Myeloblasts on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The myeloblast is a
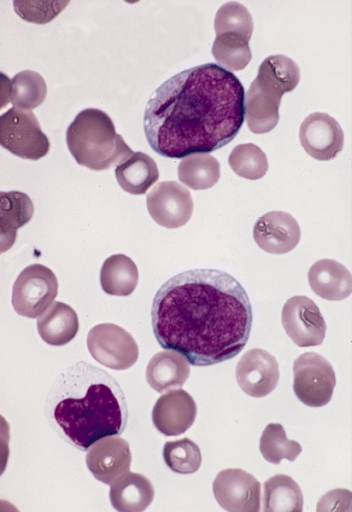 Myeloblasts reside extravascularly in the bone marrow. Hematopoiesis takes place in the extravascular cavities between the sinuses of the marrow. The wall of the sinuses is composed of two different types of cells, endothelial cells and adventitial reticular cells. The hemopoietic cells are aligned in cords or wedges between these sinuses, with myeloblasts and other granular progenitors concentrated in the subcortical regions of these hemopoietic cords.
Myeloblasts are rather small cells with a diameter between 14 and 18μm. The major part is occupied by a large oval
Myeloblasts reside extravascularly in the bone marrow. Hematopoiesis takes place in the extravascular cavities between the sinuses of the marrow. The wall of the sinuses is composed of two different types of cells, endothelial cells and adventitial reticular cells. The hemopoietic cells are aligned in cords or wedges between these sinuses, with myeloblasts and other granular progenitors concentrated in the subcortical regions of these hemopoietic cords.
Myeloblasts are rather small cells with a diameter between 14 and 18μm. The major part is occupied by a large oval

File:Leukopoiese.JPG
File:Granulopoiesis.jpg
unipotent
In mathematics, a unipotent element ''r'' of a ring ''R'' is one such that ''r'' − 1 is a nilpotent element; in other words, (''r'' − 1)''n'' is zero for some ''n''.
In particular, a square matrix ''M'' is a unipoten ...
stem cell which differentiates into the effectors of the granulocyte series. It is found in the bone marrow. Stimulation of myeloblasts by G-CSF
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF or GCSF), also known as colony-stimulating factor 3 (CSF 3), is a glycoprotein that stimulates the bone marrow to produce granulocytes and stem cells and release them into the bloodstream.
Functiona ...
and other cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
s triggers maturation, differentiation, proliferation and cell survival.
Structure
 Myeloblasts reside extravascularly in the bone marrow. Hematopoiesis takes place in the extravascular cavities between the sinuses of the marrow. The wall of the sinuses is composed of two different types of cells, endothelial cells and adventitial reticular cells. The hemopoietic cells are aligned in cords or wedges between these sinuses, with myeloblasts and other granular progenitors concentrated in the subcortical regions of these hemopoietic cords.
Myeloblasts are rather small cells with a diameter between 14 and 18μm. The major part is occupied by a large oval
Myeloblasts reside extravascularly in the bone marrow. Hematopoiesis takes place in the extravascular cavities between the sinuses of the marrow. The wall of the sinuses is composed of two different types of cells, endothelial cells and adventitial reticular cells. The hemopoietic cells are aligned in cords or wedges between these sinuses, with myeloblasts and other granular progenitors concentrated in the subcortical regions of these hemopoietic cords.
Myeloblasts are rather small cells with a diameter between 14 and 18μm. The major part is occupied by a large oval nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
* Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
composed of very fine nonaggregated chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important roles in r ...
and possessing 3 or more nucleoli
The nucleolus (, plural: nucleoli ) is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis, which is the synthesis of ribosomes. The nucleolus also participates in the formation of s ...
. The cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
has a basophilic
Basophilic is a technical term used by pathologists. It describes the appearance of cells, tissues and cellular structures as seen through the microscope after a histological section has been stained with a basic dye. The most common such dye i ...
character and is devoid of granules, which is a major difference from the myeloblast's successor, the promyelocyte
A promyelocyte (or progranulocyte) is a granulocyte precursor, developing from the myeloblast and developing into the myelocyte. Promyelocytes measure 12-20 microns in diameter. The nucleus of a promyelocyte is approximately the same size as a mye ...
. The nucleolus
The nucleolus (, plural: nucleoli ) is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis, which is the synthesis of ribosomes. The nucleolus also participates in the formation of ...
is the site of assembly of ribosomal
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to for ...
proteins, which are located in various particles dispersed over the cytoplasm. Mitochondria are present but have a rather small size.
The main features that distinguish a myeloblast from a lymphoblast
__NOTOC__
A lymphoblast is a modified naive lymphocyte with altered cell morphology. It occurs when the lymphocyte is activated by an antigen (from antigen-presenting cells) and increased in volume by nucleus and cytoplasm growth as well as new mRN ...
upon microscopic examination are the presence of cytoplasmic granules, the lesser degree of condensation in the nuclear chromatin, and the increased prominence of the nucleoli.Figure 12-14 in:
Development
These cells descend from the primitive reticulum cells, which are found in the stroma of the marrow. There is also an intermediate phase between the myeloblast and these primitive reticulum cells, namely thehemocytoblast
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the stem cells that give rise to other blood cells. This process is called haematopoiesis. In vertebrates, the very first definitive HSCs arise from the ventral endothelial wall of the embryonic aorta within ...
