Murder Of Casey-Lyanne Kearney on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Murder is the unlawful killing of another human without
Murder is the unlawful killing of another human without
7 Cal. 4th 797, 30 Cal. Rptr. 2d 50, 872 P.2d 591
(1994). This holding has two implications. Firstly, a defendant in California can be convicted of murder for killing a fetus which the mother herself could have terminated without committing a crime. And secondly, as stated by Justice
 Under
Under
 In the
In the
 The World Health Organization reported in October 2002 that a person is murdered every 60 seconds. An estimated 520,000 people were murdered in 2000 around the globe. Another study estimated the worldwide murder rate at 456,300 in 2010 with a 35% increase since 1990. Two-fifths of them were young people between the ages of 10 and 29 who were killed by other young people. Because murder is the least likely crime to go unreported, statistics of murder are seen as a bellwether of overall crime rates.
Murder rates vary greatly among countries and societies around the world. In the Western world, murder rates in most countries have declined significantly during the 20th century and are now between 1 and 4 cases per 100,000 people per year. Latin America and the Caribbean, the region with the highest murder rate in the world, experienced more than 2.5 million murders between 2000 and 2017.
The World Health Organization reported in October 2002 that a person is murdered every 60 seconds. An estimated 520,000 people were murdered in 2000 around the globe. Another study estimated the worldwide murder rate at 456,300 in 2010 with a 35% increase since 1990. Two-fifths of them were young people between the ages of 10 and 29 who were killed by other young people. Because murder is the least likely crime to go unreported, statistics of murder are seen as a bellwether of overall crime rates.
Murder rates vary greatly among countries and societies around the world. In the Western world, murder rates in most countries have declined significantly during the 20th century and are now between 1 and 4 cases per 100,000 people per year. Latin America and the Caribbean, the region with the highest murder rate in the world, experienced more than 2.5 million murders between 2000 and 2017.

here
/small>). The following absolute murder counts per-country are not comparable because they are not adjusted by each country's total population. Nonetheless, they are included here for reference, with 2010 used as the base year (they may or may not include justifiable homicide, depending on the jurisdiction). There were 52,260 murders in Brazil, consecutively elevating the record set in 2009. Over half a million people were shot to death in Brazil between 1979 and 2003. 33,335 murder cases were registered across India, approximately 17,000 murders in Colombia (the murder rate was 38 per 100,000 people, in 2008 murders went down to 15,000), approximately 16,000 murders in South Africa, approximately 15,000 murders in the United States, approximately 26,000 murders in Mexico, about 8,000 murders committed in Russia, approximately 13,000 murders in Venezuela, approximately 4,000 murders in El Salvador, approximately 1,400 murders in Jamaica, approximately 550 murders in Canada and approximately 470 murders in Trinidad and Tobago. Pakistan reported 12,580 murders.
 In the United States, 666,160 people were killed between 1960 and 1996. Approximately 90% of murders in the US are committed by males. Between 1976 and 2005, 23.5% of all murder victims and 64.8% of victims murdered by intimate partners were female. For women in the US, homicide is the leading cause of death in the workplace. Chapter 6, Responding to Workplace Violence and Staff Victimization.
In the US, murder is the leading cause of death for African American males aged 15 to 34. Between 1976 and 2008, African Americans were victims of 329,825 homicides. In 2006,
In the United States, 666,160 people were killed between 1960 and 1996. Approximately 90% of murders in the US are committed by males. Between 1976 and 2005, 23.5% of all murder victims and 64.8% of victims murdered by intimate partners were female. For women in the US, homicide is the leading cause of death in the workplace. Chapter 6, Responding to Workplace Violence and Staff Victimization.
In the US, murder is the leading cause of death for African American males aged 15 to 34. Between 1976 and 2008, African Americans were victims of 329,825 homicides. In 2006,
 According to scholar Pieter Spierenburg
According to scholar Pieter Spierenburg
"Rap Sheet Why is American history so murderous?"
by A similar, but less pronounced pattern has been seen in major European countries as well. The murder rate in the United Kingdom fell to 1 per 100,000 by the beginning of the 20th century and as low as 0.62 per 100,000 in 1960, and was at 1.28 per 100,000 . The murder rate in France (excluding Corsica) bottomed out after World War II at less than 0.4 per 100,000, quadrupling to 1.6 per 100,000 since then.
The specific factors driving this dynamics in murder rates are complex and not universally agreed upon. Much of the raise in the U.S. murder rate during the first half of the 20th century is generally thought to be attributed to gang violence associated with Prohibition. Since most murders are committed by young males, the near simultaneous low in the murder rates of major developed countries circa 1960 can be attributed to low birth rates during the Great Depression and World War II. Causes of further moves are more controversial. Some of the more exotic factors claimed to affect murder rates include the availability of abortion and the likelihood of chronic exposure to lead during childhood (due to the use of leaded paint in houses and tetraethyllead as a gasoline additive in internal combustion engines).
A similar, but less pronounced pattern has been seen in major European countries as well. The murder rate in the United Kingdom fell to 1 per 100,000 by the beginning of the 20th century and as low as 0.62 per 100,000 in 1960, and was at 1.28 per 100,000 . The murder rate in France (excluding Corsica) bottomed out after World War II at less than 0.4 per 100,000, quadrupling to 1.6 per 100,000 since then.
The specific factors driving this dynamics in murder rates are complex and not universally agreed upon. Much of the raise in the U.S. murder rate during the first half of the 20th century is generally thought to be attributed to gang violence associated with Prohibition. Since most murders are committed by young males, the near simultaneous low in the murder rates of major developed countries circa 1960 can be attributed to low birth rates during the Great Depression and World War II. Causes of further moves are more controversial. Some of the more exotic factors claimed to affect murder rates include the availability of abortion and the likelihood of chronic exposure to lead during childhood (due to the use of leaded paint in houses and tetraethyllead as a gasoline additive in internal combustion engines).
Lord Mustill on the Common Law concerning murder
* Sir Edward Coke Co. Inst., Pt. III, ch.7, p. 50
Introduction and Updated Information on the Seville Statement on Violence
The Seville Statement
– U.S. Centers for Disease Control
Cezanne's depiction of "The Murder"
– National Museums Liverpool {{Authority control Crimes Crimes against humanity Violent crime Violence
justification
Justification may refer to:
* Justification (epistemology), a property of beliefs that a person has good reasons for holding
* Justification (jurisprudence), defence in a prosecution for a criminal offenses
* Justification (theology), God's act of ...
or valid excuse, especially the unlawful killing of another human with malice aforethought. ("The killing of another person without justification or excuse, especially the crime of killing a person with malice aforethought or with recklessness manifesting extreme indifference to the value of human life.") This state of mind may, depending upon the jurisdiction, distinguish murder from other forms of unlawful homicide
Homicide occurs when a person kills another person. A homicide requires only a volitional act or omission that causes the death of another, and thus a homicide may result from accidental, reckless, or negligent acts even if there is no inten ...
