Muscle Testing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Kinesiology () is the scientific study of human body movement. Kinesiology addresses
Kinesiology () is the scientific study of human body movement. Kinesiology addresses
 Adaptation through
Adaptation through
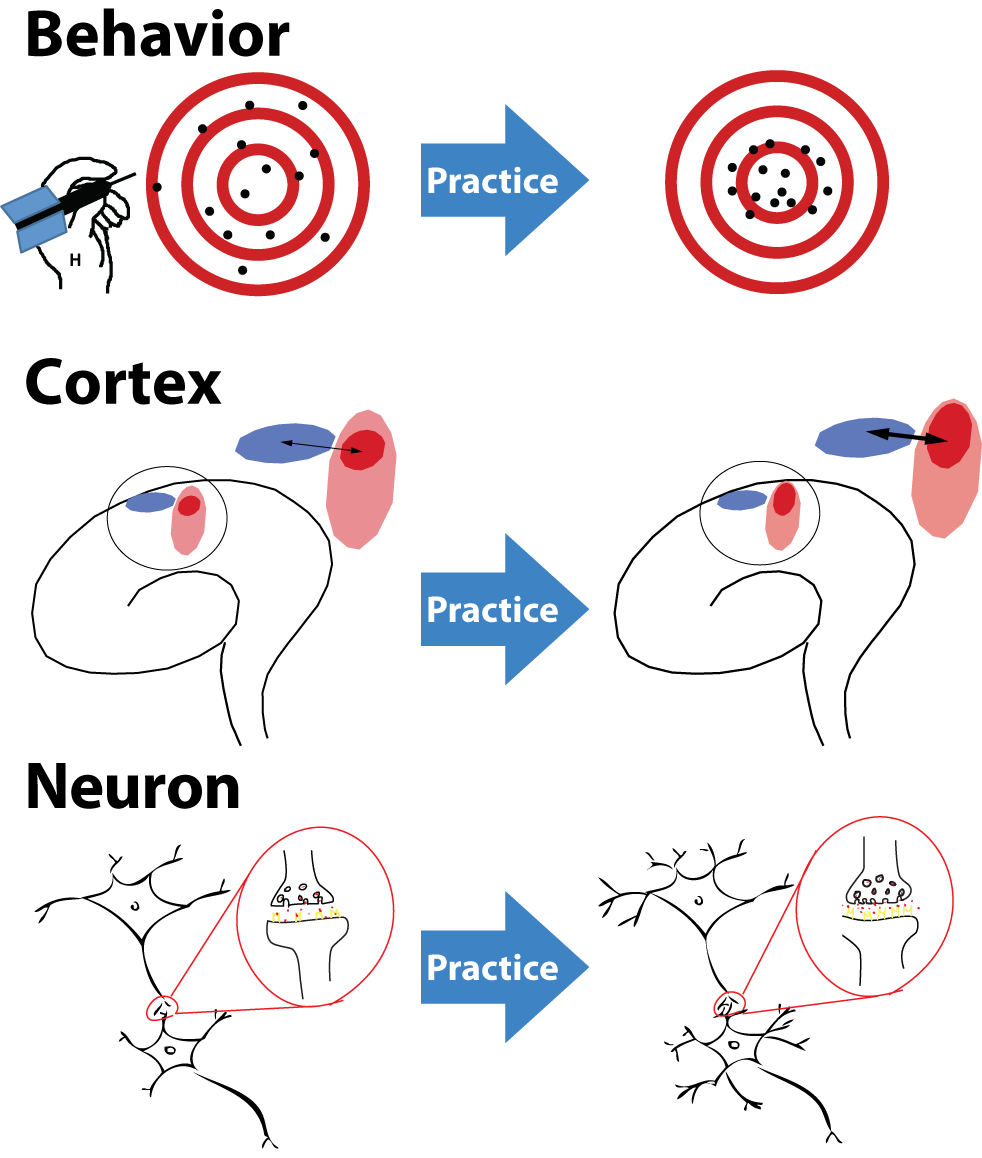 Neuroplasticity is also a key scientific principle used in kinesiology to describe how movement and changes in the brain are related. The human brain adapts and acquires new motor skills based on this principle. The brain can be exposed to new stimuli and experiences and therefore learn from them and create new neural pathways hence leading to brain adaptation. These new adaptations and skills include both adaptive and maladaptive brain changes.