. At this time several developing blood cell
A blood cell, also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte, is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes) ...
lines are available, like erythropoiesis
Erythropoiesis (from Greek 'erythro' meaning "red" and 'poiesis' "to make") is the process which produces red blood cells (erythrocytes), which is the development from erythropoietic stem cell to mature red blood cell.
It is stimulated by decrea ...
and thrombopoiesis. Granulopoiesis
Granulopoiesis (or granulocytopoiesis) is a part of haematopoiesis, that leads to the production of granulocytes. A granulocyte, also referred to as a polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN), is a type of white blood cell that has multi lobed nuclei, u ...
is regulated by humoral agents, like colony-stimulating factor
Colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) are secreted glycoproteins that bind to receptor proteins on the surfaces of hemopoietic stem cells, thereby activating intracellular signaling pathways that can cause the cells to proliferate and differentia ...
(CSF) and interleukin 3
Interleukin 3 (IL-3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IL3'' gene localized on chromosome 5q31.1. Sometimes also called colony-stimulating factor, multi-CSF, mast cell growth factor, MULTI-CSF, MCGF; MGC79398, MGC79399: the protein ...
.
Function
Granulopoiesis
Granulopoiesis (or granulocytopoiesis) is a part of haematopoiesis, that leads to the production of granulocytes. A granulocyte, also referred to as a polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN), is a type of white blood cell that has multi lobed nuclei, u ...
consists of 5 stages, in which the myeloblast is the first recognizable cell. Next in the differentiation sequence is the monoblast
Monoblasts are the committed progenitor cells that differentiated from a committed macrophage or dendritic cell precursor (MDP) in the process of hematopoiesis. They are the first developmental stage in the monocyte series leading to a macrophage ...
and the promyelocyte
A promyelocyte (or progranulocyte) is a granulocyte precursor, developing from the myeloblast and developing into the myelocyte. Promyelocytes measure 12-20 microns in diameter. The nucleus of a promyelocyte is approximately the same size as a mye ...
, which can develop into one of three different precursor cells: the neutrophilic
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in ...
, basophilic
Basophilic is a technical term used by pathologists. It describes the appearance of cells, tissues and cellular structures as seen through the microscope after a histological section has been stained with a basic dye. The most common such dye i ...
or eosinophilic
Eosinophilic (Greek suffix -phil-, meaning ''loves eosin'') is the staining of tissues, cells, or organelles after they have been washed with eosin, a dye.
Eosin is an acidic dye for staining cell cytoplasm, collagen, and muscle fibers. ''E ...
myelocyte. This proliferation takes five divisions before the final stage is obtained. These divisions all take place in the first three stages of granulopoiesis.
Clinical significance
The most common problem with malfunctioning myeloblasts isacute myeloblastic leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with normal blood cell production. Symptoms may include ...
. The main clinical features of acute myeloblastic leukemia are caused by failure of hemopoiesis with anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, t ...
, hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, v ...
and infection as a result. There is a progressive accumulation of leukemic cells, because some blast progenitor cells
In genealogy, the progenitor (rarer: primogenitor; german: Stammvater or ''Ahnherr'') is the – sometimes legendary – founder of a family, line of descent, clan or tribe, noble house, or ethnic group..
Ebenda''Ahnherr:''"Stammvater eines G ...
renew themselves and have a limited differentiated division. Sometimes acute myeloblastic leukemia can be initiated by earlier hematologic disorders, like myelodysplastic syndrome
A myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is one of a group of cancers in which immature blood cells in the bone marrow do not mature, and as a result, do not develop into healthy blood cells. Early on, no symptoms typically are seen. Later, symptoms may ...
, pancytopenia
Pancytopenia is a medical condition in which there is significant reduction in the number of almost all blood cells (red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, monocytes, lymphocytes, etc.).
If only two parameters from the complete blood coun ...
, or hypoplasia of the bone marrow.
See also
*Granulopoiesis
Granulopoiesis (or granulocytopoiesis) is a part of haematopoiesis, that leads to the production of granulocytes. A granulocyte, also referred to as a polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN), is a type of white blood cell that has multi lobed nuclei, u ...
* Hematopoiesis
Haematopoiesis (, from Greek , 'blood' and 'to make'; also hematopoiesis in American English; sometimes also h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells ...
* Pluripotential hemopoietic stem cell
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the stem cells that give rise to other blood cells. This process is called haematopoiesis. In vertebrates, the very first definitive HSCs arise from the ventral endothelial wall of the embryonic aorta within t ...
* Myeloid leukemia
Myeloid leukemia is a type of leukemia affecting myeloid tissue.
Types include:
* Acute myeloid leukemia
* Chronic myelogenous leukemia
* Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia
* Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm
See also
* Hematological m ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * {{Authority control Non-terminally differentiated (blast) cells Blood cells