Multituberculates on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Multituberculata (commonly known as multituberculates, named for the multiple
 The multituberculates had a cranial and dental anatomy superficially similar to rodents such as mice and rats, with cheek-teeth separated from the chisel-like front teeth by a wide tooth-less gap (the diasteme). Each cheek-tooth displayed several rows of small cusps (or
The multituberculates had a cranial and dental anatomy superficially similar to rodents such as mice and rats, with cheek-teeth separated from the chisel-like front teeth by a wide tooth-less gap (the diasteme). Each cheek-tooth displayed several rows of small cusps (or
p. 299
/ref> Multituberculates are notable for the presence of a massive fourth lower premolar, the plagiaulacoid; other mammals, like Plesiadapiformes and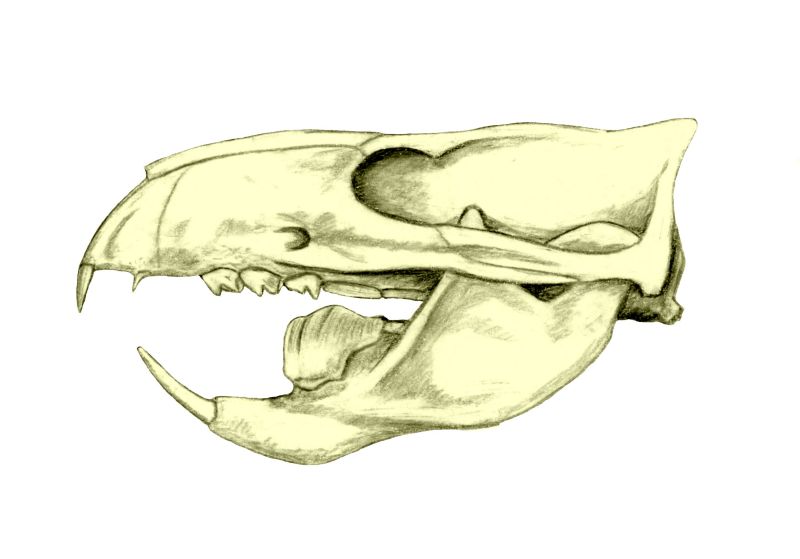 Unlike rodents and similar therians, multituberculates had a palinal jaw stroke (front-to-back), instead of a propalinal (back-to-front) or transverse (side-to-side) one; as a consequence, their jaw musculature and cusp orientation is radically different. Palinal jaw strokes are almost entirely absent in modern mammals (with the possible exception of the
Unlike rodents and similar therians, multituberculates had a palinal jaw stroke (front-to-back), instead of a propalinal (back-to-front) or transverse (side-to-side) one; as a consequence, their jaw musculature and cusp orientation is radically different. Palinal jaw strokes are almost entirely absent in modern mammals (with the possible exception of the 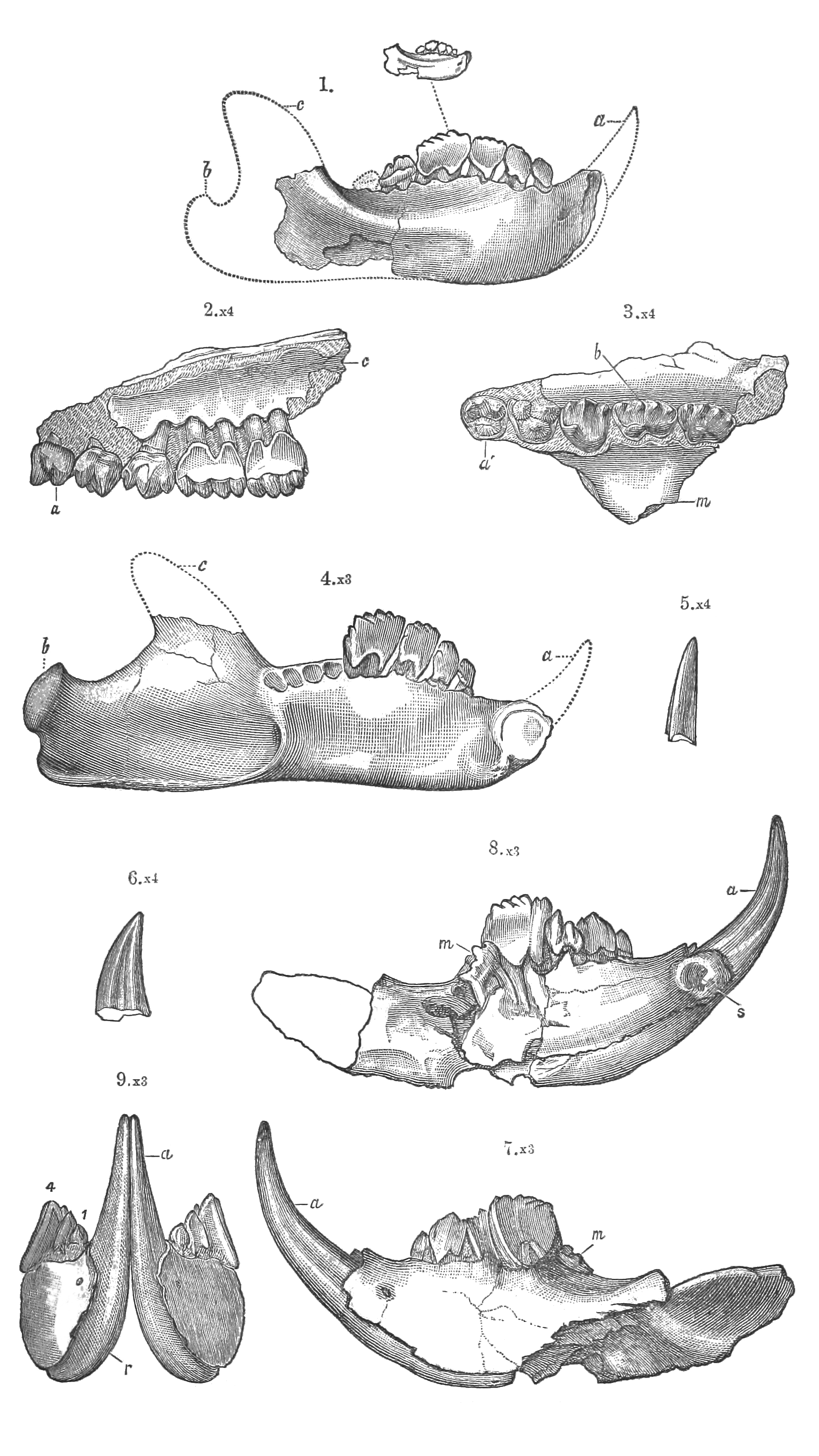 The structure of the pelvis in the Multituberculata suggests that they gave birth to tiny helpless, underdeveloped young, similar to modern
The structure of the pelvis in the Multituberculata suggests that they gave birth to tiny helpless, underdeveloped young, similar to modern
 Another group of multituberculates, the taeniolabids, were heavier and more massively built, indicating that they lived a fully terrestrial life. The largest specimens weighted probably as much as 100 kg, making them comparable in size to large rodents like ''
Another group of multituberculates, the taeniolabids, were heavier and more massively built, indicating that they lived a fully terrestrial life. The largest specimens weighted probably as much as 100 kg, making them comparable in size to large rodents like ''
 In their 2001 study, Kielan-Jaworowska and
In their 2001 study, Kielan-Jaworowska and
 Based on the combined works of Mikko's Phylogeny ArchiveMikko's Phylogeny Archive
Based on the combined works of Mikko's Phylogeny ArchiveMikko's Phylogeny Archive
and Paleofile.com. Suborder †
tubercle
In anatomy, a tubercle (literally 'small tuber', Latin for 'lump') is any round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on external or internal organs of a plant or an animal.
In plants
A tubercle is generally a wart-like projection ...
s of their teeth) is an extinct order of rodent-like mammals with a fossil record spanning over 130 million years. They first appeared in the Middle Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
, and reached a peak diversity during the Late Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
and Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''pal ...
. They eventually declined from the mid Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''pal ...
onwards, disappearing from the known fossil record in the late Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
. They are the most diverse order of Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
mammals with more than 200 species known, ranging from mouse-sized to beaver-sized. These species occupied a diversity of ecological niches, ranging from burrow-dwelling to squirrel-like arborealism to jerboa
Jerboas (from ar, جربوع ') are hopping desert rodents found throughout North Africa and Asia, and are members of the family Dipodidae. They tend to live in hot deserts.
When chased, jerboas can run at up to . Some species are preyed on b ...
-like hoppers. Multituberculates are usually placed as crown
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, partic ...
mammals outside either of the two main groups of living mammals—Theria
Theria (; Greek: , wild beast) is a subclass of mammals amongst the Theriiformes. Theria includes the eutherians (including the placental mammals) and the metatherians (including the marsupials) but excludes the egg-laying monotremes.
...
, including placental
Placental mammals (infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placentalia contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguishe ...
s and marsupial
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species is that the young are carried in a ...
s, and MonotremataAgustí-Antón 2002, pp 3-4—but usually as closer to Theria than to monotremes. They are considered to be closely related to Euharamiyida
Euharamiyida also known as Eleutherodontida, is clade of early mammals or mammal-like cynodonts from the Middle Jurassic to Early Cretaceous of Eurasia and possibly North America. The group is sometimes considered a sister group to Multitubercula ...
and Gondwanatheria
Gondwanatheria is an extinct group of mammaliaforms that lived in parts of Gondwana, including Madagascar, India, South America, Africa and Antarctica during the Upper Cretaceous through the Paleogene (and possibly much earlier, if '' Allostaff ...
as part of Allotheria
Allotheria (meaning "other beasts", from the Greek , '–other and , '–wild animal) is an extinct branch of successful Mesozoic mammals. The most important characteristic was the presence of lower molariform teeth equipped with two longitudin ...
.
Description
 The multituberculates had a cranial and dental anatomy superficially similar to rodents such as mice and rats, with cheek-teeth separated from the chisel-like front teeth by a wide tooth-less gap (the diasteme). Each cheek-tooth displayed several rows of small cusps (or
The multituberculates had a cranial and dental anatomy superficially similar to rodents such as mice and rats, with cheek-teeth separated from the chisel-like front teeth by a wide tooth-less gap (the diasteme). Each cheek-tooth displayed several rows of small cusps (or tubercle
In anatomy, a tubercle (literally 'small tuber', Latin for 'lump') is any round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on external or internal organs of a plant or an animal.
In plants
A tubercle is generally a wart-like projection ...
s, hence the name) that operated against similar rows in the teeth of the jaw; the exact homology of these cusps to theria
Theria (; Greek: , wild beast) is a subclass of mammals amongst the Theriiformes. Theria includes the eutherians (including the placental mammals) and the metatherians (including the marsupials) but excludes the egg-laying monotremes.