Adaptive plasticity
Recent empirical evidence indicates the significant impact of physical activity on brain function; for example, greater amounts of physical activity are associated with enhanced cognitive function in older adults. The effects of physical activity can be distributed throughout the whole brain, such as higher gray matter density and white matter integrity after exercise training, and/or on specific brain areas, such as greater activation in prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Neuroplasticity is also the underlying mechanism of skill acquisition. For example, after long-term training, pianists showed greater gray matter density in sensorimotor cortex and white matter integrity in the internal capsule compared to non-musicians.
Maladaptive plasticity
Maladaptive plasticity is defined as neuroplasticity with negative effects or detrimental consequences in behavior. Movement abnormalities may occur among individuals with and without brain injuries due to abnormal remodeling in central nervous system.
Neuroplasticity is also a key scientific principle used in kinesiology to describe how movement and changes in the brain are related. The human brain adapts and acquires new motor skills based on this principle. The brain can be exposed to new stimuli and experiences and therefore learn from them and create new neural pathways hence leading to brain adaptation. These new adaptations and skills include both adaptive and maladaptive brain changes.
Adaptive plasticity
Recent empirical evidence indicates the significant impact of physical activity on brain function; for example, greater amounts of physical activity are associated with enhanced cognitive function in older adults. The effects of physical activity can be distributed throughout the whole brain, such as higher gray matter density and white matter integrity after exercise training, and/or on specific brain areas, such as greater activation in prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Neuroplasticity is also the underlying mechanism of skill acquisition. For example, after long-term training, pianists showed greater gray matter density in sensorimotor cortex and white matter integrity in the internal capsule compared to non-musicians.
Maladaptive plasticity
Maladaptive plasticity is defined as neuroplasticity with negative effects or detrimental consequences in behavior. Movement abnormalities may occur among individuals with and without brain injuries due to abnormal remodeling in central nervous system.
 Motor redundancy is a widely used concept in kinesiology and
Motor redundancy is a widely used concept in kinesiology and
 * Health promotion
: Kinesiologists working in the health promotion industry work with individuals to enhance the health, fitness, and well-being of the individual. Kinesiologists can be found working in fitness facilities, personal training/corporate wellness facilities, and industry.
* Clinical/rehabilitation
: Kinesiologists work with individuals with disabling conditions to assist in regaining their optimal physical function. They work with individuals in their home, fitness facilities, rehabilitation clinics, and at the worksite. They also work alongside physiotherapists and occupational therapists.
* Ergonomics
: Kinesiologists work in industry to assess suitability of design of workstations and provide suggestions for modifications and assistive devices.
* Health and safety
: Kinesiologists are involved in consulting with industry to identify hazards and provide recommendations and solutions to optimize the health and safety of workers.
* Disability management/case coordination
: Kinesiologists recommend and provide a plan of action to return an injured individual to their optimal function in all aspects of life.
* Management/research/administration
: Kinesiologists frequently fulfill roles in all above areas, perform research, and manage businesses.
* Health education
: Kinesiologists working in health education teach people about behaviors that promote wellness. They develop and implement strategies to improve the health of individuals and communities. Community health workers collect data and discuss health concerns with members of specific populations or communities.
* Athletic training
: Kinesiologists working in athletic training work in cooperation with physicians. Athletic trainers strive to prevent athletes from suffering injuries, diagnose them if they have suffered an injury and apply the appropriate treatment.
* Athletic coaches and scouts
: Kinesiologists who pursue a career as an athletic coach develop new talent and guide an athlete's progress in a specific sport. They teach amateur or professional athletes the skills they need to succeed at their sport. Many coaches are also involved in scouting. Scouts look for new players and evaluate their skills and likelihood for success at the college, amateur, or professional level.
