MMS Architecture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The MMS Architecture is the set of standards used by the
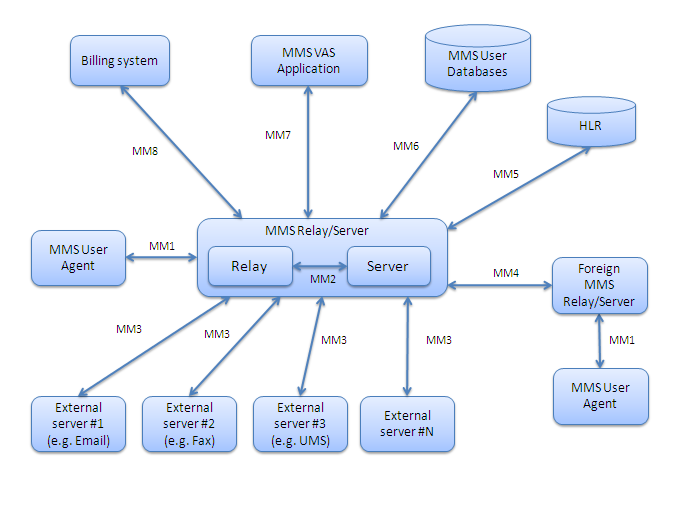 The standard consists of a number of interfaces between components found in the mobile network:
* MM1: the interface between MMS User Agent and MMS Center (MMSC, the combination of the MMS Relay & Server). Delivered as HTTP over a packet switched data session.
* MM2: the interface between MMS Relay and MMS Server.
* MM3: the interface between MMSC and other messaging systems. Using SMTP.
* MM4: the interface between MMSC and foreign network providers. Using SMTP.
* MM5: the interface between MMSC and HLR.
* MM6: the interface between MMSC and user databases.
* MM7: the interface between MMS
The standard consists of a number of interfaces between components found in the mobile network:
* MM1: the interface between MMS User Agent and MMS Center (MMSC, the combination of the MMS Relay & Server). Delivered as HTTP over a packet switched data session.
* MM2: the interface between MMS Relay and MMS Server.
* MM3: the interface between MMSC and other messaging systems. Using SMTP.
* MM4: the interface between MMSC and foreign network providers. Using SMTP.
* MM5: the interface between MMSC and HLR.
* MM6: the interface between MMSC and user databases.
* MM7: the interface between MMS
"OMA STI 1.0"
/ref> MM11 is designed to ensure compatibility of transcoders with MMSCs. Integration with a transcoder without using MM11 is possible by implementing the transcoder as a proxy server. By placing the transcoder on the MM1 interface between the user equipment and the MMSC, messages can be transparently transcoded. A possible disadvantage of this implementation is that transcoders are typically licensed in transactions per second. All transactions will be sent through the transcoder, rather than just those marked to allow adaptations.
3GPP TS 23.140
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Mms Architecture GSM standard Mobile telecommunications standards 3GPP standards Application layer protocols
Multimedia Messaging Service
Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) is a standard way to send messages that include multimedia content to and from a mobile phone over a cellular network. Users and providers may refer to such a message as a PXT, a picture message, or a multimedia ...
in mobile networks. The standards are prepared by 3GPP.
Overview
 The standard consists of a number of interfaces between components found in the mobile network:
* MM1: the interface between MMS User Agent and MMS Center (MMSC, the combination of the MMS Relay & Server). Delivered as HTTP over a packet switched data session.
* MM2: the interface between MMS Relay and MMS Server.
* MM3: the interface between MMSC and other messaging systems. Using SMTP.
* MM4: the interface between MMSC and foreign network providers. Using SMTP.
* MM5: the interface between MMSC and HLR.
* MM6: the interface between MMSC and user databases.
* MM7: the interface between MMS
The standard consists of a number of interfaces between components found in the mobile network:
* MM1: the interface between MMS User Agent and MMS Center (MMSC, the combination of the MMS Relay & Server). Delivered as HTTP over a packet switched data session.
* MM2: the interface between MMS Relay and MMS Server.
* MM3: the interface between MMSC and other messaging systems. Using SMTP.
* MM4: the interface between MMSC and foreign network providers. Using SMTP.
* MM5: the interface between MMSC and HLR.
* MM6: the interface between MMSC and user databases.
* MM7: the interface between MMS Value-added service
A value-added service (VAS) is a popular telecommunications industry{{cite web, url=http://www.prweb.com/releases/2013/11/prweb11284640.htm, title=Global Mobile Value Added Services (VAS) Market: Worldwide Industry Share, Investment Trends, Growth, ...
applications and MMSC. Typically Content Providers using HTTP / SOAP for delivery.
* MM8: the interface between MMSC and the billing systems.
* MM9: the interface between MMSC and an online charging system
Online charging system (OCS) is a system allowing a communications service provider to charge their customers, in real time, based on service usage.
Architecture Event based charging
An event-based charging function (EBCF) is used to charge event ...
.
* MM10: the interface between MMSC and a message service control function.
* MM11: the interface between MMSC and an external transcoder.