...
n ones is still a matter of debate. Unlike rodents, which have ever-growing teeth, multituberculates underwent dental replacement patterns typical to most mammals (though in at least some species the lower incisors continued to erupt long after the root's closure). Kielan-Jaworowska, Zofia, Richard L. Cifelli, and Zhe-Xi Luo (2005). ''Mammals from the Age of Dinosaurs: Origins, Evolution, and Structure ''p. 299
/ref> Multituberculates are notable for the presence of a massive fourth lower premolar, the plagiaulacoid; other mammals, like Plesiadapiformes and
diprotodontia
Diprotodontia (, from Greek "two forward teeth") is the largest extant order of marsupials, with about 155 species, including the kangaroos, wallabies, possums, koala, wombats, and many others. Extinct diprotodonts include the hippopotamus-sized ...
n marsupials, also have similar premolars in both upper and lower jaws, but in multituberculates this tooth is massive and the upper premolars aren't modified this way. In basal multituberculates all three lower premolars were plagiaulacoids, increasing in size posteriorly, but in Cimolodonta
Cimolodonta is a taxon of extinct mammals that lived from the Cretaceous to the Eocene. They were some of the more derived members of the extinct order Multituberculata. They probably lived something of a rodent-like existence until their ...
only the fourth lower premolar remained, with the third one remaining only as a vestigial peg-like tooth, and in several taxa like taeniolabidoidea
Taeniolabidoidea is a group of extinct mammals known from North America and Asia. They were the largest members of the extinct order Multituberculata, as well as the largest non-therian mammals. ''Lambdopsalis'' even provides direct fossil eviden ...
ns, the plagiaulacoid disappeared entirely or was reconverted into a molariform tooth.
 Unlike rodents and similar therians, multituberculates had a palinal jaw stroke (front-to-back), instead of a propalinal (back-to-front) or transverse (side-to-side) one; as a consequence, their jaw musculature and cusp orientation is radically different. Palinal jaw strokes are almost entirely absent in modern mammals (with the possible exception of the
Unlike rodents and similar therians, multituberculates had a palinal jaw stroke (front-to-back), instead of a propalinal (back-to-front) or transverse (side-to-side) one; as a consequence, their jaw musculature and cusp orientation is radically different. Palinal jaw strokes are almost entirely absent in modern mammals (with the possible exception of the dugong
The dugong (; ''Dugong dugon'') is a marine mammal. It is one of four living species of the order Sirenia, which also includes three species of manatees. It is the only living representative of the once-diverse family Dugongidae; its closest m ...
), but are also present in haramiyidans, argyrolagoideans and tritylodontid
Tritylodontidae ("three-knob teeth", named after the shape of their cheek teeth) is an extinct family of small to medium-sized, highly specialized mammal-like cynodonts, bearing several mammalian traits like erect limbs, endothermy and details ...
s, the former historically united with multituberculates on that basis. Multituberculate mastication is thought to have operated in a two stroke cycle: first, food held in place by the last upper premolar was sliced by the bladelike lower pre-molars as the dentary moved orthally (upward). Then the lower jaw moved palinally, grinding the food between the molar cusp rows.
 The structure of the pelvis in the Multituberculata suggests that they gave birth to tiny helpless, underdeveloped young, similar to modern
The structure of the pelvis in the Multituberculata suggests that they gave birth to tiny helpless, underdeveloped young, similar to modern marsupial
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species is that the young are carried in a ...
s, such as kangaroos. However, a 2022 study reveals that they might actually have had long gestation periods like placentals.
At least two lineages developed hypsodonty
Hypsodont is a pattern of dentition with high-crowned teeth and enamel extending past the gum line, providing extra material for wear and tear. Some examples of animals with hypsodont dentition are cows and horses; all animals that feed on gritt ...
, in which tooth enamel extends beyond the gumline: lambdopsalid taeniolabidoidea
Taeniolabidoidea is a group of extinct mammals known from North America and Asia. They were the largest members of the extinct order Multituberculata, as well as the largest non-therian mammals. ''Lambdopsalis'' even provides direct fossil eviden ...
ns and sudamericid gondwanatheres
Gondwanatheria is an extinct group of mammaliaforms that lived in parts of Gondwana, including Madagascar, India, South America, Africa and Antarctica during the Upper Cretaceous through the Paleogene (and possibly much earlier, if '' Allostaff ...
.
Studies published in 2018 demonstrated that multituberculates had relatively complex brains, some braincase regions even absent in therian mammals.
Evolution
Multituberculates first appear in the fossil record during theJurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
period, and then survived and even dominated for over one hundred million years, longer than any other order of mammaliforms, including placental mammals. The earliest known multituberculates are from the Middle Jurassic (Bathonian
In the geologic timescale the Bathonian is an age and stage of the Middle Jurassic. It lasted from approximately 168.3 Ma to around 166.1 Ma (million years ago). The Bathonian Age succeeds the Bajocian Age and precedes the Callovian Age.
Str ...
~166-168 million years ago) of England and Russia, including '' Hahnotherium'' ''and Kermackodon'' from the Forest Marble Formation
The Forest Marble is a geological formation in England. Part of the Great Oolite Group, it dates to the late Bathonian stage of the Middle Jurassic.Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution (Middle Jurassic, Europe)." In: Weisha ...
of England, and '' Tashtykia'' and '' Tagaria'' from the Itat Formation
The Itat Formation ( Russian: итатская свита) is a geologic formation in western Siberia. It was deposited in the Bajocian to Bathonian ages of the Middle Jurassic. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from ...
of Russia. These forms are only known from isolated teeth, which bear close similarity to those of euharamyidans, which they are suspected to be closely related. During the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous, primitive multituberculates, collectively grouped into the paraphyletic "Plagiaulacida
Plagiaulacida is a group of extinct multituberculate mammals. Multituberculates were among the most common mammals of the Mesozoic, "the age of the dinosaurs". Plagiaulacids are a paraphyletic grouping, containing all multituberculates that lie ...
" were abundant and widespread across Laurasia (including Europe, Asia and North America). During the Aptian stage of the Early Cretaceous, the advanced subgroup Cimolodonta
Cimolodonta is a taxon of extinct mammals that lived from the Cretaceous to the Eocene. They were some of the more derived members of the extinct order Multituberculata. They probably lived something of a rodent-like existence until their ...
appeared in North America, characterised by a reduced number of lower premolars, with a blade-like lower fourth premolar. By the early Late Cretaceous ( Cenomanian) Cimolodonta had replaced all other multituberculate lineages.
During the Late Cretaceous, multituberculates experienced an adaptive radiation
In evolutionary biology, adaptive radiation is a process in which organisms diversify rapidly from an ancestral species into a multitude of new forms, particularly when a change in the environment makes new resources available, alters biotic int ...
, corresponding with a shift towards herbivory. Multituberculates reached their peak diversity during the early Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''pal ...
, shortly after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event (also known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction) was a sudden mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth, approximately 66 million years ago. With the ...
, but declined from the mid Paleocene onwards, likely due to competition with placental mammals such as rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are na ...
s and ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, ...
s, the group finally became extinct in the Late Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
. There are some isolated records of multituberculates from the Southern Hemisphere, including the cimolodontan '' Corriebaatar'' from the Early Cretaceous of Australia, and fragmentary remains from the Late Cretaceous Maevarano Formation
The Maevarano Formation is a Late Cretaceous sedimentary rock formation found in the Mahajanga Province of northwestern Madagascar. It is most likely Maastrichtian in age, and records a seasonal, semiarid environment with rivers that had greatly v ...
of Madagascar. The family Ferugliotheriidae
Ferugliotheriidae is one of three known families in the order Gondwanatheria, an enigmatic group of extinct mammals. Gondwanatheres have been classified as a group of uncertain affinities or as members of Multituberculata, a major extinct mammal ...
from the Late Cretaceous of South America, traditionally considered gondwanatherians, may actually be cimolodontan multituberculates.
During the Late Cretaceous and Paleocene the multituberculates radiated into a wide variety of morphotype
In biology, polymorphism is the occurrence of two or more clearly different morphs or forms, also referred to as alternative ''phenotypes'', in the population of a species. To be classified as such, morphs must occupy the same habitat at the s ...
s, including the squirrel-like arboreal ptilodonts. The peculiar shape of their last lower premolar
The premolars, also called premolar teeth, or bicuspids, are transitional teeth located between the canine and molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per quadrant in the permanent set of teeth, making eight premolars total in the mouth ...
is their most outstanding feature. These teeth were larger and more elongated than the other cheek-teeth and had an occlusive
In phonetics, an occlusive, sometimes known as a stop, is a consonant sound produced by occluding (i.e. blocking) airflow in the vocal tract, but not necessarily in the nasal tract. The duration of the block is the ''occlusion'' of the consonan ...
surface forming a serrated slicing blade. Though it can be assumed that this was used for crushing seeds and nuts, it is believed that most small multituberculates also supplemented their diet with insects, worms, and fruits. Tooth marks attributed to multituberculates are known on ''Champsosaurus
''Champsosaurus'' is an extinct genus of crocodile-like choristodere reptile, known from the Late Cretaceous and early Paleogene periods of North America and Europe (Campanian-Paleocene). The name ''Champsosaurus'' is thought to come from , () ...
'' fossils, indicating that at least some of these mammals were scavengers. A ptilodont that thrived in North America was ''Ptilodus
''Ptilodus'' (meaning "soft-haired") is a genus of mammals from the extinct order of Multituberculata, and lived during the Paleocene in North America.
''Ptilodus'' was a relatively large multituberculate of in length, which is about the same s ...
''. Thanks to the well-preserved ''Ptilodus'' specimens found in the Bighorn Basin
The Bighorn Basin is a plateau region and intermontane basin, approximately 100 miles (160 km) wide, in north-central Wyoming in the United States. It is bounded by the Absaroka Range on the west, the Pryor Mountains on the north, the Bigho ...
, Wyoming
Wyoming () is a U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho to the west, Utah to the south ...
, we know that these multituberculates were able to abduct and adduct their big toes, and thus that their foot mobility was similar to that of modern squirrels, which descend trees head first.
 Another group of multituberculates, the taeniolabids, were heavier and more massively built, indicating that they lived a fully terrestrial life. The largest specimens weighted probably as much as 100 kg, making them comparable in size to large rodents like ''
Another group of multituberculates, the taeniolabids, were heavier and more massively built, indicating that they lived a fully terrestrial life. The largest specimens weighted probably as much as 100 kg, making them comparable in size to large rodents like ''Castoroides
''Castoroides'' (Latin: "beaver" (castor), "like" (oides)), or giant beaver, is an extinct genus of enormous, bear-sized beavers that lived in North America during the Pleistocene. Two species are currently recognized, ''C. dilophidus'' in the S ...
''.
They reached their highest diversity in Asia during the late Cretaceous and Paleocene, which suggests that they originated from there.
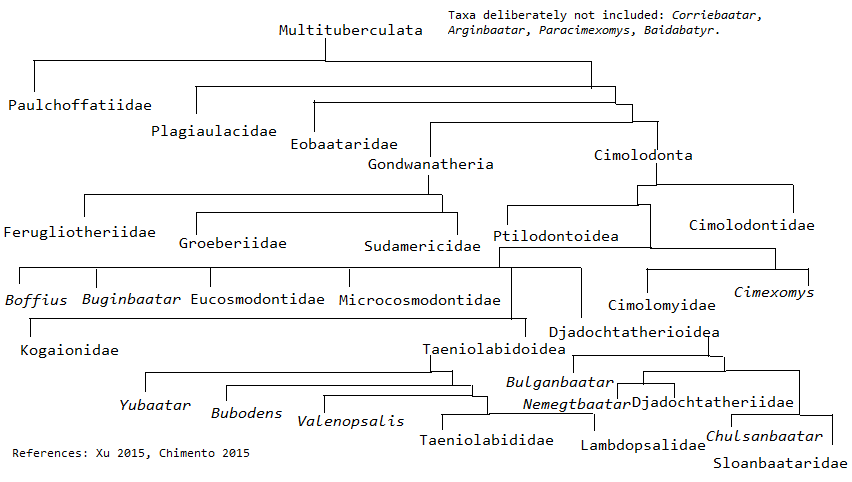
Classification
Multituberculate is generally placed in theAllotheria
Allotheria (meaning "other beasts", from the Greek , '–other and , '–wild animal) is an extinct branch of successful Mesozoic mammals. The most important characteristic was the presence of lower molariform teeth equipped with two longitudin ...
alongside Euharamiyida
Euharamiyida also known as Eleutherodontida, is clade of early mammals or mammal-like cynodonts from the Middle Jurassic to Early Cretaceous of Eurasia and possibly North America. The group is sometimes considered a sister group to Multitubercula ...