* Physical education teacher
: Kinesiologists working as physical education teachers are responsible for teaching fitness, sports and health. They help students stay both mentally and physically fit by teaching them to make healthy choices.
:* Physical therapy
:Kinesiologists working in physical therapy diagnose physical abnormalities, restore mobility to the client, and promote proper function of joints.
* Health promotion
: Kinesiologists working in the health promotion industry work with individuals to enhance the health, fitness, and well-being of the individual. Kinesiologists can be found working in fitness facilities, personal training/corporate wellness facilities, and industry.
* Clinical/rehabilitation
: Kinesiologists work with individuals with disabling conditions to assist in regaining their optimal physical function. They work with individuals in their home, fitness facilities, rehabilitation clinics, and at the worksite. They also work alongside physiotherapists and occupational therapists.
* Ergonomics
: Kinesiologists work in industry to assess suitability of design of workstations and provide suggestions for modifications and assistive devices.
* Health and safety
: Kinesiologists are involved in consulting with industry to identify hazards and provide recommendations and solutions to optimize the health and safety of workers.
* Disability management/case coordination
: Kinesiologists recommend and provide a plan of action to return an injured individual to their optimal function in all aspects of life.
* Management/research/administration
: Kinesiologists frequently fulfill roles in all above areas, perform research, and manage businesses.
* Health education
: Kinesiologists working in health education teach people about behaviors that promote wellness. They develop and implement strategies to improve the health of individuals and communities. Community health workers collect data and discuss health concerns with members of specific populations or communities.
* Athletic training
: Kinesiologists working in athletic training work in cooperation with physicians. Athletic trainers strive to prevent athletes from suffering injuries, diagnose them if they have suffered an injury and apply the appropriate treatment.
* Athletic coaches and scouts
: Kinesiologists who pursue a career as an athletic coach develop new talent and guide an athlete's progress in a specific sport. They teach amateur or professional athletes the skills they need to succeed at their sport. Many coaches are also involved in scouting. Scouts look for new players and evaluate their skills and likelihood for success at the college, amateur, or professional level.
* Physical education teacher
: Kinesiologists working as physical education teachers are responsible for teaching fitness, sports and health. They help students stay both mentally and physically fit by teaching them to make healthy choices.
:* Physical therapy
:Kinesiologists working in physical therapy diagnose physical abnormalities, restore mobility to the client, and promote proper function of joints.

The term ''Kinesiology'' is a literal translation to Greek+English from the original Swedish word ''Rörelselära'', meaning "Movement Science". It was the foundation of the Medical Gymnastics, the original
 Kinesiology () is the scientific study of human body movement. Kinesiology addresses
Kinesiology () is the scientific study of human body movement. Kinesiology addresses physiological
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical ...
, anatomical
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having it ...
, biomechanical, pathological, neuropsychological
Neuropsychology is a branch of psychology concerned with how a person's cognition and behavior are related to the brain and the rest of the nervous system. Professionals in this branch of psychology often focus on how injuries or illnesses of ...
principles and mechanisms of movement. Applications of kinesiology to human health include biomechanics and orthopedics; strength and conditioning Conditioning may refer to:
Science, computing, and technology
* Air conditioning, the removal of heat from indoor air for thermal comfort
** Automobile air conditioning, air conditioning in a vehicle
** Ice storage air conditioning, air condition ...
; sport psychology
Sport psychology was defined by the European Federation of Sport in 1996, as the study of the psychological basis, processes, and effects of sport. Otherwise, sport is considered as any physical activity where the individuals engage for competi ...
; motor control
Motor control is the regulation of movement in organisms that possess a nervous system. Motor control includes reflexes as well as directed movement.
To control movement, the nervous system must integrate multimodal sensory information (both f ...
; skill acquisition and motor learning; methods of rehabilitation
Rehabilitation or Rehab may refer to:
Health
* Rehabilitation (neuropsychology), therapy to regain or improve neurocognitive function that has been lost or diminished
* Rehabilitation (wildlife), treatment of injured wildlife so they can be retur ...