, such as manslaughter
Manslaughter is a common law legal term for homicide considered by law as less culpable than murder. The distinction between murder and manslaughter is sometimes said to have first been made by the ancient Athenian lawmaker Draco in the 7th cen ...
. Manslaughter is killing committed in the absence of ''malice'',This is "malice" in a technical legal sense, not the more usual English sense denoting an emotional state. See malice (law)
Malice is a law, legal term which refers to a party's intent (law), intention to do injury to another party. Malice is either ''expressed'' or ''implied''. For example, malice is expressed when there is manifested a deliberate intention to unlaw ...
. brought about by reasonable provocation, or diminished capacity. ''Involuntary'' manslaughter, where it is recognized, is a killing that lacks all but the most attenuated guilty intent, recklessness.
Most societies consider murder to be an extremely serious crime, and thus that a person convicted of murder should receive harsh punishments for the purposes of retribution
Retribution may refer to:
* Punishment
* Retributive justice, a theory of justice
** Divine retribution, retributive justice in a religious context
* Revenge, a harmful action against a person or group in response to a grievance
Film and televis ...
, deterrence, rehabilitation
Rehabilitation or Rehab may refer to:
Health
* Rehabilitation (neuropsychology), therapy to regain or improve neurocognitive function that has been lost or diminished
* Rehabilitation (wildlife), treatment of injured wildlife so they can be retur ...
, or incapacitation. In most countries, a person convicted of murder generally faces a long-term prison sentence, a life sentence, or capital punishment.
Etymology
The modern English word "murder" descends from the Proto-Indo-European ''*mŕ̥-trom'' which meant "killing", a noun derived from ''*mer-'' "to die". Proto-Germanic in fact had two nouns derived from this word, later merging into the modern English noun: ''*murþrą'' "death, killing, murder" (directly from Proto-Indo-European''*mŕ̥-trom''), whenceOld English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
''morðor'' "secret or unlawful killing of a person, murder; mortal sin, crime; punishment, torment, misery"; and ''*murþrijô'' "murderer; homicide" (from the verb ''*murþrijaną'' "to murder"), giving Old English ''myrþra'' "homicide, murder; murderer". There was a third word for "murder" in Proto-Germanic, continuing Proto-Indo-European ''*mr̥tós'' "dead" (compare Latin ''mors''), giving Proto-Germanic ''*murþą'' "death, killing, murder" and Old English ''morþ'' "death, crime, murder" (compare German ''Mord'').
The ''-d-'' first attested in Middle English ''mordre, mourdre, murder, murdre'' could have been influenced by Old French ''murdre'', itself derived from the Germanic noun via Frankish ''*murþra'' (compare Old High German ''murdreo, murdiro''), though the same sound development can be seen with ''burden'' (from ''burthen''). The alternative ''murther'' (attested up to the 19th century) springs directly from the Old English forms. Middle English ''mordre'' is a verb from Anglo-Saxon ''myrðrian'' from Proto-Germanic ''*murþrijaną'', or, according to the '' Oxford English Dictionary'', from the noun.
Use of the term
In many countries, in news reports, out of concern for being accused ofdefamation
Defamation is the act of communicating to a third party false statements about a person, place or thing that results in damage to its reputation. It can be spoken (slander) or written (libel). It constitutes a tort or a crime. The legal defini ...
, journalists
A journalist is an individual that collects/gathers information in form of text, audio, or pictures, processes them into a news-worthy form, and disseminates it to the public. The act or process mainly done by the journalist is called journalism ...
are generally careful not to identify a suspect as a murderer until the suspect is convicted of murder in a court of law. After arrest, for example, journalists may instead write that the person was "arrested on suspicion of murder", or, after a prosecutor files charges, as an "accused murderer".
Opponents of abortion consider abortion a form of murder. In some countries, a fetus is a legal person who can be murdered, and killing a pregnant woman is considered a double homicide.
Definition
The eighteenth-century English jurist William Blackstone (citingEdward Coke
Edward is an English given name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortune; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”.
History
The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-Sa ...
), in his ''Commentaries on the Laws of England
The ''Commentaries on the Laws of England'' are an influential 18th-century treatise on the common law of England by Sir William Blackstone, originally published by the Clarendon Press at Oxford, 1765–1770. The work is divided into four volume ...
'' set out the common law definition of murder, which by this definition occurs
The elements of common law murder are:
* unlawful
* killing
* through criminal act or omission
* of a human
* by another human
* with malice aforethought.
* ''Unlawful'' – This distinguishes murder from killings that are done within the boundaries of law, such as capital punishment, justified self-defense, or the killing of enemy combatant
Combatant is the legal status of an individual who has the right to engage in hostilities during an armed conflict. The legal definition of "combatant" is found at article 43(2) of Additional Protocol I (AP1) to the Geneva Conventions of 1949. It ...
s by lawful combatants as well as causing collateral damage to non-combatants during a war.
* ''Killing'' – At common law life ended with cardiopulmonary arrest
Cardiac arrest is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. It is a medical emergency that, without immediate medical intervention, will result in sudden cardiac death within minutes. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and possib ...
– the total and irreversible cessation of blood circulation and respiration. With advances in medical technology courts have adopted irreversible cessation of all brain function as marking the end of life.
* ''Criminal act or omission'' – Killing can be committed by an act or an omission.
* ''Of a human'' – This element presents the issue of when life begins. At common law, a fetus was not a human being. Life began when the fetus passed through the vagina and took its first breath.
* ''By another human'' – In early common law, suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and s ...
was considered murder. The requirement that the person killed be someone other than the perpetrator excluded suicide from the definition of murder.
* ''With malice aforethought'' – Originally '' malice aforethought'' carried its everyday meaning – a deliberate and premeditated (prior intent) killing of another motivated by ill will. Murder necessarily required that an appreciable time pass between the formation and execution of the intent to kill. The courts broadened the scope of murder by eliminating the requirement of actual premeditation and deliberation as well as true malice. All that was required for malice aforethought to exist is that the perpetrator act with one of the four states of mind that constitutes "malice".