, a clade of mammals known from the Middle Jurassic to Early Cretaceous of the Asia and possibly Europe that several morphological similarities to multituberculates.
Gondwanatheria
Gondwanatheria is an extinct group of mammaliaforms that lived in parts of Gondwana, including Madagascar, India, South America, Africa and Antarctica during the Upper Cretaceous through the Paleogene (and possibly much earlier, if '' Allostaff ...
is a monophyletic group of allotherians that was diverse in the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', ...
of South America, India, Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
and possibly Africa and occurs onwards into the Paleogene of South America and Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest contine ...
. Their placement within Allotheria is highly controversial, with some phylogenies recovering the group as deeply nested within multituberculates, while others recover them as a distinct branch of allotherians separate from multituberculates. In their 2001 study, Kielan-Jaworowska and
In their 2001 study, Kielan-Jaworowska and Hurum
Hurum was a municipality in Buskerud county, Norway. As of 1 January 2020 Hurum has merged with the municipalities of Røyken and Asker to form the new Asker Municipality located in the newly formed Viken county. The administrative centre of the ...
found that most multituberculates could be referred to two suborders: "Plagiaulacida
Plagiaulacida is a group of extinct multituberculate mammals. Multituberculates were among the most common mammals of the Mesozoic, "the age of the dinosaurs". Plagiaulacids are a paraphyletic grouping, containing all multituberculates that lie ...
" and Cimolodonta
Cimolodonta is a taxon of extinct mammals that lived from the Cretaceous to the Eocene. They were some of the more derived members of the extinct order Multituberculata. They probably lived something of a rodent-like existence until their ...
. The exception is the genus '' Arginbaatar'', which shares characteristics with both groups.
"Plagiaulacida" is paraphyletic, representing the more primitive evolutionary grade
A grade is a taxon united by a level of morphological or physiological complexity. The term was coined by British biologist Julian Huxley, to contrast with clade, a strictly phylogenetic unit.
Definition
An evolutionary grade is a group of sp ...
. Its members are the more basal Multituberculata. Chronologically, they ranged from perhaps the Middle Jurassic until the mid-Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
. This group is further subdivided into three informal groupings: the allodontid line, the paulchoffatiid line, and the plagiaulacid line.
Cimolodonta
Cimolodonta is a taxon of extinct mammals that lived from the Cretaceous to the Eocene. They were some of the more derived members of the extinct order Multituberculata. They probably lived something of a rodent-like existence until their ...
is, apparently, a natural (monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic gro ...
) suborder. This includes the more derived Multituberculata, which have been identified from the lower Cretaceous to the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
. The superfamilies Djadochtatherioidea
Djadochtatherioidea is a group of extinct mammals known from the upper Cretaceous of Central Asia. They were members of an also extinct order called Multituberculata. These were generally somewhat rodent-like creatures, who scurried around duri ...
, Taeniolabidoidea
Taeniolabidoidea is a group of extinct mammals known from North America and Asia. They were the largest members of the extinct order Multituberculata, as well as the largest non-therian mammals. ''Lambdopsalis'' even provides direct fossil eviden ...
, Ptilodontoidea
Ptilodontoidea is a group of extinct mammals from the Northern Hemisphere.
They were generally small, somewhat rodent-like creatures of the extinct order Multituberculata.
Some of these genera boast a great many species, though remains are g ...
are recognized, as is the Paracimexomys group
''Paracimexomys'' is a genus of extinct mammals in the also extinct Multituberculata order. ''Paracimexomys'' lived during the Cretaceous period. The few fossils remains come from North America. Some Romanian fossils were also tentatively assig ...
. Additionally, there are the families Cimolomyidae
Cimolomyidae is a family of fossil mammal within the extinct order Multituberculata. Representatives are known from the Upper Cretaceous and the Paleocene of North America and perhaps Mongolia. The family is part of the suborder Cimolodonta. Oth ...
, Boffiidae, Eucosmodontidae
Eucosmodontidae is a poorly preserved family of fossil mammals within the extinct order Multituberculata. Representatives are known from strata dating from the Upper Cretaceous through the Lower Eocene of North America, as well as the Paleocene ...
, Kogaionidae
Kogaionidae is a family of fossil mammals within the extinct order Multituberculata. Representatives are known from the Upper Cretaceous and the Paleocene of Europe. Having started as island endemics on Hateg Island during the Upper Cretaceous, ...
, Microcosmodontidae
Microcosmodontidae is a poorly preserved family of fossil mammals within the extinct order Multituberculata. Representatives are known from the Lower Paleocene of North America. The family is part of the suborder Cimolodonta. Other than that, the ...
and the two genera '' Uzbekbaatar'' and '' Viridomys''. More precise placement of these types awaits further discoveries and analysis.Dykes ''Multituberculata (Cope 1884)''
Taxonomy
 Based on the combined works of Mikko's Phylogeny ArchiveMikko's Phylogeny Archive
Based on the combined works of Mikko's Phylogeny ArchiveMikko's Phylogeny Archiveand Paleofile.com. Suborder †
Plagiaulacida
Plagiaulacida is a group of extinct multituberculate mammals. Multituberculates were among the most common mammals of the Mesozoic, "the age of the dinosaurs". Plagiaulacids are a paraphyletic grouping, containing all multituberculates that lie ...
Simpson 1925
* Genus ?†'' Argillomys'' Cifelli, Gordon & Lipka 2013
** Species †'' Argillomys marylandensis'' Cifelli, Gordon & Lipka 2013
* Genus ?†''Janumys
''Janumys'' is a genus of extinct mammal of the middle Cretaceous. It was a member of the order of Multituberculata (also extinct). It lived in North America during the Mesozoic era, also known as the "age of the reptiles." It has been provi ...
'' Eaton & Cifelli 2001
** Species †''Janumys erebos
''Janumys'' is a genus of extinct mammal of the middle Cretaceous. It was a member of the order of Multituberculata (also extinct). It lived in North America during the Mesozoic era, also known as the "age of the reptiles." It has been provi ...
'' Eaton & Cifelli 2001
* Super family †Allodontoidea Marsh 1889
** Genus †?''Glirodon
''Glirodon'' is a genus of extinct mammal from the Upper Jurassic. It was a relatively early member of the also-extinct order of Multituberculata, suborder "Plagiaulacida". These mammals lived in North America during the Mesozoic, also known a ...
'' Engelmann & Callison, 2001
*** Species †'' G. grandis'' Engelmann & Callison, 2001
** Family †Arginbaataridae
''Arginbaatar'' is a genus of extinct mammal from the Lower Cretaceous of Mongolia. It was a member of the Multituberculata, an order which is also extinct. It belongs to the family Arginbaataridae (Hahn & Hahn 1983). The genus ''Arginbaatar'' w ...
Hahn & Hahn, 1983
*** Genus †'' Arginbaatar'' Trofimov, 1980
**** Species †'' A. dmitrievae'' Trofimov, 1980
** Family † Zofiabaataridae Bakker, 1992
*** Genus †'' Zofiabaatar'' Bakker & Carpenter, 1990
**** Species †'' Z. pulcher'' Bakker & Carpenter, 1990
** Family †Allodontidae
Allodontidae (from ancient Greek "ἄλλος" "ὀδούς", "different tooth") is a family of extinct multituberculate mammal that lived in what is now North America during the Upper Jurassic period. They were relatively early mammals and ar ...
Marsh, 1889
*** Genus †'' Passumys'' Cifelli, Davis & Sames 2014
**** Species †'' Passumys angelli'' Cifelli, Davis & Sames 2014
*** Genus †''Ctenacodon
''Ctenacodon'' ("comb needle tooth" from Ancient Greek κτενός (ktenós), "comb" + Latin acus, "needle" + Ancient Greek ὀδών (odṓn), "tooth") is a genus of extinct mammal that lived in what is now North America during the Upper Jura ...
'' Marsh, 1879
**** Species †'' C. serratus'' Marsh, 1879
**** Species †'' C. nanus'' Marsh, 1881
**** Species †'' C. laticeps'' (Marsh, 1881) 'Allodon laticeps'' Marsh 1881
**** Species †'' C. scindens'' Simpson, 1928
*** Genus †'' Psalodon'' Simpson, 1926
**** Species †'' P. potens'' (Marsh, 1887) 'Ctenacodon potens'' Marsh 1887**** Species †'' P. fortis'' (Marsh, 1887) Simpson 1929 'Allodon fortis'' Marsh 1887**** Species †'' P. marshi'' Simpson, 1929
* Super family † Paulchoffatioidea Hahn 1969 sensu Hahn & Hahn 2003
** Genus ?†''Mojo
Mojo may refer to:
* Mojo (African-American culture), a magical charm bag used in voodoo
Arts, entertainment and media Film and television
* MOJO HD, an American television network
* ''Mojo'' (play), by Jez Butterworth, made into a 1997 film
* ' ...
'' Hahn, LePage & Wouters 1987
*** Species †'' Mojo usuratus'' Hahn, LePage & Wouters 1987
** Genus ?†''Rugosodon
''Rugosodon'' is an extinct genus of multituberculate (rodent-like) mammals from eastern China that lived 160 million years ago during the Jurassic period. The discovery of its type species and currently only known species ''Rugosodon eurasiaticu ...
'' Yuan et al., 2013
*** Species †'' Rugosodon eurasiaticus'' Yuan et al., 2013
** Family †Pinheirodontidae
Pinheirodontidae is a poorly known family of fossil mammals which belong to the informal suborder "Plagiaulacida" within the order Multituberculata. Remains are known from the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous of Europe, (predominantly Portugal ...
Hahn & Hahn, 1999
*** Genus †''Bernardodon
''Bernardodon'' was a small, Lower Cretaceous mammal from Portugal. It is part of the extinct order Multituberculata, living at the same time as the dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first ...
'' Hahn & Hahn, 1999
**** Species †'' B. atlanticus'' Hahn & Hahn, 1999
**** Species †''B. sp.'' Hahn & Hahn, 1999
*** Genus †'' Cantalera'' Badiola, Canudo & Cuenca-Bescos, 2008
**** Species †'' Cantalera abadi'' Badiola, Canudo & Cuenca-Bescos, 2008
*** Genus †'' Ecprepaulax'' Hahn & Hahn, 1999
**** Species †'' E. anomala'' Hahn & Hahn, 1999
*** Genus †'' Gerhardodon'' Kielan-Jaworowska & Ensom, 1992
**** Species †'' G. purbeckensis'' Kielan-Jaworowska & Ensom, 1992
*** Genus †''Iberodon
''Iberodon'' is a small, extinct mammal of the Lower Cretaceous from Portugal. It was a member of the also extinct order Multituberculata, and led its obscure and plant-eating existence in the company of dinosaurs. It lies within the suborder ...