MM1
MM1 is the interface between a Mobile Station (MS) and an MMSC. MM1 is used in the following actions: * The sender subscriber sends anMMS MMS may refer to:
Science and technology Network communication protocols
* Multimedia Messaging Service for mobile phones
* Microsoft Media Server, a content-streaming protocol (mms://)
* Manufacturing Message Specification for real time proces ...
to the MMSC
* The MMSC notifies the recipient subscriber that they have an MMS waiting for retrieval
* The recipient subscriber retrieves the MMS from the MMSC
* The MMSC notifies the sender that the recipient has retrieved the message
* The recipient subscriber manages their mailbox in the MMSC (uploads MMS, deletes MMS, ...)
The MM1 interface is based on the WAP
WAP or Wap may refer to:
Music
* "WAP" (song), a 2020 song by Cardi B featuring Megan Thee Stallion
Organizations
* Weatherization Assistance Program, for US energy costs
* Western Australia Party, a political party founded in 2016
* Western A ...
protocol. It includes the PAP notifications that are transformed to SMS's by the WAP gateway A WAP gateway sits between mobile devices using the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) and the World Wide Web, passing pages from one to the other much like a proxy. This translates pages into a form suitable for the mobiles, for instance using the ...
for the notifications.
MM2
MM2 is an interface between aMMS MMS may refer to:
Science and technology Network communication protocols
* Multimedia Messaging Service for mobile phones
* Microsoft Media Server, a content-streaming protocol (mms://)
* Manufacturing Message Specification for real time proces ...
Relay (MMS-R) and an MMS storage database, two components of an MMSC platform.
MM3
MM3 is the interface between MMSC and external servers such as Email server or SMS Centers SMSC. This interface typically uses TCP/IP based protocols for e.g. Simple Mail Transfer Protocol ( SMTP ) Generally, it is the responsibility of MMSC to do the transformation of MMS multi-part binary data to MIME format of email in both the direction MM3 is used in the following actions: * To exchange messages with external servers such as Email Server or SMS CentersMM4
MM4 is the interface used to exchange messages between two different MMSCs. These MMSCs are generally located in two distinct Mobile Networks This interface is also known as the MMSR interface in theWireless Application Protocol
Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) is a technical standard for accessing information over a mobile wireless network. A WAP browser is a web browser for mobile devices such as mobile phones that use the protocol. Introduced in 1999, WAP achieve ...
(WAP) and the Open Mobile Alliance
OMA SpecWorks, previously the Open Mobile Alliance (OMA) is a standards organization which develops open, international technical standards for the mobile phone industry. It is a nonprofit Non-governmental organization (NGO), not a formal governme ...
(OMA) standards.
MM5
MM5 is the interface between MMSC and other network elements like HLR or Domain Name Server. The communication over MM5 Interface is generally to fetch the routing information. MM5 has been defined by the 3GPP in TS 23.140 as a simple reference toMobile Application Part
The Mobile Application Part (MAP) is an SS7 protocol that provides an application layer for the various nodes in GSM and UMTS mobile core networks and GPRS core networks to communicate with each other in order to provide services to users. The ...
.
MM7
MM7 is the interface between MMSC and a value-added service provider (VASP). The MM7 interface is used to sendMMS MMS may refer to:
Science and technology Network communication protocols
* Multimedia Messaging Service for mobile phones
* Microsoft Media Server, a content-streaming protocol (mms://)
* Manufacturing Message Specification for real time proces ...
from 3rd party providers (e.g., a bank sending a statement or an advertiser sending publicity). It is based on SOAP
Soap is a salt of a fatty acid used in a variety of cleansing and lubricating products. In a domestic setting, soaps are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing, and other types of housekeeping. In industrial settings, soaps are use ...
with attachments, using HTTP
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, ...
as the transport protocol. HTTP
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, ...
request shall be a POST.
The message is a MIME
Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) is an Internet standard that extends the format of email messages to support text in character sets other than ASCII, as well as attachments of audio, video, images, and application programs. Message ...
which encapsulates the SOAP
Soap is a salt of a fatty acid used in a variety of cleansing and lubricating products. In a domestic setting, soaps are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing, and other types of housekeeping. In industrial settings, soaps are use ...
envelope and the encoded attachments. The SOAP
Soap is a salt of a fatty acid used in a variety of cleansing and lubricating products. In a domestic setting, soaps are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing, and other types of housekeeping. In industrial settings, soaps are use ...
envelope is an XML
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing arbitrary data. It defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. T ...
where tags are the MM7 protocol data.
MM11
MM11 is specified by OMA STI (Standard Transcoding Interface) 1.0./ref> MM11 is designed to ensure compatibility of transcoders with MMSCs. Integration with a transcoder without using MM11 is possible by implementing the transcoder as a proxy server. By placing the transcoder on the MM1 interface between the user equipment and the MMSC, messages can be transparently transcoded. A possible disadvantage of this implementation is that transcoders are typically licensed in transactions per second. All transactions will be sent through the transcoder, rather than just those marked to allow adaptations.
See also
*ID-MM7
ID-MM7 is a protocol developed and promoted by the Liberty Alliance, driven by major mobile operators such as Vodafone and Telefónica Móviles, to standardize identity-based web services interfaces to mobile messaging.
The ID-MM7 specification ...
*
References
External links
3GPP TS 23.140
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Mms Architecture GSM standard Mobile telecommunications standards 3GPP standards Application layer protocols