The four states of mind recognized as constituting "malice" are:
Under state of mind (i), intent to kill, the ''deadly weapon rule'' applies. Thus, if the defendant intentionally uses a deadly weapon
A deadly weapon, sometimes dangerous weapon (although some jurisdictions differentiate between the two) or lethal weapon, is an item that can inflict mortal or great bodily harm. By statutory definition, certain items, especially firearms, are de ...
or instrument against the victim, such use authorizes a permissive inference of intent to kill. Examples of deadly weapons and instruments include but are not limited to guns, knives, deadly toxins or chemicals or gases and even vehicles when intentionally used to harm one or more victims.
Under state of mind (iii), an "abandoned and malignant heart", the killing must result from the defendant's conduct involving a reckless indifference to human life and a conscious disregard of an unreasonable risk of death or serious bodily injury. In Australian jurisdictions, the unreasonable risk must amount to a foreseen probability of death (or grievous bodily harm in most states), as opposed to possibility.; but the common law has been modified in NSW: .
Under state of mind (iv), the felony-murder doctrine, the felony committed must be an inherently dangerous felony, such as burglary, arson, rape, robbery or kidnapping. Importantly, the underlying felony ''cannot'' be a lesser included offense such as assault, otherwise all criminal homicides would be murder as all are felonies.
In Spanish criminal law, murder takes place when any of these requirements concur: Treachery (the use of means to avoid risk for the aggressor or to ensure that the crime goes unpunished), price or reward (financial gain) or viciousness (deliberately increasing the pain of the victim). After the last reform of the Spanish Criminal Code
The Criminal Code is a law that codifies most criminal offences in Spain. The Code is established by an organic law, the Organic Law 10/1995, of 23 November, of the Criminal Code (''Ley Orgánica 10/1995, de 23 de noviembre, del Código Penal' ...
, in force since July 1, 2015, another circumstance that turns homicide into murder is the desire to facilitate the commission of another crime or to prevent it from being discovered.
As with most legal terms, the precise definition of murder varies between jurisdictions and is usually codified in some form of legislation. Even when the legal distinction between murder and manslaughter is clear, it is not unknown for a jury to find a murder defendant guilty of the lesser offense. The jury might sympathize with the defendant (e.g. in a crime of passion, or in the case of a bullied victim who kills their tormentor), and the jury may wish to protect the defendant from a sentence of life imprisonment or execution.
Degrees of murder
Some jurisdictions divide murder by degrees. The distinction between first- and second-degree murder exists, for example, in Canadian murder law and U.S. murder law. The most common division is between first- and second-degree murder. Generally, second-degree murder is common law murder, and first-degree is an aggravated form. The aggravating factors of first-degree murder depend on the jurisdiction, but may include a specific intent to kill, premeditation, or deliberation. In some, murders committed by acts such as strangulation, poisoning, orlying in wait
In criminal law, lying in wait refers to the act of hiding and waiting for an individual with the intent to kill or inflict serious bodily harm to that person. Because lying in wait involves premeditation, some jurisdictions have established that ...
are also treated as first-degree murder. A few states in the U.S. further distinguish third-degree murder, but they differ significantly in which kinds of murders they classify as second-degree versus third-degree. For example, Minnesota defines third-degree murder as depraved-heart murder, whereas Florida defines third-degree murder as felony murder
The rule of felony murder is a legal doctrine in some common law jurisdictions that broadens the crime of murder: when someone is killed (regardless of intent to kill) in the commission of a dangerous or enumerated crime (called a felony in s ...
(except when the underlying felony is specifically listed in the definition of first-degree murder).
Some jurisdictions also distinguish premeditated murder. This is the crime of wrongfully and intentionally causing the death of another human being (also known as murder) after rationally considering the timing or method of doing so, in order to either increase the likelihood of success, or to evade detection or apprehension. State laws in the United States vary as to definitions of "premeditation". In some states, premeditation may be construed as taking place mere seconds before the murder. Premeditated murder is one of the most serious forms of homicide, and is punished more severely than manslaughter or other types of homicide, often with a life sentence without the possibility of parole, or in some countries, the death penalty
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned practice of deliberately killing a person as a punishment for an actual or supposed crime, usually following an authorized, rule-governed process to conclude that t ...
. In the U.S, federal law () criminalizes premeditated murder, felony murder and second-degree murder committed under situations where federal jurisdiction applies. In Canada, the criminal code classifies murder as either first- or second-degree. The former type of murder is often called premeditated murder, although premeditation is not the only way murder can be classified as first-degree.
Common law
According to Blackstone, English common law identified murder as a ''public wrong''. According to common law, murder is considered to be '' malum in se'', that is, an act which is evil within itself. An act such as murder is wrong or evil by its very nature, and it is the very nature of the act which does not require any specific detailing or definition in the law to consider murder a crime. Some jurisdictions still take a common law view of murder. In such jurisdictions, what is considered to be murder is defined by precedent case law or previous decisions of the courts of law. However, although the common law is by nature flexible and adaptable, in the interests both of certainty and of securing convictions, most common law jurisdictions have codified their criminal law and now have statutory definitions of murder.Exclusions
General
Although laws vary by country, there are circumstances of exclusion that are common in many legal systems. * The killing of enemy combatants who have not surrendered, when committed by lawful combatants in accordance with lawful orders in war, is generally not considered murder. Illicit killings within a war may constitute murder or homicidal war crimes; see Laws of war. * Self-defense: acting in self-defense or in defense of another person is generally accepted as legal justification for killing a person in situations that would otherwise have been murder. However, a self-defense killing might be considered manslaughter if the killer established control of the situation before the killing took place. In the case of self-defense, it is called a "justifiable homicide". * Unlawful killings without malice or intent are considered manslaughter. * In many common law countries, provocation is a partial defense to a charge of murder which acts by converting what would otherwise have been murder into manslaughter (this is voluntary manslaughter, which is more severe than involuntary manslaughter). * Accidental killings are considered homicides. Depending on the circumstances, these may or may not be considered criminal offenses; they are often considered manslaughter. * Suicide does not constitute murder in most societies. Assisting a suicide, however, may be considered murder in some circumstances.Specific to certain countries
* Capital punishment: some countries practice the death penalty. Capital punishment may be ordered by a legitimate court of law as the result of a conviction in a criminal trial withdue process
Due process of law is application by state of all legal rules and principles pertaining to the case so all legal rights that are owed to the person are respected. Due process balances the power of law of the land and protects the individual pers ...
for a serious crime. All member states of the Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold European Convention on Human Rights, human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. ...
are prohibited from using the death penalty.
