.: Barbara Nichtweiß, Philipp v. Zabern Publishers, Mainz 1998
* ''Der Dom zu Mainz - Geschichte und Beschreibung des Baues und seiner Wiederherstellung'', Friedrich Schneider, Publishers Ernst and Korn, Berlin, 1886
* ''Der Dom zu Mainz - Ein Handbuch'', August Schuchert, Wilhelm Jung, Verlag Druckhaus Schmidt & Bödige GmbH, 3rd Edition, Mainz, 1984
* ''Deutsche Romanik'', Bernhard Schütz, Wolfgang Müller; Herder Publishers, Freiburg i. Br. 1989
* ''Mainz - Die Geschichte der Stadt'', edits: Franz Dumont
Franz Dumont (22 January 1945 – 3 November 2012) was a German historian.
Life
Born in Waldbröl, Dumont lived in Mainz from 1954 onwards and took his Abitur at the Rabanus-Maurus-Gymnasium in Mainz in 1964. During his school years, he had a ...
, Ferdinand Scherf
Ferdinand Scherf (born in 1943 in Mayen), is a German professor and historian. From 1970 to 2007 he was a teacher at the Rabanus-Maurus-Gymnasium in Mainz and editor of local historical works.
Life
After studying history and German language and ...
, Friedrich Schütz; 2nd Edition; PublishersPhilipp von Zabern, Mainz 1999
Additional (web) sources for the article include:
Mainz Online: Cathedral
(extended history of the cathedral)
(another history of the cathedral; in German)
Cathedral Museum Mainz
(documentation of artefacts in the cathedral; in German)
Terce (= Mid-Morning Prayer) and Pontifical High Mass in Mainz Cathedral
- Pentecost 2015 with
Karl Cardinal Lehmann
Karl Lehmann (16 May 1936 – 11 March 2018) was a German Cardinal prelate of the Catholic Church. He served as Bishop of Mainz from 1983 to 2016, being elevated to Cardinal in 2001. He also served as Chairman of the Conference of the Ger ...
{{Authority control
Roman Catholic cathedrals in Rhineland-Palatinate
Cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the ''cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominations ...
Romanesque architecture in Germany
Imperial cathedrals
10th-century churches in Germany