'' Hahn & Hahn, 1999
**** Species †'' I. quadrituberculatus'' Hahn & Hahn, 1999
*** Genus †'' Lavocatia'' Canudo & Cuenca-Bescós, 1996
**** Species †'' L. alfambrensis'' Canudo & Cuenca-Bescós, 1996
*** Genus †'' Pinheirodon'' Hahn & Hahn, 1999
**** Species †'' P. pygmaeus'' Hahn & Hahn, 1999
**** Species †'' P. vastus'' Hahn & Hahn, 1999
** Family †Paulchoffatiidae
Paulchoffatiidae is a family of extinct mammals that lived predominantly during the Upper Jurassic period, though a couple of Genus, genera are known from the Early Cretaceous. Fossils have been reported from Europe (Portugal, Spain, Germany and ...
Hahn, 1969
*** Genus ?†'' Galveodon'' Hahn & Hahn, 1992
**** Species †'' G. nannothus'' Hahn & Hahn, 1992
*** Genus ?†'' Sunnyodon'' Kielan-Jaworowska & Ensom, 1992
**** Species †'' S. notleyi'' Kielan-Jaworowska & Ensom, 1992
*** subfamily †Paulchoffatiinae
Paulchoffatiidae is a family of extinct mammals that lived predominantly during the Upper Jurassic period, though a couple of Genus, genera are known from the Early Cretaceous. Fossils have been reported from Europe (Portugal, Spain, Germany and ...
Hahn, 1971
**** Genus †''Paulchoffatia
''Paulchoffatia'' is a genus of extinct mammal of the Upper Jurassic - Lower Cretaceous. It was a relatively early member of the also extinct order Multituberculata, within the suborder "Plagiaulacida" and family Paulchoffatiidae. It lived in ...
'' Kühne, 1961
***** Species †'' P. delgador'' Kühne, 1961
**** Genus †'' Pseudobolodon'' Hahn, 1977
***** Species †'' P. oreas'' Hahn, 1977
***** Species †'' P. krebsi'' Hahn & Hahn, 1994
**** Genus †'' Henkelodon'' Hahn, 1987
***** Species †'' H. naias'' Hahn, 1987
**** Genus †'' Guimarotodon'' Hahn, 1969
***** Species †'' G. leiriensis'' Hahn, 1969
**** Genus †''Meketibolodon
''Meketibolodon'' is a genus of extinct mammal from the Kimmeridgian (Upper Jurassic) Camadas de Guimarota of Guimarota, Portugal. It was a relatively early member of the also extinct order Multituberculata, suborder Plagiaulacida, family ...
'' (Hahn, 1978) Hahn, 1993
***** Species †'' M. robustus'' (Hahn, 1978) Hahn, 1993 'Pseudobolodon robusutus'' Hahn 1978**** Genus †''Plesiochoffatia
''Plesiochoffatia'' is an extinct mammal of the Upper Jurassic. It was a relatively early member of the also extinct order Multituberculata. It was a resident of Portugal during the "age of the dinosaurs." It's in the suborder "Plagiaulacida" ...
'' Hahn & Hahn, 1999 'Parachoffatia'' Hahn & Hahn 1998 non Mangold 1970***** Species †'' P. thoas'' (Hahn & Hahn, 1998) Hahn & Hahn 1999 'Parachoffatia thoa'' Hahn & Hahn 1998***** Species †'' P. peparethos'' (Hahn & Hahn, 1998) Hahn & Hahn 1999 'Parachoffatia peparethos'' Hahn & Hahn 1998***** Species †'' P. staphylos'' (Hahn & Hahn, 1998) Hahn & Hahn 1999 'Parachoffatia staphylos'' Hahn & Hahn 1998**** Genus †''Xenachoffatia
''Xenachoffatia'' is a small Jurassic mammal from Portugal. It was a relatively early member of the also extinct order of Multituberculata. It lived during "the age of the dinosaurs" and belongs to the suborder Plagiaulacida, family Paulchoffa ...
'' Hahn & Hahn, 1998
***** Species †'' X. oinopion'' Hahn & Hahn, 1998
**** Genus †''Bathmochoffatia
''Bathmochoffatia'' is an extinct mammal of the Upper Jurassic. It was a relatively early member of the also extinct order Multituberculata. It lived in Portugal at about the same time as the far more famous dinosaur, Allosaurus. It is in the s ...
'' Hahn & Hahn, 1998
***** Species †'' B. hapax'' Hahn & Hahn, 1998
**** Genus †''Kielanodon
''Kielanodon'' is an extinct mammal of the Portuguese Upper Jurassic. It was a relatively early member of the also extinct order of Multituberculata. It eked out a living during the Mesozoic era, also known as the "Age of the Dinosaurs." It i ...
'' Hahn, 1987
***** Species †'' K. hopsoni'' Hahn, 1987
**** Genus †''Meketichoffatia
''Meketichoffatia'' was a small mammal from the Upper Jurassic of Portugal. It was a relatively early member of the extinct order Multituberculata. It lived at the same time as dinosaurs such as Allosaurus. It's within the suborder "Plagiaul ...
'' Hahn, 1993
***** Species †'' M. krausei'' Hahn, 1993
**** Genus †'' Renatodon'' Hahn, 2001
***** Species †'' Renatodon amalthea'' Hahn, 2001
*** Subfamily † Kuehneodontinae Hahn, 1971
**** Genus †''Kuehneodon
''Kuehneodon'' is a genus of extinct mammal of the Upper Jurassic - Lower Cretaceous of Europe. It was a relatively early member of the also extinct order of Multituberculata. Members of this genus lived alongside such dinosaurs as Allosaurus. ...
'' Hahn, 1969
***** Species †'' K. dietrichi'' Hahn, 1969
***** Species †'' K. barcasensis'' Hahn & Hahn, 2001
***** Species †'' K. dryas'' Hahn, 1977
***** Species †'' K. guimarotensis'' Hahn, 1969
***** Species †'' K. hahni'' Antunes, 1988
***** Species †'' K. simpsoni'' Hahn, 1969
***** Species †'' K. uniradiculatus'' Hahn, 1978
* Super family †Plagiaulacoidea Ameghino, 1894
** Family †Plagiaulacidae
Plagiaulacidae is a family of fossil mammals within the order Multituberculata. Remains are known from the Upper Jurassic and earliest Cretaceous of North America and Europe. They were among the more derived representatives of the informal subo ...
Gill, 1872 sensu Kielan-Jaworowska & Hurum, 2001 olodontidae Osborn 1887
*** Genus ?†'' Morrisonodon'' Hahn & Hahn, 2004
**** Species †'' Morrisonodon brentbaatar'' (Bakker, 1998) Hahn & Hahn, 2004 'Ctenacodon brentbaatar'' Bakker, 1998*** Genus †''Plagiaulax
''Plagiaulax'' is a genus of mammal from the Lower Cretaceous of Europe. It was a member of the also extinct order Multituberculata, and shared the world with dinosaurs. It is of the suborder "Plagiaulacida" and family Plagiaulacidae. The genus ...
'' Falconer, 1857
**** Species †'' P. becklesii'' Falconer, 1857
**** Species †'' P. dawsoni'' Woodward, 1891 'Plioprion dawsoni'' Woodward, 1891; ''Loxaulax dawsoni'' (Woodward, 1891) Sloan, 1979*** Genus †''Bolodon
''Bolodon'' ("lump tooth" from Ancient Greek βῶλος (bôlos), “clod, lump” + ὀδών (odṓn), "tooth") is a genus of extinct mammal from the Lower Cretaceous of Europe and North America. It was a member of the extinct order of Multi ...
'' Owen, 1871 'Plioprion''_Cope,_1884.html" ;"title="Plioprion.html" ;"title="' 'Plioprion''_Cope,_1884">Plioprion.html"_;"title="'Plioprion">'Plioprion''_Cope,_1884****_Species_†'' 'Plioprion''_Cope,_1884">Plioprion.html"_;"title="'Plioprion">'Plioprion''_Cope,_1884****_Species_†''Bolodon_crassidens">B._crassidens''_Owen,_1871
****_Species_†''Bolodon_falconeri.html" ;"title="Bolodon_crassidens.html" ;"title="Plioprion">'Plioprion'' Cope, 1884">Plioprion.html" ;"title="'Plioprion">'Plioprion'' Cope, 1884**** Species †''Bolodon crassidens">B. crassidens'' Owen, 1871
**** Species †''Bolodon falconeri">B. falconeri'' Owen, 1871 [''Pligiaulax falconeri'' Owen, 1871; ''Plioprion falconeri'' (Owen, 1871)]
**** Species †''Bolodon hydei, B. hydei'' Cifelli, Davis & Sames, 2014
**** Species †''Bolodon minor, B. minor'' Falconer, 1857 [''Pligiaulax minor'' Falconer, 1857; ''Plioprion minor'' (Falconer, 1857)]
**** Species †'' Bolodon osborni, B. osborni'' Simpson, 1928 'Plioprion osborni'' (Simpson, 1928); ''Ctenacodon osborni'' Simpson, 1928**** Species ?†'' B. elongatus'' Simpson, 1928
* Family †Eobaataridae
Eobaataridae is a family of fossil mammals within the order Multituberculata. Remains are known from the Lower Cretaceous of Europe and Asia. They are among the most derived representatives of the informal suborder "Plagiaulacida", and closely re ...
Kielan-Jaworowska, Dashzeveg & Trofimov, 1987
** Genus †''Eobaatar
''Eobaatar'' is a genus of extinct mammal from the Lower Cretaceous of Mongolia, Spain and England. A member of the also extinct order Multituberculata, it lies within the suborder Plagiaulacida and family Eobaataridae. The genus ''Eobaatar'' w ...
'' Kielan-Jaworowska, Dashzeveg & Trofimov, 1987
*** Species †'' E. clemensi'' Sweetman, 2009
*** Species †'' E. hispanicus'' Hahn & Hahn, 1992
*** Species †'' E. magnus'' Kielan-Jaworowska, Dashzeveg & Trofimov, 1987
*** Species †'' E. minor'' Kielan-Jaworowska, Dashzeveg & Trofimov, 1987
*** Species †'' E. pajaronensis'' Hahn & Hahn, 2001
** Genus †''Hakusanobaatar
''Hakusanobaatar'' is an extinct genus of eobaatarid multituberculate which existed in Japan, during the early Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and ...
'' Kusuhashi et al., 2008
*** Species †'' H. matsuoi'' Kusuhashi et al., 2008
** Genus †''Heishanobaatar
''Heishanobaatar'' ("Heishan hero" from Chinese 黑山 (Hēishān), " Heishan" + Mongolian baatar, "hero") is an extinct genus of eobaatarid multituberculate which existed in Shahai and Fuxin formations, northeastern China, during the early Cre ...
'' Kusuhashi et al., 2010
*** Species †'' H. triangulus'' Kusuhashi et al., 2010
** Genus †'' Iberica'' Badiola et al., 2011
*** Species †'' Iberica hahni'' Badiola et al., 2011
** Genus †''Liaobaatar
''Liaobaatar changi'' is a multituberculate which existed in China during the lower Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic ...
'' Kusuhashi et al., 2009
*** Species †'' L. changi'' Kusuhashi et al., 2009
** Genus †''Loxaulax
''Loxaulax'' ("slanting groove" from Ancient Greek λοξός (loxós), “slanting, crosswise” + αὖλαξ (aûlax), "furrow, groove") is a genus of extinct mammal from the Lower Cretaceous of southern England. It was a member of the also e ...