* Euthanasia
Euthanasia (from el, εὐθανασία 'good death': εὖ, ''eu'' 'well, good' + θάνατος, ''thanatos'' 'death') is the practice of intentionally ending life to eliminate pain and suffering.
Different countries have different eut ...
, doctor-assisted suicide: the administration of lethal drugs by a doctor to a terminally ill patient, if the intention is solely to alleviate pain, in many jurisdictions it is seen as a special case (see the doctrine of double effect and the case of Dr John Bodkin Adams).
* Killing to prevent the theft of one's property may be legal, depending on the jurisdiction. In 2013, a jury in south Texas acquitted a man who killed a sex worker who attempted to run away with his money.
* Killing an intruder who is found by an owner to be in the owner's home (having entered unlawfully): legal in most US states (see Castle doctrine).
* Killing to prevent specific forms of aggravated rape or sexual assault
Sexual assault is an act in which one intentionally sexually touches another person without that person's consent, or coerces or physically forces a person to engage in a sexual act against their will. It is a form of sexual violence, which ...
– killing of attacker by the potential victim or by witnesses to the scene; legal in parts of the US and in various other countries.
* In some countries, the killing of a woman or girl in specific circumstances (e.g., when she commits adultery and is killed by her husband or other family members, known as honor killing) is not considered murder.
* In the United States, in some states and in federal jurisdiction, a killing by a police officer is excluded from prosecution if the officer believes they are being threatened with deadly force by the victim. This may include such actions by the victim as reaching into a glove compartment or pocket for license and registration, if the officer thinks that the victim might be reaching for a gun.
Victim
All jurisdictions require that the victim be a natural person; that is, a human being who was still alive before being murdered. In other words, under the law one cannot murder a corpse, a corporation, a non-human animal, or any other non-human organism such as a plant or bacterium. California's murder statute,penal code
A criminal code (or penal code) is a document that compiles all, or a significant amount of a particular jurisdiction's criminal law. Typically a criminal code will contain offences that are recognised in the jurisdiction, penalties that might ...
section 187, expressly mentioned a fetus as being capable of being killed, and was interpreted by the Supreme Court of California
The Supreme Court of California is the highest and final court of appeals in the courts of the U.S. state of California. It is headquartered in San Francisco at the Earl Warren Building, but it regularly holds sessions in Los Angeles and Sacra ...
in 1994 as not requiring any proof of the viability of the fetus as a prerequisite to a murder conviction.''People v. Davis''7 Cal. 4th 797, 30 Cal. Rptr. 2d 50, 872 P.2d 591
(1994). This holding has two implications. Firstly, a defendant in California can be convicted of murder for killing a fetus which the mother herself could have terminated without committing a crime. And secondly, as stated by Justice
Stanley Mosk
Morey Stanley Mosk (September 4, 1912 – June 19, 2001) was an American jurist, politician, and attorney. He served as Associate Justice of the California Supreme Court for 37 years (1964–2001), the longest tenure in that court's history.
...
in his dissent, because women carrying nonviable fetuses may not be visibly pregnant, it may be possible for a defendant to be convicted of intentionally murdering a person they did not know existed.
Mitigating circumstances
Some countries allow conditions that "affect the balance of the mind" to be regarded as mitigating circumstances. This means that a person may be found guilty of "manslaughter" on the basis of "diminished responsibility" rather than being found guilty of murder, if it can be proved that the killer was suffering from a condition that affected their judgment at the time. Depression, post-traumatic stress disorder and medication side-effects are examples of conditions that may be taken into account when assessing responsibility.Insanity
Mental disorder may apply to a wide range of disorders including psychosis caused by schizophrenia and dementia, and excuse the person from the need to undergo the stress of a trial as to liability. Usually, sociopathy and other personality disorders are not legally considered insanity. In some jurisdictions, following the pre-trial hearing to determine the extent of the disorder, the defense of "not guilty by reason of insanity" may be used to get a not guilty verdict. This defense has two elements: * That thedefendant
In court proceedings, a defendant is a person or object who is the party either accused of committing a crime in criminal prosecution or against whom some type of civil relief is being sought in a civil case.
Terminology varies from one jurisdic ...
had a serious mental illness, disease, or defect
* That the defendant's mental condition, at the time of the killing, rendered the perpetrator unable to determine right from wrong, or that what they were doing was wrong
 Under
Under New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
law, for example:
Under the French Penal Code:
Those who successfully argue a defense based on a mental disorder are usually referred to mandatory clinical treatment until they are certified safe to be released back into the community, rather than prison., note: this text refers to the procedure of involuntary commitment
Involuntary commitment, civil commitment, or involuntary hospitalization/hospitalisation is a legal process through which an individual who is deemed by a qualified agent to have symptoms of severe mental disorder is detained in a psychiatric hos ...
by the demand of the public authority, but the prefect systematically use that procedure whenever a man is discharged due to his dementia.
Postpartum depression
Postpartum depression (also known as post-natal depression) is recognized in some countries as a mitigating factor in cases ofinfanticide
Infanticide (or infant homicide) is the intentional killing of infants or offspring. Infanticide was a widespread practice throughout human history that was mainly used to dispose of unwanted children, its main purpose is the prevention of reso ...
. According to Susan Friedman, "Two dozen nations have infanticide laws that decrease the penalty for mothers who kill their children of up to one year of age. The United States does not have such a law, but mentally ill mothers may plead not guilty by reason of insanity." In the law of the Republic of Ireland, infanticide was made a separate crime from murder in 1949, applicable for the mother of a baby under one year old where "the balance of her mind was disturbed by reason of her not having fully recovered from the effect of giving birth to the child or by reason of the effect of lactation consequent upon the birth of the child". Since independence, death sentences for murder in such cases had always been commuted; the new act was intended "to eliminate all the terrible ritual of the black cap and the solemn words of the judge pronouncing sentence of death in those cases ... where it is clear to the Court and to everybody, except perhaps the unfortunate accused, that the sentence will never be carried out." In Russia, murder of a newborn child by the mother has been a separate crime since 1996.