, such as physical
Physical may refer to:
*Physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally co ...
and occupational therapy
Occupational therapy (OT) is a global healthcare profession. It involves the use of assessment and intervention to develop, recover, or maintain the meaningful activities, or ''occupations'', of individuals, groups, or communities. The field of ...
; and sport and exercise physiology
Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise. It is one of the allied health professions, and involves the study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to exercise. Exercise physiologists are the highest qualified exercise ...
. Studies of human and animal motion include measures from motion tracking systems, electrophysiology of muscle and brain activity, various methods for monitoring physiological function, and other behavioral and cognitive research techniques.
Basics
Kinesiology studies the science of human movement, performance, and function by applying the fundamental sciences ofCell Biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and ...
, Molecular Biology, Chemistry
Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions ...
, Biochemistry, Biophysics, Biomechanics, Biomathematics, Biostatistics
Biostatistics (also known as biometry) are the development and application of statistical methods to a wide range of topics in biology. It encompasses the design of biological experiments, the collection and analysis of data from those experime ...
, Physiology, Exercise Physiology
Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise. It is one of the allied health professions, and involves the study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to exercise. Exercise physiologists are the highest qualified exercise ...
, Anatomy, Neuroscience, and Nutritional science. A bachelor's degree in kinesiology can provide strong preparation for graduate study in biomedical research, as well as in professional programs, such as medicine, dentistry, physical therapy, and occupational therapy.
Whereas the term "kinesiologist" is neither a licensed nor professional designation in the United States nor most countries (with the exception of Canada), individuals with training in this area can teach physical education, work as personal trainers and sport coaches, provide consulting services, conduct research and develop policies related to rehabilitation, human motor performance, ergonomics, and occupational health and safety. In North America, kinesiologists may study to earn a Bachelor of Science, Master of Science, or Doctorate of Philosophy degree in Kinesiology or a Bachelor of Kinesiology
A bachelor is a man who is not and has never been married.Bachelors are, in Pitt & al.'s phrasing, "men who live independently, outside of their parents' home and other institutional settings, who are neither married nor cohabitating". ().
Etymo ...
degree, while in Australia or New Zealand, they are often conferred an Applied Science (Human Movement) degree (or higher). Many doctoral level faculty in North American kinesiology programs received their doctoral training in related disciplines, such as neuroscience, mechanical engineering, psychology, and physiology.
In 1965, the University of Massachusetts Amherst created the United States' first Department of Exercise Science (now called Kinesiology) under the leadership of visionary researchers and academicians in the field of exercise science. In 1967, the University of Waterloo launched Canada's first kinesiology department.
Principles
Adaptation through exercise
 Adaptation through
Adaptation through exercise
Exercise is a body activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness.
It is performed for various reasons, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardiovascular system, hone athletic ...
is a key principle of kinesiology that relates to improved fitness in athletes as well as health and wellness in clinical populations. Exercise is a simple and established intervention for many movement disorders and musculoskeletal conditions due to the neuroplasticity of the brain and the adaptability of the musculoskeletal system. Therapeutic exercise has been shown to improve neuromotor control and motor capabilities in both normal and pathological populations.
There are many different types of exercise interventions that can be applied in kinesiology to athletic, normal, and clinical populations. Aerobic exercise interventions help to improve cardiovascular endurance. Anaerobic strength training programs can increase muscular strength, power, and lean body mass. Decreased risk of falls and increased neuromuscular control can be attributed to balance intervention programs. Flexibility programs can increase functional range of motion and reduce the risk of injury.
As a whole, exercise programs can reduce symptoms of depression and risk of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Additionally, they can help to improve quality of life, sleeping habits, immune system function, and body composition.
The study of the physiological responses to physical exercise and their therapeutic applications is known as exercise physiology
Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise. It is one of the allied health professions, and involves the study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to exercise. Exercise physiologists are the highest qualified exercise ...
, which is an important area of research within kinesiology.