'' Simpson, 1928 'Parendotherium''_Crusafont_Pairó_&_Adrover,_1966.html" ;"title="Parendotherium.html" ;"title="' 'Parendotherium''_Crusafont_Pairó_&_Adrover,_1966">Parendotherium.html"_;"title="'Parendotherium">'Parendotherium''_Crusafont_Pairó_&_Adrover,_1966***_Species_†''Loxaulax.html" ;"title="Parendotherium">'Parendotherium'' Crusafont Pairó & Adrover, 1966">Parendotherium.html" ;"title="'Parendotherium">'Parendotherium'' Crusafont Pairó & Adrover, 1966*** Species †''Loxaulax">L. valdensis'' (Woodward, 1911) Simpson, 1928[''Dipriodon valdensis'' Woodward, 1911]
*** Species †''Loxaulax, L. herreroi'' (Crusafont Pairó & Adrover, 1966) [''Parendotherium herreroi'' Crusafont Pairó & Adrover 1966]
** Genus †''Monobaatar'' Kielan-Jaworowska, Dashzeveg & Trofimov, 1987
*** Species †'' M. mimicus'' Kielan-Jaworowska, Dashzeveg & Trofimov, 1987
** Genus †'' Sinobaatar'' Hu & Wang, 2002
*** Species †'' S. lingyuanensis'' Hu & Wang, 2002
*** Species †'' S. xiei'' Kusuhashi et al., 2009
*** Species †'' S. fuxinensis'' Kusuhashi et al., 2009
** Genus †'' Tedoribaatar'' Kusuhashi et al., 2008
*** Species †'' T. reini'' Kusuhashi et al., 2008
** Genus †'' Teutonodon'' Martin et al., 2016
*** Species †'' Teutonodon langenbergensis'' Martin et al. 2016
* Family † Albionbaataridae Kielan-Jaworowska & Ensom, 1994
** Genus †'' Albionbaatar'' Kielan-Jaworowska & Ensom, 1994
*** Species †'' A. denisae'' Kielan-Jaworowska & Ensom, 1994
** Genus †'' Kielanobaatar'' Kusuhashi et al., 2010
*** Species †'' K. badaohaoensis'' ''Kusuhashi et al.'', 2010
** Genus †'' Proalbionbaatar'' Hahn & Hahn, 1998
*** Species †'' P. plagiocyrtus'' Hahn & Hahn, 1998
* Suborder †Gondwanatheria
Gondwanatheria is an extinct group of mammaliaforms that lived in parts of Gondwana, including Madagascar, India, South America, Africa and Antarctica during the Upper Cretaceous through the Paleogene (and possibly much earlier, if '' Allostaff ...
McKenna 1971 ondwanatheroidea Krause & Bonaparte 1993** Family †Groeberiidae
Groeberiidae is a family of strange non-placental mammals from the Eocene and Oligocene epochs of Patagonia, Argentina and Chile, South America. Originally classified as paucituberculate marsupials, they were suggested to be late representativ ...
Patterson, 1952
*** Genus †'' Groeberia'' Patterson 1952
**** Species †'' G. minoprioi'' Ryan Patterson, 1952
**** Species †'' G. pattersoni'' G. G. Simpson
George Gaylord Simpson (June 16, 1902 – October 6, 1984) was an American paleontologist. Simpson was perhaps the most influential paleontologist of the twentieth century, and a major participant in the Modern synthesis (20th century), modern ...
, 1970
*** Genus †'' Klohnia'' Flynn & Wyss 1999
**** Species †'' K. charrieri'' Flynn & Wyss 1999
**** Species †'' K. major'' Goin et al., 2010
*** Genus ?†'' Epiklohnia'' Goin et al., 2010
**** Species †'' Epiklohnia verticalis'' Goin et al., 2010
*** Genus ?†'' Praedens'' Goin et al., 2010
**** Species †'' Praedens aberrans'' Goin et al., 2010
** Family †Ferugliotheriidae
Ferugliotheriidae is one of three known families in the order Gondwanatheria, an enigmatic group of extinct mammals. Gondwanatheres have been classified as a group of uncertain affinities or as members of Multituberculata, a major extinct mammal ...
Bonaparte, 1986
*** Genus †''Ferugliotherium
''Ferugliotherium'' is a genus of fossil mammals in the family Ferugliotheriidae from the Campanian and/or Maastrichtian period (Late Cretaceous; around 70 million years ago) of Argentina. It contains a single species, ''Ferugliotherium windhause ...
'' Bonaparte, 1986a 'Vucetichia''_Bonaparte,_1990.html" ;"title="Vucetichia.html" ;"title="' 'Vucetichia''_Bonaparte,_1990">Vucetichia.html"_;"title="'Vucetichia">'Vucetichia''_Bonaparte,_1990****_†''Ferugliotherium_windhauseni.html" ;"title="Vucetichia">'Vucetichia'' Bonaparte, 1990">Vucetichia.html" ;"title="'Vucetichia">'Vucetichia'' Bonaparte, 1990**** †''Ferugliotherium windhauseni">Vucetichia">'Vucetichia'' Bonaparte, 1990">Vucetichia.html" ;"title="'Vucetichia">'Vucetichia'' Bonaparte, 1990**** †''Ferugliotherium windhauseni'' Bonaparte, 1986a [''Vucetichia gracilis'' Bonaparte, 1990]
*** Genus †''Trapalcotherium'' Rougier et al., 2008
**** †''Trapalcotherium matuastensis'' Rougier et al., 2008
** Family †Sudamericidae Scillato-Yané & Pascual, 1984 ondwanatheridae Bonaparte, 1986; Patagonidae Pascual & Carlini, 1987*** Genus †''Greniodon
''Greniodon'' is a genus of extinct gondwanatherian mammal known from the Early to Middle Eocene ( Lutetian age, Mustersan to Divisaderan The Divisaderan age is a South American land mammal age, covering a period of geologic time (42.0–36.0 M ...
'' Goin et al., 2012
**** †'' Greniodon sylvanicus'' Goin et al., 2012
*** Genus †''Vintana
''Vintana sertichi'' (from Malagasy vintana, "luck" ) is an early groundhog-like mammal dating from the Late Cretaceous, approximately 66 million years ago. Scientists found the lone fossil, a skull, on Madagascar's west coast in the Maastrichti ...
'' Krause et al., 2014
**** †'' Vintana sertichi'' Krause et al., 2014
*** Genus †'' Dakshina'' Wilson, Das Sarama & Anantharaman, 2007
**** †'' Dakshina jederi'' Wilson, Das Sarama & Anantharaman, 2007
*** Genus †'' Gondwanatherium'' Bonaparte, 1986
**** †'' Gondwanatherium patagonicum'' Bonaparte, 1986
*** Genus †''Sudamerica
''Sudamerica'', literally "South America" in Spanish, is a genus of mammal from the extinct suborder Gondwanatheria that lived in Patagonia, Argentina (Salamanca Formation) and Antarctica (La Meseta Formation) from the Middle Paleocene (Peligr ...
'' Scillato-Yané & Pascual, 1984
**** †'' Sudamerica ameghinoi'' Scillato-Yané & Pascual, 1984
*** Genus †''Lavanify
''Lavanify'' is a mammalian genus from the late Cretaceous (probably Maastrichtian, about 71 to 66 million years ago) of Madagascar. The only species, ''L. miolaka'', is known from two isolated teeth, one of which is damaged. The teeth were ...
'' Krause et al., 1997
**** †''Lavanify miolaka
''Lavanify'' is a mammalian genus from the late Cretaceous (probably Maastrichtian, about 71 to 66 million years ago) of Madagascar. The only species, ''L. miolaka'', is known from two isolated teeth, one of which is damaged. The teeth were ...
'' Krause et al., 1997
*** Genus †''Bharattherium
''Bharattherium'' is a mammal that lived in India during the Maastrichtian (latest Cretaceous) and possibly the Paleocene. The genus has a single species, ''Bharattherium bonapartei''. It is part of the gondwanathere family Sudamericidae, which i ...
'' Prasad et al., 2007
**** †''Bharattherium bonapartei
''Bharattherium'' is a mammal that lived in India during the Maastrichtian (latest Cretaceous) and possibly the Paleocene. The genus has a single species, ''Bharattherium bonapartei''. It is part of the Gondwanatheria, gondwanathere family Sudamer ...
'' Prasad et al.,, 2007
*** Genus †''Patagonia
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and g ...
'' Pascual & Carlini' 1987
**** †'' Patagonia peregrina'' Pascual & Carlini' 1987
* Suborder †Cimolodonta
Cimolodonta is a taxon of extinct mammals that lived from the Cretaceous to the Eocene. They were some of the more derived members of the extinct order Multituberculata. They probably lived something of a rodent-like existence until their ...
McKenna, 1975
** Genus ?†''Allocodon'' non Marsh, 1881
*** Species †'' A. fortis'' Marsh, 1889
*** Species †'' A. lentus'' Marsh, 1892 'Cimolomys lentus''*** Species †'' A. pumilis'' Marsh, 1892 'Cimolomys pumilus''*** Species †'' A. rarus'' Marsh, 1889
** Genus ?†'' Ameribaatar'' Eaton & Cifelli, 2001
*** Species †'' A. zofiae'' Eaton & Cifelli, 2001
** Genus ?†'' Bubodens'' Wilson, 1987
*** Species †'' Bubodens magnus'' Wilson, 1987
** Genus ?†''Clemensodon
''Clemensodon'' is a genus of extinct mammal from the Upper Cretaceous of North America. It lived during the end of the Mesozoic, also known as the "age of the dinosaurs". It was a member of the extinct order of Multituberculata within the subo ...
'' Krause, 1992
*** Species †'' Clemensodon megaloba'' Krause, 1992 'Kimbetohia cambi'', in partim** Genus ?†'' Fractinus'' Higgins 2003
*** Species †'' Fractinus palmorum'' Higgins, 2003
** Genus ?†'' Uzbekbaatar'' Kielan-Jaworowska & Nesov, 1992
*** Species †''Uzbekbaatar kizylkumensis
''Uzbekbaatar'' is a genus of extinct mammal from the Upper Cretaceous of Uzbekistan. It was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta, though its further affinities are unclear. The genus was named by Kiela ...
'' Kielan-Jaworowska & Nesov, 1992
** Genus ?†'' Viridomys'' Fox 1971
*** Species †'' Viridomys orbatus'' Fox 1971
** Family † Corriebaataridae Rich et al., 2009
*** Genus ?†'' Corriebaatar'' Rich et al., 2009
**** Species †'' Corriebaatar marywaltersae'' Rich et al., 2009
** ''Paracimexomys
''Paracimexomys'' is a genus of extinct mammals in the also extinct Multituberculata order. ''Paracimexomys'' lived during the Cretaceous period. The few fossils remains come from North America. Some Romanian fossils were also tentatively assig ...
'' group
*** Genus ''Paracimexomys
''Paracimexomys'' is a genus of extinct mammals in the also extinct Multituberculata order. ''Paracimexomys'' lived during the Cretaceous period. The few fossils remains come from North America. Some Romanian fossils were also tentatively assig ...
'' Archibald, 1982
**** Species? †'' P. crossi'' Cifelli, 1997
**** Species? †'' P. dacicus'' Grigorescu & Hahn, 1989
**** Species? †'' P. oardaensis'' (Codrea et al., 2014) 'Barbatodon oardaensis'' Codrea et al., 2014**** Species †'' P. magnus'' (Sahni, 1972) Archibald, 1982 'Cimexomys magnus'' Sahni, 1972**** Species †'' P. magister'' (Fox, 1971) Archibald, 1982 'Cimexomys magister'' Fox, 1971**** Species †'' P. perplexus'' Eaton & Cifelli, 2001
**** Species †'' P. robisoni'' Eaton & Nelson, 1991
**** Species †'' P. priscus'' (Lillegraven, 1969) Archibald, 1982 'Cimexomys priscus'' Lillegraven, 1969; genotype Paracimexomys sensu Eaton & Cifelli, 2001**** Species †'' P. propriscus'' Hunter, Heinrich & Weishampel 2010
*** Genus ''Cimexomys
''Cimexomys'' is an extinct North American mammal that lived from the Upper Cretaceous to the Paleocene. For a while, it shared the world with dinosaurs, but outlived them. It was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata and lies within t ...