Unintentional
For a killing to be considered murder in nine out of fifty states in the US, there normally needs to be an element of intent. A defendant may argue that they took precautions not to kill, that the death could not have been anticipated, or was unavoidable. As a general rule,manslaughter
Manslaughter is a common law legal term for homicide considered by law as less culpable than murder. The distinction between murder and manslaughter is sometimes said to have first been made by the ancient Athenian lawmaker Draco in the 7th cen ...
constitutes reckless
Reckless may refer to:
Film and television Film
* ''Reckless'' (1935 film), an American musical directed by Victor Fleming
* ''Reckless'' (1951 film), a Spanish drama film directed by José Antonio Nieves Conde
* '' The Reckless'', a 1965 Itali ...
killing, but manslaughter also includes criminally negligent (i.e. grossly negligent) homicide. Unintentional killing that results from an involuntary action generally cannot constitute murder. After examining the evidence, a judge or jury (depending on the jurisdiction) would determine whether the killing was intentional or unintentional.
Diminished capacity
In jurisdictions using the Uniform Penal Code, such as California, diminished capacity may be a defense. For example, Dan White used this defense to obtain a manslaughter conviction, instead of murder, in theassassination
Assassination is the murder of a prominent or important person, such as a head of state, head of government, politician, world leader, member of a royal family or CEO. The murder of a celebrity, activist, or artist, though they may not have ...
of Mayor George Moscone and Supervisor Harvey Milk. Afterward, California amended its penal code to provide "As a matter of public policy there shall be no defense of diminished capacity, diminished responsibility, or irresistible impulse in a criminal action...."
Aggravating circumstances
Murder with specified aggravating circumstances is often punished more harshly. Depending on the jurisdiction, such circumstances may include: * Premeditation * Poisoning * Murder of a child * Multiple murders committed within the same transaction or scheme * Murder of a police officer,SeeMurder (English law)
Murder is an offence under the common law of England and Wales. It is considered the most serious form of homicide, in which one person kills another with the intention to cause either death or serious injury unlawfully. The element of intentiona ...
. Mandatory life sentences for murder of police officers. judge, firefighter or witness to a crime
* Murder of a pregnant woman
* Crime committed for pay or other reward, such as contract killing
Contract killing is a form of murder or assassination in which one party hires another party to kill a targeted person or persons. It involves an illegal agreement which includes some form of payment, monetary or otherwise. Either party may be ...
* Exceptional brutality or cruelty
* Methods which are dangerous to the public e.g. explosion, arson, shooting in a crowd etc.
* Murder for a political cause
* Murder committed in order to conceal another crime or facilitate its commission.
* Hate crimes
A hate crime (also known as a bias-motivated crime or bias crime) is a prejudice-motivated crime which occurs when a perpetrator targets a victim because of their membership (or perceived membership) of a certain social group or racial demograph ...
, which occur when a perpetrator targets a victim because of their perceived membership in a certain social group.
* Treachery (e.g. '' Heimtücke'' in German law)
In the United States and Canada, these murders are referred to as first-degree or aggravated
Aggravation, in law, is "any circumstance attending the commission of a crime or tort which increases its guilt or enormity or adds to its injurious consequences, but which is above and beyond the essential constituents of the crime or tort itself. ...
murders. Under English criminal law, murder
Murder is the unlawful killing of another human without justification (jurisprudence), justification or valid excuse (legal), excuse, especially the unlawful killing of another human with malice aforethought. ("The killing of another person wit ...
always carries a mandatory life sentence, but is not classified into degrees. Penalties for murder committed under aggravating circumstances are often higher under English law than the 15-year minimum non-parole period that otherwise serves as a starting point for a murder committed by an adult.
Felony murder rule
A legal doctrine in some common law jurisdictions broadens the crime of murder: when an offender kills in the commission of a dangerous crime, (regardless of intent), he or she is guilty of murder. The felony murder rule is often justified by its supporters as a means of preventing dangerous felonies, but the case of Ryan Holle shows it can be used very widely.Year-and-a-day rule
In some common law jurisdictions, adefendant
In court proceedings, a defendant is a person or object who is the party either accused of committing a crime in criminal prosecution or against whom some type of civil relief is being sought in a civil case.
Terminology varies from one jurisdic ...
accused of murder is not guilty if the victim survives for longer than one year and one day after the attack. This reflects the likelihood that if the victim dies, other factors will have contributed to the cause of death, breaking the chain of causation; and also means that the responsible person does not have a charge of murder "hanging over their head indefinitely". Subject to any statute of limitations, the accused could still be charged with an offense reflecting the seriousness of the initial assault.
With advances in modern medicine, most countries have abandoned a fixed time period and test causation on the facts of the case. This is known as "delayed death" and cases where this was applied or was attempted to be applied go back to at least 1966.
In England and Wales, the "year-and-a-day rule" was abolished by the Law Reform (Year and a Day Rule) Act 1996. However, if death occurs three years or more after the original attack then prosecution can take place only with the attorney-general's approval.
In the United States, many jurisdictions have abolished the rule as well. Abolition of the rule has been accomplished by enactment of statutory criminal codes, which had the effect of displacing the common-law definitions of crimes and corresponding defenses. In 2001 the Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
held that retroactive application of a state supreme court decision abolishing the year-and-a-day rule did not violate the Ex Post Facto Clause of Article I of the United States Constitution.
The potential effect of fully abolishing the rule can be seen in the case of 74-year-old William Barnes, charged with the murder of a Philadelphia police officer Walter T. Barclay Jr., who he had shot nearly 41 years previously. Barnes had served 16 years in prison for attempting to murder Barkley, but when the policeman died on August 19, 2007, this was alleged to be from complications of the wounds suffered from the shooting – and Barnes was charged with his murder. He was acquitted on May 24, 2010.
Contributing factors
According to Peter Morall, the motivations for murder fit into the following 4 categories: * '' Lust:'' The murderer seeks to kill rivals to obtain objects of their sexual desire * '' Love:'' The murderer seeks to "mercy kill
''Star Wars: X-wing'' is a ten-book series of ''Star Wars'' novels by Michael A. Stackpole (who also co-wrote the similarly named comic book series) and Aaron Allston. Stackpole's contributions cover the adventures of a new Rogue Squadron formed ...
" a loved one with a major deformity or an incurable illness.
* '' Loathing:'' The murderer seeks to kill a loathed person (such as an abusive parent) or members of a loathed group or culture.
* ''Loot
Loot may refer to:
Film
*''Loot'' (1919 film), a film by William C. Dowlan
* ''Loot'' (1970 film), a British film by Silvio Narizzano
* ''Loot'' (2008 film), a documentary
* ''Loot'' (2011 film), an Indian film
* ''Loot'' (2012 film), a Nepali fil ...
:'' The murderer seeks some form of financial gain.