Neuroplasticity
 Neuroplasticity is also a key scientific principle used in kinesiology to describe how movement and changes in the brain are related. The human brain adapts and acquires new motor skills based on this principle. The brain can be exposed to new stimuli and experiences and therefore learn from them and create new neural pathways hence leading to brain adaptation. These new adaptations and skills include both adaptive and maladaptive brain changes.
Adaptive plasticity
Recent empirical evidence indicates the significant impact of physical activity on brain function; for example, greater amounts of physical activity are associated with enhanced cognitive function in older adults. The effects of physical activity can be distributed throughout the whole brain, such as higher gray matter density and white matter integrity after exercise training, and/or on specific brain areas, such as greater activation in prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Neuroplasticity is also the underlying mechanism of skill acquisition. For example, after long-term training, pianists showed greater gray matter density in sensorimotor cortex and white matter integrity in the internal capsule compared to non-musicians.
Maladaptive plasticity
Maladaptive plasticity is defined as neuroplasticity with negative effects or detrimental consequences in behavior. Movement abnormalities may occur among individuals with and without brain injuries due to abnormal remodeling in central nervous system.
Neuroplasticity is also a key scientific principle used in kinesiology to describe how movement and changes in the brain are related. The human brain adapts and acquires new motor skills based on this principle. The brain can be exposed to new stimuli and experiences and therefore learn from them and create new neural pathways hence leading to brain adaptation. These new adaptations and skills include both adaptive and maladaptive brain changes.
Adaptive plasticity
Recent empirical evidence indicates the significant impact of physical activity on brain function; for example, greater amounts of physical activity are associated with enhanced cognitive function in older adults. The effects of physical activity can be distributed throughout the whole brain, such as higher gray matter density and white matter integrity after exercise training, and/or on specific brain areas, such as greater activation in prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Neuroplasticity is also the underlying mechanism of skill acquisition. For example, after long-term training, pianists showed greater gray matter density in sensorimotor cortex and white matter integrity in the internal capsule compared to non-musicians.
Maladaptive plasticity
Maladaptive plasticity is defined as neuroplasticity with negative effects or detrimental consequences in behavior. Movement abnormalities may occur among individuals with and without brain injuries due to abnormal remodeling in central nervous system. Learned non-use Learned non-use of a limb is a learning phenomenon whereby movement is suppressed initially due to adverse reactions and failure of any activity attempted with the affected limb, which then results in the suppression of behavior. Continuation of thi ...
is an example commonly seen among patients with brain damage, such as stroke. Patients with stroke learned to suppress paretic limb movement after unsuccessful experience in paretic hand use; this may cause decreased neuronal activation at adjacent areas of the infarcted motor cortex.
There are many types of therapies
A therapy or medical treatment (often abbreviated tx, Tx, or Tx) is the attempted remediation of a health problem, usually following a medical diagnosis.
As a rule, each therapy has indications and contraindications. There are many different ...
that are designed to overcome maladaptive plasticity in clinic and research, such as constraint-induced movement therapy
Constraint-induced movement therapy (CI, CIT, or CIMT) is a form of rehabilitation therapy that improves upper extremity function in stroke and other central nervous system damage patients by increasing the use of their affected upper limb.
(CIMT), body weight support treadmill training (BWSTT) and virtual reality therapy. These interventions are shown to enhance motor function in paretic limbs and stimulate cortical reorganization in patients with brain damage.
Motor redundancy
 Motor redundancy is a widely used concept in kinesiology and
Motor redundancy is a widely used concept in kinesiology and motor control
Motor control is the regulation of movement in organisms that possess a nervous system. Motor control includes reflexes as well as directed movement.
To control movement, the nervous system must integrate multimodal sensory information (both f ...
which states that, for any task the human body can perform, there are effectively an unlimited number of ways the nervous system could achieve that task. This redundancy appears at multiple levels in the chain of motor execution:
* Kinematic
Kinematics is a subfield of physics, developed in classical mechanics, that describes the motion of points, bodies (objects), and systems of bodies (groups of objects) without considering the forces that cause them to move. Kinematics, as a fie ...
redundancy means that for a desired location of the endpoint (e.g. the hand or finger), there are many configurations of the joints that would produce the same endpoint location in space.
* Muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
redundancy means that the same net joint torque could be generated by many different relative contributions of individual muscles.
* Motor unit
A motor unit is made up of a motor neuron and all of the skeletal muscle fibers innervated by the neuron's axon terminals, including the neuromuscular junctions between the neuron and the fibres. Groups of motor units often work together as a mot ...
redundancy means that for the same net muscle force
In physics, a force is an influence that can change the motion of an object. A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (e.g. moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate. Force can also be described intuitively as a p ...
could be generated by many different relative contributions of motor units within that muscle.
The concept of motor redundancy is explored in numerous studies, usually with the goal of describing the relative contribution of a set of motor elements (e.g. muscles) in various human movements, and how these contributions can be predicted from a comprehensive theory. Two distinct (but not incompatible) theories have emerged for how the nervous system coordinates redundant elements: simplification and optimization. In the simplification theory, complex movements and muscle actions are constructed from simpler ones, often known as primitives or synergies, resulting in a simpler system for the brain to control. In the optimization theory, motor actions arise from the minimization of a control parameter, such as the energetic cost of movement or errors in movement performance.
Scope of practice
In Canada, kinesiology is a professional designation as well as an area of study. In the province of Ontario the scope has been officially defined as, "the assessment of human movement and performance and its rehabilitation and management to maintain, rehabilitate or enhance movement and performance" Kinesiologists work in a variety of roles as health professionals. They work as rehabilitation providers in hospitals, clinics and private settings working with populations needing care for musculoskeletal, cardiac and neurological conditions. They provide rehabilitation to persons injured at work and in vehicular accidents. Kinesiologists also work as functional assessment specialists, exercise therapists, ergonomists, return to work specialists, case managers and medical legal evaluators. They can be found in hospital, long-term care, clinic, work, and community settings. Additionally, kinesiology is applied in areas of health and fitness for all levels of athletes, but more often found with training of elite athletes.Licensing and regulation
Canada
In Canada, kinesiology has been designated a regulated health profession in Ontario. Kinesiology was granted the right to regulate in the province of Ontario in the summer of 2007 and similar proposals have been made for other provinces. The College of Kinesiologists of Ontario achieved proclamation on April 1, 2013, at which time the professional title "Kinesiologist" became protected by law. In Ontario only members of the college may call themselves a Registered Kinesiologist. Individuals who have earned degrees in kinesiology can work in research, the fitness industry, clinical settings, and in industrial environments. They also work in cardiac rehabilitation, health and safety, hospital and long-term care facilities and community health centers just to name a few.Health service
 * Health promotion
: Kinesiologists working in the health promotion industry work with individuals to enhance the health, fitness, and well-being of the individual. Kinesiologists can be found working in fitness facilities, personal training/corporate wellness facilities, and industry.
* Clinical/rehabilitation
: Kinesiologists work with individuals with disabling conditions to assist in regaining their optimal physical function. They work with individuals in their home, fitness facilities, rehabilitation clinics, and at the worksite. They also work alongside physiotherapists and occupational therapists.
* Ergonomics
: Kinesiologists work in industry to assess suitability of design of workstations and provide suggestions for modifications and assistive devices.
* Health and safety
: Kinesiologists are involved in consulting with industry to identify hazards and provide recommendations and solutions to optimize the health and safety of workers.
* Disability management/case coordination
: Kinesiologists recommend and provide a plan of action to return an injured individual to their optimal function in all aspects of life.
* Management/research/administration
: Kinesiologists frequently fulfill roles in all above areas, perform research, and manage businesses.
* Health education
: Kinesiologists working in health education teach people about behaviors that promote wellness. They develop and implement strategies to improve the health of individuals and communities. Community health workers collect data and discuss health concerns with members of specific populations or communities.