'' Sloan & Van Valen, 1965
**** Species †'' C. antiquus'' Fox, 1971
**** Species †'' C. gregoryi'' Eaton, 1993
**** Species †'' C. judithae'' Sahni, 1972 'Paracimexomys judithae'' (Sahni, 1972) Archibald, 1982**** Species †'' C. arapahoensis'' Middleton & Dewar, 2004
**** Species †'' C. minor'' Sloan & Van Valen, 1965
**** Species? †'' C. gratus'' (Jepson, 1930) Lofgren, 1995 'Cimexomys hausoi'' Archibald, 1983; ''Eucosmodon gratus'' Jepson, 1930; ''Mesodma ambigua''? Jepson, 1940; ''Stygimus gratus'' Jepson, 1930*** Genus †''Bryceomys
''Bryceomys'' is an extinct mammal that lived during the late Cretaceous period (between 100 and 66 million years ago) and thus shared the world with dinosaurs. It was a member of the also extinct order of Multituberculata. It was within the sub ...
'' Eaton, 1995
**** Species †'' B. fumosus'' Eaton, 1995
**** Species †'' B. hadrosus'' Eaton, 1995
**** Species †'' B. intermedius'' Eaton & Cifelli, 2001
*** Genus †''Cedaromys
''Cedaromys'' ("Cedar mouse") is an extinct mammal which lived during the Upper Cretaceous, at the same time as many dinosaurs. It was a member of the also extinct order of Multituberculata. It's within the suborder of Cimolodonta, and a possibl ...
'' Eaton & Cifelli, 2001
**** Species †'' C. bestia'' (Eaton & Nelson, 1991) Eaton & Cifelli, 2001 'Paracimexomys bestia'' Eaton & Nelson, 1991/small>
**** Species †'' C. hutchisoni'' Eaton 2002
**** Species †'' C. minimus'' Eaton 2009
**** Species †'' C. parvus'' Eaton & Cifelli, 2001
*** Genus †'' Dakotamys'' Eaton, 1995
**** Species? †''D. sp.'' Eaton, 1995
**** Species †'' D. malcolmi'' Eaton, 1995
**** Species †'' D. shakespeari'' Eaton 2013
** Family † Boffidae Hahn & Hahn, 1983 sensu Kielan-Jaworowska & Hurum 2001
*** Genus †''Boffius
''Boffius'' is a genus of mammal from the Paleocene of Europe, which was named by Vianey-Liaud M. in 1979. It is a member of the extinct order of Multituberculata.
Boffius lies within the suborder Cimolodonta and is the only known member of ...
'' Vianey-Liaud, 1979
**** Species †'' Boffius splendidus'' Vianey-Liaud, 1979 offiidae Hahn & Hahn, 1983 sensu Kielan-Jaworowska & Hurum, 2001** Family †Cimolomyidae
Cimolomyidae is a family of fossil mammal within the extinct order Multituberculata. Representatives are known from the Upper Cretaceous and the Paleocene of North America and perhaps Mongolia. The family is part of the suborder Cimolodonta. Oth ...
Marsh, 1889 sensu Kielan-Jaworowska & Hurum, 2001
*** Genus †'' Paressodon'' Wilson, Dechense & Anderson, 2010
**** Species †'' Paressodon nelsoni'' Wilson, Dechense & Anderson, 2010
*** Genus †''Cimolomys
''Cimolomys'' is a mammal genus from the Upper Cretaceous of North America. It was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta and family Cimolomyidae.
The genus ''Cimolomys'' was named by Othniel Charles Mar ...
'' Marsh, 1889 ''Allacodon''_Marsh,_1889;_''Selenacodon.html" ;"title="Allacodon.html" ;"title="''Allacodon">''Allacodon'' Marsh, 1889; ''Selenacodon">Allacodon.html" ;"title="''Allacodon">''Allacodon'' Marsh, 1889; ''Selenacodon'' Marsh, 1889]
**** Species †''Cimolomys clarki, C. clarki'' Sahni, 1972
**** Species †''Cimolomys gracilis, C. gracilis'' Marsh, 1889 [''Cimolomys digona'' Marsh, 1889; ''Meniscoessus brevis''; ''Ptilodus gracilis'' Osborn, 1893 non Gidley 1909; ''Selenacodon brevis'' Marsh, 1889]
**** Species †'' Cimolomys trochuus, C. trochuus'' Lillegraven, 1969
**** Species †'' C. milliensis'' Eaton, 1993a
**** Species ?†'' C. bellus'' Marsh, 1889
*** Genus ?†''Essonodon
''Essonodon'' is a mammal genus from the Upper Cretaceous of North America. It was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata and lived towards the end of the "age of the dinosaurs." It is within the suborder Cimolodonta and perhaps the ...
'' Simpson, 1927
**** Species †'' E. browni'' Simpson, 1927 imolodontidae? Kielan-Jaworowska & Hurum 2001*** Genus ?†'' Buginbaatar'' Kielan-Jaworowska & Sochava, 1969
**** Species †'' Buginbaatar transaltaiensis'' Kielan-Jaworowska & Sochava, 1969
*** Genus ?†'' Meniscoessus'' Cope, 1882 'Dipriodon''_Marsh,_1889;_''Tripriodon.html" ;"title="Dipriodon.html" ;"title="'Dipriodon">'Dipriodon'' Marsh, 1889; ''Tripriodon">Dipriodon.html" ;"title="'Dipriodon">'Dipriodon'' Marsh, 1889; ''Tripriodon'' Marsh, 1889 ''nomen dubium''; ''Triprotodon'' Chure & McIntosh, 1989 ''nomen dubium''; ''Selenacodon'' Marsh, 1889, ''Halodon'' Marsh, 1889, ''Oracodon'' Marsh, 1889]
**** Species †'' M. caperatus'' Marsh, 1889
**** Species †'' M. collomensis'' Lillegraven, 1987
**** Species †'' M. conquistus'' Cope 1882
**** Species †'' M. ferox'' Fox, 1971a
**** Species †'' M. intermedius'' Fox, 1976b
**** Species †'' M. major'' (Russell, 1936) 'Cimolomys major'' Russell 1937**** Species †'' M. robustus'' (Marsh, 1889) [''Dipriodon robustus'' Marsh 1889; ''Dipriodon lacunatus'' Marsh, 1889; ''Tripriodon coelatus'' Marsh, 1889; ''Meniscoessus coelatus'' Marsh, 1889; ''Selenacodon fragilis'' Marsh, 1889; ''Meniscoessus fragilis'' Marsh, 1889; ''Halodon sculptus'' (Marsh, 1889); ''Cimolomys sculptus'' Marsh, 1889; ''Meniscoessus sculptus'' Marsh, 1889; ''Oracodon anceps'' Marsh, 1889; ''Oracodon conulus'' Marsh, 1892; ''Meniscoessus borealis'' Simpson, 1927c; ''Meniscoessus greeni'' Wilson, 1987]
**** Species †''Meniscoessus seminoensis, M. seminoensis'' Eberle & Lillegraven, 1998a
** Family †Kogaionidae
Kogaionidae is a family of fossil mammals within the extinct order Multituberculata. Representatives are known from the Upper Cretaceous and the Paleocene of Europe. Having started as island endemics on Hateg Island during the Upper Cretaceous, ...
Rãdulescu & Samson, 1996
*** Genus †'' Kogaionon'' Rãdulescu & Samson, 1996
**** Species †'' K. ungureanui'' Rãdulescu & Samson, 1996
*** Genus †'' Hainina'' Vianey-Liaud, 1979
**** Species †'' H. belgica'' Vianey-Liaud, 1979
**** Species †'' H. godfriauxi'' Vianey-Liaud, 1979
**** Species †'' H. pyrenaica'' Peláez-Campomanes, López-Martínez, Álvarez-Sierra & Daams, 2000
**** Species †'' H. vianeyae'' Peláez-Campomanes, López-Martínez, Álvarez-Sierra & Daams, 2000
*** Genus †''Barbatodon
''Barbatodon'' is a mammal genus from the Upper Cretaceous period. It lived in Transylvania at the same time as some of the last dinosaurs and was a member of the extinct order of Multituberculata. It is within the suborder of Cimolodonta, and t ...
'' Rãdulescu & Samson, 1986
**** Species †'' B. transylvanicum'' Rãdulescu & Samson, 1986
** Family †Eucosmodontidae
Eucosmodontidae is a poorly preserved family of fossil mammals within the extinct order Multituberculata. Representatives are known from strata dating from the Upper Cretaceous through the Lower Eocene of North America, as well as the Paleocene ...
Jepsen, 1940 sensu Kielan-Jaworowska & Hurum, 2001 ucosmodontidae: Eucosmodontinae Jepsen, 1940 sensu McKenna & Bell, 1997*** Genus †''Eucosmodon
''Eucosmodon'' is a genus of extinct mammal from the Paleocene of North America. It is a member of the extinct order of Multituberculata within the suborder of Cimolodonta, and the family Eucosmodontidae. This genus has partly also been known a ...
'' Matthew & Granger, 1921
**** Species †'' E. primus'' Granger & Simpson, 1929
**** Species †'' E. americanus'' Cope, 1885
**** Species †'' E. molestus'' Cope, 1869 'Neoplagiaulax molestus'' Cope, 1869*** Genus †'' Stygimys'' Sloan & Van Valen, 1965
**** Species †'' S. camptorhiza'' Johnston & Fox, 1984
**** Species †'' S. cupressus'' Fox, 1981
**** Species †'' S. kuszmauli'' 'Eucosmodon kuszmauli''**** Species †'' S. jepseni'' Simpson, 1935
**** Species †'' S. teilhardi'' Granger & Simpson, 1929
** Family †Microcosmodontidae
Microcosmodontidae is a poorly preserved family of fossil mammals within the extinct order Multituberculata. Representatives are known from the Lower Paleocene of North America. The family is part of the suborder Cimolodonta. Other than that, the ...
Holtzman & Wolberg, 1977 ucosmodontidae: Microcosmodontinae Holtzman & Wolberg, 1977 sensu McKenna & Bell, 1997*** Genus †''Pentacosmodon
''Pentacosmodon'' is a mammal genus from the Paleocene of North America, so it lived somewhat after the "age of the dinosaurs". It was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata. It's within the suborder Cimolodonta and family Microcosmodonti ...
''Jepsen, 1940
**** Species †'' P. pronus'' Jepsen, 1940 jadochtatheroid? (Kielan-Jaworowska & Hurum, 2001)*** Genus †'' Acheronodon'' Archibald, 1982
**** Species †'' A. garbani'' Archibald, 1982
*** Genus †'' Microcosmodon'' Jepsen, 1930
**** Species †'' M. conus'' Jepsen, 1930
**** Species †'' M. rosei'' Krause, 1980
**** Species †'' M. arcuatus'' Johnston & Fox, 1984
**** Species †'' M. woodi'' Holtzman & Wolberg, 1977 ucosmodontine?**** Species †'' M. harleyi'' Weil, 1998
** Superfamily †Ptilodontoidea
Ptilodontoidea is a group of extinct mammals from the Northern Hemisphere.