Morall argues that a motive alone is insufficient to explain criminal killing, as people can experience those impulse without killing. Morall insists risk factors that may increase the chance that somebody will commit a murder include:
* Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, is correlated with competitive and assertive behaviour.
* Reduction in serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vas ...
increases likelihood of impulsive hostile behaviour.
* Alteration in the breakdown of glucose appears to affect mood and behaviour.
* Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose circulates in the blood plasma. This is generally a blood sugar level higher than 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL), but symptoms may not start to become noticeable until even ...
and Hypoglycemia can both lead to aggression.
* Consumption of alcohol can lead to reduced self control.
* Environmental pollutants
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse change. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the ...
circulating in the body are linked to heightened aggression.
* Malnutrition from eating too much junk food can provoke aggressive behaviour and even murder.
Certain personality disorders are associated with an increased homicide rate, most notably narcissistic, anti-social, and histrionic personality disorders and those associated with psychopathology.
Some aspects of homicide
Homicide occurs when a person kills another person. A homicide requires only a volitional act or omission that causes the death of another, and thus a homicide may result from accidental, reckless, or negligent acts even if there is no inten ...
s, including the genetic relations or proximity between murderers and their victims, (as in the Cinderella effect), may potentially be explained by the evolution theory or evolutionary psychology.
Several studies have shown that there is a correlation between murder rates and poverty
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little income. Poverty can have diverse social, economic, and political causes and effects. When evaluating poverty in ...
. A 2000 study showed that regions of the state of São Paulo in Brazil with lower income also had higher rates of murder.
Religious attitudes
Abrahamic context
 In the
In the Abrahamic religion
The Abrahamic religions are a group of religions centered around worship of the God of Abraham. Abraham, a Hebrew patriarch, is extensively mentioned throughout Abrahamic religious scriptures such as the Bible and the Quran.
Jewish tradition ...
s, the first ever murder was committed by Cain
Cain ''Káïn''; ar, قابيل/قايين, Qābīl/Qāyīn is a Biblical figure in the Book of Genesis within Abrahamic religions. He is the elder brother of Abel, and the firstborn son of Adam and Eve, the first couple within the Bible. He wa ...
against his brother Abel out of jealousy. In the past, certain types of homicide were lawful and justified. Georg Oesterdiekhoff wrote:
In many such societies the redress was not via a legal system, but by blood revenge, although there might also be a form of payment that could be made instead—such as the weregild which in early Germanic society could be paid to the victim's family in lieu
Many words in the English vocabulary are of French origin, most coming from the Anglo-Norman spoken by the upper classes in England for several hundred years after the Norman Conquest, before the language settled into what became Modern Engli ...
of their right of revenge.
One of the oldest-known prohibitions against murder appears in the Sumerian Code of Ur-Nammu
The Code of Ur-Nammu is the oldest known law code surviving today. It is from Mesopotamia and is written on tablets, in the Sumerian language c. 2100–2050 BCE.
Discovery
The first copy of the code, in two fragments found at Nippur, in what is ...
written sometime between 2100 and 2050 BC. The code states, "If a man commits a murder, that man must be killed."
Judeo-Christian standard
InJudeo-Christian
The term Judeo-Christian is used to group Christianity and Judaism together, either in reference to Christianity's derivation from Judaism, Christianity's borrowing of Jewish Scripture to constitute the "Old Testament" of the Christian Bible, or ...
traditions, the prohibition against murder is one of the Ten Commandments given by God to Moses in (Exodus: 20v13) and (Deuteronomy 5v17). The Vulgate and subsequent early English translations of the Bible used the term ''secretly killeth his neighbour'' or ''smiteth his neighbour secretly'' rather than ''murder'' for the Latin ''clam percusserit proximum''. Later editions such as Young's Literal Translation and the World English Bible have translated the Latin ''occides'' simply as ''murder'' rather than the alternatives of ''kill'', ''assassinate'', ''fall upon'', or ''slay''.
In Islam
InIslam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
according to the Qur'an, one of the greatest sins is to kill a human being who has committed no fault.
"Do not take a ˹human˺ life—made sacred by Allah—except with ˹legal˺ right."
"That is why We ordained for the Children of Israel that whoever takes a life—unless as a punishment for murder or mischief in the land—it will be as if they killed all of humanity; and whoever saves a life, it will be as if they saved all of humanity."
"˹They are˺ those who do not invoke any other god besides Allah, nor take a ˹human˺ life—made sacred by Allah—except with ˹legal˺ right,1 nor commit fornication. And whoever does ˹any of˺ this will face the penalty."
Historical attitudes
The term ''assassin'' derives from Hashshashin, a militantIsmaili
Isma'ilism ( ar, الإسماعيلية, al-ʾIsmāʿīlīyah) is a branch or sub-sect of Shia Islam. The Isma'ili () get their name from their acceptance of Imam Isma'il ibn Jafar as the appointed spiritual successor (imām) to Ja'far al-Sa ...
Shi'ite sect, active from the 8th to 14th centuries. This mystic secret society
A secret society is a club or an organization whose activities, events, inner functioning, or membership are concealed. The society may or may not attempt to conceal its existence. The term usually excludes covert groups, such as intelligence a ...
killed members of the Abbasid, Fatimid, Seljuq Seljuk or Saljuq (سلجوق) may refer to:
* Seljuk Empire (1051–1153), a medieval empire in the Middle East and central Asia
* Seljuk dynasty (c. 950–1307), the ruling dynasty of the Seljuk Empire and subsequent polities
* Seljuk (warlord) (d ...
and Crusade
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were i ...
r elite for political and religious reasons. The Thuggee
Thuggee (, ) are actions and crimes carried out by Thugs, historically, organised gangs of professional robbers and murderers in India. The English word ''thug'' traces its roots to the Hindi ठग (), which means 'swindler' or 'deceiver'. Rela ...
cult that plagued India was devoted to Kali, the goddess of death and destruction. According to some estimates the Thuggees murdered 1 million people between 1740 and 1840. The Aztecs believed that without regular offerings of blood the sun god Huitzilopochtli would withdraw his support for them and destroy the world as they knew it. According to Ross Hassig, author of ''Aztec Warfare'', "between 10,000 and 80,400 persons" were sacrificed
Sacrifice is the offering of material possessions or the lives of animals or humans to a deity as an act of propitiation or worship. Evidence of ritual animal sacrifice has been seen at least since ancient Hebrews and Greeks, and possibly exis ...
in the 1487 re-consecration of the Great Pyramid of Tenochtitlan
The (Spanish: Main Temple) was the main temple of the Mexica people in their capital city of Tenochtitlan, which is now Mexico City. Its architectural style belongs to the late Postclassic period of Mesoamerica. The temple was called ' in ...