* Athletic training
: Kinesiologists working in athletic training work in cooperation with physicians. Athletic trainers strive to prevent athletes from suffering injuries, diagnose them if they have suffered an injury and apply the appropriate treatment.
* Athletic coaches and scouts
: Kinesiologists who pursue a career as an athletic coach develop new talent and guide an athlete's progress in a specific sport. They teach amateur or professional athletes the skills they need to succeed at their sport. Many coaches are also involved in scouting. Scouts look for new players and evaluate their skills and likelihood for success at the college, amateur, or professional level.
* Physical education teacher
: Kinesiologists working as physical education teachers are responsible for teaching fitness, sports and health. They help students stay both mentally and physically fit by teaching them to make healthy choices.
:* Physical therapy
:Kinesiologists working in physical therapy diagnose physical abnormalities, restore mobility to the client, and promote proper function of joints.
* Health promotion
: Kinesiologists working in the health promotion industry work with individuals to enhance the health, fitness, and well-being of the individual. Kinesiologists can be found working in fitness facilities, personal training/corporate wellness facilities, and industry.
* Clinical/rehabilitation
: Kinesiologists work with individuals with disabling conditions to assist in regaining their optimal physical function. They work with individuals in their home, fitness facilities, rehabilitation clinics, and at the worksite. They also work alongside physiotherapists and occupational therapists.
* Ergonomics
: Kinesiologists work in industry to assess suitability of design of workstations and provide suggestions for modifications and assistive devices.
* Health and safety
: Kinesiologists are involved in consulting with industry to identify hazards and provide recommendations and solutions to optimize the health and safety of workers.
* Disability management/case coordination
: Kinesiologists recommend and provide a plan of action to return an injured individual to their optimal function in all aspects of life.
* Management/research/administration
: Kinesiologists frequently fulfill roles in all above areas, perform research, and manage businesses.
* Health education
: Kinesiologists working in health education teach people about behaviors that promote wellness. They develop and implement strategies to improve the health of individuals and communities. Community health workers collect data and discuss health concerns with members of specific populations or communities.
* Athletic training
: Kinesiologists working in athletic training work in cooperation with physicians. Athletic trainers strive to prevent athletes from suffering injuries, diagnose them if they have suffered an injury and apply the appropriate treatment.
* Athletic coaches and scouts
: Kinesiologists who pursue a career as an athletic coach develop new talent and guide an athlete's progress in a specific sport. They teach amateur or professional athletes the skills they need to succeed at their sport. Many coaches are also involved in scouting. Scouts look for new players and evaluate their skills and likelihood for success at the college, amateur, or professional level.
* Physical education teacher
: Kinesiologists working as physical education teachers are responsible for teaching fitness, sports and health. They help students stay both mentally and physically fit by teaching them to make healthy choices.
:* Physical therapy
:Kinesiologists working in physical therapy diagnose physical abnormalities, restore mobility to the client, and promote proper function of joints.
History of kinesiology

Royal Central Institute of Gymnastics
The Swedish School of Sport and Health Sciences ( sv, Gymnastik- och idrottshögskolan, GIH) in Stockholm is a Swedish institution offering higher education in the fields of teaching profession in Physical Education, Sports coaching and Preventive ...
( sv) G.C.I. was founded 1813 in Stockholm, Sweden by Pehr Henrik Ling. It was the first Physiotherapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patient ...
school in the world, training hundreds of medical gymnasts who spread the Swedish physical therapy around the entire world.
In 1887, Sweden was the first country in the world to give a national state licence to physiotherapists/physical therapists.
The Swedish medical gymnast and kinesiologist Carl August Georgii Carl may refer to:
*Carl, Georgia, city in USA
*Carl, West Virginia, an unincorporated community
*Carl (name), includes info about the name, variations of the name, and a list of people with the name
*Carl², a TV series
* "Carl", an episode of tel ...
( sv), Professor at the Royal Gymnastic Central Institute GCI in Stockholm, was the one who created and coined the new international word Kinesiology in 1854.The term ''Kinesiology'' is a literal translation to Greek+English from the original Swedish word ''Rörelselära'', meaning "Movement Science". It was the foundation of the Medical Gymnastics, the original
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patient ...
and Physical Therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patient ...