They were generally small, somewhat rodent-like creatures of the extinct order Multituberculata.
Some of these genera boast a great many species, though remains are g ...
Cope, 1887 sensu McKenna & Bell, 1997 e Kielan-Jaworowska & Hurum, 2001
*** Family †Cimolodontidae
Cimolodontidae is a family of fossil mammals within the extinct order Multituberculata. Representatives are known from the Upper Cretaceous and Paleocene of North America. The family Cimolodontidae was named by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1889 a ...
Marsh, 1889 sensu Kielan-Jaworowska & Hurum, 2001
**** Genus †''Liotomus
''Liotomus'' is a genus of extinct mammal from the Paleocene epoch (early Cenozoic era). It lived in Europe and North America, and was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata, lying within the suborder Cimolodonta and possibly the fami ...
'' Lemoine, 1882 'Neoctenacodon'' Lemoine 1891
***** Species? †'' L. marshi'' (Lemoine, 1882) Cope, 1884 'Neoctenacodon marshi'' Lemoine, 1882; ''Neoplagiaulax marshi'' (Lemoine 1882); ''Plagiaulax marshi'' (Lemoine 1882) ucosmodontidae? McKenna & Bell, 1997/small>
**** Genus †'' Yubaatar'' Xu et al., 2015
***** Species †'' Yubaatar zhongyuanensis'' Xu et al., 2015
**** Genus †''Anconodon
''Anconodon'' is an extinct genus of mammal from the Paleocene of North America, and thus lived just after the " age of the dinosaurs". It was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta and possibly the fami ...
'' Jepsen, 1940
***** Species? †'' A. lewisi'' (Simpson 1935) Sloan, 1987
***** Species †'' A. gibleyi'' (Simpson, 1935) 'Ptilodus gidleyi'' Simpson, 1935***** Species †'' A. cochranensis'' (Russell, 1929) 'Liotomus russelli'' (Simpson, 1935); ''Anconodon russelli'' (Simpson, 1935) Sloan, 1987; ''Ectopodon cochranensis'' (Russell, 1967)**** Genus †''Cimolodon
''Cimolodon'' is a genus of the extinct mammal order of Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta and the family Cimolodontidae. Specimens are known from the Late Cretaceous of North America.
Systematics
The genus ''Cimolodon'' was nam ...
'' Marsh, 1889 'Nanomys''_Marsh,_1889,_''Nanomyops.html" ;"title="Nanomys.html" ;"title="'Nanomys">'Nanomys'' Marsh, 1889, ''Nanomyops">Nanomys.html" ;"title="'Nanomys">'Nanomys'' Marsh, 1889, ''Nanomyops'' Marsh, 1892]
***** Species †''Cimolodon agilis, C. agilis'' Marsh, 1889
***** Species †''Cimolodon foxi, C. foxi'' Eaton, 2002
***** Species †''Cimolodon gracilis, C. gracilis'' Marsh, 1889
***** Species †'' Cimolodon electus, C. electus'' Fox, 1971
***** Species †'' C. nitidus'' Marsh, 1889 [''Allacodon rarus'' Marsh, 1892 sensu Clemens, 1964a; ''Nanomys minutus'' Marsh, 1889; ''Nanomyops minutus'' (Marsh, 1889) Marsh, 1892; ''Halodon serratus'' Marsh, 1889; ''Ptilodus serratus'' (Marsh, 1889) Gidley 1909]
***** Species †''Cimolodon parvus, C. parvus'' Marsh, 1889
***** Species †''Cimolodon peregrinus, C. peregrinus'' Donohue, Wilson & Breithaupt, 2013
***** Species †'' C. similis'' Fox, 1971
***** Species †'' C. wardi'' Eaton, 2006
*** Family ''Incertae sedis
' () or ''problematica'' is a term used for a taxonomic group where its broader relationships are unknown or undefined. Alternatively, such groups are frequently referred to as "enigmatic taxa". In the system of open nomenclature, uncertain ...
''
**** Genus ''Neoliotomus
''Neoliotomus'' is a genus of North American mammal from the Paleocene. It existed in the age immediately following the extinction of the last dinosaurs and was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata. It lies within the suborder Cimolo ...
'' Jepsen, 1930
***** Species †'' N. conventus'' Jepsen, 1930
***** Species †'' N. ultimus'' (Granger & Simpson, 1928)
*** Family †Neoplagiaulacidae
Neoplagiaulacidae is a family of mammal within the extinct order Multituberculata. Fossil remains are known from the Upper Cretaceous through to the latest Eocene/early Oligocene. Representatives have been found in North America, Europe and Asi ...
Ameghino, 1890 tilodontidae: Neoplagiaulacinae Ameghino, 1890 sensu McKenna & Bell, 1997**** Genus †''Mesodma
''Mesodma'' is an extinct genus of mammal, a member of the extinct order Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta, family Neoplagiaulacidae. It lived during the upper Cretaceous and Paleocene Periods of what is now North America. The e ...
'' Jepsen, 1940
***** Species? †'' M. hensleighi'' Lillegraven, 1969
***** Species? †'' M. senecta'' Fox, 1971
***** Species †'' M. ambigua'' Jepsen, 1940
***** Species? †'' M. pygmaea'' Sloan, 1987
***** Species †'' M. formosa'' (Marsh, 1889) alodon formosus Marsh, 1889/small>
***** Species †'' M. primaeva'' (Lambe, 1902)
***** Species †'' M. thompsoni'' Clemens, 1964
**** Genus '' Ectypodus'' Matthew & Cranger, 1921 harlesmooria Kühne, 1969 /small>
***** Species †'' E. aphronorus'' Sloan, 1981
***** Species? †'' E. childei'' Kühne, 1969
***** Species? †'' E. elaphus'' Scott, 2005
***** Species? †'' E. lovei'' (Sloan, 1966) Krishtlaka & Black, 1975
***** Species †'' E. musculus'' Matthew & Granger, 1921
***** Species †'' E. powelli'' Jepsen, 1940
***** Species? †'' E. simpsoni'' Jepsen, 1930
***** Species †'' E. szalayi'' Sloan, 1981
***** Species †'' E. tardus'' Jepsen, 1930
**** Genus †''Mimetodon
''Mimetodon'' is a small mammal from the Paleocene of North America and perhaps Europe. It was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta and family Neoplagiaulacidae.
The genus ''Mimetodon'' was named by Je ...
'' Jepsen, 1940
***** Species †'' M. krausei'' Sloan, 1981
***** Species †'' M. nanophus'' Holtzman, 1978 'Neoplagiaulax nanophus'' Holtzman, 1978/small>
***** Species †'' M. siberlingi''(Simpson, 1935) Schiebout, 1974
***** Species †'' M. churchilli'' Jepsen, 1940
**** Genus †''Neoplagiaulax
''Neoplagiaulax'' is a mammal genus from the Paleocene of Europe and North America. In the case of the latter continent, there may possibly be some slightly earlier, Upper Cretaceous material too. It existed in the age immediately following the e ...
'' Lemoine, 1882
***** Species †'' N. annae'' Vianey-Liaud, 1986
***** Species? †'' N. burgessi'' Archibald, 1982
***** Species †'' N. cimolodontoides'' Scott, 2005
***** Species †'' N. copei'' Lemoine, 1885
***** Species †'' N. donaldorum'' Scott & Krause, 2006
***** Species †'' N. eocaenus'' Lemoine, 1880
***** Species †'' N. grangeri'' Simpson, 1935
***** Species †'' N. hazeni'' Jepsen, 1940
***** Species †'' N. hunteri'' Krishtalka, 1973
***** Species †'' N. jepi'' Sloan, 1987
***** Species †'' N. kremnus'' Johnston & Fox, 1984
***** Species †'' N. macintyrei'' Slaon, 1981
***** Species †'' N. macrotomeus'' Wilson, 1956
***** Species †'' N. mckennai'' Sloan, 1987
***** Species †'' N. nelsoni'' Sloan, 1987
***** Species †'' N. nicolai'' Vianey-Liaud, 1986
***** Species †'' N. paskapooensis'' Scott, 2005
***** Species? †'' N. serrator'' Scott, 2005
***** Species †'' N. sylvani'' Vianey-Liaud, 1986
**** Genus †''Parectypodus
''Parectypodus'' (meaning "besides '' Ectypodus''") is an extinct genus of mammals that lived from Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) to Eocene time in North America. It is a member of the extinct order of Multituberculata, suborder Cimolodonta, f ...
'' Jepsen, 1930
***** Species †'' P. armstrongi'' Johnston & Fox, 1984
***** Species? †'' P. corystes'' Scott, 2003
***** Species? †'' P. foxi'' Storer, 1991
***** Species †'' P. laytoni'' Jepsen, 1940
***** Species †'' P. lunatus'' Krause, 1982 'P. childei'' Kühne, 1969***** Species †'' P. simpsoni'' Jepsen, 1940
***** Species †'' P. sinclairi'' Simpson, 1935
***** Species †'' P. sloani'' Schiebout, 1974
***** Species †'' P. trovessartianus'' Cope, 1882 'P. trouessarti''; ''Ptilodus''; ''Mimetodon''; ''Neoplagiaulax''***** Species †'' P. sylviae'' Rigsby, 1980 ctypodus sylviae Rigby, 1980***** Species? †'' P. vanvaleni'' Sloan, 1981
**** Genus †''Cernaysia
''Cernaysia'' is an extinct genus of mammal from the Paleocene of France and the United States. It existed in the age immediately following the extinction of the last dinosaurs. This animal was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata with ...
'' Vianey-Liaud, 1986
***** Species †'' C. manueli'' Vianey-Liaud, 1986
***** Species †'' C. davidi'' Vianey-Liaud, 1986
**** Genus †''Krauseia
''Krauseia'' is an extinct genus of small mammal from the Paleocene of North America. It was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata and is within the suborder of Cimolodonta, family Neoplagiaulacidae. The genus was nemed by Vianey-Liaud ...
'' Vianey-Liaud, 1986
***** Species †'' K. clemensi'' Sloan, 1981 'Parectypodus clemensi'' Sloan, 1981**** Genus †''Xyronomys
''Xyronomys'' is an extinct genus of small mammals from the Paleocene of North America, with two described species. The genus lies within the extinct order Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta and family Neoplagiaulacidae.
The spec ...
''Rigby, 1980
***** Species †'' X. swainae'' Rigby, 1980 ironomys (sic); ?Eucosmodontidae**** Genus †''Xanclomys
''Xanclomys'' is a small mammal from the Paleocene of North America. It was a genus within the extinct order Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta and family Neoplagiaulacidae.
The genus ''Xanclomys'', named by Rigby J.K. in 1980, ...
'' Rigby, 1980
***** Species †'' X. mcgrewi''Rigby, 1980
**** Genus †''Mesodmops
''Mesodmops'' is a genus of small mammal from the Eocene of China. It was a late member of the extinct order of Multituberculata. It's within the suborder of Cimolodonta and family Neoplagiaulacidae
Neoplagiaulacidae is a family of mammal ...
'' Tong & Wang, 1994
***** Species †'' M. dawsonae'' Tong & Wang, 1994
*** Family †Ptilodontidae
Ptilodontidae is a family of primitive mammals within the extinct order Multituberculata. Representatives are known from the Upper Cretaceous and Paleocene of North America.
The Ptilodontidae family was originally named Ptilodontinae and classi ...