. Japanese samurai had the right to strike with their sword at anyone of a lower class who compromised their honour.
Slavery
Southern slave codes did make willful killing of aslave
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
illegal in most cases. For example, the 1860 Mississippi case of ''Oliver v. State'' charged the defendant with murdering his own slave. In 1811, the wealthy white planter Arthur Hodge was hanged for murdering several of his slaves on his plantation in the Virgin Islands.
Honor killings in Corsica
InCorsica
Corsica ( , Upper , Southern ; it, Corsica; ; french: Corse ; lij, Còrsega; sc, Còssiga) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the 18 regions of France. It is the fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of ...
, vendetta was a social code that required Corsicans to kill anyone who wronged their family honor. Between 1821 and 1852, no fewer than 4,300 murders were perpetrated in Corsica.
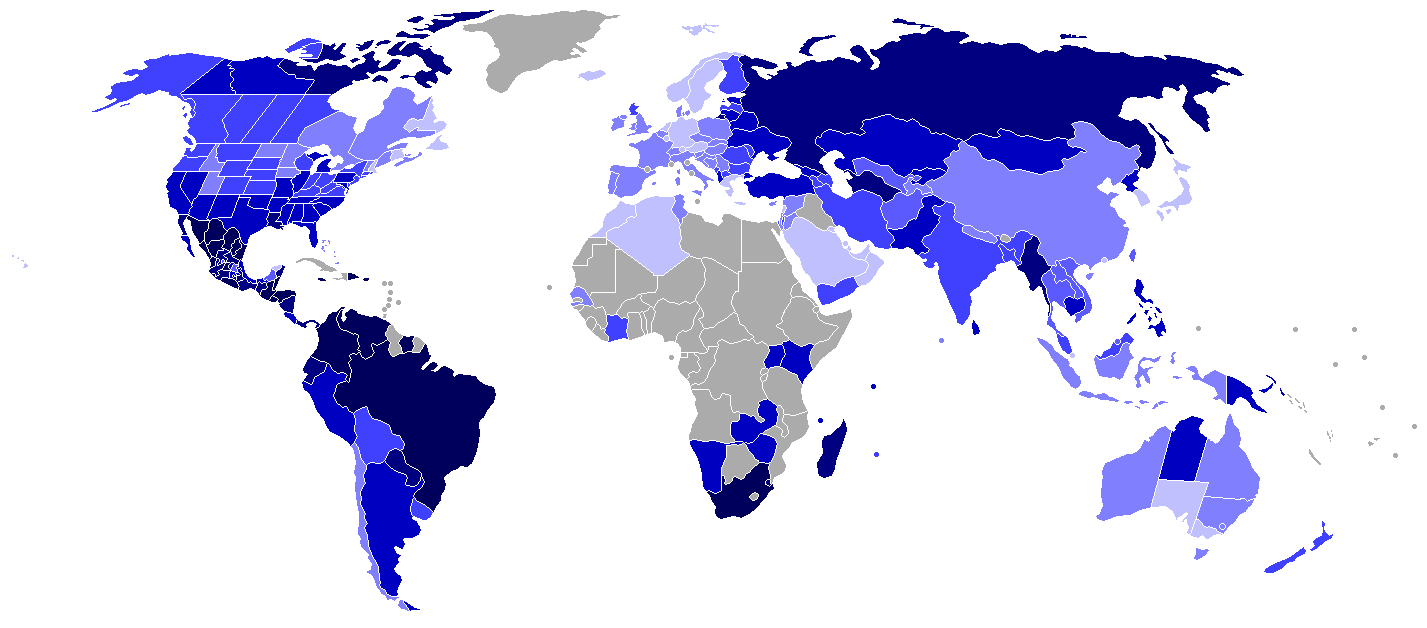
Incidence

Murder rates by varies countries
Murder rates in jurisdictions such as Japan, Singapore, Hong Kong, Iceland, Switzerland, Italy, Spain and Germany are among the lowest in the world, around 0.3–1 cases per 100,000 people per year; the rate of the United States is among the highest of developed countries, around 4.5 in 2014, with rates in larger cities sometimes over 40 per 100,000. The top ten highest murder rates are in Honduras (91.6 per 100,000), El Salvador, Ivory Coast, Venezuela, Belize, Jamaica,U.S. Virgin Islands
The United States Virgin Islands,. Also called the ''American Virgin Islands'' and the ''U.S. Virgin Islands''. officially the Virgin Islands of the United States, are a group of Caribbean islands and an unincorporated and organized territory ...
, Guatemala, Saint Kitts and Nevis and Zambia. (UNODC, 2011 – full tablhere
/small>). The following absolute murder counts per-country are not comparable because they are not adjusted by each country's total population. Nonetheless, they are included here for reference, with 2010 used as the base year (they may or may not include justifiable homicide, depending on the jurisdiction). There were 52,260 murders in Brazil, consecutively elevating the record set in 2009. Over half a million people were shot to death in Brazil between 1979 and 2003. 33,335 murder cases were registered across India, approximately 17,000 murders in Colombia (the murder rate was 38 per 100,000 people, in 2008 murders went down to 15,000), approximately 16,000 murders in South Africa, approximately 15,000 murders in the United States, approximately 26,000 murders in Mexico, about 8,000 murders committed in Russia, approximately 13,000 murders in Venezuela, approximately 4,000 murders in El Salvador, approximately 1,400 murders in Jamaica, approximately 550 murders in Canada and approximately 470 murders in Trinidad and Tobago. Pakistan reported 12,580 murders.
Murder in the United States
 In the United States, 666,160 people were killed between 1960 and 1996. Approximately 90% of murders in the US are committed by males. Between 1976 and 2005, 23.5% of all murder victims and 64.8% of victims murdered by intimate partners were female. For women in the US, homicide is the leading cause of death in the workplace. Chapter 6, Responding to Workplace Violence and Staff Victimization.
In the US, murder is the leading cause of death for African American males aged 15 to 34. Between 1976 and 2008, African Americans were victims of 329,825 homicides. In 2006,
In the United States, 666,160 people were killed between 1960 and 1996. Approximately 90% of murders in the US are committed by males. Between 1976 and 2005, 23.5% of all murder victims and 64.8% of victims murdered by intimate partners were female. For women in the US, homicide is the leading cause of death in the workplace. Chapter 6, Responding to Workplace Violence and Staff Victimization.