, developed for over 100 years in Sweden (starting 1813).
The new medical therapy created in Sweden was originally called Rörelselära ( sv), and later in 1854 translated to the new and invented international word "Kinesiology". The Kinesiology consisted of nearly 2,000 physical movements and 50 different types of massage therapy techniques.
They were all used to affect various dysfunctions and even illnesses, not only in the movement apparatus, but also into the internal physiology of man.
Thus, the original classical and Traditional Kinesiology was not only a system of rehabilitation for the body, or biomechanics like in modern Academic Kinesiology, but also a new therapy for relieving and curing diseases, by affecting the autonomic nervous system, organs and glands in the body.,
In 1886, the Swedish Medical Gymnast Nils Posse
Nils is a Scandinavian given name, a chiefly Norwegian, Danish, Swedish and Latvian variant of Niels, cognate to Nicholas.
People and animals with the given name
* Nils Bergström (born 1985), Swedish ice hockey player
*Nils Björk (1898–1989), ...
(1862-1895) introduced the term kinesiology in the U.S. Nils Posse was a graduate of the Royal Gymnastic Central Institute in Stockholm, Sweden and founder of the Posse Gymnasium in Boston, MA. He was teaching at Boston Normal School of Gymnastics
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- most p ...
BNSG.
''The Special Kinesiology Of Educational Gymnastics'' was the first book ever written in the world with the word "Kinesiology" in the title of the book. It was written by Nils Posse and published in Boston, 1894–1895. Posse was elected posthumously as an Honorary Fellow in Memoriam in the National Academy of Kinesiology.
The National Academy of Kinesiology was formally founded in 1930 in the United States. The Academy's dual purpose is to encourage and promote the study and educational applications of the art and science of human movement and physical activity and to honor by election to its membership persons who have directly or indirectly contributed significantly to the study of and/or application of the art and science of human movement and physical activity. Membership in the National Academy of Kinesiology is by election and those elected are known as Fellows. Fellows are elected from around the world. Election into the National Academy of Kinesiology is considered a pinnacle achievement and recognition with the discipline. For further information see: http://nationalacademyofkinesiology.org
Technology in kinesiology
Motion capture
Motion capture (sometimes referred as mo-cap or mocap, for short) is the process of recording the movement of objects or people. It is used in military, entertainment, sports, medical applications, and for validation of computer vision and robo ...
technology has application in measuring human movement, and thus kinesiology. Historically, motion capture labs have recorded high fidelity data. While accurate and credible, these systems can come at high capital and operational costs. Modern-day systems have increased accessibility to mocap technology.
See also
* Anatomical terms of motion *Exercise physiology
Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise. It is one of the allied health professions, and involves the study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to exercise. Exercise physiologists are the highest qualified exercise ...
* Human musculoskeletal system
* Kinanthropometry Kinanthropometry is defined as the study of human size, shape, proportion, composition, maturation, and gross function, in order to understand growth, exercise, performance, and nutrition.
It is a scientific discipline that is concerned with the me ...
* Kinesiogenomics Kinesiogenomics refers to the study of genetics in the various disciplines of the field of kinesiology, the study of human movement. The field has also been referred to as "exercise genomics" or "exercisenomics." Areas of study within kinesiogenomic ...
* Mental practice of action
* Motor imagery
Motor imagery is a mental process by which an individual rehearses or simulates a given action. It is widely used in sport training as mental practice of action, neurological rehabilitation, and has also been employed as a research paradigm in cogn ...
* Movement assessment Movement assessment is the practice of analysing movement performance during functional tasks to determine the kinematics of individual joints and their effect on the kinetic chain. Three-dimensional or two-dimensional analysis of the biomechanics i ...
* Neurology
* Physical therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patient ...
(USA)
* Sports science
References
External links
* {{Authority control Ergonomics Applied sciences Human physiology Motor control Exercise physiology