Cope, 1887 tilodontidae: Ptilodontinae Cope, 1887 sensu McKenna & Bell, 1997**** Genus †'' Kimbetohia'' Simpson, 1936
***** Species †'' K. cambi'' small>Granger, Gregory & Colbert in Matthew, 1937, or Simpson, 1936***** Species †K. sp. cf. ''K. cambi''
**** Genus †''Ptilodus
''Ptilodus'' (meaning "soft-haired") is a genus of mammals from the extinct order of Multituberculata, and lived during the Paleocene in North America.
''Ptilodus'' was a relatively large multituberculate of in length, which is about the same s ...
'' Cope, 1881 hirox Cope, 1884***** Species? †'' P. fractus''
***** Species †'' P. kummae'' Krause, 1977
***** Species †'' P. gnomus'' Scott, Fox & Youzwyshyn, 2002 f. ''Ectypodus hazeni'' (Jepsen, 1940) Gazin, 1956***** Species †'' P. mediaevus'' Cope, 1881 'Ptilodus plicatus'' (Cope, 1884); ''Chirox plicatus'' Cope, 1884 ''P. ferronensis'' Gazin, 1941***** Species †'' P. montanus'' Douglass, 1908 'P. gracilis'' Gidley, 1909; ''P. admiralis'' Hay, 1930***** Species †'' P. tsosiensis'' Sloan, 1981
***** Species †'' P. wyomingensis'' Jepsen, 1940
**** Genus †'' Baiotomeus'' Krause, 1987
***** Species †'' B. douglassi'' Simpson, 1935 'Ptilodus''; ''Mimetodon''; ''Neoplagiaulax''***** Species †'' B. lamberti'' Krause, 1987
***** Species †'' B. russelli'' Scott, Fox & Youzwyshyn, 2002
***** Species †'' B. rhothonion'' Scott, 2003
**** Genus †'' Prochetodon'' Jepsen, 1940
***** Species †'' P. cavus'' Jespen, 1940
***** Species †'' P. foxi'' Krause, 1987
***** Species †'' P. taxus'' Krause, 1987
***** Species? †'' P. speirsae'' Scott, 2004
** Superfamily †Taeniolabidoidea
Taeniolabidoidea is a group of extinct mammals known from North America and Asia. They were the largest members of the extinct order Multituberculata, as well as the largest non-therian mammals. ''Lambdopsalis'' even provides direct fossil eviden ...
Granger & Simpson, 1929 sensu Kielan-Jaworowska & Hurum, 2001
*** Genus †'' Prionessus'' Matthew & Granger, 1925
**** Species †'' P. lucifer'' Matthew & Granger, 1925
*** Family † Lambdopsalidae
**** Genus †'' Lambdopsalis'' Chow & Qi, 1978
***** Species †'' L. bulla'' Chow & Qi, 1978
**** Genus †'' Sphenopsalis'' Matthew, Granger & Simpson, 1928
***** Species †'' S. nobilis'' Matthew, Granger & Simpson, 1928
*** Family †Taeniolabididae
Taeniolabididae is one of the two multituberculate clades within Taeniolabidoidea. Originally basically synonymous with Taeniolabidoidea, it has more recently been found to be a specific clade including '' Kimbetopsalis'', '' Taeniolabis'' and so ...
Granger & Simpson, 1929
**** Genus †''Taeniolabis
''Taeniolabis'' ("banded incisor") is a genus of extinct multituberculate mammal from the Paleocene of North America.
Description
It is the largest known member of the extinct order Multituberculata, as well as the largest non-therian m ...
'' Cope, 1882
***** Species †'' T. lamberti'' Simmons, 1987
***** Species †'' T. taoensis'' Cope, 1882
**** Genus †'' Kimbetopsalis''
***** Species †'' K. simmonsae''
** Superfamily †Djadochtatherioidea
Djadochtatherioidea is a group of extinct mammals known from the upper Cretaceous of Central Asia. They were members of an also extinct order called Multituberculata. These were generally somewhat rodent-like creatures, who scurried around duri ...
Kielan-Jaworowska & Hurum, 1997 sensu Kielan-Jaworowska & Hurum, 2001 jadochtatheria Kielan-Jaworowska & Hurum, 1997*** Genus? †''Bulganbaatar
''Bulganbaatar'' is a Central Asian mammal genus from the Upper Cretaceous. It existed in the company of dinosaurs. This animal was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata. It's within the suborder Cimolodonta and is a member of the sup ...
'' Kielan-Jaworowska, 1974
**** Species? †'' B. nemegtbaataroides'' Kielan-Jaworowska, 1974
*** Genus †''Nemegtbaatar
''Nemegtbaatar'' is a genus of mammal from the Upper Cretaceous Period of what is now Mongolia. It existed in the company of much larger dinosaurs, found together in the Nemegt Basin. This creature was a member of the extinct order Multituber ...
'' Kielan-Jaworowska, 1974
**** Species? †'' N. gobiensis'' Kielan-Jaworowska, 1974
*** Family †Chulsanbaataridae
''Chulsanbaatar'' is a genus of mammal from the Cretaceous of Mongolia. It lived during the Mesozoic, also known as the "age of the dinosaurs." This small creature was a member of the extinct order of Multituberculata and is within the suborder ...
Kielan-Jaworowska, 1974
**** Genus †''Chulsanbaatar
''Chulsanbaatar'' is a genus of mammal from the Cretaceous of Mongolia. It lived during the Mesozoic, also known as the "age of the dinosaurs." This small creature was a member of the extinct order of Multituberculata and is within the suborde ...
'' Kielan-Jaworowska, 1974
***** Species †'' C. vulgaris'' Kielan-Jaworowska, 1974
*** Family † Sloanbaataridae Kielan-Jaworowska, 1974
**** Genus †''Kamptobaatar
''Kamptobaatar'' is a Mongolian mammal genus from the Upper Cretaceous. It lived at the same time as the later dinosaurs. This animal was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta and family Sloanbaatarid ...
'' Kielan-Jaworowska, 1970
***** Species? †'' K. kuczynskii'' Kielan-Jaworowska, 1970
**** Genus †'' Nessovbaatar'' Kielan-Jaworowska & Hurum, 1997
***** Species †'' N. multicostatus'' Kielan-Jaworowska & Hurum, 1997
**** Genus †'' Sloanbaatar'' Kielan-Jaworowska, 1974
***** Species †'' S. mirabilis'' Kielan-Jaworowska, 1974 loanbaatarinae*** Family †Djadochtatheriidae
Djadochtatheriidae is a family of fossil mammals within the extinct order Multituberculata. Remains are known from the Upper Cretaceous of Central Asia. These animals lived during the Mesozoic, also known as the "age of the dinosaurs". This famil ...
Kielan-Jaworowska $ Hurum, 1997
**** Genus †''Djadochtatherium
''Djadochtatherium'' is a mammal genus that lived in Mongolia during the Upper Cretaceous. It coexisted with some of the late dinosaurs. This animal was a member of the extinct order of Multituberculata. It is within the suborder of Cimolodon ...
'' Simpson, 1925
***** Species †'' D. matthewi'' Simpson, 1925 'Catopsalis matthewi'' Simpson, 1925**** Genus †''Catopsbaatar
''Catopsbaatar'' is a genus of multituberculate, an extinct order of rodent-like mammals. It lived in what is now Mongolia during the late Campanian age of the Late Cretaceous epoch, about 72 million years ago. The first fossils were colle ...
'' Kielan-Jaworowska, 1974
***** Species †'' C. catopsaloides'' (Kielan-Jaworowska, 1974) Kielan-Jaworowska, 1994 'Djadochtatherium catopsaloides'' Kielan-Jaworowska, 1974**** Genus †''Tombaatar
''Tombaatar'' is a mammal genus that existed during the Mongolian Upper Cretaceous period. It co-existed with some of the late dinosaurs. This animal was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata, within the suborder Cimolodonta and famil ...
'' Kielan-Jaworowska, 1974
***** Species †'' T. sabuli'' Rougier, Novacek & Dashzeveg, 1997
**** Genus †''Kryptobaatar
''Kryptobaatar''and also known as ''Gobibaatar'' or ''Tugrigbaatar'' is an extinct mammalian genus dating from the Upper Cretaceous Period and identified in Central Asia. This animal was a member of the extinct order of Multituberculata within ...
'' Kielan-Jaworowska, 1970 'Gobibaatar'' Kielan-Jaworowska, 1970, ''Tugrigbaatar'' Kielan-Jaworowska & Dashzeveg, 1978***** Species †'' K. saichanensis'' Kielan-Jaworowska & Dashzeveg, 1978 [''Tugrigbaatar saichaenensis'' Kielan-Jaworowska & Dashzeveg, 1978??]
***** Species †''Kryptobaatar dashzevegi, K. dashzevegi'' Kielan-Jaworowska, 1970
***** Species †''Kryptobaatar mandahuensis, K. mandahuensis'' Smith, Guo & Sun, 2001
***** Species †''Kryptobaatar gobiensis, K. gobiensis'' Kielan-Jaworowska, 1970 [''Gobibaatar parvus'' Kielan-Jaworowska, 1970 ]
Paleoecology
Behaviour
Multituberculates are some of the earliest mammals to display complex social behaviours One species, ''Filikomys,'' from the Late Cretaceous of North America, engaged in multi-generational group nesting and burrowing.Extinction
The extinction of multituberculates has been a topic of controversy for several decades. After at least 88 million years of dominance over most mammalian assemblies, multituberculates reached the peak of their diversity in the early Palaeocene, before gradually declining across the final stages of the epoch and theEocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
, finally disappearing in the early Oligocene. Traditionally, the extinction of multituberculates has been linked to the rise of rodents (and, to a lesser degree, earlier placental
Placental mammals (infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placentalia contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguishe ...
competitors like Hyopsodontidae, hyopsodonts and Plesiadapiformes), which supposedly Competitive exclusion principle, competitively excluded multituberculates from most mammalian faunas.
However, the idea that multituberculates were replaced by rodents and other placentals has been criticised by several authors. For one thing, it relies on the assumption that these mammals are "inferior" to more derived placentals, and ignores the fact that rodents and multituberculates had co-existed for at least 15 million years. According to some researchers, multituberculate "decline" is shaped by sharp extinction events, most notably after the Tiffanian, where a sudden drop in diversity occurs. Finally, the youngest known multituberculates do not exemplify patterns of competitive exclusion; the Oligocene '' Ectypodus'' is a rather generalistic species, rather than a specialist. This combination of factors suggests that, rather than gradually declining due to pressure from rodents and similar placentals, multituberculates simply could not cope with climatic and vegetation changes, as well as the rise of new predatory eutherians, such as Miacidae, miacids.
More recent studies show a mixed effect. Multituberculate faunas in North America and Europe do indeed decline in correlation to the introduction of rodents in these areas. However, Asian multituberculate faunas co-existed with rodents with minimal extinction events, implying that competition was not the main cause for the extinction of Asiatic multituberculates. As a whole, it seems that Asian multituberculates, unlike North American and European species, never recovered from the KT event, which allowed the evolution and propagation of rodents in the first place. A recent study seems to indeed indicate that eutherians recovered more quickly from the KT event than multituberculates. Conversely, another study has shown that placental radiation did not start significantly until after the decline of multituberculates.
References
Sources
* * * {{Taxonbar, from=Q131181 Multituberculates, Prehistoric animal orders Prehistoric mammals Mammal orders Oligocene extinctions Kimmeridgian first appearances Taxa named by Edward Drinker Cope Fossil taxa described in 1884 Tertiary extinctions of vertebrate taxa