In the US, murder is the leading cause of death for African American males aged 15 to 34. Between 1976 and 2008, African Americans were victims of 329,825 homicides. In 2006, Federal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the United States and its principal federal law enforcement agency. Operating under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Justice, t ...
's Supplementary Homicide Report indicated that nearly half of the 14,990 murder victims that year were Black (7421). In the year 2007, there were 3,221 black victims and 3,587 white victims of non-negligent homicides. While 2,905 of the black victims were killed by a black offender, 2,918 of the white victims were killed by white offenders. There were 566 white victims of black offenders and 245 black victims of white offenders. The "white" category in the Uniform Crime Reports (UCR) includes non-black Hispanics.
Murder demographics are affected by the improvement of trauma care, which has resulted in reduced lethality of violent assaults – thus the murder rate may not necessarily indicate the overall level of social violence.
Workplace homicide, which tripled during the 1980s, is the fastest growing category of murder in America.
Development of murder rates over time in different countries is often used by both supporters and opponents of capital punishment and gun control
Gun control, or firearms regulation, is the set of laws or policies that regulate the manufacture, sale, transfer, possession, modification, or use of firearms by civilians.
Most countries have a restrictive firearm guiding policy, with on ...
. Using properly filtered data, it is possible to make the case for or against either of these issues. For example, one could look at murder rates in the United States from 1950 to 2000, and notice that those rates went up sharply shortly after a moratorium on death sentences was effectively imposed in the late 1960s. This fact has been used to argue that capital punishment serves as a deterrent and, as such, it is morally justified. Capital punishment opponents frequently counter that the United States has much higher murder rates than Canada and most European Union countries, although all those countries have abolished the death penalty. Overall, the global pattern is too complex, and on average, the influence of both these factors may not be significant and could be more social, economic, and cultural.
Despite the immense improvements in forensics
Forensic science, also known as criminalistics, is the application of science to criminal and civil laws, mainly—on the criminal side—during criminal investigation, as governed by the legal standards of admissible evidence and crimina ...
in the past few decades, the fraction of murders solved has decreased in the United States, from 90% in 1960 to 61% in 2007. Solved murder rates in major U.S. cities varied in 2007 from 36% in Boston, Massachusetts to 76% in San Jose, California. Major factors affecting the arrest rate include witness cooperation and the number of people assigned to investigate the case.
History of murder rates
 According to scholar Pieter Spierenburg
According to scholar Pieter Spierenburg homicide rates
The list of countries by UNODC homicide rate is typically expressed in units of deaths per 100,000 individuals per year. A mortality rate of 30 (out of 100,000) in a population of 100,000 would mean 30 deaths per year in that entire population, or ...
per 100,000 in Europe have fallen over the centuries, from 35 per 100,000 in medieval times, to 20 in 1500 AD, 5 in 1700, to below two per 100,000 in 1900.Spierenburg, Pieter, ''A History of Murder: Personal Violence in Europe from the Middle Ages to the Present'', Polity, 2008. Referred to i"Rap Sheet Why is American history so murderous?"
by
Jill Lepore
Jill Lepore is an American historian and journalist. She is the David Woods Kemper '41 Professor of American History at Harvard University and a staff writer at ''The New Yorker'', where she has contributed since 2005. She writes about American ...
New Yorker, November 9, 2009
In the United States, murder rates have been higher and have fluctuated. They fell below 2 per 100,000 by 1900, rose during the first half of the century, dropped in the years following World War II, and bottomed out at 4.0 in 1957 before rising again. The rate stayed in 9 to 10 range most of the period from 1972 to 1994, before falling to 5 in present times. The increase since 1957 would have been even greater if not for the significant improvements in medical techniques and emergency response times, which mean that more and more attempted homicide victims survive. According to one estimate, if the lethality levels of criminal assaults of 1964 still applied in 1993, the country would have seen the murder rate of around 26 per 100,000, almost triple the actually observed rate of 9.5 per 100,000.
Investigation
The success rate of criminal investigations into murders (the clearance rate) tends to be relatively high for murder compared to other crimes, due to its seriousness. In the United States, the clearance rate was 62.6% in 2004.See also
Lists related to murder
* Lists of murders * List of types of killing ** Axe murder * List of unsolved deathsRelated topics
* Child murder * Culpable homicide * Depraved-heart murder * Double murder * Execution-style murder * Letting die *Mass murder
Mass murder is the act of murdering a number of people, typically simultaneously or over a relatively short period of time and in close geographic proximity. The United States Congress defines mass killings as the killings of three or more pe ...
* Misdemeanor murder
Misdemeanor murder is a term used to describe a situation in which a person is suspected of murder, but there is not enough evidence to convict the suspect of murder in court. The suspect is then either released without charges or the suspect ...
* Murder conviction without a body
* Seven laws of Noah
In Judaism, the Seven Laws of Noah ( he, שבע מצוות בני נח, ''Sheva Mitzvot B'nei Noach''), otherwise referred to as the Noahide Laws or the Noachian Laws (from the Hebrew pronunciation of "Noah"), are a set of universal moral law ...
* Stigmatized property
In real estate, stigmatized property is property that buyers or tenants may shun for reasons that are unrelated to its physical condition or features. These can include death of an occupant, murder, suicide, and even the belief that a house is haun ...
* Thrill killing
* Capital murder
Capital murder was a statutory offence of aggravated murder in Great Britain, and Northern Ireland, and the Republic of Ireland, which was later adopted as a legal provision to define certain forms of aggravated murder in the United States. In som ...
* Assassination
Assassination is the murder of a prominent or important person, such as a head of state, head of government, politician, world leader, member of a royal family or CEO. The murder of a celebrity, activist, or artist, though they may not have ...
, the murder of a prominent person, such as a head of state or head of government.
Murder laws by country
*Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
* Brazil
* Canada
* China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
* Cuba
* Denmark
* England and Wales
* Finland
* France
* Germany
* Hong Kong
* India
* Israel
* Italy
* Netherlands
* Northern Ireland
* Norway
* Peru
* Portugal
* Romania
* Russia
* Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
* Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
* United States
Notes
References
Bibliography
Lord Mustill on the Common Law concerning murder
* Sir Edward Coke Co. Inst., Pt. III, ch.7, p. 50
External links
Introduction and Updated Information on the Seville Statement on Violence
The Seville Statement
– U.S. Centers for Disease Control
Cezanne's depiction of "The Murder"
– National Museums Liverpool {{Authority control Crimes Crimes against humanity Violent crime Violence